Immunological Aspects of Richter Syndrome: From Immune Dysfunction to Immunotherapy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Morphology of Richter Syndrome
1.2. Epidemiology
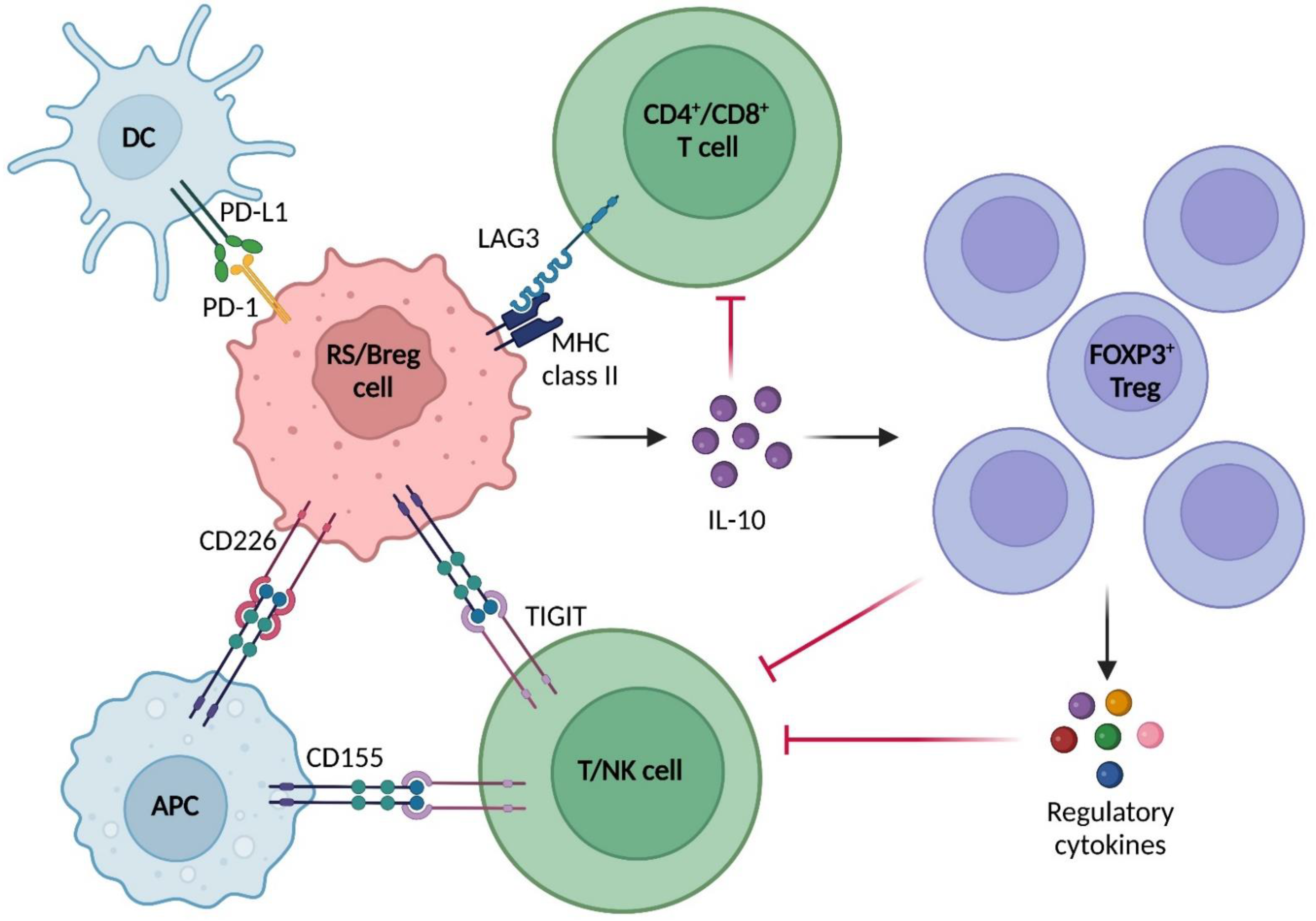
2. Immunological Aspects of RS
2.1. BCR Hyperactivation in RS
2.2. Transformation Mediated by Immune Dysfunction
2.3. Immune Microenvironment in RS
3. Immune Therapy Approaches
3.1. Standard of Care for RS
3.2. Immune Checkpoint Blockade
3.3. Bispecific Antibodies
3.4. Drug Conjugated Antibodies
3.5. CAR-T Cell Therapy
| Ref | Treatment Regimen | N. RS Patient | Response Rate (%) | Overall Survival (mo) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORR | CR | ||||
| [93] | R-CHOP | 15 | 67 | 7 | 21 |
| [95] | CHOP-O | 37 | 46 | 27 | 11.4 |
| [148] | HyperCVXD | 29 | 41 | 38 | 10 |
| [149] | Rituximab and GM-CSF with alternating hyperCVXD and MTX/cytarabine | 30 | 43 | 38 | 8 |
| [150] | OFAR1 | 20 | 50 | 20 | 8 |
| [151] | OFAR2 | 35 | 39 | 6.5 | 6.6 |
| [152] | DHAP, ESHAP | 28 | 43 | 25 | 8 |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, revised 4th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2017; Volume 2.
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.D.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Martino, G.; Lazzi, S. A comparison of the International Consensus and 5th World Health Organization classifications of mature B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2022, 37, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Raffeld, M.; Richter, M.; Krugmann, J.; Burek, C.; Hartmann, E.; Rudiger, T.; Jaffe, E.S.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; et al. IgVH Mutational Status and Clonality Analysis of Richter’s Transformation: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma in association with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) represent 2 different pathways of disease evolution. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnair, R.; Ellithi, M.; Kallam, A.; Shostrom, V.; Bociek, R.G. Outcomes of Richter’s transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL): An analysis of the SEER database. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 2513–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonegawa, S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature 1983, 302, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhssine, S.; Gaidano, G. Richter Syndrome: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Druggable Targets. Cancers 2022, 14, 4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Deambrogi, C.; Rasi, S.; Laurenti, L.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Arcaini, L.; Lucioni, M.; Rocque, G.B.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; et al. The genetics of Richter syndrome reveals disease heterogeneity and predicts survival after transformation. Blood 2011, 117, 3391–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favini, C.; Talotta, D.; Almasri, M.; Andorno, A.; Rasi, S.; Adhinaveni, R.; Kogila, S.; Awikeh, B.; Schipani, M.; Boggione, P.; et al. Clonally unrelated Richter syndrome are truly de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphomas with a mutational profile reminiscent of clonally related Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condoluci, A.; Rossi, D. Biology and Treatment of Richter Transformation. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 829983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Gaidano, G. Richter syndrome: Pathogenesis and management. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federmann, B.; Mueller, M.R.; Steinhilber, J.; Horger, M.S.; Fend, F. Diagnosis of Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Histology tips the scales. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Ding, W.; Viswanatha, D.S.; Chen, D.; Shi, M.; Van Dyke, D.; Tian, S.; Dao, L.N.; Parikh, S.A.; Shanafelt, T.D.; et al. PD-1 Expression in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and Large B-cell Richter Transformation (DLBCL-RT): A Characteristic Feature of DLBCL-RT and Potential Surrogate Marker for Clonal Relatedness. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Chen, W.W.; Sorbara, L.; Davies-Hill, T.; Pittaluga, S.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Hodgkin lymphoma variant of Richter transformation: Morphology, Epstein-Barr virus status, clonality, and survival analysis—With comparison to Hodgkin-like lesion. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 55, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Mittal, A.; Duggal, R.; Dadu, T.; Agarwal, A.; Handoo, A. Hodgkin Variant of Richter’s Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): An Illustrative Case Report and Literature Review. Int. J. Hematol. Stem Cell Res. 2021, 15, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia-Cancer Stat Facts. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. 2022. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/clyl.html (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Rossi, D.; Gaidano, G. Richter Syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 792, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solh, M.; Rai, K.R.; Peterson, B.L.; Kolitz, J.E.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Tallman, M.S.; Belch, A.; Larson, R.; Morrison, V.A. The impact of initial fludarabine therapy on transformation to Richter syndrome or prolymphocytic leukemia in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Analysis of an intergroup trial (CALGB 9011). Leuk. Lymphoma 2012, 54, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma-Cancer Stat Facts. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. 2022. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/dlbcl.html (accessed on 29 October 2022).
- Hodgkin Lymphoma-Cancer Stat Facts. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. 2022. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/hodg.html (accessed on 29 October 2022).
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Robrecht, S.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Cramer, P.; Tresckow, J.V.; Lange, E.; Kiehl, M.; Dreyling, M.; Ritgen, M.; et al. Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)—A pooled analysis of German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG) front line treatment trials. Leukemia 2020, 35, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Greil, R.; Demirkan, F.; Tedeschi, A.; Anz, B.; Larratt, L.; Simkovic, M.; Samoilova, O.; Novak, J.; Ben-Yehuda, D.; et al. Ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (iLLUMINATE): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 20, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, J.P.; Egyed, M.; Jurczak, W.; Skarbnik, A.; Pagel, J.M.; Flinn, I.W.; Kamdar, M.; Munir, T.; Walewska, R.; Corbett, G.; et al. Acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil and obinutuzumab for treatment-naive chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ELEVATE-TN): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Keating, M.; Thompson, P.; Ferrajoli, A.; Burger, J.; Borthakur, G.; Takahashi, K.; Estrov, Z.; Fowler, N.; Kadia, T.; et al. Ibrutinib and Venetoclax for First-Line Treatment of CLL. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; D’Rozario, J.; Assouline, S.; Owen, C.; Gerecitano, J.; Robak, T.; De la Serna, J.; et al. Venetoclax–Rituximab in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, T.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Barr, P.M.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Final analysis from RESONATE: Up to six years of follow-up on ibrutinib in patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, I.E.; Underbayev, C.; Albitar, A.; Herman, S.E.; Tian, X.; Maric, I.; Arthur, D.C.; Wake, L.; Pittaluga, S.; Yuan, C.M.; et al. Clonal evolution leading to ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Hillmen, P.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.E.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; Barr, P.M.; et al. Extended follow-up and impact of high-risk prognostic factors from the phase 3 RESONATE study in patients with previously treated CLL/SLL. Leukemia 2017, 32, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Gaidano, G. Biology and treatment of Richter syndrome. Blood 2018, 131, 2761–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaźmierczak, M.; Kroll-Balcerzak, R.; Balcerzak, A.; Czechowska, E.; Gil, L.; Sawiński, K.; Szczepaniak, A.; Komarnicki, M. Hodgkin lymphoma transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Cases report and discussion. Med. Oncol. 2013, 31, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimberidou, A.-M.; Keating, M.J. Richter syndrome. Cancer 2005, 103, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Porto, J.M.; Gauld, S.B.; Merrell, K.T.; Mills, D.; Pugh-Bernard, A.E.; Cambier, J. B cell antigen receptor signaling 101. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 41, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Sengupta, P.; Brzostowski, J.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Pierce, S.K. The nanoscale spatial organization of B-cell receptors on immunoglobulin M– and G–expressing human B-cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Meckel, T.; Tolar, P.; Sohn, H.W.; Pierce, S.K. Intrinsic Properties of immunoglobulin IgG1 Isotype-Switched B Cell Receptors Promote Microclustering and the Initiation of Signaling. Immunity 2010, 32, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Wiestner, A. Targeting B cell receptor signalling in cancer: Preclinical and clinical advances. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 148–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aagaard-Tillery, K.M.; Jelinek, D.F. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation in normal human B lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 4543–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Martines, C.; Porro, F.; Fortunati, I.; Bonato, A.; Dimishkovska, M.; Piazza, S.; Yadav, B.S.; Innocenti, I.; Fazio, R.; et al. B-cell receptor signaling and genetic lesions in TP53 and CDKN2A/CDKN2B cooperate in Richter transformation. Blood 2021, 138, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martines, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Vujovikj, M.; Gobessi, S.; Vaisitti, T.; Deaglio, S.; Laurenti, L.; Dimovski, A.J.; Efremov, D.G. Macrophage- and BCR- but not TLR-derived signals support the growth of CLL and Richter syndrome murine models in vivo. Blood 2022, 140, 2335–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herishanu, Y.; Pérez-Galán, P.; Liu, D.; Biancotto, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Vire, B.; Gibellini, F.; Njuguna, N.; Lee, E.; Stennett, L.; et al. The lymph node microenvironment promotes B-cell receptor signaling, NF-κB activation, and tumor proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringshausen, I.; Schneller, F.; Bogner, C.; Hipp, S.; Duyster, J.; Peschel, C.; Decker, T. Constitutively activated phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI-3K) is involved in the defect of apoptosis in B-CLL: Association with protein kinase Cδ. Blood 2002, 100, 3741–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlhaas, V.; Blakemore, S.J.; Al-Maarri, M.; Nickel, N.; Pal, M.; Roth, A.; Hoevelmeyer, N.; Schäfer, S.C.; Knittel, G.; Lohneis, P.; et al. Active Akt signaling triggers CLL toward Richter transformation via overactivation of Notch1. Blood 2021, 137, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dühren-Von Minden, M.; Übelhart, R.; Schneider, D.; Wossning, T.; Bach, M.P.; Buchner, M.; Hofmann, D.; Surova, E.; Follo, M.; Köhler, F.; et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia is driven by antigen-independent cell-autonomous signalling. Nature 2012, 489, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Chiorazzi, N. B cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.K.; Forconi, F.; Kipps, T.J. Exploring the pathways to chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2021, 138, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatopoulos, K.; Belessi, C.; Moreno, C.; Boudjograh, M.; Guida, G.; Smilevska, T.; Belhoul, L.; Stella, S.; Stavroyianni, N.; Crespo, M.; et al. Over 20% of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia carry stereotyped receptors: Pathogenetic implications and clinical correlations. Blood 2006, 109, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerousi, M.; Laidou, S.; Gemenetzi, K.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Chatzidimitriou, A. Distinctive Signaling Profiles With Distinct Biological and Clinical Implications in Aggressive CLL Subsets With Stereotyped B-Cell Receptor Immunoglobulin. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 771454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Cerri, M.; Rasi, S.; Deambrogi, C.; De Paoli, L.; Laurenti, L.; Maffei, R.; Forconi, F.; Bertoni, F.; et al. Stereotyped B-Cell Receptor Is an Independent Risk Factor of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Transformation to Richter Syndrome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4415–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Bomben, R.; Rasi, S.; Bo, M.D.; Bruscaggin, A.; Rossi, F.M.; Monti, S.; Degan, M.; Ciardullo, C.; et al. Association between molecular lesions and specific B-cell receptor subsets in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 4902–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounari, M.; Ntoufa, S.; Apollonio, B.; Papakonstantinou, N.; Ponzoni, M.; Chu, C.C.; Rossi, D.; Gaidano, G.; Chiorazzi, N.; Stamatopoulos, K.; et al. Excessive antigen reactivity may underlie the clinical aggressiveness of chronic lymphocytic leukemia stereotyped subset #8. Blood 2015, 125, 3580–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Coyle, L.; Kerridge, I.; Stevenson, W.; Arthur, C.; McKinlay, N.; Fay, K.; Ward, C.; Greenwood, M.; Best, O.G.; et al. Second primary malignancies in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: Skin, solid organ, haematological and Richter’s syndrome. Ejhaem 2021, 3, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griggio, V.; Perutelli, F.; Salvetti, C.; Boccellato, E.; Boccadoro, M.; Vitale, C.; Coscia, M. Immune Dysfunctions and Immune-Based Therapeutic Interventions in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 594556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, A.W., IV; Jillab, M.; Smith, M.R.; Alpaugh, R.K.; Cole, M.E.; Litwin, S.; Millenson, M.M.; Al-Saleem, T.; Cohen, A.D.; Campbell, K.S. NK cell dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is associated with loss of the mature cells expressing inhibitory killer cell Ig-like receptors. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1330235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, E.M.; Mele, J.M.; Cheney, C.; Timmerman, E.A.; Fiazuddin, F.; Strattan, E.J.; Mo, X.; Byrd, J.C.; Muthusamy, N.; Awan, F.T. Therapeutic CD94/NKG2A blockade improves natural killer cell dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Onco. Immunol. 2016, 5, e1226720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, R.; Audrito, V.; Vacca, P.; Rossi, D.; Brusa, D.; Stignani, M.; Bortolotti, D.; D’Arena, G.; Coscia, M.; Laurenti, L.; et al. HLA-G is a component of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia escape repertoire to generate immune suppression: Impact of the HLA-G 14 base pair (rs66554220) polymorphism. Haematologica 2013, 99, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowdell, M.W.; Lamb, L.; Hoyle, C.; Velardi, A.; Prentice, H.G. Non-MHC-restricted cytotoxic cells: Their roles in the control and treatment of leukaemias. Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 114, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Weerdt, I.; Hofland, T.; Lameris, R.; Endstra, S.; Jongejan, A.; Moerland, P.D.; de Bruin, R.C.G.; Remmerswaal, E.B.M.; Berge, I.J.M.T.; Liu, N.; et al. Improving CLL Vγ9Vδ2-T–cell fitness for cellular therapy by ex vivo activation and ibrutinib. Blood 2018, 132, 2260–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardi, A.; Agathangelidis, A.; Stalika, E.; Karypidou, M.; Siorenta, A.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Rosenquist, R.; Hadzidimitriou, A.; Ghia, P.; Sutton, L.-A.; et al. Antigen Selection Shapes the T-cell Repertoire in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riches, J.C.; Davies, J.K.; McClanahan, F.; Fatah, R.; Iqbal, S.; Agrawal, S.; Ramsay, A.G.; Gribben, J.G. T cells from CLL patients exhibit features of T-cell exhaustion but retain capacity for cytokine production. Blood 2013, 121, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzywnowicz, M.; Karczmarczyk, A.; Skorka, K.; Zajac, M.; Zaleska, J.; Chocholska, S.; Tomczak, W.; Giannopoulos, K. Expression of Programmed Death 1 Ligand in Different Compartments of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Acta. Haematol. 2015, 134, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arena, G.; Laurenti, L.; Minervini, M.M.; Deaglio, S.; Bonello, L.; De Martino, L.; De Padua, L.; Savino, L.; Tarnani, M.; De Feo, V.; et al. Regulatory T-cell number is increased in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients and correlates with progressive disease. Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Sakaguchi, S. Regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2016, 27, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Burger, J.A.; Khoury, J.D. CLL progression after one cycle of FCR: R ichter’s transformation versus EBV-associated lympho-proliferation. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 1113–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, D.; Kaiser, A.; Spizzo, G.; Gastl, G.; Tzankov, A. Hodgkin’s disease variant of Richter’s syndrome in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia patients previously treated with fludarabine. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 129, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, P.D.; Bellas, C.; Santon, A.; Shah, G.; Pocock, C.; Wotherspoon, A.C.; Matutes, E.; Catovsky, D. Richter’s transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: The possible role of fludarabine and the Epstein–Barr virus in its pathogenesis. Leuk. Res. 2005, 29, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, S.M.; Li, C.Y.; Lloyd, R.V.; Phyliky, R.L. Epstein-Barr virus infection in Richter’s transformation. Am. J. Hematol. 1999, 60, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, E.; Guarini, A.; Chiaretti, S.; Mauro, F.R.; Foa, R. The circulating dendritic cell compartment in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia is severely defective and unable to stimulate an effective T-cell response. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4497–4506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gabrilovich, D.I. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, B.S.; Öztürk, S.; Seiffert, M. Beyond bystanders: Myeloid cells in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 110, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sinha, S.; Wellik, L.E.; Secreto, C.R.; Rech, K.L.; Call, T.G.; Parikh, S.A.; Kenderian, S.S.; Muchtar, E.; Hayman, S.R.; et al. Distinct immune signatures in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter syndrome. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behdad, A.; Griffin, B.; Chen, Y.H.; Ma, S.; Kelemen, K.; Lu, X.; Chen, Q.C. PD -1 is highly expressed by neoplastic B-cells in Richter transformation. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 185, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Sozzani, S.; Locati, M.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A. Macrophage polarization: Tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augé, H.; Notarantonio, A.-B.; Morizot, R.; Quinquenel, A.; Fornecker, L.-M.; Hergalant, S.; Feugier, P.; Broséus, J. Microenvironment Remodeling and Subsequent Clinical Implications in Diffuse Large B-Cell Histologic Variant of Richter Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 594841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougiakakos, D.; Choudhury, A.; Lladser, A.; Kiessling, R.; Johansson, C.C. Regulatory T Cells in Cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2010, 107, 57–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.W.; Ngiow, S.F.; Ribas, A.; Smyth, M.J. Classifying Cancers Based on T-cell Infiltration and PD-L1. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2139–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; LaPlant, B.R.; Call, T.G.; Parikh, S.A.; Leis, J.F.; He, R.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Sinha, S.; Le-Rademacher, J.; Feldman, A.L.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with CLL and Richter transformation or with relapsed CLL. Blood 2017, 129, 3419–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Du, H.; Zhan, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Lan, J.; PuYang, L.; Wan, Y.; Qu, Q.; Wang, S.; et al. The interaction between the soluble programmed death ligand-1 (sPD-L1) and PD-1(+) regulator B cells mediates immunosuppression in triple-negative breast cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 830606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Lao, X.-M.; Chen, M.-M.; Liu, R.-X.; Wei, Y.; Ouyang, F.-Z.; Chen, D.-P.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.-F.; et al. PD-1hi Identifies a Novel Regulatory B-cell Population in Human Hepatoma That Promotes Disease Progression. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, B.; Han, N.; Li, J.; Lu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Q.; et al. PD-1-expressing B cells suppress CD4+ and CD8+ T cells via PD-1/PD-L1-dependent pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 109, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gallastegui, N.; Rosenblatt, J.D. Regulatory B cells in anti-tumor immunity. Int. Immunol. 2015, 27, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, C.; Lickiss, J.; Kankanige, Y.; Yerneni, S.; Lade, S.; Gandhi, M.K.; Chin, C.; Yannakou, C.K.; Villa, D.; Slack, G.W.; et al. Characterisation of immune checkpoints in Richter syndrome identifies LAG3 as a potential therapeutic target. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 195, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triebel, F.; Jitsukawa, S.; Baixeras, E.; Roman-Roman, S.; Genevee, C.; Viegas-Pequignot, E.; Hercend, T. LAG-3, a novel lymphocyte activation gene closely related to CD4. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 171, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannier, S.; Triebel, F. The MHC class II ligand lymphocyte activation gene-3 is co-distributed with CD8 and CD3–TCR molecules after their engagement by mAb or peptide–MHC class I complexes. Int. Immunol. 1999, 11, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffo, E.; Wu, R.C.; Bruno, T.C.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. Lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG3): The next immune checkpoint receptor. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 42, 101305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemon, P.; Jean-Louis, F.; Ramgolam, K.; Brignone, C.; Viguier, M.; Bachelez, H.; Triebel, F.; Charron, D.; Aoudjit, F.; Al-Daccak, R.; et al. MHC Class II Engagement by Its Ligand LAG-3 (CD223) Contributes to Melanoma Resistance to Apoptosis. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5173–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjunpää, H.; Guillerey, C. TIGIT as an emerging immune checkpoint. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 200, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Qi, G.; Miller, J.S.; Zheng, S.G. CD226: An Emerging Role in Immunologic Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruga, F.; Iannello, A.; Ioannou, N.; Todesco, A.M.; Coscia, M.; Moia, R.; Gaidano, G.; Allan, J.N.; Furman, R.; Vaisitti, T.; et al. The Tigit/CD226/CD155 Immunomodulatory Axis Is Deregulated in CLL and Contributes to B-Cell Anergy. Blood 2021, 138, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruga, F.; Gyau, B.B.; Iannello, A.; Vitale, N.; Vaisitti, T.; Deaglio, S. Immune Response Dysfunction in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Dissecting Molecular Mechanisms and Microenvironmental Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, P.J.; Lazar, G.A. Next generation antibody drugs: Pursuit of the ‘high-hanging fruit’. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 17, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, A.; Williams, A.; Blagden, S.; Plummer, R.; Hochhauser, D.; Krebs, M.G.; Pacey, S.; Evans, J.; Whelan, S.; Nandakumar, S.; et al. PB2099: A First-In-Human Phase 1 Trial Of Nx-1607, A First-In-Class Oral Cbl-B Inhibitor, In Patients With Advanced Malignancies Including Richter Transformation Dlbcl. Hemasphere 2022, 6, 1970–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrisqueta, P.; Delgado, J.; Alcoceba, M.; Oliveira, A.C.; Loscertales, J.; Hernández-Rivas, J.A.; Ferrà, C.; Cordoba, R.; Yáñez, L.; Medina, A.; et al. Clinical outcome and prognostic factors of patients with Richter syndrome: Real-world study of the Spanish Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Study Group (GELLC). Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.-M.; O’Brien, S.; Khouri, I.; Giles, F.J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Champlin, R.; Wen, S.; Do, K.-A.; Smith, S.C.; Lerner, S.; et al. Clinical Outcomes and Prognostic Factors in Patients With Richter’s Syndrome Treated With Chemotherapy or Chemoimmunotherapy With or Without Stem-Cell Transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerbeins, P.; Busch, R.; Anheier, N.; Dürig, J.; Bergmann, M.; Goebeler, M.-E.; Hurtz, H.-J.; Stauch, M.B.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Döhner, H.; et al. Poor efficacy and tolerability of R-CHOP in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter transformation. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, E239–E243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadmor, T.; Shvidel, L.; Bairey, O.; Goldschmidt, N.; Ruchlemer, R.; Fineman, R.; Rahimi-Levene, N.; Herishanu, Y.; Yuklea, M.; Arad, A.; et al. Richter’s transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A retrospective study reporting clinical data, outcome, and the benefit of adding rituximab to chemotherapy, from the Israeli CLLStudy Group. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, E218–E222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, T.A.; Clifford, R.; Bloor, A.; Boyle, L.; Roberts, C.; Cabes, M.; Collins, G.P.; Devereux, S.; Follows, G.; Fox, C.P.; et al. NCRI phase II study of CHOP in combination with ofatumumab in induction and maintenance in newly diagnosed Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 175, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.S.; Rogers, K.A.; Tyekucheva, S.; Wang, Z.; Pazienza, S.; Renner, S.K.; Montegaard, J.; Ihuoma, U.; Lehmberg, T.Z.; Parry, E.M.; et al. Venetoclax plus dose-adjusted R-EPOCH for Richter syndrome. Blood 2022, 139, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwynarski, K.; Van Biezen, A.; De Wreede, L.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Bunjes, D.; Metzner, B.; Koza, V.; Mohty, M.; Remes, K.; Russell, N.; et al. Autologous and Allogeneic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Transformed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (Richter’s Syndrome): A Retrospective Analysis From the Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Subcommittee of the Chronic Leukemia Working Party and Lymphoma Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A.; Kumar, A.; Stingo, F.E.; Khimani, F.; Hussaini, M.; Ayala, E.; Nishihori, T.; Shah, B.; Locke, F.L.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; et al. Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Richter Syndrome: A Single-Center Experience. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017, 18, e35–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.T.; Baker, P.O.; Parry, E.; Davids, M.; Alyea, E.P.; Ho, V.T.; Cutler, C.; Koreth, J.; Gooptu, M.; Romee, R.; et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation outcomes in patients with Richter’s transformation. Haematologica 2021, 106, 3219–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahoud, O.B.; Devlin, S.M.; Maloy, M.A.; Roeker, L.E.; Dahi, P.B.; Ponce, D.M.; Gyurkocza, B.; Koehne, G.; Young, J.W.; Castro-Malaspina, H.R.; et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter’s transformation. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2879–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Jamroz, A.; Huang, S.; Villa, D.; Freeman, C.L.; Scott, D.W.; Slack, G.; Sehn, L.H.; Connors, J.M.; Toze, C.L.; et al. Outcomes of Hodgkin variant Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma in British Columbia. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.-M.; O’Brien, S.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Koller, C.; Hagemeister, F.B.; Fayad, L.; Lerner, S.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; Keating, M.J. Hodgkin transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: The M. D. Anderson Cancer Center experience. Cancer 2006, 107, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadmor, T.; Shvidel, L.; Goldschmidt, N.; Ruchlemer, R.; Fineman, R.; Bairey, O.; Rahimi-Levene, N.; Herishanu, Y.; Yuklea, M.; Arad, A.; et al. Hodgkin’s variant of Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia; a retrospective study from the Israeli CLL study group. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 785–790. [Google Scholar]
- Bockorny, B.; Codreanu, I.; Dasanu, C.A. Hodgkin lymphoma as Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A retrospective analysis of world literature. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 156, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Monti, S.; Rodig, S.J.; Juszczyński, P.; Currie, T.; O’Donnell, E.; Chapuy, B.; Takeyama, K.; Neuberg, D.; Golub, T.R.; et al. Integrative analysis reveals selective 9p24.1 amplification, increased PD-1 ligand expression, and further induction via JAK2 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2010, 116, 3268–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twa, D.D.; Chan, F.C.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Woolcock, B.W.; Mottok, A.; Tan, K.L.; Slack, G.W.; Gunawardana, J.; Lim, R.S.; McPherson, A.W.; et al. Genomic rearrangements involving programmed death ligands are recurrent in primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2014, 123, 2062–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagiv-Barfi, I.; Kohrt, H.E.; Czerwinski, D.K.; Ng, P.P.; Chang, B.Y.; Levy, R. Therapeutic antitumor immunity by checkpoint blockade is enhanced by ibrutinib, an inhibitor of both BTK and ITK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E966–E972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, A.; Brody, J.; Carpio, C.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Ben-Yehuda, D.; Ferhanoglu, B.; Nagler, A.; Ozcan, M.; Avivi, I.; Bosch, F.; et al. Safety and activity of ibrutinib in combination with nivolumab in patients with relapsed non-Hodgkin lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A phase 1/2a study. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e67–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shouse, G.; Siddiqi, T.; Popplewell, L.L.; Muir, A.; Melgar, I.; Orand, K.; Gonzalez, B.; Puverel, S.; Wang, L.; Kittai, A.S.; et al. A Phase I Trial of PI3Kαδ Inhibitor Copanlisib in Combination with Nivolumab in Patients with Richter’s Transformation (RT) or Transformed Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (tNHL). Blood 2022, 140, 6633–6634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Ferrajoli, A.; Thompson, P.A.; Konopleva, M.; Green, M.R.; Sampath, D.; Neelapu, S.S.; Takahashi, K.; Strati, P.; Burger, J.A.; et al. Venetoclax, Obinutuzumab and Atezolizumab (PD-L1 Checkpoint Inhibitor) for Treatment for Patients with Richter Transformation. Blood 2021, 138, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolino, M.; Thien, C.B.F.; Gruber, T.; Hinterleitner, R.; Baier, G.; Langdon, W.Y.; Penninger, J.M. Essential Role of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Activity in Cbl-b–Regulated T Cell Functions. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monticone, G.; Huang, Z.; Csibi, F.; Leit, S.; Ciccone, D.; Champhekar, A.S.; Austin, J.E.; Ucar, D.A.; Hossain, F.; Ibba, S.V.; et al. Targeting the Cbl-b-Notch1 axis as a novel immunotherapeutic strategy to boost CD8+ T-cell responses. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 987298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.J.; Kole, H.K.; Brown, K.; Naramura, M.; Fukuhara, S.; Hu, R.-J.; Jang, I.K.; Gutkind, J.S.; Shevach, E.; Gu, H. Cbl-b regulates the CD28 dependence of T-cell activation. Nature 2000, 403, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalon, O.; Barda-Saad, M. Cbl ubiquitin ligases mediate the inhibition of natural killer cell activity. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2016, 9, e1216739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xing, Z.; Mi, L.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wei, T.; Wu, W. Novel Agents For Relapsed and Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Review. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 929012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Murawski, N.; Molin, D.; Zain, J.; Eichhorst, B.; Gulbas, Z.; Hawkes, E.A.; Pagel, J.M.; Phillips, T.; Ribrag, V.; et al. Pembrolizumab in relapsed or refractory Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, e117–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, G.; Wang, Z.; Hao, M.; Li, J. Bispecific antibodies and their applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisonoff, A.; Wissler, F.C.; Lipman, L.N. Properties of the Major Component of a Peptic Digest of Rabbit Antibody. Science 1960, 132, 1770–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staerz, U.D.; Kanagawa, O.; Bevan, M.J. Hybrid antibodies can target sites for attack by T cells. Nature 1985, 314, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.J.; Benani, D.J. A review of blinatumomab, a novel immunotherapy. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract 2015, 22, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, M.; Köse, M.C.; Duray, E.; Einsele, H.; Beguin, Y.; Caers, J. Bispecific, T-Cell-Recruiting Antibodies in B-Cell Malignancies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.A.; Jiang, X.; Banerjee, P.; Basar, R.; Garg, N.; Chen, K.; Kaplan, M.; Nandivada, V.; Cortes, A.K.N.; Ferrajoli, A.; et al. A phase two study of high dose blinatumomab in Richter’s syndrome. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2228–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guieze, R.; Ysebaert, L.; Roos-Weil, D.; Fornecker, L.-M.; Ferrant, E.; Molina, L.; Aurran-Schleinitz, T.; Clavert, A.; de Guibert, S.; Michallet, A.-S.; et al. Blinatumomab for Patients with Richter Syndrome: Final Results of the Phase 2 Blinart Trial from the Filo Group. Blood 2022, 140, 6631–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kater, A.P.; Ye, J.C.; Sandoval-Sus, J.; Bellido, M.; Christensen, J.H.; Mato, A.R.; Janssens, A.; Oki, T.; Hoehn, D.; Rios, M.; et al. Subcutaneous Epcoritamab in Patients with Richter’s Syndrome: Early Results from Phase 1b/2 Trial (EPCORE CLL-1). Blood 2022, 140, 850–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongorzul, P.; Ling, C.J.; Khan, F.U.; Ihsan, A.U.; Zhang, J. Antibody–Drug Conjugates: A Comprehensive Review. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualberto, A. Brentuximab Vedotin (SGN-35), an antibody–drug conjugate for the treatment of CD30-positive malignancies. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2011, 21, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisitti, T.; Braggio, E.; Allan, J.N.; Arruga, F.; Serra, S.; Zamò, A.; Tam, W.; Chadburn, A.; Furman, R.R.; Deaglio, S. Novel Richter Syndrome Xenograft Models to Study Genetic Architecture, Biology, and Therapy Responses. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3413–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Playa-Albinyana, H.; Arenas, F.; Royo, R.; Giró, A.; López, I.; Lopez-Guerra, M.; Beà, S.; Campo, E.; Nadeu, F.; Colomer, D. Generation of Richter Transformation Models throughout Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patient-Derived Xenografts: A Clonal Evolution Model. Blood 2022, 140, 1534–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisitti, T.; Arruga, F.; Vitale, N.; Lee, T.-T.; Ko, M.; Chadburn, A.; Braggio, E.; Di Napoli, A.; Iannello, A.; Allan, J.N.; et al. ROR1 targeting with the antibody-drug conjugate VLS-101 is effective in Richter syndrome patient–derived xenograft mouse models. Blood 2021, 137, 3365–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, Y.; Lu, B.; Zhao, Z.J.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y. Tyrosine Kinase ROR1 as a Target for Anti-Cancer Therapies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 680834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, U.; Tu, Y.; Stolovitzky, G.A.; Mattioli, M.; Cattoretti, G.; Husson, H.; Freedman, A.; Inghirami, G.; Cro, L.; Baldini, L.; et al. Gene Expression Profiling of B Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Reveals a Homogeneous Phenotype Related to Memory B Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskar, S.; Kwong, K.Y.; Hofer, T.; Levy, J.M.; Kennedy, M.G.; Lee, E.; Staudt, L.M.; Wilson, W.H.; Wiestner, A.; Rader, C. Unique Cell Surface Expression of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase ROR1 in Human B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, A.; Daneshmanesh, A.H.; Moshfegh, A.; Kokhaei, P.; Vågberg, J.; Schultz, J.; Olin, T.; Harrysson, S.; Smedby, K.E.; Drakos, E.; et al. ROR1 Is Expressed in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) and a Small Molecule Inhibitor of ROR1 (KAN0441571C) Induced Apoptosis of Lymphoma Cells. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipps, T.J. ROR1: An orphan becomes apparent. Blood 2022, 140, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisitti, T.; Vitale, N.; Micillo, M.; Brandimarte, L.; Iannello, A.; Papotti, M.G.; Jaksic, O.; Lopez, G.; Di Napoli, A.; Cutrin, J.C.; et al. Anti-CD37 α-amanitin–conjugated antibodies as potential therapeutic weapons for Richter syndrome. Blood 2022, 140, 1565–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckwith, K.A.; Byrd, J.C.; Muthusamy, N. Tetraspanins as therapeutic targets in hematological malignancy: A concise review. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvetti, C.; Vitale, C.; Griggio, V.; Drandi, D.; Jones, R.; Bonello, L.; Bomben, R.; Bragoni, A.; Bagnara, D.; Fais, F.; et al. Case Report: Sequential Development of Three Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms in a Single Patient: Clonal Relationship and Molecular Insights. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 917115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Addona, M.; Giudice, V.; Pezzullo, L.; Ciancia, G.; Baldi, C.; Gorrese, M.; Bertolini, A.; Campana, A.; Fresolone, L.; Manzo, P.; et al. Hodgkin Lymphoma and Hairy Cell Leukemia Arising from Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Case Reports and Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliotou, A.N.; Papadopoulou, L.C. CAR T-cell Therapy: A New Era in Cancer Immunotherapy. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2018, 19, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoldo, B.; Ramos, C.A.; Liu, E.; Mims, M.P.; Keating, M.J.; Carrum, G.; Kamble, R.T.; Bollard, C.M.; Gee, A.P.; Mei, Z.; et al. CD28 costimulation improves expansion and persistence of chimeric antigen receptor–modified T cells in lymphoma patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1822–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, A.H.; Haso, W.M.; Shern, J.F.; Wanhainen, K.M.; Murgai, M.; Ingaramo, M.; Smith, J.P.; Walker, A.J.; Kohler, M.E.; Venkateshwara, V.R.; et al. 4-1BB costimulation ameliorates T cell exhaustion induced by tonic signaling of chimeric antigen receptors. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, L.; Silbert, S.K.; Maude, S.L.; Nastoupil, L.J.; Ramos, C.A.; Brentjens, R.J.; Sauter, C.S.; Shah, N.N.; Abou-El-Enein, M. Preparing for CAR T cell therapy: Patient selection, bridging therapies and lymphodepletion. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensaber, H.; Bachy, E.; Beauvais, D.; Dulery, R.; Gastinne, T.; Villemagne, B.; Roulin, L.; Paubelle, E.; Castilla-Llorente, C.; Longval, T.; et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy for Patients with Richter Syndrome: A Lysa Study from the Descar-T Registry. Blood 2022, 140, 3803–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Maldonado, V.; Frigola, G.; Español-Rego, M.; Balagué, O.; Martínez-Cibrián, N.; Magnano, L.; Giné, E.; Pascal, M.; Correa, J.G.; Martínez-Roca, A.; et al. Results of ARI-0001 CART19 Cells in Patients With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Richter’s Transformation. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 828471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittai, A.S.; Bond, D.A.; William, B.; Saad, A.; Penza, S.; Efebera, Y.; Larkin, K.; Wall, S.A.; Choe, H.K.; Bhatnagar, B.; et al. Clinical activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in adult patients with Richter syndrome. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4648–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabaja, B.S.; O’Brien, S.M.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.E.; Thomas, D.A.; Albitar, M.; Schlette, E.S.; Faderl, S.; Sarris, A.; Keating, M.J.; et al. Fractionated Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, Liposomal Daunorubicin (Daunoxome), and Dexamethasone (HyperCVXD) Regimen in Richter’s Syndrome. Leuk. Lymphoma 2001, 42, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.; Thomas, D.A.; Faderl, S.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Verstovsek, S.; Ferrajoli, A.; Wierda, W.; Alvarado, Y.; et al. Fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, liposomal daunorubicin, and dexamethasone plus rituximab and granulocyte-macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) alternating with methotrexate and cytarabine plus rituximab and GM-CSF in patients with Richter syndrome or fludarabine-refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 2003, 97, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Wierda, W.G.; Plunkett, W.; Kurzrock, R.; O’Brien, S.; Wen, S.; Ferrajoli, A.; Ravandi-Kashani, F.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Estrov, Z.; et al. Phase I-II Study of Oxaliplatin, Fludarabine, Cytarabine, and Rituximab Combination Therapy in Patients With Richter’s Syndrome or Fludarabine-Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Wierda, W.G.; Wen, S.; Plunkett, W.; O’Brien, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Jones, J.A.; Badoux, X.; Kantarjian, H.; Keating, M.J. Phase I-II Clinical Trial of Oxaliplatin, Fludarabine, Cytarabine, and Rituximab Therapy in Aggressive Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia or Richter Syndrome. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013, 13, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durot, E.; Michallet, A.-S.; Leprêtre, S.; Le, Q.-H.; Leblond, V.; Delmer, A. Platinum and high-dose cytarabine-based regimens are efficient in ultra high/high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter’s syndrome: Results of a French retrospective multicenter study. Eur. J. Haematol. 2015, 95, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NCT Number | Status | Interventions | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05458297 | Recruiting | Single agent: Zilovertamab vedotin | Phase II |
| NCT05388006 | Recruiting | Combination Product: Acalabrutinib with Durvalumab and Venetoclax | Phase II |
| NCT05025800 | Recruiting | Combination Product: CD47 Antagonist ALX148 with Lenalidomide and Rituximab | Phase I/II |
| NCT04939363 | Recruiting | Combination Product: Obinutuzumab with Ibrutinib and Venetoclax | Phase II |
| NCT04806035 | Recruiting | Combination Product: Cosibelimab (TG-1501) plus Ublituximab vs. Cosibelimab (TG-1501) alone | Phase I |
| NCT04781855 | Recruiting | Combination Product: Ibrutinib with Ipilimumab and Nivolumab vs. Ipilimumab plus ibrutinib | Phase I |
| NCT04679012 | Recruiting | Combination Product: Polatuzumab vedotin plus R-EPCH | Phase II |
| NCT04623541 | Recruiting | Single agent: Epcoritamab | Phase I/II |
| NCT04491370 | Recruiting | Autologous SCT followed by Polatuzumab vedotin | Phase I/II |
| NCT04271956 | Recruiting | Combination Product: Tislelizumab plus Zanubrutinib | Phase II |
| NCT04082897 | Recruiting | Combination Product: Obinutuzumabwith Atezolizumab and Venetoclax | Phase II |
| NCT03884998 | Recruiting | Combination Product: Copanlisib plus Nivolumab | Phase I |
| NCT03778073 | Terminated | Combination Product: Cosibelimab (TG-1501) with Ublituximab and Bendamustine | Phase I |
| NCT03153514 | Terminated | Obinutuzumab plus Allogeneic SCT | Phase II |
| NCT03145480 | Terminated | Combination Product: Obinutuzumab plus Ibrutinib vs. Obinutuzumab with Ibrutinib and CHOP | Phase II |
| NCT03121534 | Completed | Single agent: Blinatumomab | Phase II |
| NCT03113695 | Completed | Combination Product: Obinutuzumab with Lenalidomide and HDMP | Phase I |
| NCT02846623 | Recruiting | Combination Product: Atezolizumab with Obinutuzumab and Venetoclax | Phase II |
| NCT02576990 | Completed | Single agent: Pembrolizumab | Phase II |
| NCT02535286 | Completed | Combination Product: Umbralisib with Ublituximab and Cosibelimab (TG-1501) | Phase I |
| NCT02420912 | Completed | Combination Product: Ibrutinib plus Nivolumab | Phase II |
| NCT03054896 | Recruiting | Combination Product: Venetoclax plus DA-EPOCH-R vs Venetoclax plus R-CHOP | Phase II |
| NCT02332980 | Active, not recruiting | Combination product: Pembrolizumab plus Ibrutinib vs. Pembrolizumab plus Idelalisib vs. Pembrolizumab alone | Phase II |
| NCT02329847 | Completed | Combination product: Ibrutinib with Nivolumab | Phase I/II |
| NCT03931642 | Active, not recruiting | Combination product: R-CHOP debulking followed by Blinatumomab | Phase II |
| NCT01217749 | Completed | Combination Product: PCI-32765 plus Ofatumumab | Phase I/II |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmoud, A.M.; Gaidano, G.; Mouhssine, S. Immunological Aspects of Richter Syndrome: From Immune Dysfunction to Immunotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041015
Mahmoud AM, Gaidano G, Mouhssine S. Immunological Aspects of Richter Syndrome: From Immune Dysfunction to Immunotherapy. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041015
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmoud, Abdurraouf Mokhtar, Gianluca Gaidano, and Samir Mouhssine. 2023. "Immunological Aspects of Richter Syndrome: From Immune Dysfunction to Immunotherapy" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041015
APA StyleMahmoud, A. M., Gaidano, G., & Mouhssine, S. (2023). Immunological Aspects of Richter Syndrome: From Immune Dysfunction to Immunotherapy. Cancers, 15(4), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041015






