Comparison of Recurrence Patterns between Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma after Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early-Stage Lung Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Pretreatment Evaluation
2.3. SBRT
2.4. Follow-Up and Collection and Evaluation of Data
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Outcomes
3.3. Univariate and Multivariate Analyses of Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Lymph Node Metastasis | Distant Metastasis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | Multivariate | Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (per year) | 0.99 (0.93–1.07) | 0.88 | 0.99 (0.92–1.07) | 0.77 | 1.01 (0.97–1.06) | 0.57 | 1.01 (0.97–1.06) | 0.65 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 1.57 (0.69–3.58) | 0.28 | 1.24 (0.47–3.24) | 0.66 | 1.21 (0.68–2.15) | 0.51 | 1.06 (0.56–2.0) | 0.85 |
| PS (2, 3 vs. 0, 1) | 0.32 (0.042–2.41) | 0.27 | 0.25 (0.030–2.0) | 0.19 | 1.33 (0.55–3.21) | 0.53 | 1.13 (0.41–3.12) | 0.81 |
| FEV1 (L) (≤1.5 vs. >1.5) | 0.76 (0.36–1.59) | 0.46 | 0.74 (0.36–1.53) | 0.42 | 0.68 (0.39–1.19) | 0.18 | 0.68 (0.37–1.22) | 0.19 |
| Tumor diameter (per 0.1 cm) | 1.02 (0.98–1.06) | 0.41 | 1.01 (0.97–1.05) | 0.73 | 1.01 (0.99–1.04) | 0.26 | 1.01 (0.99–1.04) | 0.37 |
| Histological type (SCC vs. ADC) | 1.91 (0.95–3.83) | 0.071 | 1.90 (0.92–3.93) | 0.084 | 1.13 (0.64–1.97) | 0.68 | 1.02 (0.56–1.86) | 0.95 |
| Biological effective dose (≤110 vs. >110) | 1.75 (0.83–3.7) | 0.14 | 1.63 (0.74–3.59) | 0.23 | 1.03 (0.61–1.75) | 0.90 | 0.94 (0.54–1.64) | 0.82 |
References
- de Koning, H.J.; van der Aalst, C.M.; de Jong, P.A.; Scholten, E.T.; Nackaerts, K.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Lammers, J.J.; Weenink, C.; Yousaf-Khan, U.; Horeweg, N.; et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with volume CT screening in a randomized trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.Y.; Senan, S.; Paul, M.A.; Mehran, R.J.; Louie, A.V.; Balter, P.; Groen, H.J.; McRae, S.E.; Widder, J.; Feng, L.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus lobectomy for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: A pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaj-Levra, N.; Borghetti, P.; Bruni, A.; Ciammella, P.; Cuccia, F.; Fozza, A.; Franceschini, D.; Scotti, V.; Vagge, S.; Alongi, F. Current radiotherapy techniques in NSCLC: Challenges and potential solutions. Expert. Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2020, 20, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotti, V.; Bruni, A.; Francolini, G.; Perna, M.; Vasilyeva, P.; Loi, M.; Simontacchi, G.; Viggiano, D.; Lanfranchi, B.; Gonfiotti, A.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy as an alternative to lobectomy in patients with medically operable stage I NSCLC: A retrospective, multicenter analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, e53–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, N.; Okuda, K.; Kita, N.; Niwa, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Murai, T.; Ishikura, S.; Nakanishi, R.; Shibamoto, Y. Role of stereotactic body radiotherapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer in patients borderline for surgery due to impaired pulmonary function. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 18, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Shibuya, K.; Nagata, Y.; Norihisa, Y.; Narabayashi, M.; Sakanaka, K.; Ueki, N.; Mizowaki, T.; Hiraoka, M. Preliminary report of late recurrences, at 5 years or more, after stereotactic body radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woody, N.M.; Stephans, K.L.; Andrews, M.; Zhuang, T.; Gopal, P.; Xia, P.; Farver, C.F.; Raymond, D.P.; Peacock, C.D.; Cicenia, J.; et al. A Histologic Basis for the Efficacy of SBRT to the lung. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijsseldijk, M.A.; Shoni, M.; Siegert, C.; Wiering, B.; van Engelenburg, A.K.; Tsai, T.C.; Ten Broek, R.P.; Lebenthal, A. Oncologic outcomes of surgery versus SBRT for non-small-cell lung carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, e235–e292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, N.; Okuda, K.; Osaga, S.; Miyakawa, A.; Nakanishi, R.; Shibamoto, Y. Surgery versus stereotactic body radiotherapy for clinical stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: Propensity score-matching analysis including the ratio of ground glass nodules. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V.; et al. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: Proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (Eighth) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, F.; Shibamoto, Y.; Tomita, N.; Ikeya-Hashizume, C.; Oda, K.; Ayakawa, S.; Ogino, H.; Sugie, C. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for stage I lung cancer and small lung metastasis: Evaluation of an immobilization system for suppression of respiratory tumor movement and preliminary results. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyakawa, A.; Shibamoto, Y.; Baba, F.; Manabe, Y.; Murai, T.; Sugie, C.; Yanagi, T.; Takaoka, T. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer using higher doses for larger tumors: Results of the second study. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibamoto, Y.; Otsuka, S.; Iwata, H.; Sugie, C.; Ogino, H.; Tomita, N. Radiobiological evaluation of the radiation dose as used in high-precision radiotherapy: Effect of prolonged delivery time and applicability of the linear-quadratic model. J. Radiat. Res. 2012, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.; Dahele, M.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; Senan, S. A critical review of recent developments in radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baine, M.J.; Verma, V.; Schonewolf, C.A.; Lin, C.; Simone, C.B., 2nd. Histology significantly affects recurrence and survival following SBRT for early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 118, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools-Lartigue, J.; Ferri, L. Should multidisciplinary treatment differ for esophageal adenocarcinoma versus esophageal squamous cell cancer? Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 1014–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.C.; Lu, C.H.; Lin, J.C.; Hsu, C.Y.; Wang, L. Treatment outcomes of locally advanced cervical cancer by histopathological types in a single institution: A propensity score matching study. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2018, 117, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Monk, B.; Devouassoux-Shisheboran, M. Adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix: Why is it different? Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 16, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceppi, P.; Volante, M.; Saviozzi, S.; Rapa, I.; Novello, S.; Cambieri, A.; Lo Iacono, M.; Cappia, S.; Papotti, M.; Scagliotti, G.V. Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung compared with other histotypes shows higher messenger RNA and protein levels for thymidylate synthase. Cancer 2006, 107, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelillo, R.M.; Ramella, S. Are We Ready for Histology-Driven Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1441–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.M.; Mady, H.H.; Yu, G.Y.; Siegfried, J.M.; Luketich, J.D.; Melhem, M.F.; Keohavong, P. Comparison of p53 mutations between adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the lung: Unique spectra involving G to A transitions and G to T transversions in both histologic types. Lung Cancer 2003, 40, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, B.; Findeis-Hosey, J.J.; Li, F.; McMahon, L.A.; Yang, Q.; Xu, H. High frequency of coexpression of maspin with p63 and p53 in squamous cell carcinoma but not in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 2542–2547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guckenberger, M.; Andratschke, N.; Dieckmann, K.; Hoogeman, M.S.; Hoyer, M.; Hurkmans, C.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Lartigau, E.; Méndez Romero, A.; Senan, S.; et al. ESTRO ACROP consensus guideline on implementation and practice of stereotactic body radiotherapy for peripherally located early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parzen, J.S.; Almahariq, M.F.; Quinn, T.J.; Siddiqui, Z.A.; Thompson, A.B.; Guerrero, T.; Lee, K.; Stevens, C.; Grills, I.S. Higher biologically effective dose is associated with improved survival in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 160, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Hasan, S.; Verma, V.; Weksler, B.; Colonias, A.; Horne, Z.D.; Wegner, R.E. Establishing a histology-specific biologically effective dose threshold for lung stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR): Is ≥100 Gy10 enough? Lung Cancer 2019, 135, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Ohtsu, S.; Nishimura, T.; Terada, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Mizowaki, T. Impact of histology on patterns of failure and clinical outcomes in patients treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, Y.; Jingu, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Matsushita, H.; Umezawa, R.; Ishikawa, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Takeda, K.; Tasaka, S.; Kadoya, N. Differences in patterns of recurrence of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma after radiotherapy for stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2021, 39, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.D.; Paulus, R.; Komaki, R.; Masters, G.; Blumenschein, G.; Schild, S.; Bogart, J.; Hu, C.; Forster, K.; Magliocco, A.; et al. Standard-dose versus high-dose conformal radiotherapy with concurrent and consolidation carboplatin plus paclitaxel with or without cetuximab for patients with stage IIIA or IIIB non-small-cell lung cancer (RTOG 0617): A randomised, two-by-two factorial phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; John, T.; Grohe, C.; Majem, M.; Goldman, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Kato, T.; Laktionov, K.; Vu, H.V.; Wang, Z.; et al. Postoperative chemotherapy use and outcomes from ADAURA: Osimertinib as adjuvant therapy for resected EGFR-mutated NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Gray, J.E.; Vicente, D.; Planchard, D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Vansteenkiste, J.F.; Garassino, M.C.; Hui, R.; Quantin, X.; et al. Five-year survival outcomes from the PACIFIC trial: Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubas, M.J.; Kumar, S.S. The combined use of SBRT and immunotherapy—A literature review. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaue, D.; Ratikan, J.A.; Iwamoto, K.S.; McBride, W.H. Maximizing tumor immunity with fractionated radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, 1306–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljanic, M.; Montalvo, S.; Aliru, M.; Song, T.; Leon-Camarena, M.; Innella, K.; Vujovic, D.; Komaki, R.; Iyengar, P. The evolving interplay of SBRT and the immune system, along with future directions in the field. Cancers 2022, 14, 4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubin, S.; Gupta, S.; Grusch, M.; Popper, H.H.; Brcic, L.; Ashdown, M.L.; Khleif, S.N.; Peter-Vörösmarty, B.; Hyden, M.; Negrini, S.; et al. Shifting the immune-suppressive to predominant immune-stimulatory radiation effects by SBRT-PArtial tumor irradiation targeting HYpoxic segment (SBRT-PATHY). Cancers 2020, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, R.; Shibamoto, Y.; Sasai, K.; Oya, N.; Shibata, T.; Takagi, T.; Abe, M. Reoxygenation after single irradiation in rodent tumors of different types and sizes. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1996, 34, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, N.; Ishiyama, H.; Makita, C.; Ohshima, Y.; Nagai, A.; Baba, F.; Kuno, M.; Otsuka, S.; Kondo, T.; Sugie, C.; et al. Daily irradiation versus irradiation at two- to three-day intervals in stereotactic radiotherapy for patients with 1–5 brain metastases: Study protocol for a multicenter open-label randomized phase II trial. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Demaria, S.; Ohno, T. The role of radiotherapy in the age of immunotherapy. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 51, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanpouille-Box, C.; Alard, A.; Aryankalayil, M.J.; Sarfraz, Y.; Diamond, J.M.; Schneider, R.J.; Inghirami, G.; Coleman, C.N.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. DNA exonuclease Trex1 regulates radiotherapy-induced tumour immunogenicity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videtic, G.M.M.; Donington, J.; Giuliani, M.; Heinzerling, J.; Karas, T.Z.; Kelsey, C.R.; Lally, B.E.; Latzka, K.; Lo, S.S.; Moghanaki, D.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: Executive summary of an ASTRO evidence-based guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 7, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

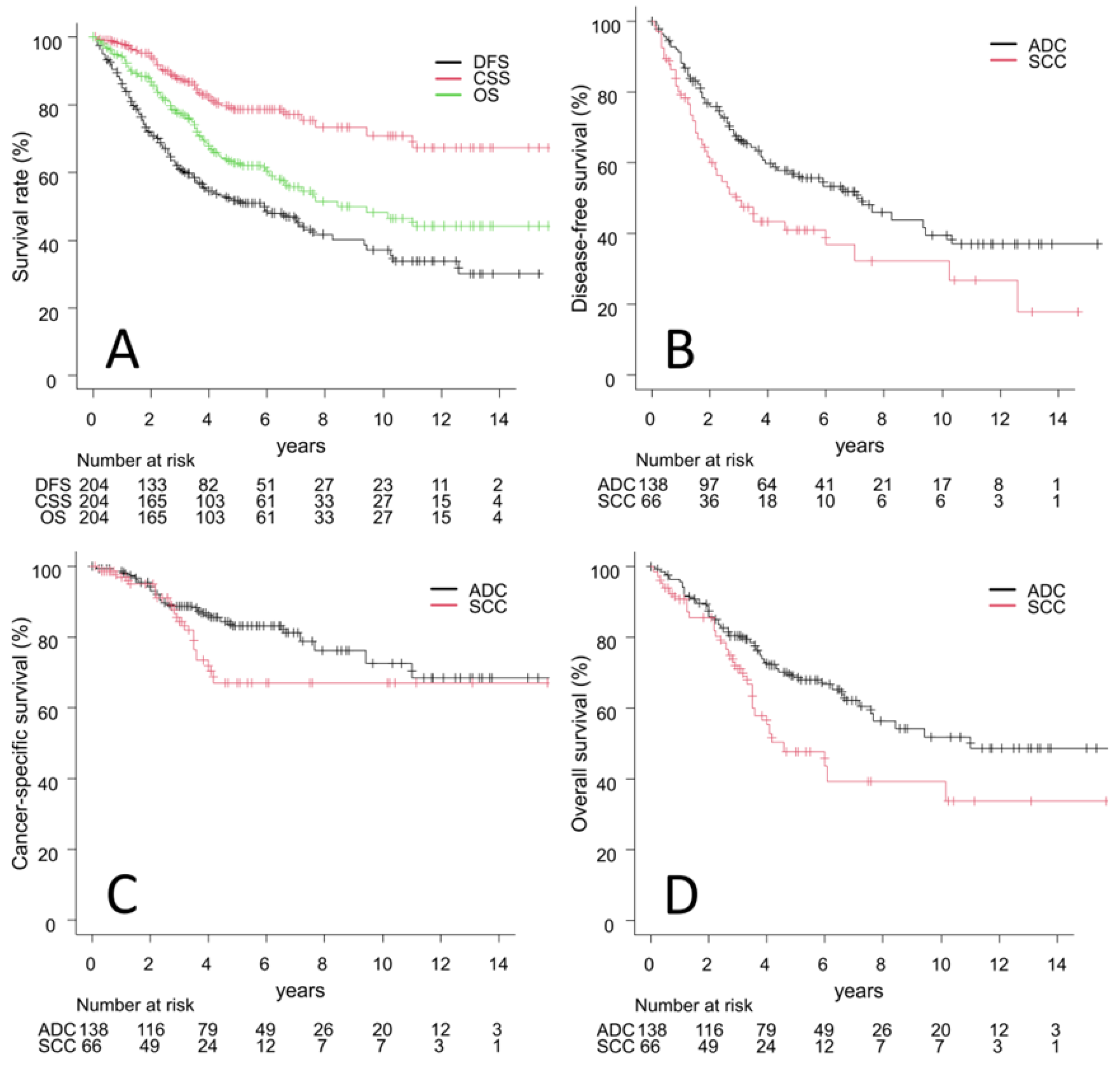
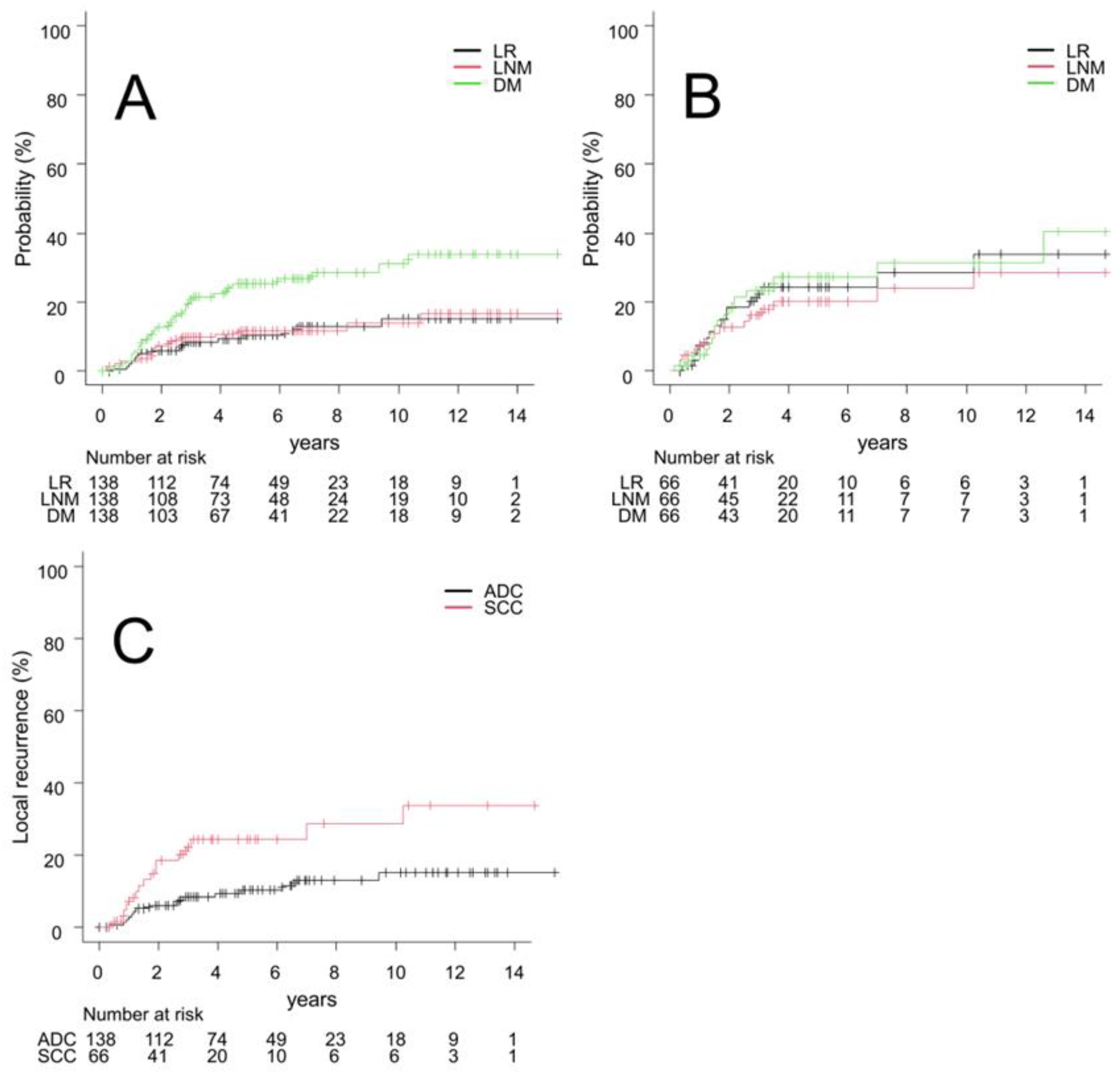
| Characteristics | All (n = 204) | ADC Group (n = 138) | SCC Group (n = 66) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 77 (29–89) | 77 (29–89) | 78 (58–89) | 0.25 |
| Male/female | 142 (70%)/62 (30%) | 85 (62%)/53 (38%) | 57 (86%)/9 (14%) | <0.001 |
| PS 0/1/2/3 | 98 (48%)/85 (42%)/17 (8%)/4 (2%) | 69 (50%)/59 (43%)/8 (6%)/2 (1%) | 29 (44%)/26 (39%)/9 (14%)/2 (3%) | 0.23 |
| Current smoker/ex/non/missing | 60 (29%)/88 (43%)/50 (25%)/6 (3%) | 30 (22%)/56 (41%)/48 (35%)/4 (3%) | 30 (45%)/32 (48%)/2 (3%)/2 (3%) | <0.001 |
| FEV1 (L) | 1.7 (0.6–3.3) | 1.7 (0.7–3.3) | 1.6 (0.6–3.0) | 0.28 |
| Tumor diameter (cm) | 2.4 (0–5.0) | 2.2 (0–4.7) | 2.6 (0.9–5.0) | <0.001 |
| Tis/T1mi/T1a/T1b/T1c/T2a/T2b | 4 (2%)/5 (2%)/13 (6%)/47 (23%)/82 (40%)/42 (21%)/11 (5%) | 4 (3%)/5 (4%)/12 (9%)/35 (25%)/51 (37%)/26 (19%)/5 (4%) | 0 (0%)/0 (0%)/1 (2%)/12 (18%)/31 (47%)/16 (24%)/6 (9%) | 0.041 |
| Tumor location | ||||
| Upper lobe/middle or lower lobe | 116 (57%)/88 (43%) | 74 (54%)/64 (46%) | 42 (64%)/24 (36%) | 0.23 |
| Central/peripheral | 29 (14%)/175 (86%) | 16 (12%)/122 (88%) | 13 (20%)/53 (80%) | 0.18 |
| Total dose (Gy) | 50 (44–64) | 50 (44–64) | 50 (48–60) | 0.041 |
| Fractions | 4 (4–8) | 4 (4–8) | 4 (4–8) | 0.16 |
| Biological effective dose (α/β = 10) | 113 (92–110) | 113 (92–120) | 113 (105–120) | 0.23 |
| Operable/inoperable/missing | 74 (36%)/128 (63%)/2 (1%) | 53 (38%) /84 (61%) /1 (1%) | 21 (32%) /44 (67%) /1 (2%) | 0.47 |
| Disease-Free Survival | Overall Survival | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | Multivariate | Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (per year) | 1.03 (1.0–1.06) | 0.059 | 1.02 (0.99–1.04) | 0.24 | 1.05 (1.02–1.09) | 0.005 | 1.03 (1.0–1.07) | 0.037 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 1.78 (1.13–2.79) | 0.012 | 1.55 (0.96–2.49) | 0.075 | 2.44 (1.39–4.28) | 0.002 | 2.04 (1.13–3.68) | 0.018 |
| PS (2, 3 vs. 0, 1) | 2.14 (1.19–3.85) | 0.011 | 1.91 (1.05–3.47) | 0.034 | 2.48 (1.27–4.86) | 0.008 | 2.15 (1.08–4.29) | 0.030 |
| FEV1 (L) (≤1.5 vs. >1.5) | 0.87 (0.58–1.29) | 0.47 | 0.86 (0.57–1.29) | 0.47 | 0.74 (0.46–1.19) | 0.21 | 0.73 (0.45–1.18) | 0.20 |
| Tumor diameter (per 0.1 cm) | 1.04 (1.02–1.05) | <0.001 | 1.03 (1.01–1.054) | 0.004 | 1.05 (1.03–1.07) | <0.001 | 1.05 (1.02–1.08) | <0.001 |
| Histological type (SCC vs. ADC) | 1.63 (1.09–2.42) | 0.017 | 1.23 (0.81–1.88) | 0.34 | 1.72 (1.09–2.71) | 0.021 | 1.11 (0.68–1.81) | 0.67 |
| Biological effective dose (≤110 vs. >110) | 1.20 (0.81–1.77) | 0.37 | 0.91 (0.60–1.39) | 0.67 | 1.10 (0.71–1.72) | 0.67 | 0.77 (0.47–1.25) | 0.28 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (per year) | 0.98 (0.94–1.03) | 0.39 | 0.97 (0.93–1.02) | 0.23 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 1.04 (0.51–2.13) | 0.92 | 0.87 (0.43–1.75) | 0.70 |
| PS (2, 3 vs. 0, 1) | 0.31 (0.043–2.30) | 025 | 0.25 (0.033–1.81) | 0.17 |
| FEV1 (L) (≤1.5 vs. >1.5) | 1.62 (0.82–3.21) | 0.17 | 1.44 (0.73–2.84) | 0.29 |
| Tumor diameter (per 0.1 cm) | 1.05 (1.02–1.08) | 0.002 | 1.05 (1.01–1.08) | 0.009 |
| Histological type (SCC vs. ADC) | 2.52 (1.27–4.99) | 0.008 | 2.41 (1.21–4.77) | 0.012 |
| Biological effective dose (≤110 vs. >110) | 1.34 (0.65–2.74) | 0.43 | 0.95 (0.42–2.16) | 0.90 |
| Tumor Diameter ≤ 2.5 cm (n = 113) | Tumor Diameter > 2.5 cm (n = 91) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | Multivariate | Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (per year) | 1.0 (0.94–1.06) | 0.88 | 0.97 (0.90–1.05) | 0.48 | 0.97 (0.93–1.01) | 0.18 | 0.96 (0.91–1.02) | 0.20 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 1.16 (0.36–3.75) | 0.81 | 0.93 (0.28–3.09) | 0.90 | 0.81 (0.34–1.94) | 0.64 | 0.69 (0.29–1.67) | 0.42 |
| PS (2, 3 vs. 0, 1) | 0.00004 (0.00002–0.0001) | <0.001 | 0.000031 (0.00001–0.00009) | <0.001 | 0.39 (0.053–2.87) | 0.35 | 0.34 (0.044–2.57) | 0.29 |
| FEV1 (L) (≤1.5 vs. >1.5) | 1.58 (0.52–4.80) | 0.42 | 1.52 (0.49–4.72) | 0.47 | 1.62 (0.69–3.81) | 0.27 | 1.36 (0.58–3.20) | 0.49 |
| Tumor diameter (per 0.1 cm) | 1.10 (0.99–1.23) | 0.082 | 1.11 (0.98–1.25) | 0.10 | 1.01 (0.95–1.07) | 0.78 | 1.02 (0.95–1.09) | 0.62 |
| Histological type (SCC vs. ADC) | 2.40 (0.79–7.3) | 0.12 | 1.68 (0.59–4.76) | 0.33 | 2.11 (0.89–5.04) | 0.092 | 2.61 (1.07–6.41) | 0.036 |
| Biological effective dose (≤110 vs. >110) | 1.52 (0.49–4.71) | 0.47 | 1.54 (0.41–5.74) | 0.52 | 1.01 (0.40–2.53) | 0.99 | 0.80 (0.27–2.34) | 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kita, N.; Tomita, N.; Takaoka, T.; Sudo, S.; Tsuzuki, Y.; Okazaki, D.; Niwa, M.; Torii, A.; Takano, S.; Niimi, A.; et al. Comparison of Recurrence Patterns between Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma after Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early-Stage Lung Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030887
Kita N, Tomita N, Takaoka T, Sudo S, Tsuzuki Y, Okazaki D, Niwa M, Torii A, Takano S, Niimi A, et al. Comparison of Recurrence Patterns between Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma after Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early-Stage Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030887
Chicago/Turabian StyleKita, Nozomi, Natsuo Tomita, Taiki Takaoka, Shuou Sudo, Yusuke Tsuzuki, Dai Okazaki, Masanari Niwa, Akira Torii, Seiya Takano, Akio Niimi, and et al. 2023. "Comparison of Recurrence Patterns between Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma after Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early-Stage Lung Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 3: 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030887
APA StyleKita, N., Tomita, N., Takaoka, T., Sudo, S., Tsuzuki, Y., Okazaki, D., Niwa, M., Torii, A., Takano, S., Niimi, A., & Hiwatashi, A. (2023). Comparison of Recurrence Patterns between Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma after Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Early-Stage Lung Cancer. Cancers, 15(3), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030887







