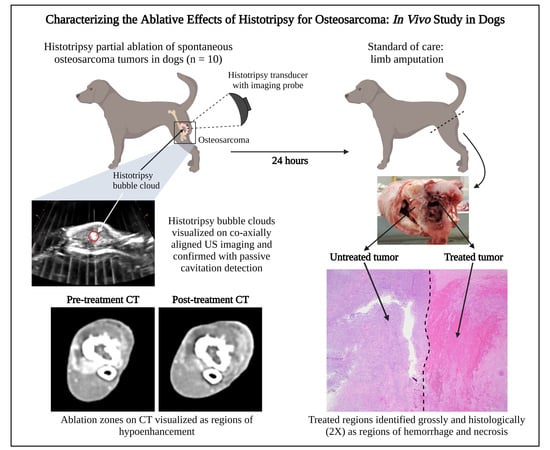
Characterizing the Ablative Effects of Histotripsy for Osteosarcoma: In Vivo Study in Dogs
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
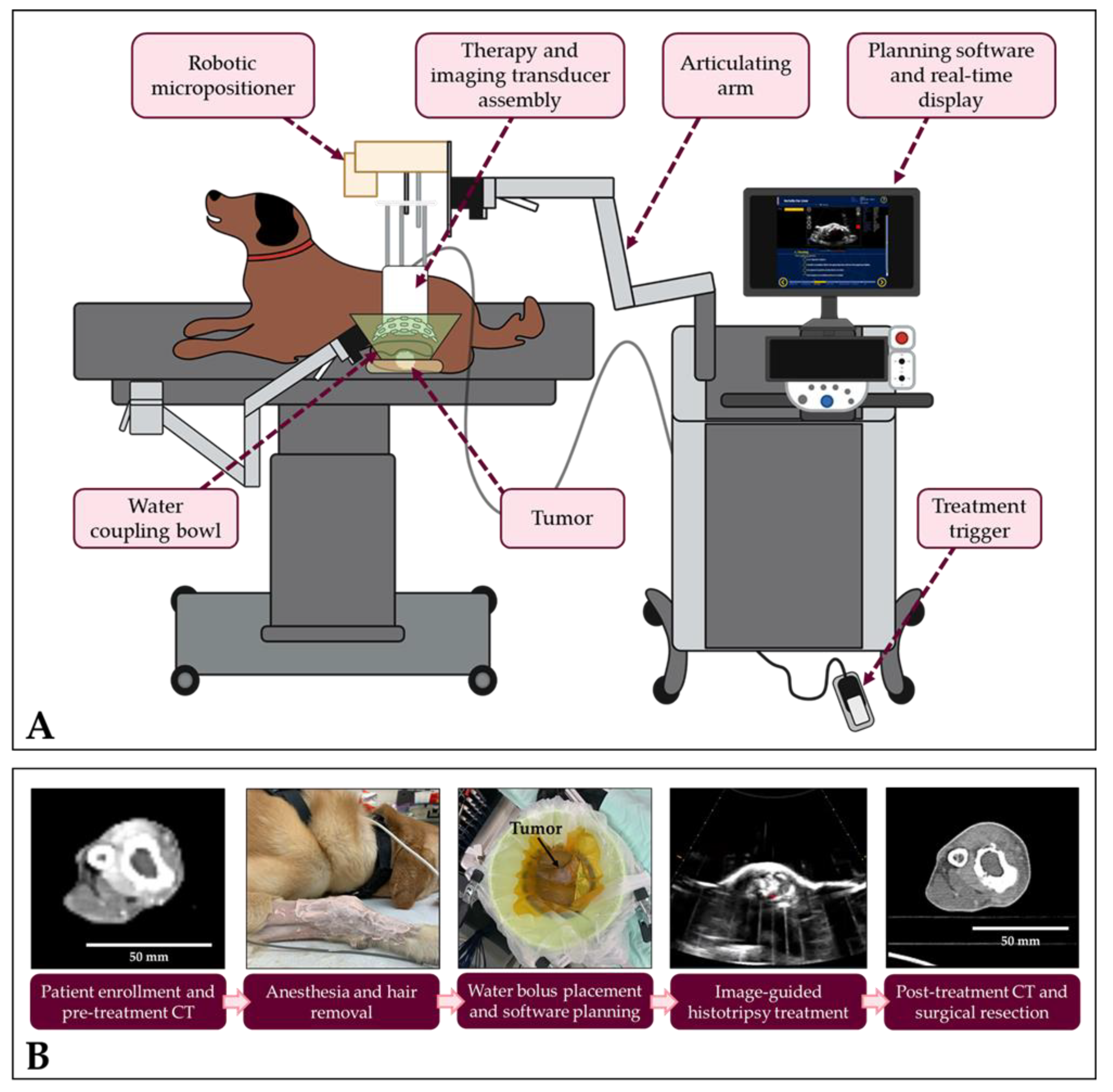
2.1. Patient Screening and Enrollment
2.2. Computed Tomography Imaging
2.3. Histotripsy System and Calibration
2.4. Histotripsy Treatment
2.5. Adverse Event Reporting
2.6. Surgical Resection of Tumor
2.7. Gross and Microscopic Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population
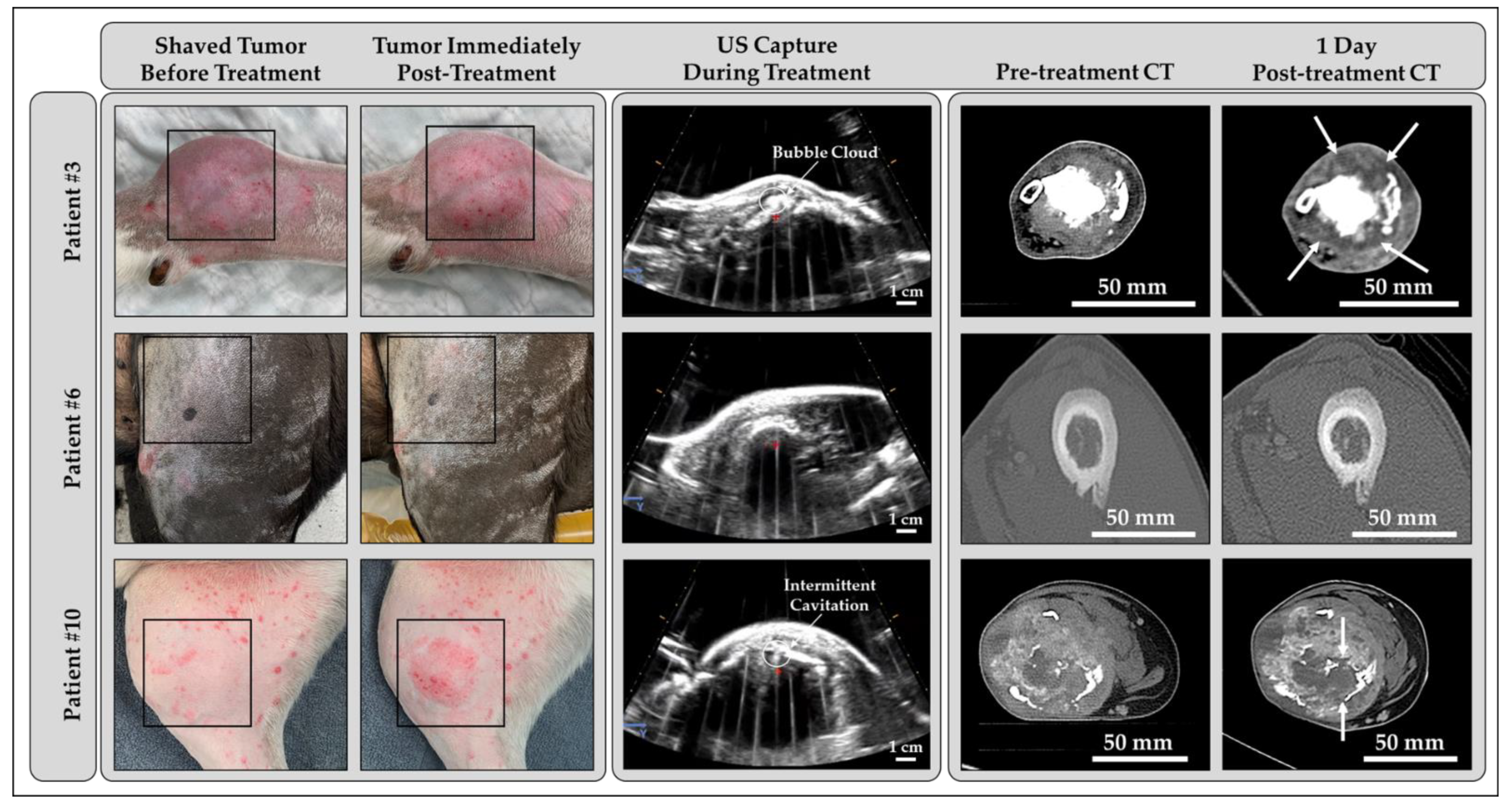
3.2. Histotripsy Treatment Outcomes
3.3. Adverse Events
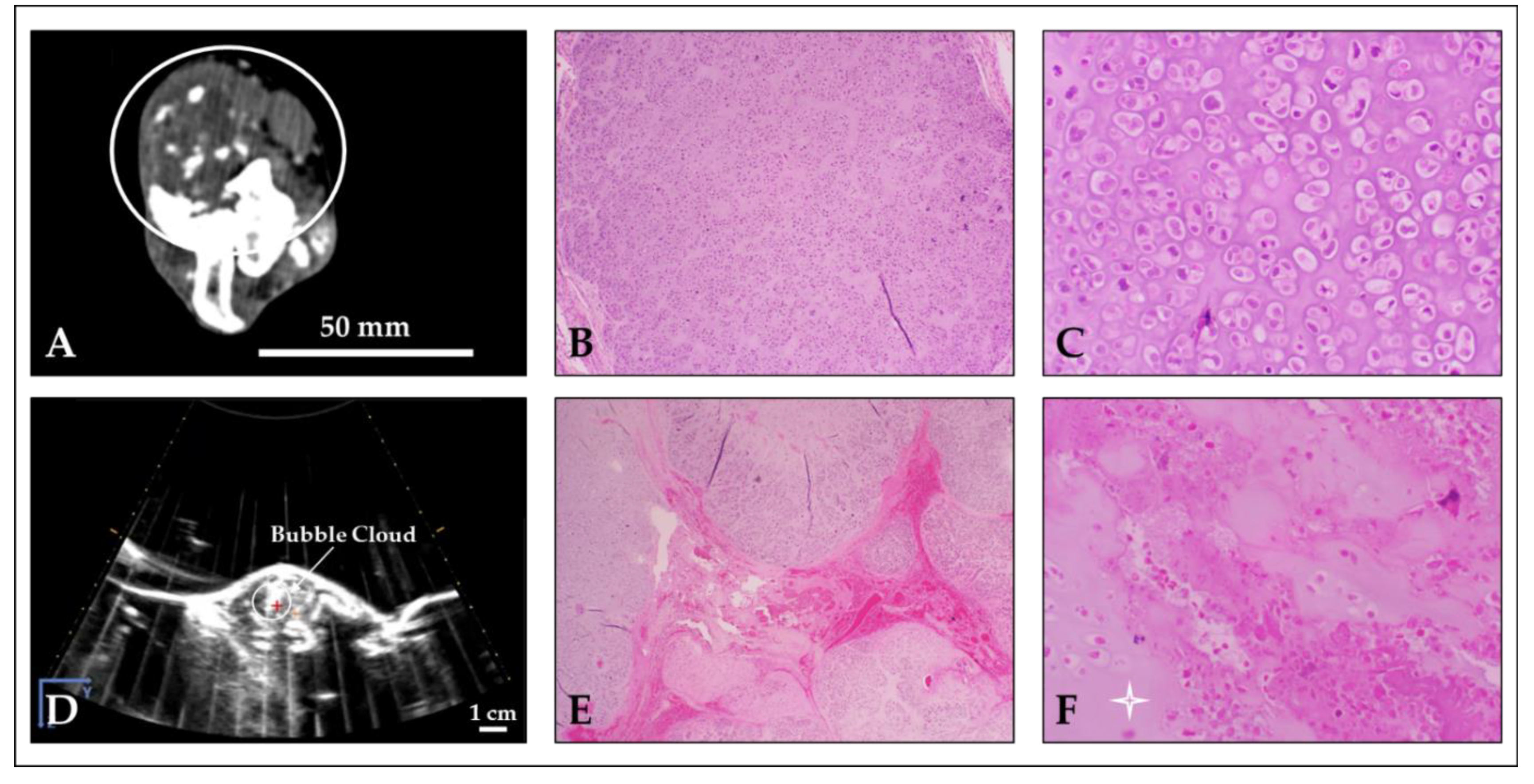
3.4. Computed Tomography Outcomes
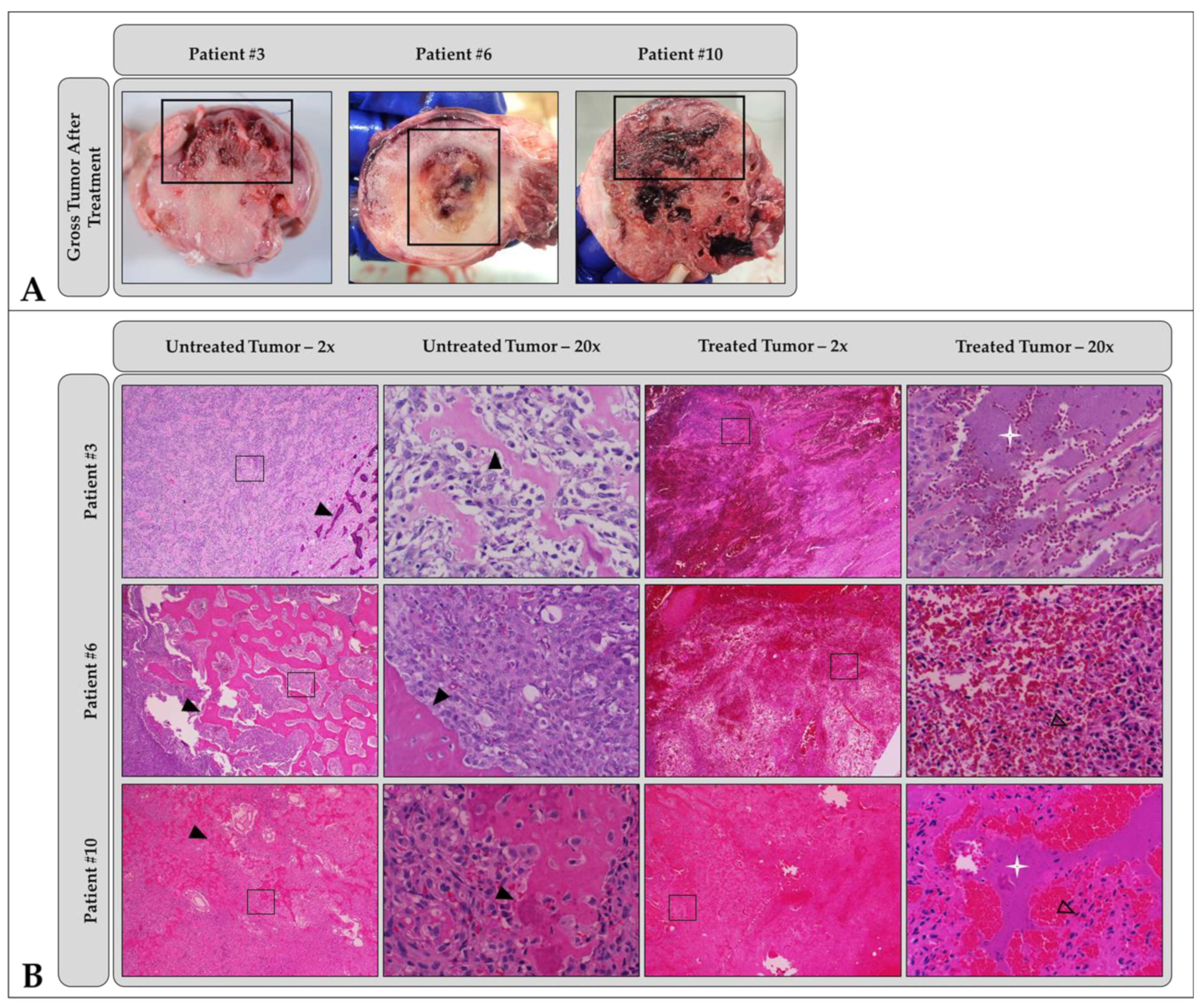
3.5. Gross and Microscopic Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Patient # | Remaining Tumor Cells | Matrix Ablation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Large groups | None observed |
| 2 | N/A * | N/A * |
| 3 | Individual cells to small clusters randomly dispersed | Hyalinization and fragmentation of osteoid matrix |
| 4 | Within vessels | None observed |
| 5 | N/A ** | N/A ** |
| 6 | Randomly dispersed | Little to none observed |
| 7 | At periphery, surrounding vessels, and multifocally throughout treated volume | Equal osteoid and chondroid matrix degeneration |
| 8 | Few random aggregates | Moderate osteoid and mild chondroid matrix degeneration |
| 9 | Randomly dispersed | Multifocal hyalinization of chondroid matrix |
| 10 | Demarcated from necrotic areas at periphery of sample | Osteoid matrix degeneration localized near tumor cells |
References
- Abate, M.; Longhi, A.; Galletti, S.; Ferrari, S.; Bacci, G. Non-metastatic osteosarcoma of the extremities in children aged 5 years or younger. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 55, 652–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kager, L.; Zoubek, A.; Potschger, U.; Kastner, U.; Flege, S.; Kempf-Bielack, B.; Branscheid, D.; Kotz, R.; Salzer-Kuntschik, M.; Winkelmann, W.; et al. Primary metastatic osteosarcoma: Presentation and outcome of patients treated on neoadjuvant Cooperative Osteosarcoma Study Group protocols. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2011–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakos, E.; Nearchou, A.; Grimer, R.; Koumoullis, H.; Abudu, A.; Bramer, J.; Jeys, L.; Franchi, A.; Scoccianti, G.; Campanacci, D.; et al. Prognostic factors and outcomes for osteosarcoma: An international collaboration. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu, A.K.; Wood, G.A.; Viloria-Petit, A.M. Recent Advances in the Discovery of Biomarkers for Canine Osteosarcoma. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.; Dunning, M.; de Brot, S.; Grau-Roma, L.; Mongan, N.; Rutland, C. Comparative review of human and canine osteosarcoma: Morphology, epidemiology, prognosis, treatment and genetics. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenger, J.; London, C.; Kisseberth, W. Canine osteosarcoma: A naturally occurring disease to inform pediatric oncology. ILAR J. 2014, 55, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebele, J.; Peck, J.; Pan, X.; Abdel-Rasoul, M.; Mayerson, J. Osteosarcoma: A Meta-Analysis and Review of the Literature. Am. J. Orthop. 2015, 44, 547–553. [Google Scholar]
- Meazza, C.; Scanagatta, P. Metastatic osteosarcoma: A challenging multidisciplinary treatment. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2016, 16, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.; Boston, S.; Kung, M.; Dry, S.; Straw, R.; Ehrhart, N.; Ryan, S. Outcomes of Limb-Sparing Surgery Using Two Generations of Metal Endoprosthesis in 45 Dogs with Distal Radial Osteosarcoma. A Veterinary Society of Surgical Oncology Retrospective Study. Vet. Surg. 2016, 45, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinberg, S.Z.; Posta, A.; Weber, K.L.; Wilson, R.J. Limb Salvage and Reconstruction Options in Osteosarcoma. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1257, 13–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ottaviani, G.; Robert, R.S.; Huh, W.W.; Jaffe, N. Functional, psychosocial and professional outcomes in long-term survivors of lower-extremity osteosarcomas: Amputation versus limb salvage. Cancer Treat. Res. 2009, 152, 421–436. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, J.; Hopkins, T.; Morris, J.; Tran, N.D.; David, E.; Massari, F.; Farid, H.; Vogel, A.; O’Connell, W.G.; Sunenshine, P.; et al. Radiofrequency Ablation for the Palliative Treatment of Bone Metastases: Outcomes from the Multicenter OsteoCool Tumor Ablation Post-Market Study (OPuS One Study) in 100 Patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salyer, S.A.; Wavreille, V.A.; Fenger, J.M.; Jennings, R.N.; Selmic, L.E. Evaluation of microwave ablation for local treatment of dogs with distal radial osteosarcoma: A pilot study. Vet. Surg. 2020, 49, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrar, K.; Stafford, R.J. Magnetic resonance imaging-guided laser ablation of bone tumors. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 14, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, J.W.; Prologo, J.D.; Garnon, J.; Gangi, A.; Buy, X.; Palussiere, J.; Kurup, A.N.; Callstrom, M.; Genshaft, S.; Abtin, F.; et al. Cryoablation for Palliation of Painful Bone Metastases: The MOTION Multicenter Study. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2021, 3, e200101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, A.; Anzidei, M.; Marincola, B.; Brachetti, G.; Ciolina, F.; Cartocci, G.; Marsecano, C.; Zaccagna, F.; Marchetti, L.; Cortesi, E.; et al. Primary pain palliation and local tumor control in bone metastases treated with magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound. Investig. Radiol. 2013, 48, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, K.; Su, H.; Jin, C.; Zhou, K.; Bai, J.; Wu, F.; Wang, Z. Primary Bone Malignancy: Effective Treatment with High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Ablation. Radiology 2010, 255, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzato, R.L.; Rubeis, G.D.; Marini, P.D.; Dalili, D.; Koch, G.; Auloge, P.; Garnon, J.; Gangi, A. Percutaneous microwave ablation of bone tumors: A systematic review. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3530–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzato, R.L.; Palussiere, J.; Auloge, P.; Rousseau, C.; Koch, G.; Dalili, D.; Buy, X.; Garnon, J.; Marini, P.D.; Gangi, A. Complications Following Percutaneous Image-guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Bone Tumors: A 10-year Dual-Center Experience. Radiology 2020, 269, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errani, C.; Longhi, A.; Rossi, G.; Rimondi, E.; Biazoo, A.; Toscano, A. Palliative therapy for osteosarcoma. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2011, 11, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, K.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Maxwell, A. For Whom the Bubble Grows: Physical Principles of Bubble Nucleation and Dynamics in Hisotripsy Ultrasound Therapy. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 1056–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaisavljevich, E.; Maxwell, A.; Mancia, L.; Johnsen, E.; Cain, C.; Xu, Z. Visualizing the Histotripsy Process: Bubble Cloud-Cancer Cell Interactions in a Tissue-Mimicking Environment. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 2466–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Hall, T.L.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Lee, F.T., Jr. Histotripsy: The first noninvasive, non-ionizing, non-thermal ablation technique based on ultrasound. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Ludomirsky, A.; Eun, L.; Hall, T.L.; Tran, B.; Fowlkes, J.B.; Cain, C.A. Controlled ultrasound tissue erosion. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2004, 51, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, J.E.; Cain, C.A.; Abrams, G.D.; Fowlkes, J.B. Pulsed cavitational ultrasound therapy for controlled tissue homogenization. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2006, 32, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.W.; Kim, Y.; Maxwell, A.; Wang, T.-Y.; Hall, T.L.; Xu, Z.; Fowlkes, J.B.; Cain, C. Histotripsy beyond the instrinsic cavitation threshold using very short ultrasound pulses: Microtripsy. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2014, 61, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, A.M.; Hall, T.L.; Kieran, K.; Fowlkes, J.B.; Cain, C.A.; Roberts, W.W. Histotripsy: A Minimally Invasive Technology for Prostate Tissue Ablation in an In-vivo Canine Model. Urology 2008, 72, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, A.M.; Xu, Z.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Cain, C.A.; Roberts, W.W. Renal ablation by histotripsy—Does it spare the collecting system? J. Urol. 2008, 179, 1150–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaisavljevich, E.; Kim, Y.; Allen, S.; Owens, G.; Pelletier, S.; Cain, C.; Ives, K.; Xu, Z. Image-Guided Non-Invasive Ultrasound Liver Ablation Using Histotripsy: Feasibility Study in an in vivo Porcine Model. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaisavljevich, E.; Kim, Y.; Owens, G.; Roberts, W.; Cain, C.; Xu, Z. Effects of Tissue Mechanical Properties on Susceptibility to Histotripsy-Induced Tissue Damage. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaisavljevich, E.; Maxwell, A.; Warnez, M.; Johnsen, E.; Cain, C.; Xu, Z. Histotripsy-induced cavitation cloud initiation thresholds in tissues of different mechanical properties. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2014, 61, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolock, A.R.; Cristescu, M.M.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Gendron-Fitzpatrick, A.; Green, C.; Cannata, J.; Ziemlewicz, T.J.; Lee, F.T., Jr. Robotically Assisted Sonic Therapy as a Noninvasive Nonthermal Ablation Modality: Proof of Concept in a Porcine Liver Model. Radiology 2018, 287, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, G.; Keller, J.; Ives, K.; Cheng, X.; Rosol, T.; Keller, E.; Roberts, W. Histotripsy focal ablation of implanted prostate tumor in an ACE-1 canine cancer model. J. Urol. 2012, 188, 1957–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, G.; Wang, Y.; D’Andrea, S.; Hwang, J.; Liles, W.; Khokhlova, T. Boiling Histotripsy Ablation of Renal Cell Carcinoma in the Eker Rat Promotes a Systemic Inflammatory Response. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worlikar, T.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Gerhardson, T.; Greve, J.; Wan, S.; Kuruvilla, S.; Lundt, J.; Ives, K.; Hall, T.; Welling, T.H.; et al. Histotripsy for Non-Invasive Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Tumor in a Subcutaneous Xenograft Murine Model. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2018, 2018, 6064–6067. [Google Scholar]
- Worlikar, T.; Zhang, M.; Ganguly, A.; Hall, T.L.; Shi, J.; Zhao, L.; Lee, F.T.; Mendiratta-Lala, M.; Cho, C.S.; Xu, Z. Impact of Histotripsy on Development of Intrahepatic Metastases in a Rodent Liver Tumor Model. Cancers 2022, 14, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks-Wenger, A.; Weber, P.; Simon, A.; Saunier, S.; Coutermarsh-Ott, S.; Grider, D.; Jove, J.V.; Allen, I.C.; Luyimbazi, D.; Vlaisavljevich, E. Histotripsy for the Treatment of Cholangiocarcinoma Liver Tumors: In Vivo Feasibility and Ex Vivo Dosimetry Study. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2021, 68, 2953–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks-Wenger, A.; Sereno, J.; Gannon, J.; Zeher, A.; Brock, R.M.; Betiel-White, N.; Simon, A.; Davalos, R.V.; Coutermarsh-Ott, S.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; et al. Histotripsy Ablation Alters the Tumor Microenvironment and Promotes Immune System Activation in a Subcutaneous Model of Pancreatic Cancer. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2021, 68, 2987–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardson, T.; Pal, A.; Sheetz, L.; Sukovich, J.; Lundt, J.; Hall, T.L.; Chertok, B.; Rehemtulla, A.; Cain, C.A.; Xu, Z. Histotripsy Mediated Immunomodulation in a Mouse GL261 Intracranial Glioma Model. Int. Symp. Ther. Ultrasound 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Jove, J.; Serres, X.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Cannata, J.; Duryea, A.; Miller, R.; Merino, X.; Velat, M.; Kam, Y.; Bolduan, R.; et al. First-in-man histotripsy of hepatic tumors: The THERESA trial, a feasibility study. Int. J. Hyperth. 2022, 39, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, L.; Hendricks-Wenger, A.; Coutermarsh-Ott, S.; Gannon, J.; Hay, A.N.; Dervisis, N.G.; Klahn, S.; Allen, I.C.; Tuohy, J.; Vlaisavljevich, E. Histotripsy Ablation of Bone Tumors: Feasibility Study in Excised Canine Osteosarcoma Tumors. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 3435–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruger, L.; Hay, A.; Gannon, J.; Sheppard, H.; Coutermarsh-Ott, S.; Daniel, G.; Kierski, K.; Ciepluch, B.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Tuohy, J. Histotripsy Ablation of Spontaneously Occurring Canine Bone Tumors In Vivo. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 70, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruger, L.; Yang, E.; Gannon, J.; Sheppard, H.; Coutermarsh-Ott, S.; Ziemlewicz, T.J.; Dervisis, N.; Allen, I.C.; Daniel, G.B.; Tuohy, J.; et al. Mechanical High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (Histotripsy) in Dogs with Spontaneously Occurring Soft Tissue Sarcomas. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, J.; Cain, C.; Fowlkes, J.B. Cost-effective assembly of a basic fiber-optic hydrophone for measurement of high-amplitude therapeutic ultrasound fields. J Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, L.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Owens, G.; Gurm, H.S.; Cain, C.A.; Xu, Z. Non-invasive Thrombolysis using Microtripsy: A Parameter Study. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2015, 62, 2092–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaisavljevich, E.; Lin, K.W.; Maxwell, A.; Warnez, M.T.; Mancia, L.; Singh, R.; Putnam, A.J.; Fowlkes, B.; Johnsen, E.; Cain, C.; et al. Effects of ultrasound frequency and tissue stiffness on the histotripsy intrinsic threshold for cavitation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 1651–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, A.K.; Atherton, M.; Bentley, R.T.; Boudreau, C.E.; Burton, J.H.; Curran, K.M.; Dow, S.; Giuffrida, M.A.; Kellihan, H.B.; Mason, N.J.; et al. Veterinary Cooperative Oncology Group-Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (VCOG-CTCAE v2) following investigational therapy in dogs and cats. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2021, 19, 311–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodey, R. The use of naturally occurring cancer in domestic animals for research into human cancer: General considerations and a review of canine skeletal osteosarcoma. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1979, 52, 345–361. [Google Scholar]
- Brodey, R.S.; Sauer, R.M.; Medway, W. Canine Bone Neoplasms. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1963, 143, 473–495. [Google Scholar]
- Vlaisavljevich, E.; Lin, K.-W.; Warnez, M.T.; Singh, R.; Mancia, L.; Putnam, A.J.; Johnsen, E.; Cain, C.; Xu, Z. Effects of tissue stiffness, ultrasound frequency, and pressure on histotripsy-induced cavitation bubble behavior. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 2271–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-J.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.-G.; Zhu, W.; Hua, Y.-Q.; Sun, W.; Cai, Z.-D. Telangiectatic osteosarcoma: A review of literature. OncoTargets Ther. 2013, 6, 592–602. [Google Scholar]
- Worlikar, T.; Mendiratta-Lala, M.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Hubbard, R.; Shi, J.; Hall, T.L.; Cho, C.S.; Lee, F.T.; Greve, J.; Xu, Z. Effects of Histotripsy on Local Tumor Progression in an in vivo Orthotopic Rodent Liver Tumor Model. BME Front. 2020, 2020, 9830304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaisavljevich, E.; Greve, J.; Cheng, X.; Ives, K.; Shi, J.; Jin, L.; Arvidson, A.; Hall, T.; Welling, T.H.; Owens, G.; et al. Non-Invasive Ultrasound Liver Ablation Using Histotripsy: Chronic Study in an In Vivo Rodent Model. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 1890–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahk, K.; Shin, C.; Bae, I.; Yang, Y.; Kim, S.; Pahk, K.; Kim, H.; Oh, S. Boiling Histotripsy-induced Partial Mechanical Ablation Modulates Tumour Microenvironment by Promoting Immunogenic Cell Death of Cancers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukovich, J.; Macoskey, J.E.; Lundt, J.; Gerhardson, T.; Hall, T.L.; Xu, Z. Real-Time Transcranial Histotripsy Treatment Localization and Mapping Using Acoustic Cavitation Emission Feedback. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2020, 67, 1178–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Shi, J.; Hernandez-Garcia, L.; Cain, C.; Xu, Z.; Hall, T.L. The response of MRI contrast parameters in in vitro tissues and tissue mimicking phantoms to fractionation by histotripsy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 7167–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Hall, T.L.; Cain, C.; Hernandez-Garcia, L. Controlling cavitation-based image contrast in focused ultrasound histotripsy surgery. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 73, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, G.; Cova, L.; De Beni, S.; Ierace, T.; Tondolo, T.; Cerri, A.; Goldberg, S.N.; Solbiati, L. Real-Time US-CT/MRI Image Fusion for Guidance of Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors Undetectable with US: Results in 295 Cases. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2014, 38, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundt, J.; Allen, S.; Shi, J.; Hall, T.L.; Cain, C.A.; Xu, Z. Noninvasive, Rapid Ablation of Tissue Volume Using Histotripsy. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 2834–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardson, T.; Sukovich, J.; Pandey, A.; Hall, T.L.; Cain, C.A.; Xu, Z. Effect of Frequency and Focal Spacing on Transcranial Histotripsy Clot Liquefaction, Using Electronic Focal Steering. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 2302–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macoskey, J.J.; Choi, S.W.; Hall, T.L.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Lundt, J.E.; Lee, F.T., Jr.; Johnsen, E.; Cain, C.A.; Xu, Z. Using the cavitation collapse time to indicate extent of histotripsy-induced tissue fractionation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 055013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient # | Breed | Age (years) | Gender | Weight (kg) | Tumor Location | Tumor Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Malamute | 6 | MN | 50 | Distal radius | Osteosarcoma |
| 2 | Great Pyrenees | 7.5 | F | 33 | Distal tibia | Osteosarcoma |
| 3 | Shepherd Mix | 2 | MN | 27 | Distal radius | Osteosarcoma |
| 4 | Labrador Retriever | 10 | FS | 46 | Distal tibia | Osteosarcoma |
| 5 | Doberman | 8 | MN | 45 | Proximal tibia | Osteosarcoma |
| 6 | Mixed breed | 7 | MN | 48 | Mid to distal femur | Osteosarcoma |
| 7 | Border Collie | 9 | FS | 22 | Mid radius | Osteosarcoma |
| 8 | Great Pyrenees | 7 | MN | 57 | Distal radius | Osteosarcoma |
| 9 | Mixed breed | 3 | MN | 17 | Distal humerus | Chondrosarcoma |
| 10 | Mixed breed | 8 | MN | 35 | Proximal tibia | Osteosarcoma |
| Patient # | Treatment Pressure (MPa) | Treatment Depth (cm) | Bubble Cloud Visibility | Pre-Focal Cavitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23.75 | 2.3 | No | Yes |
| 2 | 23.75 | 2.2 | Intermittent | Yes |
| 3 | 25.10 | 2.4 | Yes | Intermittent |
| 4 | 33.11 | 1.7 | No | Yes |
| 5 | 30.46 | 2.0 | No | Yes |
| 6 | 30.46 | 2.8 | No | Intermittent |
| 7 | 26.45 | 2.1 | Yes | Intermittent |
| 8 | 23.75 | 2.1 | Yes | Intermittent |
| 9 | 21.03 | 1.8 | Yes | Yes |
| 10 | 27.79 | 2.5 | Intermittent | No |
| Patient # | Tumor Dimensions (cm) | Treatment Zone Dimensions (cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Treatment | Post-Treatment | ||
| 1 | 3.1 × 2.9 × 3.9 | 3.2 × 2.8 × 4.4 | 3.4 × 2.7 × 3.6 |
| 2 | 3.5 × 4.0 × 7.3 | 3.7 × 4.4 × 7.8 | 2.6 × 2.4 × 4.4 |
| 3 | 4.2 × 4.2 × 10.6 | 4.6 × 4.6 × 11.2 | 5.0 × 4.2 × 6.7 |
| 4 | 2.4 × 2.3 × 10.1 | 2.4 × 2.4 × 10.3 | 1.4 × 1.7 × 6.9 |
| 5 | 3.9 × 1.9 × 3.4 | 4.1 × 2.0 × 2.8 | 2.0 × 1.6 × 1.4 |
| 6 | 3.9 × 2.6 × 11.0 | 3.5 × 2.5 × 7.4 | N/A ** |
| 7 | 2.2 × 2.5 × 11.2 | 3.3 × 2.3 × 8.1 | 3.0 × 2.0 × 4.6 |
| 8 | 2.6 × 3.1 × 6.5 | 2.8 × 3.6 × 6.2 | 2.2 × 2.0 × 2.6 |
| 9 | 4.1 × 3.9 × 4.3 | N/A * | N/A * |
| 10 | 6.3 × 5.3 × 7.4 | 6.1 × 5.3 × 7.3 | 3.0 × 2.8 × 3.1 |
| Patient # | Pre-Treatment Tumor Description | Bone Lysis | Soft Tissue Involvement | New Bone Production | Treatment Zone Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Enhancing mass with bony remodeling | Mild | Severe | Mild | Hypoenhancing intramedullary |
| 2 | Predominantly enhancing mass with foci of necrosis and bony remodeling | Severe | Severe | Moderate | Hypoenhancing with thin enhancing rim |
| 3 | Enhancing mass with bony remodeling | Mild | Severe | Moderate | Hypoenhancing with thin enhancing rim |
| 4 | Enhancing mass with mild bony remodeling | None | None | Moderate | Hypoenhancing intramedullary |
| 5 | Enhancing mass with mild bony remodeling | Moderate | Mild | Mild | Hypoenhancing intramedullary |
| 6 | Mild bony remodeling with intramedullary soft tissue | None | None | Moderate | N/A ** |
| 7 | Enhancing mass with extensive bony remodeling | Mild | Severe | Moderate | Hypoenhancing with thin enhancing rim |
| 8 | Bony remodeling without defined soft tissue | Mild | Moderate | Severe | Hypoenhancing with thin enhancing rim |
| 9 | Enhancing mass with bony remodeling | Severe | Severe | Mild | N/A * |
| 10 | Enhancing mass with extensive bony erosion and remodeling | Severe | Severe | Mild | Hypoenhancing with no perceptible rim |
| Patient # | Gross Tumor Characteristics | Microscopic Tumor Characteristics | Histologic Tumor Diagnosis | Gross Ablation Characteristics | Microscopic Ablation Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Firm, white, soft tissue component | Primarily cellular with small fragments of osteoid matrix | PD: Osteosarcoma ST: Osteoblastic, productive | Hemorrhage, tissue softening (necrosis) | Lytic and coagulative necrosis, acute hemorrhage |
| 2 | Hard and soft tissue components | Primarily cellular with some osteoid matrix | PD: Osteosarcoma ST: Osteoblastic productive | Hemorrhage | Lytic and coagulative necrosis, acute hemorrhage |
| 3 | Hard and soft tissue components | Half cellular, half osteoid matrix | PD: Osteosarcoma ST: Osteoblastic, productive | Hemorrhage, tissue softening (necrosis) | Lytic and coagulative necrosis, hemorrhage, loss of architecture, basophilic stippling |
| 4 | Primarily soft tissue, blood filled cavities with minimal osteoid matrix | Primarily cellular with minimal osteoid matrix, blood filled cavities | PD: Osteosarcoma ST: Telangiectatic | Hemorrhage and edema, tissue loss | No discernable difference between treated and untreated tumor cells |
| 5 | Hard and soft tissue components | Primarily cellular with minimal osteoid matrix | PD: Osteosarcoma ST: Osteoblastic, productive | Hemorrhage | Hemorrhage |
| 6 | Hard cortical bone surrounding a central hard mass | Cellular invasion into bone, minimal tumor osteoid | PD: Osteosarcoma ST: Osteoblastic, minimally productive | Hemorrhage | Hemorrhage, necrosis similar in both treated and untreated cells |
| 7 | Extensive soft tissue component outside cortex | High osteoid and moderate chondroid matrix production | PD: Osteosarcoma ST: Osteoblastic, productive | Hemorrhage, tissue softening (necrosis) | Large foci of mixed necrosis, hemorrhage |
| 8 | Equal soft and hard tissue components | Moderate osteoid and chondroid matrix production | PD: Osteosarcoma ST: Osteoblastic and chondroblastic, minimally productive | Hemorrhage, tissue softening (necrosis) | Coagulative and lytic necrosis, hemorrhage, basophilic stippling |
| 9 | Hard and soft tissue components | Chondroid matrix | PD: Chondrosarcoma | Hemorrhage, tissue softening (necrosis) | Mixed necrosis, acute hemorrhage, basophilic stippling |
| 10 | Hard and soft tissue components | Moderate-to-high anastomosing osteoid matrix | PD: Osteosarcoma ST: Osteoblastic and chondroblastic, minimally productive | Hemorrhage | Extensive coagulative necrosis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruger, L.N.; Hay, A.N.; Vickers, E.R.; Coutermarsh-Ott, S.L.; Gannon, J.M.; Covell, H.S.; Daniel, G.B.; Laeseke, P.F.; Ziemlewicz, T.J.; Kierski, K.R.; et al. Characterizing the Ablative Effects of Histotripsy for Osteosarcoma: In Vivo Study in Dogs. Cancers 2023, 15, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030741
Ruger LN, Hay AN, Vickers ER, Coutermarsh-Ott SL, Gannon JM, Covell HS, Daniel GB, Laeseke PF, Ziemlewicz TJ, Kierski KR, et al. Characterizing the Ablative Effects of Histotripsy for Osteosarcoma: In Vivo Study in Dogs. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030741
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuger, Lauren N., Alayna N. Hay, Elliana R. Vickers, Sheryl L. Coutermarsh-Ott, Jessica M. Gannon, Hannah S. Covell, Gregory B. Daniel, Paul F. Laeseke, Timothy J. Ziemlewicz, Katharine R. Kierski, and et al. 2023. "Characterizing the Ablative Effects of Histotripsy for Osteosarcoma: In Vivo Study in Dogs" Cancers 15, no. 3: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030741
APA StyleRuger, L. N., Hay, A. N., Vickers, E. R., Coutermarsh-Ott, S. L., Gannon, J. M., Covell, H. S., Daniel, G. B., Laeseke, P. F., Ziemlewicz, T. J., Kierski, K. R., Ciepluch, B. J., Vlaisavljevich, E., & Tuohy, J. L. (2023). Characterizing the Ablative Effects of Histotripsy for Osteosarcoma: In Vivo Study in Dogs. Cancers, 15(3), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030741