Sialyl LewisX/A and Cytokeratin Crosstalk in Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Clinical Data
2.2. Immunohistochemical Staining of TNBC Sections
2.3. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.4. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. TCGA Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biomarker Characterisation and Correlation with Clinical Features
3.2. sLeX/A and E-SL Expression Negatively Correlate with CK5/6 Expression in TNBC
3.3. sLeX/A Inhibition Leads to Increased CK5/6 Expression in a Breast Cancer Cell Line
3.4. sLeX/A Decorates α6 Integrin and Affects the Associated Signalling Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Stagg, J.; Allard, B. Immunotherapeutic approaches in triple-negative breast cancer: Latest research and clinical prospects. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2013, 5, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkus, E.; Kyriakides, S.; Ohno, S.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Poortmans, P.; Rutgers, E.; Zackrisson, S.; Cardoso, F. ESMO Guidelines Committee. Primary breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2015, 26 (Suppl. 5), v8–v30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipriano, É.; Mesquita, A. Emerging Therapeutic Drugs in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Basic Clin. Res. 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, R.; Trudeau, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Hanna, W.M.; Kahn, H.K.; Sawka, C.A.; Lickley, L.A.; Rawlinson, E.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Features and Patterns of Recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4429–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, A.; Trapani, D.; Viale, G.; Criscitiello, C.; Curigliano, G. Practical classification of triple-negative breast cancer: Intratumoral heterogeneity, mechanisms of drug resistance, and novel therapies. NPJ Breast Cancer 2020, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, S.K.K.; Tay, A.; Nair, S.; Leong, C.-O. Triple-negative breast cancer is associated with EGFR, CK5/6 and c-KIT expression in Malaysian women. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2012, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesar, M.; Stanec, M.; Lesar, N.; Vrdoljak, D.V.; Zore, Z.; Banović, M.; Brozović, G. Immunohistochemical Differentiation of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Acta Clin. Croat. 2016, 55, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofech-Mozes, S.; Trudeau, M.; Kahn, H.K.; Dent, R.; Rawlinson, E.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A.; Hanna, W.M. Patterns of recurrence in the basal and non-basal subtypes of triple-negative breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 118, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V. Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Tumor Metastasis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2018, 13, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, J.F.; Skhinas, J.N.; Fey, D.; Croucher, D.R.; Cox, T.R. The extracellular matrix as a key regulator of intracellular signalling networks. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 176, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenta, T.; Schmidt, A.; Zhang, Q.; Devarajan, R.; Singh, P.; Yang, X.; Ahtikoski, A.; Vaarala, M.; Wei, G.-H.; Manninen, A. Disassembly of α6β4-mediated hemidesmosomal adhesions promotes tumorigenesis in PTEN-negative prostate cancer by targeting plectin to focal adhesions. Oncogene 2022, 41, 3804–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEver, R.P. Selectins: Initiators of leucocyte adhesion and signalling at the vascular wall. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 107, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestweber, D.; Blanks, J.E. Mechanisms That Regulate the Function of the Selectins and Their Ligands. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 181–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Videira, P.A.; Sackstein, R. E-Selectin Ligands in the Human Mononuclear Phagocyte System: Implications for Infection, Inflammation, and Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 8, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweitzer, K.M.; Dräger, A.M.; Van Der Valk, P.; Thijsen, S.F.; Zevenbergen, A.; Theijsmeijer, A.P.; E Van Der Schoot, C.; Langenhuijsen, M.M. Constitutive expression of E-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 on endothelial cells of hematopoietic tissues. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 148, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Videira, P.A.; Silva, M.; Martin, K.C.; Sackstein, R. Ligation of the CD44 Glycoform HCELL on Culture-Expanded Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells Programs Transendothelial Migration. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Cui, L.; Liu, F.; Fan, Y.; Lang, R.; Gu, F.; Guo, X.; Tang, P.; Fu, L. E-selectin and Sialyl Lewis X Expression Is Associated with Lymph Node Metastasis of Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Breast. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 18, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.G.; Carrascal, M.; Mineiro, A.G.; Bugalho, A.; Borralho, P.; Silva, Z.; Dall’olio, F.; Videira, P.A. Carcinoembryonic antigen is a sialyl Lewis x/a carrier and an E-selectin ligand in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A.; Peired, A.J.; Wild, M.K.; Vestweber, D.; Frenette, P.S. Complete Identification of E-Selectin Ligands on Neutrophils Reveals Distinct Functions of PSGL-1, ESL-1, and CD44. Immunity 2007, 26, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrascal, M.A.; Silva, M.; Ferreira, J.A.; Azevedo, R.; Ferreira, D.; Silva, A.M.N.; Ligeiro, D.; Santos, L.L.; Sackstein, R.; Videira, P.A. A functional glycoproteomics approach identifies CD13 as a novel E-selectin ligand in breast cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 2069–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, R.K.; Shaikh, A.R.; Gorle, S.; Kaur, M.; Videira, P.A.; Cavallo, L.; Chawla, M. Structural Insights in Mammalian Sialyltransferases and Fucosyltransferases: We Have Come a Long Way, but It Is Still a Long Way Down. Molecules 2021, 26, 5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.N.; Fouad, T.M.; Lee, B.-N.; Arun, B.K.; Liu, D.; Tin, S.; Barrera, A.M.G.; Miura, T.; Kiyokawa, I.; Yamashita, J.; et al. Elevated serum levels of sialyl Lewis X (sLeX) and inflammatory mediators in patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 176, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julien, S.; Ivetic, A.; Grigoriadis, A.; QiZe, D.; Burford, B.; Sproviero, D.; Picco, G.; Gillett, C.; Papp, S.L.; Schaffer, L.; et al. Selectin Ligand Sialyl-Lewis x Antigen Drives Metastasis of Hormone-Dependent Breast Cancers. Cancer Res 2011, 71, 7683–7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, S.S.; Matos, A.J.; Lopes, C.; Marcos, N.T.; Carvalheira, J.; A Reis, C.; Gärtner, F. Sialyl Lewis x expression in canine malignant mammary tumours: Correlation with clinicopathological features and E-Cadherin expression. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renkonen, J.; Paavonen, T.; Renkonen, R. Endothelial and epithelial expression of sialyl Lewis(x) and sialyl Lewis(a) in lesions of breast carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 74, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, N.; Narita, T.; Mitsuoka, C.; Kimura, N.; Kannagi, R.; Imai, T.; Funahashi, H.; Takagi, H. Increased level of circulating adhesion molecules in the sera of breast cancer patients with distant metastases. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 27, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascal, M.A.; Talina, C.; Borralho, P.; Mineiro, A.G.; Henriques, A.R.; Pen, C.; Martins, M.; Braga, S.; Sackstein, R.; Videira, P.A. Staining of E-selectin ligands on paraffin-embedded sections of tumor tissue. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascal, M.A.; Silva, M.; Ramalho, J.S.; Pen, C.; Martins, M.; Pascoal, C.; Amaral, C.; Serrano, I.; Oliveira, M.J.; Sackstein, R.; et al. Inhibition of fucosylation in human invasive ductal carcinoma reduces E-selectin ligand expression, cell proliferation, andERK1/2 and p38MAPKactivation. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.B.; Veríssimo, A.; Carrasquinha, E.; Casimiro, S.; Beerenwinkel, N.; Vinga, S. Ensemble outlier detection and gene selection in triple-negative breast cancer data. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: The R Project for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Therneau, T.M.; Grambsch, P.M. Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- Trinchera, M.; Aronica, A.; Dall’Olio, F. Selectin Ligands Sialyl-Lewis a and Sialyl-Lewis x in Gastrointestinal Cancers. Biology 2017, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, A.; Manjari, M.; Kahlon, S.; Kumar, P.; Kalra, N. Cytokeratin 5/6 expression in benign and malignant breast lesions. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2010, 53, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inanc, M.; Ozkan, M.; Karaca, H.; Berk, V.; Bozkurt, O.; Duran, A.O.; Ozaslan, E.; Akgun, H.; Tekelioglu, F.; Elmali, F. Cytokeratin 5/6, c-Met expressions, and PTEN loss prognostic indicators in triple-negative breast cancer. Med. Oncol. 2013, 31, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefansson, I.M.; Salvesen, H.B.; Akslen, L.A. Loss of p63 and cytokeratin 5/6 expression is associated with more aggressive tumors in endometrial carcinoma patients. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 118, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivusalo, S.; Schmidt, A.; Manninen, A.; Wenta, T. Regulation of Kinase Signaling Pathways by α6β4-Integrins and Plectin in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezniczek, G.A.; de Pereda, J.M.; Reipert, S.; Wiche, G. Linking Integrin α6β4-based Cell Adhesion to the Intermediate Filament Cytoskeleton: Direct Interaction between the β4 Subunit and Plectin at Multiple Molecular Sites. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 141, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensenyat-Mendez, M.; Llinàs-Arias, P.; Orozco, J.I.J.; Íñiguez-Muñoz, S.; Salomon, M.P.; Sesé, B.; DiNome, M.L.; Marzese, D.M. Current Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Subtypes: Dissecting the Most Aggressive Form of Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugalho, A.; Martins, C.; Dias, S.; Nunes, G.; Silva, Z.; Correia, M.; Gomes, M.J.M.; Videira, P. Cytokeratin 19, Carcinoembryonic Antigen, and Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Detect Lung Cancer Lymph Node Metastasis in Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Aspiration Samples. Clin. Lung Cancer 2013, 14, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, C.; Almeida, A.; Barreira, A.; Calheiros, J.; Pinto, F.; Abrantes, R.; Costa, A.; Polonia, A.; Campos, D.; Osório, H.; et al. Carcinoembryonic antigen carrying SLeX as a new biomarker of more aggressive gastric carcinomas. Theranostics 2019, 9, 7431–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschepper, F.; Zoppi, R.; Pirro, M.; Hensbergen, P.; Dall’Olio, F.; Kotsias, M.; Gardner, R.; Spencer, D.; Videira, P. L1CAM as an E-selectin Ligand in Colon Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livasy, C.A.; Karaca, G.; Nanda, R.; Tretiakova, M.S.; Olopade, O.I.; Moore, D.T.; Perou, C.M. Phenotypic evaluation of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, T.O.; Hsu, F.D.; Jensen, K.; Cheang, M.; Karaca, G.; Hu, Z.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; Livasy, C.; Cowan, D.; Dressler, L.; et al. Immunohistochemical and Clinical Characterization of the Basal-Like Subtype of Invasive Breast Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5367–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinn, O.; Ward, A.V.; Fettig, L.M.; Riley, D.; Ivie, J.; Paul, K.V.; Kabos, P.; Finlay-Schultz, J.; Sartorius, C.A. Cytokeratin 5 alters β-catenin dynamics in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2020, 39, 2478–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laval, S.; Laklai, H.; Fanjul, M.; Pucelle, M.; Laurell, H.; Billon-Galés, A.; Le Guellec, S.; Delisle, M.-B.; Sonnenberg, A.; Susini, C.; et al. Dual roles of hemidesmosomal proteins in the pancreatic epithelium: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase decides. Oncogene 2013, 33, 1934–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, T.; Shiozaki, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Miyazaki, S.; Satomi, S.; Kato, K.; Sakuraba, H.; Miyagi, T. Contribution of sialidase NEU1 to suppression of metastasis of human colon cancer cells through desialylation of integrin β4. Oncogene 2009, 28, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velloso, F.J.; Bianco, A.F.R.; O Farias, J.; Torres, N.E.; Ferruzo, P.Y.; Anschau, V.; Jesus-Ferreira, H.C.; Chang, T.H.-T.; Sogayar, M.; Zerbini, L.F.; et al. The crossroads of breast cancer progression: Insights into the modulation of major signaling pathways. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 5491–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
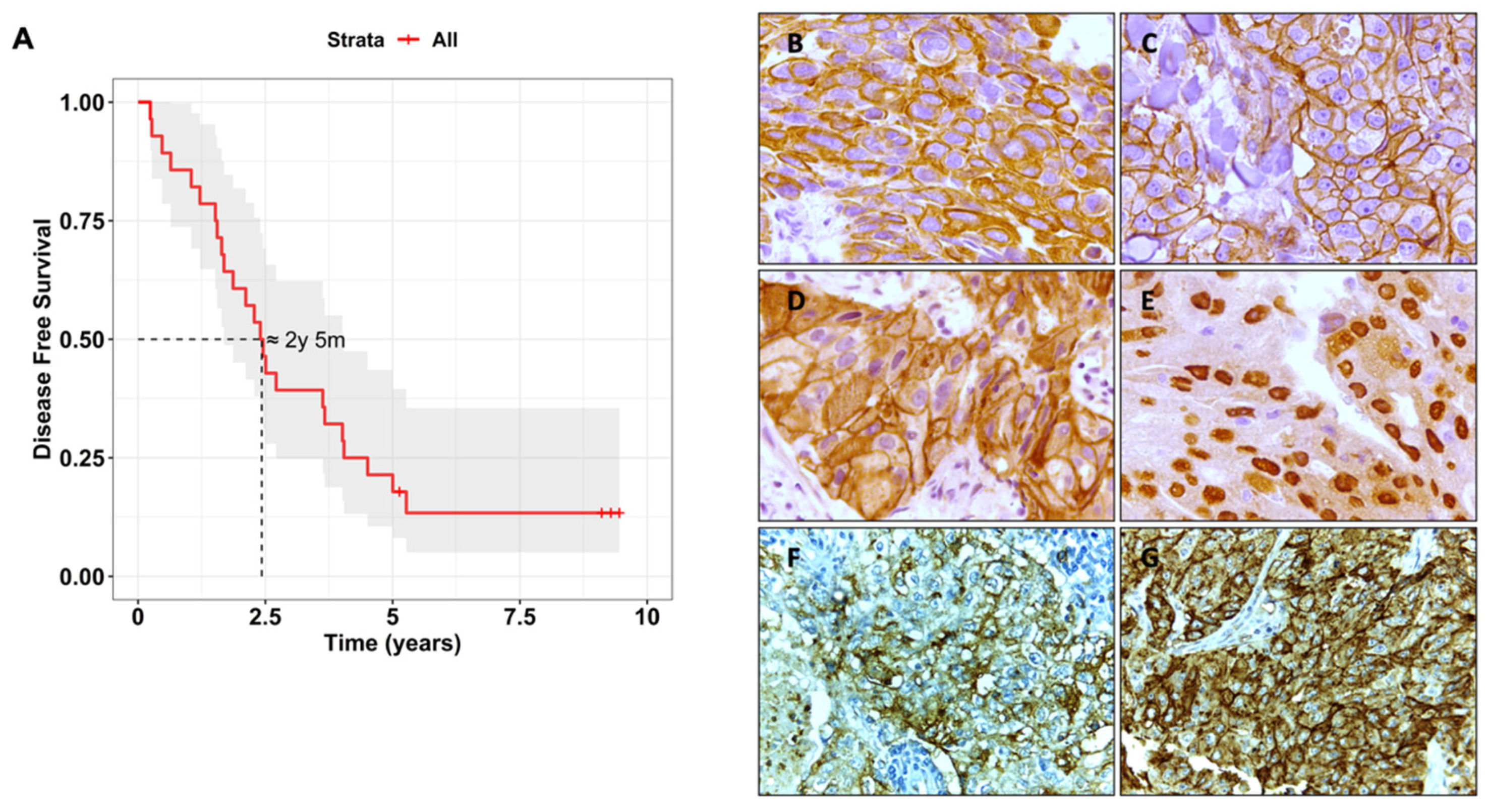
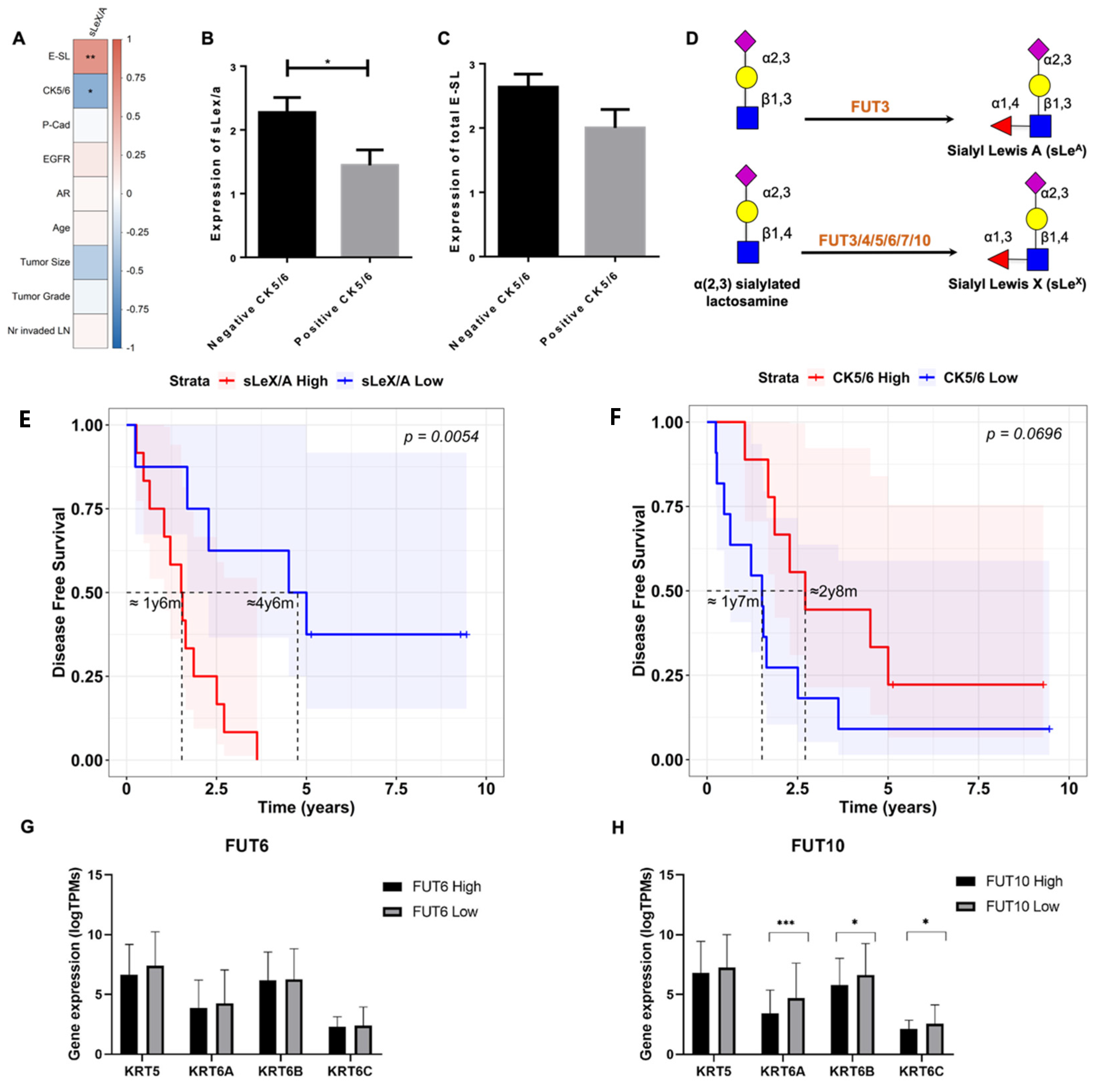
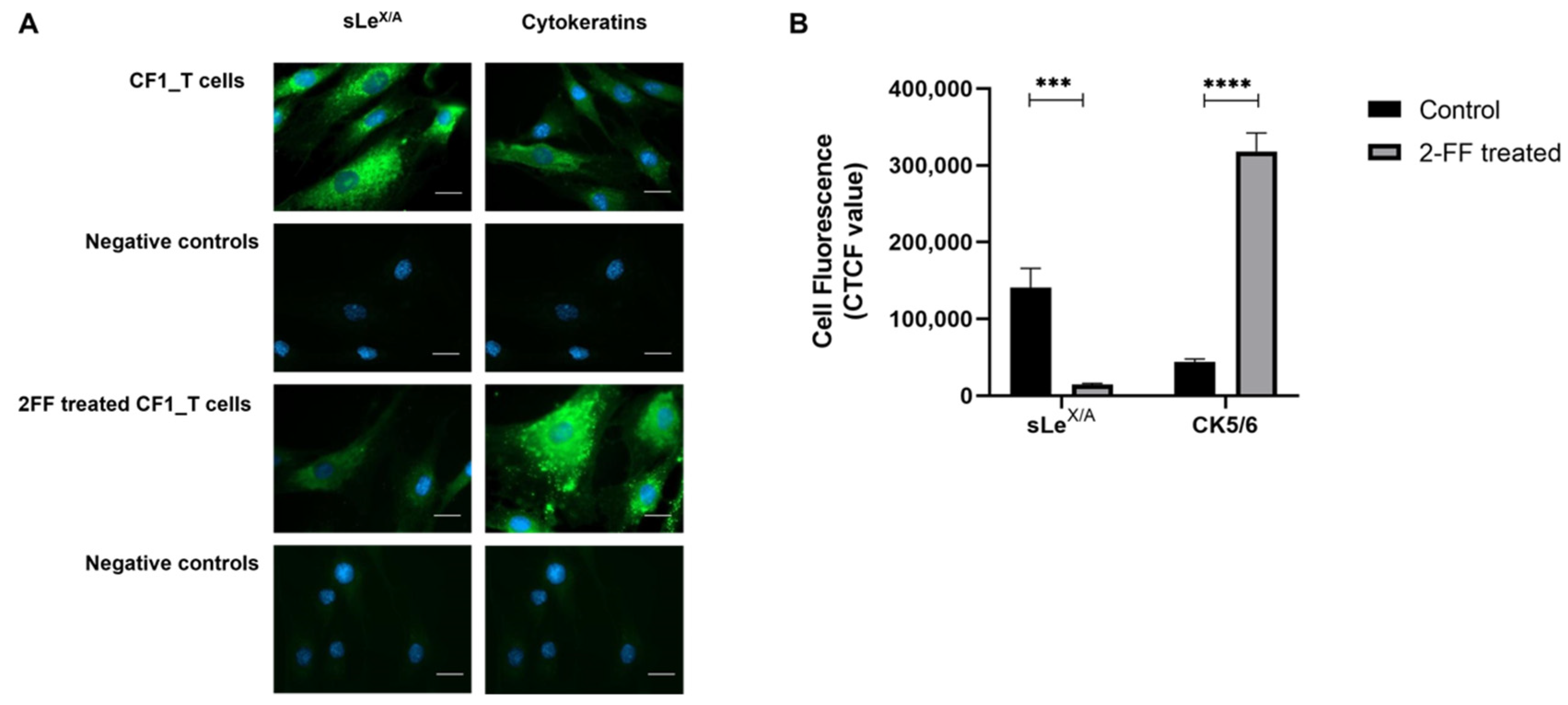
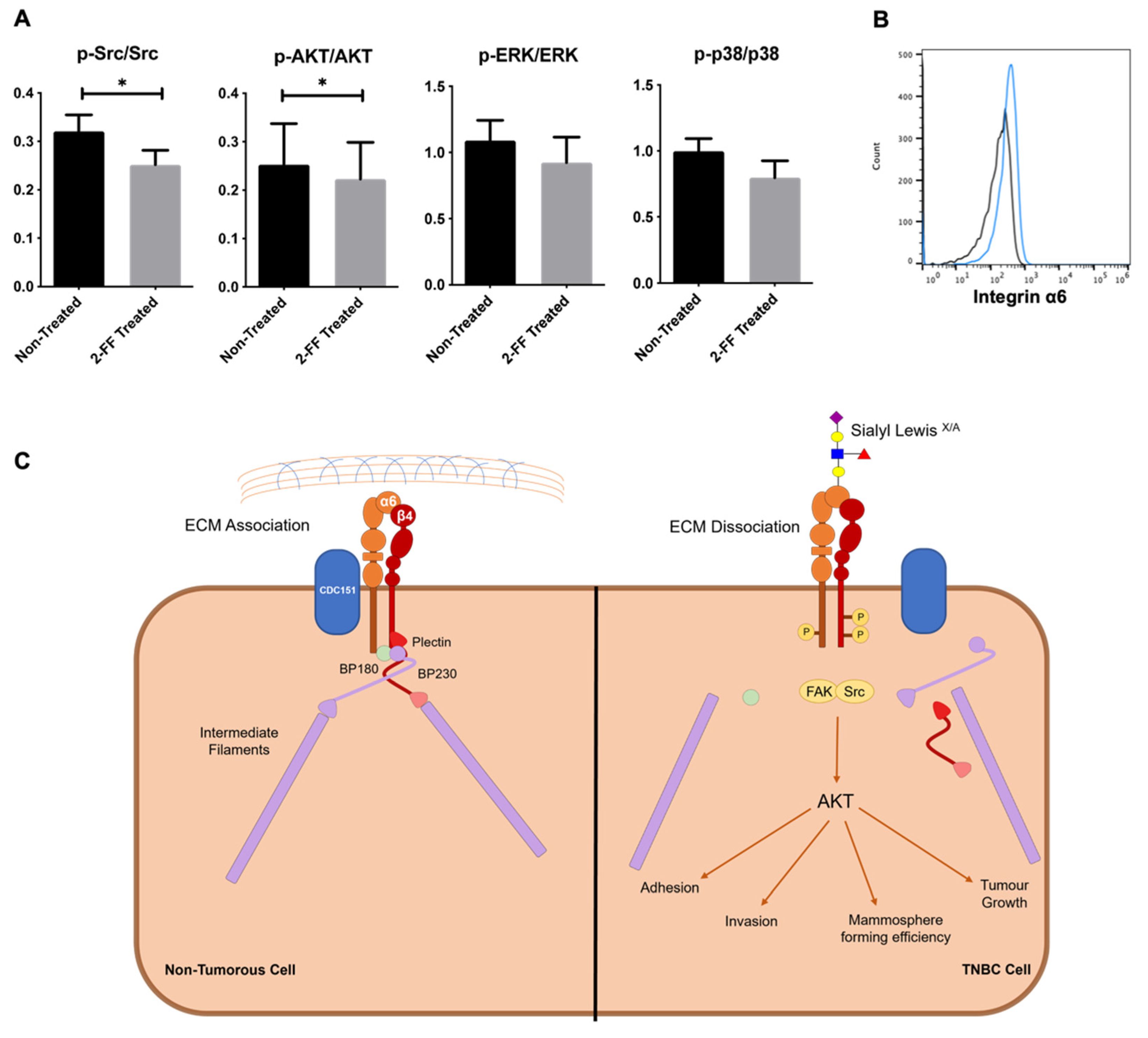
| Biomarker | Biomarker Staining 1 | % of Cases |
|---|---|---|
| CK5/6 | 0 | 56% |
| 1 | 24% | |
| 2 | 12% | |
| 3 | 8% | |
| EGFR | 0 | 30% |
| 1 | 30% | |
| 2 | 26% | |
| 3 | 14% | |
| AR | Negative | 66% |
| Positive | 34% | |
| P-cadherin | Negative | 4% |
| Positive | 96% | |
| sLeX/A | 0 | 0% |
| 1 | 40% | |
| 2 | 30% | |
| 3 | 30% | |
| E-SL | 0 | 0% |
| 1 | 20% | |
| 2 | 25% | |
| 3 | 55% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pascoal, C.; Carrascal, M.A.; Barreira, D.F.; Lourenço, R.A.; Granjo, P.; Grosso, A.R.; Borralho, P.; Braga, S.; Videira, P.A. Sialyl LewisX/A and Cytokeratin Crosstalk in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030731
Pascoal C, Carrascal MA, Barreira DF, Lourenço RA, Granjo P, Grosso AR, Borralho P, Braga S, Videira PA. Sialyl LewisX/A and Cytokeratin Crosstalk in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030731
Chicago/Turabian StylePascoal, Carlota, Mylène A. Carrascal, Daniela F. Barreira, Rita A. Lourenço, Pedro Granjo, Ana R. Grosso, Paula Borralho, Sofia Braga, and Paula A. Videira. 2023. "Sialyl LewisX/A and Cytokeratin Crosstalk in Triple Negative Breast Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 3: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030731
APA StylePascoal, C., Carrascal, M. A., Barreira, D. F., Lourenço, R. A., Granjo, P., Grosso, A. R., Borralho, P., Braga, S., & Videira, P. A. (2023). Sialyl LewisX/A and Cytokeratin Crosstalk in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers, 15(3), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030731








