A Highly Sensitive Flow Cytometric Approach to Detect Rare Antigen-Specific T Cells: Development and Comparison to Standard Monitoring Tools
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Samples
2.2. Glioma Vaccine Peptides and CRC-Related Peptides Used for Immune Monitoring
2.3. CRC Peptide Pools and Assay Controls
2.4. T-Cell Polyfunctional Assay
2.5. ELISpot-Like Flow Cytometry (ELF) Analysis
2.6. ELISpot Assay
2.7. Defining Assay Sensitivity Using Background Noise—Theoretical Considerations
3. Results
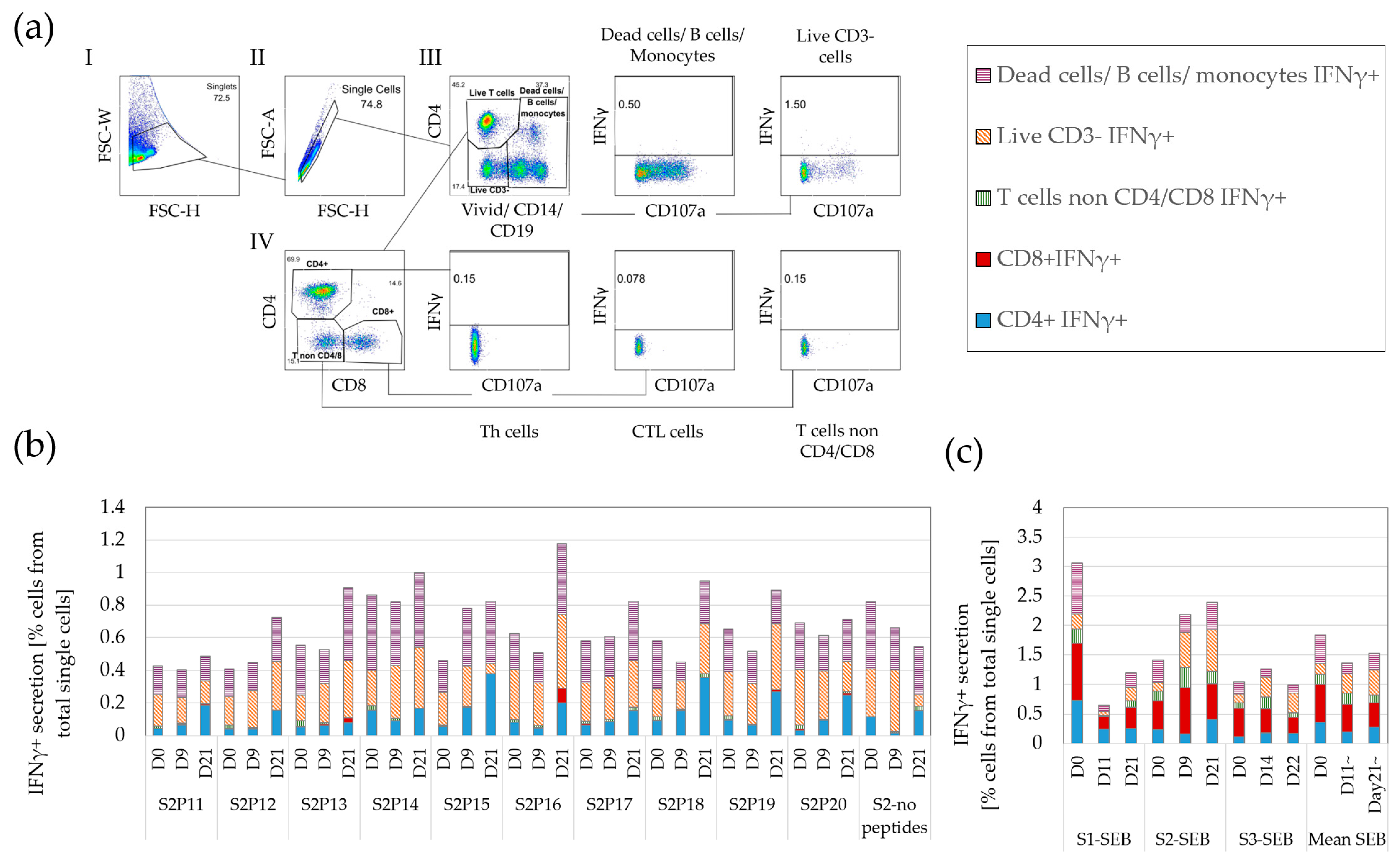
3.1. A Variety of Cells, including T Cells, Secrete IFNγ
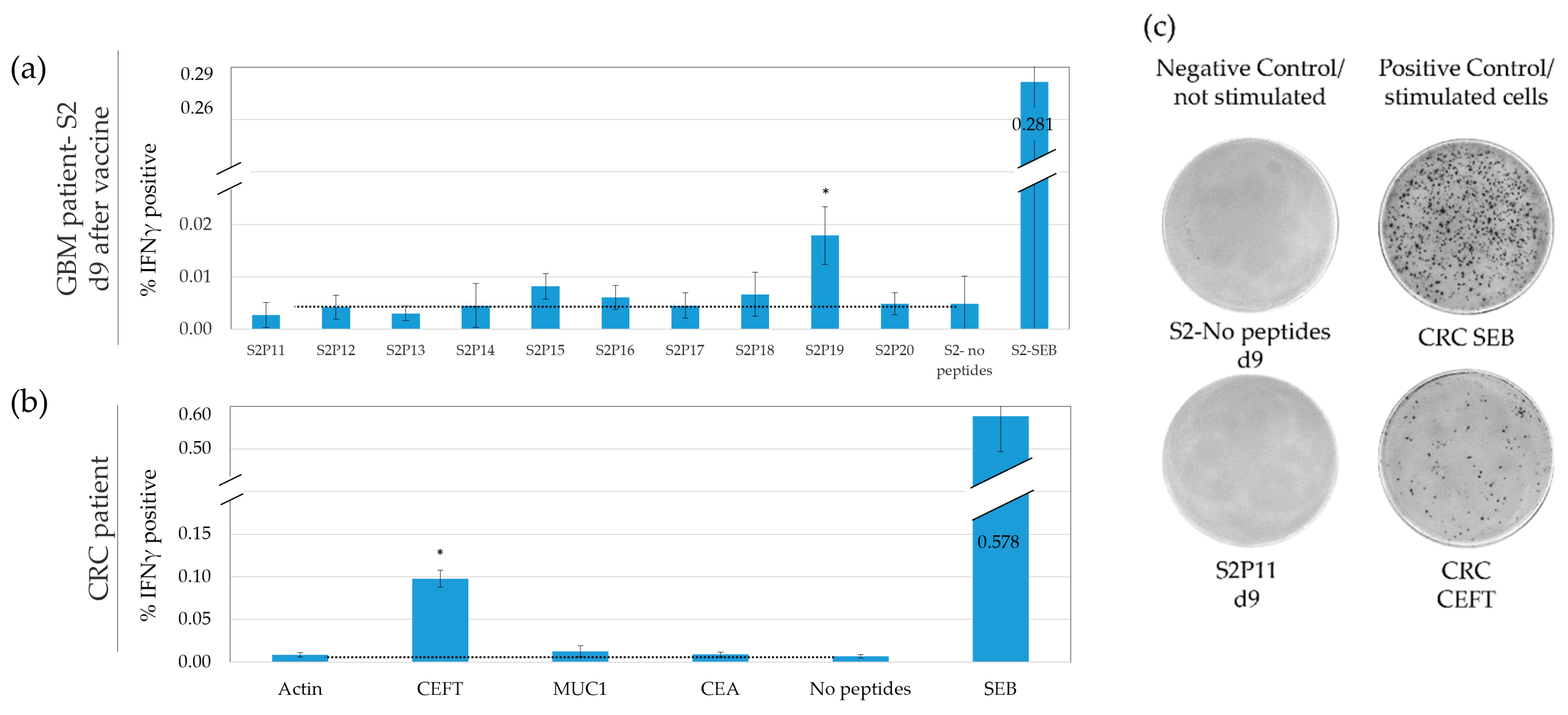
3.2. IFNγ ELISpot Demonstrates a Low but Highly Variable Background
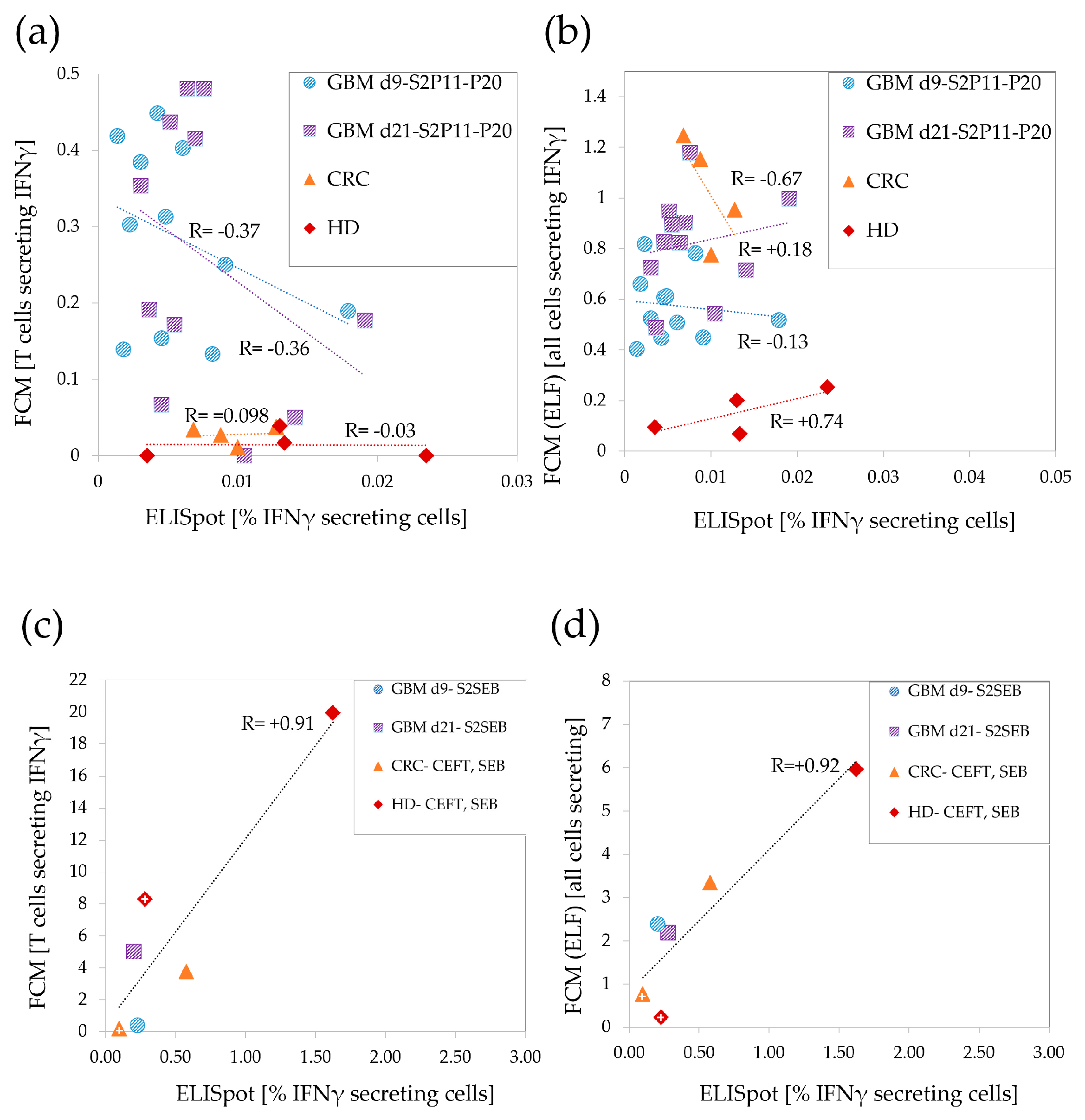
3.3. Low Correlations between ELISpot and FCM in the Weaker T-Cell Response Range
3.4. IFNγ Background in Standard FCM Is High and Variable, Impeding Accurate Detection of Rare Responding T Cells
3.5. Inclusion of Early Activation Markers Enable the Detection of Weak T-Cell Responses by Significantly Reducing Assay Background
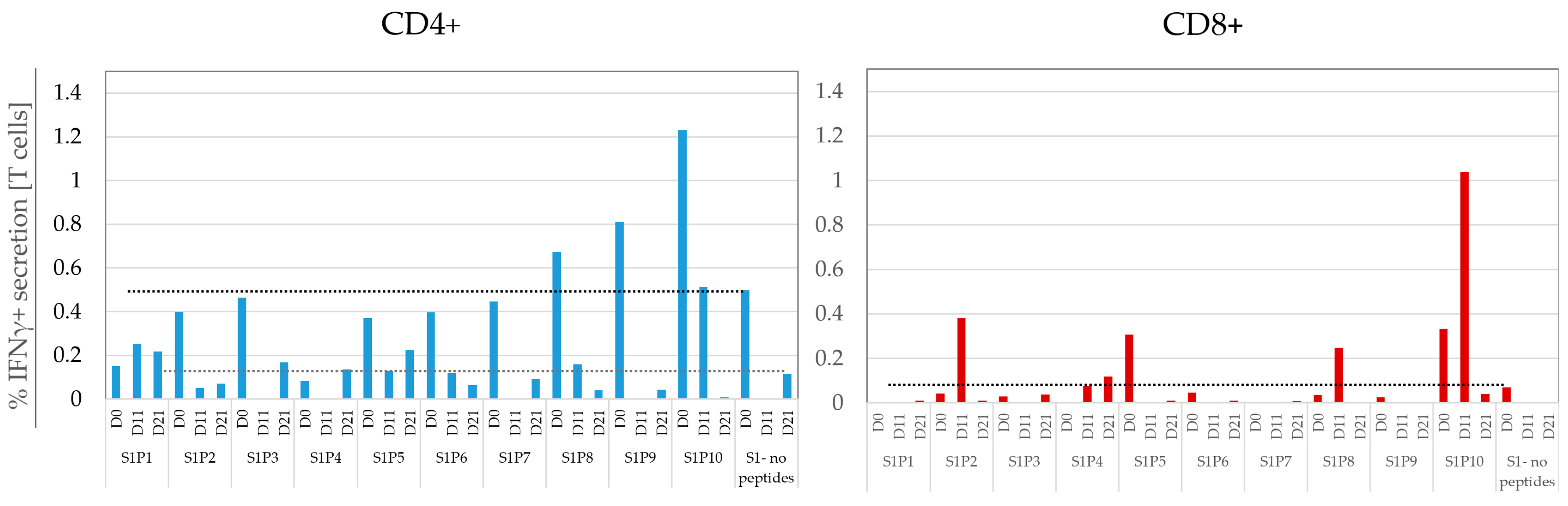
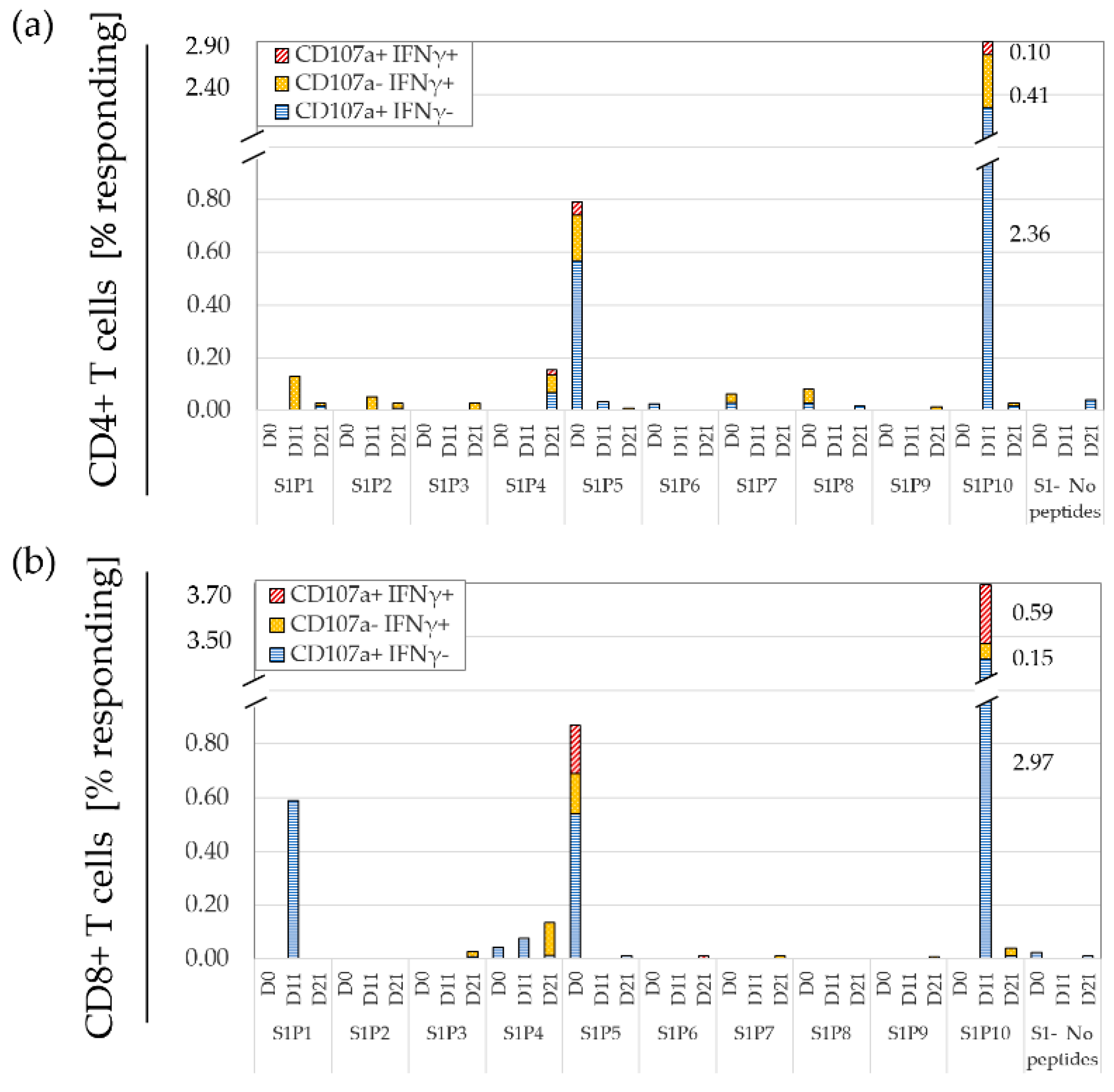
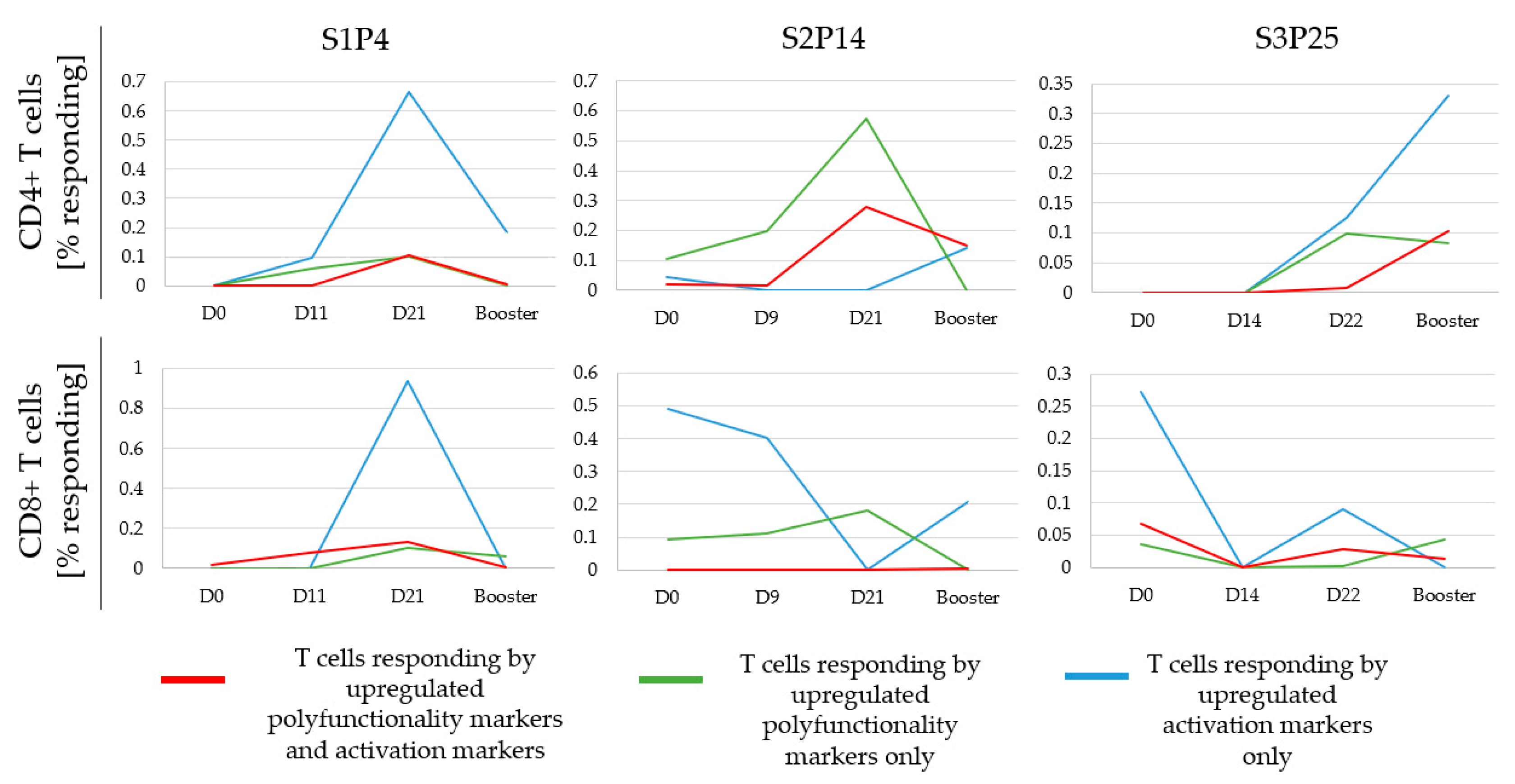
3.6. Monitoring the Temporal Dynamics of Peptide Responses
3.7. Defining a Responding Peptide and Comparing the Sensitivity of FCM to A-FCM
3.8. Comparing A-FCM to ELISpot
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ott, P.A.; Hu, Z.; Keskin, D.B.; Shukla, S.A.; Sun, J.; Bozym, D.J.; Zhang, W.; Luoma, A.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Peter, L.; et al. An Immunogenic Personal Neoantigen Vaccine for Patients with Melanoma. Nature 2017, 547, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, U.; Derhovanessian, E.; Miller, M.; Kloke, B.P.; Simon, P.; Löwer, M.; Bukur, V.; Tadmor, A.D.; Luxemburger, U.; Schrörs, B.; et al. Personalized RNA Mutanome Vaccines Mobilize Poly-Specific Therapeutic Immunity against Cancer. Nature 2017, 547, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shraibman, B.; Barnea, E.; Kadosh, D.M.; Haimovich, Y.; Slobodin, G.; Rosner, I.; López-Larrea, C.; Hilf, N.; Kuttruff, S.; Song, C.; et al. Identification of Tumor Antigens among the HLA Peptidomes of Glioblastoma Tumors and Plasma. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2019, 18, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, N.; Ikeda, H.; Tawara, I.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Nishikawa, H.; Kato, T.; Shiku, H. Glucocorticoid-Induced Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Stimulation Enhances the Multifunctionality of Adoptively Transferred Tumor Antigen-Specific CD8+ T Cells with Tumor Regression. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, B.; Chin, S.F.; Rueda, O.M.; Vollan, H.K.M.; Provenzano, E.; Bardwell, H.A.; Pugh, M.; Jones, L.; Russell, R.; Sammut, S.J.; et al. The Somatic Mutation Profiles of 2,433 Breast Cancers Refines Their Genomic and Transcriptomic Landscapes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, D.B.; Anandappa, A.J.; Sun, J.; Tirosh, I.; Mathewson, N.D.; Li, S.; Oliveira, G.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Felt, K.; Gjini, E.; et al. Neoantigen Vaccine Generates Intratumoral T Cell Responses in Phase Ib Glioblastoma Trial. Nature 2019, 565, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; He, Y. A Novel Era of Cancer/Testis Antigen in Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 98, 107889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Vogel, M.; Riether, C.; Muller, J.; Salatino, S.; Ternette, N.; Gomes, A.C.; Cabral-Miranda, G.; El-Turabi, A.; Ruedl, C.; et al. Targeting Mutated plus Germline Epitopes Confers Pre-Clinical Efficacy of an Instantly Formulated Cancer Nano-Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, W.; Heslop, H.E. Adoptive Immunotherapy with Antigen-Specific T Cells Expressing a Native TCR. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittel, A.; Keilholz, U.; Thiel, E.; Scheibenbogen, C. Quantification of Tumor-Specific T Lymphocytes with the ELISPOT Assay. J. Immunother. 2000, 23, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, T.; Coulie, P.G.; Van Den Eynde, B.J.; Van Der Bruggen, P. Human T Cell Responses against Melanoma. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 175–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Galon, J. The Immune Contexture in Human Tumours: Impact on Clinical Outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, W.; Protzer, U.; Lohse, A.W.; Gerken, G.; zum Büschenfelde KH, M.; Wölfel, T. Quantification of CD8+ T Lymphocytes Responsive to Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Peptide Antigens in HIV-Infected Patients and Seronegative Persons at High Risk for Recent HIV Exposure. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaritskaya, L.; Shurin, M.R.; Sayers, T.J.; Malyguine, A.M. New Flow Cytometric Assays for Monitoring Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2010, 9, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slota, M.; Lim, J.B.; Dang, Y.; Disis, M.L. ELISpot for Measuring Human Immune Responses to Vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2011, 10, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.G.; Levin, M.; Vessey, R.; Chan, I.S.F.; Hayward, A.R.; Liu, X.; Kaufhold, R.M.; Clair, J.; Chalikonda, I.; Chan, C.; et al. Measurement of Cell-Mediated Immunity with a Varicella-Zoster Virus-Specific Interferon-γ ELISPOT Assay: Responses in an Elderly Population Receiving a Booster Immunization. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 70, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janetzki, S.; Britten, C.M.; Kalos, M.; Levitsky, H.I.; Maecker, H.T.; Melief, C.J.M.; Old, L.J.; Romero, P.; Hoos, A.; Davis, M.M. “MIATA”-Minimal Information about T Cell Assays. Immunity 2009, 31, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, F.; Cardoso, A.P.; Gonçalves, R.M.; Serre, K.; Oliveira, M.J. Interferon-Gamma at the Crossroads of Tumor Immune Surveillance or Evasion. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacher, P.; Scheffold, A. Flow-Cytometric Analysis of Rare. Cytom. Part A 2013, 83A, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, C. HIV Protocols. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoreaux, L.; Roederer, M.; Koup, R. Intracellular Cytokine Optimization and Standard Operating Procedure. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janetzki, S.; Price, L.; Schroeder, H.; Britten, C.M.; Welters, M.J.P.; Hoos, A. Guidelines for the Automated Evaluation of Elispot Assays. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1098–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimmers, F.; Aarntzen, E.H.J.G.; Duiveman-deBoer, T.; Figdor, C.G.; Jacobs, J.F.M.; Tel, J.; de Vries, I.J.M. Long-Lasting Multifunctional CD8+ T Cell Responses in End-Stage Melanoma Patients Can Be Induced by Dendritic Cell Vaccination. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1067745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankenstein, T.; Qin, Z. The Role of IFN-γ in Tumor Transplantation Immunity and Inhibition of Chemical Carcinogenesis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betts, M.R.; Brenchley, J.M.; Price, D.A.; De Rosa, S.C.; Douek, D.C.; Roederer, M.; Koup, R.A. Sensitive and Viable Identification of Antigen-Specific CD8+ T Cells by a Flow Cytometric Assay for Degranulation. J. Immunol. Methods 2003, 281, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenbrunn, A.; Frentsch, M.; Kohler, S.; Keye, J.; Dooms, H.; Moewes, B.; Dong, J.; Loddenkemper, C.; Sieper, J.; Wu, P.; et al. A Converse 4-1BB and CD40 Ligand Expression Pattern Delineates Activated Regulatory T Cells (Treg) and Conventional T Cells Enabling Direct Isolation of Alloantigen-Reactive Natural Foxp3 + Treg. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5985–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, R.; Wang, Y.J.; Schoen, R.E.; Finn, O.J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L. Colorectal Cancer Prevention: Immune Modulation Taking the Stage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Rev. Cancer 2018, 1869, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roederer, M. How Many Events Is Enough? Are You Positive? Cytom. Part A 2008, 73, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, J.; Zimmerman, R.; Goetz, C.; Bonnevier, J.; Houchins, J.P.; Reagan, K.; Kalyuzhny, A.E. Comparative Multi-Donor Study of IFNγ Secretion and Expression by Human PBMCS Using ELISPOT Side-by-Side with ELISA and Flow Cytometry Assays. Cells 2015, 4, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A.; Haussmann, K.; Streitz, M.; Schlickeiser, S.; Tietze-Buerger, C.; Blau, I.W.; Uharek, L. Standardized Assay for Assessment of Minimal Residual Disease in Blood, Bone Marrow and Apheresis from Patients with Plasma Cell Myeloma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelde, A.; Rammensee, H.G.; Walz, J.S. The Peptide Vaccine of the Future. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2021, 20, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thieme, C.J.; Anft, M.; Paniskaki, K.; Blazquez-Navarro, A.; Doevelaar, A.; Seibert, F.S.; Hoelzer, B.; Konik, M.J.; Berger, M.M.; Brenner, T.; et al. Robust T Cell Response Toward Spike, Membrane, and Nucleocapsid SARS-CoV-2 Proteins Is Not Associated with Recovery in Critical COVID-19 Patients. Cell Reports Med. 2020, 1, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frentsch, M.; Stark, R.; Matzmohr, N.; Meier, S.; Durlanik, S.; Schulz, A.R.; Stervbo, U.; Jürchott, K.; Gebhardt, F.; Heine, G.; et al. CD40L Expression Permits CD8+ T Cells to Execute Immunologic Helper Functions. Blood 2013, 122, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, A.J.; Padilla, M.G.; Hokey, D.A. OMIP-022: Comprehensive Assessment of Antigen-Specific Human T-Cell Functionality and Memory. Cytom. Part A 2014, 85, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowiak, T.; Curran, M.A. 4-1BB Agonists: Multi-Potent Potentiators of Tumor Immunity. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, N.H.R.; de Wit, E.A.; Baan, C.C.; Betjes, M.G.H. Activation-Induced CD137 Is a Fast Assay for Identification and Multi-Parameter Flow Cytometric Analysis of Alloreactive T Cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 174, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, S.; Snyder, J.T.; Shen, J.; Azmi, H.; Hu, P.Q.; Chen, Q.; Ragheb, J.A. Human CD14hi Monocytes and Myeloid Dendritic Cells Provide a Cell Contact-Dependent Costimulatory Signal for Early CD40 Ligand Expression. Blood 2011, 117, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetto, S.P.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Lamoreaux, L.; Nguyen, R.; Ambrozak, D.; Koup, R.A.; Roederer, M. Amine Reactive Dyes: An Effective Tool to Discriminate Live and Dead Cells in Polychromatic Flow Cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods 2006, 313, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wölfl, M.; Kuball, J.; Eyrich, M.; Schlegel, P.G.; Greenberg, P.D. Use of CD137 to Study the Full Repertoire of CD8+ T Cells without the Need to Know Epitope Specificities. Cytom. Part A 2008, 73, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Saito, T. CD4 CTL, a Cytotoxic Subset of CD4+ T Cells, Their Differentiation and Function. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Couturier, J.; Yu, X.; Medina, M.A.; Kozinetz, C.A.; Lewis, D.E. Granzyme B Secretion by Human Memory CD4 T Cells Is Less Strictly Regulated Compared to Memory CD8 T Cells. BMC Immunol. 2014, 15, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.M.; Horn, S.E.; Grant, M.L.; Lang, H.; Sani, G.; Jensen-Wachspress, M.A.; Kankate, V.V.; Datar, A.; Lazarski, C.A.; Bollard, C.M.; et al. T-Cell Therapeutics Targeting Human Parainfluenza Virus 3 Are Broadly Epitope Specific and Are Cross Reactive With Human Parainfluenza Virus 1. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 575977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidleman, J.; Luo, X.; McGregor, M.; Xie, G.; Murray, V.; Greene, W.C.; Lee, S.A.; Roan, N.R. Mrna Vaccine-Induced t Cells Respond Identically to Sars-Cov-2 Variants of Concern but Differ in Longevity and Homing Properties Depending on Prior Infection Status. Elife 2021, 10, e72619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rius, C.; Attaf, M.; Tungatt, K.; Bianchi, V.; Legut, M.; Bovay, A.; Donia, M.; thor Straten, P.; Peakman, M.; Svane, I.M.; et al. Peptide–MHC Class I Tetramers Can Fail To Detect Relevant Functional T Cell Clonotypes and Underestimate Antigen-Reactive T Cell Populations. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2263–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIH Tetramer Core Facility. Available online: https://tetramer.yerkes.emory.edu/ (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Nepom, G.T. MHC Class II Tetramers. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 2477–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, S.; Gouttefangeas, C.; Besedovsky, L.; Jensen, A.T.R.; Chandran, P.A.; Rusch, E.; Businger, R.; Schindler, M.; Lange, T.; Born, J.; et al. Activated Integrins Identify Functional Antigen-Specific CD8+ T Cells within Minutes after Antigen Stimulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5536–E5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Womersley, H.J.; Wang, J.; Scolnick, J.A.; Cheow, L.F. Time-Resolved Assessment of Single-Cell Protein Secretion by Sequencing. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Nam, K.O.; Seo, S.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, H.; Kwon, B.S. 4-1BB Cross-Linking Enhances the Survival and Cell Cycle Progression of CD4 T Lymphocytes. Cell. Immunol. 2003, 223, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfl, M.; Kuball, J.; Ho, W.Y.; Nguyen, H.; Manley, T.J.; Bleakley, M.; Greenberg, P.D. Activation-Induced Expression of CD137 Permits Detection, Isolation, and Expansion of the Full Repertoire of CD8+ T Cells Responding to Antigen without Requiring Knowledge of Epitope Specificities. Blood 2007, 110, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dongen, J.J.M.; Lhermitte, L.; Böttcher, S.; Almeida, J.; Van Der Velden, V.H.J.; Flores-Montero, J.; Rawstron, A.; Asnafi, V.; Lécrevisse, Q.; Lucio, P.; et al. EuroFlow Antibody Panels for Standardized N-Dimensional Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping of Normal, Reactive and Malignant Leukocytes. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1908–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, A.C.; Martin, J.N.; Younger, S.R.; Bredt, B.M.; Epling, L.; Ronquillo, R.; Varma, A.; Deeks, S.G.; McCune, J.M.; Nixon, D.F.; et al. Comparison of the ELISPOT and Cytokine Flow Cytometry Assays for the Enumeration of Antigen-Specific T Cells. J. Immunol. Methods 2003, 283, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelands, J.; Kuppen, P.J.K.; Vermeulen, L.; Maccalli, C.; Decock, J.; Wang, E.; Marincola, F.M.; Bedognetti, D.; Hendrickx, W. Immunogenomic Classification of Colorectal Cancer and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallas, E.G.; Grunenberg, N.A.; Yu, C.; Manso, B.; Pantaleo, G.; Casapia, M.; Baden, L.R.; Valencia, J.; Sobieszczyk, M.; van Tieu, H.; et al. Antigenic Competition in CD4+ T Cell Responses in a Randomized, Multicenter, Double-Blind Clinical HIV Vaccine Trial. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmann, J.; Keller-Matschke, K.; Weinschenk, T.; Kratt, T.; Heck, T.; Becker, H.D.; Stevanović, S.; Rammensee, H.G.; Gouttefangeas, C. CD8+ T-Cell Response against MUC1-Derived Peptides in Gastrointestinal Cancer Survivors. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2005, 54, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzileontiadou, D.S.M.; Sloane, H.; Nguyen, A.T.; Gras, S.; Grant, E.J. The Many Faces of CD4+ T Cells: Immunological and Structural Characteristics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.K.; Lahesmaa, R. Transcriptional and Epigenetic Regulation of T-Helper Lineage Specification. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 261, 62–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.R.; Nelson, M.H.; Himes, R.A.; Li, Z.; Mehrotra, S.; Paulos, C.M. Th17 Cells in Cancer: The Ultimate Identity Crisis. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resop, R.S.; Uittenbogaart, C.H. Human T-Cell Development and Thymic Egress: An Infectious Disease Perspective. For. Immunopathol. Dis. Therap. 2015, 6, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spijkerman, R.; Hesselink, L.; Hellebrekers, P.; Vrisekoop, N.; Hietbrink, F.; Leenen, L.P.H.; Koenderman, L. Automated Flow Cytometry Enables High Performance Point-of-Care Analysis of Leukocyte Phenotypes. J. Immunol. Methods 2019, 474, 112646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| IFNγ Only | Peptides Identified by A-FCM (P1–P30) | Peptides Identified by FCM (P1–P30) | % Overlap between the Two Analyzed Methods | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | % | # | % | # (overlap) | % (overlap) | |
| CD4 | 10 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CD8 | 14 | 47 | 14 | 47 | 9/14 | 64 |
| Total # peptides | 15 | 53 | 14 | 47 | 9/15–9/14 | 60-64 |
| IFNγ and/or CD107a | Peptides Identified by A-FCM (P1–P30) | Peptides Identified by FCM (P1–P30) | % Overlap between the Two Analyzed Methods | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | % | # | % | # (overlap) | % (overlap) | |
| CD4 | 13 | 43 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CD8 | 14 | 47 | 14 | 47 | 11/14 | 79 |
| Total # peptides | 18 | 60 | 14 | 47 | 11/18–11/14 | 61–79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dror Levinsky, M.; Brenner, B.; Yalon, M.; Levi, Z.; Livneh, Z.; Cohen, Z.; Paz-Elizur, T.; Grossman, R.; Ram, Z.; Volovitz, I. A Highly Sensitive Flow Cytometric Approach to Detect Rare Antigen-Specific T Cells: Development and Comparison to Standard Monitoring Tools. Cancers 2023, 15, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030574
Dror Levinsky M, Brenner B, Yalon M, Levi Z, Livneh Z, Cohen Z, Paz-Elizur T, Grossman R, Ram Z, Volovitz I. A Highly Sensitive Flow Cytometric Approach to Detect Rare Antigen-Specific T Cells: Development and Comparison to Standard Monitoring Tools. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030574
Chicago/Turabian StyleDror Levinsky, Meytal, Baruch Brenner, Michal Yalon, Zohar Levi, Zvi Livneh, Zoya Cohen, Tamar Paz-Elizur, Rachel Grossman, Zvi Ram, and Ilan Volovitz. 2023. "A Highly Sensitive Flow Cytometric Approach to Detect Rare Antigen-Specific T Cells: Development and Comparison to Standard Monitoring Tools" Cancers 15, no. 3: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030574
APA StyleDror Levinsky, M., Brenner, B., Yalon, M., Levi, Z., Livneh, Z., Cohen, Z., Paz-Elizur, T., Grossman, R., Ram, Z., & Volovitz, I. (2023). A Highly Sensitive Flow Cytometric Approach to Detect Rare Antigen-Specific T Cells: Development and Comparison to Standard Monitoring Tools. Cancers, 15(3), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030574







