ImmunoPET Targeting Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: Clinical Applications
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) Family
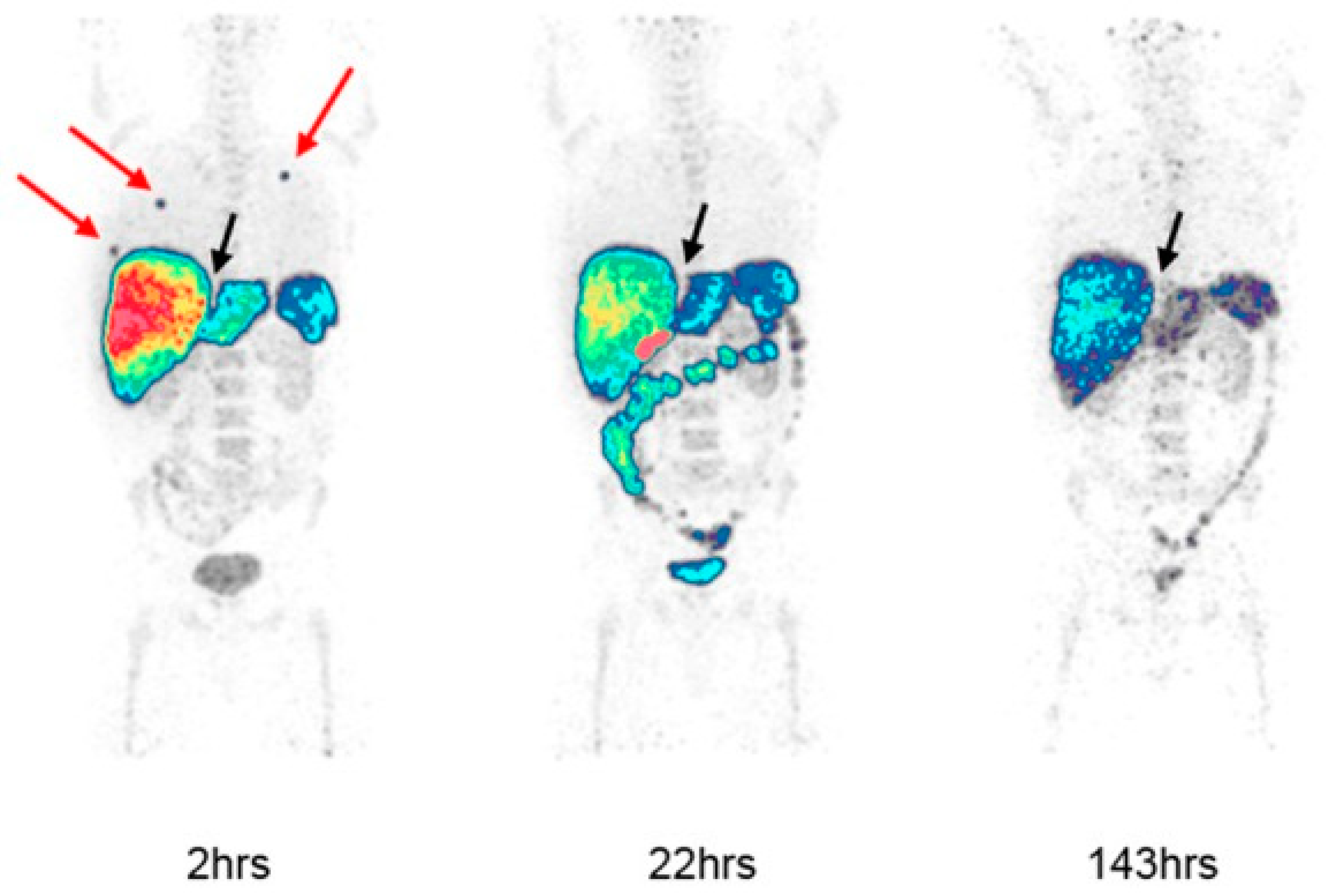
2.1. EGFR
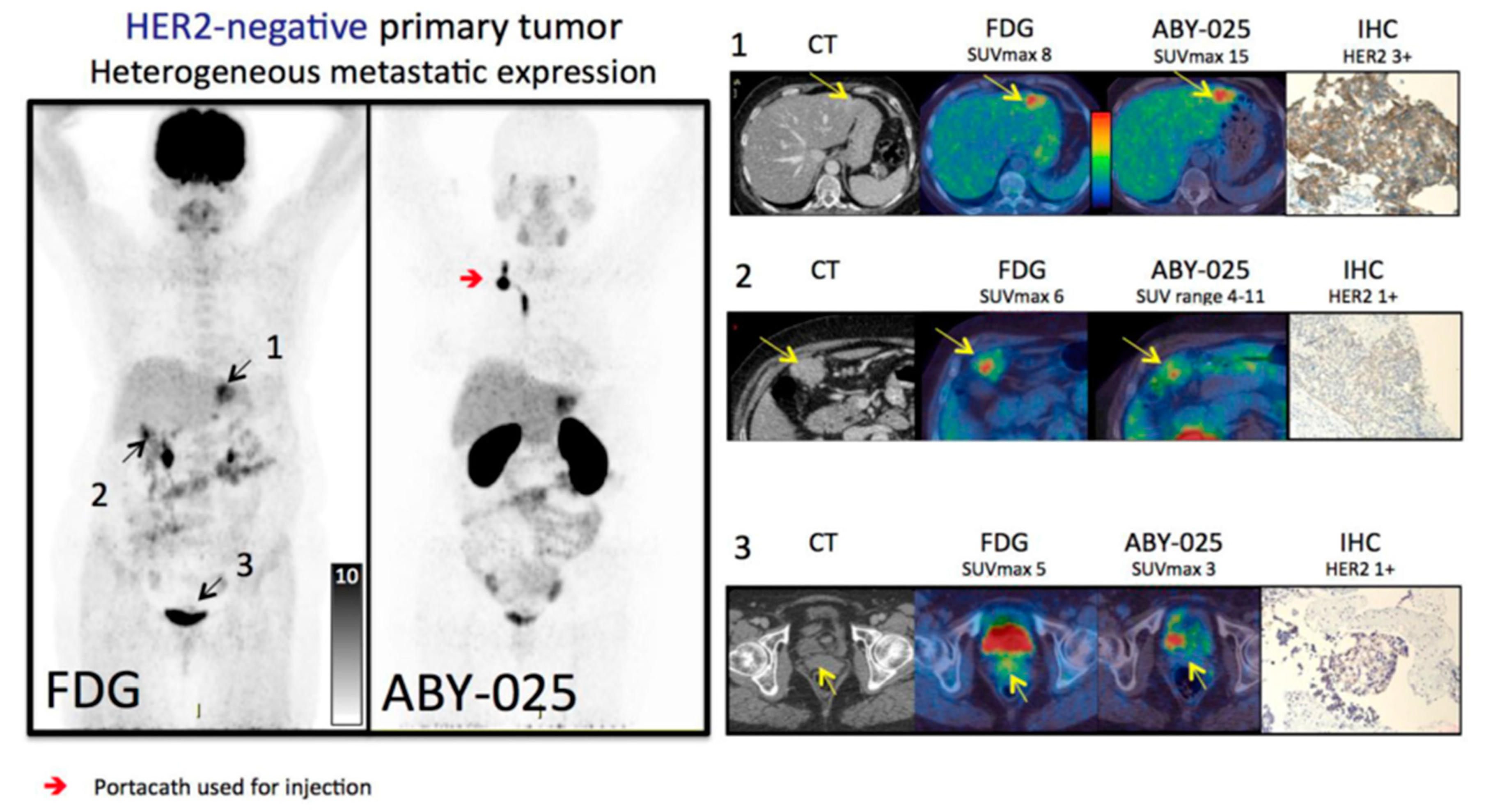
2.2. HER2
2.3. HER3
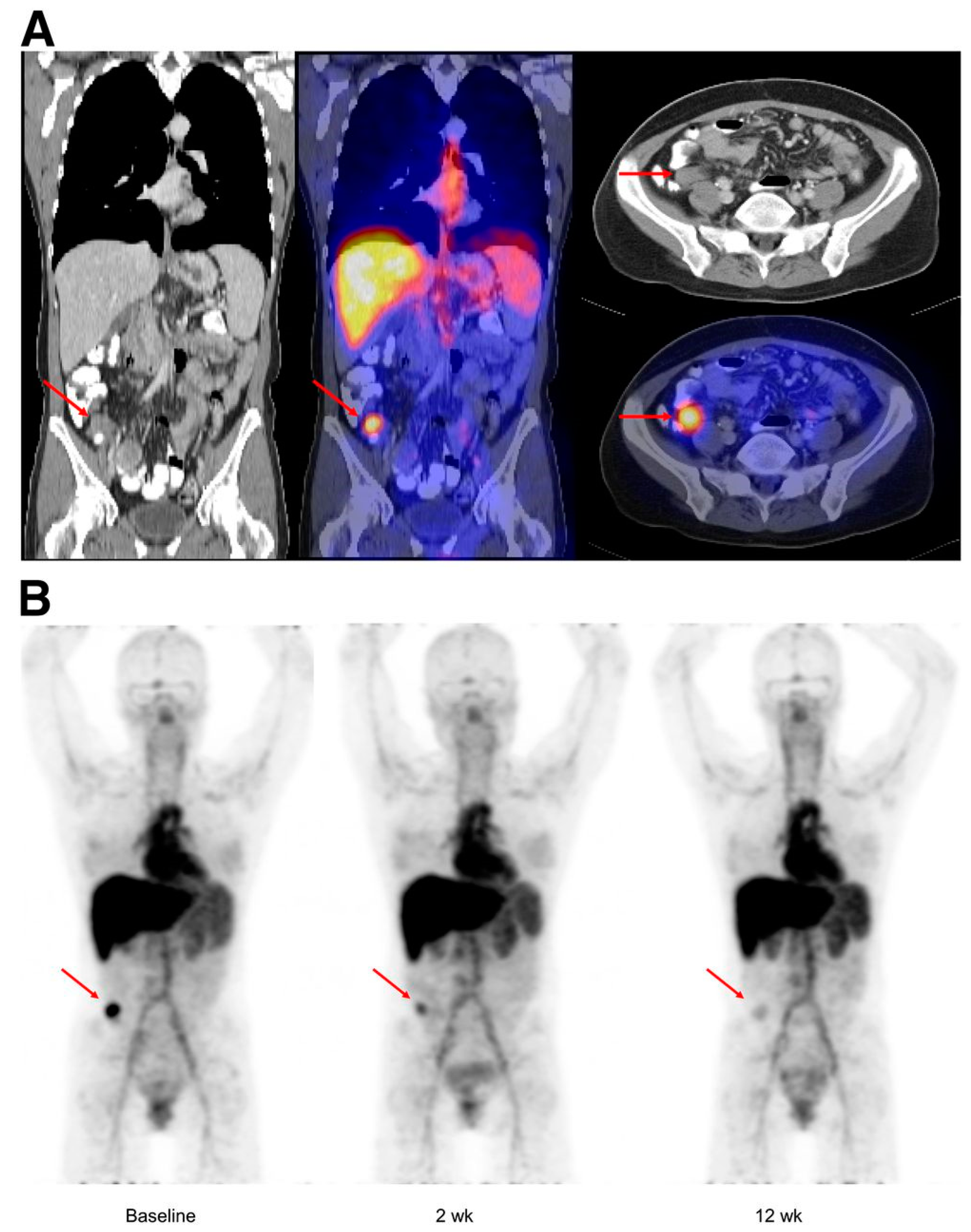
2.4. VEGF
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mulder, W.J.M.; Ochando, J.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Fayad, Z.A.; Netea, M.G. Therapeutic targeting of trained immunity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, P.L.; Hyman, D.M.; Davids, M.S.; Siu, L.L. Small molecules, big impact: 20 years of targeted therapy in oncology. Lancet 2020, 395, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raval, R.R.; Sharabi, A.B.; Walker, A.J.; Drake, C.G.; Sharma, P. Tumor immunology and cancer immunotherapy: Summary of the 2013 SITC primer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2014, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukswai, N.; Khoury, J.D. Immunohistochemistry innovations for diagnosis and tissue-based biomarker detection. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2019, 14, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Rosenkrans, Z.T.; Liu, J.; Huang, G.; Luo, Q.Y.; Cai, W. ImmunoPET: Concept, Design, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3787–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulero, F. ImmunoPET in oncology. Rev. Esp. Med. Nucl. Imagen. Mol. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 41, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Robinson, M.K. Immuno-positron emission tomography in cancer models. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2010, 40, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochacka-Ćwikła, A.; Mączyński, M.; Regiec, A. FDA-Approved Small Molecule Compounds as Drugs for Solid Cancers from Early 2011 to the End of 2021. Molecules 2022, 27, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manafi-Farid, R.; Ataeinia, B.; Ranjbar, S.; Jamshidi Araghi, Z.; Moradi, M.M.; Pirich, C.; Beheshti, M. ImmunoPET: Antibody-Based PET Imaging in Solid Tumors. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 916693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugat, A.; Bailly, C.; Chérel, M.; Rousseau, C.; Kraeber-Bodéré, F.; Bodet-Milin, C.; Bourgeois, M. Immuno-PET: Design options and clinical proof-of-concept. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1026083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dongen, G.A.; Poot, A.J.; Vugts, D.J. PET imaging with radiolabeled antibodies and tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Immuno-PET and TKI-PET. Tumour Biol. 2012, 33, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, T.; Rezaei, R.; Surendran, A.; Singaravelu, R.; Boulton, S.; Dave, J.; Bell, J.C.; Ilkow, C.S. Hippo Signaling Pathway as a Central Mediator of Receptors Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) in Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2020, 12, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, P.M.R.; Norfleet, J.; Lewis, J.S.; Escorcia, F.E. Immuno-PET Detects Changes in Multi-RTK Tumor Cell Expression Levels in Response to Targeted Kinase Inhibition. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaram, P.; Chandra, P.; Ticku, S.; Pallavi, B.K.; Rudresh, K.B.; Mansabdar, P. Epidermal growth factor receptor: Role in human cancer. Indian. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 28, 687–694. [Google Scholar]
- Esparís-Ogando, A.; Montero, J.C.; Arribas, J.; Ocaña, A.; Pandiella, A. Targeting the EGF/HER Ligand-Receptor System in Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 5887–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume-Jensen, P.; Hunter, T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature 2001, 411, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, N.E.; MacDonald, G. ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.F. Structure and function of tyrosine kinase receptors. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1991, 23, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voldborg, B.R.; Damstrup, L.; Spang-Thomsen, M.; Poulsen, H.S. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and EGFR mutations, function and possible role in clinical trials. Ann. Oncol. 1997, 8, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.T.; Mandleywala, K.; Viray, T.; Tan, K.V.; Lewis, J.S.; Pereira, P.M.R. EGFR-Targeted ImmunoPET of UMUC3 Orthotopic Bladder Tumors. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2022, 24, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, V.; Stintzing, S.; Kirchner, T.; Boeck, S.; Jung, A. Clinical relevance of EGFR- and KRAS-status in colorectal cancer patients treated with monoclonal antibodies directed against EGFR. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009, 35, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornasier, G.; Francescon, S.; Baldo, P. An Update of Efficacy and Safety of Cetuximab in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Narrative Review. Adv. Ther. 2018, 35, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardiello, F.; Tortora, G. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) as a target in cancer therapy: Understanding the role of receptor expression and other molecular determinants that could influence the response to anti-EGFR drugs. Eur. J. Cancer. 2003, 39, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blick, S.K.; Scott, L.J. Cetuximab: A review of its use in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck and metastatic colorectal cancer. Drugs 2007, 67, 2585–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetto, R.; Massicano, A.V.F.; Crenshaw, B.K.; Oliveira, R.; Reis, R.M.; Araújo, E.B.; Lapi, S.E. 89Zr-DFO-Cetuximab as a Molecular Imaging Agent to Identify Cetuximab Resistance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2019, 34, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menke-van der Houven van Oordt, C.W.; Gootjes, E.C.; Huisman, M.C.; Vugts, D.J.; Roth, C.; Luik, A.M.; Mulder, E.R.; Schuit, R.C.; Boellaard, R.; Hoekstra, O.S.; et al. 89Zr-cetuximab PET imaging in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 30384–30393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divgi, C.R.; Welt, S.; Kris, M.; Real, F.X.; Yeh, S.D.; Gralla, R.; Merchant, B.; Schweighart, S.; Unger, M.; Larson, S.M.; et al. Phase I and imaging trial of indium 111-labeled anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor monoclonal antibody 225 in patients with squamous cell lung carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1991, 83, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Loon, J.; Even, A.J.G.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Öllers, M.; Hoebers, F.; van Elmpt, W.; Dubois, L.; Dingemans, A.C.; Lalisang, R.I.; Kempers, P.; et al. PET imaging of zirconium-89 labelled cetuximab: A phase I trial in patients with head and neck and lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 122, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even, A.J.; Hamming-Vrieze, O.; van Elmpt, W.; Winnepenninckx, V.J.; Heukelom, J.; Tesselaar, M.E.; Vogel, W.V.; Hoeben, A.; Zegers, C.M.; Vugts, D.J.; et al. Quantitative assessment of Zirconium-89 labeled cetuximab using PET/CT imaging in patients with advanced head and neck cancer: A theragnostic approach. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 3870–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, Y.J.; Cunningham, D. Panitumumab. Drugs Today 2006, 42, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenberg, L.; Adler, S.; Turkbey, I.B.; Mertan, F.; Ton, A.; Do, K.; Kummar, S.; Gonzalez, E.M.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Jacobs, P.M.; et al. Dosimetry and first human experience with 89Zr-panitumumab. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 7, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, N.; Iqbal, N. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) in Cancers: Overexpression and Therapeutic Implications. Mol. Biol. Int. 2014, 2014, 852748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranić, S.; Bešlija, S.; Gatalica, Z. Targeting HER2 expression in cancer: New drugs and new indications. Bosn. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2021, 21, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Liu, T.; Fan, Q.; Bai, L.; Bi, F.; Qin, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, N.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, Y.; et al. Optimal regimen of trastuzumab in combination with oxaliplatin/capecitabine in first-line treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer (CGOG1001): A multicenter, phase II trial. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bánkfalvi, A. HER-2 diagnosztika [HER-2 diagnostics]. Magy Onkol. 2002, 46, 11–15. (In Hungarian) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leong, T.Y.; Leong, A.S. Controversies in the assessment of HER-2: More questions than answers. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2006, 13, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Kurihara, H.; Yonemori, K.; Tsuda, H.; Suzuki, J.; Kono, Y.; Honda, N.; Kodaira, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Yunokawa, M.; et al. 64Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab PET imaging in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasquillo, J.A.; Morris, P.G.; Humm, J.L.; Smith-Jones, P.M.; Beylergil, V.; Akhurst, T.; O’donoghue, J.A.; Ruan, S.; Modi, S.; Hudis, C.A.; et al. Copper-64 trastuzumab PET imaging: A reproducibility study. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 63, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, J.E.; Bading, J.R.; Colcher, D.M.; Conti, P.S.; Frankel, P.H.; Carroll, M.I.; Tong, S.; Poku, E.; Miles, J.K.; Shively, J.E.; et al. Functional imaging of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer using (64)Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, J.E.; Bading, J.R.; Frankel, P.H.; Carroll, M.I.; Yuan, Y.; Park, J.M.; Tumyan, L.; Gidwaney, N.; Poku, E.K.; Shively, J.E.; et al. Use of 64Cu-DOTA-Trastuzumab PET to Predict Response and Outcome of Patients Receiving Trastuzumab Emtansine for Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Pilot Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkers, E.C.; Oude Munnink, T.H.; Kosterink, J.G.; Brouwers, A.H.; Jager, P.L.; de Jong, J.R.; van Dongen, G.A.; Schröder, C.P.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; de Vries, E.G. Biodistribution of 89Zr-trastuzumab and PET imaging of HER2-positive lesions in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 87, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensch, F.; Brouwers, A.H.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; de Jong, J.R.; van der Vegt, B.; Sleijfer, S.; de Vries, E.G.E.; Schröder, C.P. 89Zr-trastuzumab PET supports clinical decision making in breast cancer patients, when HER2 status cannot be determined by standard work up. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2018, 45, 2300–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauw, Y.W.; Menke-van der Houven van Oordt, C.W.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Hendrikse, N.H.; Vugts, D.J.; Zijlstra, J.M.; Huisman, M.C.; van Dongen, G.A. Immuno-Positron Emission Tomography with Zirconium-89-Labeled Monoclonal Antibodies in Oncology: What Can We Learn from Initial Clinical Trials? Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaykema, S.B.; Schröder, C.P.; Vitfell-Rasmussen, J.; Chua, S.; Oude Munnink, T.H.; Brouwers, A.H.; Bongaerts, A.H.; Akimov, M.; Fernandez-Ibarra, C.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; et al. 89Zr-trastuzumab and 89Zr-bevacizumab PET to evaluate the effect of the HSP90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 in metastatic breast cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3945–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhart, G.; Lamberts, L.E.; Wimana, Z.; Garcia, C.; Emonts, P.; Ameye, L.; Stroobants, S.; Huizing, M.; Aftimos, P.; Tol, J.; et al. Molecular imaging as a tool to investigate heterogeneity of advanced HER2-positive breast cancer and to predict patient outcome under trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1): The ZEPHIR trial. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauw, Y.W.; Zijlstra, J.M.; de Jong, D.; Vugts, D.J.; Zweegman, S.; Hoekstra, O.S.; van Dongen, G.A.; Huisman, M.C. Performance of 89Zr-Labeled-Rituximab-PET as an Imaging Biomarker to Assess CD20 Targeting: A Pilot Study in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.M.; Baselga, J.; Kim, S.B.; Ro, J.; Semiglazov, V.; Campone, M.; Ciruelos, E.; Ferrero, J.M.; Schneeweiss, A.; Heeson, S.; et al. Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaner, G.A.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; Riedl, C.; Ruan, S.; Zanzonico, P.B.; Lake, D.; Jhaveri, K.; Zeglis, B.; Lewis, J.S.; O’Donoghue, J.A. First-in-Human Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Targeted Imaging Using 89Zr-Pertuzumab PET/CT: Dosimetry and Clinical Application in Patients with Breast Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyaerts, M.; Xavier, C.; Heemskerk, J.; Devoogdt, N.; Everaert, H.; Ackaert, C.; Vanhoeij, M.; Duhoux, F.P.; Gevaert, T.; Simon, P.; et al. Phase I Study of 68Ga-HER2-Nanobody for PET/CT Assessment of HER2 Expression in Breast Carcinoma. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sörensen, J.; Velikyan, I.; Sandberg, D.; Wennborg, A.; Feldwisch, J.; Tolmachev, V.; Orlova, A.; Sandström, M.; Lubberink, M.; Olofsson, H.; et al. Measuring HER2-Receptor Expression In Metastatic Breast Cancer Using [68Ga]ABY-025 Affibody PET/CT. Theranostics 2016, 6, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, D.; Tolmachev, V.; Velikyan, I.; Olofsson, H.; Wennborg, A.; Feldwisch, J.; Carlsson, J.; Lindman, H.; Sörensen, J. Intra-image referencing for simplified assessment of HER2-expression in breast cancer metastases using the Affibody molecule ABY-025 with PET and SPECT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donoghue, J.A.; Lewis, J.S.; Pandit-Taskar, N.; Fleming, S.E.; Schöder, H.; Larson, S.M.; Beylergil, V.; Ruan, S.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; Zanzonico, P.B.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, Biodistribution, and Radiation Dosimetry for 89Zr-Trastuzumab in Patients with Esophagogastric Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Vega, F.; Hechtman, J.F.; Castel, P.; Ku, G.Y.; Tuvy, Y.; Won, H.; Fong, C.J.; Bouvier, N.; Nanjangud, G.J.; Soong, J.; et al. EGFR and MET Amplifications Determine Response to HER2 Inhibition in ERBB2-Amplified Esophagogastric Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, D.N.; Campbell, M.R.; Moasser, M.M. The role of HER3, the unpretentious member of the HER family, in cancer biology and cancer therapeutics. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, H.; Han, A.; Polsdofer, E.; Liu, S.; Liu, B. Understanding the biology of HER3 receptor as a therapeutic target in human cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Cao, B. The function of human epidermal growth factor receptor-3 and its role in tumors (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2563–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mishra, R.; Patel, H.; Alanazi, S.; Yuan, L.; Garrett, J.T. HER3 signaling and targeted therapy in cancer. Oncol. Rev. 2018, 12, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uliano, J.; Corvaja, C.; Curigliano, G.; Tarantino, P. Targeting HER3 for cancer treatment: A new horizon for an old target. ESMO Open. 2023, 8, 100790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwisscha van Scheltinga, A.G.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; Abiraj, K.; Schröder, C.P.; Pot, L.; Bossenmaier, B.; Thomas, M.; Hölzlwimmer, G.; Friess, T.; Kosterink, J.G.; et al. ImmunoPET and biodistribution with human epidermal growth factor receptor 3 targeting antibody ⁸⁹Zr-RG7116. In Mabs; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2014; Volume 6, pp. 1051–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Haikala, H.M.; Jänne, P.A. Thirty Years of HER3: From Basic Biology to Therapeutic Interventions. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3528–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.K.; Millward, M.; Jalving, M.; Garrido-Laguna, I.; Lickliter, J.D.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Lolkema, M.P.; Van Herpen, C.L.M.; Hug, B.; Tang, L.; et al. A Phase I, First-in-Human Study of GSK2849330, an Anti-HER3 Monoclonal Antibody, in HER3-Expressing Solid Tumors. Oncologist 2021, 26, e1844–e1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaid, H.; Skedzielewski, T.; Rambo, M.V.; Hunsinger, K.; Hoang, B.; Fieles, W.; Long, E.R.; Tunstead, J.; Vugts, D.J.; Cleveland, M.; et al. Non invasive imaging assessment of the biodistribution of GSK2849330, an ADCC and CDC optimized anti HER3 mAb, and its role in tumor macrophage recruitment in human tumor-bearing mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menke-van der Houven van Oordt, C.W.; McGeoch, A.; Bergstrom, M.; McSherry, I.; Smith, D.A.; Cleveland, M.; Al-Azzam, W.; Chen, L.; Verheul, H.; Hoekstra, O.S.; et al. Immuno-PET Imaging to Assess Target Engagement: Experience from 89Zr-Anti-HER3 mAb (GSK2849330) in Patients with Solid Tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirschberger, C.; Schiller, C.B.; Schräml, M.; Dimoudis, N.; Friess, T.; Gerdes, C.A.; Reiff, U.; Lifke, V.; Hoelzlwimmer, G.; Kolm, I.; et al. RG7116, a therapeutic antibody that binds the inactive HER3 receptor and is optimized for immune effector activation. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5183–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koganemaru, S.; Kuboki, Y.; Koga, Y.; Kojima, T.; Yamauchi, M.; Maeda, N.; Kagari, T.; Hirotani, K.; Yasunaga, M.; Matsumura, Y.; et al. U3-1402, a Novel HER3-Targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate, for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockhart, A.C.; Liu, Y.; Dehdashti, F.; Laforest, R.; Picus, J.; Frye, J.; Trull, L.; Belanger, S.; Desai, M.; Mahmood, S.; et al. Phase 1 Evaluation of [(64)Cu]DOTA-Patritumab to Assess Dosimetry, Apparent Receptor Occupancy, and Safety in Subjects with Advanced Solid Tumors. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabeta, P.; Steenkamp, V. The VEGF/VEGFR Axis Revisited: Implications for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitohy, B.; Nagy, J.A.; Dvorak, H.F. Anti-VEGF/VEGFR therapy for cancer: Reassessing the target. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Solimando, A.G.; Pezzella, F. The Anti-VEGF(R) Drug Discovery Legacy: Improving Attrition Rates by Breaking the Vicious Cycle of Angiogenesis in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fei, D.; Vanderlaan, M.; Song, A. Biological activity of bevacizumab, a humanized anti-VEGF antibody in vitro. Angiogenesis 2004, 7, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Hurwitz, H.I.; Sandler, A.B.; Miles, D.; Coleman, R.L.; Deurloo, R.; Chinot, O.L. Bevacizumab (Avastin®) in cancer treatment: A review of 15 years of clinical experience and future outlook. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 86, 102017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaykema, S.B.; Brouwers, A.H.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; Pleijhuis, R.G.; Timmer-Bosscha, H.; Pot, L.; van Dam, G.M.; van der Meulen, S.B.; de Jong, J.R.; Bart, J.; et al. 89Zr-bevacizumab PET imaging in primary breast cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahce, I.; Huisman, M.C.; Verwer, E.E.; Ooijevaar, R.; Boutkourt, F.; Vugts, D.J.; van Dongen, G.A.; Boellaard, R.; Smit, E.F. Pilot study of (89)Zr-bevacizumab positron emission tomography in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. EJNMMI Res. 2014, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosting, S.F.; Brouwers, A.H.; van Es, S.C.; Nagengast, W.B.; Oude Munnink, T.H.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; Hollema, H.; de Jong, J.R.; de Jong, I.J.; de Haas, S.; et al. 89Zr-bevacizumab PET visualizes heterogeneous tracer accumulation in tumor lesions of renal cell carcinoma patients and differential effects of antiangiogenic treatment. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Asselt, S.J.; Oosting, S.F.; Brouwers, A.H.; Bongaerts, A.H.; de Jong, J.R.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; Oude Munnink, T.H.; Fiebrich, H.B.; Sluiter, W.J.; Links, T.P.; et al. Everolimus Reduces (89)Zr-Bevacizumab Tumor Uptake in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ImmunoPET Tracer | Status | Identifier Number | Phase | Study Type | Target | Study Title | Conditions | Country | Last Update |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [89Zr]Zr-DFO-nimotuzumab | Recruiting | NCT04235114 | I, II | Interventional | EGFR | Evaluation of [89Zr]Zr-DFO-nimotuzumab for Non-invasive Imaging of EGFR+ Cancers by Positron Emission Tomography (PET) | Lung Cancer Colorectal Cancer | Saskatchewan, Canada | 2022-05 |
| [89Zr]Zr-panitumumab | Recruiting | NCT05747625 | I | Interventional | EGFR | ([89Zr]Zr-Panitumumab) With PET/CT for Diagnosing Metastases in Patients With Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stage IV Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck | Nashville, USA | 2023-07 |
| [89Zr]Zr-panitumumab | Not yet recruiting | NCT05423197 | II | Interventional | EGFR | Study Evaluating Zr-Panitumumab for Assessment of Suspected Metastatic Lesions on 2-[18F]FDG-PET/CT in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma | San Francisco, USA | 2023-09 |
| [89Zr]Zr-Panitumumab | Recruiting | NCT05183048 | Early Phase I | Interventional | EGFR | Comparison of [89Zr]Zr-Panitumumab and [18F]-Fluorodeoxyglucose to Identify Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Birmingham, USA | 2023-10 |
| [64Cu]Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab | Active, not recruiting | NCT01093612 | NA | Interventional | HER2 | Positron Emission Tomography in Women With Advanced HER2-Positive Breast Cancer | Breast Cancer Stage IV Breast Cancer | Duarte, USA | 2023-03 |
| [64Cu]Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab | Active, not recruiting | NCT02226276 | NA | Interventional | HER2 | Copper Cu 64-DOTA-Trastuzumab PET in Predicting Response to Treatment With Ado-Trastuzumab Emtansine in Patients With Metastatic HER2 Positive Breast Cancer | Bone Metastases, HER2-positive Breast Cancer, Liver Metastases, Lung Metastases, Recurrent Breast Cancer, Soft Tissue Metastases, Stage IV Breast Cancer | Duarte, USA | 2023-02 |
| [64Cu]Cu-DOTA-Trastuzumab | Active, not recruiting | NCT02827877 | II | Interventional | HER2 | [64Cu]Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab PET and Markers Predicting Response to Neoadjuvant Trastuzumab + Pertuzum in HER2+ Breast Cancer | HER2-Positive Breast Carcinoma, Stage IIIA Breast Cancer, Stage IIIB Breast Cancer, Stage IIIC Breast Cancer | Duarte, USA | 2023-08 |
| [89Zr]Zr-DFO*-Trastuzumab | Recruiting | NCT05955833 | I | Interventional | HER2 | [89Zr]-DFO*-Trastuzumab PET in Patients With Gastric or Breast Cancer—a Pilot Study (HER Image) | Breast Cancer, Metastatic Breast Cancer, HER2-Positive Breast Cancer, Gastric Cancer, Metastatic Gastric Cancer, HER2-Positive Gastric Cancer | Amsterdam, The Netherlands | 2023-07 |
| [64Cu]Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab | Recruiting | NCT05376878 | IV | Interventional | HER2 | An Investigational Scan ([64Cu]Cu-DOTA-Trastuzumab PET/MRI) in Imaging Patients With HER2+ Breast Cancer With Brain Metastasis | Anatomic Stage IV Breast Cancer, AJCC v8 Metastatic Breast Carcinoma, Metastatic Malignant Neoplasm in the Brain | Duarte, USA | 2023-02 |
| [89Zr]Zr-Trastuzumab | Recruiting | NCT03321045 | Early Phase I | Interventional | HER2 | Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Imaging With Zirconium-89 (89Zr)-Trastuzumab for Prediction of HER2 Targeted Therapy Effectiveness | Breast Cancer | Birmingham, USA | 2023-02 |
| [64Cu]Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab | Active, not recruiting | NCT01939275 | NA | Interventional | HER2 | [64Cu]Cu-DOTA-Trastuzumab PET/CT in Studying Patients With Gastric Cancer | Adenocarcinoma of the Gastroesophageal Junction, Diffuse Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach, Intestinal Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach, Mixed Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach, Stage IA-IV Gastric cancer | Duarte, USA | 2023-05 |
| [89Zr]Zr-trastuzumab | Active, not recruiting | NCT01565200 | II | Interventional | HER2 | HER2 Imaging Study to Identify HER2 Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Patient Unlikely to Benefit From T-DM1 (ZEPHIR) | HER-2-Positive Breast Cancer | Brussels, Belgium | 2023-08 |
| [68Ga]Ga-HER2-affibody | Recruiting | NCT04769050 | NA | Observational | HER2 | Dynamic Observational Study With PET of [68Ga]Ga-HER2-affibody in Anti-HER2 Treatment | Breast Cancer | Shanghai, China | 2022-04 |
| [68Ga]Ga-HER2-affibody | Recruiting | NCT04281641 | NA | Observational | HER2 | Markers to Evaluate the Efficacy of PH-based Regimen as a Neoadjuvant Therapy for Operable HER2 Positive Breast Cancer (PHC-BC) | Shanghai, China | 2020-05 | |
| [18F]F-GE-226 | Recruiting | NCT03827317 | NA | Interventional | HER2 | HERPET-A Novel PET Imaging Study of HER2 in Breast Cancer | Breast Cancer | London, UK | 2023-01 |
| [89Zr]Zr-ss-pertuzumab | Recruiting | NCT04692831 | I | Interventional | HER2 | Testing a New Imaging Agent to Identify Cancer | HER-2-Positive Malignant Carcinoma, of Breast HER-2 Protein Overexpression, HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer | New York, Newport Beach, USA | 2023-11 |
| [68Ga]Ga-ABY-025 | Recruiting | NCT05619016 | II | Interventional | HER2 | [68Ga]Ga-ABY-025 PET for Quantification of HER2-status in Solid Tumors | Esophageal Neoplasms, Gastric Neoplasms, Malignant Breast Cancer, HER2-Positive Gastric Cancer | Stockholm, Sweden | 2022-11 |
| [18F]F-HER2 | Not yet recruiting | NCT05983796 | NA | Interventional | HER2 | [18F]F-HER2 PET in Evaluating the Efficacy of Anti-HER2 Therapy for Urothelial Carcinoma. | Urothelial Carcinoma | Hangzhou, China | 2023-08 |
| [68Ga]Ga-GaNOTA-Anti-HER2 VHH1 | Recruiting | NCT03924466 | II | Interventional | HER2 | Repeatability of [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-Anti-HER2 VHH1 PET/CT in Breast Carcinoma Patients (VUBAR) | Metastatic Breast Carcinoma, Locally Advanced Breast Cancer, Cancer of Pancreas, Solid Tumor With Intermediate or High HER2 Expression, Salivary Gland Cancer, Gastric Cancer, Endometrial Cancer, Uterine Cancer, Non Small Cell Lung Cancer, Biliary Tract Cancer, Cholangiocarcinoma, Colorectal Cancer, Urothelial Carcinoma, Prostate Cancer | Brussels, Belgium | 2023-01 |
| [68Ga]Ga-ABY-025 | Recruiting | NCT03655353 | II/III | Interventional | HER2 | A Study of [68Ga]Ga-ABY-025 PET for Non-invasive Quantification of HER2-expression in Advanced Breast Cancer (Affibody-3) | HER2-positive Breast Cancer | Uppsala, Sweden | 2021-09 |
| [68Ga]Ga-HER2-Affibody, [18F]-FDG | Recruiting | NCT04758416 | II | Observational | HER2 | Study on the Value of Non-invasive Dual-Pet Information in Subtype of Metastatic Breast Cancer | Breast Cancer | Shanghai, China | 2022-04 |
| [68Ga]Ga-HER2 Affibody | Recruiting | NCT05535621 | NA | Observational | HER2 | [68Ga]Ga-HER2 Affibody PET/CT Imaging for HER2-Positive Cancer Patients | HER2-Positive Cancer | Wuhan, China | 2023-02 |
| [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-Anti-HER2 VHH1 | Recruiting | NCT03331601 | II | Interventional | HER2 | Evaluation of [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-Anti-HER2 VHH1 Uptake in Brain Metastasis of Breast Carcinoma Patients | Breast Neoplasm, Breast Carcinoma Receptor, ErbB-2 | Brussels, Belgium | 2023-07 |
| [68Ga]/[18F]-HER2 Affibody | Recruiting | NCT04547309 | NA | Interventional | HER2 | Research for the Molecular Imaging of the HER2 Targeting Tracer | HER2-Positive or Suspicious Positive Tumors | Beijing, China | 2023-11 |
| [68Ga]Ga-HER2 Affibody | Not yet recruiting | NCT05411432 | Early Phase I | Interventional | HER2 | Clinical Study of [68Ga]-Labeled HER2 Affibody Analogues | HER2-Positive Breast Cancer and Gastric Cancer | Xijing, China | 2022-06 |
| [18F]F-ISO-1 | Not yet recruiting | NCT02284919 | Phase I | Interventional | HER2 | [18F]F-ISO-1 Positron Emission Tomography (PET/CT) in Primary Breast Cancer (ISO-1Primary) | Breast Cancer | Philadelphia, USA | 2023-01 |
| [68Ga]/[131I] SGMIB-5F7 | Recruiting | NCT05982626 | NA | Interventional | HER2 | Study of [68Ga]/[131I] SGMIB-5F7 PET Imaging Targeting HER2-positive in the Diagnosis of Metastatic Breast Cancer | HER2-Positive Breast Cancer | Shanghai, China | 2023-11 |
| [18F]F-GEH121224 | Not yet recruiting | NCT05634954 | I | Interventional | HER2 | Study to Evaluate Safety and Dosimetry of [18F]F-GEH121224 in Patients With Locally Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer | Breast Cancer | Houston, USA | 2023-09 |
| [89Zr]Zr-Bevacizumab | Recruiting | NCT05685836 | NA | Observational | VEGF | [89Zr]Zr-Bevacizumab PET/CT Imaging in NF2 Patients | Neurofibromatosis 2 | Leiden, The Netherlands | 2023-01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Linguanti, F.; Abenavoli, E.M.; Calabretta, R.; Berti, V.; Lopci, E. ImmunoPET Targeting Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: Clinical Applications. Cancers 2023, 15, 5886. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245886
Linguanti F, Abenavoli EM, Calabretta R, Berti V, Lopci E. ImmunoPET Targeting Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: Clinical Applications. Cancers. 2023; 15(24):5886. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245886
Chicago/Turabian StyleLinguanti, Flavia, Elisabetta Maria Abenavoli, Raffaella Calabretta, Valentina Berti, and Egesta Lopci. 2023. "ImmunoPET Targeting Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: Clinical Applications" Cancers 15, no. 24: 5886. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245886
APA StyleLinguanti, F., Abenavoli, E. M., Calabretta, R., Berti, V., & Lopci, E. (2023). ImmunoPET Targeting Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: Clinical Applications. Cancers, 15(24), 5886. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245886







