In Vitro Organoid-Based Assays Reveal SMAD4 Tumor-Suppressive Mechanisms for Serrated Colorectal Cancer Invasion
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Organoid Culture
2.3. Organoid Transduction with pINDUCER-SMAD4
2.4. Organoid Imaging
2.5. Organoid Transplantation
2.6. Tissue Histology and Imaging
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Organoid Immunofluorescence and Imaging
2.9. RNA-Seq and Analysis
2.10. ChIP-Seq
2.11. Transwell Invasion Assay
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Smad4KO BRAFV600E/+ Tumor Organoids Exhibit Invasive-like Behavior
3.2. SMAD4 Suppresses Invasive Behavior in Tumor Organoids
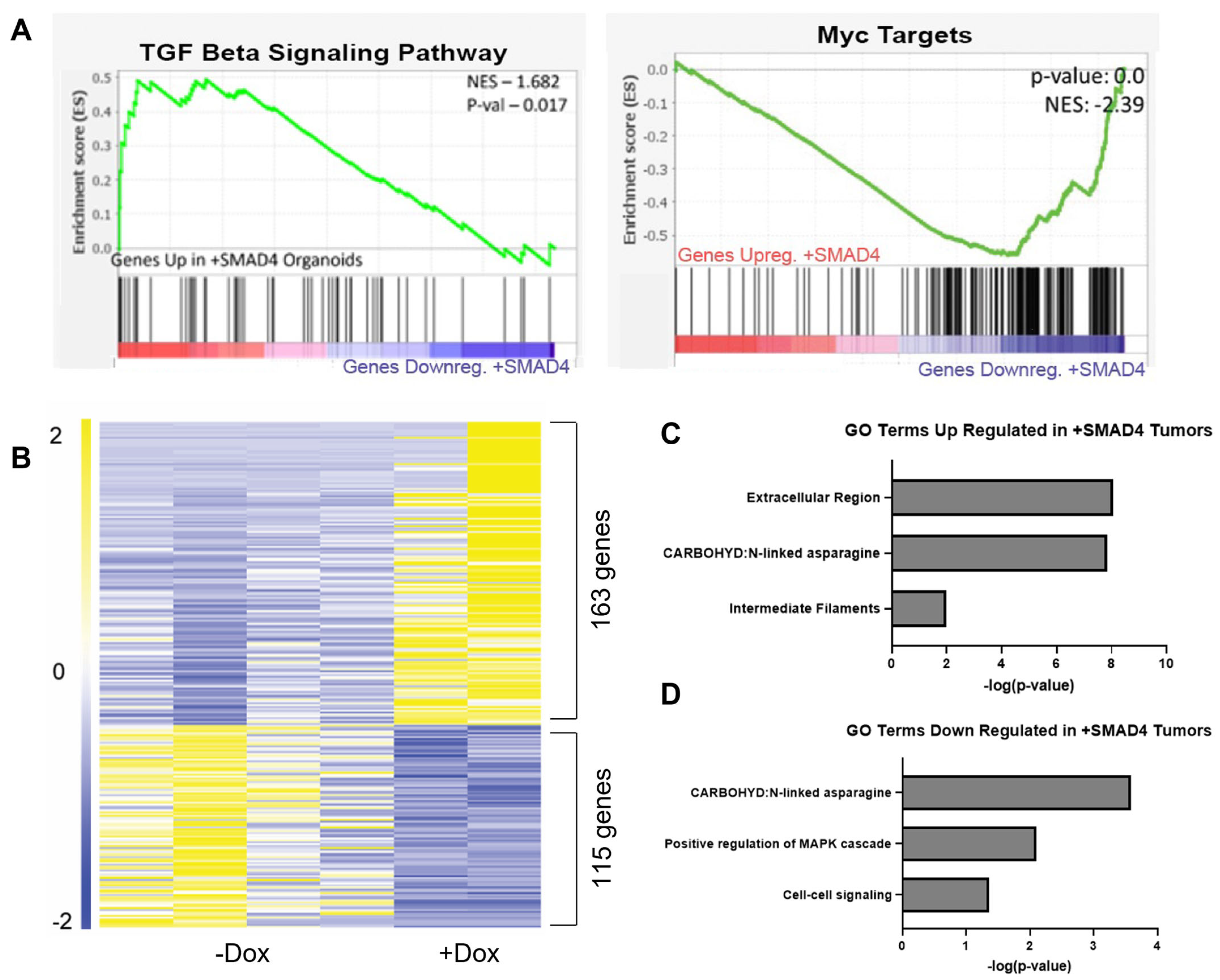
3.3. SMAD4 Regulates Extracellular Environment Genes
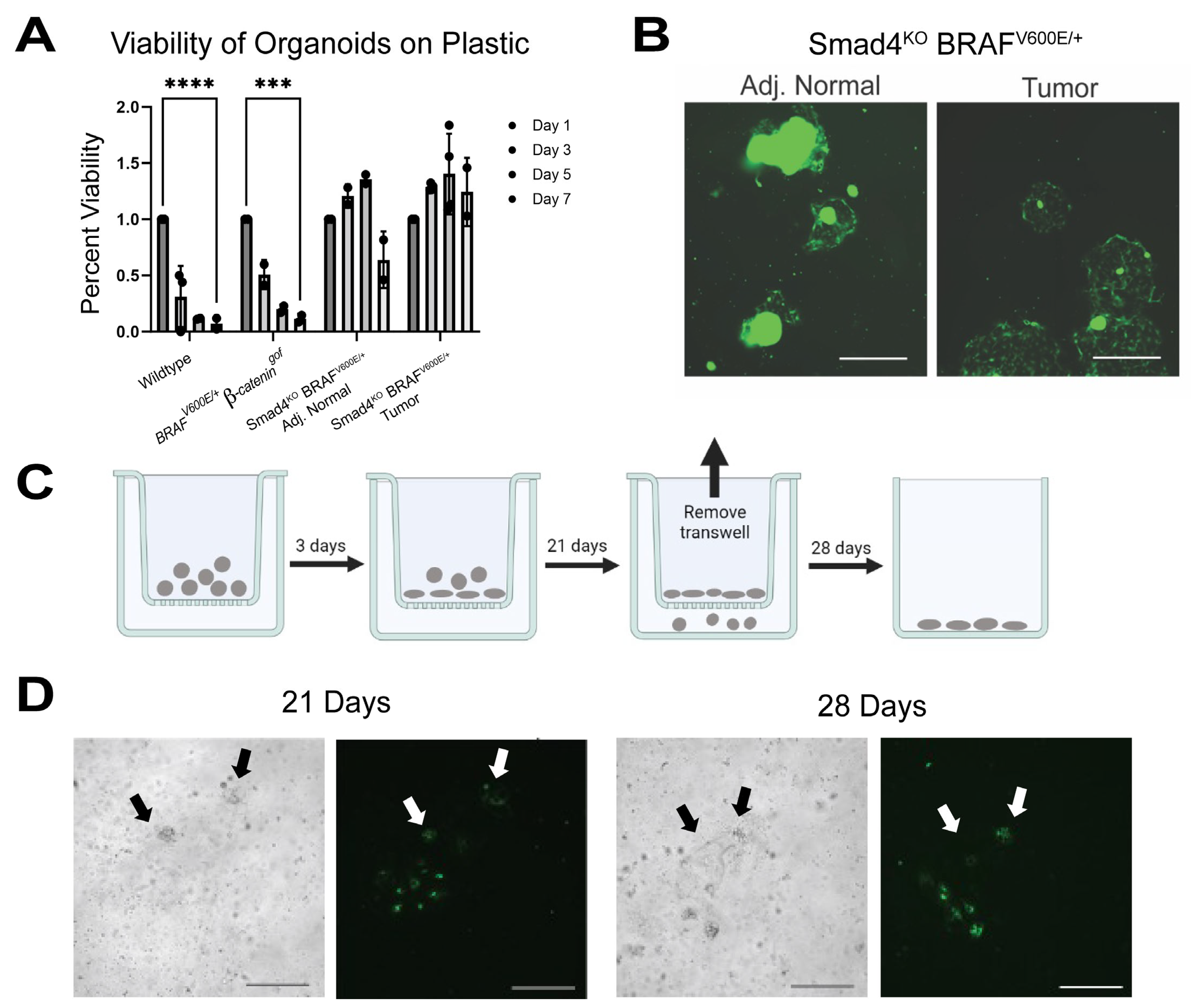
3.4. SMAD4 Loss Enables Organoid Survival Independent of Extracellular Matrix
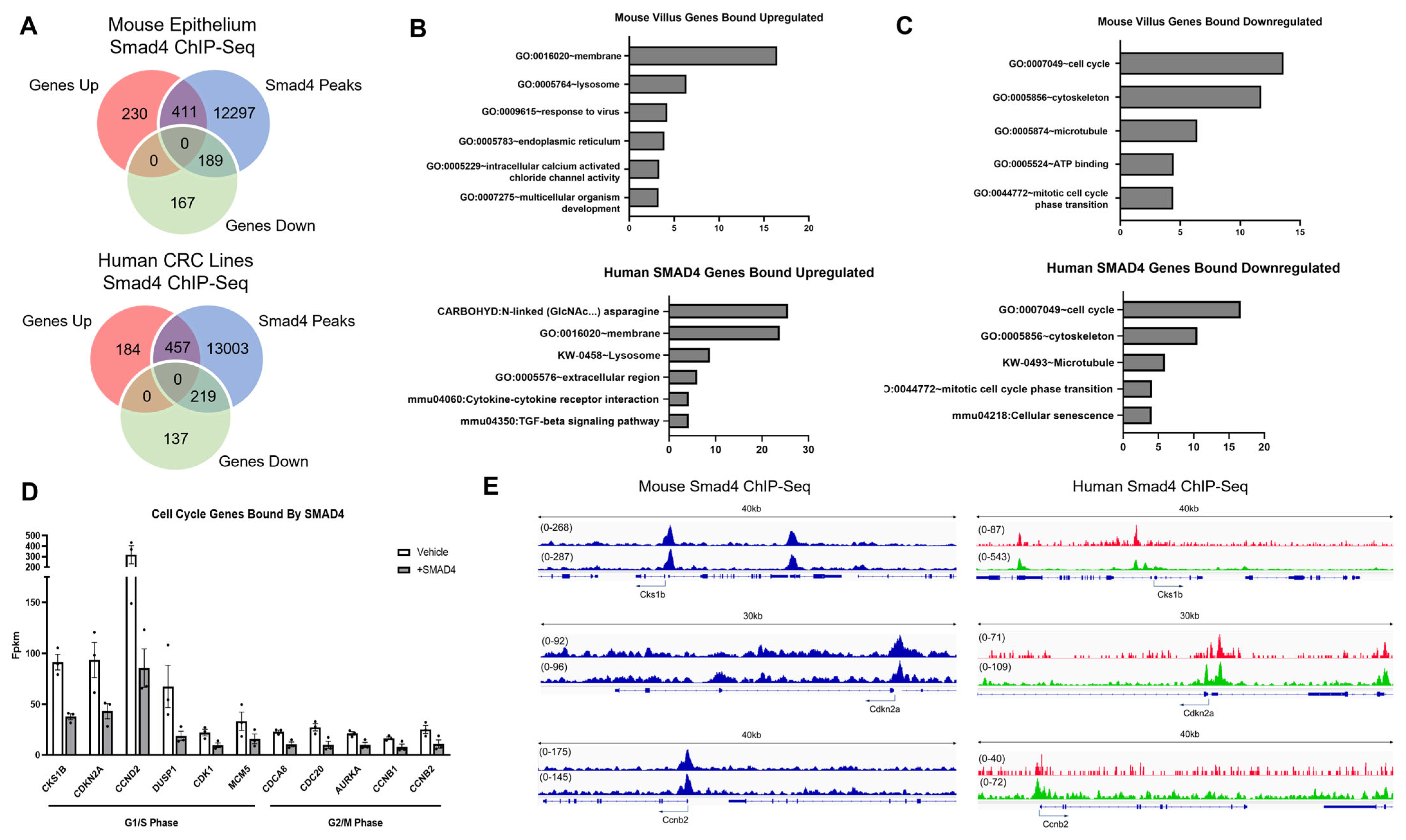
3.5. SMAD4 Differentially Regulates Genes Dependent on Environment
4. Discussion
4.1. Loss of SMAD4 Promotes BRAF-Driven Serrated Cancer Invasion
4.2. SMAD4 Directly Suppresses Organoid Invasive Capabilities In Vitro
4.3. SMAD4-Dependent Suppression of Invasion Differs Based on Extracellular Environment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, X.N.; Shang, F.M.; Jiang, H.Y.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Deng, S.H.; Fan, J.; Dong, X.C.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Clinicopathological Features and Prognostic Value of KRAS/NRAS/BRAF Mutations in Colorectal Cancer Patients of Central China. Curr. Med. Sci. 2021, 41, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djanani, A.; Eller, S.; Ofner, D.; Troppmair, J.; Maglione, M. The Role of BRAF in Metastatic Colorectal Carcinoma-Past, Present, and Future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margonis, G.A.; Buettner, S.; Andreatos, N.; Kim, Y.; Wagner, D.; Sasaki, K.; Beer, A.; Schwarz, C.; Loes, I.M.; Smolle, M.; et al. Association of BRAF Mutations with Survival and Recurrence in Surgically Treated Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Liver Cancer. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, e180996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedrin, D.; Gala, M.K. Genetics of the serrated pathway to colorectal cancer. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leggett, B.; Whitehall, V. Role of the serrated pathway in colorectal cancer pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2088–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patai, A.V.; Molnar, B.; Tulassay, Z.; Sipos, F. Serrated pathway: Alternative route to colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palma, F.D.E.; D’Argenio, V.; Pol, J.; Kroemer, G.; Maiuri, M.C.; Salvatore, F. The Molecular Hallmarks of the Serrated Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carragher, L.A.; Snell, K.R.; Giblett, S.M.; Aldridge, V.S.; Patel, B.; Cook, S.J.; Winton, D.J.; Marais, R.; Pritchard, C.A. V600EBraf induces gastrointestinal crypt senescence and promotes tumour progression through enhanced CpG methylation of p16INK4a. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, R.; Cadinanos, J.; Rad, L.; Varela, I.; Strong, A.; Kriegl, L.; Constantino-Casas, F.; Eser, S.; Hieber, M.; Seidler, B.; et al. A genetic progression model of Braf(V600E)-induced intestinal tumorigenesis reveals targets for therapeutic intervention. Cancer cell 2013, 24, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Pellon-Cardenas, O.; Sirihorachai, V.R.; Warder, B.N.; Kothari, O.A.; Perekatt, A.O.; Fokas, E.E.; Fullem, R.L.; Zhou, A.; Thackray, J.K.; et al. Degree of Tissue Differentiation Dictates Susceptibility to BRAF-Driven Colorectal Cancer. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3833–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiderus, A.; Barker, N.; Tergaonkar, V. Serrated colorectal cancer: Preclinical models and molecular pathways. Trends Cancer 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, R.K.; Bettington, M.; Srivastava, A.; Rosty, C. An update on the morphology and molecular pathology of serrated colorectal polyps and associated carcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1390–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murcia, O.; Juarez, M.; Hernandez-Illan, E.; Egoavil, C.; Giner-Calabuig, M.; Rodriguez-Soler, M.; Jover, R. Serrated colorectal cancer: Molecular classification, prognosis, and response to chemotherapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3516–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, M.; Kouvaras, E.; Papamichali, R.; Samara, M.; Chiotoglou, I.; Koukoulis, G. Smad4 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition proteins in colorectal carcinoma: An immunohistochemical study. J. Mol. Histol. 2018, 49, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, H.; Zheng, L.; Jiao, W.; Mei, H.; Li, D.; Song, H.; Fang, E.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Huang, K.; et al. Smad4 suppresses the tumorigenesis and aggressiveness of neuroblastoma through repressing the expression of heparanase. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lannagan, T.R.M.; Lee, Y.K.; Wang, T.; Roper, J.; Bettington, M.L.; Fennell, L.; Vrbanac, L.; Jonavicius, L.; Somashekar, R.; Gieniec, K.; et al. Genetic editing of colonic organoids provides a molecularly distinct and orthotopic preclinical model of serrated carcinogenesis. Gut 2019, 68, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumagalli, A.; Drost, J.; Suijkerbuijk, S.J.; van Boxtel, R.; de Ligt, J.; Offerhaus, G.J.; Begthel, H.; Beerling, E.; Tan, E.H.; Sansom, O.J.; et al. Genetic dissection of colorectal cancer progression by orthotopic transplantation of engineered cancer organoids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2357–E2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, A.M.; Fennell, L.J.; Liu, C.; Borowsky, J.; McKeone, D.M.; Bond, C.E.; Kazakoff, S.; Patch, A.M.; Koufariotis, L.T.; Pearson, J.; et al. Alterations in signaling pathways that accompany spontaneous transition to malignancy in a mouse model of BRAF mutant microsatellite stable colorectal cancer. Neoplasia 2020, 22, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Kothari, O.A.; Haro, K.S.; Panda, A.; Bandari, M.M.; Carrick, J.N.; Hur, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Chan, C.S.; Xing, J.; et al. SMAD4 is critical in suppression of BRAF-V600E serrated tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2021, 40, 6034–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, J.D.G.; Vlahov, N.; Tsantoulis, P.; Ridgway, R.A.; Flanagan, D.J.; Gilroy, K.; Sphyris, N.; Vazquez, E.G.; Vincent, D.F.; Faller, W.J.; et al. Oncogenic BRAF, unrestrained by TGFbeta-receptor signalling, drives right-sided colonic tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemer, P.; Sreekumar, A.; Reinke, S.; Rad, R.; Schafer, R.; Sers, C.; Blaker, H.; Herrmann, B.G.; Morkel, M. Transgenic expression of oncogenic BRAF induces loss of stem cells in the mouse intestine, which is antagonized by beta-catenin activity. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3164–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reischmann, N.; Andrieux, G.; Griffin, R.; Reinheckel, T.; Boerries, M.; Brummer, T. BRAF(V600E) drives dedifferentiation in small intestinal and colonic organoids and cooperates with mutant p53 and Apc loss in transformation. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6053–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, N.; Feng, Y.; Stolfi, C.; Kurosu, Y.; Green, M.; Lin, J.; Green, M.E.; Sentani, K.; Yasui, W.; McMahon, M.; et al. BRAF(V600E) cooperates with CDX2 inactivation to promote serrated colorectal tumorigenesis. Elife 2017, 6, e20331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Vries, R.G.; Snippert, H.J.; van de Wetering, M.; Barker, N.; Stange, D.E.; van Es, J.H.; Abo, A.; Kujala, P.; Peters, P.J.; et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 2009, 459, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Shah, Y.M. In vitro organoid culture of primary mouse colon tumors. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 75, e50210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lidth de Jeude, J.F.; Vermeulen, J.L.; Montenegro-Miranda, P.S.; Van den Brink, G.R.; Heijmans, J. A protocol for lentiviral transduction and downstream analysis of intestinal organoids. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 98, e52531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, K.P.; Loizou, E.; Livshits, G.; Schatoff, E.M.; Baslan, T.; Manchado, E.; Simon, J.; Romesser, P.B.; Leach, B.; Han, T.; et al. Transplantation of engineered organoids enables rapid generation of metastatic mouse models of colorectal cancer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Toke, N.H.; Luo, S.; Vasoya, R.P.; Fullem, R.L.; Parthasarathy, A.; Perekatt, A.O.; Verzi, M.P. A reinforcing HNF4-SMAD4 feed-forward module stabilizes enterocyte identity. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Meyer, C.A.; Eeckhoute, J.; Johnson, D.S.; Bernstein, B.E.; Nusbaum, C.; Myers, R.M.; Brown, M.; Li, W.; et al. Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, C.Y.; Bristor, D.; Hiller, M.; Clarke, S.L.; Schaar, B.T.; Lowe, C.B.; Wenger, A.M.; Bejerano, G. GREAT improves functional interpretation of cis-regulatory regions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopmans, F.; van Nierop, P.; Andres-Alonso, M.; Byrnes, A.; Cijsouw, T.; Coba, M.P.; Cornelisse, L.N.; Farrell, R.J.; Goldschmidt, H.L.; Howrigan, D.P.; et al. SynGO: An Evidence-Based, Expert-Curated Knowledge Base for the Synapse. Neuron 2019, 103, 217–234.e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hira, V.V.; Breznik, B.; Van Noorden, C.J.; Lah, T.; Molenaar, R.J. 2D and 3D in vitro assays to quantify the invasive behavior of glioblastoma stem cells in response to SDF-1alpha. Biotechniques 2020, 69, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perekatt, A.O.; Shah, P.P.; Cheung, S.; Jariwala, N.; Wu, A.; Gandhi, V.; Kumar, N.; Feng, Q.; Patel, N.; Chen, L.; et al. SMAD4 Suppresses WNT-Driven Dedifferentiation and Oncogenesis in the Differentiated Gut Epithelium. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4878–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madisen, L.; Zwingman, T.A.; Sunkin, S.M.; Oh, S.W.; Zariwala, H.A.; Gu, H.; Ng, L.L.; Palmiter, R.D.; Hawrylycz, M.J.; Jones, A.R.; et al. A robust and high-throughput Cre reporting and characterization system for the whole mouse brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, S.P.; Martin, K.E.; Reinhart-King, C.A. Three-dimensional collagen matrix induces a mechanosensitive invasive epithelial phenotype. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandhoke, A.S.; Chanda, A.; Karve, K.; Deng, L.; Bonni, S. The PIAS3-Smurf2 sumoylation pathway suppresses breast cancer organoid invasiveness. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 21001–21014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas-Vera, Y.M.; Valdes, J.; Perez-Navarro, Y.; Mandujano-Lazaro, G.; Marchat, L.A.; Ramos-Payan, R.; Nunez-Olvera, S.I.; Perez-Plascencia, C.; Lopez-Camarillo, C. Three-Dimensional 3D Culture Models in Gynecological and Breast Cancer Research. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 826113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas, N. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofving, T.; Elias, E.; Rehammar, A.; Inge, L.; Altiparmak, G.; Persson, M.; Kristiansson, E.; Johansson, M.E.; Nilsson, O.; Arvidsson, Y. SMAD4 haploinsufficiency in small intestinal neuroendocrine tumors. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, T.; Cloyd, J.M.; Vicente, D.; Omichi, K.; Chun, Y.S.; Kopetz, S.E.; Maru, D.; Conrad, C.; Tzeng, C.D.; Wei, S.H.; et al. SMAD4 gene mutation predicts poor prognosis in patients undergoing resection for colorectal liver metastases. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 44, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Tong, L.; Li, L.; Xu, J.; Xie, S.; Ji, L.; Fu, J.; Liu, Q.; Shen, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Loss of Smad4 promotes aggressive lung cancer metastasis by de-repression of PAK3 via miRNA regulation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, P.T., Jr.; Creighton, C.J.; Matzuk, M.M. Insights into SMAD4 Loss in Pancreatic Cancer from Inducible Restoration of TGF-Beta Signaling. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 1440–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, T.J.; Smith, J.J.; Chen, X.; Washington, M.K.; Roland, J.T.; Means, A.L.; Eschrich, S.A.; Yeatman, T.J.; Deane, N.G.; Beauchamp, R.D. Smad4-mediated signaling inhibits intestinal neoplasia by inhibiting expression of beta-catenin. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 562–571.e562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Xie, W.; et al. BMP restricts stemness of intestinal Lgr5+ stem cells by directly suppressing their signature genes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Du, H.; Fu, X.; Li, K.; Li, A.; Zhang, Y. Smad4 restoration leads to a suppression of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling activity and migration capacity in human colon carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 380, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorneveld, P.W.; Kodach, L.L.; Jacobs, R.J.; van Noesel, C.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Korkmaz, K.S.; Molendijk, I.; Dekker, E.; Morreau, H.; van Pelt, G.W.; et al. The BMP pathway either enhances or inhibits the Wnt pathway depending on the SMAD4 and p53 status in CRC. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.; Dong, T.T.; Wang, L.L.; Zhou, H.M.; Zhao, H.C.; Dong, F.; Zheng, M.H. Colorectal cancer migration and invasion initiated by microRNA-106a. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhou, R.; Yang, T.; Liu, S.; Cui, Z.; Qiao, Q.; Zhang, J. Hypoxia promotes colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion in a SIRT1-dependent manner. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justus, C.R.; Leffler, N.; Ruiz-Echevarria, M.; Yang, L.V. In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. J. Vis. Exp. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, N.; Walzl, A.; Unger, C.; Rosner, M.; Krupitza, G.; Hengstschlager, M.; Dolznig, H. In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. Mutat. Res. 2013, 752, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandra, M.; Atencio, I.; Rahman, A.; Vaillancourt, M.; Zou, A.; Avanzini, J.; Wills, K.; Bookstein, R.; Shabram, P. Restoration of transforming growth factor Beta signaling by functional expression of smad4 induces anoikis. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6045–6051. [Google Scholar]
- Alazzouzi, H.; Alhopuro, P.; Salovaara, R.; Sammalkorpi, H.; Jarvinen, H.; Mecklin, J.P.; Hemminki, A.; Schwartz, S., Jr.; Aaltonen, L.A.; Arango, D. SMAD4 as a prognostic marker in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2606–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaki, M.; Iijima, T.; Konishi, M.; Sakai, K.; Ishii, A.; Yasuno, M.; Hishima, T.; Koike, M.; Shitara, N.; Iwama, T.; et al. Higher frequency of Smad4 gene mutation in human colorectal cancer with distant metastasis. Oncogene 1999, 18, 3098–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgis, P.; Cheng, K.; Ozturk, S.; Gong, Y.; Lambert, A.W.; Abdolmaleky, H.M.; Zhou, J.R.; Thiagalingam, S. Smad4 inactivation promotes malignancy and drug resistance of colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Halder, S.K.; Kashikar, N.D.; Cho, Y.J.; Datta, A.; Gorden, D.L.; Datta, P.K. Antimetastatic role of Smad4 signaling in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 969–980.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotovac, J.R.; Fujihara, K.M.; Phillips, W.A.; Clemons, N.J. TGF-beta signaling and its targeted therapy in gastrointestinal cancers. Discov. Med. 2018, 26, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, E.; Nakayama, M.; Oshima, H.; Kouyama, Y.; Niida, A.; Fujii, S.; Ochiai, A.; Nakayama, K.I.; Mimori, K.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Combined Mutation of Apc, Kras, and Tgfbr2 Effectively Drives Metastasis of Intestinal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parigoris, E.; Lee, S.; Mertz, D.; Turner, M.; Liu, A.Y.; Sentosa, J.; Djomehri, S.; Chang, H.C.; Luker, K.; Luker, G.; et al. Cancer Cell Invasion of Mammary Organoids with Basal-In Phenotype. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2000810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Navarro-Serer, B.; Jeong, Y.J.; Chianchiano, P.; Xia, L.; Luchini, C.; Veronese, N.; Dowiak, C.; Ng, T.; Trujillo, M.A.; et al. Pattern of Invasion in Human Pancreatic Cancer Organoids Is Associated with Loss of SMAD4 and Clinical Outcome. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 2804–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dai, W.; Xia, X.; Wang, R.; Zhao, J.; Han, L.; Mo, S.; Xiang, W.; Du, L.; Zhu, G.; et al. Modeling tumor development and metastasis using paired organoids derived from patients with colorectal cancer liver metastases. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westcott, J.M.; Prechtl, A.M.; Maine, E.A.; Dang, T.T.; Esparza, M.A.; Sun, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Y.; Pearson, G.W. An epigenetically distinct breast cancer cell subpopulation promotes collective invasion. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1927–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, H.S.; Oh, J.H.; Choi, E.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Nam, E.J. Preclinical investigation of patient-derived cervical cancer organoids for precision medicine. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2023, 34, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jiao, D.; Liu, A.; Wu, K. Tumor organoids: Applications in cancer modeling and potentials in precision medicine. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Cong, L.; Cong, X. Patient-Derived Organoids in Precision Medicine: Drug Screening, Organoid-on-a-Chip and Living Organoid Biobank. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 762184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.G. BMP signaling in homeostasis, transformation and inflammatory response of intestinal epithelium. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, R.; van Driel, M.S.; Vermeulen, L.; van Neerven, S.M. Intestinal stem cell dynamics in homeostasis and cancer. Trends Cancer 2022, 8, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Goswami, S.; Hu, Y.; Tang, F.; Zafra, M.P.; Murphy, C.; Cao, Z.; Poirier, J.T.; Khurana, E.; Elemento, O.; et al. Lineage Reversion Drives WNT Independence in Intestinal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1590–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huels, D.J.; Sansom, O.J. Stem vs non-stem cell origin of colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, H.M.; Kaestner, K.H. Mammalian Intestinal Development and Differentiation-The State of the Art. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 16, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, D.; Iglesias, M.; Vary, C.P.; Quintanilla, M. Functional blockade of Smad4 leads to a decrease in beta-catenin levels and signaling activity in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jabaji, Z.; Sears, C.M.; Brinkley, G.J.; Lei, N.Y.; Joshi, V.S.; Wang, J.; Lewis, M.; Stelzner, M.; Martin, M.G.; Dunn, J.C. Use of collagen gel as an alternative extracellular matrix for the in vitro and in vivo growth of murine small intestinal epithelium. Tissue Eng. Part. C Methods 2013, 19, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Ko, J.; Hahn, S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Park, E.; Choi, S.Y.; Jeong, S.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Development of Collagen-Based 3D Matrix for Gastrointestinal Tract-Derived Organoid Culture. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 8472712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neophytou, C.M.; Panagi, M.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Papageorgis, P. The Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer Metastasis: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cancers 2021, 13, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezakhani, S.; Gjorevski, N.; Lutolf, M.P. Extracellular matrix requirements for gastrointestinal organoid cultures. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 121020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bockstal, M.; Lambein, K.; Van Gele, M.; De Vlieghere, E.; Limame, R.; Braems, G.; Van den Broecke, R.; Cocquyt, V.; Denys, H.; Bracke, M.; et al. Differential regulation of extracellular matrix protein expression in carcinoma-associated fibroblasts by TGF-beta1 regulates cancer cell spreading but not adhesion. Oncoscience 2014, 1, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.; Mojares, E.; Del Rio Hernandez, A. Role of Extracellular Matrix in Development and Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, N.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Kujala, P.; Peters, P.J.; Clevers, H. Intestinal epithelial organoids fuse to form self-organizing tubes in floating collagen gels. Development 2017, 144, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, E.H. The colon cancer stem cell microenvironment holds keys to future cancer therapy. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2014, 18, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racu, M.L.; Lebrun, L.; Schiavo, A.A.; Van Campenhout, C.; De Clercq, S.; Absil, L.; Minguijon Perez, E.; Maris, C.; Decaestecker, C.; Salmon, I.; et al. The Role of SMAD4 Inactivation in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: The Missing Link? Cancers 2022, 14, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, J.J.; Neikes, H.K.; Rezaeifard, S.; Ma, X.; Voest, E.E.; Tauriello, D.V.F.; Vermeulen, M. Multiomics of Colorectal Cancer Organoids Reveals Putative Mediators of Cancer Progression Resulting from SMAD4 Inactivation. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumibao, J.C.; Okhovat, S.R.; Peck, K.L.; Lin, X.; Lande, K.; Yomtoubian, S.; Ng, I.; Tiriac, H.; Lowy, A.M.; Zou, J.; et al. The impact of extracellular matrix on the precision medicine utility of pancreatic cancer patient-derived organoids. JCI Insight 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnol, G.; Sensi, F.; De Tommasi, O.; Marchetti, M.; Bonaldo, G.; Xhindoli, L.; Noventa, M.; Agostini, M.; Tozzi, R.; Saccardi, C. Patient Derived Organoids (PDOs), Extracellular Matrix (ECM), Tumor Microenvironment (TME) and Drug Screening: State of the Art and Clinical Implications of Ovarian Cancer Organoids in the Era of Precision Medicine. Cancers 2023, 15, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, K.; Bandari, M.; Carrick, J.N.; Zenkevich, A.; Kothari, O.A.; Shamshad, E.; Stefanik, K.; Haro, K.S.; Perekatt, A.O.; Verzi, M.P. In Vitro Organoid-Based Assays Reveal SMAD4 Tumor-Suppressive Mechanisms for Serrated Colorectal Cancer Invasion. Cancers 2023, 15, 5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245820
Tong K, Bandari M, Carrick JN, Zenkevich A, Kothari OA, Shamshad E, Stefanik K, Haro KS, Perekatt AO, Verzi MP. In Vitro Organoid-Based Assays Reveal SMAD4 Tumor-Suppressive Mechanisms for Serrated Colorectal Cancer Invasion. Cancers. 2023; 15(24):5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245820
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Kevin, Manisha Bandari, Jillian N. Carrick, Anastasia Zenkevich, Om A. Kothari, Eman Shamshad, Katarina Stefanik, Katherine S. Haro, Ansu O. Perekatt, and Michael P. Verzi. 2023. "In Vitro Organoid-Based Assays Reveal SMAD4 Tumor-Suppressive Mechanisms for Serrated Colorectal Cancer Invasion" Cancers 15, no. 24: 5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245820
APA StyleTong, K., Bandari, M., Carrick, J. N., Zenkevich, A., Kothari, O. A., Shamshad, E., Stefanik, K., Haro, K. S., Perekatt, A. O., & Verzi, M. P. (2023). In Vitro Organoid-Based Assays Reveal SMAD4 Tumor-Suppressive Mechanisms for Serrated Colorectal Cancer Invasion. Cancers, 15(24), 5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245820






