Interleukin-6 Induces Stem Cell Propagation through Liaison with the Sortilin–Progranulin Axis in Breast Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.2. Drug Treatments
2.3. Proximity Extension Assay (PEA)
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Mammosphere Formation Assay
2.6. Alamar Blue Viability Assay
2.7. Competative Fluorescent Polarization Assay (FPA)
2.8. RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.9. Patient-Derived Scaffolds (PDSs)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
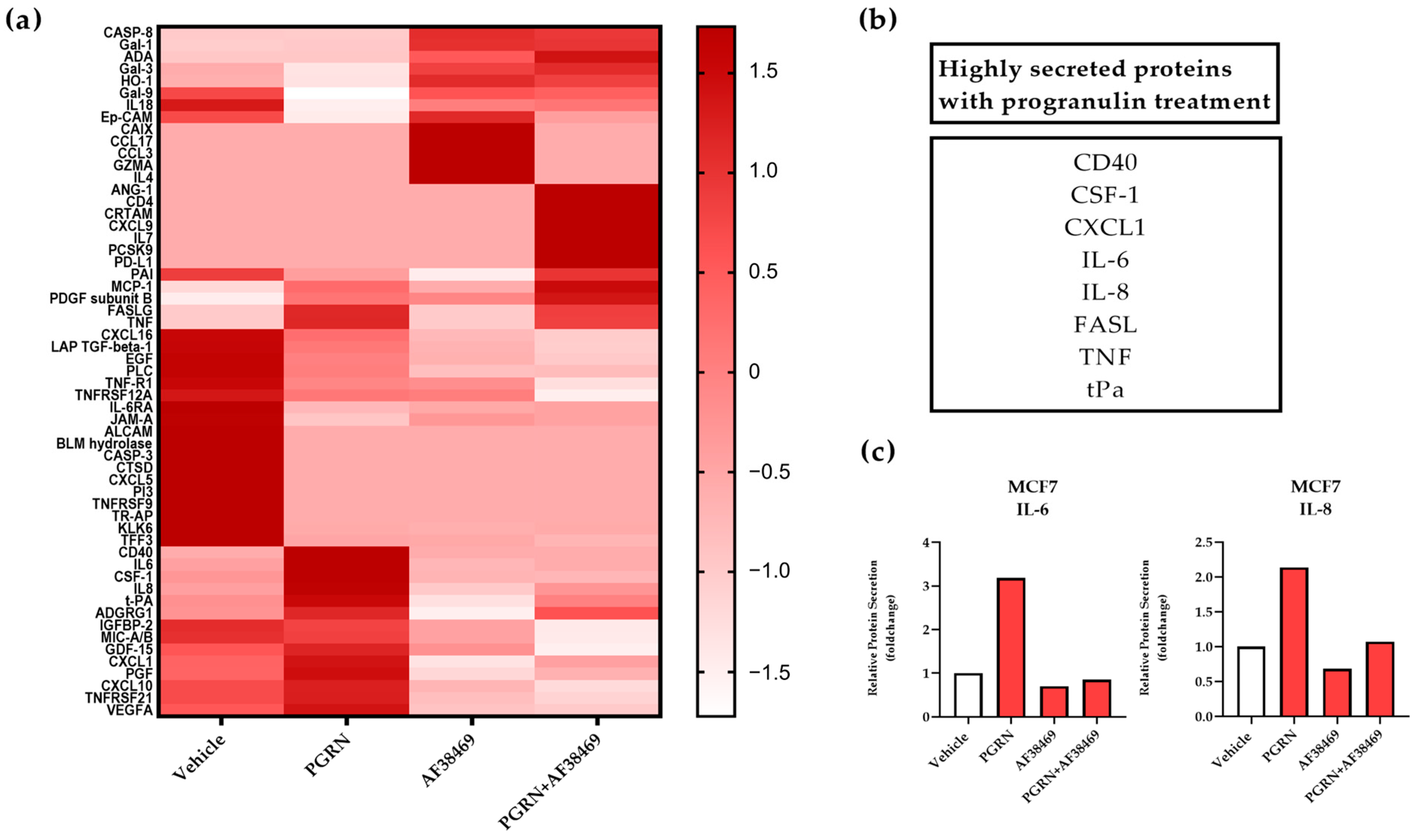
3.1. Progranulin Treatment Promotes Secretion of IL-6 and IL-8 in Breast Cancer
3.2. A Crosstalk between Progranulin and IL-6/8 Expression
3.3. IL-6-Mediated Sphere Formation Is Dependent on Sortilin
3.4. Increased Gene Expression of Progranulin, IL-6 and IL-8 in Breast Cancer Cells Adapting to an In Vivo-like 3D Growth System
3.5. Correlation between IL-6, IL-8 and Progranulin Secretion in Breast Cancer Cells Grown on Patient-Derived Scaffolds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Conley, S.J.; Gheordunescu, E.; Kakarala, P.; Newman, B.; Korkaya, H.; Heath, A.N.; Clouthier, S.G.; Wicha, M.S. Antiangiogenic agents increase breast cancer stem cells via the generation of tumor hypoxia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2784–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meacham, C.E.; Morrison, S.J. Tumour heterogeneity and cancer cell plasticity. Nature 2013, 501, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. IL-6 and related cytokines as the critical lynchpins between inflammation and cancer. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromberg, J.; Wang, T.C. Inflammation and cancer: IL-6 and STAT3 complete the link. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippitz, B.E. Cytokine patterns in patients with cancer: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e218–e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elinav, E.; Nowarski, R.; Thaiss, C.A.; Hu, B.; Jin, C.; Flavell, R.A. Inflammation-induced cancer: Crosstalk between tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soysal, S.D.; Tzankov, A.; Muenst, S.E. Role of the Tumor Microenvironment in Breast Cancer. Pathobiology 2015, 82, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkaya, H.; Liu, S.; Wicha, M.S. Breast cancer stem cells, cytokine networks, and the tumor microenvironment. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3804–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Muynck, L.; Van Damme, P. Cellular effects of progranulin in health and disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 45, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechavaleta-Velasco, F.; Perez-Juarez, C.E.; Gerton, G.L.; Diaz-Cueto, L. Progranulin and its biological effects in cancer. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abella, V.; Pino, J.; Scotece, M.; Conde, J.; Lago, F.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Mera, A.; Gómez, R.; Mobasheri, A.; Gualillo, O. Progranulin as a biomarker and potential therapeutic agent. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhost, S.; Hughes, É.; Harrison, H.; Rafnsdottir, S.; Jacobsson, H.; Gregersson, P.; Magnusson, Y.; Fitzpatrick, P.; Andersson, D.; Berger, K.; et al. Sortilin inhibition limits secretion-induced progranulin-dependent breast cancer progression and cancer stem cell expansion. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Padukkavidana, T.; Vægter, C.B.; Brady, O.A.; Zheng, Y.; Mackenzie, I.R.; Feldman, H.H.; Nykjaer, A.; Strittmatter, S.M. Sortilin-mediated endocytosis determines levels of the frontotemporal dementia protein, progranulin. Neuron 2010, 68, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Lu, Y.; Tian, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, F.J.; Liu, G.Y.; Muzaffar Syed, N.; Lai, Y.; Alan Lin, E.; Kong, L.; et al. The growth factor progranulin binds to TNF receptors and is therapeutic against inflammatory arthritis in mice. Science 2011, 332, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neill, T.; Goyal1, A.; Buraschi, S.; Sharpe, C.; Natkanski, E.; Schaefer, L.; Morrione, A.; Iozzo, R.V. EphA2 is a functional receptor for the growth factor progranulin. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 215, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermey, G. The Vps10p-domain receptor family. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 2677–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Almeida, S.; Prudencio, M.; Caulfield, T.R.; Zhang, Y.J.; Tay, W.M.; Bauer, P.O.; Chew, J.; Sasaguri, H.; Jansen-west, K.R.; et al. Targeted manipulation of the sortilin-progranulin axis rescues progranulin haploinsufficiency. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 1467–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.M.; Naves, T.; Al Akhrass, H.; Vincent, F.; Melloni, B.; Bonnaud, F.; Lalloué, F.; Jauberteau, M.O. A new role under sortilin’s belt in cancer. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2016, 9, e1130192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roselli, S.; Pundavela, J.; Demont, Y.; Faulkner, S.; Keene, S.; Attia, J.; Jiang, C.C.; Zhang, X.D.; Walker, M.M.; Hondermarck, H. Sortilin is associated with breast cancer aggressiveness and contributes to tumor cell adhesion and invasion. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10473–10486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe-Wada, T.; Matsuba, S.; Takeda, K.; Sato, T.; Suyama, M.; Ohkawa, Y.; Takai, T.; Shi, H.; Philpott, C.C.; Nakamura, A. TLR signals posttranscriptionally regulate the cytokine trafficking mediator sortilin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herda, S.; Raczkowski, F.; Mittrücker, H.W.; Willimsky, G.; Gerlach, K.; Kühl, A.A.; Breiderhoff, T.; Willnow, T.E.; Dörken, B.; Höpken, U.E.; et al. The sorting receptor Sortilin exhibits a dual function in exocytic trafficking of interferon-γ and granzyme A in T cells. Immunity 2012, 37, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, F.L.; Harrison, H.; Spence, K.; Ablett, M.P.; Simoes, B.M.; Farnie, G.; Clarke, R.B.; Simões, B.M.; Farnie, G.; Clarke, R.B. A detailed mammosphere assay protocol for the quantification of breast stem cell activity. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2012, 17, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landberg, G.; Fitzpatrick, P.; Isakson, P.; Jonasson, E.; Karlsson, J.; Larsson, E.; Svanström, A.; Rafnsdottir, S.; Persson, E.; Gustafsson, A.; et al. Patient-derived scaffolds uncover breast cancer promoting properties of the microenvironment. Biomaterials 2020, 235, 119705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picelli, S.; Faridani, O.R.; Björklund, Å.K.; Winberg, G.; Sagasser, S.; Sandberg, R. Full-length RNA-seq from single cells using Smart-seq2. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dethlefsen, C.; Højfeldt, G.; Hojman, P. The role of intratumoral and systemic IL-6 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 138, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrøder, T.J.; Christensen, S.; Lindberg, S.; Langgård, M.; David, L.; Maltas, P.J.; Eskildsen, J.; Jacobsen, J.; Tagmose, L.; Simonsen, K.B.; et al. The identification of AF38469: An orally bioavailable inhibitor of the VPS10P family sorting receptor Sortilin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, E.; Gregersson, P.; Gustafsson, A.; Fitzpatrick, P.; Rhost, S.; Ståhlberg, A.; Landberg, G. Patient-derived scaffolds influence secretion profiles in cancer cells mirroring clinical features and breast cancer subtypes. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.P.; Li, J.; Tewari, A.K. Inflammation and prostate cancer: The role of interleukin 6 (IL-6). BJU Int. 2014, 113, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setrerrahmane, S.; Xu, H. Tumor-related interleukins: Old validated targets for new anti-cancer drug development. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.O.; Moody, W.M.; Shields, J.D. Microenvironmental modulation of the developing tumour: An immune-stromal dialogue. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 2600–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knüpfer, H.; Preiß, R. Significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in breast cancer (review). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 102, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinado, H.; Zhang, H.; Matei, I.R.; Costa-Silva, B.; Hoshino, A.; Rodrigues, G.; Psaila, B.; Kaplan, R.N.; Bromberg, J.F.; Kang, Y.; et al. Pre-metastatic niches: Organ-specific homes for metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sceneay, J.; Smyth, M.J.; Möller, A. The pre-metastatic niche: Finding common ground. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013, 32, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paltridge, J.L.; Belle, L.; Khew-Goodall, Y. The secretome in cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovski, T.; De Sousa E Melo, F.; Vermeulen, L.; Medema, J.P. Cancer stem cell niche: The place to be. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Liu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, B.; Li, M.; Song, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; et al. CXCL1 derived from tumor-associated macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via activating NF-κB/SOX4 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavey, C.; Bibeau, F.; Gourgou-Bourgade, S.; Burlinchon, S.; Boissière, F.; Laune, D.; Roques, S.; Lazennec, G. Oestrogen receptor negative breast cancers exhibit high cytokine content. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9, R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, G.; Invernizzi, P.; Bernuzzi, F.; Pae, H.Y.; Quinn, M.; Horvat, D.; Galindo, C.; Huang, L.; McMillin, M.; Cooper, B.; et al. Interleukin-6-driven progranulin expression increases cholangiocarcinoma growth by an Akt-dependent mechanism. Gut 2012, 61, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, W.; Yang, F.; Feng, T.; Zhou, M.; Yu, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhao, W.; Yi, F.; Tang, W.; et al. Interleukin-6-stimulated progranulin expression contributes to the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating mTOR signaling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T.; Mita, A.; Minami, K.; Hosooka, T.; Kitazawa, S.; Takahashi, K.; Tamori, Y.; Yokoi, N.; Watanabe, M.; Matsuo, E.I.; et al. PGRN is a key adipokine mediating high fat diet-induced insulin resistance and obesity through IL-6 in adipose tissue. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Das, A.; Bhatt, A.N. Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 11553–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masjedi, A.; Hashemi, V.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Azizi, G.; Yousefi, M.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. The significant role of interleukin-6 and its signaling pathway in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayatilaka, H.; Tyle, P.; Chen, J.J.; Kwak, M.; Ju, J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.S.H.; Wu, P.H.; Gilkes, D.M.; Fan, R.; et al. Synergistic IL-6 and IL-8 paracrine signalling pathway infers a strategy to inhibit tumour cell migration. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Qin, Y.; Liu, S. Cytokines, breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) and chemoresistance. Clin. Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Montero, P.; Londoño-Vallejo, A.; Vernot, J.P. Senescence-associated IL-6 and IL-8 cytokines induce a self- and cross-reinforced senescence/inflammatory milieu strengthening tumorigenic capabilities in the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Cell Commun. Signal. 2017, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Miao, Y.; Xu, P.; Qiu, X. IL-8 regulates the stemness properties of cancer stem cells in the small-cell lung cancer cell line H446. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 5723–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrò, C.; Healy, M.E.; Engler, S.; Bodenmiller, B.; Li, Z.; Schraml, P.; Weber, A.; Frew, I.J.; Rechsteiner, M.; Moch, H. IL-8 and CXCR1 expression is associated with cancer stem cell-like properties of clear cell renal cancer. J. Pathol. 2019, 248, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabdollahi, M.; Javanmard, S.H.; Sadeghi-Aliabadi, H. In Vitro Assessment of Cytokine Expression Profile of MCF-7 Cells in Response to hWJ-MSCs Secretome. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, P.; Storci, G.; Tavolari, S.; Guarnieri, T.; Giovannini, C.; Taffurelli, M.; Ceccarelli, C.; Santini, D.; Paterini, P.; Marcu, K.B.; et al. IL-6 triggers malignant features in mammospheres from human ductal breast carcinoma and normal mammary gland. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3988–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.K.; Simões, B.M.; Howell, S.J.; Farnie, G.; Clarke, R.B. Recent advances reveal IL-8 signaling as a potential key to targeting breast cancer stem cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.P.; Gaspar, V.M.; Mano, J.F. Decellularized Extracellular Matrix for Bioengineering Physiomimetic 3D in Vitro Tumor Models. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1397–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Calar, K.; De La Puente, P. Mimicking tumor hypoxia and tumor-immune interactions employing three-dimensional in vitro models. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-García, L.A.; Nava-Castro, K.E.; Ochoa-Mercado, T.D.L.; Palacios-Arreola, M.I.; Ruiz-Manzano, R.A.; Segovia-Mendoza, M.; Solleiro-Villavicencio, H.; Cázarez-Martínez, C.; Morales-Montor, J. Breast Cancer Metastasis: Are Cytokines Important Players During Its Development and Progression? J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, B.; Wang, T.; Sun, B.; Xu, J.; Xu, D.; Liao, Y.; Song, H.; Guo, W.; Li, K.; Hu, M.; et al. IL6/STAT3 Signaling Orchestrates Premetastatic Niche Formation and Immunosuppressive Traits in Lung. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garre, E.; Gustafsson, A.; Leiva, M.C.; Håkansson, J.; Ståhlberg, A.; Kovács, A.; Landberg, G. Breast Cancer Patient-Derived Scaffolds Can Expose Unique Individual Cancer Progressing Properties of the Cancer Microenvironment Associated with Clinical Characteristics. Cancers 2022, 14, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, S.; Ståhlberg, A.; Holdfeldt, A.; Bexe Lindskog, E.; Landberg, G. 5-fluorouracil treatment of patient-derived scaffolds from colorectal cancer reveal clinically critical information. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anna, G.; Elena, G.; Maria Carmen, L.; Simona, S.; Anders, S.; Göran, L. Patient-derived scaffolds as a drug-testing platform for endocrine therapies in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, M.C.; Garre, E.; Gustafsson, A.; Svanström, A.; Bogestål, Y.; Håkansson, J.; Ståhlberg, A.; Landberg, G. Breast cancer patient-derived scaffolds as a tool to monitor chemotherapy responses in human tumor microenvironments. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 4709–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, G.T.; Salerno, S.; Ranji, P.; Håkansson, J.; Bogestål, Y.; Wettergren, Y.; Ståhlberg, A.; Lindskog, E.B.; Landberg, G. Patient-derived scaffolds as a model of colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berger, K.; Persson, E.; Gregersson, P.; Ruiz-Martínez, S.; Jonasson, E.; Ståhlberg, A.; Rhost, S.; Landberg, G. Interleukin-6 Induces Stem Cell Propagation through Liaison with the Sortilin–Progranulin Axis in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 5757. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245757
Berger K, Persson E, Gregersson P, Ruiz-Martínez S, Jonasson E, Ståhlberg A, Rhost S, Landberg G. Interleukin-6 Induces Stem Cell Propagation through Liaison with the Sortilin–Progranulin Axis in Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(24):5757. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245757
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerger, Karoline, Emma Persson, Pernilla Gregersson, Santiago Ruiz-Martínez, Emma Jonasson, Anders Ståhlberg, Sara Rhost, and Göran Landberg. 2023. "Interleukin-6 Induces Stem Cell Propagation through Liaison with the Sortilin–Progranulin Axis in Breast Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 24: 5757. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245757
APA StyleBerger, K., Persson, E., Gregersson, P., Ruiz-Martínez, S., Jonasson, E., Ståhlberg, A., Rhost, S., & Landberg, G. (2023). Interleukin-6 Induces Stem Cell Propagation through Liaison with the Sortilin–Progranulin Axis in Breast Cancer. Cancers, 15(24), 5757. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245757




