A Review of Advanced Cutaneous Melanoma Therapies and Their Mechanisms, from Immunotherapies to Lysine Histone Methyl Transferase Inhibitors
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Advanced Melanoma Treatments
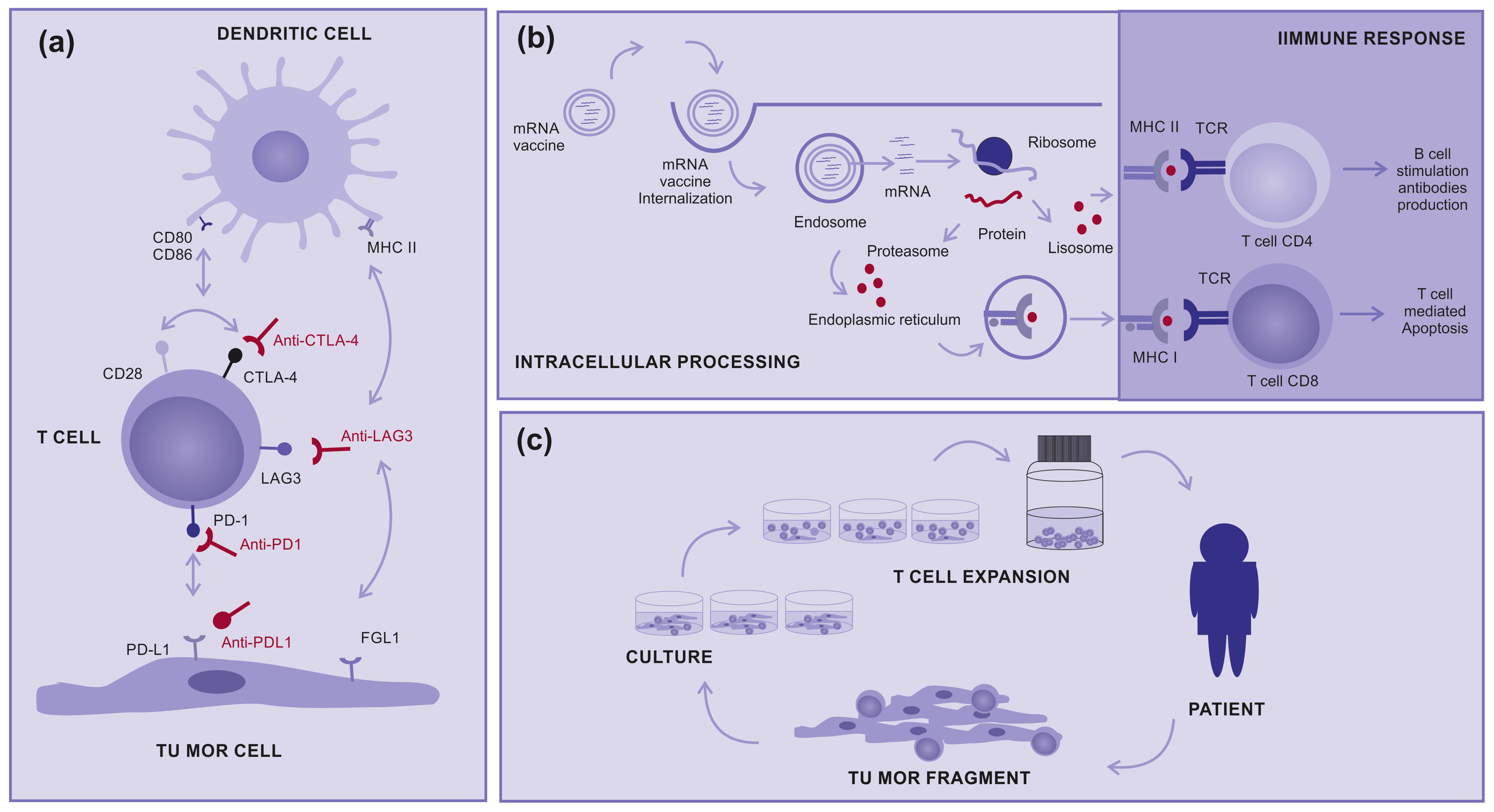
2.1. Immunotherapy
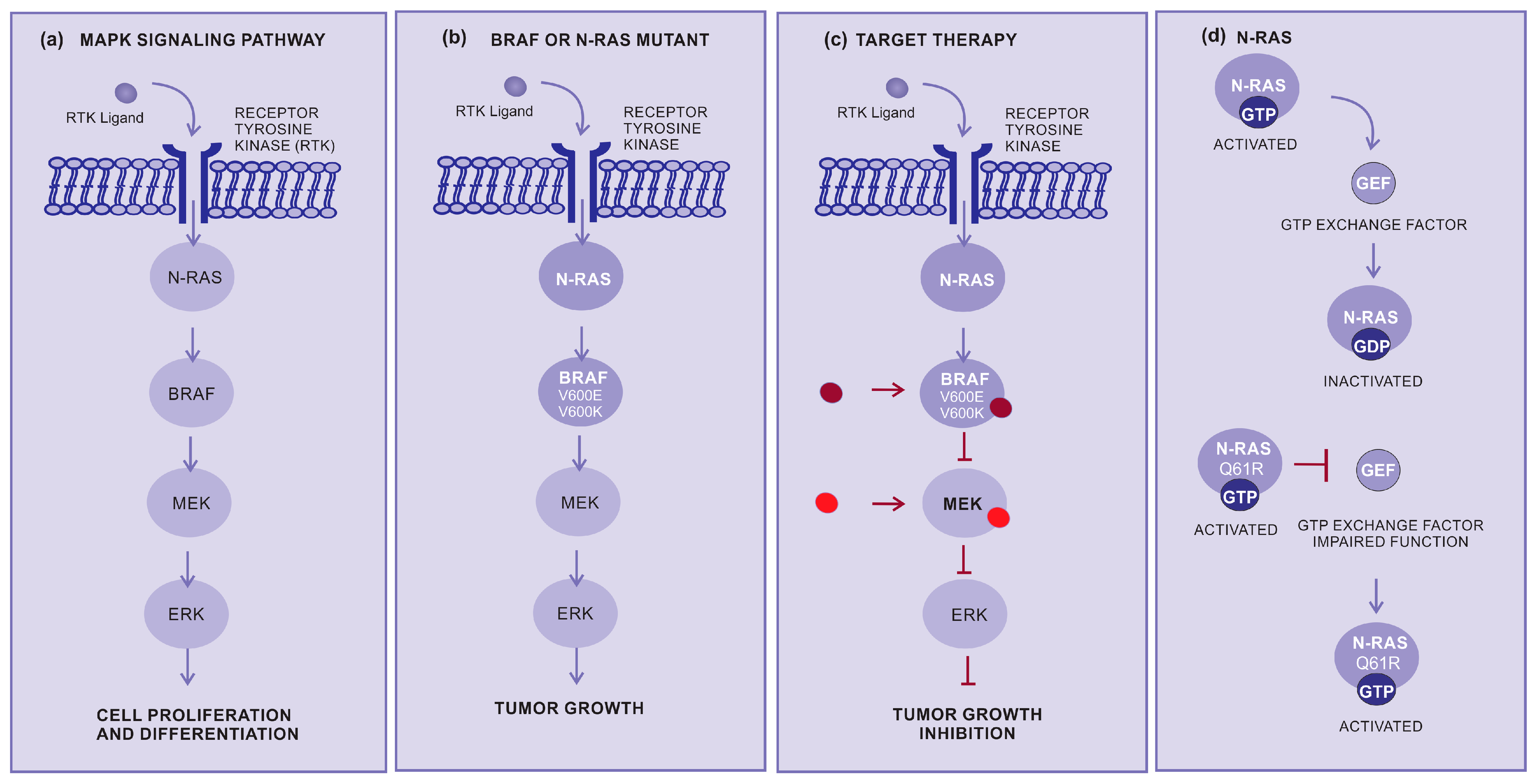
2.2. Target Therapy
2.3. Lysine Histone Methyl Transferase Inhibitors
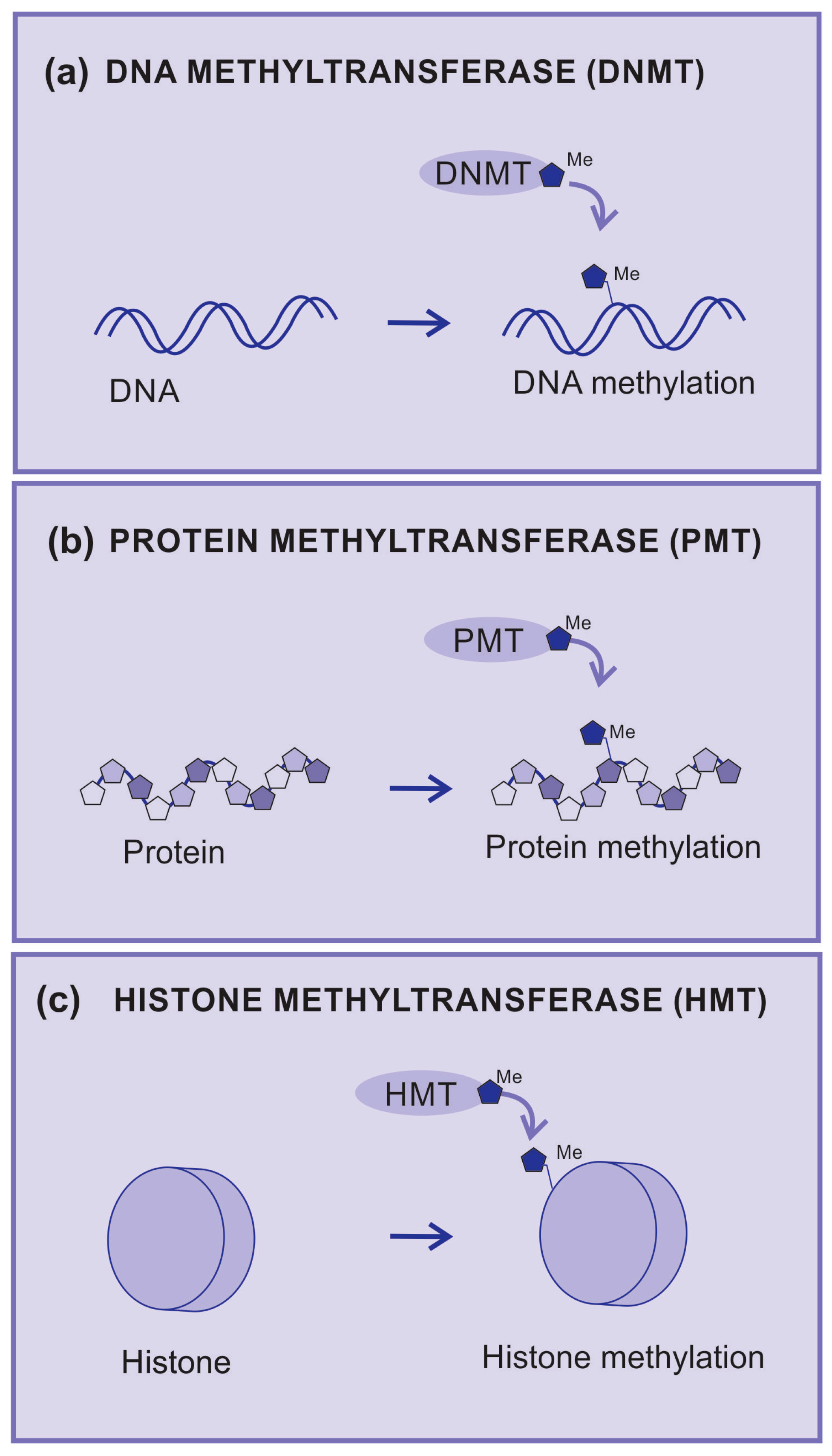
2.3.1. Methyltransferases
2.3.2. DNA Methyltransferases
2.3.3. Protein Methyltransferases
2.3.4. Histones and Their Methylation
2.3.5. Histone Methyltransferases (HMTs)
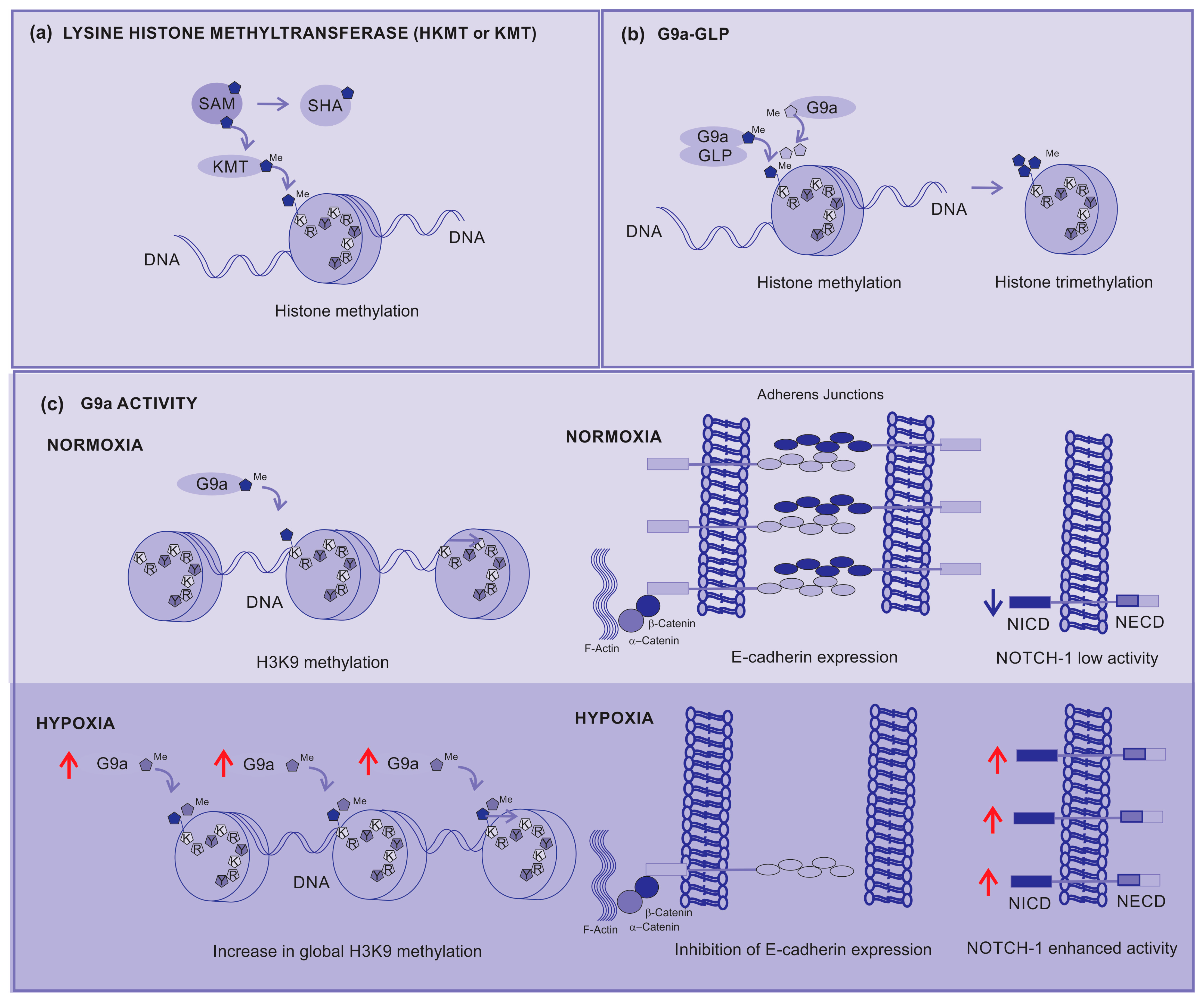
2.3.6. Lysine Histone Methyltransferases (KMTs)
2.3.7. KMT Inhibitors
- -
- Selective inhibitors: These inhibitors target a specific KMT enzyme. This allows a precise approach by targeting specific epigenetic modifications at specific histone sites. Examples of selective inhibitors include those that target KMT for H3K9 or H3K27 methylation [67].
- -
- Broad-spectrum inhibitors: These inhibitors target multiple KMTs in a less specific manner. They affect a broader spectrum of epigenetic modifications and may have widespread effects on cells. This can be beneficial for manipulating gene expression, but may also result in off-targeting side effects [67]. Research into KMT inhibitors is an expanding area with significant implications in basic research and the development of potential new drugs. However, the complexity of epigenetic regulation, and the interconnection of cell signaling pathways, is a challenge. Furthermore, specificity is a critical aspect because the inappropriate inhibition of a KMT can lead to off-target side effects.
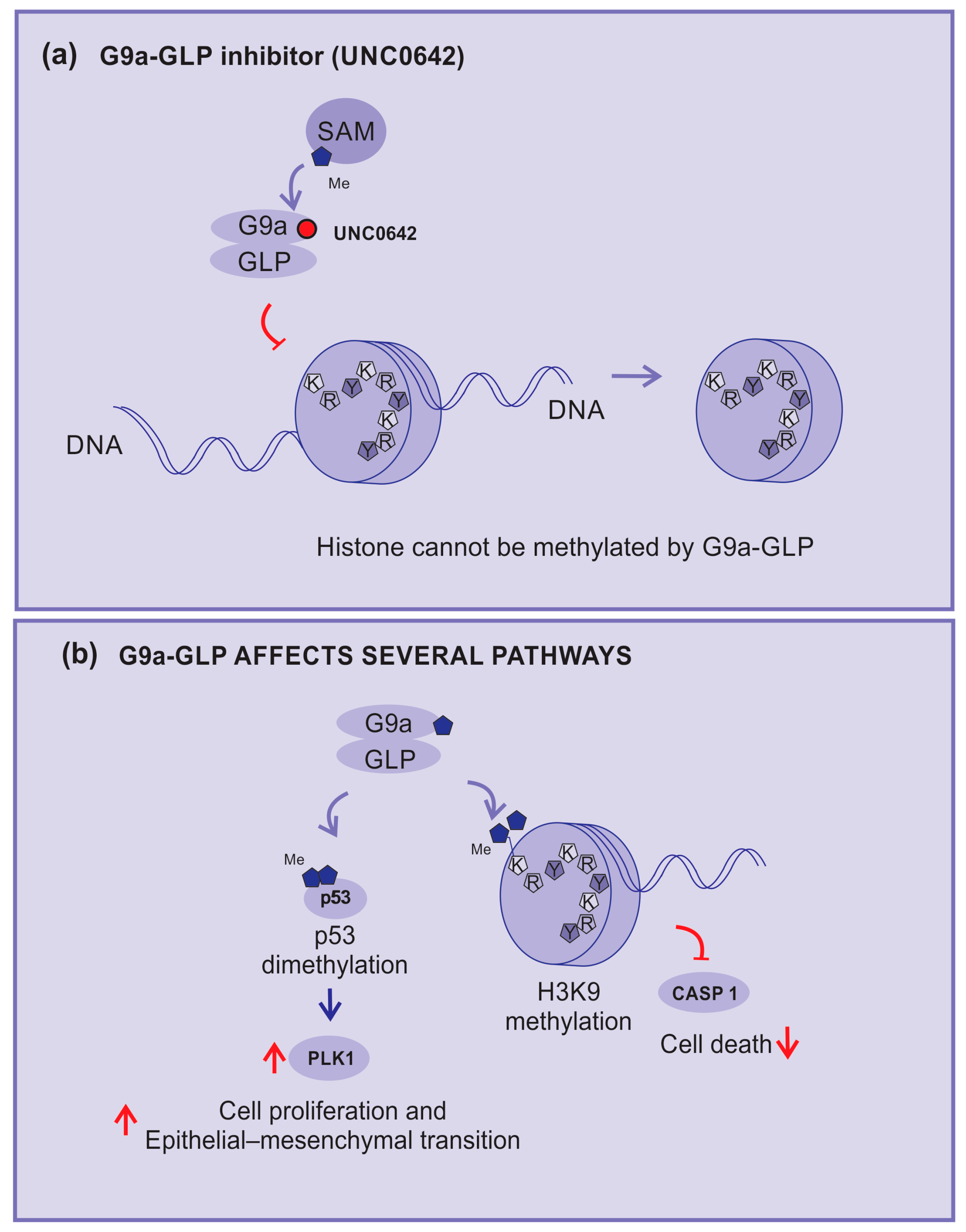
2.3.8. G9a–GLP Inhibitors
3. Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shain, A.H.; Bastian, B.C. From melanocytes to melanomas. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potrony, M.; Badenas, C.; Aguilera, P.; Puig-Butille, J.A.; Carrera, C.; Malvehy, J.; Puig, S. Update in genetic susceptibility in melanoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keung, E.Z.; Gershenwald, J.E. The eighth edition American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) melanoma staging system: Implications for melanoma treatment and care. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2018, 18, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerry, D.; Synnestvedt, M.; Elder, D.E.; Schultz, D. Lessons from Tumor Progression: The Invasive Radial Growth Phase of Melanoma Is Common, Incapable of Metastasis, and Indolent. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 100, 342S–345S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, N.; Aoto, T.; Uhara, H.; Yamazaki, S.; Akutsu, H.; Umezawa, A.; Nakauchi, H.; Miyachi, Y.; Saida, T.; Nishimura, E.K. A melanocyte–melanoma precursor niche in sweat glands of volar skin. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2014, 27, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitara, D.; Nascimento, M.M.; Puig, S.; Yamada, S.; Enokihara, M.M.S.S.; Michalany, N.; Bagatin, E. Nevus-Associated Melanomas. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 142, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, A.; Schmidt-Kittler, O.; Fischer, J.; Ellwanger, U.; Rassner, G.; Riethmüller, G.; Fierlbeck, G.; Klein, C.A. Immunomagnetic Enrichment, Genomic Characterization, and Prognostic Impact of Circulating Melanoma Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.L.; Millward, M.; Pearce, R.; Lee, M.; Frank, M.H.; Ireland, A.; Monshizadeh, L.; Rai, T.; Heenan, P.; Medic, S.; et al. Markers of circulating tumour cells in the peripheral blood of patients with melanoma correlate with disease recurrence and progression. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 168, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zheng, M. Advances in targeted therapy and immunotherapy for melanoma (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 26, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved Survival with Ipilimumab in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermont, A.M.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Grob, J.-J.; Dummer, R.; Wolchok, J.D.; Schmidt, H.; Hamid, O.; Robert, C.; Ascierto, P.A.; Richards, J.M.; et al. Prolonged Survival in Stage III Melanoma with Ipilimumab Adjuvant Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.; Mandalà, M.; Del Vecchio, M.; Gogas, H.J.; Arance, A.M.; Cowey, C.L.; Dalle, S.; Schenker, M.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Marquez-Rodas, I.; et al. Adjuvant Nivolumab versus Ipilimumab in Resected Stage III or IV Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1824–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Schadendorf, D.; Lipson, E.J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Matamala, L.; Gutiérrez, E.C.; Rutkowski, P.; Gogas, H.J.; Lao, C.D.; De Menezes, J.J.; et al. Relatlimab and Nivolumab versus Nivolumab in Untreated Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Dai, Z.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, W.-J.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Q. Regulatory mechanisms of immune checkpoints PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruhashi, T.; Sugiura, D.; Okazaki, I.-M.; Okazaki, T. LAG-3: From molecular functions to clinical applications. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.; Chen, N.; Li, L.; Du, N.; Bai, L.; Lv, Z.; Tian, H.; Cui, J. Mechanisms of Cancer Resistance to Immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Camacho, L.H.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Pavlov, D.; Bulanhagui, C.A.; Millham, R.; Comin-Anduix, B.; Reuben, J.M.; Seja, E.; Parker, C.A.; et al. Antitumor Activity in Melanoma and Anti-Self Responses in a Phase I Trial with the Anti-Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte–Associated Antigen 4 Monoclonal Antibody CP-675,206. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8968–8977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Shroff, S.; Kamiya-Matsuoka, C.; Tummala, S. Atypical neurological complications of ipilimumab therapy in patients with metastatic melanoma. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, A.; Kostine, M.; Barnetche, T.; Truchetet, M.-E.; Schaeverbeke, T. Immune related adverse events associated with anti-CTLA-4 antibodies: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.C.; Joller, N.; Kuchroo, V.K. Lag-3, Tim-3, and TIGIT: Co-inhibitory Receptors with Specialized Functions in Immune Regulation. Immunity 2016, 44, 989–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihara, N.; Madi, A.; Kondo, T.; Zhang, H.; Acharya, N.; Singer, M.; Nyman, J.; Marjanovic, N.D.; Kowalczyk, M.S.; Wang, C.; et al. Induction and transcriptional regulation of the co-inhibitory gene module in T cells. Nature 2018, 558, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, Z. LAG3-PD-1 Combo Overcome the Disadvantage of Drug Resistance. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 831407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Yang, J.C.; Sherry, R.M.; Kammula, U.S.; Hughes, M.S.; Phan, G.Q.; Citrin, D.E.; Restifo, N.P.; Robbins, P.F.; Wunderlich, J.R.; et al. Durable Complete Responses in Heavily Pretreated Patients with Metastatic Melanoma Using T-Cell Transfer Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4550–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnaik, A.A.; Hamid, O.; Khushalani, N.I.; Lewis, K.D.; Medina, T.; Kluger, H.M.; Thomas, S.S.; Domingo-Musibay, E.; Pavlick, A.C.; Whitman, E.D.; et al. Lifileucel, a Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Therapy, in Metastatic Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2656–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitter, S.J.; Sherry, R.M.; Yang, J.C.; Robbins, P.F.; Shindorf, M.L.; Copeland, A.R.; McGowan, C.T.; Epstein, M.; Shelton, T.E.; Langhan, M.M.; et al. Impact of Prior Treatment on the Efficacy of Adoptive Transfer of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5289–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Tang, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, K.; Fan, N.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, Q.; Li, G.; Teng, Y.; Wu, M.; et al. mRNA-based therapeutics: Powerful and versatile tools to combat diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T. Personalized anti-cancer vaccine combining mRNA and immunotherapy tested in melanoma trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2379–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Lotze, M.T.; Muul, L.M.; Leitman, S.; Chang, A.E.; Ettinghausen, S.E.; Matory, Y.L.; Skibber, J.M.; Shiloni, E.; Vetto, J.T.; et al. Observations on the Systemic Administration of Autologous Lymphokine-Activated Killer Cells and Recombinant Interleukin-2 to Patients with Metastatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Fan, T.; Hai, Y.; Gao, Y.; He, J. Reigniting hope in cancer treatment: The promise and pitfalls of IL-2 and IL-2R targeting strategies. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andtbacka, R.H.I.; Collichio, F.; Harrington, K.J.; Middleton, M.R.; Downey, G.; Öhrling, K.; Kaufman, H.L. Final analyses of OPTiM: A randomized phase III trial of talimogene laherparepvec versus granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in unresectable stage III–IV melanoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Karin, M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 2001, 410, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, C. Regulation of MAP kinase activity by peptide receptor signalling pathway: Paradigms of multiplicity. Cell. Signal. 2001, 13, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, A.M.; Simeone, E.; Ascierto, P.A. The role of MEK inhibitors in the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2014, 26, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, N.; Lyons, J. Recent progress in targeting the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway with inhibitors in cancer drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, R.E.; Mpilla, G.; Kim, S.; Philip, P.A.; Azmi, A.S. Ras and exosome signaling. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 54, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papke, B.; Der, C.J. Drugging RAS: Know the enemy. Science 2017, 355, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, A.M.; Simeone, E.; Festino, L.; Vanella, V.; Strudel, M.; Ascierto, P.A. MEK Inhibitors in the Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma and Solid Tumors. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2017, 18, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Gaspar, M.M.; Reis, C.P. Melanoma Management: From Epidemiology to Treatment and Latest Advances. Cancers 2022, 14, 4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Ji, D.; Fan, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, P.; Sun, P.; et al. First-in-human phase I dose-escalation and dose-expansion trial of the selective MEK inhibitor HL-085 in patients with advanced melanoma harboring NRAS mutations. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.M.; Guhan, S.; Tsao, H. KIT and Melanoma: Biological Insights and Clinical Implications. Yonsei Med. J. 2020, 61, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forschner, A.; Forchhammer, S.; Bonzheim, I. NTRK gene fusions in melanoma: Detection, prevalence and potential therapeutic implications. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2020, 18, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconi, V.M.D.C.; Torres-Arciga, K.; Matus-Ortega, G.; Díaz-Chávez, J.; Herrera, L.A. DNA Methyltransferases: From Evolution to Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniskan, H.Ü.; Martini, M.L.; Jin, J. Inhibitors of Protein Methyltransferases and Demethylases. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 989–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, M.; Matsumura, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Kimura, H.; Shinkai, Y. G9a/GLP complexes independently mediate H3K9 and DNA methylation to silence transcription. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2681–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barski, A.; Cuddapah, S.; Cui, K.; Roh, T.-Y.; Schones, D.E.; Wang, Z.; Wei, G.; Chepelev, I.; Zhao, K. High-Resolution Profiling of Histone Methylations in the Human Genome. Cell 2007, 129, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.C.; Van Rechem, C.; Whetstine, J.R. Histone Lysine Methylation Dynamics: Establishment, Regulation, and Biological Impact. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Rank, G.; Tan, Y.T.; Li, H.; Moritz, R.L.; Simpson, R.J.; Cerruti, L.; Curtis, D.J.; Patel, D.J.; Allis, C.D.; et al. PRMT5-mediated methylation of histone H4R3 recruits DNMT3A, coupling histone and DNA methylation in gene silencing. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, S.; Eisenhaber, F.; O’Carroll, D.; Strahl, B.D.; Sun, Z.-W.; Schmid, M.; Opravil, S.; Mechtler, K.; Ponting, C.P.; Allis, C.D.; et al. Regulation of chromatin structure by site-specific histone H3 methyltransferases. Nature 2000, 406, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.E. Epigenetic Therapies for Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, B.; Silva, R.; Perry, A.S.; Gallagher, W.M. Epigenetics of malignant melanoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 51, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, T.; Lupski, J. Genomic disorders 20 years on—Mechanisms for clinical manifestations. Clin. Genet. 2021, 93, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Deng, Y. Current insights into the epigenetic mechanisms of skin cancer. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacev, B.A.; Feng, L.; Bagert, J.D.; Lemiesz, A.E.; Gao, J.; Soshnev, A.A.; Kundra, R.; Schultz, N.; Muir, T.W.; Allis, C.D. The expanding landscape of ‘oncohistone’ mutations in human cancers. Nature 2019, 567, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husmann, D.; Gozani, O. Histone lysine methyltransferases in biology and disease. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fath, M.K.; Azargoonjahromi, A.; Soofi, A.; Almasi, F.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Khalili, S.; Sheikhi, K.; Ferdousmakan, S.; Owrangi, S.; Fahimi, M.; et al. Current understanding of epigenetics role in melanoma treatment and resistance. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciello, F.; Windloch, K.; Gannon, F.; Lee, J.S. Functional Role of G9a Histone Methyltransferase in Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazian, M.D.; Zhang, K.; Grunstein, M. Histone H2B Ubiquitylation Controls Processive Methylation but Not Monomethylation by Dot1 and Set1. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, M.; Ueda, J.; Fukuda, M.; Takeda, N.; Ohta, T.; Iwanari, H.; Sakihama, T.; Kodama, T.; Hamakubo, T.; Shinkai, Y. Histone methyltransferases G9a and GLP form heteromeric complexes and are both crucial for methylation of euchromatin at H3-K9. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Xing, Y.; Wen, X.; Jia, R.; Ni, H.; He, J.; Ding, X.; Pan, H.; Qian, G.; Ge, S.; et al. Long non-coding RNA ROR decoys gene-specific histone methylation to promote tumorigenesis. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Yang, J.; Ge, S.; Chai, P.; Fan, J.; Jia, R. Novel insights into histone lysine methyltransferases in cancer therapy: From epigenetic regulation to selective drugs. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 13, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, N.-N.; Jiao, J.; Meng, X.; An, Y.; Han, C.; Huang, S. Abnormal overexpression of G9a in melanoma cells promotes cancer progression via upregulation of the Notch1 signaling pathway. Aging 2020, 12, 2393–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, R.S.d.O.; Peixoto, G.R.; Sangiuliano, L.D.C.; de Oliveira, D.A. Notch receptors as a therapeutic target in melanoma: A narrative bibliographic review. Braz. J. Nat. Sci. 2021, 4, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, F.; Osborne, B.A. Non-Canonical Notch Signaling in Cancer and Immunity. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedogni, B. Notch signaling in melanoma: Interacting pathways and stromal influences that enhance Notch targeting. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2014, 27, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wong, P.; Salvaggio, C.; Salhi, A.; Osman, I.; Bedogni, B. Synchronized Targeting of Notch and ERBB Signaling Suppresses Melanoma Tumor Growth through Inhibition of Notch1 and ERBB3. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Xiao, W.R.; Liao, Y.Y.; Li, L.; Xiao, X.; Xu, X.P.; Feng, H. EGFL7 silencing inactivates the Notch signaling pathway; enhancing cell apoptosis and suppressing cell proliferation in human cutaneous melanoma. Neoplasma 2019, 66, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, K.P.; Kaniskan, H.Ü.; Jin, J.; Gozani, O. Epigenetics and beyond: Targeting writers of protein lysine methylation to treat disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 265–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugo, H.S.; Jacobs, I.; Sharma, S.; Scappaticci, F.; Paul, T.A.; Jensen-Pergakes, K.; Malouf, G.G. The Promise for Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors for Epigenetic Therapy in Clinical Oncology: A Narrative Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 3059–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, P.A.; Gangisetty, O.; James, S.R.; Woloszynska-Read, A.; Tachibana, M.; Shinkai, Y.; Karpf, A.R. Distinct Roles for Histone Methyltransferases G9a and GLP in Cancer Germ-Line Antigen Gene Regulation in Human Cancer Cells and Murine Embryonic Stem Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweis, R.F.; Pliushchev, M.; Brown, P.J.; Guo, J.; Li, F.; Maag, D.; Petros, A.M.; Soni, N.B.; Tse, C.; Vedadi, M.; et al. Discovery and Development of Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Histone Methyltransferase G9a. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-S.; Xiong, Y.; Yim, H.; Velez, J.; Babault, N.; Kumar, P.; Liu, J.; Jin, J. Discovery of the First-in-Class G9a/GLP Covalent Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 10506–10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Barsyte-Lovejoy, D.; Li, F.; Xiong, Y.; Korboukh, V.; Huang, X.-P.; Allali-Hassani, A.; Janzen, W.P.; Roth, B.L.; Frye, S.V.; et al. Discovery of an in Vivo Chemical Probe of the Lysine Methyltransferases G9a and GLP. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8931–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flesher, J.L.; Fisher, D.E. G9a: An Emerging Epigenetic Target for Melanoma Therapy. Epigenomes 2021, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Li, L.; Yang, D.; Zeng, L.; Yewei, X.; Yu, B.; Liao, G.; Chen, J. Recent progress in histone methyltransferase (G9a) inhibitors as anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 179, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, L.; Mazzotta, A.; Garofoli, M.; Di Fonte, R.; Guida, G.; Guida, M.; Tommasi, S.; Azzariti, A. Active notch protects MAPK activated melanoma cell lines from MEK inhibitor cobimetinib. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 111006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Levy, C. Negative Regulatory Loop between Microphthalmia-Associated Transcription Factor (MITF) and Notch Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Weng, Q.Y.; Insco, M.L.; Chen, K.Y.; Muralidhar, S.; Pozniak, J.; Diaz, J.M.S.; Drier, Y.; Nguyen, N.; Lo, J.A.; et al. Gain-of-Function Genetic Alterations of G9a Drive Oncogenesis. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 980–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, G.M.; Al-Ejeh, F.; McCuaig, R.; Casciello, F.; Kamal, N.A.; Ferguson, B.; Pritchard, A.L.; Ali, S.; Silva, I.P.; Wilmott, J.S.; et al. G9a Inhibition Enhances Checkpoint Inhibitor Blockade Response in Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 2624–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompei, V.; Salvolini, E.; Rubini, C.; Lucarini, G.; Molinelli, E.; Brisigotti, V.; Pozzi, V.; Sartini, D.; Campanati, A.; Offidani, A.; et al. Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase in nonmelanoma skin cancers. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49, e13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzetti, G.; Sartini, D.; Campanati, A.; Rubini, C.; Molinelli, E.; Brisigotti, V.; Cecati, M.; Pozzi, V.; Campagna, R.; Offidani, A.; et al. Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase: Potential involvement in cutaneous malignant melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2018, 28, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartini, D.; Molinelli, E.; Pozzi, V.; Campagna, R.; Salvolini, E.; Rubini, C.; Goteri, G.; Simonetti, O.; Campanati, A.; Offidani, A.; et al. Immunohistochemical expression of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase in lymph node metastases from cutaneous malignant melanoma. Hum. Cell 2023, 36, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Haren, M.J.; Zhang, Y.; Thijssen, V.; Buijs, N.; Gao, Y.; Mateuszuk, L.; Fedak, F.A.; Kij, A.; Campagna, R.; Sartini, D.; et al. Macrocyclic peptides as allosteric inhibitors of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT). RSC Chem. Biol. 2021, 2, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; van Haren, M.J.; Buijs, N.; Innocenti, P.; Zhang, Y.; Sartini, D.; Campagna, R.; Emanuelli, M.; Parsons, R.B.; Jespers, W.; et al. Potent Inhibition of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase by Alkene-Linked Bisubstrate Mimics Bearing Electron Deficient Aromatics. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 12938–12963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Journal | Study Subject | Study Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qin and Zeng, 2023 [9] | Exp. Ther. Med. | Targeted therapy and immunotherapy for melanoma | Review Article |
| Hold et al., 2010 [10] | N. Engl. J. Med. | Ipilimumab and patient suvival in melanoma | Original Article (Clinical trial) |
| Eggermont et al., 2016 [11] | N. Engl. J. Med. | Ipilimumab and patient suvival in melanoma | Original Article (Clinical trial) |
| Weber et al., 2017 [12] | N. Engl. J. Med. | Nivolumab versus ipilimumab in resected Stage III or IV melanoma | Original Article (Clinical trial) |
| Tawbi et al., 2022 [13] | N. Engl. J. Med. | Relatlimab and nivolumab versus nivolumab in untreated advanced melanoma | Original Article (Clinical trial) |
| Zhang et al., 2021 [14] | J. Exp. Clin. Cancer | Regulatory mechanisms of immune checkpoints PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in cancer | Review Article |
| Maruhashi et al., 2020 [15] | J. Immunother. Cancer | LAG-3 molecular functions and clinical applications | Review Article |
| Bai et al., 2020 [16] | Front. Oncol. | Mechanisms of cancer resistance to immunotherapy | Review Article |
| Ribas et al., 2005 [17] | J. Clin. Oncol. | Phase I trial with CTLA4 in melanoma | Original Article |
| Liao et al., 2014 [18] | Neuro Oncol. | Neurological complications related to ipimumab | Case Report |
| Bertrand et al., 2015 [19] | BMC Med. | Meta-analysis on related adverse events associated with anti-CTLA-4 antibodies | Review Article |
| Anderson et al., 2016 [20] | Immunity | Immune function of Lag-3, Tim-3, and TIGIT | Review Article |
| Chibara et al., 2018 [21] | Nature | Transcriptional regulation of co-receptors PD-1, Tim-3, Lag-3, and TIGIT and description of new ones | Original Article |
| Wei and Li, 2022 [22] | Front. Oncol. | Drug synergy of PD-1 and LAG-3 and drug resistance to overcome | Original Article |
| Tawbi et al., 2022 [13] | N. Engl. J. Med. | Relatlimab and nivolumab versus nivolumab in untreated advanced melanoma | Original Article |
| Rosenberg et al., 2011 [23] | Clin. Cancer Res. | T-cell transfer immunotherapy and patient response | Original Article |
| Sarnaik et al., 2021 [24] | J. Clin. Oncol. | Lifileucel, a tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte therapy, in metastatic melanoma | Original Article |
| Seitter et al., 2021 [25] | Clin. Cancer Res. | Adoptive transfer of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with metastatic melanoma | Original Article |
| Qin et al., 2022 [26] | Signal Transduct Target Ther. | mRNA-based therapeutics | Review Article |
| Carvalho T, 2023 [27] | Nat. Med. | mRNA and immunotherapy tested in melanoma trial | Original Article |
| Rosenberg et al., 1985 [28] | N. Engl. J. Med. | T-cell transfer immunotherapy and IL-2 in melanoma | Original Article |
| Muhammad et al., 2023 [29] | Mol. Cancer | IL-2 and IL-2R targeting strategies | Review Article |
| Andtbacka et al., 2019 [30] | J. Immunother. Cancer | Talimogene laherparepvec litic virus in melanoma | Original Article |
| Reference | Journal | Study Subject | Study Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chang et al., 2001 [31] | Nature | MAPK signaling | Review Article |
| Liebmann et al., 2001 [32] | Cell Signal | MAPK signaling | Review Article |
| Grimaldi et al., 2014 [33] | Curr. Opin. Oncol. | MEK inhibitors in metastatic melanoma | Review Article |
| Thompson and Lyons, 2005 [34] | Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. | Advances in MEK pathway inhibitors in cancer | Review Article |
| Sexton et al., 2019 [35] | Semin. Cancer Biol. | RAS and exosome signaling | Review Article |
| Papke and Der, 2017 [36] | Science | Drugs targting RAS | Review Article |
| Grimaldi et al., 2017 [37] | Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. | MEK inhibitors in the treatment of metastatic melanoma | Review Article |
| Lopes et al., 2022 [38] | Cancers | Melanoma epidemiology, treatment, and latest advances | Review Article |
| Wang et al., 2023 [39] | BMC Med. | Phase I dose-escalation and dose-expansion trial of a selective MEK inhibitor | Original Article (Clinical trial) |
| Pham and Tsao, 2023 [40] | Yonsei Med. J. | KIT and melanoma: biological insights and clinical implications | Review Article |
| Forschner et al., 2020 [41] | J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. | NTRK gene fusions in melanoma and potential therapeutic implications | Review Article |
| Reference | Journal | Study Subject | Study Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Del Castilho et al., 2022 [42] | Int. J. Mol. Sci. | DNA methyltransferases evolution to clinical applications | Review Article |
| Kaniskan et al., 2018 [43] | Chem. Rev. | Inhibitors of protein methyltransferases and demethylases | Review Article |
| Tachibana et al., 2008 [44] | EMBO | G9a/GLP complexes mediate H3K9 and DNA methylation | Original Article |
| Barski et al., 2007 [45] | Cell | High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome | Original Article |
| Black et al., 2012 [46] | Mol. Cell. | Histone lysine methylation dynamics | Review Article |
| Zhao et al., 2009 [47] | Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. | Role of PRMT5 in DNA methylation and gene silencing | Original Article |
| Rea et al., 2000 [48] | Nature | Regulation of chromatin structure by histone H3 methyltransferases | Original Article |
| Bates, 2021 [49] | N. Engl. J. Med. | Epigenetic therapies for cancer | Review Article |
| Moran et al., 2021 [50] | Semin. Cancer Biol. | Epigenetics of malignant melanoma | Review Article |
| Harel and lupski, 2021 [51] | Clin. Genet. | Mechanisms on genomic disorders and clinical manifestations | Review Article |
| Sang and deng, 2019 [52] | Dermatol. Ther. | Epigenetic mechanisms of skin cancer | Review Article |
| Nacev et al., 2019 [53] | Nature | Oncohistone mutations in human cancers | Original Article |
| Husmann and Gozani, 2019 [54] | Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. | Histone lysine methyltransferase biology | Review Article |
| Karami et al., 2022 [55] | Cancer Cell Int. | Epigenetics role in melanoma treatment and resistance | Review Article |
| Casciello et al., 2015 [56] | Front. Immunol. | G9a histone methyltransferase in cancer | Review Article |
| Shahbazian et al., 2005 [57] | Mol. Cell. | Histone ubiquitylation controls processive methylation | Original Article |
| Tachibana et al., 2005 [58] | Genes Dev. | Histone methyltransferases G9a and GLP | Original Article |
| Fan et al., 2015 [59] | Genome Biol. | Gene-specific histone methylation can promote tumorigenesis | Original Article |
| Liao et al., 2023 [60] | J. Pharm. Anal. | Histone lysine methyltransferases in cancer therapy | Review Article |
| Dang et al., 2020 [61] | Aging | G9a in melanoma cells promotes upregulation of the Notch1 signaling pathway | Original Article |
| Filho et al., 2021 [62] | Braz. J. Nat. Sci. | Notch receptors as a therapeutic target in melanoma | Review Article |
| Ayaz and Osborne, 2014 [63] | Front. Oncol. | Non-canonical Notch signaling in cancer and immunity | Review Article |
| Bedogni, 2014 [64] | Pigment Cell Mel. Res. | Notch signaling in melanoma | Review Article |
| Zhang et al., 2016 [65] | J. Investig. Dermatol. | Melanoma through inhibition of Notch1 and ERBB3 | Original Article |
| Tang et al., 2019 [66] | Neoplasma | EGFL7 silencing inactivates the Notch signaling pathway in human cutaneous melanoma | Original Article |
| Bhat et al., 2021 [67] | Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. | Epigenetics and protein lysine methylation to treat disease | Review Article |
| Rugo et al., 2020 [68] | Adv. Ther. | Histone methyltransferase inhibitors in clinical oncology | Review Article |
| Link et al., 2009 [69] | Mol. Cancer Res. | Histone methyltransferases G9a and GLP in cancer germ-line antigen gene regulation | Original Article |
| Sweis et al., 2014 [70] | ACS Med. Chem. Lett. | Discovery of potent and selective inhibitors of histone methyltransferase G9a | Original Article |
| Park et al., 2022 [71] | J. Med. Chem. | Discovery of G9a/GLP covalent inhibitors | Original Article |
| Liu et al., 2013 [72] | J. Med. Chem. | Discovery of an in vivo chemical probe of the lysine methyltransferases G9a and GLP | Original Article |
| Flesher and Fisher, 2019 [73] | Eur. J. Med. Chem. | Progress in histone methyltransferase (G9a) inhibitors | Review Article |
| Cao et al., 2019 [74] | Eur. J. Med. Chem. | Progress in histone methyltransferase (G9a) inhibitors | Review Article |
| Porcelli et al., 2021 [75] | Biomed Pharmacother. | Notch protects MAPK-activated melanoma from MEK inhibitor | Review Article |
| Golan and Levy, 2019 [76] | Int. J. Mol. Sci. | Microphthalmia-Associated Transcription Factor (MITF) and Notch signaling | Original Article |
| Kato et al., 2020 [77] | Cancer Discov. | Gain-of-function genetic alterations of G9a drive oncogenesis | Original Article |
| Kelly et al., 2021 [78] | Clin. Cancer Res. | G9a inhibition enhances checkpoint inhibitor blockade response in melanoma | Original Article |
| Reference | Journal | Study Subject | Study Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pompei et al., 2019 [79] | Eur. J. Clin. Investig. | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase in nonmelanoma skin cancers | Original Article |
| Ganzetti et al., 2018 [80] | Melanoma Res. | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase presence in cutaneous malignant melanoma. | Original Article |
| Sartini et al., 2023 [81] | Hum. Cell. | Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase presence in melanoma lymph node metastasis | Original Article |
| van Haren et al., 2021 [82] | RSC Chem. Biol. | Macrocyclic peptides as allosteric inhibitors of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase | Original Article |
| Gao et al., 2012 [83] | J. Med. Chem. | Potent inhibition of nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase by alkene-linked bisubstrate | Original Article |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira Filho, R.S.; de Oliveira, D.A.; Nisimoto, M.M.; Marti, L.C. A Review of Advanced Cutaneous Melanoma Therapies and Their Mechanisms, from Immunotherapies to Lysine Histone Methyl Transferase Inhibitors. Cancers 2023, 15, 5751. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245751
de Oliveira Filho RS, de Oliveira DA, Nisimoto MM, Marti LC. A Review of Advanced Cutaneous Melanoma Therapies and Their Mechanisms, from Immunotherapies to Lysine Histone Methyl Transferase Inhibitors. Cancers. 2023; 15(24):5751. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245751
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira Filho, Renato Santos, Daniel Arcuschin de Oliveira, Melissa Maeda Nisimoto, and Luciana Cavalheiro Marti. 2023. "A Review of Advanced Cutaneous Melanoma Therapies and Their Mechanisms, from Immunotherapies to Lysine Histone Methyl Transferase Inhibitors" Cancers 15, no. 24: 5751. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245751
APA Stylede Oliveira Filho, R. S., de Oliveira, D. A., Nisimoto, M. M., & Marti, L. C. (2023). A Review of Advanced Cutaneous Melanoma Therapies and Their Mechanisms, from Immunotherapies to Lysine Histone Methyl Transferase Inhibitors. Cancers, 15(24), 5751. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245751






