Risk Factors for Radiation Necrosis and Local Recurrence after Proton Beam Therapy for Skull Base Chordoma or Chondrosarcoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brain Tumor Registry of Japan (2005–2008). Neurol. Med. Chir. 2017, 57 (Suppl. S1), 9–102. [CrossRef]
- Patra, D.P.; Hess, R.A.; Turcotte, E.L.; Welz, M.E.; Rahme, R.J.; Maiti, T.K.; Abi-Aad, K.R.; AlMekkawi, A.K.; Keole, S.; Lal, D.; et al. Surgical Outcomes with Midline versus Lateral Approaches for Cranial Base Chordomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2020, 140, 378–388.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizumoto, M.; Oshiro, Y.; Tsuboi, K. Proton beam therapy for intracranial and skull base tumors. Transl. Cancer Res. 2013, 2, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Catton, C.; O’Sullivan, B.; Bell, R.; Laperriere, N.; Cummings, B.; Fornasier, V.; Wunder, J. Chordoma: Long-term follow-up after radical photon irradiation. Radiother. Oncol. 1996, 41, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magrini, S.M.; Papi, M.G.; Marletta, F.; Tomaselli, S.; Cellai, E.; Mungai, V.; Biti, G. Chordoma-natural history, treatment and prognosis. The Florence Radiotherapy Department experience (1956–1990) and a critical review of the literature. Acta Oncol. 1992, 31, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, D.B.; Bloom, J.G. Radiotherapy for chordoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1988, 15, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, M.; Chang, D.T.; Pollom, E.L. Second cancer risk after primary cancer treatment with three-dimensional conformal, intensity-modulated, or proton beam radiation therapy. Cancer 2020, 126, 3560–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noufal, M.P.; Widesott, L.; Sharma, S.D.; Righetto, R.; Cianchetti, M.; Schwarz, M. The Role of Plan Robustness Evaluation in Comparing Protons and Photons Plans—An Application on IMPT and IMRT Plans in Skull Base Chordomas. J. Med. Phys. 2020, 45, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, M.; Oshiro, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Kohzuki, H.; Sakurai, H. Proton Beam Therapy for Pediatric Brain Tumor. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2017, 57, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, M.; Fuji, H.; Miyachi, M.; Soejima, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Aibe, N.; Demizu, Y.; Iwata, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Motegi, A.; et al. Proton beam therapy for children and adolescents and young adults (AYAs): JASTRO and JSPHO Guidelines. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 98, 102209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, M.; Oshiro, Y.; Okumura, T.; Fukumitsu, N.; Numajiri, H.; Ohnishi, K.; Aihara, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Tsuboi, K.; Sakurai, H.; et al. Proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A review of the University of Tsukuba experience. Int. J. Part Ther. 2016, 2, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizumoto, M.; Okumura, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Fukuda, K.; Oshiro, Y.; Fukumitsu, N.; Abei, M.; Kawaguchi, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Ookawa, A.; et al. Proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A comparison of three treatment protocols. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igaki, H.; Tokuuye, K.; Okumura, T.; Sugahara, S.; Kagei, K.; Hata, M.; Ohara, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Tsuboi, K.; Takano, S.; et al. Clinical results of proton beam therapy for skull base chordoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 60, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, Y.; Mizumoto, M.; Akutsu, H.; Takano, S.; Matsumura, A.; Okumura, T.; Kawabe, T.; Zenkoh, J.; Sakurai, H.; Tsuboi, K. Hyperfractionated high-dose proton beam radiotherapy for clival chordomas after surgical removal. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20151051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, J.P.; Robert, J.G. A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1999, 94, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T. A Package for Survival Analysis in R, R Package Version 3.3-1. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gerds, T.A. prodlim: Product-Limit Estimation for Censored Event History Analysis; R Package Version 2019.11.13. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, B. cmprsk: Subdistribution Analysis of Competing Risks; R Package Version 2.2-11. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Varadhan, R.; Kuk, D. crrstep: Stepwise Covariate Selection for the Fine & Gray Competing Risks Regression Model; R Package Version 2015-2.1. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, A.M.; White, I.R.; Royston, P. Multiple imputations based on the MICE method were applied to the missing co-variates. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 3227–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Buuren, S.; Groothuis-Oudshoorn, K. mice: Multivariate Imputation by Chained Equations in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 45, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demizu, Y.; Mizumoto, M.; Onoe, T.; Nakamura, N.; Kikuchi, Y.; Shibata, T.; Okimoto, T.; Sakurai, H.; Akimoto, T.; Ono, K.; et al. Proton beam therapy for bone sarcomas of the skull base and spine: A retrospective nationwide multicenter study in Japan. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacchiotti, S.; Gronchi, A.; Fossati, P.; Akiyama, T.; Alapetite, C.; Baumann, M.; Blay, J.Y.; Bolle, S.; Boriani, S.; Bruzzi, P.; et al. Best practices for the management of local-regional recurrent chordoma: A position paper by the Chordoma Global Consensus Group. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1230–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcott, B.P.; Nahed, B.V.; Mohyeldin, A.; Coumans, J.-V.; Kahle, K.T.; Ferreira, M.J. Chordoma: Current concepts, management, and future directions. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, e69–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, M.W.; Linton, O.R.; Moore, M.G.; Ting, J.Y.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A.; Shah, M.V. Influence of residual tumor volume and radiation dose coverage in outcomes for clival chordoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagundes, M.A.; Hug, E.B.; Liebsch, N.J.; Daly, W.; Efird, J.; Munzenrider, J.E. Radiation therapy for chordomas of the base of skull and cervical spine: Patterns of failure and outcome after relapse. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1995, 33, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorlu, F.; Gürkaynak, M.; Yildiz, F.; Öge, K.; Lale Atahan, İ. Conventional external radiotherapy in the management of clivus chordomas with overt residual disease. Neurol. Sci. 2000, 21, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, E.; Sekhar, L.N.; Rubinstein, E.; Wright, D.C.; Sen, C.; Janecka, I.P.; Snyderman, C.H. Chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the cranial base: Results and follow-up of 60 patients. Neurosurgery 1995, 36, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoe, J.E.; Hasegawa, A.; Takagi, R.; Bessho, H.; Onda, T.; Tsujii, H. Carbon ion radiotherapy for skull base chordoma. Skull Base 2009, 19, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, M.; Demizu, Y.; Nagano, F.; Terashima, K.; Fujii, O.; Jin, D.; Mima, M.; Niwa, Y.; Katsui, K.; Suga, M.; et al. Treatment outcomes of proton or carbon ion therapy for skull base chordoma: A retrospective study. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Yang, Q.; Xiong, Z.; Ye, N.; Li, X. Multivariate analysis and validation of the prognostic factors for skull base chordoma. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 764329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, M.; Shin, M.; Jokura, H.; Hasegawa, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsunaga, S.; Akabane, A.; Yomo, S.; Onoue, S.; et al. Outcomes of Gamma Knife radiosurgery for skull base chondrosarcomas: A multi-institutional retrospective study. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 137, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugahara, S.; Oshiro, Y.; Nakayama, H.; Fukuda, K.; Mizumoto, M.; Abei, M.; Shoda, J.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Thono, E.; Tokita, M.; et al. Proton beam therapy for large hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Fukumoto, T.; Demizu, Y.; Miyawaki, D.; Terashima, K.; Sasaki, R.; Hori, Y.; Hishikawa, Y.; Ku, Y.; Murakami, M. Clinical results and risk factors of proton and carbon ion therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2011, 117, 4890–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leo, A.N.; Holtzman, A.L.; Ho, M.W.; Morris, C.G.; Rutenberg, M.S.; Rotondo, R.L.; Bates, J.E.; Indelicato, D.J.; Rao, D.; Hasan, M.A.; et al. Vision loss following high-dose proton-based radiotherapy for skull-base chordoma and chondrosarcoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 158, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, K.; Gulidov, I.; Koryakin, S.; Smyk, D.; Makeenkova, T.; Gogolin, D.; Lepilina, O.; Golovanova, O.; Semenov, A.; Dujenko, S.; et al. Proton therapy with a fixed beamline for skull-base chordomas and chondrosarcomas: Outcomes and toxicity. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehlivan, B.; Ares, C.; Lomax, A.J.; Stadelmann, O.; Goitein, G.; Timmermann, B.; Schneider, R.A.; Hug, E.B. Temporal lobe toxicity analysis after proton radiation therapy for skull base tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ares, C.; Hug, E.B.; Lomax, A.J.; Bolsi, A.; Timmermann, B.; Rutz, H.P.; Schuller, J.C.; Pedroni, E.; Goitein, G. Effectiveness and safety of spot scanning proton radiation therapy for chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the skull base: First long-term report. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 75, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koto, M.; Hasegawa, A.; Takagi, R.; Fujikawa, A.; Morikawa, T.; Kishimoto, R.; Jingu, K.; Tsujii, H.; Kamada, T. Risk factors for brain injury after carbon ion radiotherapy for skull base tumors. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 111, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, M.W.; Linton, O.R.; Calley, C.S. Dose-volume relationships associated with temporal lobe radiation necrosis after skull base proton beam therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andruska, N.; Kennedy, W.R.; Bonestroo, L.; Anderson, R.; Huang, Y.; Robinson, C.G.; Abraham, C.; Tsien, C.; Knutson, N.; Rich, K.M.; et al. Dosimetric predictors of symptomatic radiation necrosis after five-fraction radiosurgery for brain metastases. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 156, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, P.; Min, Y.; Li, J.; Feng, M.; Xu, G.; Lang, J. Dosimetric analysis of radiation-induced brainstem necrosis for nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with IMRT. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerschbaumer, J.; Demetz, M.; Krigers, A.; Nevinny-Stickel, M.; Thomé, C.; Freyschlag, C.F. Risk factors for radiation necrosis in patients undergoing cranial stereotactic radiosurgery. Cancers 2021, 13, 4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, M.T.; Grimm, J.; Niemierko, A.; Soltys, S.G.; Moiseenko, V.; Redmond, K.J.; Yorke, E.; Sahgal, A.; Xue, J.; Mahadevan, A.; et al. Single- and multifraction stereotactic radiosurgery dose/volume tolerances of the brain. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, C.; Muzaffar, J.; Kulendra, K.; Sanghera, P.; Shaw, S.; Shad, A.; Saravanappa, N.; Paluzzi, A.; Ahmed, S. Chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the skull base: Treatment and outcome analysis in w consecutive case series of 24 patients. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, B.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, H.; Dai, M.; Zhang, B. Clival chordoma: Long-term clinical outcome in a single center. Medicine 2018, 97, e12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, F.; Feuvret, L.; Bresson, D.; Guichard, J.P.; El Zein, S.; Bernat, A.L.; Labidi, M.; Calugaru, V.; Froelich, S.; Herman, P.; et al. Surgery and protontherapy in Grade I and II skull base chondrosarcoma: A comperative retrospective study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattke, M.; Vogt, K.; Bougatf, N.; Welzel, T.; Oelmann-Avendano, J.; Hauswald, H.; Jensen, A.; Ellerbrock, M.; Jäkel, O.; Haberer, T.; et al. High Control Rates of Proton- and Carbon-Ion-Beam Treatment with Intensity-Nidulated Active Raster Scanning in 101 Patients With Skull Base Chondrosarcoma at the Heidelberg Ion Beam Therapy Center. Cancer 2018, 124, 2036–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagersberg, M.; Rahal, A.E.; Dammann, P.; Merkler, D.; Weber, D.C.; Schaller, K. Clival chordoma: A single-centre outcome analysis. Acta Neurochir. 2017, 159, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koto, M.; Ikawa, H.; Kaneko, T.; Hagiwara, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Tsuji, H. Long-term outcomes of skull base chordoma treated with high-dose carbon-ion radiotherapy. Head Neck. 2020, 42, 2607–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hottinger, A.L.; Bojaxhiu, B.; Ahlhelm, F.; Walser, M.; Bachtiary, B.; Zepter, S.; Lomax, T.; Pica, A.; Weber, D.C. Prognostic impact of the “Sekhar grading system for cranial Chordomas” in patients treated with pencil beam scanning proton therapy: An institutional analysis. Radia. Oncol. 2020, 15, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannalfi, A.; D’Ippolito, E.; Riva, G.; Molinelli, S.; Gandini, S.; Viselner, G.; Fiore, M.R.; Vischioni, B.; Vitolo, V.; Bonora, M.; et al. Proton and carbon ion radiotherapy in skull base chordomas: A prospective study based on a dual particle and a patient-customized treatment strategy. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.C.; Badiyan, S.; Malyapa, R.; Albertini, F.; Bolsi, A.; Lomax, A.J.; Schneider, R. Long-term outcomes and prognostic factors of skull-base chondrosarcoma patients treated with pencil-beam scanning proton therapy at the Paul Scherrer Institute. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, A.L.; Rotondo, R.L.; Rutenberg, M.S.; Indelicato, D.J.; De Leo, A.; Rao, D.; Patel, J.; Morris, C.G.; Mendenhall, W.M. Clinical Outcomes Following Dose-Escalated Proton Therapy for Skull-Base Chordoma. Int. J. Part Ther. 2021, 8, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, G.; Cavallo, I.; Gandini, S.; Ingargiola, R.; Pecorilla, M.; Imparato, S.; Rossi, E.; Mirandola, A.; Ciocca, M.; Orlandi, E.; et al. Particle Radiotherapy for Skull Base Chondrosarcoma: A Clinical Series from Italian National Center for Oncological Hadrontherapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattke, M.; Ohlinger, M.; Bougatf, N.; Harrabi, S.; Wolf, R.; Seidensaal, K.; Welzel, T.; Röder, F.; Gerum, S.; Ellerbrock, M.; et al. Proton and carbon ion beam treatment with active raster scanning method in 147 patients with skull base chordoma at the Heidelberg Ion Beam Therapy Center—A single-center experience. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2023, 199, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eide, J.G.; Kshirsagar, R.S.; Harris, J.C.; Civantos, A.; Brody, R.M.; Lee, J.Y.K.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Lazor, J.W.; Nabavizadeh, A.; Wang, B.Y.; et al. Multi-institutional review of sinonasal and skull base chondrosarcoma: 20-year experience. Head Neck 2022, 44, 2686–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Laack, N.; Mahajan, A.; Choby, G.; O’Brien, E.; Stokken, J.; Janus, J.; Van Gompel, J.J. Analysis of Early Outcomes of Pencil Beam Proton Therapy Compared with Passive Scattering Proton Therapy for Clival Chordoma. World Neurosurg. 2023, 171, e644–e653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Warade, A.; Jha, A.K.; Misra, B.K. Skull Base Chordoma: Long-Term Observation and Evaluation of Prognostic Factors after Surgical Resection. Neurol. India 2021, 69, 1608–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napieralska, A.; Blamek, S. Intracranial chordoma: Radiosurgery, hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy and treatment outcomes. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2021, 26, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
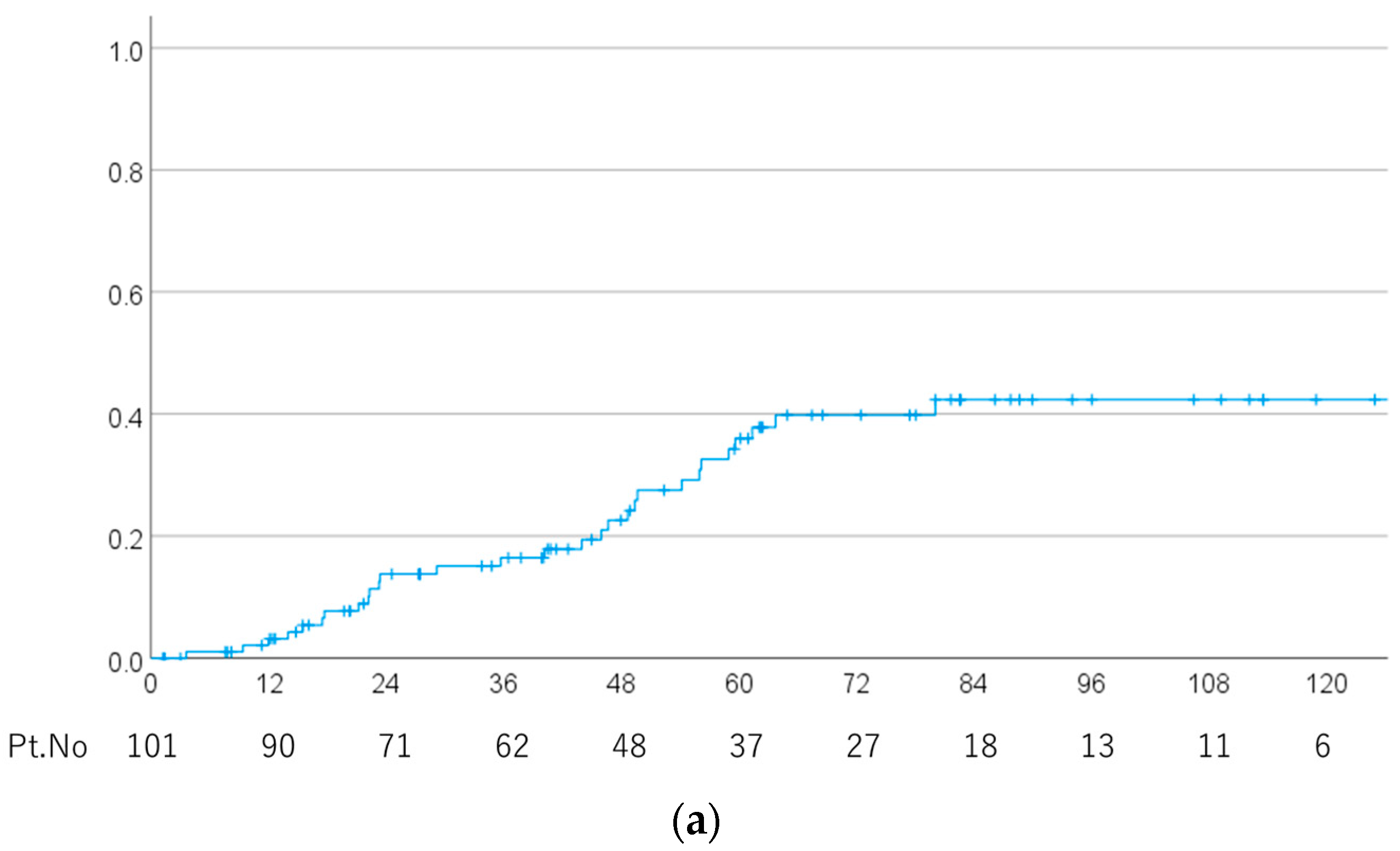
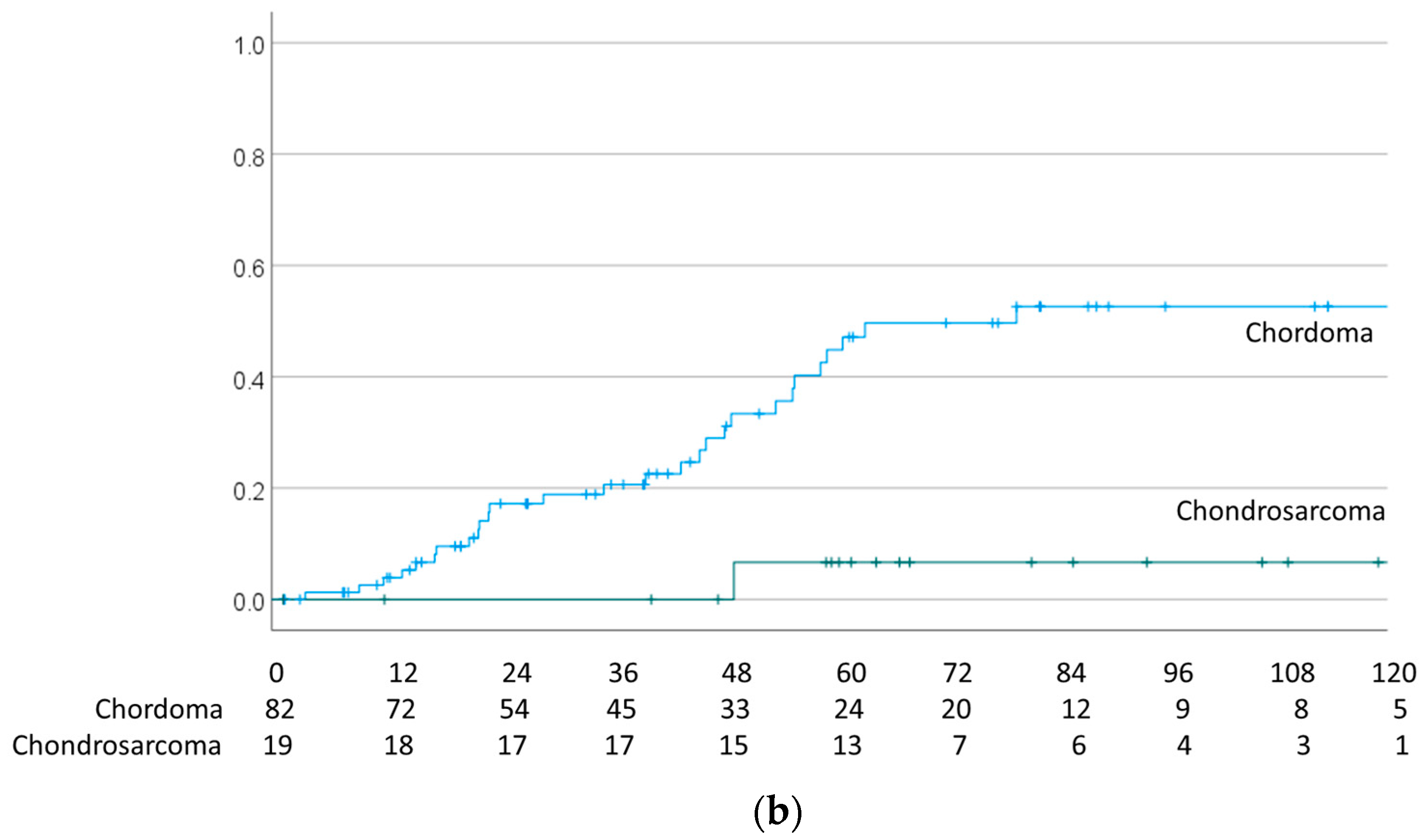
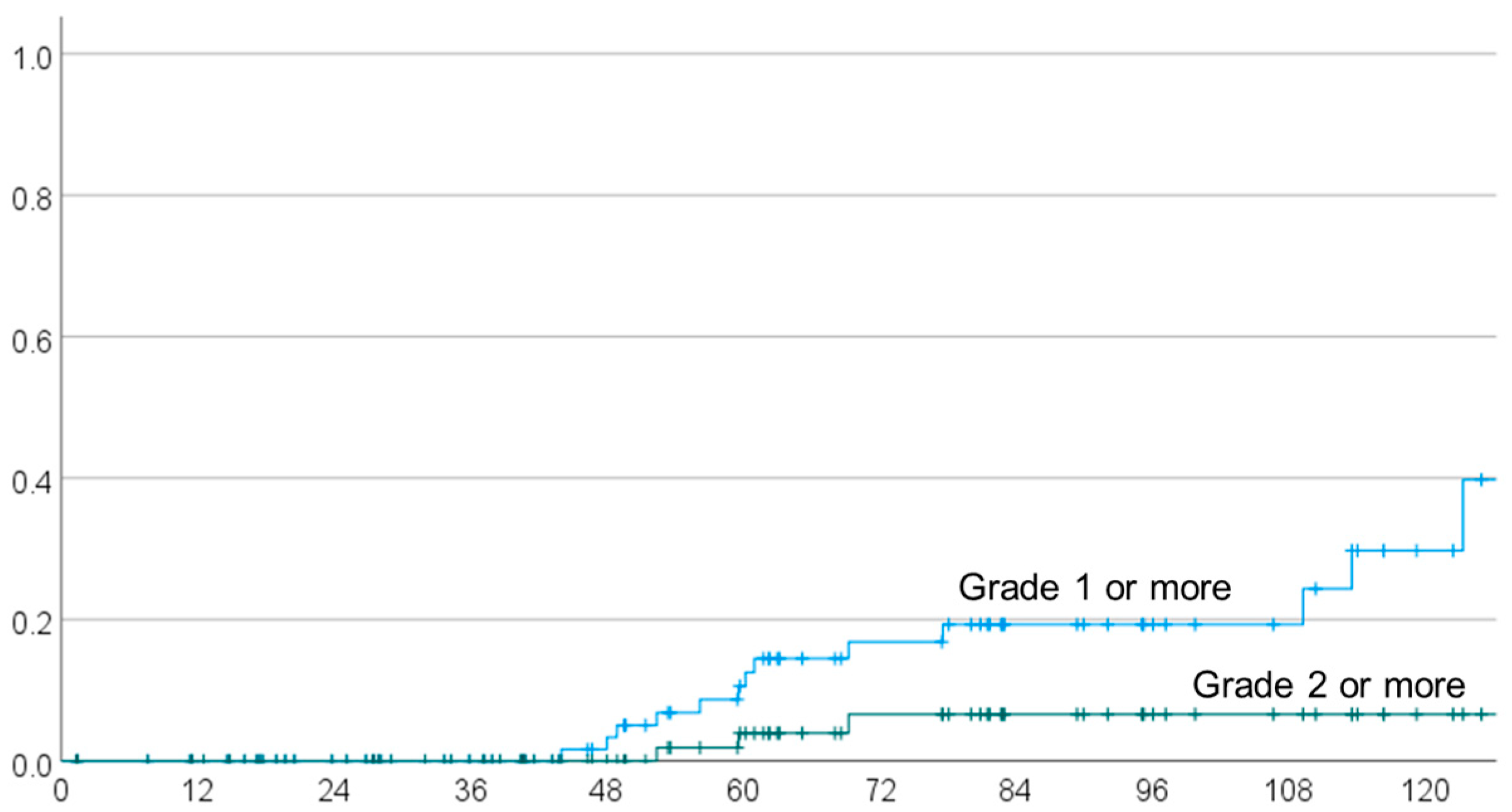

| Characteristics | Number | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 5–78 (median 51) | |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 46 | 46% |
| Female | 55 | 54% |
| Initial treatment | ||
| Yes | 84 | 83% |
| No | 17 | 17% |
| ECOG performance status | ||
| 0 | 72 | 71% |
| 1 | 27 | 27% |
| 2 | 1 | 1% |
| 3 | 1 | 1% |
| Surgical approach | ||
| Endonasal surgery | 75 | 74% |
| Others | 23 | 23% |
| Unknown | 3 | 3% |
| Surgical result | ||
| Gross-subtotal resection | 61 | 60% |
| Partial resection | 32 | 32% |
| Biopsy or non-resection | 8 | 8% |
| Pathological findings | ||
| Chordoma | 83 | 82% |
| Condrosarcoma | 18 | 18% |
| Tumor maximum diameter (mm) | 0–90 (median 20) | |
| <30 | 51 | 50% |
| 30–49 | 14 | 14% |
| ≥50 | 15 | 15% |
| Total dose (GyE) | ||
| <78.4 GyE | 44 | 44% |
| ≥78.4 GyE | 57 | 56% |
| Dose per fraction (GyE) | ||
| ≤2 GyE | 82 | 81% |
| ≥2 GyE | 19 | 19% |
| Hyperfractionated | ||
| Yes | 71 | 70% |
| No | 30 | 30% |
| Biological effective dose (α/β = 2) | ||
| <135 GyE | 80 | 79% |
| 135 GyE or more | 21 | 21% |
| Biological effective dose (α/β = 10) | ||
| <89.5 GyE | 96 | 95% |
| 89.5 GyE or more | 5 | 5% |
| Factors | PT Number | 5-Year (%) | Mean (Months) | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||||
| ≤50 | 50 | 30.1 | 133.9 | 109.3–158.5 | |
| >50 | 51 | 41.3 | 100.9 | 81.8–119.9 | 0.439 |
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 46 | 34.0 | 140.2 | 117.3–163.0 | |
| Female | 55 | 49.8 | 97.1 | 75.2–119.1 | 0.050 |
| Performance status | |||||
| 0 | 72 | 33.8 | 133.1 | 113.7–152.5 | |
| 1–3 | 29 | 41.8 | 83.8 | 58.6–109.0 | 0.137 |
| Initial treatment | |||||
| No | 17 | 61.2 | 62.0 | 31.8–92.2 | |
| Yes | 84 | 29.1 | 134.6 | 116.1–153.1 | 0.001 |
| Tumor maximum diameter (mm) | |||||
| <30 | 51 | 25.9 | 110.8 | 93.7–128.0 | |
| ≥30 | 29 | 59.6 | 96.5 | 70.2–122.8 | 0.025 |
| Surgical approach | |||||
| Endonasal surgery | 75 | 37.4 | 118.9 | 97.3–140.4 | |
| Others | 23 | 31.8 | 110.2 | 88.2–132.3 | 0.365 |
| Result of surgery | |||||
| Biopsy or partial | 40 | 42.4 | 110.9 | 85.3–136.5 | |
| Gross-subtotal resection | 61 | 31.1 | 117.7 | 100.4–134.9 | 0.242 |
| Pathology | |||||
| Chordoma | 83 | 44.0 | 111.5 | 91.4–131.6 | |
| Chondrosarcoma | 18 | 7.1 | 136.5 | 123.9–149.1 | 0.006 |
| Total dose (Gy) | |||||
| <78.4 | 44 | 45.4 | 112.2 | 85.5–138.8 | |
| ≥78.4 | 57 | 38.0 | 121.6 | 102.7–140.4 | 0.133 |
| Dose per fraction | |||||
| ≤2 | 82 | 29.2 | 109.5 | 93.2–125.9 | |
| >2 | 19 | 20.3 | 138.3 | 98.0–178.7 | 0.445 |
| Hyperfractionated | |||||
| Yes | 71 | 33.2 | 117.1 | 99.9–134.3 | |
| No | 30 | 40.9 | 113.3 | 80.7–145.9 | 0.242 |
| BEDGy2 | |||||
| >135 | 80 | 36.0 | 112.2 | 95.8–128.7 | |
| ≤135 | 21 | 31.6 | 123.9 | 84.1–163.8 | 0.990 |
| BEDGy10 | |||||
| >89.5 | 96 | 35.4 | 112.4 | 97.2–127.6 | |
| ≤89.5 | 5 | 46.7 | 115.3 | 42.2–188.4 | 0.739 |
| (a) | |||
| Factors | Odds Ratio | OR Range | p-Value |
| Radiation Necrosis | |||
| BEDGy10 | 1.211 | 1.037–1.414 | 0.016 |
| Total dose | 0.111 | 0.065–1.290 | 0.005 |
| Pathology | 3.587 | 0.790–16.292 | 0.097 |
| Gender | 0.290 | 0.065–1.290 | 0.103 |
| Local recurrence | |||
| Pathology | 0.115 | 0.013–0.988 | 0.049 |
| Tumor maximum diameter | 4.354 | 1.487–12.746 | 0.008 |
| (b) | |||
| Factors | Odds Ratio | OR Range | p-Value |
| Radiation Necrosis | |||
| BEDGy10 | 1.293 | 1.002–1.670 | 0.049 |
| Surgical approach | 6.540 | 0.584–73.221 | 0.126 |
| Total dose | 0.070 | 0.008–0.592 | 0.015 |
| Age | 1.070 | 1.001–1.144 | 0.046 |
| Local recurrence | |||
| Tumor maximum diameter | 3.842 | 1.296–11.395 | 0.016 |
| Factors | PT Number | 5-Year (%) | Mean (Months) | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||||
| ≤50 | 50 | 7.1 | 163.0 | 139.8–186.3 | |
| >50 | 51 | 14.3 | 118.6 | 97.6–139.5 | 0.308 |
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 46 | 12.6 | 141.0 | 113.1–169.0 | |
| Female | 55 | 8.0 | 161.4 | 139.1–183.8 | 0.274 |
| Performance status | |||||
| 0 | 72 | 8.9 | 151.7 | 129.0–173.8 | |
| 1–3 | 29 | 17.9 | 119.3 | 96.2–142.4 | 0.613 |
| Initial treatment | |||||
| No | 17 | 25.0 | 121.5 | 84.5–158.4 | |
| Yes | 84 | 9.7 | 149.5 | 128.1–171.0 | 0.894 |
| Tumor maximum diameter (mm) | |||||
| <30 | 51 | 24.4 | 128.5 | 97.5–159.5 | |
| ≥30 | 29 | 3.8 | 160.7 | 133.9–187.5 | 0.072 |
| Surgical approach | |||||
| Endonasal surgery | 75 | 12.9 | 140.6 | 113.9–167.2 | |
| Others | 23 | 5.3 | 167.6 | 143.1–192.0 | 0.179 |
| Results of surgery | |||||
| Biopsy or partial | 40 | 3.3 | 158.9 | 133.2–184.5 | |
| Gross-subtotal resection | 61 | 17.7 | 123.0 | 101.8–144.3 | 0.154 |
| Pathology | |||||
| Chordoma | 83 | 9.4 | 157.0 | 134.6–179.4 | |
| Chondrosarcoma | 18 | 13.8 | 110.9 | 89.1–132.7 | 0.146 |
| Total dose (Gy) | |||||
| <78.4 | 44 | 22.1 | 145.0 | 117.6–172.5 | |
| ≥78.4 | 57 | 0.0 | 136.5 | 116.3–156.7 | 0.374 |
| Dose per fraction | |||||
| ≤2 | 82 | 4.5 | 144.7 | 130.9–158.6 | |
| >2 | 19 | 30.2 | 117.7 | 81.5–153.9 | 0.011 |
| Hyperfractionated | |||||
| Yes | 71 | 144.2 | 128.7–159.7 | ||
| No | 30 | 127.1 | 94.5–159.7 | 0.027 | |
| BEDGy2 | |||||
| <135 | 80 | 4.6 | 143.7 | 129.0–158.3 | |
| ≥135 | 21 | 28.0 | 122.3 | 87.1–157.5 | 0.026 |
| BEDGy10 | |||||
| <89.5 | 96 | 13.3 | 134.6 | 118.7–150.5 | |
| ≥89.5 | 5 | 50.0 | 88.1 | 31.7–144.4 | 0.016 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahashi, M.; Mizumoto, M.; Oshiro, Y.; Kino, H.; Akutsu, H.; Nakai, K.; Sumiya, T.; Ishikawa, E.; Maruo, K.; Sakurai, H. Risk Factors for Radiation Necrosis and Local Recurrence after Proton Beam Therapy for Skull Base Chordoma or Chondrosarcoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 5687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235687
Takahashi M, Mizumoto M, Oshiro Y, Kino H, Akutsu H, Nakai K, Sumiya T, Ishikawa E, Maruo K, Sakurai H. Risk Factors for Radiation Necrosis and Local Recurrence after Proton Beam Therapy for Skull Base Chordoma or Chondrosarcoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(23):5687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235687
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahashi, Mizuki, Masashi Mizumoto, Yoshiko Oshiro, Hiroyoshi Kino, Hiroyoshi Akutsu, Kei Nakai, Taisuke Sumiya, Eiichi Ishikawa, Kazushi Maruo, and Hideyuki Sakurai. 2023. "Risk Factors for Radiation Necrosis and Local Recurrence after Proton Beam Therapy for Skull Base Chordoma or Chondrosarcoma" Cancers 15, no. 23: 5687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235687
APA StyleTakahashi, M., Mizumoto, M., Oshiro, Y., Kino, H., Akutsu, H., Nakai, K., Sumiya, T., Ishikawa, E., Maruo, K., & Sakurai, H. (2023). Risk Factors for Radiation Necrosis and Local Recurrence after Proton Beam Therapy for Skull Base Chordoma or Chondrosarcoma. Cancers, 15(23), 5687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235687







