Combined Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Infeasible for Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation: A Comparative Study with General Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation Outcomes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
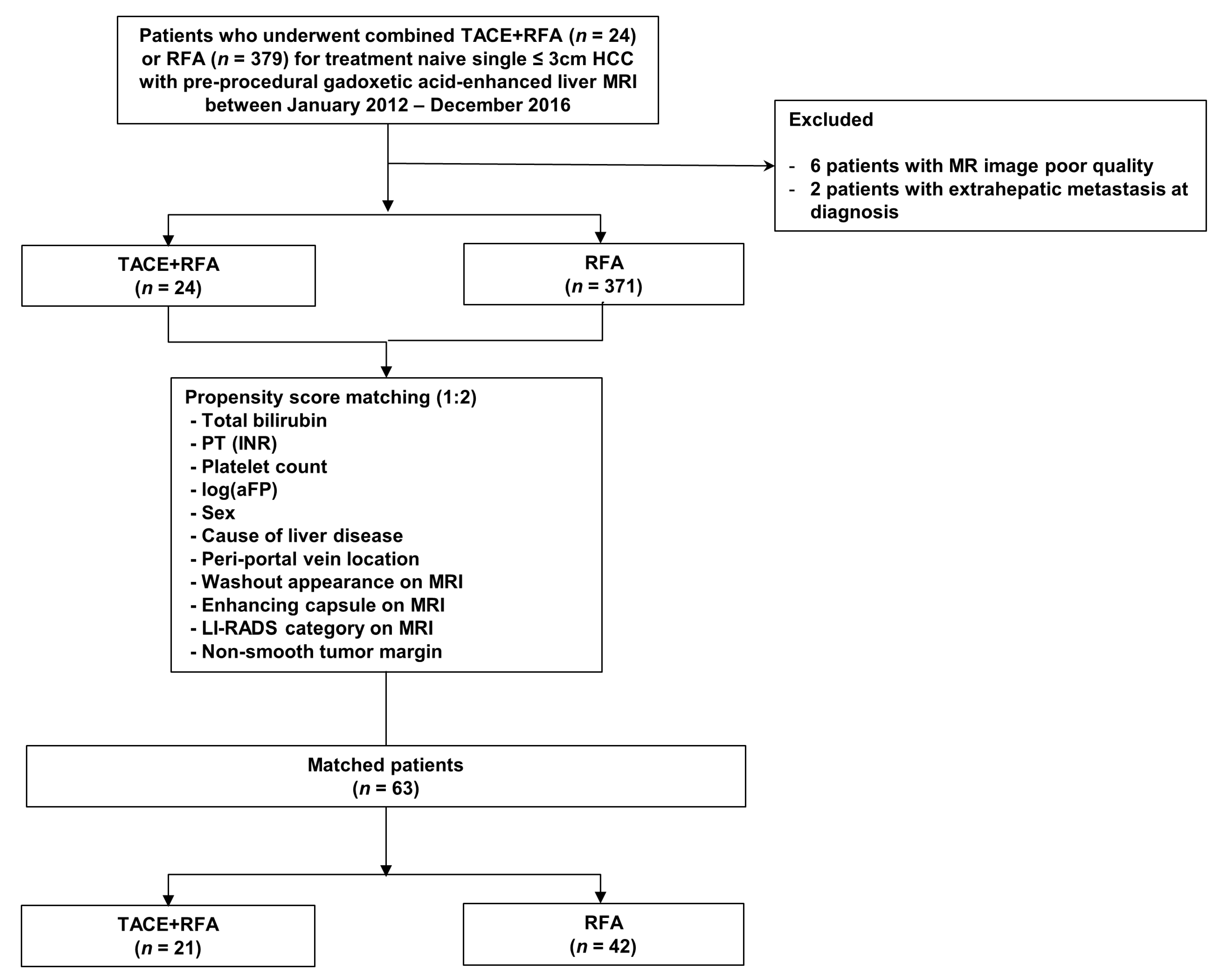
2.1. Patients
2.2. Clinical and Laboratory Factors
2.3. Image Analysis
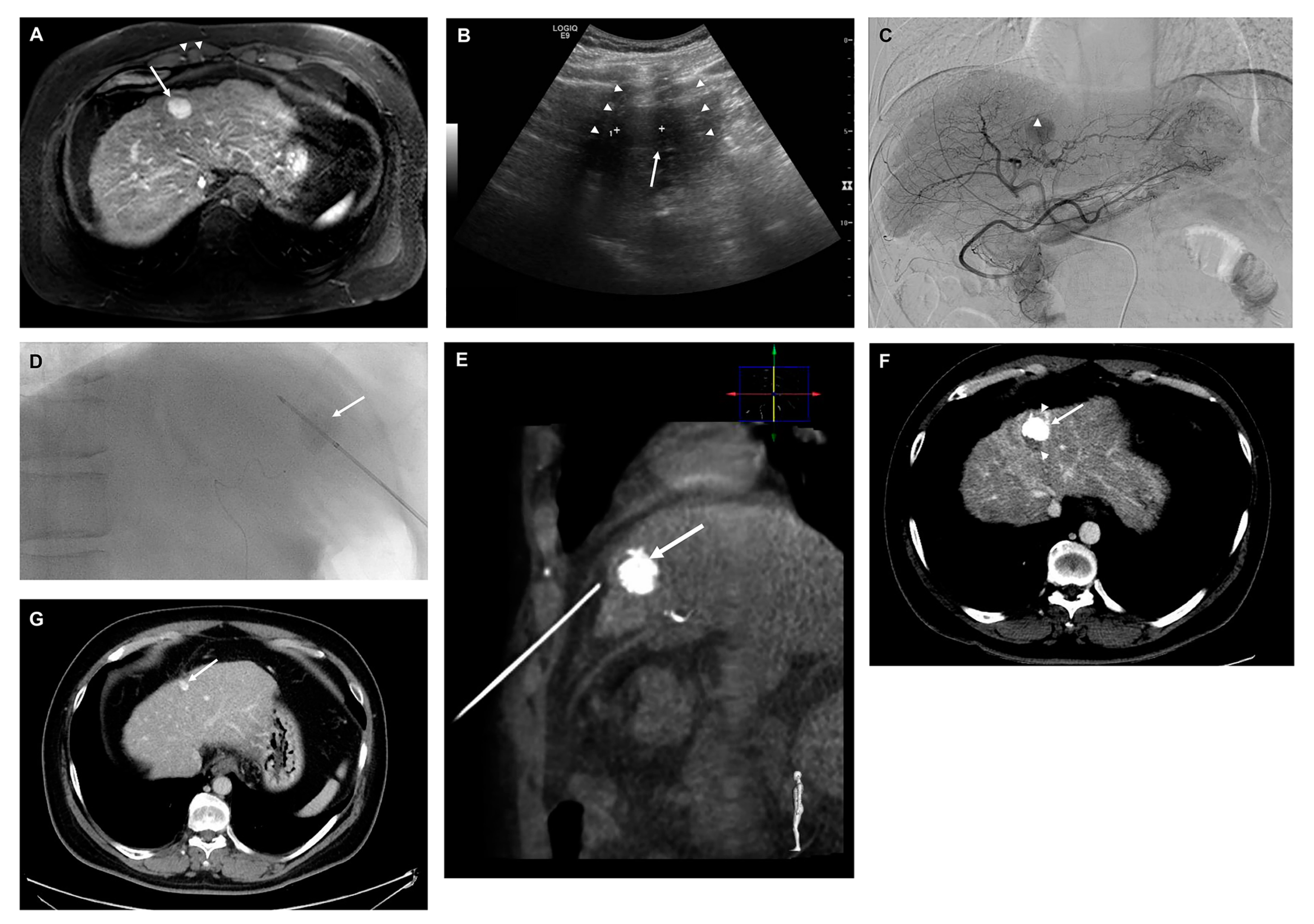
2.4. TACE + RFA and RFA Procedure and Follow-Up Protocol after Treatment
2.5. Outcome Assessment
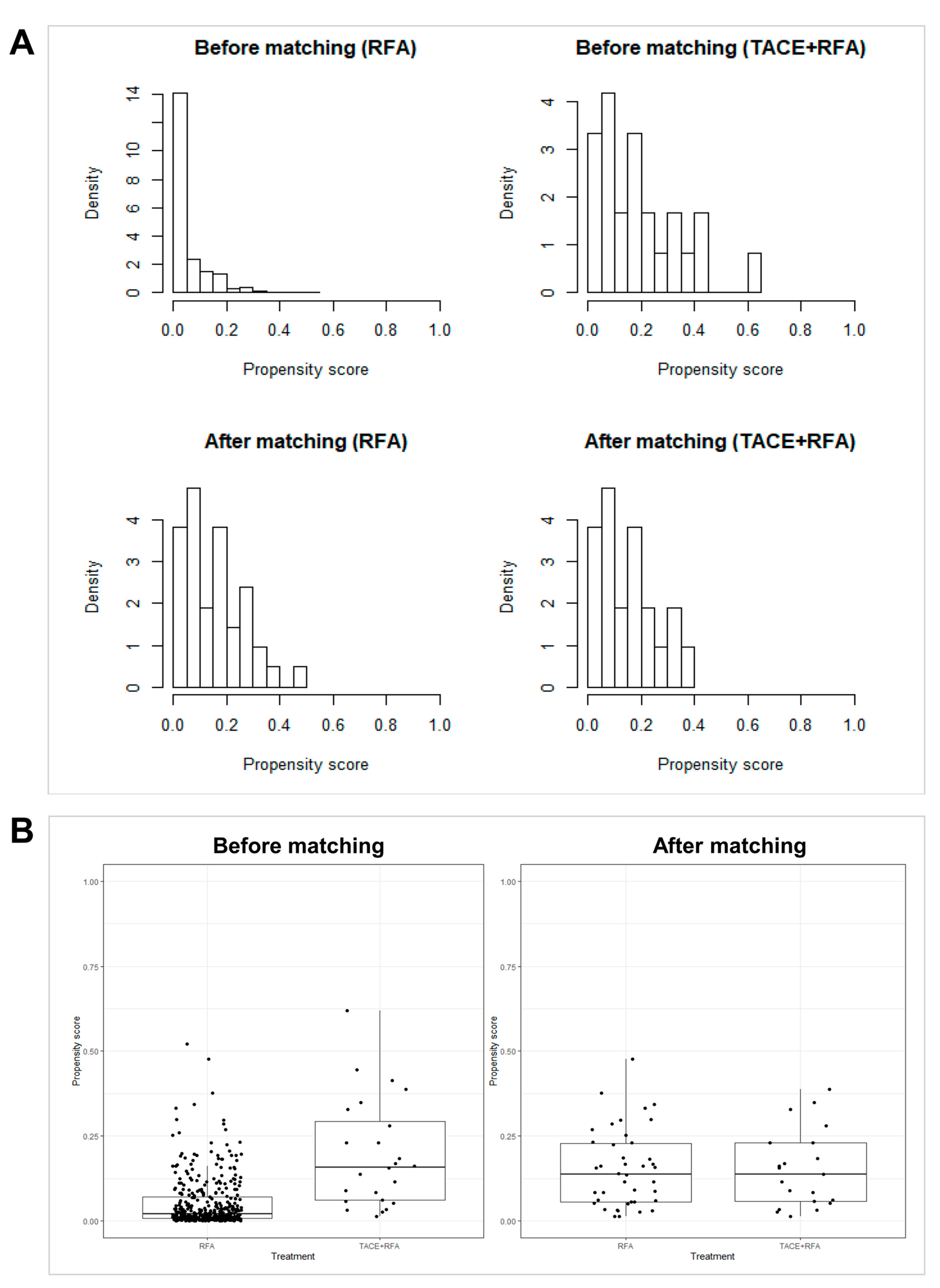
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
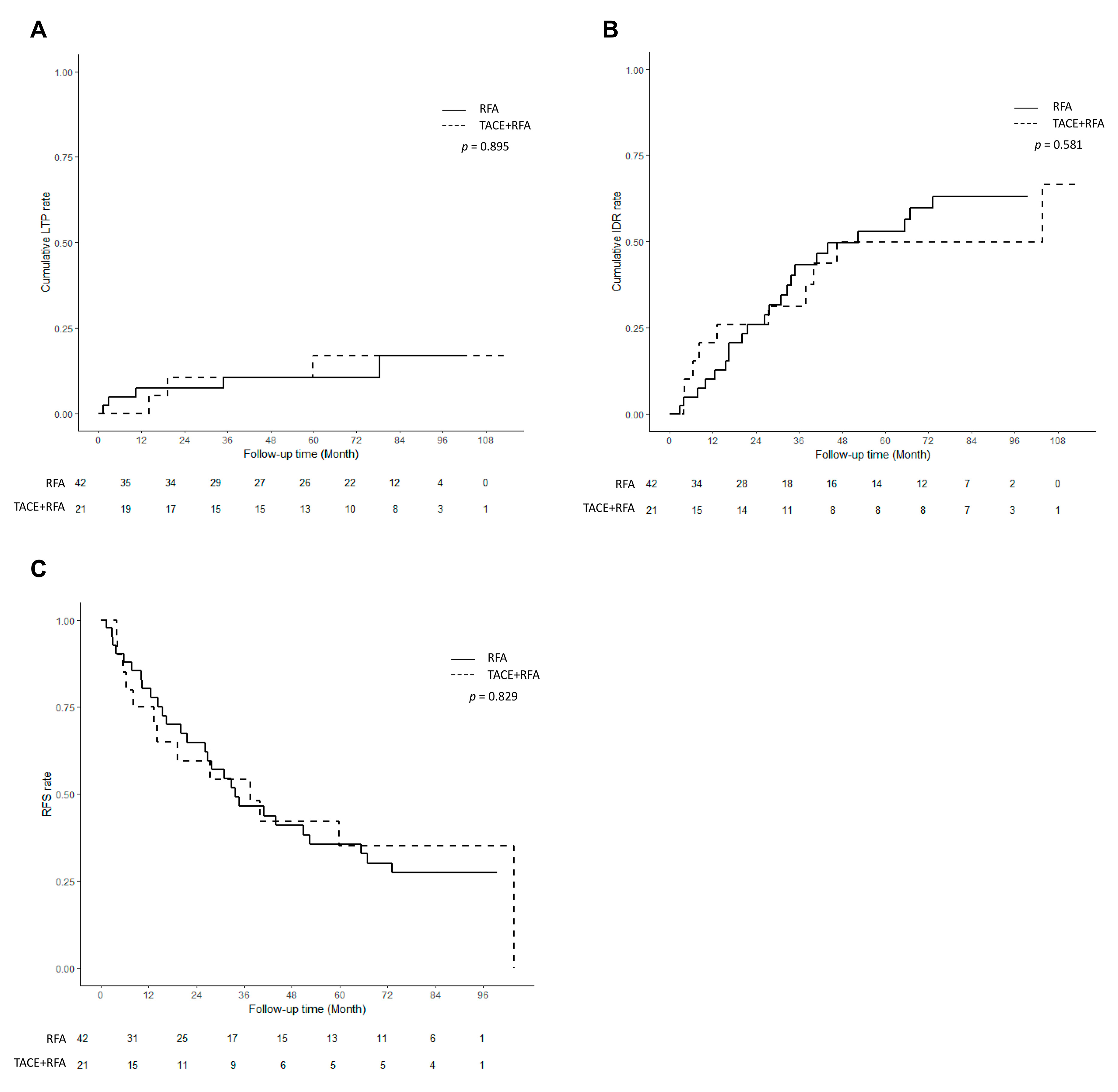
3.2. Comparison of Therapeutic Outcomes before PS Matching
3.3. Comparison of Therapeutic Outcomes after PS Matching
3.4. Multivariable Analysis Using All Patients for Each Outcome
3.5. Inter-Reader Agreement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Corrigendum to “EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma” [J Hepatol 69 (2018) 182–236]. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Liver Cancer, A.; National Cancer Center, K. 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Korean J. Radiol. 2022, 23, 1126–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Rhim, H.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, D.; Lee, W.J.; Lim, H.K. Planning sonography to assess the feasibility of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 190, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, S.W.; Hwang, J.H.; Jung, S.I.; Jeon, H.J.; Kwon, W.K. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of small hepatocellular carcinoma invisible on both ultrasonography and unenhanced CT: A preliminary study of combined treatment with transarterial chemoembolisation. Br. J. Radiol. 2009, 82, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargellini, I.; Sacco, R.; Bozzi, E.; Bertini, M.; Ginanni, B.; Romano, A.; Cicorelli, A.; Tumino, E.; Federici, G.; Cioni, R.; et al. Transarterial chemoembolization in very early and early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients excluded from curative treatment: A prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, D.; Cho, S.K.; Shin, S.W.; Park, K.B.; Park, H.S.; Choo, S.W.; Do, Y.S.; Choo, I.W.; Lee, M.W.; Rhim, H.; et al. Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinomas Not Feasible for Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation: Comparison of Transarterial Chemoembolization Alone and Combined Therapy with Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2016, 39, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veltri, A.; Moretto, P.; Doriguzzi, A.; Pagano, E.; Carrara, G.; Gandini, G. Radiofrequency thermal ablation (RFA) after transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) as a combined therapy for unresectable non-early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Eur. Radiol. 2006, 16, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, M.; Numata, K.; Kondou, M.; Nozaki, A.; Morita, S.; Tanaka, K. Midterm outcomes in patients with intermediate-sized hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized controlled trial for determining the efficacy of radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Cancer 2010, 116, 5452–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, M.S.; Xu, L.; Liang, H.H.; Lin, X.J.; Guo, R.P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Lau, W.Y. Radiofrequency ablation with or without transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Xu, L.F.; Sun, H.L.; Chen, Y.T. Meta-analysis of radiofrequency ablation in combination with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 3872–3882. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Lee, M.W.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Han, J.K. Evaluation of a serum tumour marker-based recurrence prediction model after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.S.; Raman, S.S.; Limanond, P.; Aziz, D.; Economou, J.; Busuttil, R.; Sayre, J. Influence of large peritumoral vessels on outcome of radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2003, 14, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, T.W.; Lim, H.K.; Lee, M.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Rhim, H.; Lee, W.J.; Paik, Y.H.; Kim, M.J.; Ahn, J.H. Long-term Therapeutic Outcomes of Radiofrequency Ablation for Subcapsular versus Nonsubcapsular Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matched Study. Radiology 2016, 280, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.E.; Sinn, D.H.; Park, C.K. Preoperative gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI for predicting microvascular invasion in patients with single hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, K.A.; Jeong, H.T.; Park, Y.N. Hyperintense HCC on hepatobiliary phase images of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI: Correlation with clinical and pathological features. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 3877–3882. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kang, T.W.; Song, K.D.; Lee, M.W.; Rhim, H.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Sinn, D.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, K.; et al. Effect of Microvascular Invasion Risk on Early Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Surgery and Radiofrequency Ablation. Ann. Surg. 2021, 273, 564–571. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Solbiati, L.; Brace, C.L.; Breen, D.J.; Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; Chen, M.H.; Choi, B.I.; de Baere, T.; Dodd, G.D., 3rd; et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: Standardization of terminology and reporting criteria—A 10-year update. Radiology 2014, 273, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.J.; McDonald, J.S.; Kallmes, D.F.; Carter, R.E. Behind the numbers: Propensity score analysis-a primer for the diagnostic radiologist. Radiology 2013, 269, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, F.; Yang, G.; Singh, S.; Lu, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, F.; Tang, R. Combination of radiofrequency ablation with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: An up-to-date meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 7407–7413. [Google Scholar]
- Tamai, T.; Oshige, A.; Tabu, K.; Tabu, E.; Ijyuin, S.; Sakae, H.; Onishi, H.; Muromachi, K.; Saisyoji, A.; Oda, K.; et al. Utility of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation alone or combined with transarterial chemoembolization for early hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3199–3206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.H.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, H.K.; Ko, H.K.; Gwon, D.I.; Kim, P.N.; Sung, K.B.; Ko, G.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, S.H. Chemoembolization Combined with Radiofrequency Ablation for Medium-Sized Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity-Score Analysis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.M.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.E.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation with multiple electrodes for medium-sized hepatocellular carcinomas. Korean J. Radiol. 2012, 13, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Dual switching monopolar radiofrequency ablation using a separable clustered electrode: Comparison with consecutive and switching monopolar modes in ex vivo bovine livers. Korean J. Radiol. 2013, 14, 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Woo, S.; Hwang, E.J.; Hwang, I.; Choi, W.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Switching bipolar hepatic radiofrequency ablation using internally cooled wet electrodes: Comparison with consecutive monopolar and switching monopolar modes. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20140468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocquelet, A.; Aube, C.; Rode, A.; Cartier, V.; Sutter, O.; Manichon, A.F.; Boursier, J.; N’Kontchou, G.; Merle, P.; Blanc, J.F.; et al. Comparison of no-touch multi-bipolar vs. monopolar radiofrequency ablation for small HCC. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Abd El Aziz, M.A.; Tartaglia, N.; Ramai, D.; Mohan, B.P.; Cotsoglou, C.; Pusceddu, S.; Giacomelli, L.; Ambrosi, A.; Sacco, R. Microwave Ablation Versus Radiofrequency Ablation for Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Cancers 2020, 12, 3796. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Licinio, R.; Muscatiello, N.; Di Leo, A.; Barone, M. Transarterial chemoembolization: Evidences from the literature and applications in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2009–2019. [Google Scholar]
- Varela, M.; Real, M.I.; Burrel, M.; Forner, A.; Sala, M.; Brunet, M.; Ayuso, C.; Castells, L.; Montana, X.; Llovet, J.M.; et al. Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with drug eluting beads: Efficacy and doxorubicin pharmacokinetics. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 474–481. [Google Scholar]
- Facciorusso, A.; Serviddio, G.; Muscatiello, N. Transarterial radioembolization vs chemoembolization for hepatocarcinoma patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Granito, A.; Facciorusso, A.; Sacco, R.; Bartalena, L.; Mosconi, C.; Cea, U.V.; Cappelli, A.; Antonino, M.; Modestino, F.; Brandi, N.; et al. TRANS-TACE: Prognostic Role of the Transient Hypertransaminasemia after Conventional Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciorusso, A.; Bellanti, F.; Villani, R.; Salvatore, V.; Muscatiello, N.; Piscaglia, F.; Vendemiale, G.; Serviddio, G. Transarterial chemoembolization vs bland embolization in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, Y.J.; Ahn, C.S.; Kim, K.H.; Park, K.M.; Moon, K.M.; Moon, D.B.; Ha, T.Y.; Yu, E.S.; et al. Prognostic impact of sarcomatous change of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients undergoing liver resection and liver transplantation. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2008, 12, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| TACE + RFA (n = 24) | RFA (n = 371) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) * | 57.5 (39–77) | 58 (31–85) | 0.588 |
| Sex (male) | 22 (91.7) | 272 (73.3) | 0.079 |
| Cause of liver disease | 0.023 | ||
| HBV | 12 (50) | 279 (75.2) | |
| HCV | 5 (20.8) | 38 (10.2) | |
| Alcohol | 6 (25) | 35 (9.4) | |
| Others | 1 (4.2) | 19 (5.1) | |
| Albumin (mg/dL) | 4.2 (1.9–5.1) | 4 (2.8–4.6) | 0.159 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.6 (0.2–4.5) | 0.7 (0.3–2.7) | 0.123 |
| Prothrombin time (INR) | 1.1 (0.9–1.6) | 1.2 (1–1.5) | 0.092 |
| AST (U/L) | 33 (10–552) | 33 (18–88) | 0.299 |
| Platelet count (K) | 109 (50–475) | 87.5 (27–290) | 0.102 |
| ALBI grade | 0.433 | ||
| 1 | 14 (58.3) | 253 (68.2) | |
| 2 | 10 (41.7) | 112 (30.2) | |
| 3 | 0 (0) | 6 (1.6) | |
| APRI * | 0.891 (0.422–8.148) | 0.786 (0.145–12.545) | 0.425 |
| Child–Pugh classification | 0.907 | ||
| A | 23 (95.8) | 345 (93) | |
| B | 1 (4.2) | 26 (7) | |
| log(AFP) (ng/mL) * | 1.75 (0.74–3.28) | 2.10 (0.26–7.70) | <0.001 |
| PIVKA-II (mAU/mL]) * | 27 (12–268) | 22 (9–11,078) | 0.549 |
| MoRAL score * | 62.7 (41.6–190.4) | 61.6 (36.3–1164.6) | 0.974 |
| Tumor size (cm) * | 1.5 (1–2.7) | 1.6 (1–2.9) | 0.743 |
| Tumor location | |||
| Periportal vein | 5 (20.8) | 21 (5.7) | 0.013 |
| Perihepatic vein | 1 (4.2) | 33 (8.9) | 0.671 |
| Subcapsular (reference = non-subcapsular) | 11 (45.8) | 129 (34.8) | 0.510 |
| Arterial phase hyperenhancement | 0.319 | ||
| No | 2 (8.3) | 13 (3.5) | |
| Non-rim | 21 (87.5) | 319 (86) | |
| Rim | 1 (4.2) | 39 (10.5) | |
| Washout appearance | 8 (33.3) | 194 (52.3) | 0.112 |
| Enhancing capsule | 5 (20.8) | 155 (41.8) | 0.070 |
| Peripheral washout | 0 (0) | 4 (1.1) | 1.000 |
| Progressive enhancement | 0 (0) | 13 (3.5) | 0.732 |
| Transitional phase targetoid | 0 (0) | 9 (2.4) | 0.947 |
| Hepatobiliary phase targetoid | 0 (0) | 12 (3.2) | 0.779 |
| Diffusion weighted image targetoid | 1 (4.2) | 29 (7.8) | 0.792 |
| Non-targetoid LR-M feature | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| LI-RADS category | 0.006 | ||
| 3 | 13 (54.2) | 88 (23.7) | |
| 4 | 4 (16.7) | 56 (15.1) | |
| 5 | 6 (25) | 166 (44.7) | |
| M | 1 (4.2) | 61 (16.4) | |
| Peritumoral enhancement | 2 (8.3) | 74 (19.9) | 0.258 |
| Non-smooth margin | 2 (8.3) | 103 (27.8) | 0.064 |
| Peritumoral hypointensity | 1 (4.2) | 31 (8.4) | 0.732 |
| Low SI on hepatobiliary phase (reference = iso/high) | 21 (87.5) | 354 (95.4) | 0.217 |
| MVI high-risk group | 1 (4.2) | 31 (8.4) | 0.655 |
| After Propensity Score Matching | Before Matching TACE + RFA (n = 24), RFA (n = 371) | After Matching TACE + RFA (n = 21), RFA (n = 42) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | TACE + RFA (n = 21) | RFA (n = 42) | p | SMD | p | SMD | p |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL * | 0.70 (0.3–2.7) | 0.70 (0.2–4.5) | 0.546 | 0.357 | 0.123 | 0.166 | 0.591 |
| Prothrombin time, INR * | 1.12 (0.99–1.51) | 1.17 (0.96–1.6) | 0.741 | 0.376 | 0.092 | −0.090 | 0.768 |
| Platelet count, ×109/L * | 89.00 (27–290) | 88.00 (52–241) | 0.938 | −0.357 | 0.102 | 0.017 | 0.948 |
| log(AFP) * | 1.82 (0.74–3.28) | 1.71 (0.26–5.73) | 0.723 | −0.498 | 0.001 | −0.131 | 0.727 |
| Sex | 38 (66.7%) | 19 (90.5%) | 1.000 | −0.494 | 0.006 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Cause of liver disease | |||||||
| HBV | 12 (57.1%) | 25 (44.6%) | 0.953 | −0.533 | 0.026 | −0.047 | 0.865 |
| HCV | 5 (23.8%) | 9 (16.1%) | 0.291 | 0.230 | 0.055 | 0.857 | |
| Alcohol | 3 (14.3%) | 7 (12.5%) | 0.415 | 0.102 | −0.066 | 0.792 | |
| Others | 1 (4.8%) | 1 (1.8%) | −0.045 | 0.827 | 0.109 | 0.686 | |
| Periportal vein location | 3 (14.3%) | 7 (12.5%) | 0.790 | 0.452 | 0.089 | −0.066 | 0.816 |
| Washout appearance (PVP) | 7 (33.3%) | 11 (19.6%) | 0.544 | −0.386 | 0.073 | 0.148 | 0.610 |
| Enhancing capsule | 4 (19.0%) | 11 (19.6%) | 0.510 | −0.459 | 0.025 | −0.178 | 0.560 |
| LI-RADS category | |||||||
| 3 | 11 (52.4%) | 23 (41.1%) | 0.919 | 0.649 | 0.008 | −0.047 | 0.873 |
| 4 | 4 (19.0%) | 10 (17.9%) | 0.043 | 0.846 | −0.118 | 0.686 | |
| 5 | 5 (23.8%) | 8 (14.3%) | −0.419 | 0.045 | 0.109 | 0.686 | |
| M | 1 (4.8%) | 1 (1.8%) | −0.410 | 0.011 | 0.109 | 0.686 | |
| Non-smooth tumor margin | 2 (9.5%) | 3 (5.4%) | 0.743 | −0.519 | 0.004 | 0.079 | 0.792 |
| Local Tumor Progression | Intrahepatic Distant Recurrence | Recurrence-Free Survival | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||||||
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| TACE + RFA [RFA] | 1.026 (0.319–1.026) | 0.965 | 0.949 (0.501–0.949) | 0.872 | 1.094 (0.625–1.094) | 0.753 | ||||||
| Age | 1.016 (0.987–1.016) | 0.277 | 1.012 (0.996–1.012) | 0.143 | 1.023 (1.006–1.023) | 0.009 | 1.022 (1.008–1.022) | 0.002 | 1.025 (1.009–1.025) | 0.002 | ||
| Male [Female] | 0.865 (0.430–0.865) | 0.685 | 0.86 (0.6–0.86) | 0.409 | 1.047 (0.771–1.047) | 0.767 | ||||||
| Liver disease [HBV] | ||||||||||||
| HCV | 1.384 (0.581–1.384) | 0.463 | 1.513 (0.943–1.513) | 0.086 | 2.303 (1.575–2.303) | <0.001 | 1.838 (1.182–1.838) | 0.007 | ||||
| Alcohol | 0.920 (0.326–0.920) | 0.875 | 1.088 (0.663–1.088) | 0.737 | 1.253 (0.806–1.253) | 0.317 | 0.921 (0.553–0.921) | 0.753 | ||||
| Others | 1.366 (0.419–1.366) | 0.605 | 1.718 (0.95–1.718) | 0.074 | 1.551 (0.879–1.551) | 0.130 | 1.181 (0.628–1.181) | 0.605 | ||||
| Albumin (mg/dL) | 0.946 (0.541–0.946) | 0.845 | 0.486 (0.373–0.486) | <0.001 | 0.477 (0.338–0.477) | <0.001 | 0.474 (0.374–0.474) | <0.001 | 0.501 (0.370–0.501) | <0.001 | ||
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.871 (0.486–0.871) | 0.641 | 1.56 (1.203–1.56) | 0.001 | 1.532 (1.207–1.532) | <0.001 | 1.350 (0.992–1.35) | 0.056 | ||||
| ALBI grade | ||||||||||||
| Grade 2 | 1.232 (0.663–1.232) | 0.509 | 2.019 (1.486–2.019) | <0.001 | 2.189 (1.661–2.189) | <0.001 | ||||||
| Grade 3 | 4.255 (0.797–4.255) | 0.090 | 7.271 (2.269–7.271) | 0.001 | 5.070 (1.595–5.07) | 0.006 | ||||||
| PT (INR) | 0.642 (0.083–0.642) | 0.671 | 4.633 (1.894–4.633) | 0.001 | 5.047 (2.199–5.047) | <0.001 | ||||||
| AST (U/L) | 0.998 (0.987–0.998) | 0.650 | 1.004 (1.002–1.004) | <0.001 | 1.004 (1.002–1.004) | <0.001 | 1.009 (1.000–1.009) | 0.045 | ||||
| Platelet count (K) | 0.999 (0.993–0.999) | 0.603 | 0.995 (0.992–0.995) | 0.005 | 0.997 (0.993–0.997) | 0.096 | 0.996 (0.993–0.996) | 0.006 | 0.995 (0.991–0.995) | 0.030 | ||
| APRI | 0.980 (0.757–0.98) | 0.881 | 1.194 (1.101–1.194) | <0.001 | 1.169 (1.084–1.169) | <0.001 | 0.710 (0.492–0.71) | 0.069 | ||||
| log(AFP) (ng/mL) | 1.039 (0.878–1.039) | 0.653 | 1.116 (1.027–1.116) | 0.010 | 1.104 (1.023–1.104) | 0.011 | ||||||
| Child–Pugh B [reference = A] | 1.086 (0.337–1.086) | 0.890 | 2.494 (1.53–2.494) | <0.001 | 1.695 (0.956–1.695) | 0.071 | 2.291 (1.442–2.291) | <0.001 | ||||
| PIVKA-II | 1.000 (0.999–1.000) | 0.779 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.077 | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.141 | ||||||
| MoRAL > 68 | 1.190 (0.658–1.190) | 0.565 | 1.559 (1.144–1.559) | 0.005 | 1.484 (1.051–1.484) | 0.025 | 1.494 (1.128–1.494) | 0.005 | 1.475 (1.099–1.475) | 0.010 | ||
| Tumor size | 1.488 (0.78–1.488) | 0.227 | 1.533 (1.091–1.533) | 0.014 | 1.448 (0.995–1.448) | 0.053 | 1.552 (1.145–1.552) | 0.005 | 1.653 (1.190–1.653) | 0.003 | ||
| Peri-PV | 1.415 (0.508–1.415) | 0.507 | 0.967 (0.525–0.967) | 0.913 | 0.937 (0.535–0.937) | 0.821 | ||||||
| Peri-HV | 1.021 (0.366–1.021) | 0.969 | 0.682 (0.371–0.682) | 0.220 | 0.918 (0.566–0.918) | 0.727 | ||||||
| Subcapsular | 1.929 (1.088–1.929) | 0.024 | 1.898 (1.071–1.898) | 0.028 | 1.041 (0.767–1.041) | 0.795 | 1.140 (0.866–1.14) | 0.351 | ||||
| APHE [No] | ||||||||||||
| Non-rim | 1.654 (0.227–1.654) | 0.620 | 1.533 (0.629–1.533) | 0.347 | 1.395 (0.656–1.395) | 0.387 | ||||||
| Rim | 3.128 (0.391–3.128) | 0.283 | 0.936 (0.334–0.936) | 0.900 | 1.087 (0.456–1.087) | 0.851 | ||||||
| Washout app. | 1.386 (0.774–1.386) | 0.273 | 1.051 (0.782–1.051) | 0.740 | 0.967 (0.741–0.967) | 0.808 | ||||||
| Enhancing capsule | 1.216 (0.684–1.216) | 0.506 | 1.310 (0.975–1.31) | 0.073 | 1.536 (1.115–1.536) | 0.009 | 1.103 (0.842–1.103) | 0.475 | ||||
| Peripheral washout | 1.995 (0.274–1.995) | 0.495 | 1.813 (0.579–1.813) | 0.307 | 1.360 (0.435–1.36) | 0.597 | ||||||
| Progressive Enhancement | 1.958 (0.608–1.958) | 0.26 | 0.592 (0.220–0.592) | 0.300 | 0.747 (0.332–0.747) | 0.481 | ||||||
| TP targetoid | 0.812 (0.112–0.812) | 0.837 | 0.589 (0.188–0.589) | 0.364 | 0.446 (0.143–0.446) | 0.166 | ||||||
| HBP targetoid | 2.260 (0.701–2.260) | 0.172 | 0.651 (0.241–0.651) | 0.396 | 0.640 (0.264–0.640) | 0.325 | ||||||
| DWI targetoid | 1.799 (0.764–1.799) | 0.179 | 1.048 (0.607–1.048) | 0.865 | 1.061 (0.646–1.061) | 0.815 | ||||||
| Non-targetoid LR-M | 1.907 (0.989–1.907) | 0.054 | 1.859 (0.964–1.859) | 0.064 | 0.785 (0.51–0.785) | 0.270 | 0.864 (0.590–0.864) | 0.451 | ||||
| LR category | ||||||||||||
| 4 | 1.106 (0.393–1.106) | 0.849 | 1.150 (0.711–1.15) | 0.569 | 1.050 (0.685–1.050) | 0.822 | ||||||
| 5 | 1.271 (0.578–1.271) | 0.551 | 1.194 (0.822–1.194) | 0.353 | 1.027 (0.735–1.027) | 0.876 | ||||||
| M | 2.212 (0.932–2.212) | 0.072 | 0.885 (0.534–0.885) | 0.634 | 0.884 (0.567–0.884) | 0.586 | ||||||
| Peritumoral enhancement | 1.847 (0.988–1.847) | 0.054 | 1.426 (1.011–1.426) | 0.043 | 1.215 (0.879–1.215) | 0.238 | ||||||
| Non-smooth margin | 1.465 (0.801–1.465) | 0.215 | 1.058 (0.761–1.058) | 0.736 | 1.026 (0.760–1.026) | 0.865 | ||||||
| Peritumoral hypointensity | 1.047 (0.376–1.047) | 0.931 | 1.189 (0.721–1.189) | 0.497 | 0.896 (0.546–0.896) | 0.665 | ||||||
| Low SI on HBP [iso/high] | 0.937 (0.227–0.937) | 0.928 | 0.853 (0.400–0.853) | 0.679 | 0.967 (0.512–0.967) | 0.917 | ||||||
| MVI-high risk | 0.998 (0.357–0.998) | 0.997 | 1.151 (0.697–1.151) | 0.583 | 0.967 (0.596–0.967) | 0.891 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cha, D.I.; Lee, M.W.; Hyun, D.; Ahn, S.H.; Jeong, W.K.; Rhim, H. Combined Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Infeasible for Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation: A Comparative Study with General Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation Outcomes. Cancers 2023, 15, 5193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215193
Cha DI, Lee MW, Hyun D, Ahn SH, Jeong WK, Rhim H. Combined Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Infeasible for Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation: A Comparative Study with General Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation Outcomes. Cancers. 2023; 15(21):5193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215193
Chicago/Turabian StyleCha, Dong Ik, Min Woo Lee, Dongho Hyun, Soo Hyun Ahn, Woo Kyoung Jeong, and Hyunchul Rhim. 2023. "Combined Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Infeasible for Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation: A Comparative Study with General Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation Outcomes" Cancers 15, no. 21: 5193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215193
APA StyleCha, D. I., Lee, M. W., Hyun, D., Ahn, S. H., Jeong, W. K., & Rhim, H. (2023). Combined Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Infeasible for Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation: A Comparative Study with General Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation Outcomes. Cancers, 15(21), 5193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215193






