CD30 Lateral Flow and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for Detection of BIA-ALCL: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Specimens
2.3. Pathology and Immunohistochemistry
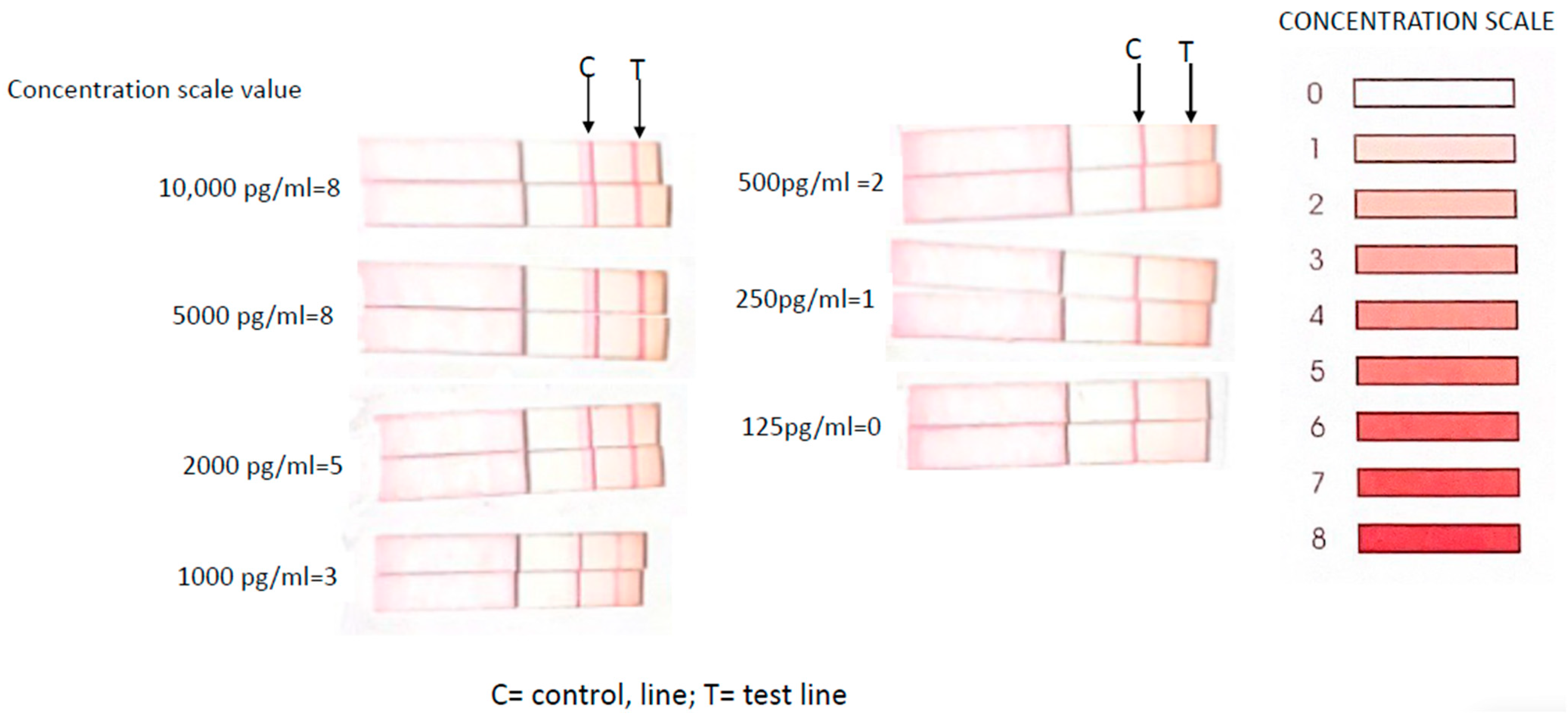
2.4. Lateral Flow Assay (LFA)
2.5. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
3. Results
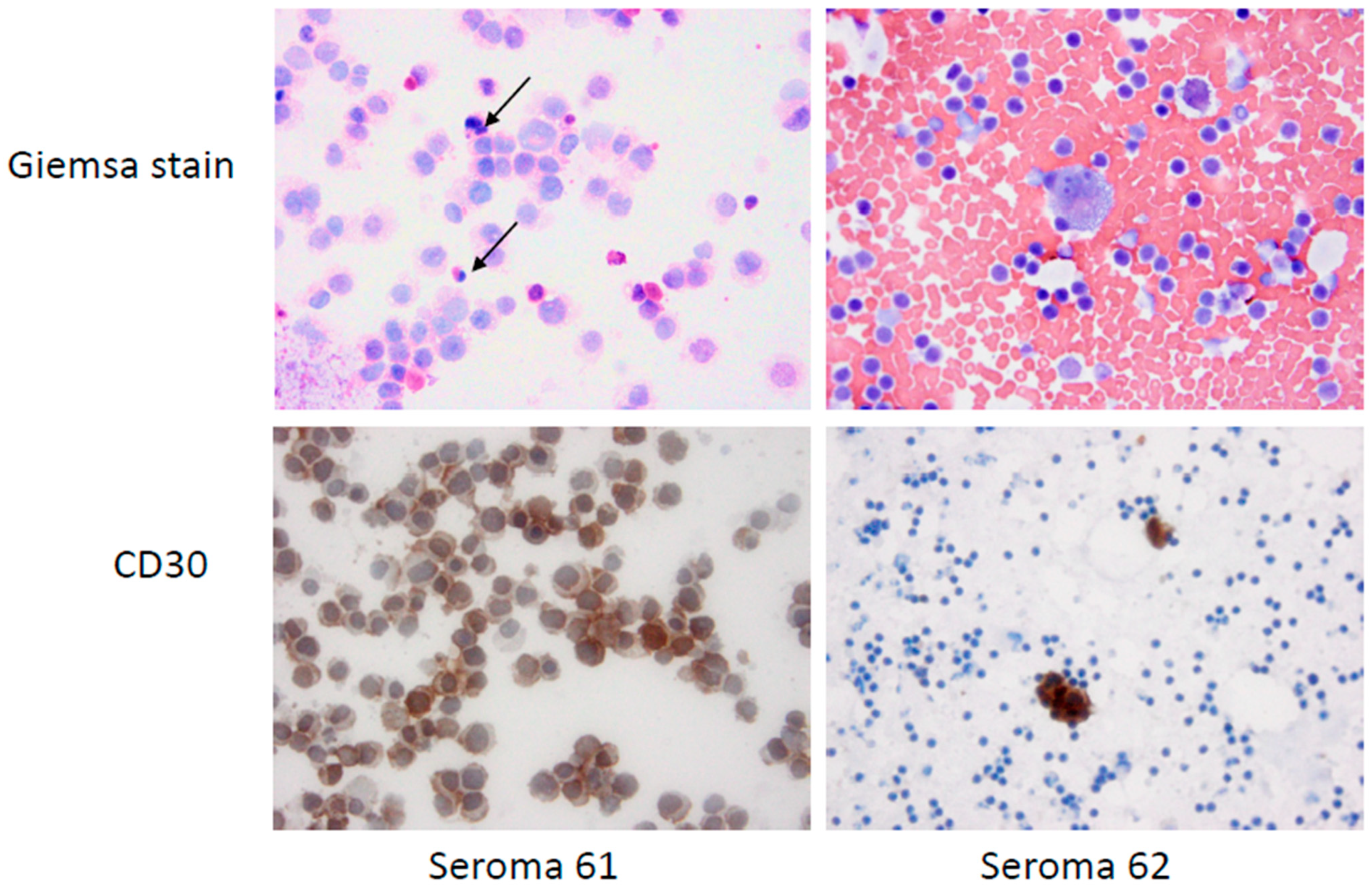
3.1. Pathology
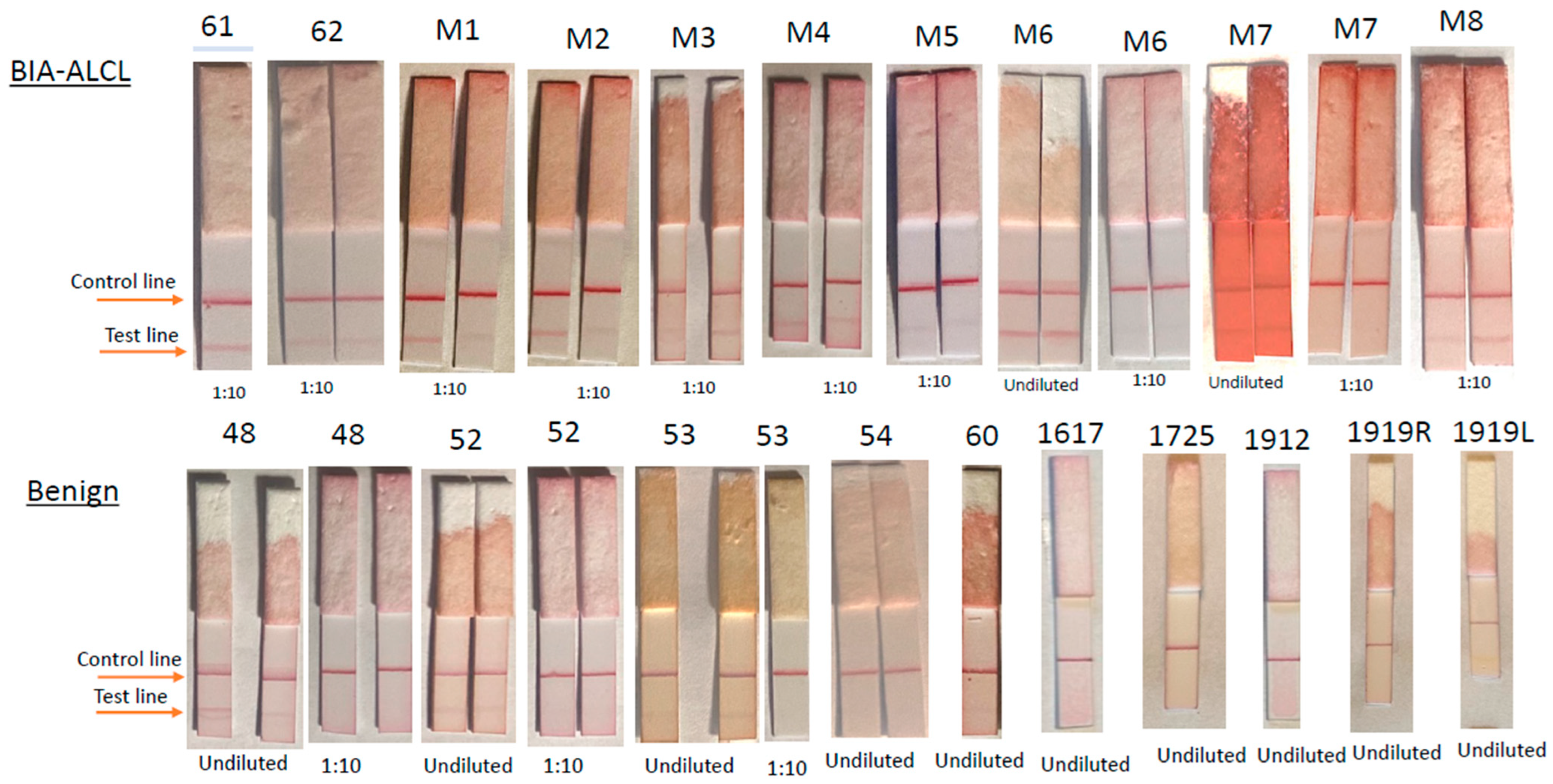
3.2. Lateral Flow Assay
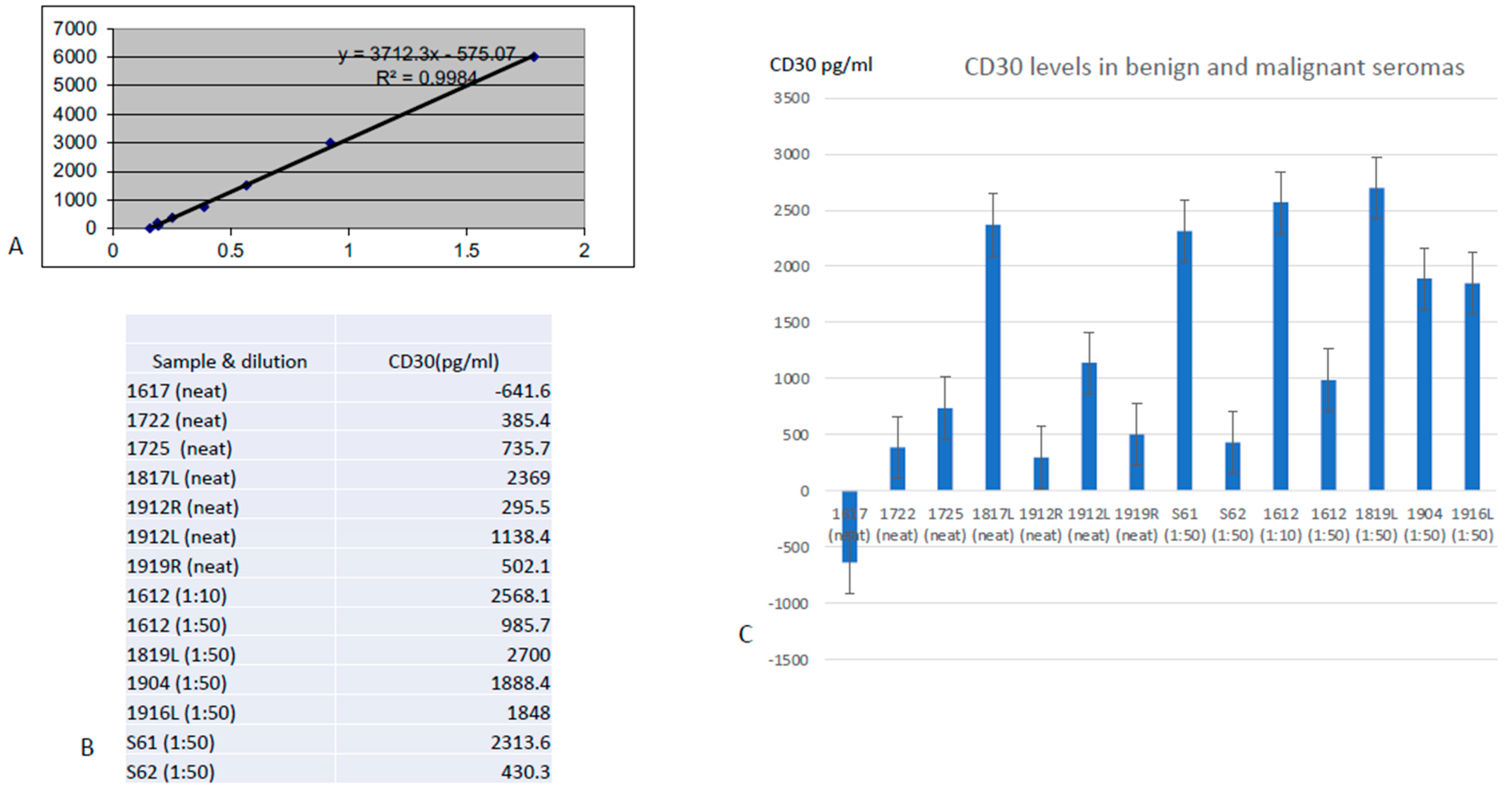
3.3. ELISA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miranda, R.N.; Aladily, T.N.; Prince, H.M.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; de Jong, D.; Fayad, L.E.; Amin, M.B.; Haideri, N.; Bhagat, G.; Brooks, G.S.; et al. Breast implant-associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Long-term follow-up of 60 patients. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, M.; van Leeuwen, F.E.; Hauptmann, M.; Overbeek, L.I.H.; de Boer, J.P.; Hijmering, N.J.; Sernee, A.; Klazen, C.A.H.; Lobbes, M.B.I.; van der Hulst, R.R.W.J.; et al. Breast Implants and the Risk of Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma in the Breast. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, P.G.; Ghione, P.; Ni, A.; Hu, Q.; Ganesan, N.; Galasso, N.; Dogan, A.; Horwitz, S.M. Risk of breast implant associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) in a cohort of 3546 women prospectively followed long term after reconstruction with textured breast implants. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2020, 73, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada, A.E.; Medeiros, L.J.; Clemens, M.W.; Ferrufino-Schmidt, M.C.; Pina-Oviedo, S.; Miranda, R.N. Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A review. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 166–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanale, A.; Di Napoli, A.; Ventimiglia, M.; Pileri, S.; Minella, D.; Curigliano, G.; Martelli, M.; De Vita, R.; Di Giulio, P.; Montorsi, M.; et al. Chest wall infiltration is a critical prognostic factor in breast implant-associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma affected patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, M.W.; Jacobsen, E.D.; Horwitz, S.M. 2019 NCCN Consensus Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL). Aesthet. Surg. J. 2019, 39, S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E.S.; Ashar, B.S.; Clemens, M.W.; Feldman, A.L.; Gaulard, P.; Miranda, R.N.; Sohani, A.R.; Stenzel, T.; Yoon, S.W. Best Practices Guideline for the Pathologic Diagnosis of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery-Goecker, C.; Fuda, F.; Krueger, J.E.; Chen, W. Immunophenotypic characteristics of breast implant-associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma by flow cytometry. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2015, 88, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Allen, C.T.; Fromm, J.R. Flow cytometry of ALK-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma of breast implant-associated effusion and capsular tissue. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2015, 88, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, S.E.; Hassid, V.J.; Branch-Brooks, C.; Liu, J.; Kadin, M.E.; Miranda, R.; Butler, C.E.; Clemens, M.W. Validation of a CD30 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbant Assay for the Rapid Detection of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2020, 40, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ding, L.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Point-of-care COVID-19 diagnostics powered by lateral flow assay. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimmer, M.D.; Ploeger, M.M.; Friedrich, M.J.; Bornemann, R.; Roessler, P.P.; Gravius, S.; Randau, T.M. The QuickLine IL-6 lateral flow immunoassay improves the rapid intraoperative diagnosis of suspected periprosthetic joint infections. Technol. Health Care 2016, 24, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, M.W.; Horwitz, S.M. NCCN Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2017, 37, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, L.J.; Marques-Piubelli, M.L.; Sangiorgio, V.F.I.; Ruiz-Cordero, R.; Vega, F.; Feldman, A.L.; Chapman, J.R.; Clemens, M.W.; Hunt, K.K.; Evans, M.G.; et al. Epstein-Barr-virus-positive large B-cell lymphoma associated with breast implants: An analysis of eight patients suggesting a possible pathogenetic relationship. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 2154–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, S.E.; Laun, J.C.; Beard, A.S.; Kuykendall, L.V. Breast Implant Capsule-Associated Squamous Cell Carcinoma during Pregnancy: A Mimicker of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 150, 926e–928e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.T.; Llaneras, J.; Willson, T.D.; Boyd, J.B.; Venegas, R.J.; Dauphine, C.; Kalantari, B.N. Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in Breast Implant Capsules. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2021, 86, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Shklovskaya, E.; Deva, A.; Xu, H.; Fan, K.; Brosamer, K.; Willson, R.; Khan, I.; Sinha, M.; Kadin, M.E. Diagnosis of breast implant associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma by analysis of cytokines in peri-implant seromas. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, E312–E314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Napoli, A.; Pepe, G.; Giarnieri, E.; Cippitelli, C.; Bonifacino, A.; Mattei, M.; Martelli, M.; Falasca, C.; Cox, M.C.; Santino, I.; et al. Cytological diagnostic features of late breast implant seromas: From reactive to anaplastic large cell lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadin, M.E.; Xu, H.; Hunsicker, L.M.; Guan, Y. Nonmalignant CD30+ Cells in Contralateral Peri-Implant Capsule of Patient with BIA-ALCL: A Premalignant Step? Aesthet. Surg. J. 2022, 42, NP125–NP129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, N.; Brody, G.S.; Ketterling, R.P.; Viswanatha, D.S.; He, R.; Dasari, S.; Mai, M.; Benson, H.K.; Sattler, C.A.; Boddicker, R.L.; et al. Genetic subtyping of breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blombery, P.; Thompson, E.; Ryland, G.L.; Joyce, R.; Byrne, D.J.; Khoo, C.; Lade, S.; Hertzberg, M.; Hapgood, G.; Marlton, P.; et al. Frequent activating STAT3 mutations and novel recurrent genomic abnormalities detected in breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 36126–36136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| CD30 LFA | # | ## | p | LCL | UCL | SE | z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 10 | 10 | 100.00% | 65.55% | 100.00% | 0 | 1.9 |
| Specificity | 7 | 10 | 70.00% | 37.37% | 91.91% | 0.14 | 1.9 |
| Positive Predictive Value | 10 | 13 | 76.92% | 45.98% | 93.84% | 0.12 | 1.9 |
| Negative Predictive Value | 7 | 7 | 100.00% | 56.09% | 100.00% | 0 | 1.9 |
| CD30 LFA 1:10 | # | ## | p | LCL | UCL | SE | z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 8 | 10 | 80.00% | 44.22% | 96.46% | 0.13 | 1.9 |
| Specificity | 10 | 10 | 100.00% | 65.55% | 100.00% | 0 | 1.9 |
| Positive Predictive Value | 8 | 8 | 100.00% | 59.77% | 100.00% | 0 | 1.9 |
| Negative Predictive Value | 10 | 12 | 83.33% | 50.88% | 97.06% | 0.11 | 1.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeyl, V.G.; Xu, H.; Khan, I.; Machan, J.T.; Clemens, M.W.; Hu, H.; Deva, A.; Glicksman, C.; McGuire, P.; Adams, W.P., Jr.; et al. CD30 Lateral Flow and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for Detection of BIA-ALCL: A Pilot Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 5128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215128
Zeyl VG, Xu H, Khan I, Machan JT, Clemens MW, Hu H, Deva A, Glicksman C, McGuire P, Adams WP Jr., et al. CD30 Lateral Flow and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for Detection of BIA-ALCL: A Pilot Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(21):5128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215128
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeyl, Victoria G., Haiying Xu, Imran Khan, Jason T. Machan, Mark W. Clemens, Honghua Hu, Anand Deva, Caroline Glicksman, Patricia McGuire, William P. Adams, Jr., and et al. 2023. "CD30 Lateral Flow and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for Detection of BIA-ALCL: A Pilot Study" Cancers 15, no. 21: 5128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215128
APA StyleZeyl, V. G., Xu, H., Khan, I., Machan, J. T., Clemens, M. W., Hu, H., Deva, A., Glicksman, C., McGuire, P., Adams, W. P., Jr., Sieber, D., Sinha, M., & Kadin, M. E. (2023). CD30 Lateral Flow and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for Detection of BIA-ALCL: A Pilot Study. Cancers, 15(21), 5128. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215128








