Review of RM-1929 Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Clinical Efficacy for Unresectable and/or Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Searches
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
3. Results
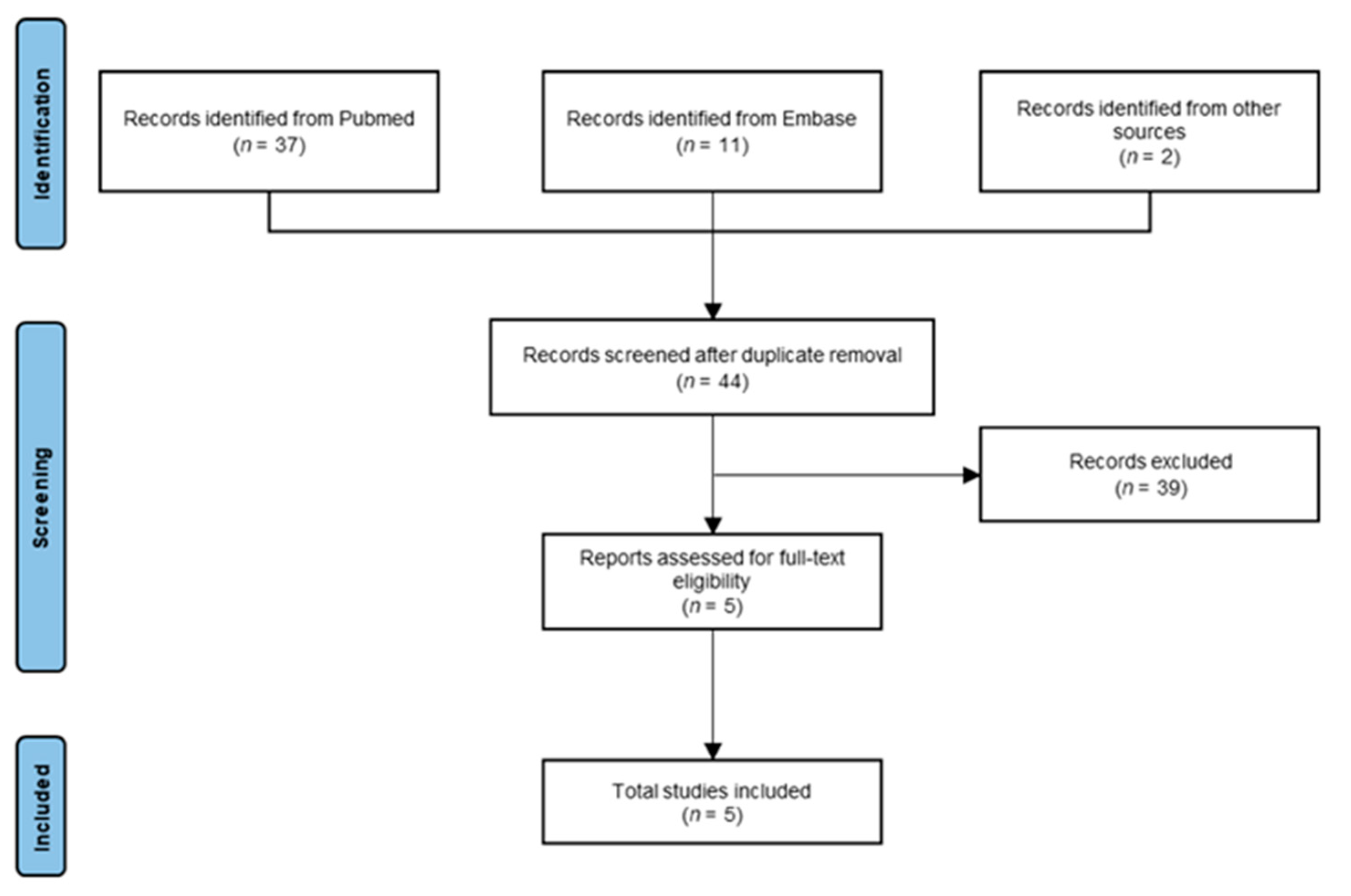
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Clinical Trial Data
3.3. Case Series and Retrospective Study Data
3.4. Qualitative Patient Measures: Quality of Life and Pain Management
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.P.; Saha, S.; Kraninger, J.L.; Swick, A.D.; Yu, M.; Lambert, P.F.; Kimple, R.J. Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus in Oropharyngeal Cancer. Cancer J. 2015, 21, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machiels, J.P.; René Leemans, C.; Golusinski, W.; Grau, C.; Licitra, L.; Gregoire, V. Reprint of “Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity, Larynx, Oropharynx and Hypopharynx: EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up”. Oral Oncol. 2021, 113, 1462–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillison, M.L.; Trotti, A.M.; Harris, J.; Eisbruch, A.; Harari, P.M.; Adelstein, D.J.; Sturgis, E.M.; Burtness, B.; Ridge, J.A.; Ringash, J.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Cetuximab or Cisplatin in Human Papillomavirus-Positive Oropharyngeal Cancer (NRG Oncology RTOG 1016): A Randomised, Multicentre, Non-Inferiority Trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, H.; Robinson, M.; Hartley, A.; Kong, A.; Foran, B.; Fulton-Lieuw, T.; Dalby, M.; Mistry, P.; Sen, M.; O’Toole, L.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Cisplatin or Cetuximab in Low-Risk Human Papillomavirus-Positive Oropharyngeal Cancer (De-ESCALaTE HPV): An Open-Label Randomised Controlled Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ridge, J.A.; Li, T.; Lango, M.N.; Churilla, T.M.; Bauman, J.R.; Galloway, T.J. Long-Term Toxicities in 10-Year Survivors of Radiation Treatment for Head and Neck Cancer. Oral Oncol. 2017, 71, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machtay, M.; Moughan, J.; Trotti, A.; Garden, A.S.; Weber, R.S.; Cooper, J.S.; Forastiere, A.; Ang, K.K. Factors Associated with Severe Late Toxicity after Concurrent Chemoradiation for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer: An RTOG Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3582–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.J.; Yao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zakeri, K.; Gelblum, D.Y.; Mcbride, S.M.; Riaz, N.; Tsai, J.; Kriplani, A.; Hung, T.K.W.; et al. Consensuses, Controversies, and Future Directions in Treatment Deintensification for Human Papillomavirus-Associated Oropharyngeal Cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 164–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.; Ford, S.; Bush, B.; Holsinger, F.C.; Moore, E.; Ghanem, T.; Carroll, W.; Rosenthal, E.; Magnuson, J.S. Salvage Surgery for Recurrent Cancers of the Oropharynx: Comparing TORS With Standard Open Surgical Approaches. JAMA Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2013, 139, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, J.R.; Li, R.; Magnuson, J.S.; Smith, R.V.; Moore, E.; Lawson, G.; Remacle, M.; Ganly, I.; Kraus, D.H.; Teng, M.S.; et al. Oncologic Outcomes After Transoral Robotic Surgery: A Multi-Institutional Study. JAMA Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2015, 141, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Cruz, A.K.; Vaish, R.; Kapre, N.; Dandekar, M.; Gupta, S.; Hawaldar, R.; Agarwal, J.P.; Pantvaidya, G.; Chaukar, D.; Deshmukh, A.; et al. Elective versus Therapeutic Neck Dissection in Node-Negative Oral Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchison, I.L.; Ridout, F.; Cheung, S.M.Y.; Shah, N.; Hardee, P.; Surwald, C.; Thiruchelvam, J.; Cheng, L.; Mellor, T.K.; Brennan, P.A.; et al. Nationwide Randomised Trial Evaluating Elective Neck Dissection for Early Stage Oral Cancer (SEND Study) with Meta-Analysis and Concurrent Real-World Cohort. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.C.J.; Kelly, J.R.; Park, H.S.; An, Y.; Judson, B.L.; Burtness, B.A.; Husain, Z.A. Patterns of Failure in High-Metastatic Node Number Human Papillomavirus-Positive Oropharyngeal Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2018, 85, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, J.E.; Li, J.G.; Pei, X.; Venigalla, P.; Zumsteg, Z.S.; Katsoulakis, E.; Lupovitch, E.; McBride, S.M.; Tsai, C.J.; Boyle, J.O.; et al. Patterns of Treatment Failure and Postrecurrence Outcomes Among Patients with Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma After Chemoradiotherapy Using Modern Radiation Techniques. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, D.G.; Spencer, S.; Adkins, D.; Birkeland, A.C.; Brizel, D.M.; Busse, P.M.; Caudell, J.J.; Cmelak, A.J.; Dimitrios Colevas, A.; Durm, G.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Version 2.2023 Head and Neck Cancers. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1437 (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Burtness, B.; Harrington, K.J.; Greil, R.; Soulières, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G.; Psyrri, A.; Basté, N.; Neupane, P.; Bratland, Å.; et al. Pembrolizumab Alone or with Chemotherapy versus Cetuximab with Chemotherapy for Recurrent or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (KEYNOTE-048): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Lancet 2019, 394, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.E.W.; Soulières, D.; Le Tourneau, C.; Dinis, J.; Licitra, L.; Ahn, M.J.; Soria, A.; Machiels, J.P.; Mach, N.; Mehra, R.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Methotrexate, Docetaxel, or Cetuximab for Recurrent or Metastatic Head-and-Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (KEYNOTE-040): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Lancet 2019, 393, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab for Recurrent Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsunaga, M.; Ogawa, M.; Kosaka, N.; Rosenblum, L.T.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Cancer Cell-Selective in Vivo near Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Targeting Specific Membrane Molecules. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.R.; Railkar, R.; Sanford, T.; Crooks, D.R.; Eckhaus, M.A.; Haines, D.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H.; Agarwal, P.K. Targeting Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) Expressing Bladder Cancer Using Combination Photoimmunotherapy (PIt) OPEN. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Mitsunaga, M.; Arihiro, S.; Saruta, M.; Matsuoka, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Tajiri, H. Molecular Targeted Photoimmunotherapy for HER2-Positive Human Gastric Cancer in Combination with Chemotherapy Results in Improved Treatment Outcomes through Different Cytotoxic Mechanisms. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, R.; Maruoka, Y.; Furusawa, A.; Inagaki, F.; Nagaya, T.; Fujimura, D.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. The Effect of Antibody Fragments on CD25 Targeted Regulatory T Cell Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 2624–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanaoka, H.; Nakajima, T.; Sato, K.; Watanabe, R.; Phung, Y.; Gao, W.; Harada, T.; Kim, I.; Paik, C.H.; Choyke, P.L.; et al. Photoimmunotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Targeting Glypican-3 Combined with Nanosized Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Weidensteiner, C.; Reichardt, W.; Gaedicke, S.; Zhu, X.; Grosu, A.L.; Kobayashi, H.; Niedermann, G. Imaging and Selective Elimination of Glioblastoma Stem Cells with Theranostic Near-Infrared-Labeled CD133-Specific Antibodies. Theranostics 2016, 6, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruoka, Y.; Furusawa, A.; Okada, R.; Inagaki, F.; Wakiyama, H.; Kato, T.; Nagaya, T.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Interleukin-15 after Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy (NIR-PIT) Enhances T Cell Response against Syngeneic Mouse Tumors. Cancers 2020, 12, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maawy, A.A.; Hiroshima, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Heim, R.; Makings, L.; Garcia-Guzman, M.; Luiken, G.A.; Kobayashi, H.; Hoffman, R.M.; Bouvet, M. Near Infra-Red Photoimmunotherapy with Anti-CEA-IR700 Results in Extensive Tumor Lysis and a Significant Decrease in Tumor Burden in Orthotopic Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandis, J.R.; Melhem, M.F.; Gooding, W.E.; Day, R.; Holst, V.A.; Wagener, M.M.; Drenning, S.D.; Tweardy, D.J. Levels of TGF-α and EGFR Protein in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Patient Survival. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998, 90, 824–832. [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn, J.; Baselga, J. Status of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Antagonists in the Biology and Treatment of Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2787–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, N.E.; Lane, H.A. ERBB Receptors and Cancer: The Complexity of Targeted Inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Tomita, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Lee, M.-J.; Lee, S.; Tomita, S.; Nagaya, T.; Sato, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Iwai, H.; et al. Immunogenic Cancer Cell Death Selectively Induced by near Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Initiates Host Tumor Immunity. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 10425–10436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Ando, K.; Okuyama, S.; Moriguchi, S.; Ogura, T.; Totoki, S.; Hanaoka, H.; Nagaya, T.; Kokawa, R.; Takakura, H.; et al. Photoinduced Ligand Release from a Silicon Phthalocyanine Dye Conjugated with Monoclonal Antibodies: A Mechanism of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity after Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.A.; Okamura, S.M.; Daniel De Magalhaes Filho, C.; Bergeron, D.M.; Rodriguez, A.; West, M.; Yadav, D.; Heim, R.; Fong, J.J.; Garcia-Guzman, M. Cancer-Targeted Photoimmunotherapy Induces Antitumor Immunity and Can Be Augmented by Anti-PD-1 Therapy for Durable Anticancer Responses in an Immunologically Active Murine Tumor Model. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2023, 72, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cognetti, D.M.; Johnson, J.M.; Curry, J.M.; Kochuparambil, S.T.; McDonald, D.; Mott, F.; Fidler, M.J.; Stenson, K.; Vasan, N.R.; Razaq, M.A.; et al. Phase 1/2a, Open-Label, Multicenter Study of RM-1929 Photoimmunotherapy in Patients with Locoregional, Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Head Neck 2021, 43, 3875–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, M.; Okano, S.; Enokida, T.; Ueda, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Shinozaki, T.; Tomioka, T.; Okano, W.; Biel, M.A.; Ishida, K.; et al. A Phase I, Single-Center, Open-Label Study of RM-1929 Photoimmunotherapy in Japanese Patients with Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 26, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, D.; Suzuki, H.; Beppu, S.; Terada, H.; Sawabe, M.; Hanai, N. Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy for Oropharyngeal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, I.; Okada, T.; Tokashiki, K.; Tsukahara, K. Quality-of-Life Evaluation of Patients with Unresectable Locally Advanced or Locally Recurrent Head and Neck Carcinoma Treated with Head and Neck Photoimmunotherapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibutani, Y.; Sato, H.; Suzuki, S.; Shinozaki, T.; Kamata, H.; Sugisaki, K.; Kawanobe, A.; Uozumi, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Hayashi, R. A Case Series on Pain Accompanying Photoimmunotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer. Healthcare 2023, 11, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, A.G.; Cohen, E.E. Current Treatment Options for Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3305–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishikawa, T.; Terada, H.; Sawabe, M.; Beppu, S.; Nishikawa, D.; Suzuki, H.; Hanai, N. Utilization of Ultrasound in Photoimmunotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer: A Case Report. J. Ultrasound 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, S.; Ehara, H.; Donishi, R.; Morisaki, T.; Ogura, T.; Taira, K.; Fukuhara, T.; Fujiwara, K. Photoimmunotherapy with Surgical Navigation and Computed Tomography Guidance for Recurrent Maxillary Sinus Carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 2023, 50, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, I.; Okada, T.; Tokashiki, K.; Tsukahara, K. A Case Treated with Photoimmunotherapy Under a Navigation System for Recurrent Lesions of the Lateral Pterygoid Muscle. In Vivo 2022, 36, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omura, G.; Honma, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shinozaki, T.; Itoyama, M.; Eguchi, K.; Sakai, T.; Yokoyama, K.; Watanabe, T.; Ohara, A.; et al. Transnasal Photoimmunotherapy with Cetuximab Sarotalocan Sodium: Outcomes on the Local Recurrence of Nasopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 2023, 50, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Okada, R.; Goto, Y.; Furusawa, A.; Inagaki, F.; Wakiyama, H.; Furumoto, H.; Daar, D.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P.L.; et al. Electron Donors Rather Than Reactive Oxygen Species Needed for Therapeutic Photochemical Reaction of Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 1689–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | Year | Design | # of Patients | Age Range | Male (N) | Female (N) | Diagnosis | Tumor Recurrence Sites (N) | CR (%) | PR (%) | SD (%) | DC (%) | PD (%) | ORR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognetti et al. [34] | 2021 | Phase I/IIa clinical trial | 30 | 39–86 | 24 | 6 | HNSCC | Neck (13) Oral cavity (9) Oropharynx (7) Skin (3) Hypopharynx (2) Sinus (2) Nasal cavity (1) Nasopharynx (1) Parotid gland (1) Occipital gland (1) | 4 (13.3) | 9 (30.0) | 11 (36.7) | 24 (80) | 6 (20.0) | 13 (43.3) |
| Tahara et al. [35] | 2021 | Phase I clinical trial | 3 | 0 | 3 | HNSCC | Soft tissue in mental/submental region (1) External auditory canal (1) Superficial cervical node (1) Oropharynx (1) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (66.7) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (66.7) | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | |
| Nishikawa et al. [36] | 2022 | Review with case report | 10 | 54–88 | 9 | 1 | HNSCC | Cervical skin (2) Oropharynx (2) s.c. facial tissue (2) Glottis (1) Tongue (1) Lower gingiva (1) Nasal cavity (1) | 3 (30.0) | 7 (70.0) | 0 (0.0) | 10 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 10 (100) |
| Okamoto et al. [37] | 2022 | Retrospective study | 9 | 67–77 | 8 | 1 | HNSCC | Oropharynx (5) Buccal mucosa (1) Tongue/upper and lower gingiva (1) Maxillary sinus (1) Cervical lymph node (1) | 2 (22.2) | 6 (66.7) | 1 (11.1) | 9 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (88.9) |
| Shibutani et al. [38] | 2023 | Case report | 5 | 51–74 | 2 | 3 | HNSCC | Buccal mucosa (2) Oropharynx (2) Nasopharynx (1) | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Overall | 57 | 39–86 | 43 | 14 | HNSCC | 9 (17.3) | 24 (46.2) | 12 (23.1) | 45 (86.5) | 7 (13.5) | 33 (63.5) |
| Author | Year | Prior Therapies (N) | NIR-PIT Parameters | Tumor Response Evaluation Method | Follow-Up Period | TEAE Evaluation | Adverse Events < Grade 3 (N) | Adverse Events > Grade 3 (N) | Patient Deaths (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognetti et al. [34] | 2021 | Surgery (30) Radiotherapy (30) Chemotherapy (21) Immunotherapy (11) Biological/hormonal/other (8) | 640 mg/m2 1–4 cycles | mRECIST 1.1 | 22.18–32.33 mo | NCI CTCAE 4.03 | Edema (15) Fatigue (10) Dysphagia (7) Constipation (6) Erythema (6) Anemia (5) Dehydration (5) Facial pain (4) Oral pain (4) Tumor pain (4) Local swelling (4) Cough (4) Oropharyngeal pain (4) Pneumonia (4) Weight loss (4) | Anemia (3) Dysphagia (2) Local pain (2) Oral pain (2) Local edema (2) Hyponatremia (2) Hemorrhage (2) Tumor pain (2) Pneumonia (2) Edema (1) | 3 |
| Tahara et al. [35] | 2021 | Surgery (1) Radiotherapy (3) Chemotherapy (3) Immuno/hormonal/biologic/other therapy (3) | 640 mg/m2 1 cycle | mRECIST 1.1 | 4 wks | NCI CTCAE 4.30 | Local pain (2) Local edema (1) Facial edema (1) Elevated BP (1) Elevated GGT (1) Decreased WBC (1) Anemia (1) Glossitis (1) Abnormal hepatic function (1) Generalized rash (1) | Local pain (1) | 0 |
| Nishikawa et al. [36] | 2022 | Surgery (2) Radiotherapy (1) Chemoradiotherapy (1) Not reported (8) | 640 mg/m2 1–3 cycles | mRECIST 1.1 | 13–16 mo | Not specified | Pain (6) Hemorrhage (1) Edema (4) Fistula (3) | Edema (1) | 0 |
| Okamoto et al. [37] | 2022 | Surgery (9) Radiotherapy (9) Chemotherapy (2) | 640 mg/m2 1–4 cycles | mRECIST 1.1 | 4 wks | NCI CTCAE 4.30 | Pain (8) Mucositis (7) Edema (4) Nausea (3) Hemorrhage (2) Diarrhea (2) Dysphagia (1) Rash (1) Fever (1) Aspiration (1) Hyperkalemia (1) Trismus (1) Constipation (1) Dehydration (1) Intratumoral broken needle fragment (1) Oral dysesthesia (1) | Edema (2) Dysphagia (2) Hyponatremia (2) Pain (1) Mucositis (1) Acute kidney injury (1) Anemia (1) Hypokalemia (1) Liver dysfunction (1) Weight loss (1) | 1 |
| Shibutani et al. [38] | 2023 | Not specified | 1–3 cycles | Not specified | 4 d | Not specified | Not specified | Not specified | 0 |
| Measure | QOL Score Change from BASELINE Least Square Mean (95% CI) | p-Value v. Baseline |
|---|---|---|
| Functional scales | ||
| Physical functioning | 2.2 (−2.9–7.3) | 0.347 |
| Role functioning | 5.6 (−12.6–23.7) | 0.500 |
| Emotional functioning | −3.7 (−10.9–3.5) | 0.272 |
| Cognitive functioning | 0.0 (−11.1–11.1) | >0.999 |
| Social functioning | 3.7 (−10.3–17.7) | 0.559 |
| Global health status | −7.4 (−20.8–6) | 0.237 |
| Domain scales | ||
| Pain | 4.6 (−6.5–15.8) | 0.366 |
| Swallowing | −5.6 (−31.0–19.9) | 0.628 |
| Sense problems | −1.9 (−6.1–2.4) | 0.347 |
| Speech problems | 0.0 (−26.7–26.7) | >0.999 |
| Trouble with social eating | −6.5 (−17.5–4.5) | 0.211 |
| Trouble with social contact | 6.7 (−6.1–19.5) | 0.264 |
| Less sexuality | −5.6 (−14.6–3.5) | 0.195 |
| Mean NRS Pain Score (Mean Opioid Dose (mg)) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffuser Type | POD-2 | POD-1 | POD0 | POD1 | POD2 | POD3 | POD4 |
| Cylindrical | 5.3 (45) | 5 (45) | 7.8 (94) | 4.6 (60) | 4.2 (66) | 3.8 (60) | 4.8 (48) |
| Frontal | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 6.8 (46.3) | 3 (56.3) | 2.8 (0) | 1.8 (0) | 1.5 (0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyazaki, N.L.; Furusawa, A.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Review of RM-1929 Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Clinical Efficacy for Unresectable and/or Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 5117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215117
Miyazaki NL, Furusawa A, Choyke PL, Kobayashi H. Review of RM-1929 Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Clinical Efficacy for Unresectable and/or Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(21):5117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215117
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyazaki, Nanami L., Aki Furusawa, Peter L. Choyke, and Hisataka Kobayashi. 2023. "Review of RM-1929 Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Clinical Efficacy for Unresectable and/or Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 15, no. 21: 5117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215117
APA StyleMiyazaki, N. L., Furusawa, A., Choyke, P. L., & Kobayashi, H. (2023). Review of RM-1929 Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Clinical Efficacy for Unresectable and/or Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 15(21), 5117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215117







