Thoracic Radiotherapy in Extensive Disease Small Cell Lung Cancer: Multicenter Prospective Observational TRENDS Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Objectives
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- VanMeerbeeck, J.P.; Fennell, D.A.; Ruysscher, D.D. Small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 2011, 378, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotman, B.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Kramer, G.; Rankin, E.; Snee, M.; Hatton, M.; Postmus, P.; Collette, L.; Musat, E.; Senan, S. Prophylactic cranial irradiation in extensive small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahel, R.A. Diagnosis, staging, and prognostic factors of small cell lung cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 1991, 3, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, A.G.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Beyruti, R.; Kubota, K.; Turrisi, A.; Eberhardt, W.E.; van Meerbeeck, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Goldstraw, P.; et al. The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the revision of the clinical and pathologic staging of small cell lung cancer in the forthcoming eight edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 11, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, W.K.; Shepherd, F.A.; Feld, R.; Osoba, D.; Dang, P.; DeBoer, G. VP-16 and cisplatin as first-line therapy for small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1985, 3, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Mansfield, A.S.; Szczęsna, A.; Havel, L.; Krzakowski, M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Huemer, F.; Losonczy, G.; Johnson, M.L.; Nishio, M.; et al. First-Line Atezolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Liu, S.; Mansfield, A.; Mok, T.; Scherpereel, A.; Reinmuth, N.; Garassino, M.; De Carpeno, J.; Califano, R.; Nishio, M.; et al. IMpower133: Updated overall survival (OS) analysis of first-line (1 L) atezolizumab (atezo) + carboplatin + etoposide in extensive-stage SCLC (ES-SCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v710–v711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab plus platinum–etoposide versus platinum–etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.G.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab ± tremelimumab + platinum-etoposide in first-line extensive-stage SCLC (ES-SCLC): Updated results from the phase III CASPIAN study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Awad, M.M.; Navarro, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peters, S.; Csőszi, T.; Cheema, P.K.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Wollner, M.; Yang, J.C.-H.; et al. Pembrolizumab or Placebo Plus Etoposide and Platinum as First-Line Therapy for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III KEYNOTE-604 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, JCO2000793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Luft, A.; Szczesna, A.; Havel, L.; Kim, S.-W.; Akerley, W.; Pietanza, M.C.; Wu, Y.-L.; Zielinski, C.; Thomas, M.; et al. Phase III randomized trial of ipilimumab plus etoposide and platinum versus placebo plus etoposide and platinum in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3740–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Luft, A.; Serwatowski, P.; Barlesi, F.; Chacko, R.; Sebastian, M.; Lu, H.; Cuillerot, J.M.; Lynch, T.J. Ipilimumab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line therapy in extensive-disease-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase 2 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruni, A.; Scotti, V.; Borghetti, P.; Vagge, S.; Cozzi, S. A Real-World, Multicenter, Observational Retrospective Study of Durvalumab after Concomitant or Sequential Chemoradiation for Unresectable Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 744956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.; Garassino, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Poltoratskiy, A.; Trukhin, D.; Hochmair, M.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.; et al. Durvalumab (D) ± tremelimumab + platinum–etoposide in first-line extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: Characterization of long-term clinical benefit of tumour mutational burden in CASPIAN. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, LBA86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Awad, M.M.; Navarro, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peters, S.; Csőszi, T.; Cheema, P.K.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Wollner, M.; Czyzewicz, G.; et al. KEYNOTE-604: Pembrolizumab (pembro) or placebo plus etopide and platinum (EP) as first-line therapy for extensive-stage (ES) small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. 9001), 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Awad, M.M.; Navarro, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peters, S.; Csőszi, T.; Cheema, P.K.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Wollner, M.; Yang, J.H.; et al. Health-related quality of life in KEYNOTE604: Pembrolizumab (pembro) or placebo added to etoposide and platinum as first-line therapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1782MO. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardoscia, L.; Pasinetti, N.; Triggiani, L.; Cozzi, S.; Sardaro, A. Biological Bases of Immune-Related Adverse Events and Potential Crosslinks with Immunogenic Effects of Radiation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 746853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, R.; Page, N.; Morgensztern, D.; Read, W.; Tierney, R.; Vlahiotis, A.; Spitznagel, E.L.; Piccirillo, J. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: Analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4539–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jett, J.R.; Schild, S.E.; Kesler, K.A.; Kalemkerian, G.P. Treatment of small cell lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2013, 143 (Suppl. 5), e400S–e419S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aupérin, A.; Arriagada, R.; Pignon, J.P.; Le Péchoux, C.; Gregor, A.; Stephens, R.J.; Kristjansen, P.E.; Johnson, B.E.; Ueoka, H.; Wagner, H.; et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer in complete remission. Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Overview Collaborative Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Seto, T.; Harada, H.; Nokihara, H.; Saka, H.; Nishio, M.; Kaneda, H.; Takayama, K.; Ishimoto, O.; et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation versus observation in patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotman, B.J.; van Tinteren, H.; Praag, J.O.; Knegjens, J.L.; El Sharouni, S.Y.; Hatton, M.; Keijser, A.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Senan, S. Use of thoracic radiotherapy for extensive stage small-cell lung cancer: A phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therasse, P.; Arbuck, S.G.; Eisenhauer, E.A.; Wanders, J.; Kaplan, R.S.; Rubinstein, L.; Verweij, J.; Van Glabbeke, M.; Van Oosterom, A.T.; Christian, M.C.; et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardizzoni, A.; Tiseo, M.; Boni, L. Validation of standard definition of sensitive versus refractory relapsed small cell lung cancer: A pooled analysis of topotecan second-line trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2211–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bi, N.; Feng, Q.; Li, J.; Lv, J.; Chen, D.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L. Thoracic radiotherapy improves the overall survival of patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer with distant metastasis. Cancer 2011, 117, 5423–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Fu, C.; Li, B. Clinical outcomes of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer patients treated with thoracic radiotherapy at different times and fractionations. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, E.M.; Hu, C.; Sun, A.Y.; Grimm, D.F.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Dunlap, N.E.; Higgins, K.A.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Allen, A.M.; Iyengar, P.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study Comparing Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Alone to Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation and Consolidative Extracranial Irradiation for Extensive-Disease Small Cell Lung Cancer (ED SCLC): NRG Oncology RTOG 0937. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Macdonald, O.K.; Suntharalingam, M. Evaluation of the use of prophylactic cranial irradiation in small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2009, 115, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, L.; Ceccarelli, C.; Menichelli, C.; Aristei, C.; Borghesi, S.; Tucci, E.; Bastiani, P.; Cozzi, S. Special stereotactic radiotherapy techniques: Procedures and equipment for treatment simulation and dose delivery. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2022, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, D.; De Rose, F.; Cozzi, S. The use of radiation therapy for oligoprogressive/oligopersistent oncogene-driven non-small cell lung cancer: State of the art. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 148, 102894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, S.; Alì, E.; Bardoscia, L.; Najafi, M.; Botti, A.; Blandino, G.; Giaccherini, L.; Ruggieri, M.P.; Augugliaro, M.; Iori, F.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) for Oligorecurrent/Oligoprogressive Mediastinal and Hilar Lymph Node Metastasis: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddalo, M.; D’Angelo, E.; Fiorica, F.; Argenone, A.; Scricciolo, M.; Cozzi, S. Thoracic re-irradiation with 3D-conformal or more advanced techniques: A systematic review of treatment safety by the Re-irradiation Study Group of the Italian Association of Radiation and Oncology AIRO. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 167, 103500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriola, E.; Wheater, M.; Galea, I.; Cross, N.; Maishman, T.; Hamid, D.; Stanton, L.; Cave, J.; Geldart, T.; Mulatero, C.; et al. Outcome and biomarker analysis from a multicentre phase 2 study of ipilimumab in combination with carboplatin and etoposide as first-line therapy for extensive-stage SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liù, S.V.; Horn, L.; Mok, T.; Mansfield, A.; De Boer, R.; Losonczy, G.; Sugawara, S.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Krzakowski, M.; Smolin, A.; et al. IMpower 133: Characterisation of long-term survivors treated first-line with chemotherapy–atezolizumab in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1718MO. [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield, A.; Każarnowicz, A.; Karaseva, N.; Sánchez, A.; De Boer, R.; Andric, Z.; Reck, M.; Atagi, S.; Lee, J.-S.; Garassino, M.; et al. Safety and patient-reported outcomes of atezolizumab, carboplatin, and etoposide in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (IMpower133): A randomized phase I/III trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, T.; Wang, Y.; Dowlati, A.; Lewis, D.A.; Chen, Y.; Mohindra, A.R.; Razaq, M.; Ahuja, H.G.; Liu, J.; King, D.M.; et al. Randomized phase II clinical trial of cisplatin/carboplatin and etoposide (CE) alone or in combination with nivolumab as frontline therapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC): ECOG-ACRIN EA5161. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. 9000), 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, B.; Menis, J.; Bironzo, P.; Gervais, R.; Greillier, L.; Monnet, I.; Livi, L.; Young, R.; Decroisette, C.; Cloarec, N.; et al. REACTION: A phase II study of etoposide and cis/carboplatin with or without pembrolizumab in untreated extensive small cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, LBA85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, F.; Schilbach, K.; Klumpp, L.; Bardoscia, L.; Sezgin, E.C.; Schwab, M.; Zips, D.; Huber, S.M. Potential Role of CXCR4 Targeting in the Context of Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy of Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Kharouta, M.; Podder, T.K.; Choi, S.; Biswas, T. Role of Thoracic Radiotherapy in Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (ES-SCLC) in the Immunotherapy Era: A National Hospital-Based Registry Analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 111, e466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.W.; Heymach, J.V.; Chen, D.; Verma, V.; Cushman, T.R.; Hess, K.R.; Shroff, G.; Tang, C.; Skoulidis, F.; Jeter, M.; et al. Phase I Trial of Pembrolizumab and Radiation Therapy after Induction Chemotherapy for Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, B.; Kim, S.; Dilling, T.; Latifi, K.; Rose, T.; Lannon, A.; Macmillan, G.; Grass, G.; Chiappori, A.; Haura, E.; et al. A prospective Single Arm Phase I/II Study: Consolidative Ipilimumab and Nivolumab with Thoracic Radiotherapy after Platinum Based Chemotherapy for Patients with Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, B.H.; Verma, N.; Shukla, U.C.; Park, H.S.; Koffer, P.P. Consolidative Thoracic Radiation Therapy after First-line Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Multi-institutional Case Series. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 7, 1000883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiddinga, B.I.; Raskin, J.; Janssens, A.; Pauwels, P.; Van Meerbeeck, J.P. Recent developments in the treatment of small cell lung cancer. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
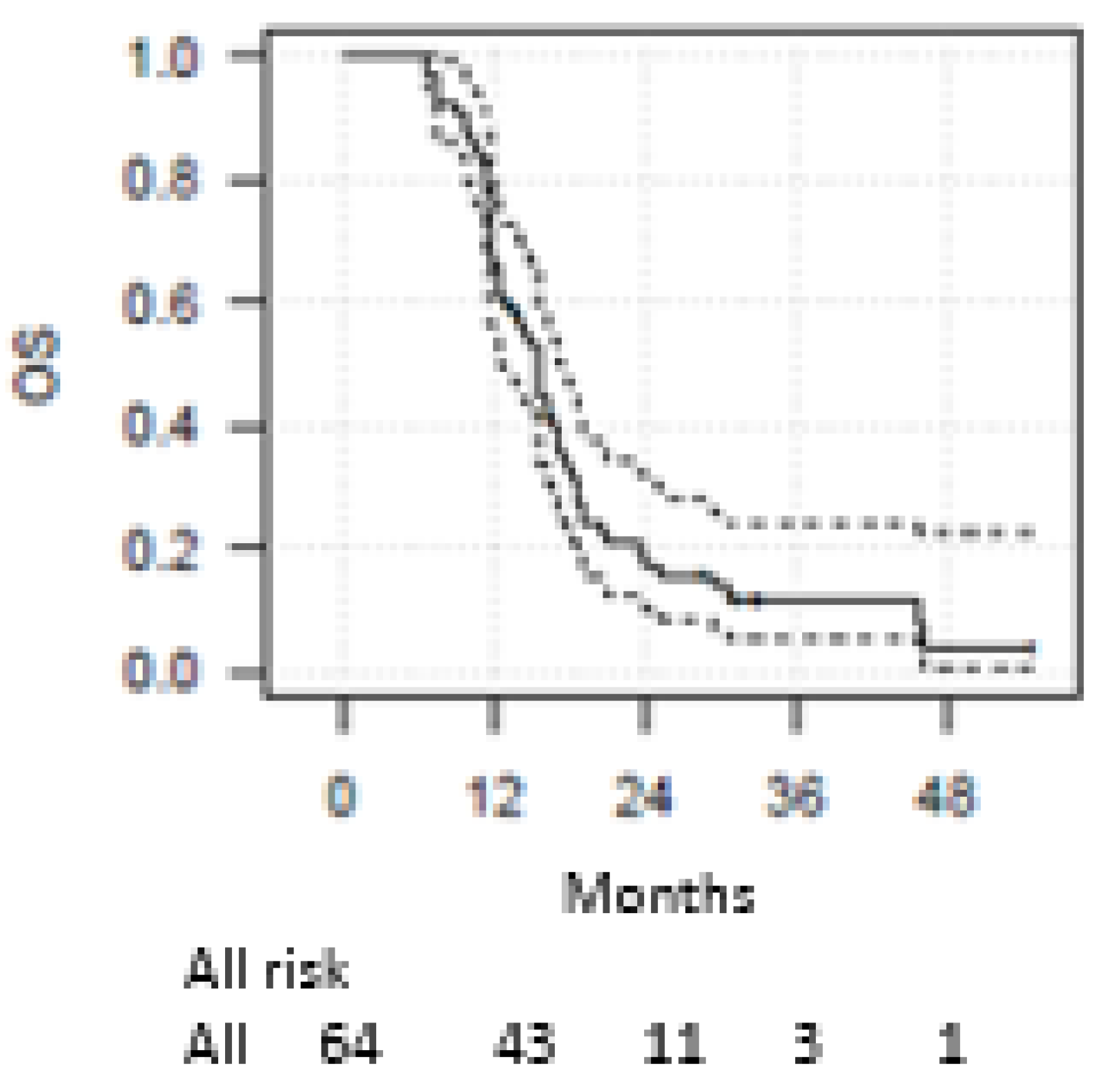
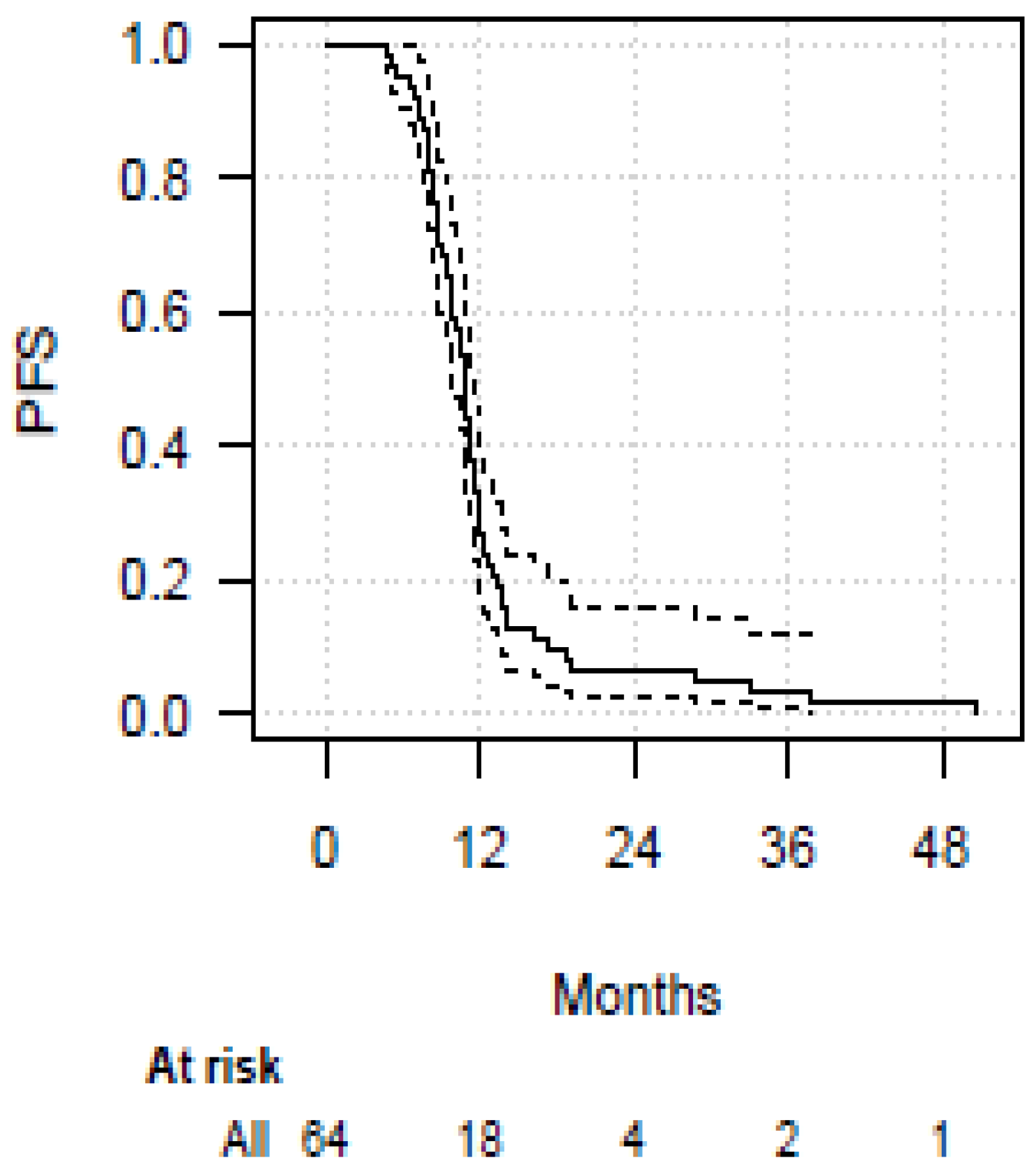
| Parameter | N (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ||
| Median | 68 (63–74) | |
| Range | 42–81 | |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 26 (41) | |
| Male | 38 (59) | |
| BMI | ||
| Median | 25 (22.7–26.2) | |
| ECOG | ||
| 0 | 34 (53) | |
| 1 | 25 (39) | |
| 2 | 5 (8) | |
| Chemotherapy scheme | ||
| carboplatin + etoposide | 42 (65.5) | |
| cisplatin + etoposide | 22 (34.5) | |
| Dose per fractions | ||
| 3 Gy × 10 fr | 35 (55) | |
| 1.8 Gy × 33 fr | 3 (5) | |
| 3 Gy × 15 fr | 16 (25) | |
| 2 Gy × 30 fr | 2 (3) | |
| 4 Gy × 5 fr | 3 (5) | |
| 3 Gy × 13 fr | 5 (7) | |
| RT technique | ||
| 3DCRT | 10 (15.5) | |
| IMRT | 54 (84.5) | |
| RT Volume | ||
| pre-cht | 8 (12.5) | |
| post-cht | 56 (87.5) | |
| PCI | ||
| Yes | 44 (69) | |
| No | 20 (31) | |
| PCI dose | ||
| 4 Gy × 5 fr | 7 (16) | |
| 2.5 Gy ×10 fr | 29 (66) | |
| 3 Gy × 10 fr | 8 (18) | |
| Toxicity | Grade | N (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Pulmonary | ||
| G0 | 54 (84) | |
| G1 | 6 (10) | |
| G2 | 4 (6) | |
| >G3 | 0 | |
| Esophagus | ||
| G0 | 39 (61) | |
| G1 | 20 (31) | |
| G2 | 5 (8) | |
| >G3 | 0 | |
| Asthenia | ||
| G0 | 61 (95.5) | |
| G1 | 1 (1.5) | |
| G2 | 1 (1.5) | |
| G3 | 1 (1.5) | |
| >G4 | 0 |
| Study [Ref.] (Experimental Arm) | TRIAL DESIGN | Median OS (Months) | Median PFS (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IMpower133 [34] | Phase 3, RCT, double-blind | 12.3 | 5.2 |
| CASPIAN [9] | Phase 3, RCT, open-label | 13 | 5.1 |
| KEYNOTE-604 [10] | Phase 3, RCT, double-blind | 10.8 | 4.5 |
| IDEATE [11] | Phase 3, RCT, double-blind | 11.0 | 4.6 |
| NCT01331525 [33] | Phase 2, RCT, double-blind | 17.0 | 6.9 |
| ECOG-ACRIN EA5161 [36] | Phase 2, RCT, double-blind | 11.3 | 5.5 |
| REACTION [37] | Phase 2, RCT | 12.3 | 5.4 |
| CREST [22] | Phase 3, RCT, open-label | 8 | 4 |
| TRENDS [our study] | Prospective single arm | 15.5 | 10.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cozzi, S.; Bruni, A.; Ruggieri, M.P.; Borghetti, P.; Scotti, V.; Franceschini, D.; Fiore, M.; Taraborrelli, M.; Salvi, F.; Galaverni, M.; et al. Thoracic Radiotherapy in Extensive Disease Small Cell Lung Cancer: Multicenter Prospective Observational TRENDS Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020434
Cozzi S, Bruni A, Ruggieri MP, Borghetti P, Scotti V, Franceschini D, Fiore M, Taraborrelli M, Salvi F, Galaverni M, et al. Thoracic Radiotherapy in Extensive Disease Small Cell Lung Cancer: Multicenter Prospective Observational TRENDS Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(2):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020434
Chicago/Turabian StyleCozzi, Salvatore, Alessio Bruni, Maria Paola Ruggieri, Paolo Borghetti, Vieri Scotti, Davide Franceschini, Michele Fiore, Maria Taraborrelli, Fabrizio Salvi, Marco Galaverni, and et al. 2023. "Thoracic Radiotherapy in Extensive Disease Small Cell Lung Cancer: Multicenter Prospective Observational TRENDS Study" Cancers 15, no. 2: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020434
APA StyleCozzi, S., Bruni, A., Ruggieri, M. P., Borghetti, P., Scotti, V., Franceschini, D., Fiore, M., Taraborrelli, M., Salvi, F., Galaverni, M., Savoldi, L., Braglia, L., Botti, A., Finocchi Ghersi, S., Niccolò, G.-L., Lohr, F., Iotti, C., & Ciammella, P. (2023). Thoracic Radiotherapy in Extensive Disease Small Cell Lung Cancer: Multicenter Prospective Observational TRENDS Study. Cancers, 15(2), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020434





