The Site of Origin of Medulloblastoma: Surgical Observations Correlated to Molecular Groups
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
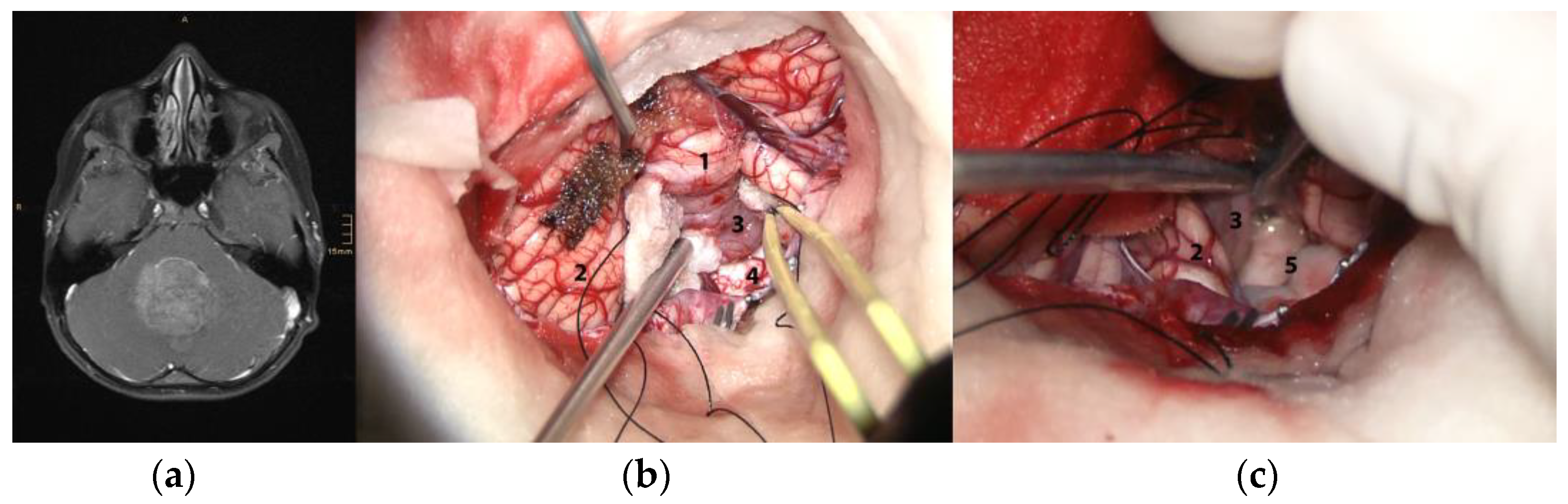
2.2. Intraoperative Definition of the STO
2.3. Statistical Analysis
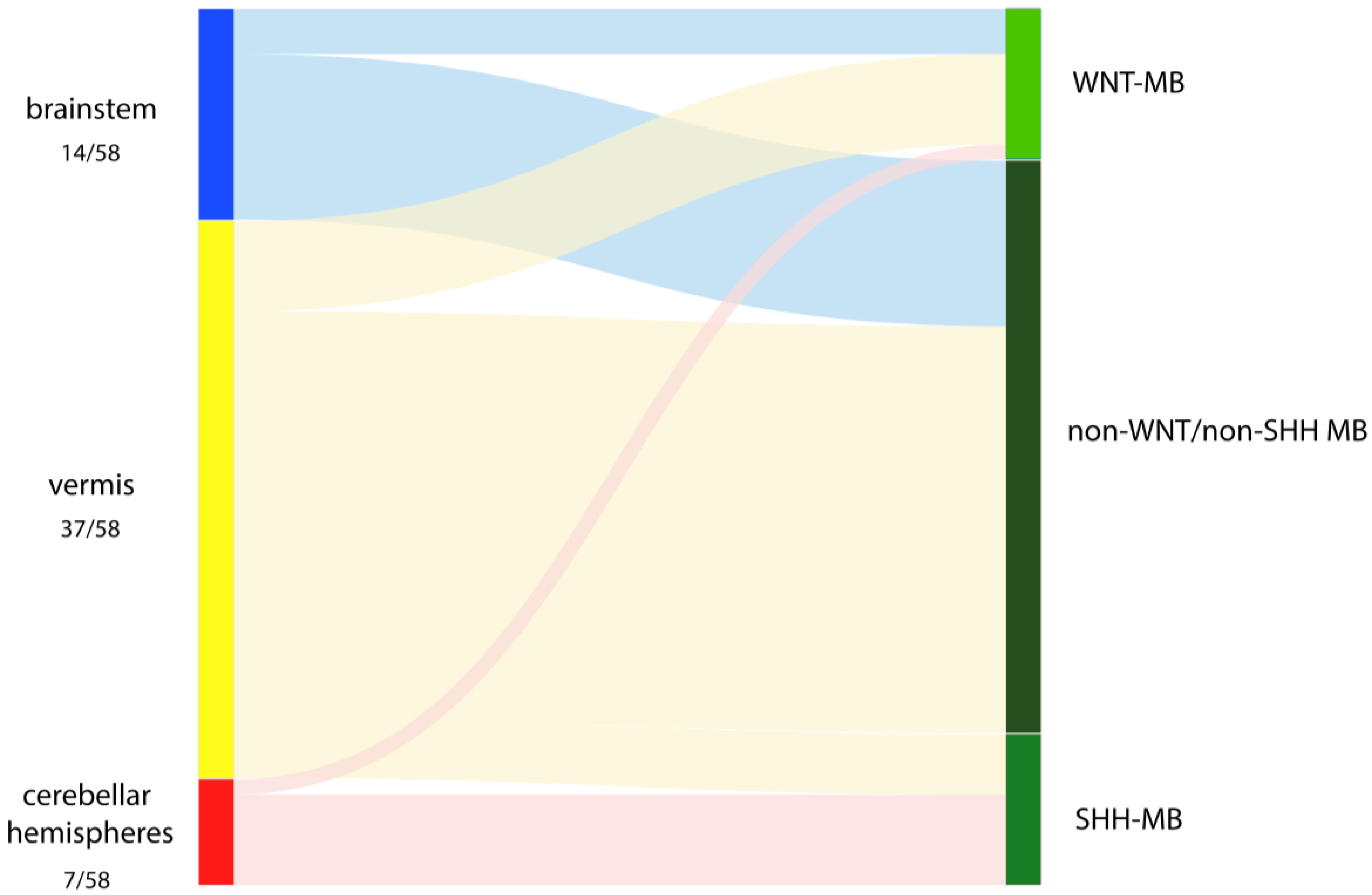
3. Results
3.1. Intraoperative Assessment
3.2. Relationship of Intraoperative Findings with Molecular MB Groups
3.3. Prediction of MB Group Based on STO
4. Discussion
4.1. Intraoperatively Observed Intra-Group Heterogeneity of STO
4.1.1. SHH-MB
4.1.2. WNT-MB
4.1.3. Non-WNT/Non-SHH MB
4.1.4. Clinical and Surgical Implications
4.1.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Truitt, G.; Boscia, A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20 (Suppl. S4), iv1–iv86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, A.L.; Wisoff, J.H.; Zeltzer, P.M.; Boyett, J.M.; Rorke, L.B.; Stanley, P. Effects of medulloblastoma resections on outcome in children: A report from the Children's Cancer Group. Neurosurgery 1996, 38, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, P.; Tong, Y.; Robinson, G.; Thompson, M.C.; Currle, D.S.; Eden, C.; Kranenburg, T.A.; Hogg, T.; Poppleton, H.; Martin, J.; et al. Subtypes of medulloblastoma have distinct developmental origins. Nature 2010, 468, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladoiu, M.C.; El-Hamamy, I.; Donovan, L.K.; Farooq, H.; Holgado, B.L.; Sundaravadanam, Y.; Ramaswamy, V.; Hendrikse, L.D.; Kumar, S.; Mack, S.C.; et al. Childhood cerebellar tumours mirror conserved fetal transcriptional programs. Nature 2019, 572, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, A.; Chintagumpala, M.; Ashley, D.; Kellie, S.; Kun, L.E.; Merchant, T.E.; Woo, S.; Wheeler, G.; Ahern, V.; Krasin, M.J.; et al. Risk-adapted craniospinal radiotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy and stem-cell rescue in children with newly diagnosed medulloblastoma (St Jude Medulloblastoma-96): Long-term results from a prospective, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.W.; Rudneva, V.A.; Buchhalter, I.; Billups, C.A.; Waszak, S.M.; Smith, K.S.; Bowers, D.C.; Bendel, A.; Fisher, P.G.; Partap, S.; et al. Risk-adapted therapy for young children with medulloblastoma (SJYC07): Therapeutic and molecular outcomes from a multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 768–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.M.; Hielscher, T.; Bouffet, E.; Remke, M.; Luu, B.; Gururangan, S.; McLendon, R.E.; Bigner, D.D.; Lipp, E.S.; Perreault, S.; et al. Prognostic value of medulloblastoma extent of resection after accounting for molecular subgroup: A retrospective integrated clinical and molecular analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajjar, A.; Sanford, R.A.; Bhargava, R.; Heideman, R.; Walter, A.; Li, Y.; Langston, J.W.; Jenkins, J.J.; Muhlbauer, M.; Boyett, J.; et al. Medulloblastoma with brain stem involvement: The impact of gross total resection on outcome. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1996, 25, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patay, Z.; DeSain, L.A.; Hwang, S.N.; Coan, A.; Li, Y.; Ellison, D.W. MR Imaging Characteristics of Wingless-Type-Subgroup Pediatric Medulloblastoma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 2386–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, S.; Ramaswamy, V.; Achrol, A.S.; Chao, K.; Liu, T.T.; Shih, D.; Remke, M.; Schubert, S.; Bouffet, E.; Fisher, P.G.; et al. MRI surrogates for molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, K.W.; Mobley, B.C.; Lober, R.M.; Andre, J.B.; Partap, S.; Vogel, H.; Barnes, P.D. Distinctive MRI features of pediatric medulloblastoma subtypes. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wefers, A.K.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Pöschl, J.; von Bueren, A.O.; Monoranu, C.M.; Seelos, K.; Peraud, A.; Tonn, J.C.; Koch, A.; Pietsch, T.; et al. Subgroup-specific localization of human medulloblastoma based on pre-operative, MRI. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 127, 931–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata-Mbemba, D.; Zapotocky, M.; Laughlin, S.; Taylor, M.D.; Ramaswamy, V.; Raybaud, C. MRI Characteristics of Primary Tumors and Metastatic Lesions in Molecular Subgroups of Pediatric Medulloblastoma: A Single-Center Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iv, M.; Zhou, M.; Shpanskaya, K.; Perreault, S.; Wang, Z.; Tranvinh, E.; Lanzman, B.; Vajapeyam, S.; Vitanza, N.A.; Fisher, P.G.; et al. MR Imaging-Based Radiomic Signatures of Distinct Molecular Subgroups of Medulloblastoma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A.; Gupta, T.; Pungavkar, S.; Shirsat, N.; Epari, S.; Chinnaswamy, G.; Mahajan, A.; Janu, A.; Moiyadi, A.; Kannan, S.; et al. Nomograms based on preoperative multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prediction of molecular subgrouping in medulloblastoma: Results from a radiogenomics study of 111 patients. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wong, S.W.; Wright, J.N.; Wagner, M.W.; Toescu, S.; Han, M.; Tam, L.T.; Zhou, Q.; Ahmadian, S.S.; Shpanskaya, K.; et al. MRI Radiogenomics of Pediatric Medulloblastoma: A Multicenter Study. Radiology 2022, 304, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrikse, L.D.; Haldipur, P.; Saulnier, O.; Millman, J.; Sjoboen, A.H.; Erickson, A.W.; Ong, W.; Gordon, V.; Coudière-Morrison, L.; Mercier, A.L.; et al. Failure of human rhombic lip differentiation underlies medulloblastoma formation. Nature 2022, 609, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, M.; Korshunov, A.; Remke, M.; Jones, D.T.; Schlanstein, M.; Northcott, P.A.; Cho, Y.J.; Koster, J.; Schouten-van Meeteren, A.; van Vuurden, D.; et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: An international meta-analysis of transcriptome, genetic aberrations, and clinical data of WNT, SHH, Group 3, and Group 4 medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, A.; Robinson, G.W.; Smith, K.S.; Lin, T.; Merchant, T.E.; Chintagumpala, M.; Mahajan, A.; Su, J.; Bouffet, E.; Bartels, U.; et al. Outcomes by Clinical and Molecular Features in Children With Medulloblastoma Treated With Risk-Adapted Therapy: Results of an International Phase III Trial (SJMB03). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Remke, M.; Bouffet, E.; Faria, C.C.; Perreault, S.; Cho, Y.J.; Shih, D.J.; Luu, B.; Dubuc, A.M.; Northcott, P.A.; et al. Recurrence patterns across medulloblastoma subgroups: An integrated clinical and molecular analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Slavc, I.; Mayr, L.; Stepien, N.; Gojo, J.; Aliotti Lippolis, M.; Azizi, A.A.; Chocholous, M.; Baumgartner, A.; Hedrich, C.S.; Holm, S.; et al. Improved Long-Term Survival of Patients with Recurrent Medulloblastoma Treated with a “MEMMAT-like” Metronomic Antiangiogenic Approach. Cancers 2022, 14, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Li, C.; Zhou, Q.; Qu, P.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Distinctive localization and MRI features correlate of molecular subgroups in adult medulloblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 135, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łastowska, M.; Jurkiewicz, E.; Trubicka, J.; Daszkiewicz, P.; Drogosiewicz, M.; Malczyk, K.; Grajkowska, W.; Matyja, E.; Cukrowska, B.; Pronicki, M.; et al. Contrast enhancement pattern predicts poor survival for patients with non-WNT/SHH medulloblastoma tumours. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 123, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, V.; Sugur, H.; Jaiswal, J.; Arvinda, H.R.; Arivazhagan, A.; Somanna, S.; Santosh, V. Medulloblastoma: Distinctive Histo-Molecular Correlation with Clinical Profile, Radiologic Characteristics, and Surgical Outcome. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2019, 54, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, P. A Study of Tumors Arising from Ependymal Cells. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1924, 11, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaf, J.; Kernohan, J.W. A study of the external granular layer in the cerebellum. The disappearance of the external granular layer and the growth of the molecular and internal granular layers in the cerebellum. Am. J. Anat. 1944, 75, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, L.D.; Echlin, F.A. Nature and Origin of Some Tumors of The Cerebellum: Medulloblastoma. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 1934, 31, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzarelli, R.; Simons, B.D.; Philpott, A. The developmental origin of brain tumours: A cellular and molecular framework. Development 2018, 145, dev162693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawauchi, D.; Robinson, G.; Uziel, T.; Gibson, P.; Rehg, J.; Gao, C.; Finkelstein, D.; Qu, C.; Pounds, S.; Ellison, D.W.; et al. A mouse model of the most aggressive subgroup of human medulloblastoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüller, U.; Heine, V.M.; Mao, J.; Kho, A.T.; Dillon, A.K.; Han, Y.G.; Huillard, E.; Sun, T.; Ligon, A.H.; Qian, Y.; et al. Acquisition of granule neuron precursor identity is a critical determinant of progenitor cell competence to form Shh-induced medulloblastoma. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Lopez, J.; Kumar, R.; Smith, K.S.; Northcott, P.A. Deconstructing Sonic Hedgehog Medulloblastoma: Molecular Subtypes, Drivers, and Beyond. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammel, D.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; von Bueren, A.O.; Kool, M.; Pietsch, T.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Rowitch, D.H.; Rutkowski, S.; Pfister, S.M.; Schüller, U. Sonic hedgehog-associated medulloblastoma arising from the cochlear nuclei of the brainstem. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northcott, P.A.; Hielscher, T.; Dubuc, A.; Mack, S.; Shih, D.; Remke, M.; Al-Halabi, H.; Albrecht, S.; Jabado, N.; Eberhart, C.G.; et al. Pediatric and adult sonic hedgehog medulloblastomas are clinically and molecularly distinct. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, A.; Mynarek, M.; Pietsch, T.; Pfister, S.M.; Clifford, S.C.; Goschzik, T.; Sturm, D.; Schwalbe, E.C.; Hicks, D.; Rutkowski, S.; et al. Imaging Characteristics of Wingless Pathway Subgroup Medulloblastomas: Results from the German HIT/SIOP-Trial Cohort. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Erkek, S.; Tong, Y.; Yin, L.; Federation, A.J.; Zapatka, M.; Haldipur, P.; Kawauchi, D.; Risch, T.; Warnatz, H.J.; et al. Active medulloblastoma enhancers reveal subgroup-specific cellular origins. Nature 2016, 530, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.S.; Bihannic, L.; Gudenas, B.L.; Haldipur, P.; Tao, R.; Gao, Q.; Li, Y.; Aldinger, K.A.; Iskusnykh, I.Y.; Chizhikov, V.V.; et al. Unified rhombic lip origins of group 3 and group 4 medulloblastoma. Nature 2022, 609, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forget, A.; Martignetti, L.; Puget, S.; Calzone, L.; Brabetz, S.; Picard, D.; Montagud, A.; Liva, S.; Sta, A.; Dingli, F.; et al. Aberrant ERBB4-SRC Signaling as a Hallmark of Group 4 Medulloblastoma Revealed by Integrative Phosphoproteomic Profiling. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 379–395.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalbe, E.C.; Lindsey, J.C.; Nakjang, S.; Crosier, S.; Smith, A.J.; Hicks, D.; Rafiee, G.; Hill, R.M.; Iliasova, A.; Stone, T.; et al. Novel molecular subgroups for clinical classification and outcome prediction in childhood medulloblastoma: A cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djirackor, L.; Halldorsson, S.; Niehusmann, P.; Leske, H.; Capper, D.; Kuschel, L.P.; Pahnke, J.; Due-Tønnessen, B.J.; Langmoen, I.A.; Sandberg, C.J.; et al. Intraoperative DNA methylation classification of brain tumors impacts neurosurgical strategy. Neurooncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab149. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | WNT (n = 10) | SHH (n = 10) | Non-WNT/Non-SHH (n = 38) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | 0.531 | |||
| Female | 5 (50.0) | 4 (40.0) | 12 (31.6) | |
| Male | 5 (50.0) | 6 (60.0) | 26 (68.4) | |
| Age at diagnosis, in years, median (range) | 8 (5–17) | 3 (0–17) | 7 (1–16) | 0.128 |
| KPS at diagnosis, median (range) | 70 (20–80) | 70 (60–80) | 70 (60–90) | 0.113 |
| Metastases at diagnosis, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| M0 | 10 (100.0) | 9 (90.0) | 15 (39.5) | |
| M+ | 0 (0.0) | 1 (10.0) | 23 (60.5) | |
| Histopathological subgroup, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Classic | 9 (90.0) | 0 (0.0) | 34 (89.5) | |
| LCA | 1 (10.0) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (10.5) | |
| DNMB | 0 (0.0) | 10 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| MBEN | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| TP53 status | NA | 10 (100.0) | NA | NA |
| wildtype mutant | NA | (0.0) | NA | |
| Extent of resection, n (%) | 0.015 | |||
| GTR | 10 (100.0) | 10 (100.0) | 26 (68.4) | |
| STR | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 12 (31.6) | |
| Radiotherapy, n (%) | 0.014 | |||
| no | 0 (0.0) | 5 (50.0) | 6 (15.8) | |
| yes | 10 (100.0) | 5 (50.0) | 32 (84.2) | |
| Chemotherapy, n (%) | NA | |||
| no | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| yes | 10 (100.0) | 10 (100.0) | 38 (100.0) | |
| KPS at last FU, median (range) | 90 (60–100) | 90 (20–100) | 80 (30–100) | 0.077 |
| Residual disease at last FU, n (%) | 0.578 1.000 | |||
| Cerebral disease | 1 (10.0) | 2 (20.0) | 3 (8.1) | |
| Metastatic disease | 1 (10.0) | 2 (20.0) | 6 (16.2) | |
| Progression, n (%) | 0.325 | |||
| no | 9 (90.0) | 8 (80.0) | 25 (65.8) | |
| yes | 1 (10.0) | 2 (20.0) | 13 (34.2) | |
| Death, n (%) | 0.881 | |||
| no | 9 (90.0) | 8 (80.0) | 34 (84.2) | |
| yes | 1 (10.0) | 2 (20.0) | 6 (15.8) |
| Primary Location | Extension | WNT (n = 10) | SHH (n = 10) | Non-WNT/Non-SHH (n = 38) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brainstem, n (%) | 3 (30.0) | 0 (0.0) | 11 (28.9) | 0.196 | |
| Caudal rhomboid Fossa, n | |||||
| including | |||||
| left lateral recess | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| right lateral recess | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||
| bilateral lateral recesses | 1 | 0 | 3 | ||
| Lateral recess, n | |||||
| including | |||||
| left lateral recess | 1 | 0 | 3 | ||
| left lateral recess and cerebellar peduncle | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| right lateral recess | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Cerebellar peduncle, n (%) | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Cerebellar hemispheres, n (%) | 1 (10.0) | 6 (60.0) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 | |
| Cerebellar vermis, n (%) | 6 (60.0) | 4 (40.0) | 27 (71.1) | 0.226 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciobanu-Caraus, O.; Czech, T.; Peyrl, A.; Haberler, C.; Kasprian, G.; Furtner, J.; Kool, M.; Sill, M.; Frischer, J.M.; Cho, A.; et al. The Site of Origin of Medulloblastoma: Surgical Observations Correlated to Molecular Groups. Cancers 2023, 15, 4877. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194877
Ciobanu-Caraus O, Czech T, Peyrl A, Haberler C, Kasprian G, Furtner J, Kool M, Sill M, Frischer JM, Cho A, et al. The Site of Origin of Medulloblastoma: Surgical Observations Correlated to Molecular Groups. Cancers. 2023; 15(19):4877. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194877
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiobanu-Caraus, Olga, Thomas Czech, Andreas Peyrl, Christine Haberler, Gregor Kasprian, Julia Furtner, Marcel Kool, Martin Sill, Josa M. Frischer, Anna Cho, and et al. 2023. "The Site of Origin of Medulloblastoma: Surgical Observations Correlated to Molecular Groups" Cancers 15, no. 19: 4877. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194877
APA StyleCiobanu-Caraus, O., Czech, T., Peyrl, A., Haberler, C., Kasprian, G., Furtner, J., Kool, M., Sill, M., Frischer, J. M., Cho, A., Slavc, I., Rössler, K., Gojo, J., & Dorfer, C. (2023). The Site of Origin of Medulloblastoma: Surgical Observations Correlated to Molecular Groups. Cancers, 15(19), 4877. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194877







