MicroRNA-34 Family in Cancers: Role, Mechanism, and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biosynthesis of miR-34s and Regulation of miR-34 Expression
2.1. Biosynthesis of miR-34s
2.2. Regulation of miR-34 Expression
3. The Roles of miR-34s in Cancers
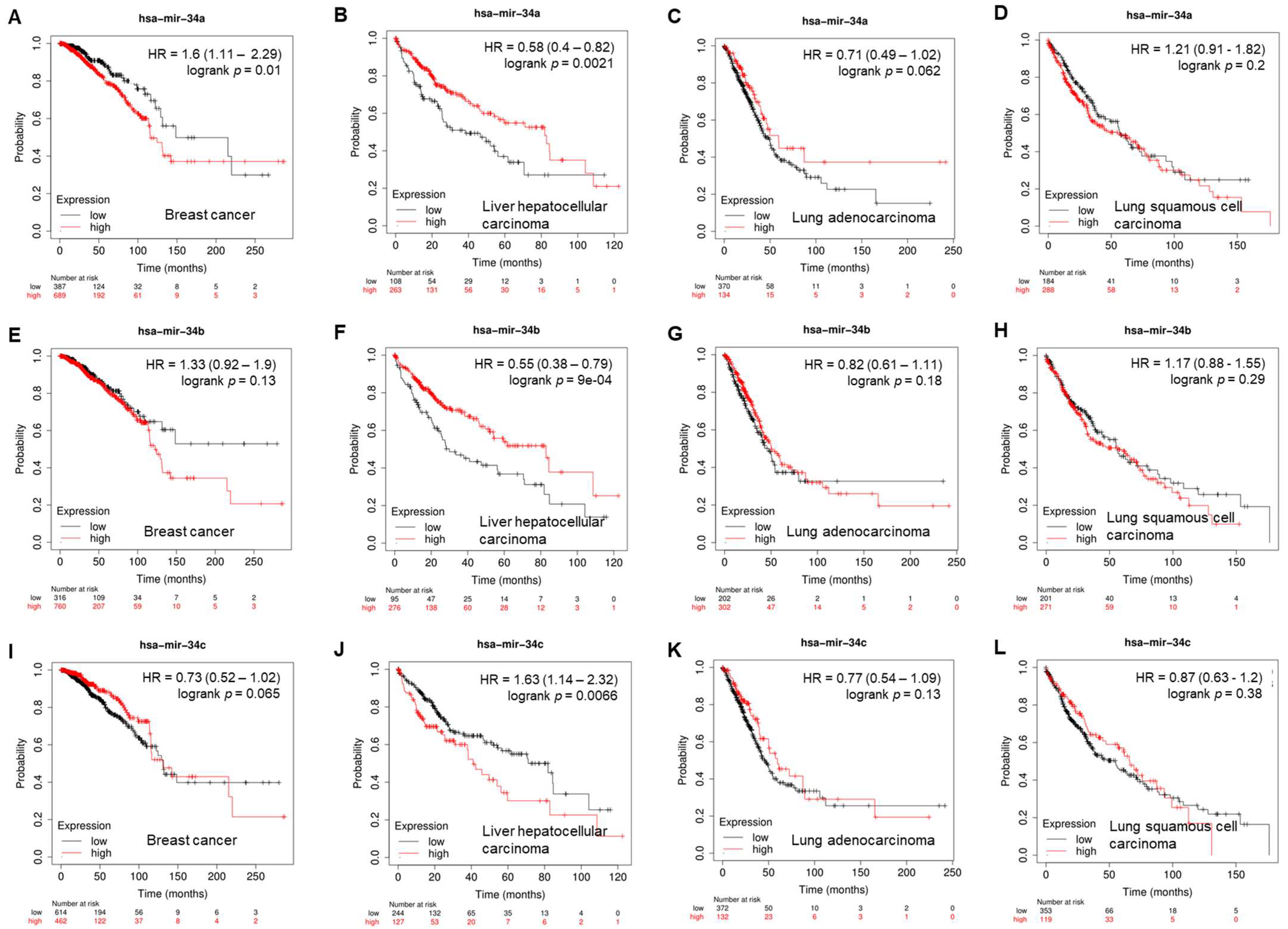
3.1. The Role of miR-34s in Breast Cancer
3.2. The Role of miR-34s in Lung Cancer
3.3. miR-34s in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
3.4. The Role of miR-34s in Head and Neck Cancer
3.5. The Role of miR-34s in Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma
3.6. The Role of miR-34s in Gastric Cancer
3.7. The Role of miR-34s in Colon Carcinoma
3.8. The Tumor-Suppressive Effects of miR-34s in Ovarian Cancer
3.9. The Role of miR-34s in Cervical Cancer
3.10. The Tumor Suppressive Function of miR-34s in Prostate Cancer
3.11. The Role of miR-34s in Osteosarcoma
3.12. The Role of miR-34s in Leukemia
3.13. The Role of miR-34s in Bladder Cancer
4. Exploring miR-34s in Drug Resistance
Overcoming Chemoresistance by Targeting CSCs
5. miR-34s and Cancer Therapy
5.1. Chemically Synthesized miR-34: Clinical Trials and Beyond
- Lung cancer: Clinical trials are currently underway to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of miR-34 mimics in patients with lung cancer. These trials aim to assess the impact of miR-34a mimic therapy on tumor growth, metastasis, and patient outcomes in different subtypes of lung cancer [162,163]. Additionally, using a preclinical mouse model of NSCLC known as 344SQ, treatment with MRX34 led to a decreased expression of PD-L1 protein, increased infiltration of tumor-fighting CD8+ cells, and decreased infiltration of PD1+ T-cells, macrophages, and T-regulatory cells, leading to delay in tumor growth [157]. Furthermore, a combination of miR-34a and let-7b by the encapsulated vehicle NOV340 reduced tumor burden and prolonged survival in therapy-resistant NSCLC mouse models [162].
- Lymphoma: The initial multicenter clinical trial (NCT01829971) included patients with lymphoma and provided evidence for the feasibility and potential benefits of miR-34 mimics therapy in this type of cancer. More studies to investigate the specific effects of miR-34 mimics on different subtypes of lymphoma and patient response rates are currently ongoing [164,165,166].
- Breast cancer: Clinical trials are being planned or conducted to explore the role of miR-34 mimics in the treatment of breast cancer. These trials aim to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of miR-34a mimics in combination with standard treatments, such as chemotherapy or targeted therapies [159,167].
5.2. Enhancing miR-34 Efficacy: Chemical Modifications and Nanodelivery Systems
5.2.1. Chemical Modifications to Enhance Stability and Potency
5.2.2. Nanodelivery Systems for Enhanced Cellular Uptake
5.3. Synergistic Effects of Codelivery of miR-34 Strategies
5.3.1. Codelivery of miR-34 Mimics with Natural Compounds
5.3.2. Codelivery with Conventional Chemotherapy Drugs
5.3.3. Codelivery with Targeted Therapies
6. Future Perspectives and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| miR-34s | miR-34 family |
| lncRNA | Long noncoding RNA |
| ceRNA | Competing endogenous RNA |
| cirRNA | Circular RNA |
| 3′-UTR | 3′-untranslated region |
| DNMT | DNA methyltransferase |
| EMT-TFs | Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factor |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
| PD-L1 | Programmed cell death-ligand 1 |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung cancer |
| NPC | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| ESCC | Esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma |
| AML | Acute myelogenous leukemia |
| TQ | Thymoquinone |
References
- Meister, G.; Tuschl, T. Mechanisms of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature 2004, 431, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bouyssou, J.M.; Manier, S.; Huynh, D.; Issa, S.; Roccaro, A.M.; Ghobrial, I.M. Regulation of microRNAs in cancer metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1845, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hermeking, H. The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Jia, Q.; Guo, X.; Li, K.; Chen, W.; Shen, Q.; Xu, C.; Fu, Y. microRNA-34 family: From mechanism to potential applications. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2022, 144, 106168. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, S.; Hu, M.; Li, C.; Zhou, X.; Chen, H. Role of miR-34 in gastric cancer: From bench to bedside (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M.; Knight, R.A. miR-34: From bench to bedside. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 872–881. [Google Scholar]
- Rokavec, M.; Li, H.; Jiang, L.; Hermeking, H. The p53/miR-34 axis in development and disease. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 6, 214–230. [Google Scholar]
- Maroof, H.; Salajegheh, A.; Smith, R.A.; Lam, A.K. Role of microRNA-34 family in cancer with particular reference to cancer angiogenesis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2014, 97, 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, R.S.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Filipowicz, W. Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: How many mechanisms? Trends Cell Biol. 2007, 17, 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, G.C.; Singh, J.; Barik, S. MicroRNAs: Processing, Maturation, Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Mol. Cell Pharmacol. 2011, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bommer, G.T.; Gerin, I.; Feng, Y.; Kaczorowski, A.J.; Kuick, R.; Love, R.E.; Zhai, Y.; Giordano, T.J.; Qin, Z.S. p53-mediated activation of miRNA34 candidate tumor-suppressor genes. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Cheng, J.; Chen, B.; Liu, Q.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y. Circulating microRNA-34 family low expression correlates with poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 3735–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Chijiwa, T.; Inoue, Y.; Abe, Y.; Suemizu, H.; Kawai, K.; Wakui, M.; Furukawa, D.; Mukai, M.; Kuwao, S. Overexpression of the miR-34 family suppresses invasive growth of malignant melanoma with the wild-type p53 gene. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 3, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Beresneva, E.V.; Rykov, S.V.; Hodyrev, D.S.; Pronina, I.V.; Ermilova, V.D.; Kazubskaia, T.P.; Braga, E.A.; Loginov, V.I. Methylation profile of group of miRNA genes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma; involvement in cancer progression. Genetika 2013, 49, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujino, T.; Yokosuka, A.; Higurashi, H.; Yokokawa, R.; Sakurai, R.; Harashima, W.; Miki, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Mimaki, Y.; Hayakawa, M. AU-1 from Agavaceae plants causes transient increase in p21/Cip1 expression in renal adenocarcinoma ACHN cells in an miR-34-dependent manner. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Hao, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Desano, J.; Fan, D.; Xu, L. Restoration of tumor suppressor miR-34 inhibits human p53-mutant gastric cancer tumorspheres. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, S.; Wei, C.; Cheng, J.; Khan, M.A.; Fu, S.; Yang, L.; Tania, M.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. MicroRNA-34a targets epithelial to mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors (EMT-TFs) and inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 21362–21379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboli, P.J.; Rahmat, A.; Ismail, P.; Ling, K.H. MicroRNA-based therapy and breast cancer: A comprehensive review of novel therapeutic strategies from diagnosis to treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 97, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyota, M.; Suzuki, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Maruyama, R.; Imai, K.; Shinomura, Y.; Tokino, T. Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-34b/c and B-cell translocation gene 4 is associated with CpG island methylation in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4123–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Ma, X.W.; Zhang, X.J.; Shen, S.Q. Erratum: Pri-miR-34b/c rs4938723 polymorphism is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma risk: A case-control study in a Chinese population. Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2017, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Xu, J.; Zheng, C.; Li, X.; Du, J. The analysis of microRNA-34 family expression in human cancer studies comparing cancer tissues with corresponding pericarcinous tissues. Gene 2015, 554, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welponer, H.; Tsibulak, I.; Wieser, V.; Degasper, C.; Shivalingaiah, G.; Wenzel, S.; Sprung, S.; Marth, C.; Hackl, H.; Fiegl, H. The miR-34 family and its clinical significance in ovarian cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corney, D.C.; Hwang, C.I.; Matoso, A.; Vogt, M.; Flesken-Nikitin, A.; Godwin, A.K.; Kamat, A.A.; Sood, A.K.; Ellenson, L.H.; Hermeking, H. Frequent downregulation of miR-34 family in human ovarian cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.; Munkacsy, G.; Gyorffy, B. Pancancer survival analysis of cancer hallmark genes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Mao, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, C.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Lin, Y.; Lv, Y. Serum exosomal miR-34a as a potential biomarker for the diagnosis and prognostic of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wei, X.; He, J.; Cao, Q.; Du, D.; Zhan, X.; Zeng, Y.; Yuan, S.; Sun, L. The comprehensive landscape of miR-34a in cancer research. Cancer Metastasis. Rev. 2021, 40, 925–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Xiao, G.G.; Mao, J.; Lu, Y.; Song, B.; Wang, L.; Fan, S.; Fan, P.; Hou, Z.; Li, J. Dysregulation of the miR-34a-SIRT1 axis inhibits breast cancer stemness. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10432–10444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yuan, L.; Luo, J.; Gao, J.; Guo, J.; Xie, X. MiR-34a inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer through down-regulation of Bcl-2 and SIRT1. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 13, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, S.; Luo, A.; Chen, H.; Ding, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. MicroRNA-34 suppresses breast cancer invasion and metastasis by directly targeting Fra-1. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4294–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akad, F.; Mocanu, V.; Peiu, S.N.; Scripcariu, V.; Filip, B.; Timofte, D.; Zugun-Eloae, F.; Cuciureanu, M.; Hancianu, M.; Oboroceanu, T. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Modulate Angiogenesis in Gastric Cancer. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, W.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, Y. Synergistic anti-tumor effect of anti-PD-L1 antibody cationic microbubbles for delivery of the miR-34a gene combined with ultrasound on cervical carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 988–1005. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Achari, C.; Winslow, S.; Ceder, Y.; Larsson, C. Expression of miR-34c induces G2/M cell cycle arrest in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raver-Shapira, N.; Marciano, E.; Meiri, E.; Spector, Y.; Rosenfeld, N.; Moskovits, N.; Bentwich, Z.; Oren, M. Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to p53-mediated apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- mRNA Vaccine Slows Melanoma Recurrence. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 1278. [CrossRef]
- Lujambio, A.; Calin, G.A.; Villanueva, A.; Ropero, S.; Sanchez-Cespedes, M.; Blanco, D.; Montuenga, L.M.; Rossi, S.; Nicoloso, M.S.; Faller, W.J. A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13556–13561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandke, P.; Wyatt, N.; Fraser, J.; Bates, B.; Berberich, S.J.; Markey, M.P. MicroRNA-34a modulates MDM4 expression via a target site in the open reading frame. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Guo, J.; Li, D.; Jia, C.; Yin, W.; Sun, R.; Lv, Z.; Cong, X. MicroRNA-34a suppresses cell proliferation by targeting LMTK3 in human breast cancer mcf-7 cell line. DNA Cell Biol. 2013, 32, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, T.V.; Hart, M.; Nickels, R.; Kim, Y.J.; Menger, M.D.; Bohle, R.M.; Keller, A.; Ludwig, N.; Meese, E. MiR-34a-3p alters proliferation and apoptosis of meningioma cells in vitro and is directly targeting SMAD4, FRAT1 and BCL2. Aging 2017, 9, 932–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.Y.; Chang, E.; Lee, E.J.; Lee, H.W.; Kang, H.G.; Chun, K.H.; Woo, Y.M.; Kong, H.K.; Ko, J.Y.; Suzuki, H. Targeting of miR34a-NOTCH1 axis reduced breast cancer stemness and chemoresistance. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7573–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Ji, M.H.; Zhong, S.L.; Zha, Q.B.; Xu, J.J.; Zhao, J.H.; Tang, J.H. MicroRNA-34a modulates chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells to adriamycin by targeting Notch1. Arch. Med. Res. 2012, 43, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Jiao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Park, E.Y.; Zhang, H. MicroRNA 34c gene down-regulation via DNA methylation promotes self-renewal and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast tumor-initiating cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, B. LncRNA NEAT1 promotes docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer by regulating ACSL4 via sponging miR-34a-5p and miR-204-5p. Cell Signal 2020, 65, 109422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Xin, H.; Yan, G.; Liu, Z. NONHSAG028908,3 sponges miR-34a-5p to promote growth of colorectal cancer via targeting ALDOA. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 49, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, J.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, Y.; Zhou, D.; He, S. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 sponges miR-34c-5p to promote osteosarcoma growth via ALDOA enhanced aerobic glycolysis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xu, C.; Cao, X.; Wang, W. Isovitexin Suppresses Cancer Stemness Property And Induces Apoptosis Of Osteosarcoma Cells By Disruption Of The DNMT1/miR-34a/Bcl-2 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 8923–8936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, F.; Wang, M. Long Noncoding RNA SNHG7 Promotes the Tumor Growth and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via Regulation of miR-34a Signals in Osteosarcoma. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2018, 33, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, X.; Niu, X.; Jiao, R.; Li, X.; Wang, S. miR-34c-5p targets Notch1 and suppresses the metastasis and invasion of cervical cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazawa, H.; Tsuchiya, N.; Izumiya, M.; Nakagama, H. Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15472–15477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, X.; Lim, L.P.; de Stanchina, E.; Xuan, Z.; Liang, Y.; Xue, W.; Zender, L.; Magnus, J.; Ridzon, D. A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature 2007, 447, 1130–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Fu, H.; Liu, Q.; Tie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xing, R.; Sun, Z. Downregulation of CCND1 and CDK6 by miR-34a induces cell cycle arrest. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1564–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Xu, X.; Zheng, E.; Ni, J.; Jiang, X.; Yang, M.; Zhao, G. LncRNA RP11-805J14.5 functions as a ceRNA to regulate CCND2 by sponging miR-34b-3p and miR-139-5p in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 48, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Ge, F.; Du, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D. MiR-34b-3p represses cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and cell apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by targeting CDK4. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5282–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigazzi, M.; Manara, E.; Baron, E.; Basso, G. miR-34b targets cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2471–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, E.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Yang, X. LINC01006 facilitates cell proliferation, migration and invasion in prostate cancer through targeting miR-34a-5p to up-regulate DAAM1. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.P.; Shih, I.H.; Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 2003, 115, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Guo, Y.; Huang, K.; Lu, R.; Peng, X.; Lin, S. MicroRNA-34a inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting E2F5. J. BUON 2019, 24, 2514–2522. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Liu, L. miR-34a-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in head and neck squamous cell cancer progression by targeting Flotillin-2. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4327–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Zhou, X.; Mao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tang, X.; Yan, S.; Tang, S. CircCRIM1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression via the miR-34c-5p/FOSL1 axis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Lu, M.; Guo, R.; Li, D.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Deng, G.; Xu, Y. miR-34a inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via regulation of FOXM1. Oncol Lett. 2019, 17, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Kong, L.; Pu, Y.; Chao, F.; Zang, C.; Qin, W.; Zhao, F.; Cai, S. Long Noncoding RNA DICER1-AS1 Functions in Methylation Regulation on the Multi-Drugresistance of Osteosarcoma Cells via miR-34a-5p and GADD45A. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 685881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Fan, B.; Ren, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y. Long noncoding RNA DANCR contributes to docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer through targeting the miR-34a-5p/JAG1 pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 5485–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Fu, J.; Xiao, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, R.C. MiR-34a regulates therapy resistance by targeting HDAC1 and HDAC7 in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 354, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markey, M.; Berberich, S.J. Full-length hdmX transcripts decrease following genotoxic stress. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6657–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ma, S.; Fu, T.; Zhao, S.; Gao, M. MicroRNA-34a-5p suppresses tumorigenesis and progression of glioma and potentiates Temozolomide-induced cytotoxicity for glioma cells by targeting HMGA2. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 852, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Lv, L. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 regulates the development of osteosarcoma through sponging miR-34a-5p to mediate HOXA13 expression as a competitive endogenous RNA. Mol. Genet. Genomic. Med. 2019, 7, e673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Gao, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, Y.; Huo, Z. MicroRNA-34c-5p exhibits anticancer properties in gastric cancer by targeting MAP2K1 to inhibit cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Biomed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7375661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, C.; Petrelli, A.; Ghiso, E.; Corso, S.; Capparuccia, L.; Eramo, A.; Comoglio, P.M.; Giordano, S. MicroRNAs impair MET-mediated invasive growth. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 10128–10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J.B.; Miao, Y.; Du, X.Y.; Wang, R.; Yang, H.; Xu, W.; Li, J.Y.; Fan, L. A feedback circuit of miR-34a/MDM4/p53 regulates apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 6143–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Song, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, M.; Ji, Y.; Wu, F.; Chen, Y.; Cui, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, L. Tumor suppressor microRNA-34a inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting MMP-2/MMP-9/FNDC3B in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.Y.; Chang, A.C.; Tsai, T.F.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, H.E.; Ho, C.Y.; Chen, P.C.; Hwang, T.I. MicroRNA-34a-5p serves as a tumor suppressor by regulating the cell motility of bladder cancer cells through matrix metalloproteinase-2 silencing. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Jing, D.; Zhu, F. Silencing of Long Non-coding RNA LINC01106 Represses Malignant Behaviors of Gastric Cancer Cells by Targeting miR-34a-5p/MYCN Axis. Mol. Biotechnol. 2022, 64, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, B.; Yuan, B.; Du, S.; Zeng, Z. The miR-34a-5p-c-MYC-CHK1/CHK2 Axis Counteracts Cancer Stem Cell-Like Properties and Enhances Radiosensitivity in Hepatocellular Cancer Through Repression of the DNA Damage Response. Radiat. Res. 2023, 199, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.S.; Song, Y.K.; Durinck, S.; Chen, Q.R.; Cheuk, A.T.; Tsang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Thiele, C.J.; Slack, A.; Shohet, J. The MYCN oncogene is a direct target of miR-34a. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5204–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liu, W.; Shi, H.; Zhou, H. Exosomal miR-34b inhibits proliferation and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting Notch2 in ovarian cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 2721–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Xu, Y.J.; Qiao, C.W. MiR-34c-3p suppresses the proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by inhibiting PAC1/MAPK pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 6312–6322. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Zeng, Y.; Qin, X.; Tan, Y.; Liang, B.; Cao, Y. p53 downregulates PD-L1 expression via miR-34a to inhibit the growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells: A potential clinical immunotherapeutic target. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Che, L.; Xu, C.; Lu, D.; Xu, Y.; Liu, M.; Chai, W. XIST/miR-34a-5p/PDL1 axis regulated the development of lung cancer cells and the immune function of CD8+ T cells. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2022, 42, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Xue, J.; Fei, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Peng, Q.; Yuan, H. ncRNA-mediated low expression of P2RY14 correlates with poor prognosis and tumor immune infiltration in ovarian carcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2023, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, S.; Qi, L.; Ling, L. Long Noncoding RNA HCG9 Promotes Osteosarcoma Progression through RAD51 by Acting as a ceRNA of miR-34b-3p. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 9978882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Zhang, D.X.; Cao, Q.; He, C.K. LncRNA HCG18 Promotes Osteosarcoma Cells Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in by Regulating miR-34a/RUNX2 Pathway. Biochem. Genet. 2023, 61, 1035–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Yang, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, W. miR-34a induces immunosuppression in colorectal carcinoma through modulating a SIRT1/NF-kappaB/B7-H3/TNF-alpha axis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 2247–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Hao, L.; Yang, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, J. miRNA-34a suppresses colon carcinoma proliferation and induces cell apoptosis by targeting SYT1. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 2887–2897. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, W.; Yue, Y.; Zeng, G. MicroRNA-34c-5p Reduces Malignant Properties of Lung Cancer Cells through Regulation of TBL1XR1/Wnt/beta-catenin Signaling. Curr. Mol. Med. 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, S.; Liang, W. miR-34 inhibits growth and promotes apoptosis of osteosarcoma in nude mice through targetly regulating TGIF2 expression. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hermeking, H. miR-34a and miR-34b/c Suppress Intestinal Tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2746–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Xu, G.C.; Liu, S.T.; Liu, T.; Geng, B. MiR-34a affects G2 arrest in prostate cancer PC3 cells via Wnt pathway and inhibits cell growth and migration. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 8349–8358. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.; Ge, X.; Geng, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhu, W.; Jiao, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, J.; Cao, J. miR-34a inhibits the migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Yin Yang-1. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumaru, Y.; Katsuta, E.; Oshi, M.; Sporn, J.C.; Yan, L.; Le, L.; Matsuhashi, N.; Futamura, M.; Akao, Y.; Yoshida, K. High Expression of miR-34a Associated with Less Aggressive Cancer Biology but Not with Survival in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetti, P.; Climent, M.; Panebianco, F.; Tordonato, C.; Santoro, A.; Marzi, M.J.; Pelicci, P.G.; Ventura, A.; Nicassio, F. Dual role for miR-34a in the control of early progenitor proliferation and commitment in the mammary gland and in breast cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhu, D.; Luo, Z.; Yang, M. Low Expression of Circulating MicroRNA-34c is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Yonsei Med. J. 2017, 58, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.; Provot, S.; Werb, Z. GATA3 in development and cancer differentiation: Cells GATA have it! J. Cell Physiol. 2010, 222, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiakou, A.; Zagouri, F.; Zografos, E.; Samelis, G.; Gazouli, M.; Kalapanida, D.; Giannos, A.; Marinopoulos, S.; Dimitrakakis, K.; Lazaris, C.A. Prognostic significance of miR-34 rs4938723 T > C polymorphism in triple negative breast cancer patients. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 68, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Wang, S.; Jiang, T.; Zheng, M.Q.; Zheng, Z.J.; Chen, C.X. Association between polymorphisms in the promoter region of pri-miR-34b/c and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Danesh, H.; Bizhani, F.; Narouie, B.; Sotoudeh, M.; Nouralizadeh, A.; Sharifiaghdas, F.; Bahari, G.; Taheri, M. Pri-miR-34b/c rs4938723 polymorphism increased the risk of prostate cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 18, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelli, D.; Pedone, C.; Majeed, M.; Sahebkar, A. Curcumin and Lung Cancer: The Role of microRNAs. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 3440–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, S.; Tan, X.; Liu, X.; Park, S.; Kang, K.; Yoon, J.S.; Ko, Y.H.; Kurie, J.M. MiR-34a and miR-34b/c have distinct effects on the suppression of lung adenocarcinomas. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Mataki, H.; Arai, T.; Okato, A. The microRNA expression signature of small cell lung cancer: Tumor suppressors of miR-27a-5p and miR-34b-3p and their targeted oncogenes. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 62, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daugaard, I.; Knudsen, A.; Kjeldsen, T.E.; Hager, H.; Hansen, L.L. The association between miR-34 dysregulation and distant metastases formation in lung adenocarcinoma. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2017, 102, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Lee, W.K.; Lee, E.B.; Son, J.W.; Kim, D.S.; Park, J.Y. Combined Effect of Metastasis-Related MicroRNA, miR-34 and miR-124 Family, Methylation on Prognosis of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, e13–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, R. LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 enhances cell invasion, migration and tumor formation in non-small cell lung cancer cells by epigenetic inhibition of miR-34a. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Fu, J.; Chen, H.; Cheng, J.; Fu, J. Roles of MicroRNA-34a in Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition, Competing Endogenous RNA Sponging and Its Therapeutic Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamani, F.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Masoumi, M.; Babashah, S. Evaluation of MiR-34 Family and DNA Methyltransferases 1, 3A, 3B Gene Expression Levels in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Following Treatment with Dendrosomal Nanocurcumin. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Wang, Y.C.; Han, Y.D. MicroRNA-34a inhibits liver cancer cell growth by reprogramming glucose metabolism. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4483–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Zhu, A.; Jiao, X.; Ge, J.; Xu, X. Combined low miR-34s are associated with unfavorable prognosis in children with hepatoblastoma: A Chinese population-based study. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 51, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Cheng, Y.L.; Matthen, M.; Yoon, A.; Schwartz, G.K.; Bala, S.; Taylor, A.M. Down-regulation of the tumor suppressor miR-34a contributes to head and neck cancer by up-regulating the MET oncogene and modulating tumor immune evasion. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, M.; Shanehbandi, D.; Mohammadpour, H.; Hashemzadeh, S.; Sepehri, B. Expression Level of miR-34a in Tumor Tissue from Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2019, 50, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.F.; Wei, S.B.; Mitchelson, K.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, Y.F.; Meng, Z.; Gan, Y.H.; Yu, G.Y. miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion of tongue squamous cell carcinoma via targeting MMP9 and MMP14. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, D.; Wang, K.; Li, C.; Han, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Cui, X.; Li, F. Hypermethylation of miR-34b/c is associated with early clinical stages and tumor differentiation in Kazakh patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 3119–3127. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Fan, B.; Chen, D.; Guo, C.; Xiang, H.; Nie, Y.; Zhong, D.; Shi, X. Human cytomegalovirus protein UL136 activates the IL-6/STAT3 signal through MiR-138 and MiR-34c in gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 1936–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, H.H.; Kwack, K.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, J.O.; Park, H.S.; Ryu, C.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Ko, D.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, N.K. Association between TP53 genetic polymorphisms and the methylation and expression of miR-34a, 34b/c in colorectal cancer tissues. Oncol Lett. 2019, 17, 4726–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, J.B.; Fichna, J.; Mosinska, P. One step ahead: miRNA-34 in colon cancer-future diagnostic and therapeutic tool? Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 132, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova-Rivas, S.; Fraire-Soto, I.; Mercado-Casas Torres, A.; Servin-Gonzalez, L.S.; Granados-Lopez, A.J.; Lopez-Hernandez, Y.; Reyes-Estrada, C.A.; Gutierrez-Hernandez, R.; Castaneda-Delgado, J.E.; Ramirez-Hernandez, L. 5p and 3p Strands of miR-34 Family Members Have Differential Effects in Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Cervical Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Cheng, H. miR-34a-5p blocks cervical cancer growth and migration by downregulating CDC25A. J. BUON 2021, 26, 1768–1774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gupta, J.; Abdulsahib, W.K.; Turki Jalil, A.; Saadi Kareem, D.; Aminov, Z.; Alsaikhan, F.; Ramirez-Coronel, A.A.; Ramaiah, P.; Farhood, B. Prostate cancer and microRNAs: New insights into apoptosis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 245, 154436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.J.; Liu, X.; Dougherty, E.M.; Tang, D.G. MicroRNA-34a, Prostate Cancer Stem Cells, and Therapeutic Development. Cancers 2022, 14, 4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhang, L.Y.; Qiao, Y.H.; Song, R.J. Long noncoding RNA LINC00662 functions as miRNA sponge to promote the prostate cancer tumorigenesis through targeting miR-34a. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 3688–3698. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, T.; Ren, X.; Yang, M.; Tu, C.; Li, Z. Mir-34a: A regulatory hub with versatile functions that controls osteosarcoma networks. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourbault, O.; Llobat, L. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Canine Osteosarcoma: A New Future? Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, W.; Li, X. The DNMT1/miR-34a Axis Is Involved in the Stemness of Human Osteosarcoma Cells and Derived Stem-Like Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 7028901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Yuan, X.; Li, G.; Ma, M.; Sun, J. Long noncoding RNA CASC11 promotes osteosarcoma metastasis by suppressing degradation of snail mRNA. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, B. Long Non-Coding RNA Metastasis-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 (MALAT1) Promotes Proliferation and Metastasis of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting c-Met and SOX4 via miR-34a/c-5p and miR-449a/b. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-Inman, H.; Kuehl, D. Acute Leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 31, 1011–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, B.; Qi, X.; Bai, L.; Li, B.; Bao, H.; Wu, X.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y. Circular RNA ATAD1 is upregulated in acute myeloid leukemia and promotes cancer cell proliferation by downregulating miR-34b via promoter methylation. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Ma, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Luo, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, L. miR-34c-5p promotes eradication of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells by inducing senescence through selective RAB27B targeting to inhibit exosome shedding. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, T.I.; Cuiu, Y.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, P.C.; Tsai, T.F.; Chou, K.Y.; Ho, C.Y.; Chen, H.E.; Chang, P.H.; Chang, A.C. Tumor suppressive functions of hsa-miR-34a on cell cycle, migration and protective autophagy in bladder cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2023, 62, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.S.; He, Y.H.; Deng, Y.S.; Peng, P.X.; Wang, J.F.; Chen, X.; Zhao, P.Y.; Zhou, X.F. MicroRNA-34a inhibits bladder cancer cell migration and invasion, and upregulates PTEN expression. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 5549–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chen, B.; Li, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Lang, B. DNMT3B silencing suppresses migration and invasion by epigenetically promoting miR-34a in bladder cancer. Aging 2020, 12, 23668–23683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juracek, J.; Stanik, M.; Vesela, P.; Radova, L.; Dolezel, J.; Svoboda, M.; Slaby, O. Tumor expression of miR-34a-3p is an independent predictor of recurrence in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer and promising additional factor to improve predictive value of EORTC nomogram. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 184.e1–184.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Huang, G.; Lu, C.; Wen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. A four-miRNA signature in serum as a biomarker for bladder cancer diagnosis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 4606–4616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naghizadeh, S.; Mohammadi, A.; Duijf, P.H.G.; Baradaran, B.; Safarzadeh, E.; Cho, W.C.; Mansoori, B. The role of miR-34 in cancer drug resistance. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 6424–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Yagüe, E.; Ji, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. miRNA-205 targets VEGFA and FGF2 and regulates resistance to chemotherapeutics in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, S.L.; Das, S. The Role of MicroRNAs in Diagnosis, Prognosis, Metastasis and Resistant Cases in Breast Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 1845–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, H.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Z.; Liu, K. MicroRNA34a is associated with chemotherapy resistance, metastasis, recurrence, survival, and prognosis in patient with osteosarcoma. Medicine 2022, 101, e30722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, L.; Guo, S.; Hu, S.; Tian, M.; Nie, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, C.; Niu, J. Targeting the miR-34a/LRPPRC/MDR1 axis collapse the chemoresistance in P53 inactive colorectal cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 2177–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Li, K.; Tao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, N.; Liu, J.; Go, V.L.W.; Guo, J.; Gao, G. MicroRNA-34a Alleviates Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Cancer by Repression of Cancer Stem Cell Renewal. Pancreas 2021, 50, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.J.; Zheng, H.L.; Ke, X.Q.; Deng, M.; Ma, Z.Z.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, Y.Y. Hsa-miR-34a-5p reverses multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells by targeting the 3’-UTR of SIRT1 and inhibiting its expression. Cell Signal 2021, 84, 110016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liang, C.; Chen, X. Exosomal LINC00355 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes bladder cancer cell resistance to cisplatin by regulating miR-34b-5p/ABCB1 axis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2021, 53, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanokura, M.; Banno, K.; Aoki, D. MicroRNA-34b expression enhances chemosensitivity of endometrial cancer cells to paclitaxel. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, L.; Liu, S.; Liang, C. MiR-34b-3p Represses the Multidrug-Chemoresistance of Bladder Cancer Cells by Regulating the CCND2 and P2RY1 Genes. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catuogno, S.; Cerchia, L.; Romano, G.; Pognonec, P.; Condorelli, G.; de Franciscis, V. miR-34c may protect lung cancer cells from paclitaxel-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2013, 32, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Z.; Lei, C.C.; Zhao, Y.P.; Sun, H.W.; Yu, Q.H.; Yang, E.J.; Zhan, X. MicroRNA-34c-3p target inhibiting NOTCH1 suppresses chemosensitivity and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520904847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, J.J.; Yang, X.R.; Yu, Y.L. Upregulation of miR-34c after silencing E2F transcription factor 1 inhibits paclitaxel combined with cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Li, Y.; Pan, Q.; Ye, M.; He, S.; Tian, Q.; Xue, M. MiR-34c/SOX9 axis regulates the chemoresistance of ovarian cancer cell to cisplatin-based chemotherapy. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 2940–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, S.L.; Huang, W.C.; Hsu, F.C.; Yang, Z.P.; Jang, T.H.; Chang, J.W.; Chuang, C.M.; Lai, C.R.; Wang, L.H. miRNA-34c-5p inhibits amphiregulin-induced ovarian cancer stemness and drug resistance via downregulation of the AREG-EGFR-ERK pathway. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ochiya, T. miRNA signaling networks in cancer stem cells. Regen. Ther. 2021, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Kasinski, A.L.; Shen, H.; Slack, F.J.; Tang, D.G. MicroRNA-34a: Potent Tumor Suppressor, Cancer Stem Cell Inhibitor, and Potential Anticancer Therapeutic. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 640587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Wen, D.; Wang, X.; Mahato, R.I. Dual responsive micelles capable of modulating miRNA-34a to combat taxane resistance in prostate cancer. Biomaterials 2019, 192, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vares, G.; Ahire, V.; Sunada, S.; Ho Kim, E.; Sai, S.; Chevalier, F.; Romeo, P.H.; Yamamoto, T.; Nakajima, T.; Saintigny, Y. A multimodal treatment of carbon ions irradiation, miRNA-34 and mTOR inhibitor specifically control high-grade chondrosarcoma cancer stem cells. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 150, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, S.; Wu, R.C.; Fu, J. MicroRNA-34 family in breast cancer: From research to therapeutic potential. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3765–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daverey, A.; Brown, K.M.; Kidambi, S. Breast Cancer/Stromal Cells Coculture on Polyelectrolyte Films Emulates Tumor Stages and miRNA Profiles of Clinical Samples. Langmuir 2015, 31, 9991–10001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, Z.; Geng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Z. Exosomal miRNA-34 from cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibits growth and invasion of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Aging 2020, 12, 8549–8564. [Google Scholar]
- Kalfert, D.; Ludvikova, M.; Pesta, M.; Ludvik, J.; Dostalova, L.; Kholova, I. Multifunctional Roles of miR-34a in Cancer: A Review with the Emphasis on Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Thyroid Cancer with Clinical Implications. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 563. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, Y.; Tang, L. MicroRNA-34 family: A potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cortez, M.A.; Ivan, C.; Valdecanas, D.; Wang, X.; Peltier, H.J.; Ye, Y.; Araujo, L.; Carbone, D.P.; Shilo, K.; Giri, D.K. PDL1 Regulation by p53 via miR-34. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djv303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Daige, C.L.; Wiggins, J.F.; Priddy, L.; Nelligan-Davis, T.; Zhao, J.; Brown, D. Systemic delivery of a miR34a mimic as a potential therapeutic for liver cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D.S.; Kang, Y.K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Brenner, A.J.; Park, K.; Lee, J.L.; Kim, T.Y. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beg, M.S.; Brenner, A.J.; Sachdev, J.; Borad, M.; Kang, Y.K.; Stoudemire, J.; Smith, S.; Bader, A.G.; Kim, S.; Hong, D.S. Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 180–188. [Google Scholar]
- Kelnar, K.; Bader, A.G. A qRT-PCR Method for Determining the Biodistribution Profile of a miR-34a Mimic. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1317, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kasinski, A.L.; Kelnar, K.; Stahlhut, C.; Orellana, E.; Zhao, J.; Shimer, E.; Dysart, S.; Chen, X.; Bader, A.G.; Slack, F.J. A combinatorial microRNA therapeutics approach to suppressing non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3547–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggins, J.F.; Ruffino, L.; Kelnar, K.; Omotola, M.; Patrawala, L.; Brown, D.; Bader, A.G. Development of a lung cancer therapeutic based on the tumor suppressor microRNA-34. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5923–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, V.J.; Tzankov, A.; Flori, M.; Schmid, C.A.; Bader, A.G.; Müller, A. Systemic microRNA-34a delivery induces apoptosis and abrogates growth of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in vivo. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2421–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, V.J.; Cogliatti, S.B.; Imig, J.; Renner, C.; Neuenschwander, S.; Rehrauer, H.; Schlapbach, R.; Dirnhofer, S.; Tzankov, A.; Müller, A. Myc-mediated repression of microRNA-34a promotes high-grade transformation of B-cell lymphoma by dysregulation of FoxP1. Blood 2011, 117, 6227–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Dong, K.; Lin, F.; Long, M.; Ouyang, Y.; Wei, J.; Chen, X.; Weng, Y.; He, T. Tumor suppressor miR-34a targets PD-L1 and functions as a potential immunotherapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Signal 2015, 27, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaldi, A.M.; Salvatore, M.; Incoronato, M. miRNA-Based Therapeutics in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 668464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Kelnar, K.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Calhoun-Davis, T.; Li, H.; Patrawala, L.; Yan, H.; Jeter, C.; Honorio, S.; et al. The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabot, S.; Orio, J.; Castanier, R.; Bellard, E.; Nielsen, S.J.; Golzio, M.; Teissié, J. LNA-based oligonucleotide electrotransfer for miRNA inhibition. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, V.; Winkler, J. miRNA-based therapies: Strategies and delivery platforms for oligonucleotide and non-oligonucleotide agents. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1967–1984. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, K.; Gupta, S.; Gokhale, S.S.; Dey, R.; Gunjal, A.D.; Kumar, V.A.; Pillai, B. Detection and knockdown of microRNA-34a using thioacetamido nucleic acid. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013, 23, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shushan, D.; Markovsky, E.; Gibori, H.; Tiram, G.; Scomparin, A.; Satchi-Fainaro, R. Overcoming obstacles in microRNA delivery towards improved cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2014, 4, 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, M.; Prakash, T.P.; Corey, D.R. Argonaute 2-dependent Regulation of Gene Expression by Single-stranded miRNA Mimics. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panebianco, F.; Climent, M.; Malvindi, M.A.; Pompa, P.P.; Bonetti, P.; Nicassio, F. Delivery of biologically active miR-34a in normal and cancer mammary epithelial cells by synthetic nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2019, 19, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, F.C.; Pichon, C.; Letourneur, D.; Chaubet, F. miRNA Delivery by Nanosystems: State of the Art and Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, M.; Nickl, L.; Walch-Rueckheim, B.; Krammes, L.; Rheinheimer, S.; Diener, C.; Taenzer, T.; Kehl, T.; Sester, M.; Lenhof, H.P. Wrinkle in the plan: miR-34a-5p impacts chemokine signaling by modulating CXCL10/CXCL11/CXCR3-axis in CD4(+), CD8(+) T cells, and M1 macrophages. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Pukale, S.; Sahel, D.K.; Singh, P.; Mittal, A.; Chitkara, D. Folate targeted hybrid lipo-polymeric nanoplexes containing docetaxel and miRNA-34a for breast cancer treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 128, 112305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, H.; Li, Q. Lipoic Acid-Modified Oligoethyleneimine-Mediated miR-34a Delivery to Achieve the Anti-Tumor Efficacy. Molecules 2021, 26, 4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, C.H.; Ioele, S.A.; Day, E.S. Layer-by-layer assembled PLGA nanoparticles carrying miR-34a cargo inhibit the proliferation and cell cycle progression of triple-negative breast cancer cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2020, 108, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukocheva, O.A.; Liu, J.; Neganova, M.E.; Beeraka, N.M.; Aleksandrova, Y.R.; Manogaran, P.; Grigorevskikh, E.M.; Chubarev, V.N.; Fan, R. Perspectives of using microRNA-loaded nanocarriers for epigenetic reprogramming of drug resistant colorectal cancers. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86 Pt 2, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Lian, G.; Yang, K.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Co-delivery of microRNA-21 antisense oligonucleotides and gemcitabine using nanomedicine for pancreatic cancer therapy. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Hushmandi, K.; Hashemi, F.; Rahmani Moghadam, E.; Raei, M.; Kalantari, M.; Tavakol, S.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Najafi, M. Progress in Natural Compounds/siRNA Co-delivery Employing Nanovehicles for Cancer Therapy. ACS Comb. Sci. 2020, 22, 669–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweef, O.; Zaabout, E.; Bakheet, A.; Halawa, M.; Gad, I.; Akela, M.; Tousson, E.; Abdelghany, A.; Furuta, S. Unraveling Therapeutic Opportunities and the Diagnostic Potential of microRNAs for Human Lung Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Vázquez, L.A.; Méndez-García, A.; Rodríguez, A.L.; Sahare, P.; Pathak, S.; Banerjee, A.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Paul, S. Applications of nanotechnologies for miRNA-based cancer therapeutics: Current advances and future perspectives. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1208547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tania, M.; Asad, A.; Li, T.; Islam, M.S.; Islam, S.B.; Hossen, M.M.; Bhuiyan, M.R.; Khan, M.A. Thymoquinone against infectious diseases: Perspectives in recent pandemics and future therapeutics. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 24, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Abtahi, N.A.; Naghib, S.M.; Haghiralsadat, F.; Akbari Edgahi, M.; Askari, E. A comparative study on biopharmaceutical function of curcumin and miR-34a by multistimuli-responsive nanoniosome carrier: In-vitro and in-vivo. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1043277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, S.; Shen, H.; Chen, W.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Sun, D.; Zhong, S.; Zhao, J.; Tang, J. Curcumin inhibits cancer progression through regulating expression of microRNAs. Tumour. Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317691680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.; Peng, Y.; Lin, F.; Singh, R.K.; Mahato, R.I. Micellar Delivery of miR-34a Modulator Rubone and Paclitaxel in Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3244–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, S.S.; Ahmed, S.; Malik, J.A.; Hani, U.; Khanam, A.; Ashraf Bhat, F.; Ahmad Mir, S.; Ghazwani, M.; Wahab, S.; Haider, N. Therapeutic Delivery of Tumor Suppressor miRNAs for Breast Cancer Treatment. Biology 2023, 12, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Cao, M.; Zhang, J.; Hu, K.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, X.; Yang, Y.; Sheng, W.; Wu, Y.; et al. Hyaluronic acid-chitosan nanoparticles for co-delivery of MiR-34a and doxorubicin in therapy against triple negative breast cancer. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4333–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlhut, C.; Slack, F.J. Combinatorial Action of MicroRNAs let-7 and miR-34 Effectively Synergizes with Erlotinib to Suppress Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussecker, D. Current issues of RNAi therapeutics delivery and development. J. Control. Release 2014, 195, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Swearson, S.; Krongbaramee, T.; Sun, H.; Hong, L.; Amendt, B.A. Exploring microRNAs in craniofacial regenerative medicine. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2023, 51, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Yang, S.; Qu, X.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, L.; Sun, X.; Lin, Y.; Luo, M.; Lei, B.; Yue, C. A bionic “Trojan horse”-like gene delivery system hybridized with tumor and macrophage cell membrane for cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2023, 358, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingle, R.G.; Fang, W.J. An Overview of the Stability and Delivery Challenges of Commercial Nucleic Acid Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.Q.; Michelle Luk, K.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Nurul, N.; Loh, S.J.; Yeow, Z.X.; Wong, Q.X.; Daniel Looi, Q.H.; Chong, P.P.; How, C.W. Small Extracellular Vesicles’ miRNAs: Biomarkers and Therapeutics for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabáková, E.; Culig, Z.; Remšík, J.; Souček, K. Alternative mechanisms of miR-34a regulation in cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, N.; Wilson, G.; Id Said, B.; Pan, A.; Deblois, G.; Fischer, N.W.; Alexandrova, R.; Casallo, G.; Paton, T.; Lupien, M. Transcriptome-wide characterization of the endogenous miR-34A-p53 tumor suppressor network. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 49611–49622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalls, D.; Tang, S.N.; Rodova, M.; Srivastava, R.K.; Shankar, S. Targeting epigenetic regulation of miR-34a for treatment of pancreatic cancer by inhibition of pancreatic cancer stem cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
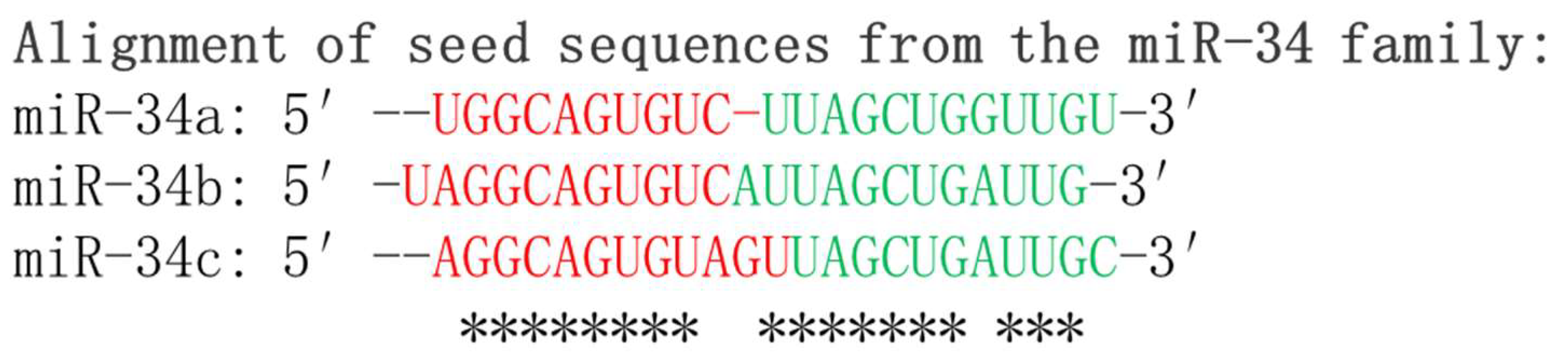

| Gene Name | miR-34 Species | Biological Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACSL4/lncRNA NEAT1 | miR-34a | Promotion of docetaxel resistance | [44] |
| ALDOA/NONHSAG028908.3 | miR-34a | Inhibition of cell growth and migration | [45] |
| ALDOA/lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 | miR-34c | Inhibition of cell growth | [46] |
| Bcl-2 | miR-34a | Apoptosis, inhibition of cell growth and migration | [47,48] |
| CAV1 | miR-34b, miR-34c | Inhibition of migration | [20] |
| CDC25A | miR-34a | Inhibition of cell growth and migration | [49] |
| CDC25C | miR-34a | G2 arrest | [50] |
| CCND1 | miR-34a | G1 arrest | [51,52] |
| CCND2/RP11-805J14.5 | miR-34a | Promoted cell cycle progression | [53] |
| CCNE2 | miR-34a, miR-34b, miR-34c | G1 arrest | [51] |
| CDK4 | miR-34a, miR-34b, miR-34c | G1 arrest, apoptosis | [54] |
| CDK6 | miR-34a, miR-34b | G1 arrest | [52] |
| CREB | miR-34b | Inhibition of proliferation | [55] |
| DAAM1/LINC01006 | miR-34a | Inhibition of proliferation, migration, and invasion | [56] |
| DLL1 | miR-34a | Influence on Notch signaling | [57] |
| E2F3 | miR-34a, miR-34c | Inhibition of proliferation, senescence | [50] |
| E2F5 | miR-34a | Transcriptional activation, cell proliferation and migration | [12,58] |
| Flotillin-2 | miR-34a | Inhibition of proliferation, migratory/invasive activity | [59] |
| FOSL1/circCRIM1 | miR-34c | Inhibition of proliferation and invasion | [60] |
| FOXM1 | miR-34a | Inhibition of cell proliferation and cell migration | [61] |
| GADD45A/lncRNA DICER1-AS1 | miR-34a | Drug resistance | [62] |
| JAG1/LncRNA DANCR | miR-34a | Promotion of docetaxel resistance | [63] |
| HDAC1/7 | miR-34a | Cell survival and therapy resistance | [64] |
| HDMX | miR-34a | Increased p53 activity | [51,65] |
| HMGA2 | miR-34a | Inhibition of proliferation, senescence | [50,66] |
| HOXA13/lncNEAT1 | miR-34a | Apoptosis | [67] |
| MAP2K1 | miR-34c | Inhibition of cell migration and invasion | [68] |
| MET | miR-34a, miR-34b, miR-34c | G1 arrest, inhibition of invasion and migration | [51,69] |
| MDM4 | miR-34a | Apoptosis, miR-34a/MDM4/p53 feedback | [70] |
| MMP2/MMP9/FNDC3B, MMP2 | miR-34a | Inhibition of cell migration and invasion | [71,72] |
| MYB | miR-34b, miR-34c | Inhibition of proliferation | [55] |
| MYCN/lncRNA LINC01106 | miR-34a | Cell viability, invasion, and migration | [73] |
| c-MYC | miR-34a, miR-34b, miR-34c | G1 arrest, counteracting cancer stem cell-like properties | [74] |
| N-MYC | miR-34a | G1 arrest | [75] |
| Notch1 | miR-34a, miR-34c | Inhibition of proliferation, metastasis and invasion, apoptosis | [18,48,49] |
| Notch2 | miR-34b | Inhibition of cell proliferation and EMT | [76] |
| PAC1 | miR-34a | Apoptosis | [77] |
| PD-L1 | miR-34a | Inhibiting the growth of TNBC cells | [78,79] |
| P2RY14/lncRNA LINC00665 | miR-34c | Tumor immune infiltration | [80] |
| RAD51/lncRNA HCG9 | miR-34b | Proliferation | [81] |
| RUNX2/lncRNA HCG18 | miR-34a | Inhibition of proliferation, migration, and invasion | [82] |
| SFRS2 | miR-34b, miR-34c | Influence on miRNA metabolism | [20] |
| SIRT1 | miR-34a | Increased p53 acetylation and activation (positive feedback loop), immunosuppression | [83] |
| SYT1 | miR-34a | Apoptosis | [84] |
| TBL1XR1 | miR-34c | Inhibition of cell proliferation, migration, and invasion | [85] |
| TGIF2 | miR-34s | Apoptosis | [86] |
| WASF1 | miR-34a, miR-34b, miR-34c | Suppression of tumor formation | [87] |
| TWIST1, ZEB1 | miR-34a | Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition | [18] |
| Wnt1 | miR-34a | G2 arrest | [88] |
| YY1 | miR-34a | Apoptosis, inhibition of migration and invasion | [89] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, J.; Imani, S.; Wu, M.-Y.; Wu, R.-C. MicroRNA-34 Family in Cancers: Role, Mechanism, and Therapeutic Potential. Cancers 2023, 15, 4723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194723
Fu J, Imani S, Wu M-Y, Wu R-C. MicroRNA-34 Family in Cancers: Role, Mechanism, and Therapeutic Potential. Cancers. 2023; 15(19):4723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194723
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Junjiang, Saber Imani, Mei-Yi Wu, and Ray-Chang Wu. 2023. "MicroRNA-34 Family in Cancers: Role, Mechanism, and Therapeutic Potential" Cancers 15, no. 19: 4723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194723
APA StyleFu, J., Imani, S., Wu, M.-Y., & Wu, R.-C. (2023). MicroRNA-34 Family in Cancers: Role, Mechanism, and Therapeutic Potential. Cancers, 15(19), 4723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15194723






