Radiomics Features on Magnetic Resonance Images Can Predict C5aR1 Expression Levels and Prognosis in High-Grade Glioma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Datasets
2.2. Prognostic Analyses Based on the TCGA Cohort
2.3. Comprehensive Analysis of Functional and Immune Characteristics Based on TCGA
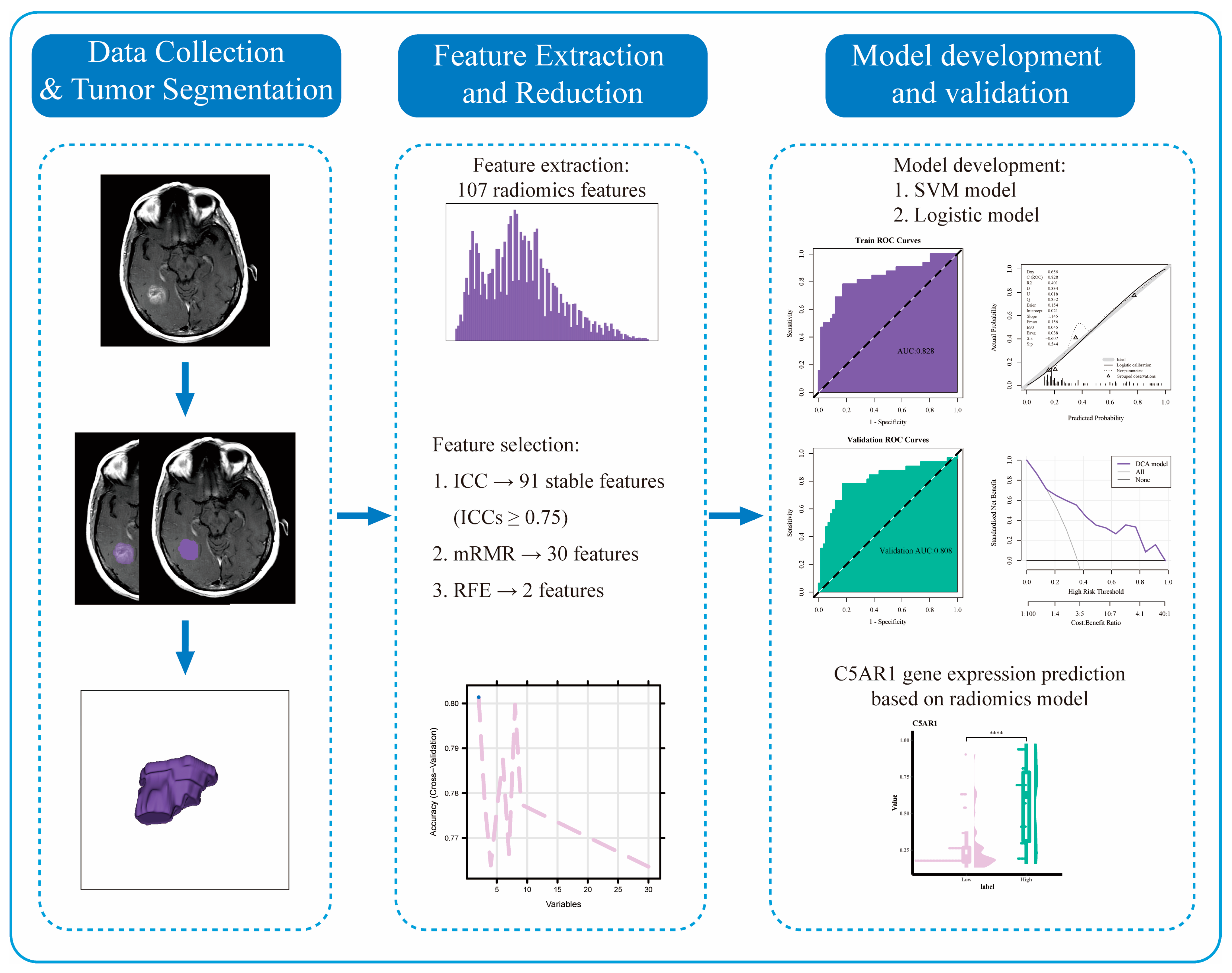
2.4. MRI Images Preprocessing
2.5. Volume-of-Interest Segmentation
2.6. Radiomics Features Extraction and Normalization
2.7. Radiomics Features Selection
2.8. Logistic Regression and Support Vector Machine Model Establishment
2.9. Model Validation and Evaluation
2.10. TCIA and TCGA Data Combination
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
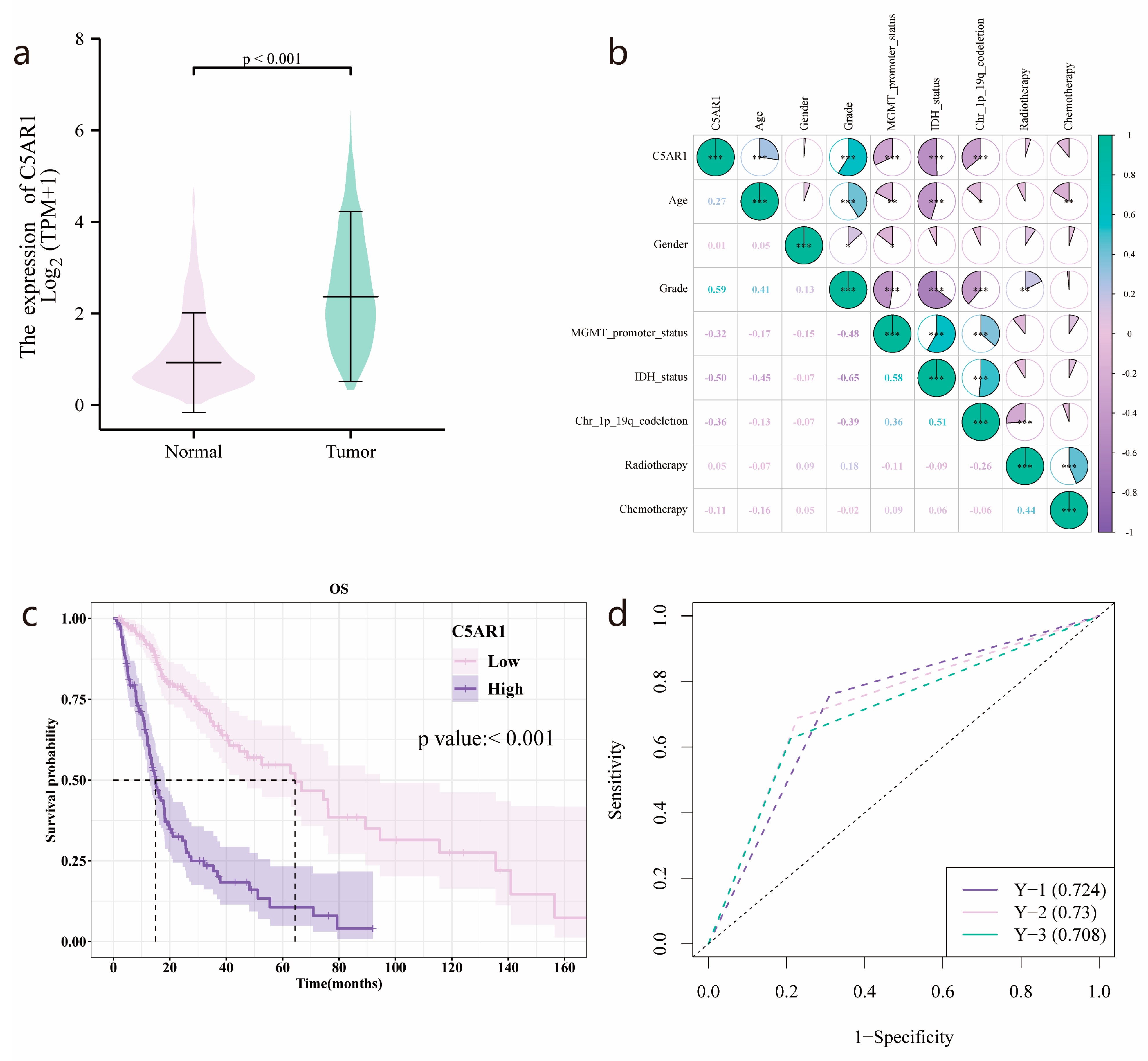
3.1. C5aR1 Expression and Correlation with Clinical Baseline Characteristics
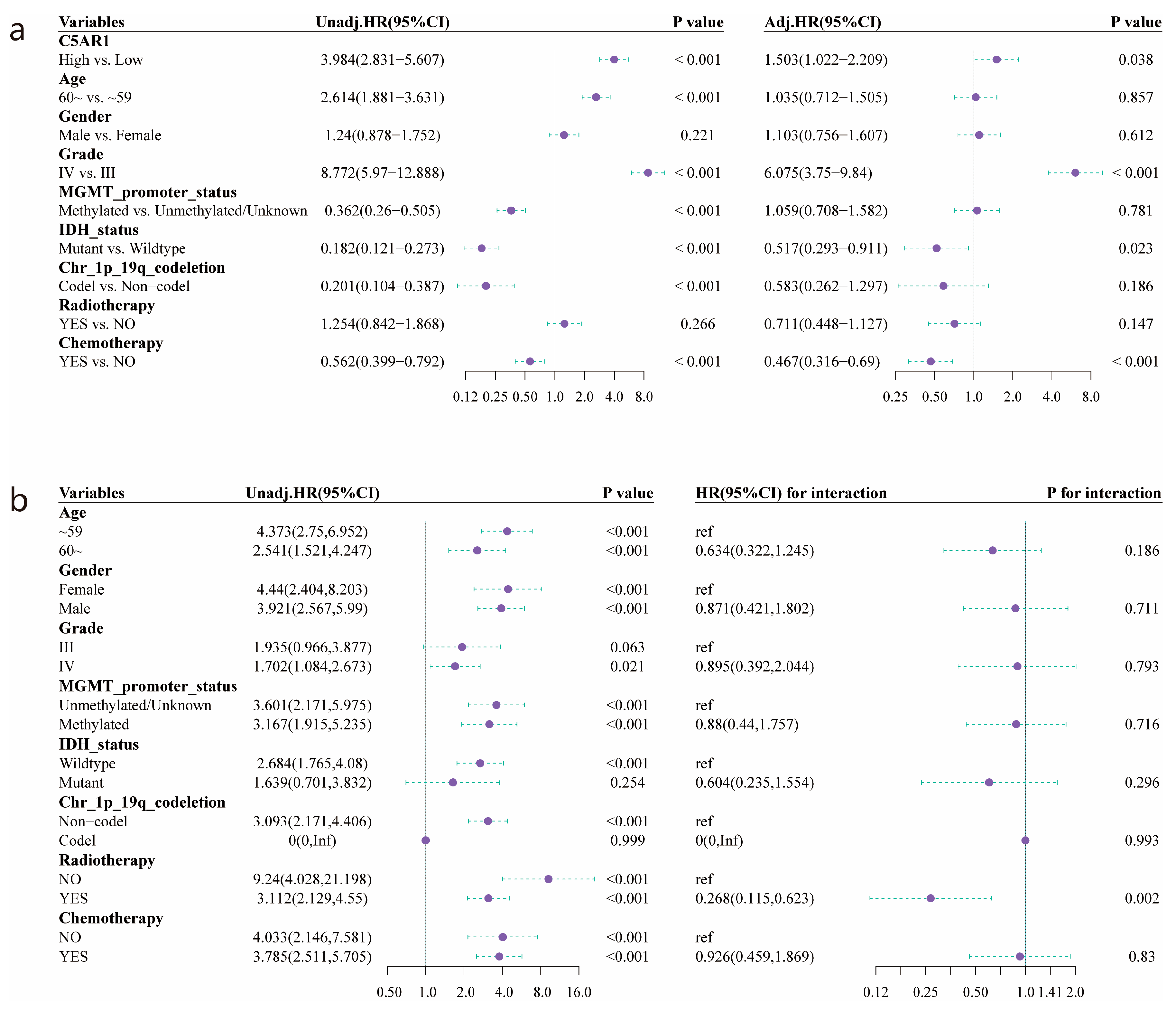
3.2. Survival Outcomes and Multivariate Analysis of Prognostic Factors for HGG
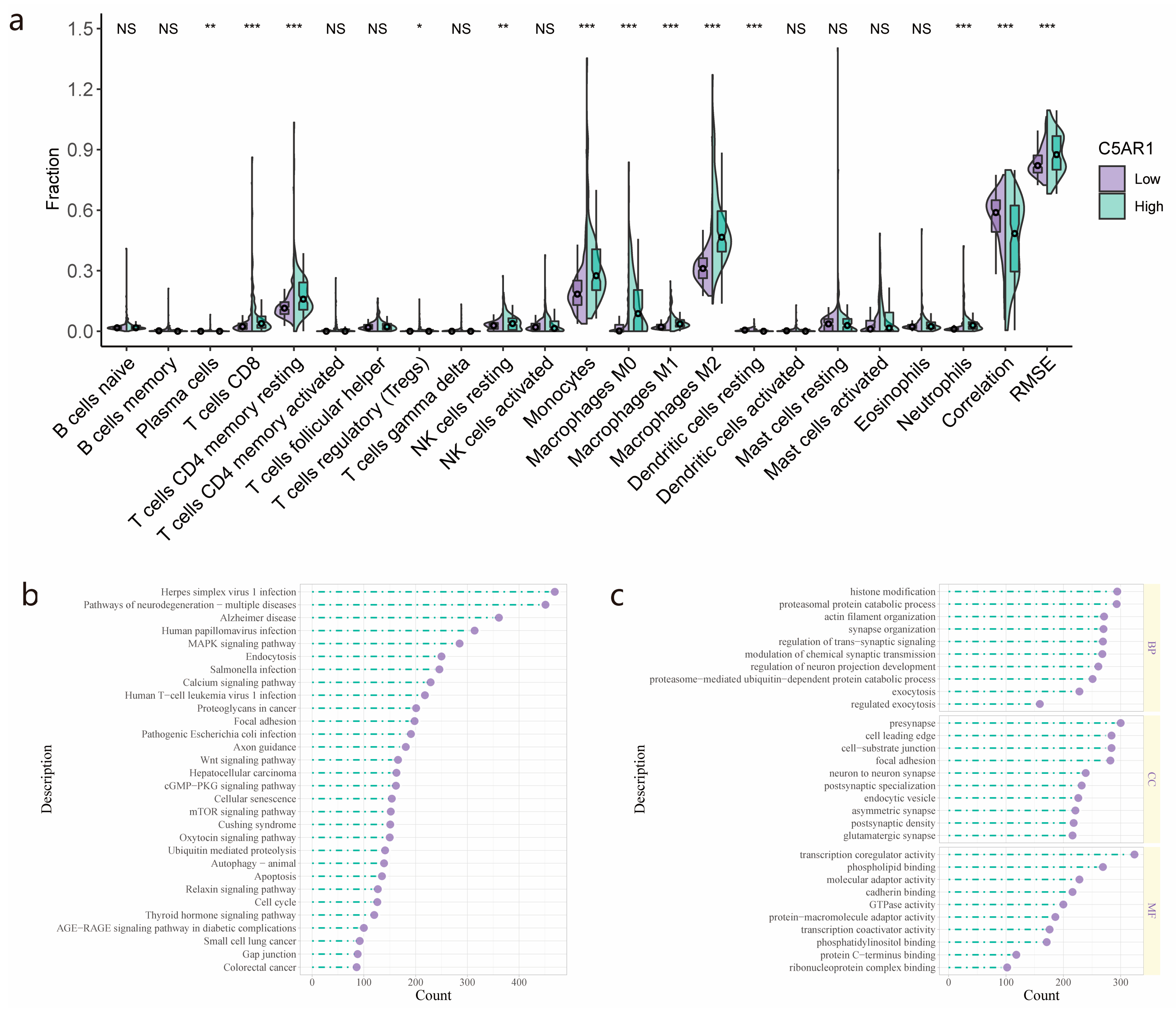
3.3. Immune Cell Fraction Analyses and GO/KEGG Pathway Analysis for Patients with High- and Low-C5aR1 Expression
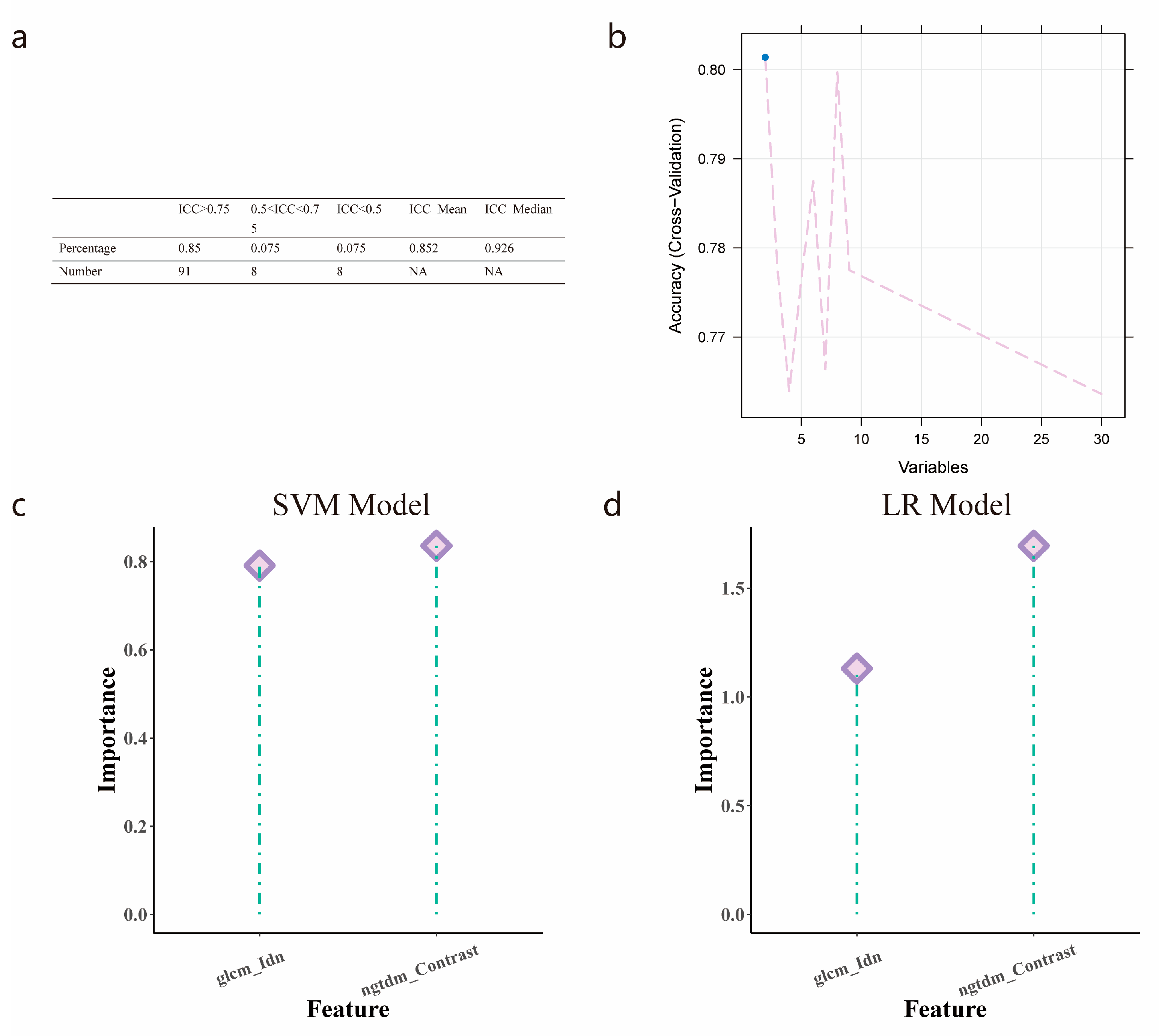
3.4. Radiomics Features Selection
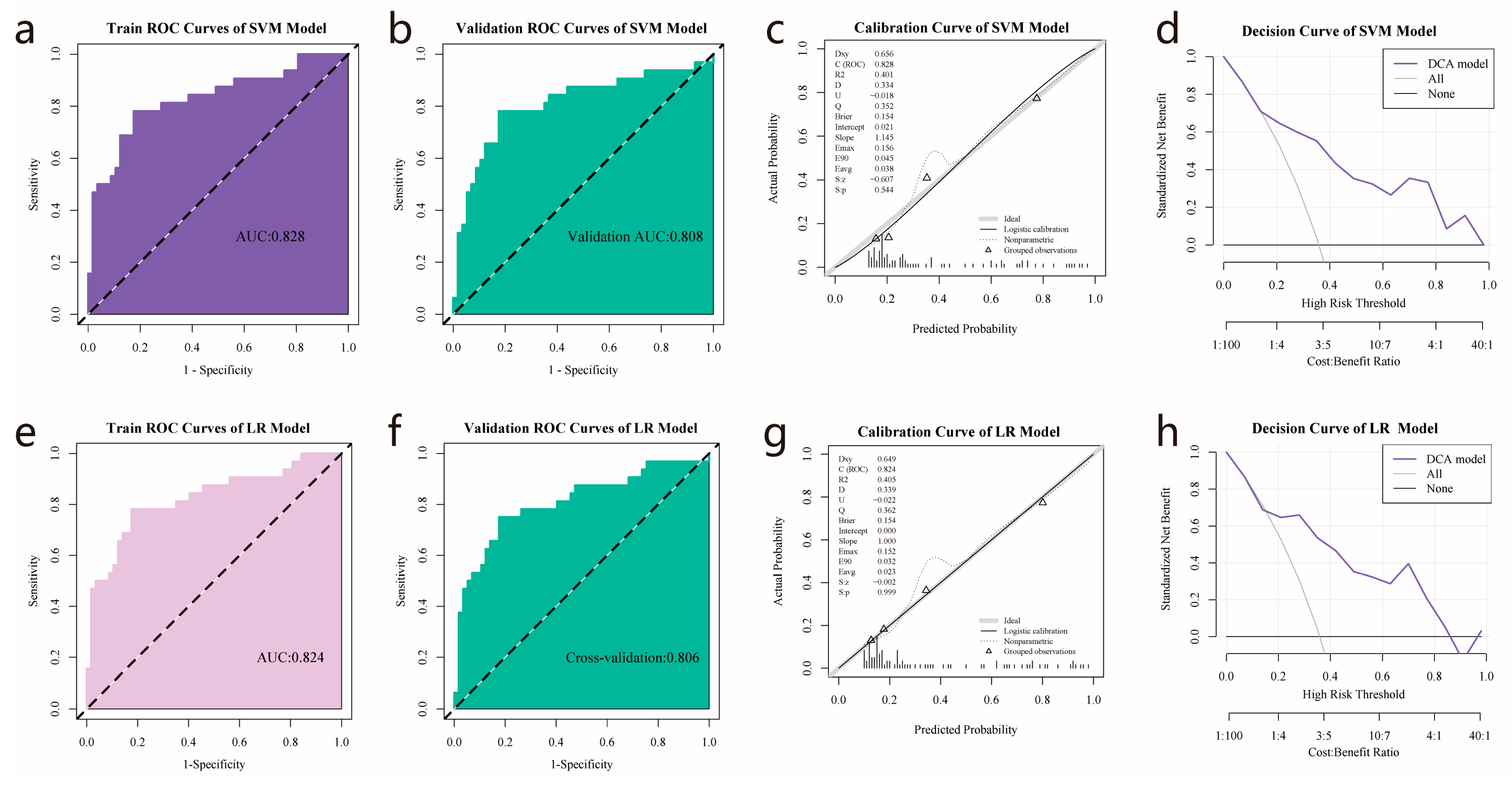
3.5. Establishment and Validation of Logistic Regression and SVM Models
3.6. TCIA and TCGA Data Combination
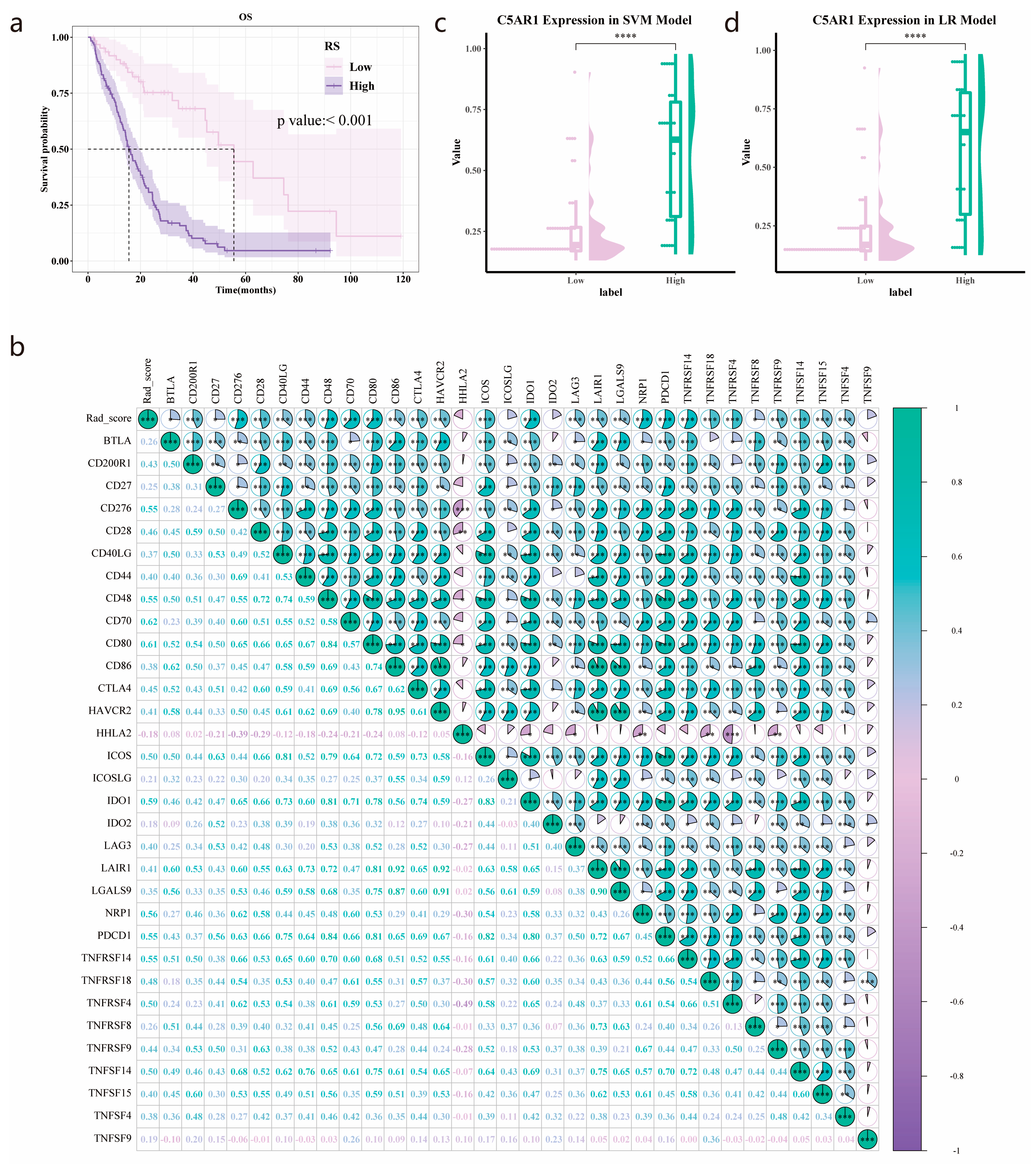
3.7. Validation of the Prognostic Value of the Radiomics Score
3.8. C5aR1 Expression Analysis in the SVM and Logistic Regression Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.C.; Ashley, D.M.; López, G.Y.; Malinzak, M.; Friedman, H.S.; Khasraw, M. Management of glioblastoma: State of the art and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, P.Y.; Weller, M.; Lee, E.Q.; Alexander, B.M.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Barthel, F.P.; Batchelor, T.T.; Bindra, R.S.; Chang, S.M.; Chiocca, E.A.; et al. Glioblastoma in adults: A Society for Neuro-Oncology (SNO) and European Society of Neuro-Oncology (EANO) consensus review on current management and future directions. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, 1073–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, N.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.; et al. Glioma targeted therapy: Insight into future of molecular approaches. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Maharana, J.; Li, X.X.; Woodruff, T.M.; Shukla, A.K. Emerging Insights into the Structure and Function of Complement C5a Receptors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2020, 45, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastellos, D.C.; Hajishengallis, G.; Lambris, J.D. A guide to complement biology, pathology and therapeutic opportunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajona, D.; Ortiz-Espinosa, S.; Moreno, H.; Lozano, T.; Pajares, M.J.; Agorreta, J.; Bértolo, C.; Lasarte, J.J.; Vicent, S.; Hoehlig, K.; et al. A Combined PD-1/C5a Blockade Synergistically Protects against Lung Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Li, L.; Lv, X.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Xu, E.; Dai, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. C5aR1 is a master regulator in Colorectal Tumorigenesis via Immune modulation. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8619–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadwa, J.; Bickett, T.E.; Darragh, L.B.; Knitz, M.W.; Bhatia, S.; Piper, M.; Van Court, B.; Bhuvane, S.; Nguyen, D.; Nangia, V.; et al. Complement C3a and C5a receptor blockade modulates regulatory T cell conversion in head and neck cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mo, X.; Chen, Q.; et al. Quantitative MRI-based radiomics for noninvasively predicting molecular subtypes and survival in glioma patients. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.E.; Jo, Y.; Shim, W.H.; Nam, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, R.E.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Incorporating diffusion- and perfusion-weighted MRI into a radiomics model improves diagnostic performance for pseudoprogression in glioblastoma patients. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Qian, Z.; Wu, F.; He, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, R.; Wang, D.; Zhai, Y.; et al. An MRI radiomics approach to predict survival and tumour-infiltrating macrophages in gliomas. Brain J. Neurol. 2022, 145, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, X.; Zou, Y.; Yan, K.; Zheng, H.; Liang, D.; Li, Z.C. Biologic Pathways Underlying Prognostic Radiomics Phenotypes from Paired MRI and RNA Sequencing in Glioblastoma. Radiology 2021, 301, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.S.; Bae, S.; Chang, J.H.; Kang, S.G.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.; Rim, T.H.; Choi, S.H.; Jain, R.; Lee, S.K. Fully automated hybrid approach to predict the IDH mutation status of gliomas via deep learning and radiomics. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, D.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Ma, Y.; Song, B.; Lui, S.; Wu, M. High IER5 Gene Expression Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Glioma Patients. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 679684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Duan, M.; Zha, Y.; Wu, Z. CENP-A is a potential prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltration levels in glioma patients. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 931222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivian, J.; Rao, A.A.; Nothaft, F.A.; Ketchum, C.; Armstrong, J.; Novak, A.; Pfeil, J.; Narkizian, J.; Deran, A.D.; Musselman-Brown, A.; et al. Toil enables reproducible, open source, big biomedical data analyses. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Chen, L.; Tang, Q.; Wei, W.; Cao, Y.; Wu, C.; Hang, J.; Zhang, K.; Shi, J.; Wang, M. A Necroptosis-Related Prognostic Model of Uveal Melanoma Was Constructed by Single-Cell Sequencing Analysis and Weighted Co-Expression Network Analysis Based on Public Databases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 847624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, D.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Ni, L.; Lin, Y.; Huang, R.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complement System to Prognosis and Immune Infiltrating in Colon Cancer and Gastric Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 553297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J. C5aR1-positive neutrophils promote breast cancer glycolysis through WTAP-dependent m6A methylation of ENO1. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Yang, B.; Zhang, T.; Wei, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, X. Identification of an Immune-Related Prognostic Signature for Glioblastoma by Comprehensive Bioinformatics and Experimental Analyses. Cells 2022, 11, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassetta, L.; Fragkogianni, S.; Sims, A.H.; Swierczak, A.; Forrester, L.M.; Zhang, H.; Soong, D.Y.H.; Cotechini, T.; Anur, P.; Lin, E.Y.; et al. Human Tumor-Associated Macrophage and Monocyte Transcriptional Landscapes Reveal Cancer-Specific Reprogramming, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Targets. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 588–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komohara, Y.; Ohnishi, K.; Kuratsu, J.; Takeya, M. Possible involvement of the M2 anti-inflammatory macrophage phenotype in growth of human gliomas. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Marisetty, A.; Schrand, B.; Gabrusiewicz, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ott, M.; Grami, Z.; Kong, L.Y.; Ling, X.; Caruso, H.; et al. Osteopontin mediates glioblastoma-associated macrophage infiltration and is a potential therapeutic target. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, N.; Zhou, Q.; Ji, M.; Jin, J.; Lai, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Jia, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Chlorogenic acid inhibits glioblastoma growth through repolarizating macrophage from M2 to M1 phenotype. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Feng, X.; Herting, C.J.; Garcia, V.A.; Nie, K.; Pong, W.W.; Rasmussen, R.; Dwivedi, B.; Seby, S.; Wolf, S.A.; et al. Cellular and Molecular Identity of Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2266–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pio, R.; Ajona, D.; Ortiz-Espinosa, S.; Mantovani, A.; Lambris, J.D. Complementing the Cancer-Immunity Cycle. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Zhao, T.; Han, M. The application of radiomics in predicting gene mutations in cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 4014–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, A.; Jang, K.; Manuguerra, M.; Liu, S.; Magnussen, J.; Di Ieva, A. Machine Learning for the Prediction of Molecular Markers in Glioma on Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosurgery 2021, 89, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Vallières, M.; Bai, H.X.; Su, C.; Tang, H.; Oldridge, D.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, B.; Liao, W.; Tao, Y.; et al. MRI features predict survival and molecular markers in diffuse lower-grade gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Voort, S.R.; Incekara, F.; Wijnenga, M.M.J.; Kapas, G.; Gardeniers, M.; Schouten, J.W.; Starmans, M.P.A.; Nandoe Tewarie, R.; Lycklama, G.J.; French, P.J.; et al. Predicting the 1p/19q Codeletion Status of Presumed Low-Grade Glioma with an Externally Validated Machine Learning Algorithm. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 7455–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.C.; Bai, H.; Sun, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, L.; Zou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, C.; Zheng, H. Multiregional radiomics features from multiparametric MRI for prediction of MGMT methylation status in glioblastoma multiforme: A multicentre study. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3640–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.S.; Hawkins-Daarud, A.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Swanson, K.R. Imaging of intratumoral heterogeneity in high-grade glioma. Cancer Lett. 2020, 477, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Nam, Y.; Jang, J.; Shin, N.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Ahn, K.J.; Kim, B.S.; Park, J.S.; Jeon, S.S.; Hong, Y.G. Radiomics may increase the prognostic value for survival in glioblastoma patients when combined with conventional clinical and genetic prognostic models. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 2084–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Choi, Y.S.; Ahn, S.S.; Chang, J.H.; Kang, S.G.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.K. Radiomic MRI Phenotyping of Glioblastoma: Improving Survival Prediction. Radiology 2018, 289, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kickingereder, P.; Neuberger, U.; Bonekamp, D.; Piechotta, P.L.; Götz, M.; Wick, A.; Sill, M.; Kratz, A.; Shinohara, R.T.; Jones, D.T.W.; et al. Radiomic subtyping improves disease stratification beyond key molecular, clinical, and standard imaging characteristics in patients with glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Total (n = 298) | Low Expression of C5aR1 (n = 174) | High Expression of C5aR1 (n = 124) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| ~59 | 197 (66) | 134 (77) | 63 (51) | |
| 60~ | 101 (34) | 40 (23) | 61 (49) | |
| Gender, n (%) | 0.917 | |||
| Female | 120 (40) | 71 (41) | 49 (40) | |
| Male | 178 (60) | 103 (59) | 75 (60) | |
| Grade, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| III | 170 (57) | 142 (82) | 28 (23) | |
| IV | 128 (43) | 32 (18) | 96 (77) | |
| MGMT_promoter_status, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Unmethylated/Unknown | 118 (40) | 46 (26) | 72 (58) | |
| Methylated | 180 (60) | 128 (74) | 52 (42) | |
| IDH_status, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Wildtype | 169 (57) | 62 (36) | 107 (86) | |
| Mutant | 129 (43) | 112 (64) | 17 (14) | |
| Chr_1p_19q_codeletion, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Non-codel | 248 (83) | 125 (72) | 123 (99) | |
| Codel | 50 (17) | 49 (28) | 1 (1) | |
| Radiotherapy, n (%) | 0.466 | |||
| NO | 70 (23) | 44 (25) | 26 (21) | |
| YES | 228 (77) | 130 (75) | 98 (79) | |
| Chemotherapy, n (%) | 0.078 | |||
| NO | 79 (27) | 39 (22) | 40 (32) | |
| YES | 219 (73) | 135 (78) | 84 (68) | |
| Training Cohort | Validation Cohort | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC (95% CI) | ACC | SPE | SEN | p | AUC (95% CI) | ACC | SPE | SEN | p | |
| SVM | 0.828 (0.731–0.924) | 0.809 | 0.825 | 0.781 | 0.808 (0.703–0.913) | 0.809 | 0.825 | 0.781 | ||
| LR | 0.824 (0.727–0.921) | 0.809 | 0.825 | 0.781 | 0.806 (0.703–0.91) | 0.798 | 0.825 | 0.75 | ||
| SVM vs. LR | 0.317 | 0.806 |
| Variables | Total (n = 182) | Low Radiomics Score (n = 63) | High Radiomics Score (n = 119) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, n (%) | 0.033 | |||
| Female | 80 (44) | 35 (56) | 45 (38) | |
| Male | 102 (56) | 28 (44) | 74 (62) | |
| Age, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| ~59 | 112 (62) | 53 (84) | 59 (50) | |
| ~60 | 70 (38) | 10 (16) | 60 (50) | |
| Grade, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| III | 62 (34) | 51 (81) | 11 (9) | |
| IV | 120 (66) | 12 (19) | 108 (91) | |
| MGMT_promoter_status, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Unmethylated/Unknown | 94 (52) | 19 (30) | 75 (63) | |
| Methylated | 88 (48) | 44 (70) | 44 (37) | |
| Chemotherapy, n (%) | 0.129 | |||
| NO | 39 (21) | 9 (14) | 30 (25) | |
| YES | 143 (79) | 54 (86) | 89 (75) | |
| Radiotherapy, n (%) | 0.059 | |||
| NO | 34 (19) | 17 (27) | 17 (14) | |
| YES | 148 (81) | 46 (73) | 102 (86) | |
| IDH_status, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Wildtype | 134 (74) | 24 (38) | 110 (92) | |
| Mutant | 48 (26) | 39 (62) | 9 (8) | |
| Chr_1p_19q_codeletion, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Non-codel | 163 (90) | 46 (73) | 117 (98) | |
| Codel | 19 (10) | 17 (27) | 2 (2) | |
| OS, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| 0 | 57 (31) | 40 (63) | 17 (14) | |
| 1 | 125 (69) | 23 (37) | 102 (86) | |
| OS time, Median (Q1, Q3) | 17.02 (9, 27.55) | 21.27 (13.85, 38.07) | 14.93 (7.57, 24.57) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zha, Y. Radiomics Features on Magnetic Resonance Images Can Predict C5aR1 Expression Levels and Prognosis in High-Grade Glioma. Cancers 2023, 15, 4661. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184661
Wu Z, Yang Y, Zha Y. Radiomics Features on Magnetic Resonance Images Can Predict C5aR1 Expression Levels and Prognosis in High-Grade Glioma. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4661. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184661
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zijun, Yuan Yang, and Yunfei Zha. 2023. "Radiomics Features on Magnetic Resonance Images Can Predict C5aR1 Expression Levels and Prognosis in High-Grade Glioma" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4661. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184661
APA StyleWu, Z., Yang, Y., & Zha, Y. (2023). Radiomics Features on Magnetic Resonance Images Can Predict C5aR1 Expression Levels and Prognosis in High-Grade Glioma. Cancers, 15(18), 4661. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184661






