Polo-like Kinase 4: A Multifaceted Marker Linking Tumor Aggressiveness and Unfavorable Prognosis, and Insights into Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Public Omics Database Acquisition for Analysis
2.2. Gene Enrichment Analysis
2.3. Single Sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
2.4. Unsupervised Clustering
2.5. Differentially Expressed Gene (DEG) Analysis and Visualization
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
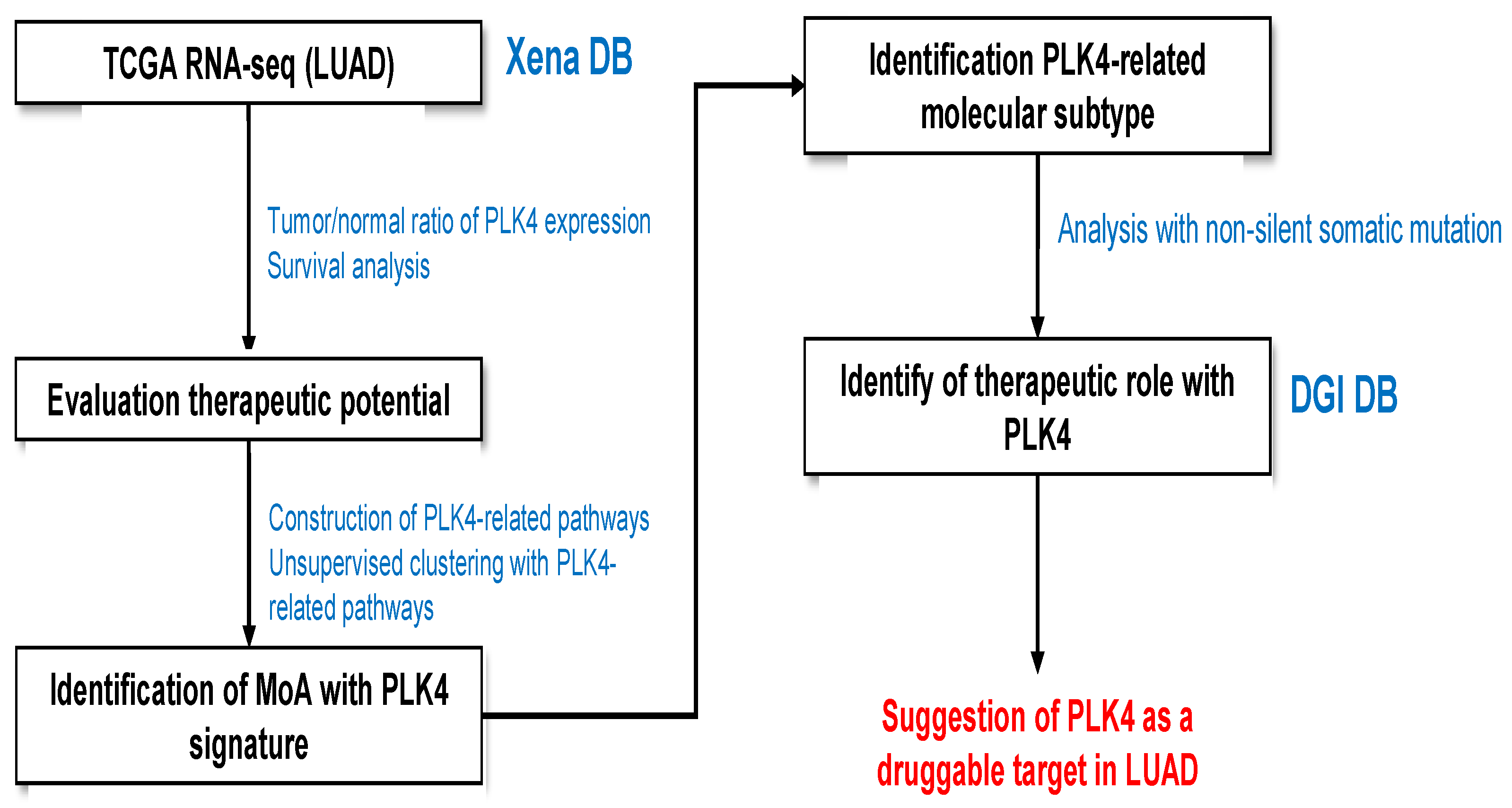
3.1. RNA-seq Analysis Workflow
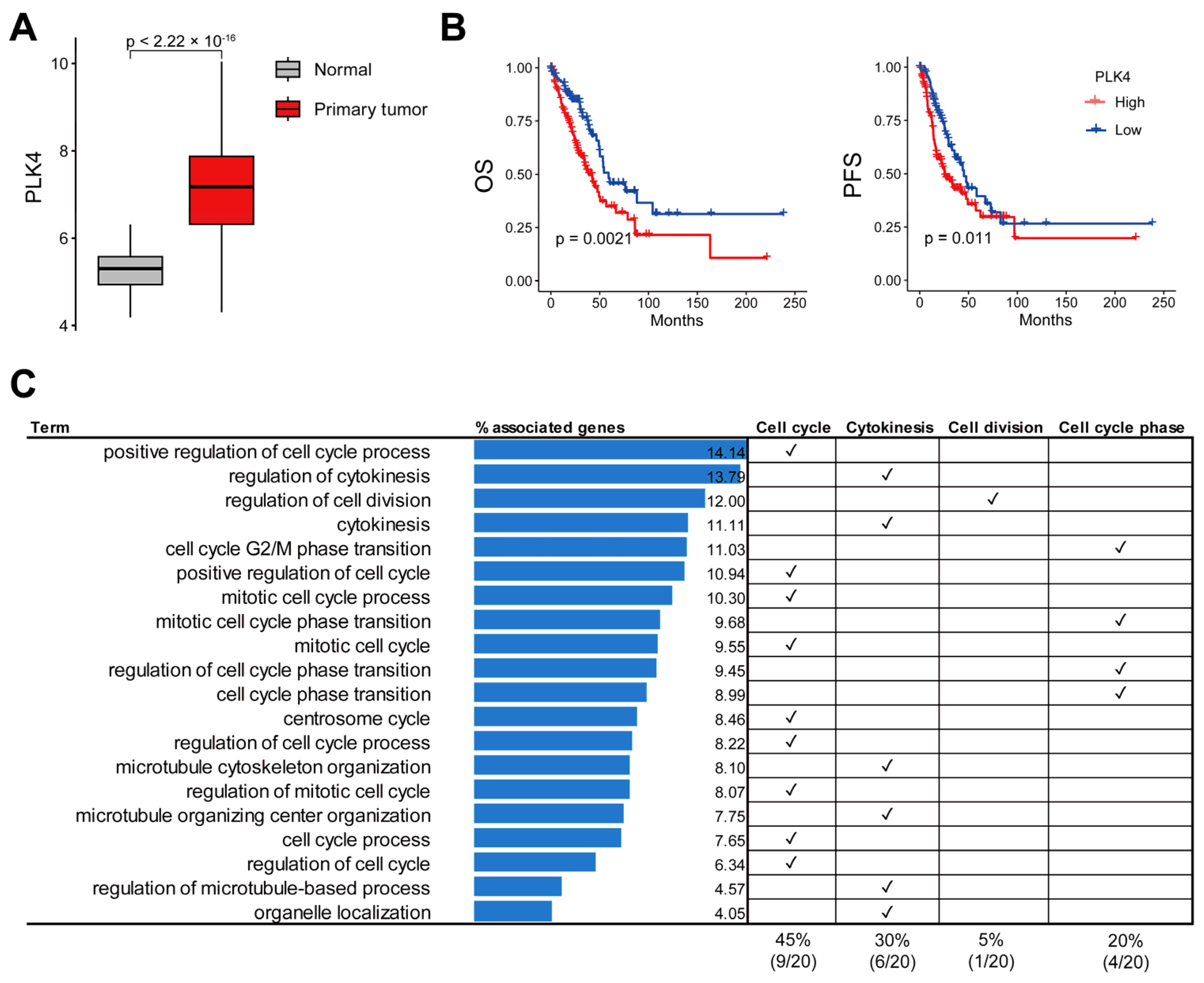
3.2. Upregulation of PLK4 in LUAD and Association with Poor Prognosis
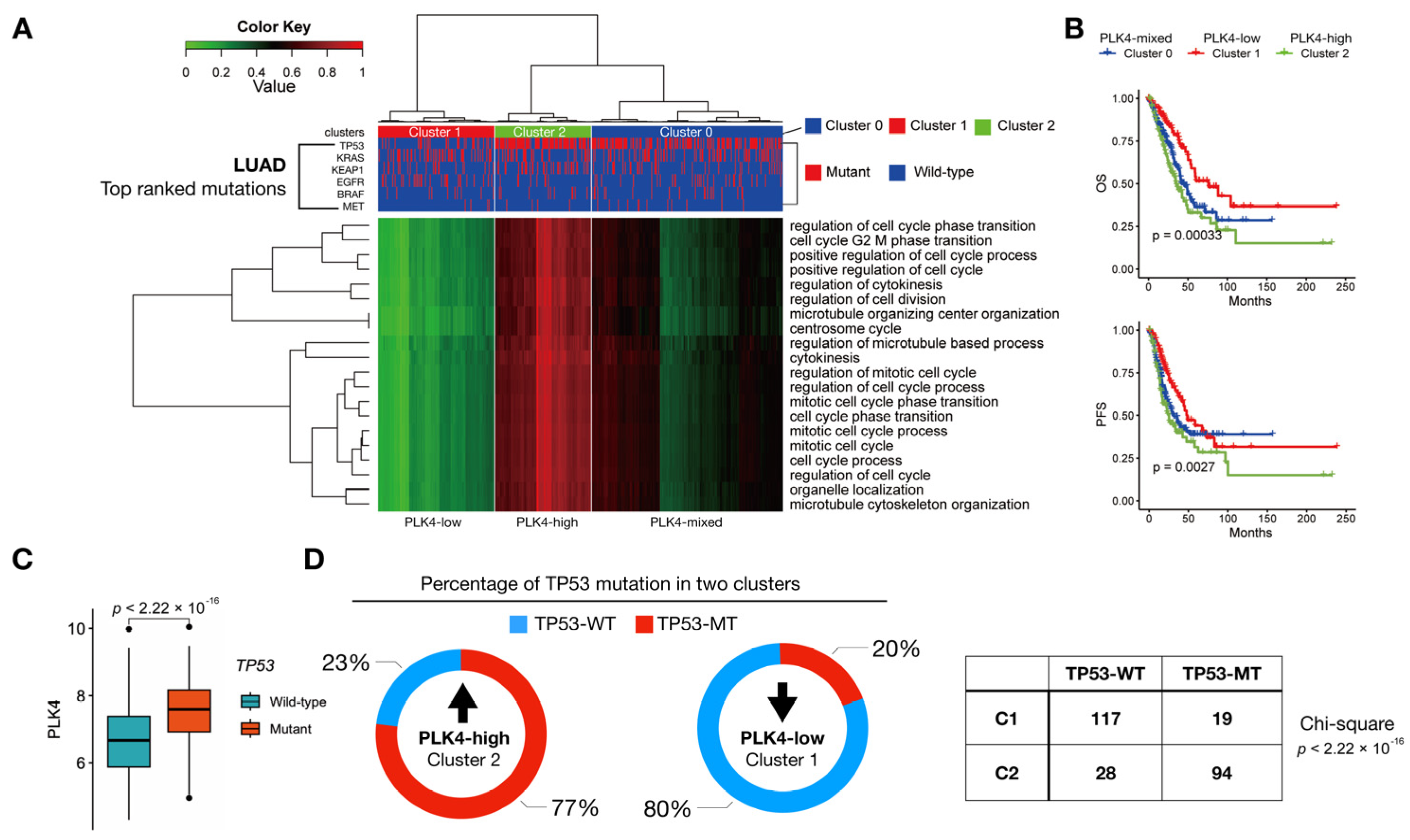
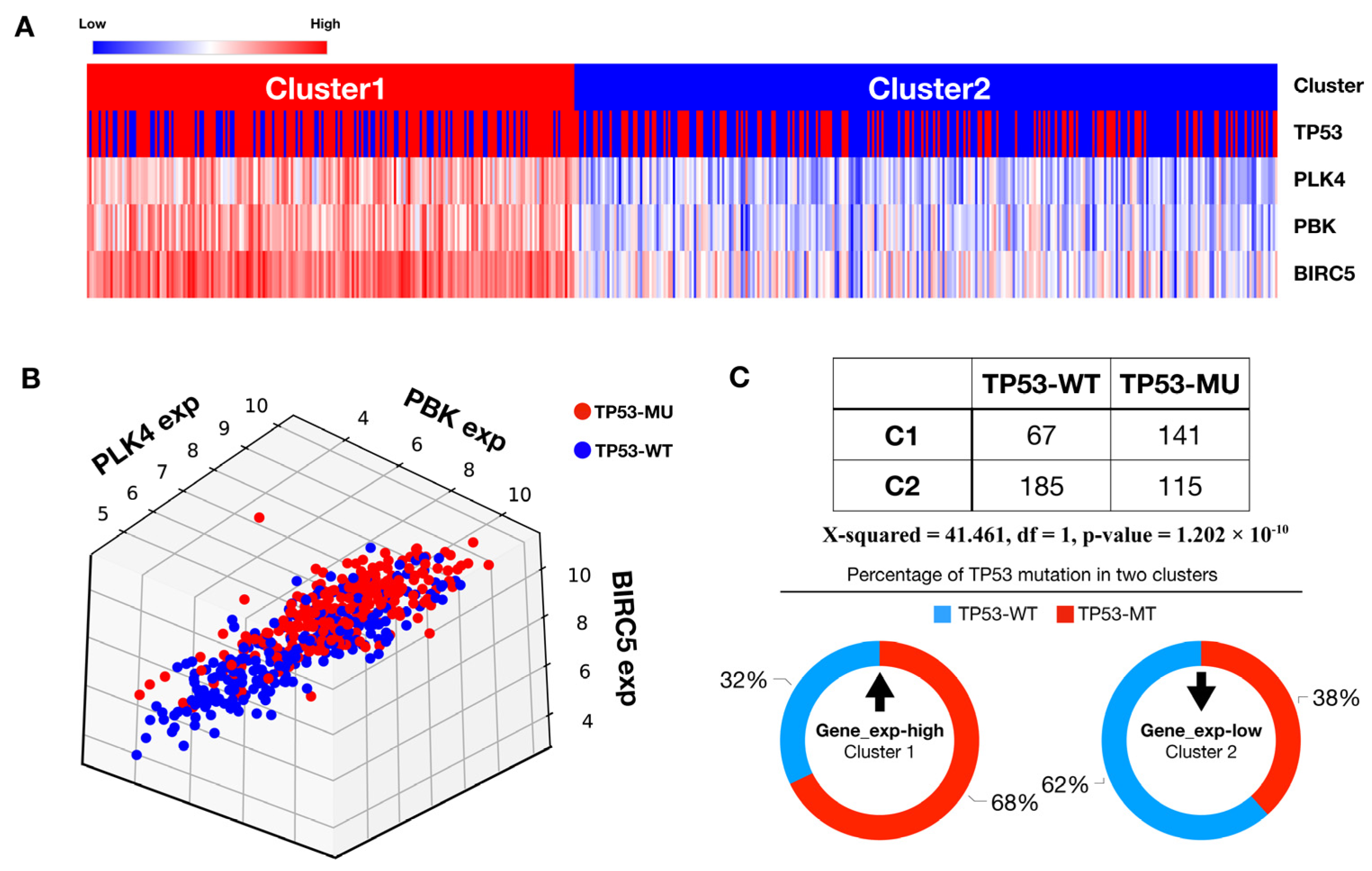
3.3. PLK4-Related Pathways Were Associated with TP53 Mutations
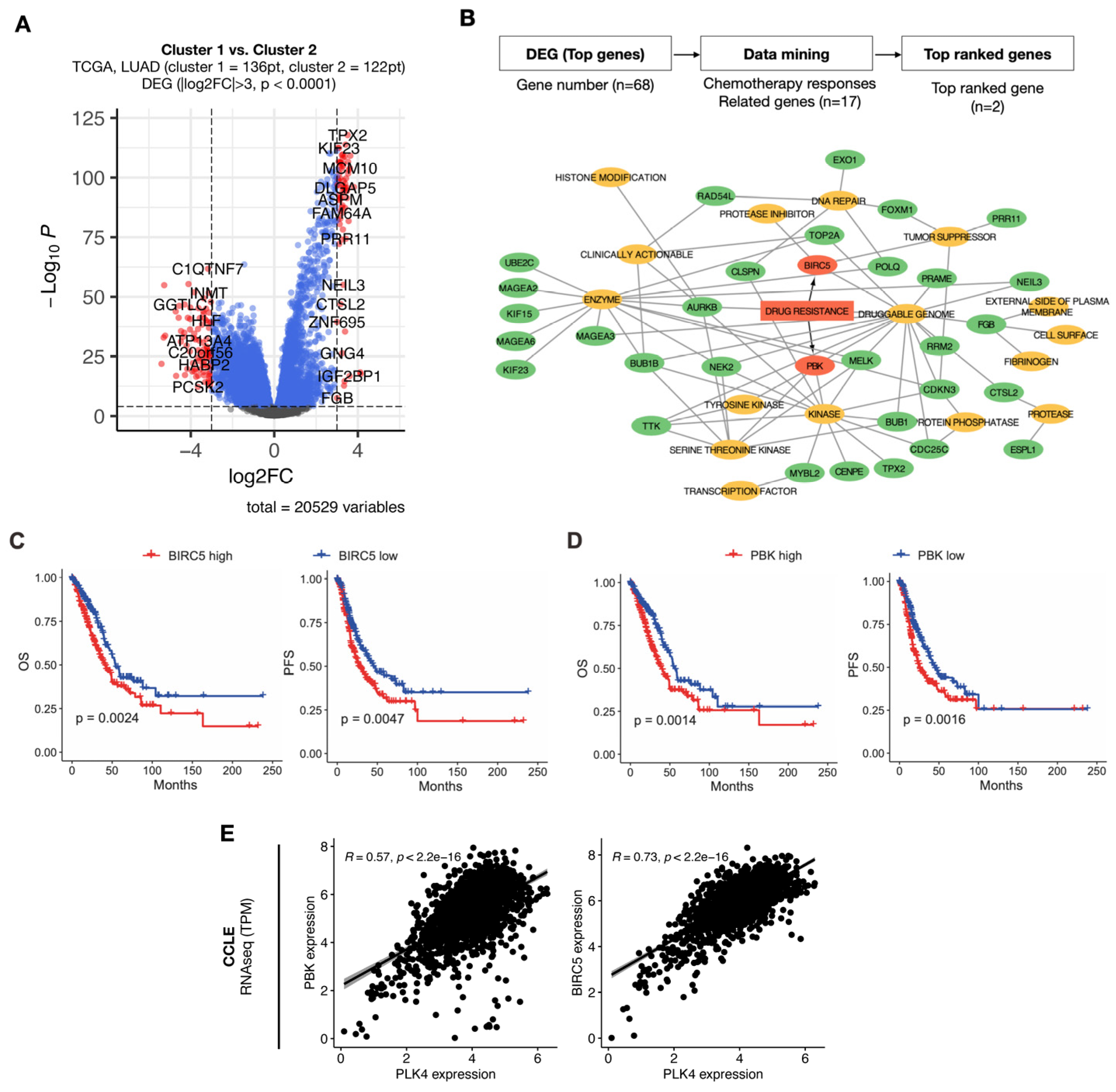
3.4. Identification of Potential Druggability in High PLK4-Related Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.; Walker, J.; Roy, U.B. 2022 cancer statistics: Focus on lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Q.; Liao, S.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, J.; Long, K.; Wu, X.; et al. A novel LUAD prognosis prediction model based on immune checkpoint-related lncRNAs. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1016449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarogoulidis, K.; Zarogoulidis, P.; Darwiche, K.; Boutsikou, E.; Machairiotis, N.; Tsakiridis, K.; Katsikogiannis, N.; Kougioumtzi, I.; Karapantzos, I.; Huang, H.; et al. Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5 (Suppl. 4), S389–S396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferone, G.; Lee, M.C.; Sage, J.; Berns, A. Cells of origin of lung cancers: Lessons from mouse studies. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguin, L.; Durandy, M.; Feral, C.C. Lung Adenocarcinoma Tumor Origin: A Guide for Personalized Medicine. Cancers 2022, 14, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furrukh, M. Tobacco Smoking and Lung Cancer: Perception-changing facts. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2013, 13, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, R.; Ding, L.; Griffith, M.; Subramanian, J.; Dees, N.D.; Kanchi, K.L.; Maher, C.A.; Fulton, R.; Fulton, L.; Wallis, J.; et al. Genomic landscape of non-small cell lung cancer in smokers and never-smokers. Cell 2012, 150, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao, W.; Miller, V.; Zakowski, M.; Doherty, J.; Politi, K.; Sarkaria, I.; Singh, B.; Heelan, R.; Rusch, V.; Fulton, L.; et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13306–13311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.R.; Chen, S. Drug resistance related genes in lung adenocarcinoma predict patient prognosis and influence the tumor microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H. Establishment of a Prognostic Model of Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Tumor Heterogeneity. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 807497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Huo, S. Establishment of a Lymph Node Metastasis-Associated Prognostic Signature for Lung Adenocarcinoma. Genet. Res. 2023, 2023, 6585109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anichini, A.; Perotti, V.E.; Sgambelluri, F.; Mortarini, R. Immune Escape Mechanisms in Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinmura, K.; Kato, H.; Kawanishi, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Tsuchiya, K.; Takahara, Y.; Hosokawa, S.; Kawase, A.; Funai, K.; Sugimura, H. POLQ Overexpression Is Associated with an Increased Somatic Mutation Load and PLK4 Overexpression in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, N.; Liu, W.; Zeng, M.; Cheng, J.; Huang, J. Analyses of expressions and prognostic values of Polo-like kinases in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 2447–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmke, C.; Becker, S.; Strebhardt, K. The role of Plk3 in oncogenesis. Oncogene 2016, 35, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, C.; Liang, H.; Han, L. Polo-Like Kinase 4’s Critical Role in Cancer Development and Strategies for Plk4-Targeted Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 587554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Zhang, L.; Bang, J.K.; Andresson, T.; DiMaio, F.; Lee, K.S. Phase separation of Polo-like kinase 4 by autoactivation and clustering drives centriole biogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habedanck, R.; Stierhof, Y.D.; Wilkinson, C.J.; Nigg, E.A. The Polo kinase Plk4 functions in centriole duplication. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2005, 7, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debec, A.; Sullivan, W.; Bettencourt-Dias, M. Centrioles: Active players or passengers during mitosis? Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2173–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, B.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, Y.; Jung, G.I.; Rhee, K. Generation and Fates of Supernumerary Centrioles in Dividing Cells. Mol. Cells 2021, 44, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.L.; Liu, C.; Fu, R.; Yan, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Q. Downregulation of PLK4 expression induces apoptosis and G0/G1-phase cell cycle arrest in keloid fibroblasts. Cell. Prolif. 2022, 55, e13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.J.; He, P. A novel tumor microenvironment-related gene signature with immune features for prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, Q.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhou, X. PLK4 Is a Potential Biomarker for Abnormal Tumor Proliferation, Immune Infiltration, and Prognosis in ccRCC. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 6302234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellrott, K.; Bailey, M.H.; Saksena, G.; Covington, K.R.; Kandoth, C.; Stewart, C.; Hess, J.; Ma, S.; Chiotti, K.E.; McLellan, M.; et al. Scalable Open Science Approach for Mutation Calling of Tumor Exomes Using Multiple Genomic Pipelines. Cell Syst. 2018, 6, 271–281.e277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, H.; Ma, W.; Wu, K.; Peng, G.; Ou, T.; Wu, S. Down-regulation of Polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) induces G1 arrest via activation of the p38/p53/p21 signaling pathway in bladder cancer. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 2631–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Wei, C.; Luo, L.; Li, S.; Zhou, J.; Liang, H.; Li, Y.; Han, L. PLK4 initiates crosstalk between cell cycle, cell proliferation and macrophages infiltration in gliomas. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1055371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marina, M.; Saavedra, H.I. Nek2 and Plk4: Prognostic markers, drivers of breast tumorigenesis and drug resistance. Front. Biosci. 2014, 19, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, I.; Mense, J.; Finke, C.; Boller, A.L.; Lorber, C.; Gyorffy, B.; Greve, B.; Gotte, M.; Espinoza-Sanchez, N.A. The cell cycle-related genes RHAMM, AURKA, TPX2, PLK1, and PLK4 are associated with the poor prognosis of breast cancer patients. J. Cell Biochem. 2022, 123, 581–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, S.F.; Zhou, Y.; Zou, W.; Chan, W.L.; Ching, Y.P. TEC kinase stabilizes PLK4 to promote liver cancer metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2022, 524, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J. The Cell-Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Functions of p53 in Tumor Initiation and Progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, T.; Uehara, S.; Nakahata, K.; Okuyama, H. Survivin selective inhibitor YM155 promotes cisplatin-induced apoptosis in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Qi, G.; Li, R.; Yang, N.; Gao, M.; Yan, S.; Yuan, C.; et al. PBK, targeted by EVI1, promotes metastasis and confers cisplatin resistance through inducing autophagy in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altieri, D.C. Validating survivin as a cancer therapeutic target. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.; Han, Y.; Gu, H.; Yang, H.; Zang, Y. TP53 mutation-associated immune infiltration and a novel risk score model in HNSCC. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2022, 32, 101359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadakekolathu, J.; Lai, C.; Reeder, S.; Church, S.E.; Hood, T.; Lourdusamy, A.; Rettig, M.P.; Aldoss, I.; Advani, A.S.; Godwin, J.; et al. TP53 abnormalities correlate with immune infiltration and associate with response to flotetuzumab immunotherapy in AML. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5011–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Saha, S.; Bettke, J.; Nagar, R.; Parrales, A.; Iwakuma, T.; van der Velden, A.W.M.; Martinez, L.A. Mutant p53 suppresses innate immune signaling to promote tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 494–508.e495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kim, D.K.; Na, K.; Lee, S.; Baek, S.; Kang, S.-s.; Yang, S.M.; Kim, M.H.; Han, H.; et al. Polo-like Kinase 4: A Multifaceted Marker Linking Tumor Aggressiveness and Unfavorable Prognosis, and Insights into Therapeutic Strategies. Cancers 2023, 15, 4663. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184663
Kim Y, Hwang JY, Kim DK, Na K, Lee S, Baek S, Kang S-s, Yang SM, Kim MH, Han H, et al. Polo-like Kinase 4: A Multifaceted Marker Linking Tumor Aggressiveness and Unfavorable Prognosis, and Insights into Therapeutic Strategies. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4663. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184663
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Youngtaek, Joon Yeon Hwang, Dong Kwon Kim, Kwangmin Na, Seul Lee, Sujeong Baek, Seong-san Kang, Seung Min Yang, Mi Hyun Kim, Heekyung Han, and et al. 2023. "Polo-like Kinase 4: A Multifaceted Marker Linking Tumor Aggressiveness and Unfavorable Prognosis, and Insights into Therapeutic Strategies" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4663. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184663
APA StyleKim, Y., Hwang, J. Y., Kim, D. K., Na, K., Lee, S., Baek, S., Kang, S.-s., Yang, S. M., Kim, M. H., Han, H., Lee, C. Y., Han, Y. J., Hong, M. H., Lee, J. B., Lim, S. M., Cho, B. C., Park, Y., & Pyo, K.-H. (2023). Polo-like Kinase 4: A Multifaceted Marker Linking Tumor Aggressiveness and Unfavorable Prognosis, and Insights into Therapeutic Strategies. Cancers, 15(18), 4663. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184663




