Hematological Adverse Events with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
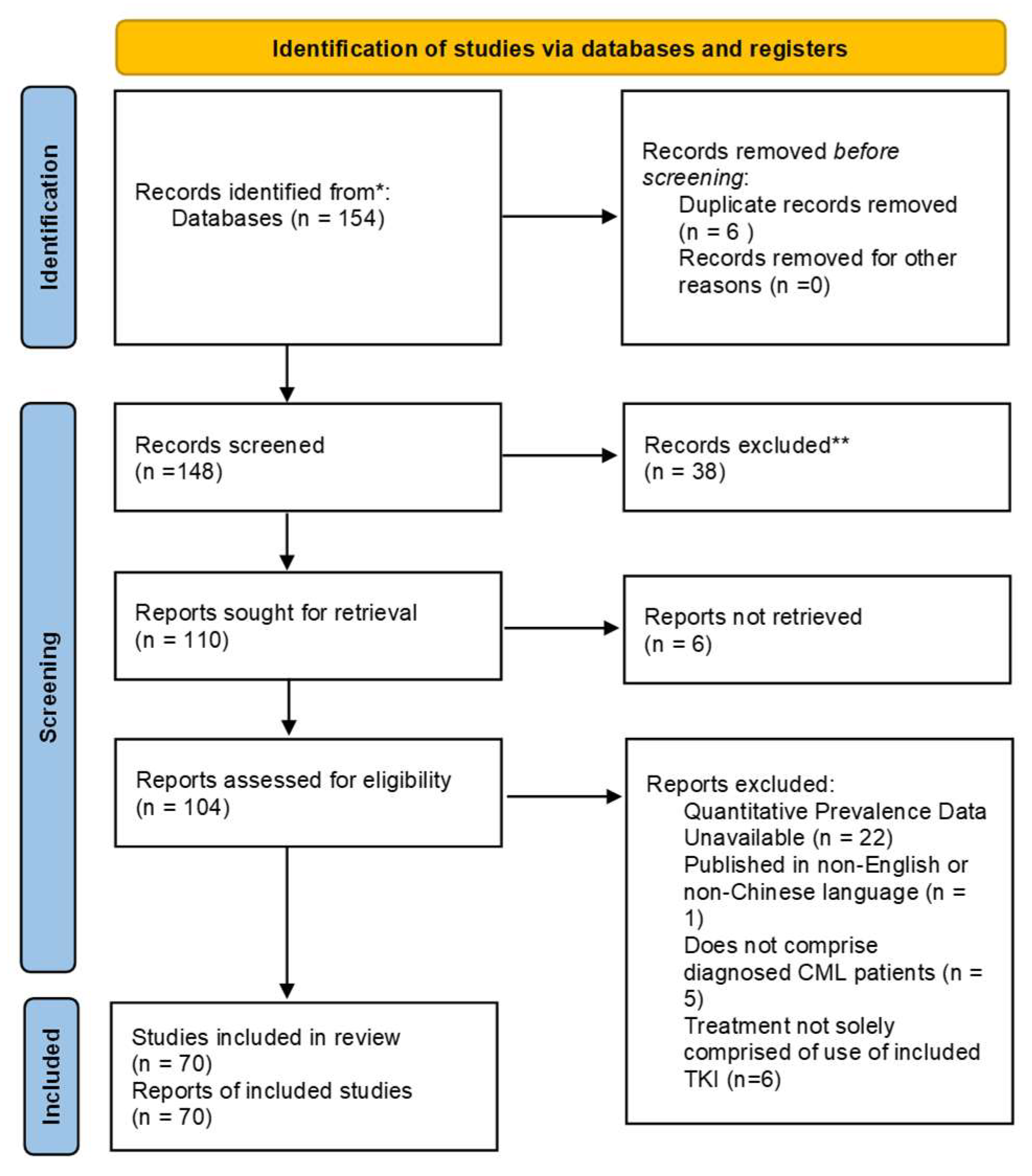
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Search Strategy
- (“chronic myeloid leukemia” OR “chronic myelogenous leukemia” OR “CML) AND (“imatinib” OR “dasatinib” OR “nilotinib” OR “bosutinib” OR “ponatinib” OR “asciminib” OR “radotinib” OR “ruxolitinib” OR “tipifarnib”)
- (“chronic myeloid leukemia” OR “chronic myelogenous leukemia” OR “CML) AND (“aplastic anemia” OR “anemia” OR “neutropenia” OR “thrombocytopenia” OR “myelosuppression” OR “pancytopenia”).
2.3. Risk of Bias and Certainty of Evidence
2.4. Data Curation and Quality Control
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Potential Bias
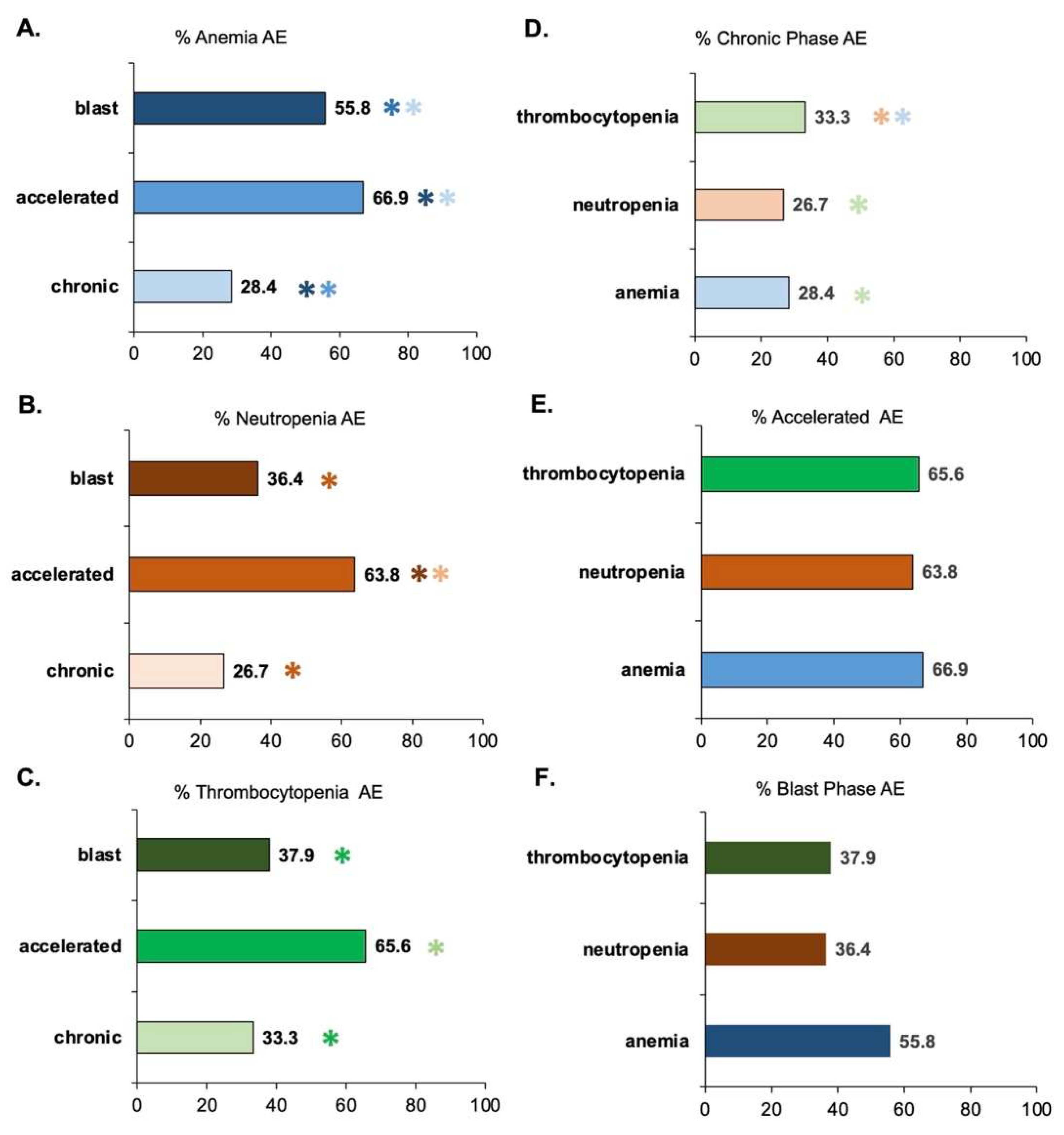
3.2. Assessment of AEs as a Function of CML Phase
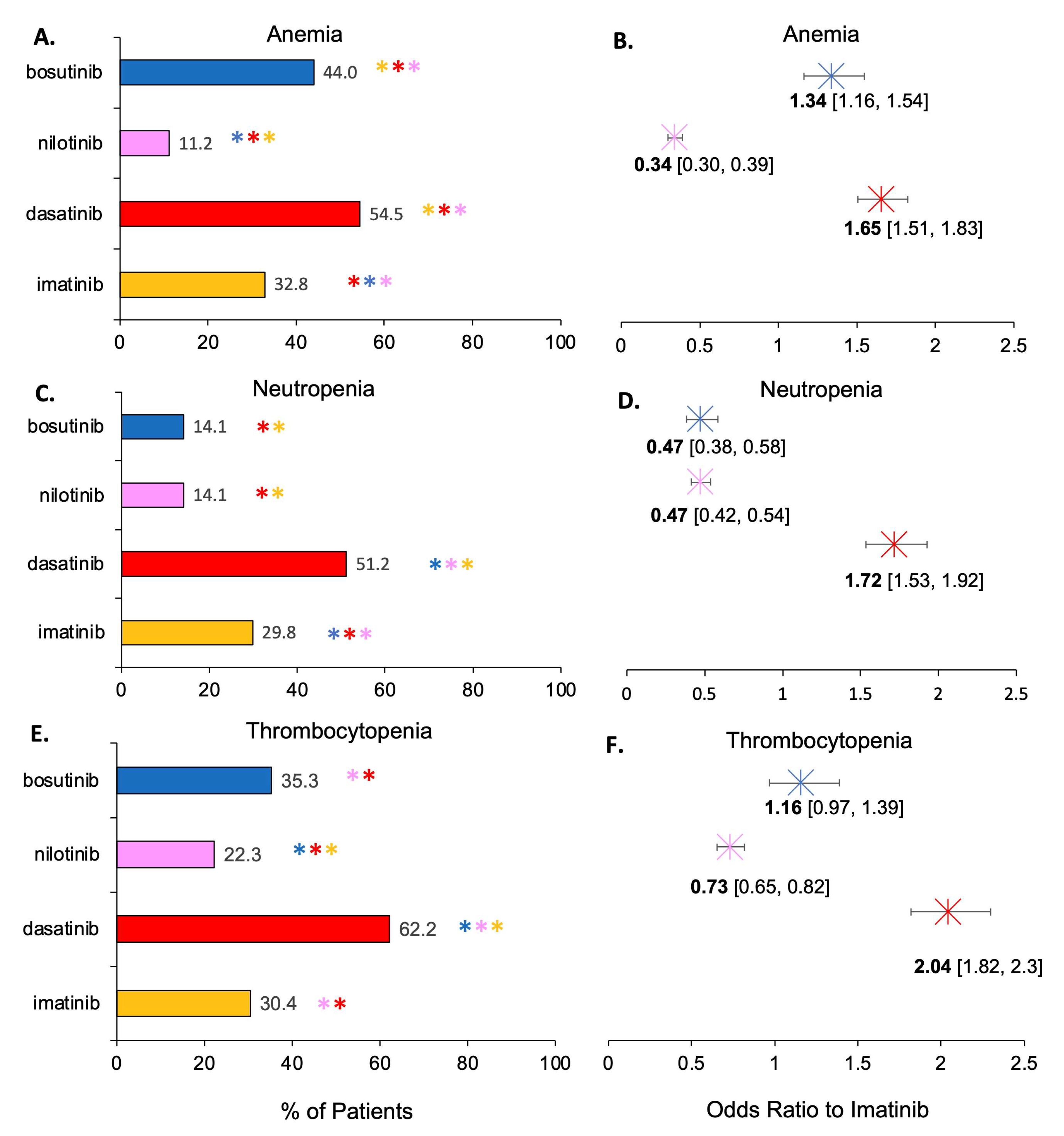
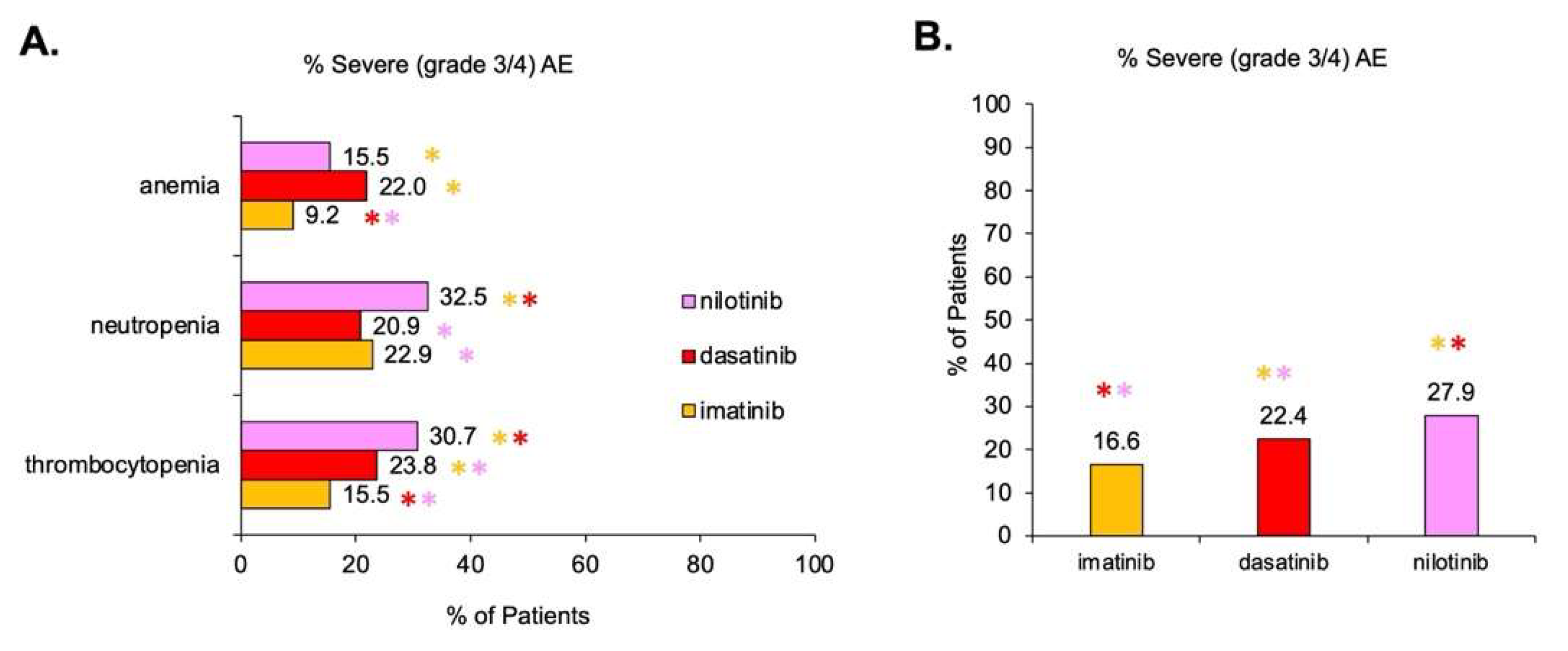
3.3. Assessment of AEs as a Function of TKI Therapy
4. Discussion
4.1. Some TKIs Have a Greater Association with Hematological AEs
4.2. The Role of Dose Titration to Minimize Toxicity and AEs
4.3. Personalized TKI Selection to Minize AEs
4.4. Investigation Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Hematological Condition | TKI Type | # of Patients with Condition from Studies of: (All Grades | Grade 3–4 Only) | # of Patients without Condition from Studies of: (All Grades | Grade 3–4 Only) | % of Patients with Condition from Studies of: (All Grades | Grade 3–4 Only) | Reference Number | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anemia | Imatinib | 1175 | 76 | 2404 | 1419 | 32.8 | 9.17 | [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56] |
| Dasatinib | 1244 | 121 | 1040 | 430 | 54.4 | 22 | [47,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65] | |
| Nilotinib | 299 | 71 | 2376 | 387 | 11.2 | 15.5 | [66,67,68,69,70] | |
| Bosutinib | 343 | N/A | 437 | N/A | 44 | N/A | [54,55,71] | |
| Ponatinib | 105 | N/A | 312 | N/A | 25.2 | N/A | [72] | |
| Asciminib | 17 | N/A | 133 | N/A | 11.3 | N/A | [73] | |
| Radotinib | 48 | 4 | 112 | 73 | 30 | 5.2 | [20,50] | |
| Ruxolitinib | 24 | N/A | 36 | N/A | 40 | N/A | [74,75] | |
| Tipifarnib | 17 | N/A | 9 | N/A | 65.4 | N/A | [22] | |
| Neutropenia | Imatinib | 1004 | 274 | 2365 | 1536 | 29.8 | 22.89 | [38,39,40,41,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,56,76,77,78,79] |
| Dasatinib | 736 | 235 | 702 | 890 | 51.2 | 20.9 | [47,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,80,81] | |
| Nilotinib | 362 | 251 | 2206 | 521 | 14.1 | 32.5 | [66,67,68,70,82,83,84] | |
| Bosutinib | 110 | N/A | 670 | N/A | 14.1 | N/A | [54,71,76] | |
| Ponatinib | 126 | N/A | 480 | N/A | 20.8 | N/A | [72,79,85] | |
| Asciminib | 16 | N/A | 134 | N/A | 10.7 | N/A | [73] | |
| Radotinib | 61 | 1 | 99 | 76 | 38.1 | 1.3 | [20,50] | |
| Ruxolitinib | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Tipifarnib | 12 | N/A | 14 | N/A | 46.2 | N/A | [22] | |
| Thrombocytopenia | Imatinib | 1075 | 308 | 2363 | 1854 | 30.4 | 15.5 | [38,39,40,41,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,77,78,79,86,87,88] |
| Dasatinib | 706 | 365 | 429 | 1171 | 62.2 | 23.8 | [47,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,80,81,88,89] | |
| Nilotinib | 601 | 237 | 2095 | 535 | 22.3 | 30.7 | [66,67,68,69,70,82,84] | |
| Bosutinib | 188 | N/A | 344 | N/A | 35.3 | N/A | [54,55,71] | |
| Ponatinib | 262 | N/A | 344 | N/A | 43.2 | N/A | [72,79,85] | |
| Asciminib | 33 | N/A | 117 | N/A | 22 | N/A | [73] | |
| Radotinib | 142 | N/A | 95 | N/A | 59.9 | N/A | [20,50] | |
| Ruxolitinib | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Tipifarnib | 10 | N/A | 16 | N/A | 38.5 | N/A | [22] | |
References
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H. Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2022 update on diagnosis, therapy, and monitoring. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 1236–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.M.; Melo, J.V. BCR-ABL in chronic myelogenous leukemia—How does it work? Acta Haematol. 2008, 119, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintas-Cardama, A.; Cortes, J. Molecular biology of bcr-abl1-positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2009, 113, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.A.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.E. Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in 2015. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 1440–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.M.; Dsouza, K.G.; Patel, M.; O’Dwyer, K. “Preleukemic or smoldering” chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML): BCR-ABL1 positive: A brief case report. Leuk. Res. Rep. 2015, 4, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Riley, L.K.; Rupert, J. Evaluation of Patients with Leukocytosis. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 92, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Yan, Z.; He, Z.; Ding, B.; Tao, S.; Li, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, C. Impact of anemia on the outcomes of chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia in TKI era. Hematology 2020, 25, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delehaye, F.; Rouger, J.; Brossier, D.; Suttorp, M.; Güneş, A.M.; Sedlacek, P.; Versluys, B.; Li, C.K.; Kalwak, K.; Lausen, B.; et al. Prevalence of anemia at diagnosis of pediatric chronic myeloid leukemia and prognostic impact on the disease course. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minciacchi, V.R.; Kumar, R.; Krause, D.S. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Model Disease of the Past, Present and Future. Cells 2021, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Larson, R.A.; Guilhot, F.; Radich, J.P.; Branford, S.; Hughes, T.P.; Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Cervantes, F.; Fujihara, S.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Imatinib Treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; Pavlovsky, C.; Saußele, S. Chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2021, 398, 1914–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachi, M.M.; Tonin, F.S.; Leonart, L.P.; Rotta, I.; Fernandez-Llimos, F.; Pontarolo, R. Haematological adverse events associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukaemia: A network meta-analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 2280–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, N.; Varmeziar, A.; Chen, X.; Kronick, O.; Fisher, R.; Kota, V.; Mitchell, C.S. Cross-Domain Text Mining to Predict Adverse Events from Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2022, 14, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Food and Drug Administration. TASIGNA (Nilotinib)—Prescribing Information; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020.
- Cortes, J.E.; Jimenez, C.A.; Mauro, M.J.; Geyer, A.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Smith, B.D. Pleural Effusion in Dasatinib-Treated Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase: Identification and Management. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017, 17, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Jiménez, M.; Derényi, I.; Szöllősi, G.J. The structure of the hematopoietic system can explain chronic myeloid leukemia progression. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulte, E.D.; Chen, H.; Price, L.S.L.; Gudi, R.; Li, H.; Okusanya, O.O.; Ma, L.; Rodriguez, L.; Vallejo, J.; Norsworthy, K.J.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Revised Indication and Dosing Regimen for Ponatinib Based on the Results of the OPTIC Trial. Oncologist 2022, 27, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpaz, M.; Silver, R.T.; Druker, B.J.; Goldman, J.M.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Guilhot, F.; Schiffer, C.A.; Fischer, T.; Deininger, M.W.N.; Lennard, A.L.; et al. Imatinib induces durable hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia: Results of a phase 2 study. Blood 2002, 99, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Lamas, L.; Luna, A.; Boque, C.; Senin, M.A.; Xicoy, B.; Giraldo, P.; Perez Lopez, R.; Ruiz Nuño, C.; De las Heras, N.; Mora Casterá, E.; et al. Toxicity of Asciminib in Real Clinical Practice; Analysis of Side Effects and Cross-Intolerance with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Blood 2022, 140, 3925–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Menon, H.; Jootar, S.; Saikia, T.; Kwak, J.Y.; Sohn, S.K.; Park, J.S.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of radotinib in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance or intolerance to BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstovsek, S.; Mesa, R.A.; Gotlib, J.; Gupta, V.; DiPersio, J.F.; Catalano, J.V.; Deininger, M.W.N.; Miller, C.B.; Silver, R.T.; Talpaz, M.; et al. Long-term treatment with ruxolitinib for patients with myelofibrosis: 5-year update from the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 COMFORT-I trial. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; Quintas-Cardama, A.; Garcia-Manero, G.; O’Brien, S.; Jones, D.; Faderl, S.; Ebarb, T.; Giles, F.; Thomas, D.; Kantarjian, H. Phase 1 study of tipifarnib in combination with imatinib for patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase after imatinib failure. Cancer 2007, 110, 2000–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, D.; Cayuela, J.M. Treatment-free remission in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2018, 108, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.T.; Cortes, J.E.; Kantarjian, H.M. Treatment value of second-generation BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors compared with imatinib to achieve treatment-free remission in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia: A modelling study. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e398–e408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolini, F.E.; Dulucq, S.; Boureau, L.; Cony-Makhoul, P.; Charbonnier, A.; Escoffre-Barbe, M.; Rigal-Huguet, F.; Coiteux, V.; Varet, B.; Dubruille, V.; et al. Evaluation of Residual Disease and TKI Duration Are Critical Predictive Factors for Molecular Recurrence after Stopping Imatinib First-line in Chronic Phase CML Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6606–6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerveira, N.; Loureiro, B.; Bizarro, S.; Correia, C.; Torres, L.; Lisboa, S.; Vieira, J.; Santos, R.; Pereira, D.; Moreira, C.; et al. Discontinuation of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in CML patients in real-world clinical practice at a single institution. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.S.; Cates, A.; Kim, R.B.; Hollinger, S.K. Undergraduate Biocuration: Developing Tomorrow’s Researchers While Mining Today’s Data. J. Undergrad. Neurosci. Educ. 2015, 14, A56–A65. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanavelu, P.; Mutnick, M.; Mehra, N.; White, B.; Kudrimoti, S.; Hernandez Kluesner, K.; Chen, X.; Nguyen, T.; Horlander, E.; Thenot, H.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Gastrointestinal Adverse Events from Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.J.; Doody, D.R.; Wilkes, J.J.; Becker, L.K.; Chennupati, S.; Morin, P.E.; Winestone, L.E.; Henk, H.J.; Lyman, G.H. Adverse events among chronic myelogenous leukemia patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A real-world analysis of health plan enrollees. Leuk. Lymphoma 2021, 62, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eşkazan, A.E. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) used in the management of chronic myeloid leukaemia are associated with haematologic toxicities-Which TKI is the safest? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 2241–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuganathan, N.; Branford, S.; Hughes, T.P.; Hiwase, D. Bone marrow fibrosis associated with long-term imatinib therapy: Resolution after switching to a second-generation TKI. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, P.; Gupta, S.K.; Ali, V.; Verma, M. Transport and metabolism of tyrosine kinase inhibitors associated with chronic myeloid leukemia therapy: A review. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 477, 1261–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copland, M. Is There a Role for Dose Modification of TKI Therapy in CML? Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2019, 14, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, K.; Jabbour, E.; Skinner, J.; Yilmaz, M.; Ferrajoli, A.; Bose, P.; Thompson, P.; Alvarado, Y.; Jain, N.; Takahashi, K.; et al. Early results of lower dose dasatinib (50 mg daily) as frontline therapy for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2018, 124, 2740–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.E.; Polydoros, F.; Apperley, J.F.; Milojkovic, D.; Pocock, C.; Smith, G.; Byrne, J.L.; de Lavallade, H.; O’Brien, S.G.; Coffey, T.; et al. De-escalation of tyrosine kinase inhibitor dose in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia with stable major molecular response (DESTINY): An interim analysis of a non-randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e310–e316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, D.; Martinelli, G.; Malagola, M.; Skert, C.; Soverini, S.; Iacobucci, I.; De Vivo, A.; Testoni, N.; Castagnetti, F.; Gugliotta, G.; et al. Effects and outcome of a policy of intermittent imatinib treatment in elderly patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 5138–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftciler, R.; Haznedaroglu, I.C. Tailored tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) based on current evidence. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 7787–7798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmanti, L.; Saussele, S.; Lauseker, M.; Muller, M.C.; Dietz, C.T.; Heinrich, L.; Hanfstein, B.; Proetel, U.; Fabarius, A.; Krause, S.W.; et al. Safety and efficacy of imatinib in CML over a period of 10 years: Data from the randomized CML-study IV. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Guan, X.; Wen, X.; Xiao, J.; An, X.; Yu, J. Clinical efficacy and safety of imatinib treatment in children and adolescents with chronic myeloid leukemia: A single-center experience in China. Medicine 2020, 99, e19150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.A.; Druker, B.J.; Guilhot, F.; O’Brien, S.G.; Riviere, G.J.; Krahnke, T.; Gathmann, I.; Wang, Y.; Group, I.S. Imatinib pharmacokinetics and its correlation with response and safety in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: A subanalysis of the IRIS study. Blood 2008, 111, 4022–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, P.; Chakrabarti, P.; Nath, U.K. A prospective, randomized study to compare the combination of imatinib and cytarabine versus imatinib alone in newly diagnosed patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Indian J. Cancer 2019, 56, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Karigane, D.; Kasahara, H.; Matsuki, E.; Hashida, R.; Yamane, Y.; Abe, R.; Koda, Y.; Toyama, T.; et al. Renal dysfunction and anemia associated with long-term imatinib treatment in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2019, 109, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Takeuchi, J.; Dobashi, N.; Kanakura, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Ezaki, K.; Nakaseko, C.; Hiraoka, A.; Okada, M.; Miyazaki, Y.; et al. Imatinib for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: Results of a prospective study in Japan. Int. J. Hematol. 2010, 92, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, W.G.; Kantarjian, H.; O’Brien, S.; Faderl, S.; Ravandi, F.; Borthakur, G.; Shan, J.; Pierce, S.; Rios, M.B.; Cortes, J. Imatinib front-line therapy is safe and effective in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia with pre-existing liver and/or renal dysfunction. Cancer 2010, 116, 3152–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Hochhaus, A.; Saglio, G.; De Souza, C.; Flinn, I.W.; Stenke, L.; Goh, Y.T.; Rosti, G.; Nakamae, H.; Gallagher, N.J.; et al. Nilotinib versus imatinib for the treatment of patients with newly diagnosed chronic phase, Philadelphia chromosome-positive, chronic myeloid leukaemia: 24-month minimum follow-up of the phase 3 randomised ENESTnd trial. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heibl, S.; Buxhofer-Ausch, V.; Schmidt, S.; Webersinke, G.; Lion, T.; Piringer, G.; Kuehr, T.; Wolf, D.; Melchardt, T.; Greil, R.; et al. A phase 1 study to evaluate the feasibility and efficacy of the addition of ropeginterferon alpha-2b to imatinib treatment in patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) not achieving a deep molecular response (molecular remission 4.5)-AGMT_CML 1. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 38, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Shah, N.P.; Cortes, J.E.; Baccarani, M.; Agarwal, M.B.; Undurraga, M.S.; Wang, J.; Ipina, J.J.; Kim, D.W.; Ogura, M.; et al. Dasatinib or imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: 2-year follow-up from a randomized phase 3 trial (DASISION). Blood 2012, 119, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, F.; Hernandez-Boluda, J.C.; Steegmann, J.L.; Conde, E.; Alvarez-Larran, A.; Lopez-Jimenez, J.; Osorio, S.; Villalon, L.; Camos, M.; Garcia-Conde, J.; et al. Imatinib mesylate therapy of chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia resistant or intolerant to interferon: Results and prognostic factors for response and progression-free survival in 150 patients. Haematologica 2003, 88, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Preudhomme, C.; Guilhot, J.; Nicolini, F.E.; Guerci-Bresler, A.; Rigal-Huguet, F.; Maloisel, F.; Coiteux, V.; Gardembas, M.; Berthou, C.; Vekhoff, A.; et al. Imatinib plus peginterferon alfa-2a in chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2511–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, S.J.; Zang, D.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.A.; Do, Y.R.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.S.; Choi, C.W.; et al. Phase III Clinical Trial (RERISE study) Results of Efficacy and Safety of Radotinib Compared with Imatinib in Newly Diagnosed Chronic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 7180–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLigeyo, A.; Rajab, J.; Ezzi, M.; Oyiro, P.; Bett, Y.; Odhiambo, A.; Ong’ondi, M.; Mwanzi, S.; Gatua, M.; Abinya, N. Cytopenia among CML Patients on Imatinib in Kenya: Types, Grades, and Time Course. Adv. Hematol. 2020, 2020, 7696204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, F.; Lopez-Garrido, P.; Montero, M.I.; Jonte, F.; Martinez, J.; Hernandez-Boluda, J.C.; Calbacho, M.; Sureda, A.; Perez-Rus, G.; Nieto, J.B.; et al. Early intervention during imatinib therapy in patients with newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: A study of the Spanish PETHEMA group. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilhot, F.; Hughes, T.P.; Cortes, J.; Druker, B.J.; Baccarani, M.; Gathmann, I.; Hayes, M.; Granvil, C.; Wang, Y. Plasma exposure of imatinib and its correlation with clinical response in the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Optimization and Selectivity Trial. Haematologica 2012, 97, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Cortes, J.E.; Lipton, J.H.; Dmoszynska, A.; Wong, R.S.; Rossiev, V.; Pavlov, D.; Gogat Marchant, K.; Duvillie, L.; Khattry, N.; et al. Safety of bosutinib versus imatinib in the phase 3 BELA trial in newly diagnosed chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.E.; Kim, D.W.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Brummendorf, T.H.; Dyagil, I.; Griskevicius, L.; Malhotra, H.; Powell, C.; Gogat, K.; Countouriotis, A.M.; et al. Bosutinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: Results from the BELA trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3486–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottmann, O.G.; Druker, B.J.; Sawyers, C.L.; Goldman, J.M.; Reiffers, J.; Silver, R.T.; Tura, S.; Fischer, T.; Deininger, M.W.; Schiffer, C.A.; et al. A phase 2 study of imatinib in patients with relapsed or refractory Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoid leukemias. Blood 2002, 100, 1965–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; Kim, D.W.; Raffoux, E.; Martinelli, G.; Ritchie, E.; Roy, L.; Coutre, S.; Corm, S.; Hamerschlak, N.; Tang, J.L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dasatinib in imatinib-resistant or -intolerant patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in blast phase. Leukemia 2008, 22, 2176–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Pan, L.Q.; Qian, S.X.; Song, P.; Yu, H.; Zhang, S.J.; Ge, Z.; Hong, M.; Tian, T.; Li, J.Y. Efficacy of dasatinib in treatment of imatinib-resistant BCR/ABL positive leukemia. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2013, 21, 581–586. [Google Scholar]
- Inokuchi, K.; Kumagai, T.; Matsuki, E.; Ohashi, K.; Shinagawa, A.; Hatta, Y.; Takeuchi, J.; Yoshida, C.; Wakita, H.; Kozai, Y.; et al. Efficacy of molecular response at 1 or 3 months after the initiation of dasatinib treatment can predict an improved response to dasatinib in imatinib-resistant or imatinib-intolerant Japanese patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia during the chronic phase. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2014, 54, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Apperley, J.F.; Cortes, J.E.; Kim, D.W.; Roy, L.; Roboz, G.J.; Rosti, G.; Bullorsky, E.O.; Abruzzese, E.; Hochhaus, A.; Heim, D.; et al. Dasatinib in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia in accelerated phase after imatinib failure: The START a trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3472–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilhot, F.; Apperley, J.; Kim, D.W.; Bullorsky, E.O.; Baccarani, M.; Roboz, G.J.; Amadori, S.; de Souza, C.A.; Lipton, J.H.; Hochhaus, A.; et al. Dasatinib induces significant hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with imatinib-resistant or -intolerant chronic myeloid leukemia in accelerated phase. Blood 2007, 109, 4143–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.P.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Kim, D.W.; Rea, D.; Dorlhiac-Llacer, P.E.; Milone, J.H.; Vela-Ojeda, J.; Silver, R.T.; Khoury, H.J.; Charbonnier, A.; et al. Intermittent target inhibition with dasatinib 100 mg once daily preserves efficacy and improves tolerability in imatinib-resistant and -intolerant chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3204–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiti, A.; Cortes, J.E.; Patel, K.P.; Masarova, L.; Borthakur, G.; Ravandi, F.; Verstovsek, S.; Ferrajoli, A.; Estrov, Z.; Garcia-Manero, G.; et al. Long-term results of frontline dasatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2020, 126, 1502–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brave, M.; Goodman, V.; Kaminskas, E.; Farrell, A.; Timmer, W.; Pope, S.; Harapanhalli, R.; Saber, H.; Morse, D.; Bullock, J.; et al. Sprycel for chronic myeloid leukemia and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia resistant to or intolerant of imatinib mesylate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bristol-Myers Squibb. Study of BMS-354825 (Dasatinib) in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Who Are Either Resistant or Intolerant to Imatinib; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Hong Kong, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Usuki, K.; Tojo, A.; Maeda, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Matsuda, A.; Ohyashiki, K.; Nakaseko, C.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tanaka, H.; Miyamura, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nilotinib in Japanese patients with imatinib-resistant or -intolerant Ph+ CML or relapsed/refractory Ph+ ALL: A 36-month analysis of a phase I and II study. Int. J. Hematol. 2012, 95, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, F.E.; Turkina, A.; Shen, Z.X.; Gallagher, N.; Jootar, S.; Powell, B.L.; De Souza, C.; Zheng, M.; Szczudlo, T.; le Coutre, P. Expanding Nilotinib Access in Clinical Trials (ENACT): An open-label, multicenter study of oral nilotinib in adult patients with imatinib-resistant or imatinib-intolerant Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in the chronic phase. Cancer 2012, 118, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.E.; Hochhaus, A.; le Coutre, P.D.; Rosti, G.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Jabbour, E.; Gillis, K.; Woodman, R.C.; Blakesley, R.E.; Giles, F.J.; et al. Minimal cross-intolerance with nilotinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic or accelerated phase who are intolerant to imatinib. Blood 2011, 117, 5600–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals. Nilotinib in Newly Diagnosed Adult Philadelphia Chromosome & or BCR-ABL Positive Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia in Chronic Phase; Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Hong Kong, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- le Coutre, P.D.; Giles, F.J.; Hochhaus, A.; Apperley, J.F.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Blakesley, R.; Shou, Y.; Gallagher, N.J.; Baccarani, M.; Cortes, J.; et al. Nilotinib in patients with Ph+ chronic myeloid leukemia in accelerated phase following imatinib resistance or intolerance: 24-month follow-up results. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Cortes, J.E.; Lipton, J.H.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Kim, D.W.; Schafhausen, P.; Crescenzo, R.; Bardy-Bouxin, N.; Shapiro, M.; Noonan, K.; et al. Safety and efficacy of second-line bosutinib for chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia over a five-year period: Final results of a phase I/II study. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E.; Kim, D.W.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; le Coutre, P.D.; Paquette, R.; Chuah, C.; Nicolini, F.E.; Apperley, J.F.; Khoury, H.J.; Talpaz, M.; et al. Ponatinib efficacy and safety in Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia: Final 5-year results of the phase 2 PACE trial. Blood 2018, 132, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Mauro, M.J.; Cortes, J.E.; Minami, H.; Rea, D.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Breccia, M.; Goh, Y.T.; Talpaz, M.; Hochhaus, A.; et al. Asciminib in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia after ABL Kinase Inhibitor Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2315–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, K.; Hazlehurst, L.; Sahakian, E.; Powers, J.; Nodzon, L.; Kayali, F.; Hyland, K.; Nelson, A.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J. A phase I clinical trial of ruxolitinib in combination with nilotinib in chronic myeloid leukemia patients with molecular evidence of disease. Leuk. Res. 2018, 74, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OHSU Knight Cancer Institute. Ruxolitinib Phosphate in Treating Patients with Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia or Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia; OHSU Knight Cancer Institute: Portland, OR, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brummendorf, T.H.; Cortes, J.E.; de Souza, C.A.; Guilhot, F.; Duvillie, L.; Pavlov, D.; Gogat, K.; Countouriotis, A.M.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C. Bosutinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukaemia: Results from the 24-month follow-up of the BELA trial. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 168, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, E.; Najfeld, V.; Schuster, M.; Roboz, G.; Chadburn, A.; Silver, R.T. The emergence of Ph-, trisomy -8+ cells in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with imatinib mesylate. Exp. Hematol. 2003, 31, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- le Coutre, P.; Ottmann, O.G.; Giles, F.; Kim, D.W.; Cortes, J.; Gattermann, N.; Apperley, J.F.; Larson, R.A.; Abruzzese, E.; O’Brien, S.G.; et al. Nilotinib (formerly AMN107), a highly selective BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is active in patients with imatinib-resistant or -intolerant accelerated-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 1834–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, J.H.; Chuah, C.; Guerci-Bresler, A.; Rosti, G.; Simpson, D.; Assouline, S.; Etienne, G.; Nicolini, F.E.; le Coutre, P.; Clark, R.E.; et al. Ponatinib versus imatinib for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukaemia: An international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintas-Cardama, A.; De Souza Santos, F.P.; Kantarjian, H.; O’Brien, S.; Faderl, S.; Awais, A.; Borthakur, G.; Cortes, J. Dynamics and management of cytopenias associated with dasatinib therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase after imatinib failure. Cancer 2009, 115, 3935–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.J.; Hu, J.D.; Li, J.Y.; Jin, J.; Meng, F.Y.; Shen, Z.X.; Liu, T.; Wu, D.P.; Wang, J.M.; Wang, J.X. Study on efficiency and safety of dasatinib in Chinese patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia who are resistant or intolerant to imatinib. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2012, 33, 889–895. [Google Scholar]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Giles, F.; Gattermann, N.; Bhalla, K.; Alimena, G.; Palandri, F.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Nicolini, F.E.; O’Brien, S.G.; Litzow, M.; et al. Nilotinib (formerly AMN107), a highly selective BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is effective in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase following imatinib resistance and intolerance. Blood 2007, 110, 3540–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Mahon, F.X.; le Coutre, P.; Petrov, L.; Janssen, J.; Cross, N.C.P.; Rea, D.; Castagnetti, F.; Hellmann, A.; Rosti, G.; et al. Nilotinib first-line therapy in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-negative/BCR-ABL-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: ENEST1st sub-analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojo, A.; Usuki, K.; Urabe, A.; Maeda, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Jinnai, I.; Ohyashiki, K.; Nishimura, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tanaka, H.; et al. A Phase I/II study of nilotinib in Japanese patients with imatinib-resistant or -intolerant Ph+ CML or relapsed/refractory Ph+ ALL. Int. J. Hematol. 2009, 89, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojo, A.; Kyo, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakamae, H.; Takahashi, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Tauchi, T.; Okamoto, S.; Miyamura, K.; Hatake, K.; et al. Ponatinib in Japanese patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia, a phase 1/2 study. Int. J. Hematol. 2017, 106, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Deventer, H.W.; Hall, M.D.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Mitchell, B.S.; Berkowitz, L.R.; Hogan, C.; Dunphy, C.H.; Koehler, J.; Shea, T.C. Clinical course of thrombocytopenia in patients treated with imatinib mesylate for accelerated phase chronic myelogenous leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2002, 71, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishima, Y.; Ogura, M.; Nishimura, M.; Yazaki, F.; Bessho, M.; Mizoguchi, H.; Chiba, S.; Hirai, H.; Tauchi, T.; Urabe, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate for patients in the first chronic phase of chronic myeloid leukemia: Results of a Japanese phase II clinical study. Int. J. Hematol. 2004, 80, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radich, J.P.; Kopecky, K.J.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Stock, W.; Malnassy, G.; Paietta, E.; Wadleigh, M.; Larson, R.A.; Emanuel, P.; et al. A randomized trial of dasatinib 100 mg versus imatinib 400 mg in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 3898–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Jiang, Q.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Jin, J.; Meng, F.; Shen, Z.; Liu, T.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; et al. Four-year follow-up of patients with imatinib-resistant or intolerant chronic myeloid leukemia receiving dasatinib: Efficacy and safety. Front. Med. 2019, 13, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kronick, O.; Chen, X.; Mehra, N.; Varmeziar, A.; Fisher, R.; Kartchner, D.; Kota, V.; Mitchell, C.S. Hematological Adverse Events with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 4354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174354
Kronick O, Chen X, Mehra N, Varmeziar A, Fisher R, Kartchner D, Kota V, Mitchell CS. Hematological Adverse Events with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2023; 15(17):4354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174354
Chicago/Turabian StyleKronick, Olivia, Xinyu Chen, Nidhi Mehra, Armon Varmeziar, Rachel Fisher, David Kartchner, Vamsi Kota, and Cassie S. Mitchell. 2023. "Hematological Adverse Events with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis" Cancers 15, no. 17: 4354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174354
APA StyleKronick, O., Chen, X., Mehra, N., Varmeziar, A., Fisher, R., Kartchner, D., Kota, V., & Mitchell, C. S. (2023). Hematological Adverse Events with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 15(17), 4354. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174354






