A Multicenter Retrospective Chart Review Study of Treatment and Disease Patterns and Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Third-Line Treatment or with T315I Mutation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
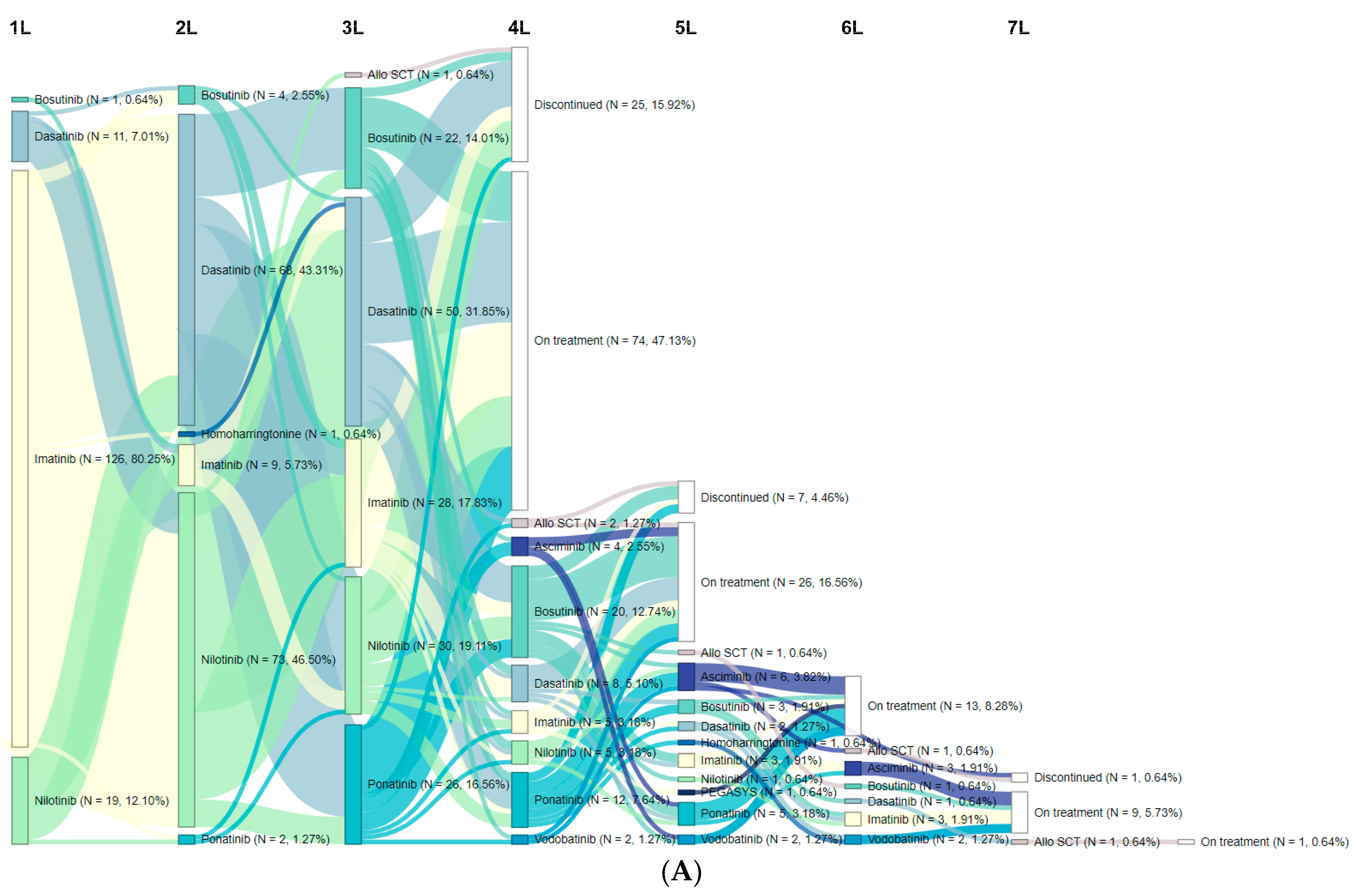
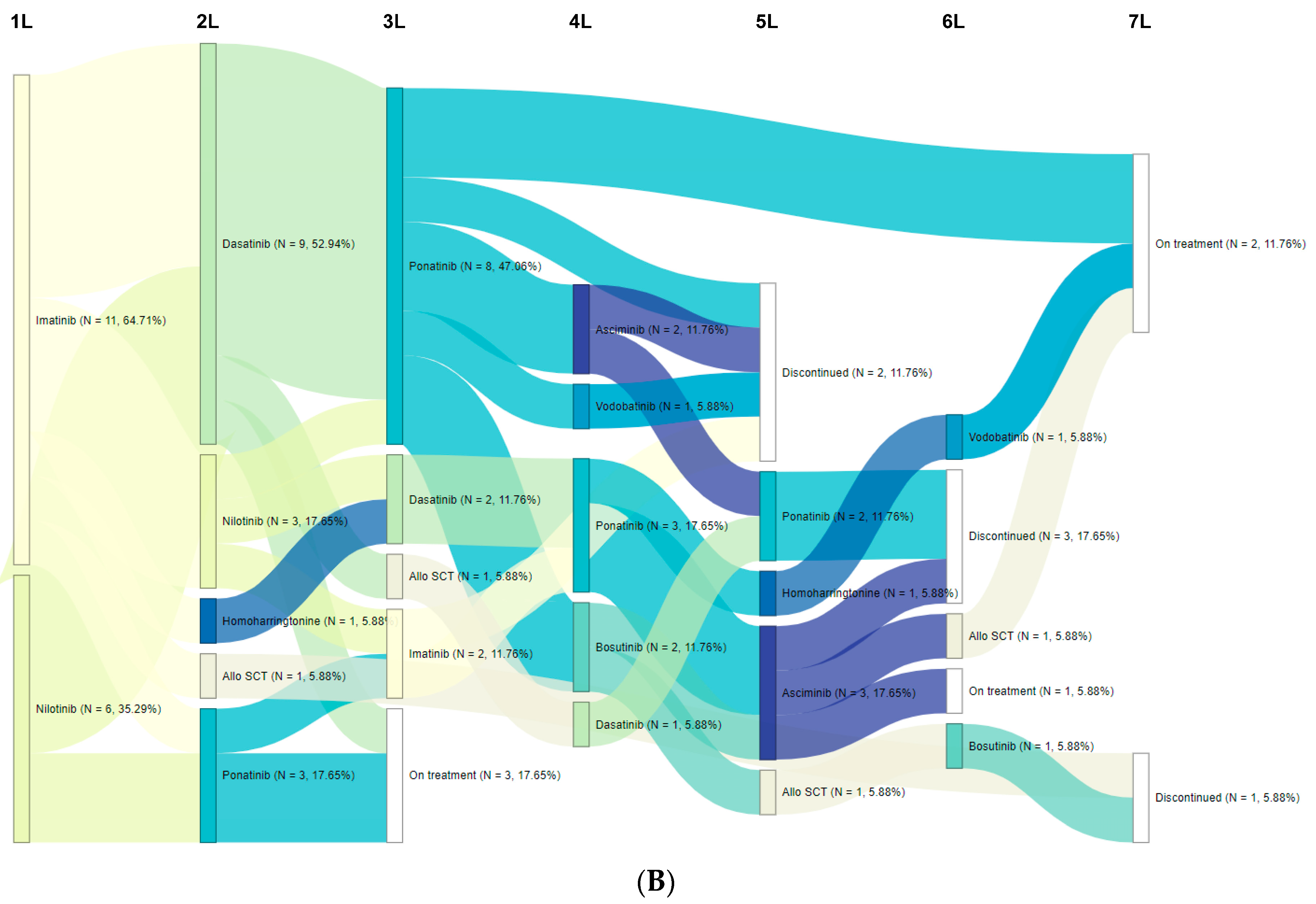
3.2. Treatment Patterns/Sequences
3.3. Clinical Outcomes
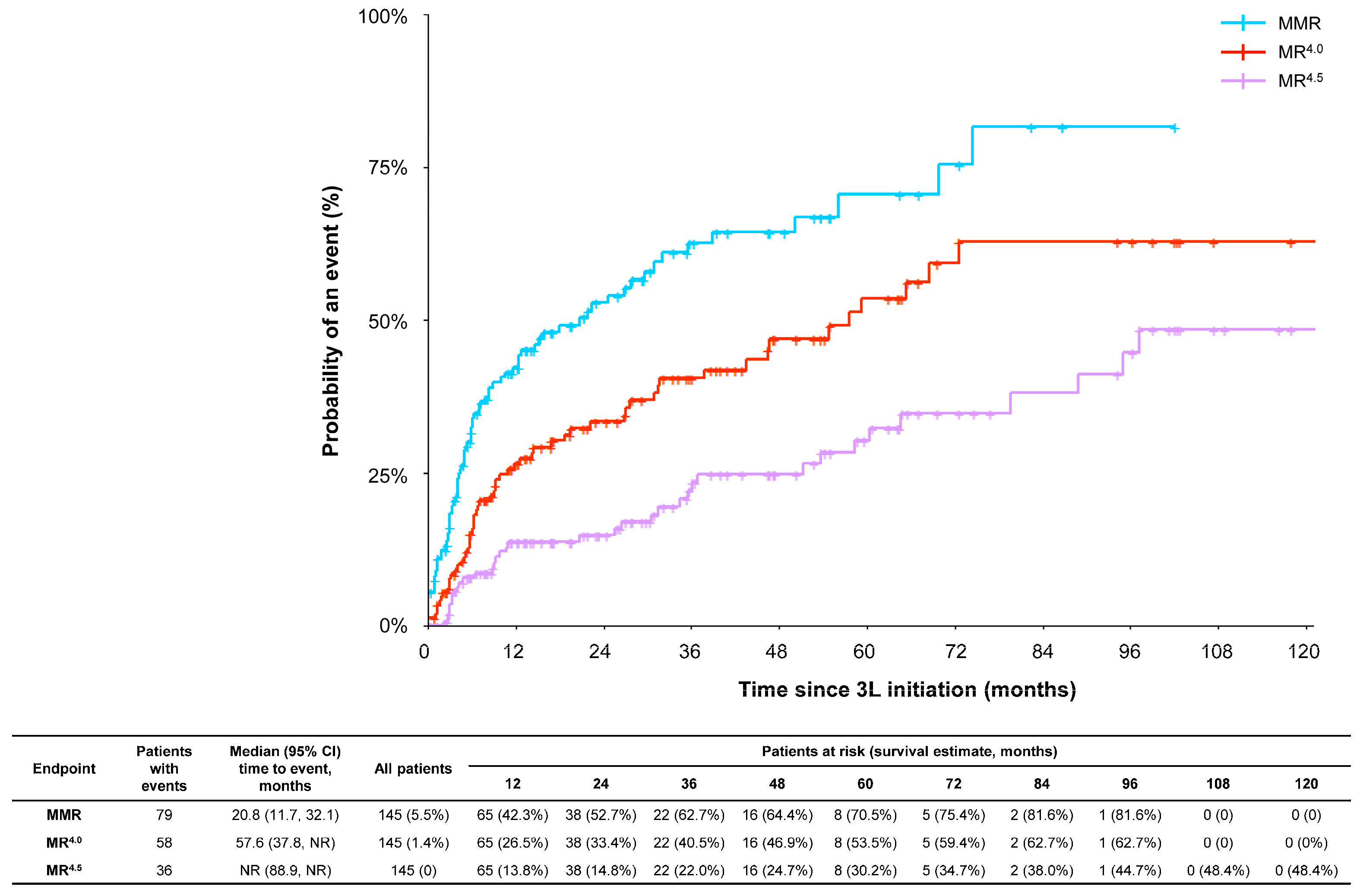
3.3.1. Molecular Response
3.3.2. Survival
3.4. AEs in 3L
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffmann, V.S.; Baccarani, M.; Hasford, J.; Castagnetti, F.; Di Raimondo, F.; Casado, L.F.; Turkina, A.; Zackova, D.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Zaritskey, A.; et al. Treatment and outcome of 2904 CML patients from the EUTOS population-based registry. Leukemia 2017, 31, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radich, J. Major progress in understanding progression in chronic myeloid leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Li, Q.; Hou, M.; Peng, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, S. Magnitude and Temporal Trend of the Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: On the Basis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2021, 7, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gutiérrez, V.; Hernández-Boluda, J.C. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Available for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Efficacy and Safety. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vener, C.; Banzi, R.; Ambrogi, F.; Ferrero, A.; Saglio, G.; Pravettoni, G.; Sant, M. First-line imatinib vs second- and third-generation TKIs for chronic-phase CML: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 2723–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glivec (Imatinib). Summary of Product Characteristics. European Medicines Agency. Updated on 5 April 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/glivec (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Tasigna (Nilotinib). Summary of Product Characteristics. European Medicines Agency. Updated on 26 October 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/tasigna (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Sprycel (Dasatinib). Summary of Product Characteristics. European Medicines Agency. Updated on 17 June 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/sprycel (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Bosulif (Bosutinib). Summary of Product Characteristics. European Medicines Agency. Updated on 9 June 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/bosulif (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Iclusig (Ponatinib). Summary of Product Characteristics. European Medicines Agency. Updated on 21 October 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/iclusig (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Chen, C.; Davis, C.; Sen, G.P.; Guyan, C.; Hehlmann, R.; Michallet, M.; Paquette, R.; Goldberg, S.L. Treatment patterns and clinical outcomes of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic-phase CML in clinical practice: 3-year European SIMPLICITY data. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 106, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehlmann, R.; Cortes, J.E.; Zyczynski, T.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Goldberg, S.L.; Mauro, M.J.; Michallet, M.; Simonsson, B.; Williams, L.A.; Gajavelli, S.; et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor interruptions, discontinuations and switching in patients with chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia in routine clinical practice: SIMPLICITY. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, D.T.; Osborn, M.P.; White, D.L.; Branford, S.; Braley, J.; Herschtal, A.; Kornhauser, M.; Issa, S.; Hiwase, D.K.; Hertzberg, M.; et al. TIDEL-II: First-line use of imatinib in CML with early switch to nilotinib for failure to achieve time-dependent molecular targets. Blood 2015, 125, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breccia, M.; Chiodi, F.; Nardozza, A.P.; Valsecchi, D.; Perrone, V.; Sangiorgi, D.; Giacomini, E.; Rendace, M.C.; Coco, P.; Premoli, E.; et al. Real-World Analysis of the Therapeutic Management and Disease Burden in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients with Later Lines in Italy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busque, L.; Harnois, M.; Szuber, N.; Delage, R.; Mollica, L.; Olney, H.; Laneuville, P.; Sirhan, S.; Cournoyer, G.; Chamakhi, I.; et al. Québec CML Research Group analysis of treatment patterns in chronic myelogenous leukemia: Switching is driven by intolerance and similar across tyrosine kinase inhibitors and lines of treatment (S159). HemaSphere 2022, 6, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.H.; Winton, E.F.; Heffner, L.T.; Gaddh, M.; Hill, B.; Neely, J.; Hatcher, A.; Joseph, M.; Arellano, M.; El-Rassi, F.; et al. Outcomes of Chronic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia after Treatment with Multiple Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milojkovic, D.; Cross, N.C.P.; Ali, S.; Byrne, J.; Campbell, G.; Dignan, F.L.; Drummond, M.; Huntly, B.; Marshall, S.; McMullin, M.F.; et al. Real-world tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment pathways, monitoring patterns and responses in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia in the United Kingdom: The UK TARGET CML study. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 192, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saußele, S.; Kohlbrenner, K.; Vogelmann, T.; Schubert, T. Incidence, Prevalence, and Real-World Treatment Patterns in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Results from a Population-Representative German Claims Data Analysis. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2022, 45, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Rosti, G.; Hochhaus, A.; Soverini, S.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood 2013, 122, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Baccarani, M.; Silver, R.T.; Schiffer, C.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Deininger, M.W.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet 2020 recommendations for treating chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2020, 34, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branford, S. Why is it critical to achieve a deep molecular response in chronic myeloid leukemia? Haematologica 2020, 105, 2730–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarry, L.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Divino, V.; Pokras, S.; Taylor, C.R.; Munakata, J.; Nieset, C.C.; Huang, H.; Jabbour, E.; Malone, D.C. Increasing economic burden of tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment failure by line of therapy in chronic myeloid leukemia. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2016, 32, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.J.; Kantarjian, H.; O’Brien, S.; Quintás-Cardama, A.; Faderl, S.; Estrov, Z.; Cortes, J. The use of nilotinib or dasatinib after failure to 2 prior tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Long-term follow-up. Blood 2009, 114, 4361–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.R.; Paliompeis, C.; Bua, M.; Milojkovic, D.; Szydlo, R.; Khorashad, J.S.; Foroni, L.; Reid, A.; de Lavallade, H.; Rezvani, K.; et al. Efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) as third-line therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase who have failed 2 prior lines of TKI therapy. Blood 2010, 116, 5497–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, H.J.; Cortes, J.E.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Baccarani, M.; Kim, D.-W.; Zaritskey, A.; Countouriotis, A.; Besson, N.; Leip, E.; et al. Bosutinib is active in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia after imatinib and dasatinib and/or nilotinib therapy failure. Blood 2012, 119, 3403–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soverini, S.; Branford, S.; Nicolini, F.E.; Talpaz, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Martinelli, G.; Müller, M.C.; Radich, J.P.; Shah, N.P. Implications of BCR-ABL1 kinase domain-mediated resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2014, 38, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penot, A.; Preux, P.-M.; Le Guyader, S.; Collignon, A.; Herry, A.; Dufour, V.; Monnereau, A.; Woronoff, A.-S.; Troussard, X.; Pons, E.; et al. Incidence of chronic myeloid leukemia and patient survival: Results of five French population-based cancer registries 1980–2009. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huguet, F.; Cayuela, J.; Cambier, N.; Carpentier, N.; Tindel, M.; Violet, I.; Zunic, P.; Lascaux, A.; Etienne, G.; Innocent, A.D.; et al. Nilotinib efficacy, safety, adherence and impact on quality of life in newly diagnosed patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia in chronic phase: A prospective observational study in daily clinical practice. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 187, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brümmendorf, T.H.; Cortes, J.E.; Milojkovic, D.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Clark, R.E.; le Coutre, P.D.; Garcia-Gutiérrez, V.; Chuah, C.; Kota, V.; Lipton, J.H.; et al. Bosutinib (BOS) Versus Imatinib for Newly Diagnosed Chronic Phase (CP) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): Final 5-Year Results from the Bfore Trial. Blood 2020, 136, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; Lang, F. Third-line therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia: Current status and future directions. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochhaus, A.; Saglio, G.; Hughes, T.P.; Larson, R.A.; Kim, D.W.; Issaragrisil, S.; Le Coutre, P.D.; Etienne, G.; Dorlhiac-Llacer, P.E.; Clark, R.E.; et al. Long-term benefits and risks of frontline nilotinib vs imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: 5-year update of the randomized ENESTnd trial. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlen, T.; Kockerols, C.; Ferreira, G.; Westerweel, P.E.; Mayer, J.; Sahmoud, T.; Wormser, D.; Yau, L.; Žácková, D. Treatment Patterns in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase in the Third Line of TKI Therapy and Beyond Based on Real-World Evidence. Blood 2021, 138, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Cortes, J.E.; Kim, N.-W.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Le Coutre, P.D.; Paquette, R.; Chuah, C.; Nicolini, F.E.; Apperley, J.F.; Khoury, H.J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Ponatinib in CP-CML Patients By Number of Prior Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: 4-Year Follow-up of the Phase 2 PACE Trial. Blood 2015, 126, 4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michallet, M.; Sobh, M.; Morisset, S.; Etienne, M.; Gadolet, E.; Labussiere, H.; Hayette, S.; Nicolini, F.E. Shorter Time to Achieve a Major Molecular Response (MMR) Is Predictive of a Faster Complete Molecular Response in CML: A Study of Characteristics and Outcomes of a Cohort of CML Patients in MMR. Blood 2011, 118, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akwaa, F.; Liesveld, J. Surrogate end points for long-term outcomes in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oriana, C.; Martin, H.; Toby, P.; Chris, C.; Ruth, G.; Claudius, R.; Rod, T. Complete Cytogenetic Response and Major Molecular Response as Surrogate Outcomes for Overall Survival in First-Line Treatment of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: A Case Study for Technology Appraisal on the Basis of Surrogate Outcomes Evidence. Value Health 2013, 16, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.E.; Khoury, H.J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Lipton, J.H.; Kim, D.; Schafhausen, P.; Matczak, E.; Leip, E.; Noonan, K.; Brümmendorf, T.H.; et al. Long-term bosutinib for chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia after failure of imatinib plus dasatinib and/or nilotinib. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulon, S.; Cony-Makhoul, P.; Guerci-Bresler, A.; Daban, M.; Kapso, R.; Tubert-Bitter, P.; Bonastre, J. Health state utility and quality of life measures in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in France. Qual. Life Res. 2021, 30, 2021–2032. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, P.; Kantarjian, H.; Boddu, P.C.; Nogueras-González, G.M.; Verstovsek, S.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Borthakur, G.; Sasaki, K.; Kadia, T.M.; Sam, P.; et al. Analysis of cardiovascular and arteriothrombotic adverse events in chronic-phase CML patients after frontline TKIs. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, M.; Mancuso, S.; Accurso, V.; Di Lisi, D.; Novo, G.; Siragusa, S. Cardiovascular Issues in Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Treatments for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Review. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 675811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treatment with Olverembatinib in CML-CP Patients Who Failed to at Least Two Previously Administered Second-Generation TKIs. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05311943. Updated 29 July 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05311943 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Jiang, Q.; Huang, X.; Chen, Z.; Niu, Q.; Shi, D.; Li, Z.; Hou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; et al. Novel BCR-ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) HQP1351 (Olverembatinib) Is Efficacious and Well Tolerated in Patients with T315I-Mutated Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): Results of Pivotal (Phase II) Trials. Blood 2020, 136, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safety and Anti-Leukemic Activity of Vodobatinib (K0706) for Treatment Refractory/Intolerant CML Failing ≥3 Prior CML Therapies. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02629692. Updated 8 December 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02629692 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Cortes, J.E.; Saikia, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Alvarado, Y.; Nicolini, F.E.; Khattry, N.; Rathnam, K.; Apperley, J.; Deininger, M.W.; de Lavallade, H.; et al. Phase 1 Trial of Vodobatinib, a Novel Oral BCR-ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI): Activity in CML Chronic Phase Patients Failing TKI Therapies Including Ponatinib. Blood 2020, 136, 51–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study to Evaluate Tolerability, Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Preliminary Efficacy of PF-114 for Oral Administration in Adults with Ph+ Chronic Myeloid Leukemia, which Is Resistant to the 2-nd Generation Bcr-Abl Inhibitors or Has T315I Mutation in the BCR-ABL Gene. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02885766. Updated 17 February 2020. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02885766 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Turkina, A.G.; Vinogradova, O.; Lomaia, E.; Shatokhina, E.; Shukhov, O.A.; Chelysheva, E.Y.; Shikhbabaeva, D.; Nemchenko, I.; Petrova, A.; Bykova, A.; et al. PF-114: A 4th Generation Tyrosine Kinase-Inhibitor for Chronic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Including BCRABL1T315I. Blood 2019, 134, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scemblix (Asciminib). Summary of Product Characteristics. European Medicines Agency. Updated on 7 September 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/scemblix (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Réa, D.; Mauro, M.J.; Boquimpani, C.; Minami, Y.; Lomaia, E.; Voloshin, S.; Turkina, A.G.; Kim, D.-W.; Apperley, J.F.; Abdo, A.; et al. A phase 3, open-label, randomized study of asciminib, a STAMP inhibitor, vs bosutinib in CML after 2 or more prior TKIs. Blood 2021, 138, 2031–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, D.; Mauro, M.J.; Hochhaus, A.; Boquimpani, C.; Lomaia, E.; Voloshin, S.; Turkina, A.G.; Kim, D.-W.; Apperley, J.; Cortes, J.E.; et al. Efficacy and safety results from ASCEMBL, a phase 3 study of asciminib versus bosutinib (BOS) in patients (pts) with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) after≥ 2 prior tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs): Week 96 update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. 16), 7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gutiérrez, V.; Luna, A.; Alonso-Dominguez, J.M.; Estrada, N.; Boque, C.; Xicoy, B.; Giraldo, P.; Angona, A.; Alvarez-Larrán, A.; Sanchez-Guijo, F.; et al. Safety and efficacy of asciminib treatment in chronic myeloid leukemia patients in real-life clinical practice. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innes, A.; Orovboni, V.; Claudiani, S.; Fernando, F.; Khan, A.; Byrne, J.; Gallipoli, P.; Copland, M.; Horne, G.; Arnold, C.; et al. Asciminib use in CML: The UK experience. P706. Hemasphere 2022, 6, 601–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkina, A.; Kuzmina, E.A.; Lomaia, E.; Morozova, E.; Shukhov, O.A.; Petrova, A.N.; Chitanava, T.; Vlasova, J.J.; Chelysheva, E.Y.; Sbityakova, E.; et al. Two-Year Updated Results of Asciminib Managed-Access Program (MAP) in Russia. Blood 2022, 140, 9654–9655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, L.C.; Lee, N.; Grigg, A.; Chen, M.; Schwarer, A.; Szer, J.; Yeung, D.T.; Hughes, T.; Shanmuganathan, N. Clinical Outcomes of Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia (CML) Patients on Asciminib through the Managed Access Program (MAP) in Australia. Blood 2022, 140, 6800–6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Lamas, L.; Luna, A.; Boque, C.; Senin, M.A.; Xicoy, B.; Giraldo, P.; Lopez, R.P.; Nuño, C.R.; Heras, N.D.L.; Casterá, E.M.; et al. Toxicity of Asciminib in Real Clinical Practice; Analysis of Side Effects and Cross-Intolerance with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. 1), 3925–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soverini, S.; Gnani, A.; Colarossi, S.; Castagnetti, F.; Abruzzese, E.; Paolini, S.; Merante, S.; Orlandi, E.; de Matteis, S.; Gozzini, A.; et al. Philadelphia-positive patients who already harbor imatinib-resistant Bcr-Abl kinase domain mutations have a higher likelihood of developing additional mutations associated with resistance to second- or third-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Blood 2009, 114, 2168–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, F.E.; Ibrahim, A.R.; Soverini, S.; Martinelli, G.; Müller, M.C.; Hochhaus, A.; Dufva, I.H.; Kim, D.-W.; Cortes, J.; Mauro, M.J.; et al. The BCR-ABLT315I mutation compromises survival in chronic phase chronic myelogenous leukemia patients resistant to tyrosine kinase inhibitors, in a matched pair analysis. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, F.; Corm, S.; Lê, Q.-H.; Sorel, N.; Hayette, S.; Bories, D.; Leguay, T.; Roy, L.; Giraudier, S.; Tulliez, M.; et al. Mutation status and clinical outcome of 89 imatinib mesylate-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia patients: A retrospective analysis from the French intergroup of CML (Fi(ϕ)-LMC GROUP). Leukemia 2006, 20, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarani, M.; Cortes, J.; Pane, F.; Niederwieser, D.; Saglio, G.; Apperley, J.; Cervantes, F.; Deininger, M.; Gratwohl, A.; Guilhot, F.; et al. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: An Update of Concepts and Management Recommendations of European LeukemiaNet. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 6041–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | 3L+ Cohort N = 157 | T315I Cohort N = 17 |
|---|---|---|
| Medical center | ||
| Centre Léon Bérard, Lyon | 65 (41.4) | 8 (47.1) |
| Hématologie Institut Bergonié, Bordeaux | 61 (38.9) | 5 (29.4) |
| Institut Universitaire du Cancer Toulouse, Toulouse | 31 (19.7) | 4 (23.5) |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 88 (56.1) | 13 (76.5) |
| Female | 69 (43.9) | 4 (23.5) |
| Age at CML-CP diagnosis, years | 52.8 ± 15.7 [55.7] | 51.1 ± 16.3 [52.2] |
| ELTS risk score at CML-CP diagnosis | ||
| Low risk (≤1.5680) | 63 (40.1) | 3 (17.6) |
| Intermediate risk (>1.5680 to ≤2.2185) | 39 (24.8) | 4 (23.5) |
| High risk (>2.2185) | 17 (10.8) | 7 (41.2) |
| Not assessed | 2 (1.3) | − |
| Unknown/not sure | 36 (22.9) | 3 (17.6) |
| Year of CML-CP diagnosis | ||
| Before 2010 | 88 (56.1) | 10 (58.8) |
| On or after 2010 | 69 (43.9) | 7 (41.2) |
| Time from CML-CP diagnosis to index date, months | 78.6 ± 56.8 [61.6] | 66.9 ± 70.6 [51.1] |
| Age at index date 1, years | 59.3 ± 15.6 [62.1] | 56.3 ± 13.1 [55.0] |
| Length of follow-up 2, months | 66.9 ± 43.3 [59.3] | 68.3 ± 48.2 [55.2] |
| BCR::ABL1 rearrangement at CML-CP diagnosis | ||
| Major | 142 (90.4) | 15 (88.2) |
| Minor | 4 (2.5) | 1 (5.9) |
| Other | 11 (7.0) | 1 (5.9) |
| BCR::ABL1 mutation status | ||
| Not assessed | 67 (42.7) | − |
| Unknown/not sure | 1 (0.6) | − |
| Assessed | 89 (56.7) | − |
| T315I | 7 (7.9) | − |
| Year T315I mutation was detected | ||
| Before 2015 | − | 11 (64.7) |
| On or after 2015 | − | 6 (35.3) |
| Line of therapy in which T315I mutation was identified | ||
| 2L | − | 6 (35.3) |
| 3L | − | 5 (29.4) |
| 4L | − | 4 (23.5) |
| 5L | − | 2 (11.8) |
| Additional chromosomal abnormalities at CML-CP diagnosis | ||
| Yes | 24 (15.3) | 6 (35.3) |
| No | 133 (84.7) | 11 (64.7) |
| EFS | OS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p Value | HR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Multivariate model (N = 145 1) | ||||||
| Age (years) at index date | 1.02 | (1.00, 1.04) | <0.05 * | 1.07 | (1.01, 1.13) | <0.05 * |
| Male (ref: Female) | 0.89 | (0.54, 1.47) | 0.65 | 0.81 | (0.24, 2.70) | 0.73 |
| ELTS risk score at CML-CP diagnosis (ref: Low risk) | ||||||
| Intermediate risk | 0.62 | (0.31, 1.21) | 0.16 | 0.81 | (0.11, 5.73) | 0.83 |
| High risk | 1.10 | (0.50, 2.43) | 0.81 | 2.76 | (0.30, 25.00) | 0.37 |
| Not assessed or unknown | 0.80 | (0.43, 1.48) | 0.47 | 2.17 | (0.45, 10.38) | 0.33 |
| Number of comorbid conditions | 1.13 | (0.97, 1.31) | 0.12 | 1.12 | (0.81, 1.55) | 0.48 |
| Additional chromosomal abnormalities at CML-CP diagnosis (ref: No additional abnormalities) | 2.35 | (1.27, 4.34) | <0.01 * | 6.02 | (1.78, 20.36) | <0.01 * |
| MMR was achieved in 3L (ref: MMR was not achieved in 3L) | 0.22 | (0.13, 0.37) | <0.001 * | 0.10 | (0.02, 0.51) | <0.01 * |
| Treatment with ponatinib (ref: Non-ponatinib) | 0.96 | (0.45, 2.02) | 0.91 | 1.36 | (0.18, 10.28) | 0.76 |
| Reason for terminating 2L is resistance or lack of efficacy (ref: No) | 1.51 | (0.83, 2.73) | 0.18 | 1.58 | (0.32, 7.78) | 0.57 |
| Reason for terminating 2L is intolerance or management of AEs (ref: No) | 0.64 | (0.34, 1.18) | 0.15 | 0.80 | (0.15, 4.22) | 0.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicolini, F.-E.; Huguet, F.; Huynh, L.; Xu, C.; Bouvier, C.; Yocolly, A.; Etienne, G. A Multicenter Retrospective Chart Review Study of Treatment and Disease Patterns and Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Third-Line Treatment or with T315I Mutation. Cancers 2023, 15, 4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164161
Nicolini F-E, Huguet F, Huynh L, Xu C, Bouvier C, Yocolly A, Etienne G. A Multicenter Retrospective Chart Review Study of Treatment and Disease Patterns and Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Third-Line Treatment or with T315I Mutation. Cancers. 2023; 15(16):4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164161
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicolini, Franck-Emmanuel, Françoise Huguet, Lynn Huynh, Churong Xu, Christophe Bouvier, Aurore Yocolly, and Gabriel Etienne. 2023. "A Multicenter Retrospective Chart Review Study of Treatment and Disease Patterns and Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Third-Line Treatment or with T315I Mutation" Cancers 15, no. 16: 4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164161
APA StyleNicolini, F.-E., Huguet, F., Huynh, L., Xu, C., Bouvier, C., Yocolly, A., & Etienne, G. (2023). A Multicenter Retrospective Chart Review Study of Treatment and Disease Patterns and Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Third-Line Treatment or with T315I Mutation. Cancers, 15(16), 4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164161






