Prediction of Surgical Outcome by Tumor Volume Doubling Time via Stereo Imaging Software in Early Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Surgery
2.3. Patient Follow-Up
2.4. Clinical Features of Patients
2.5. Analysis of VDTs
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Univariable and Multivariable Analyses
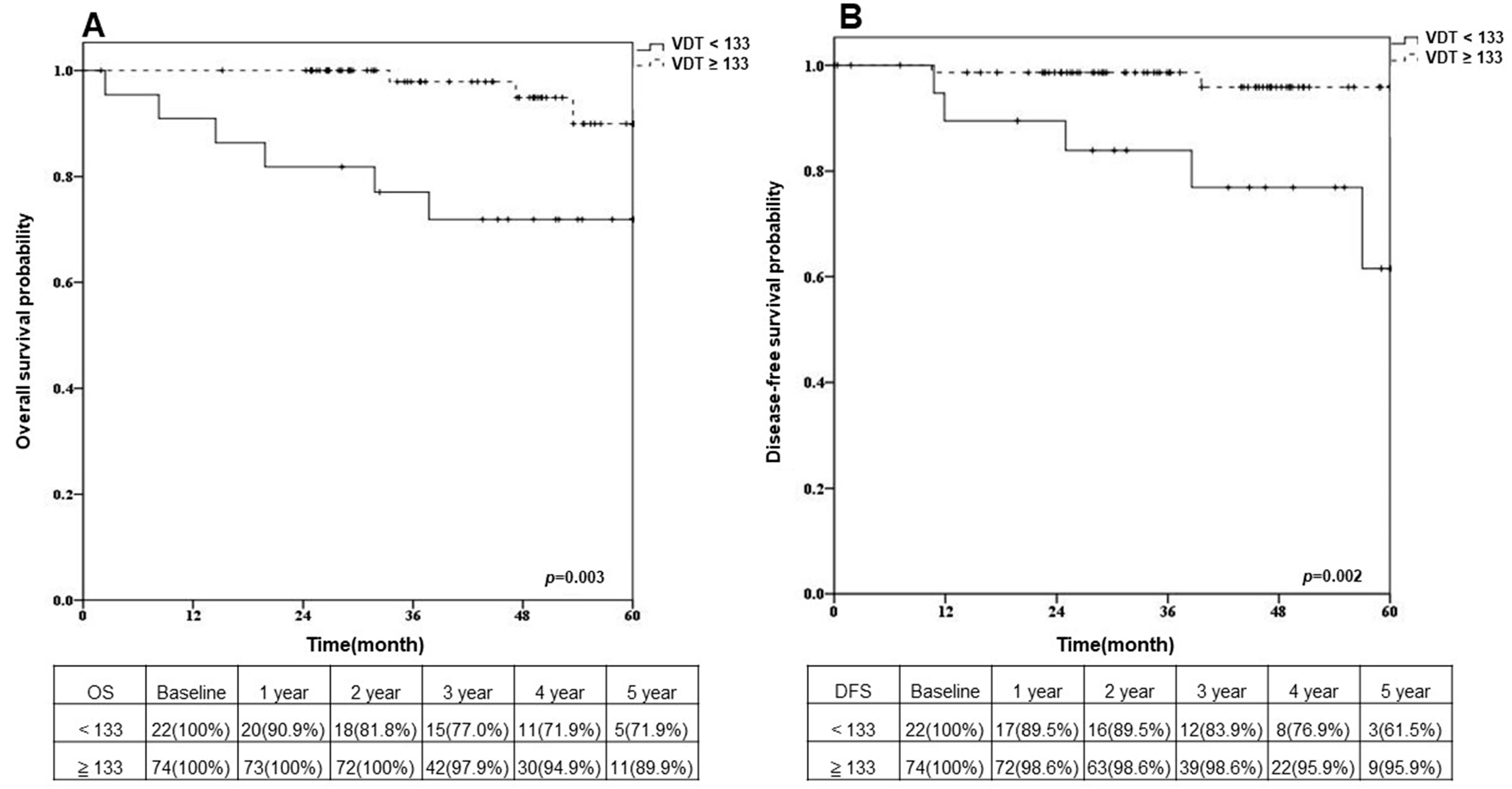
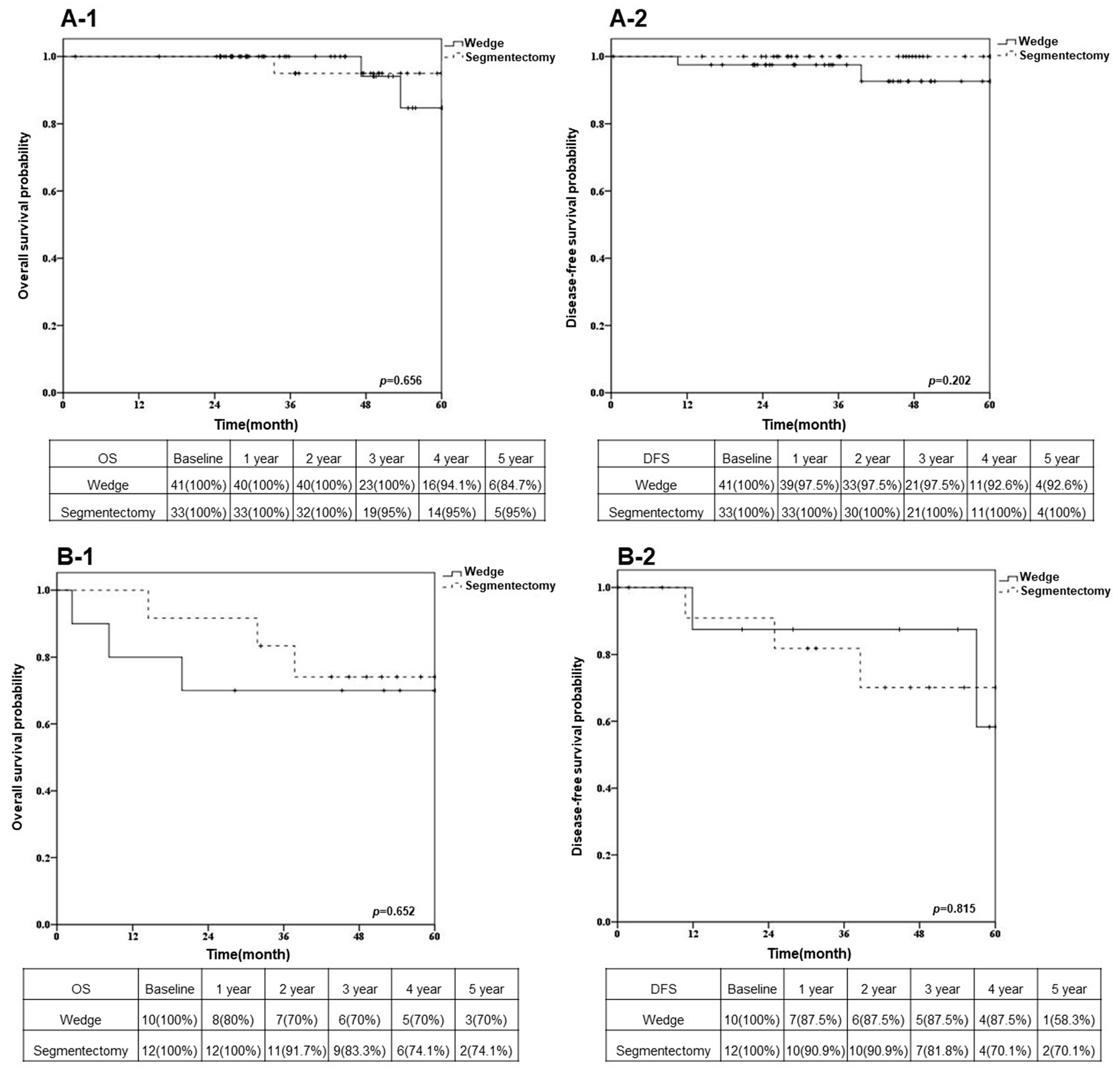
3.3. Overall Survival and Disease-Free Survival after Sublobar Resection in Different VDT Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.; Torre, L.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, S.; Barlesi, F.; Califano, R.; Cufer, T.; Ekman, S.; Levra, M.G.; Kerr, K.; Popat, S.; Reck, M.; Senan, S.; et al. Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, v1–v27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.M.; Gietema, H.; de Koning, H.; Vernhout, R.; Nackaerts, K.; Prokop, M.; Weenink, C.; Lammers, J.-W.; Groen, H.; Oudkerk, M.; et al. Nodule management protocol of the NELSON randomised lung cancer screening trial. Lung Cancer 2006, 54, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankelevitz, D.F.; Reeves, A.P.; Kostis, W.J.; Zhao, B.; Henschke, C.I. Small Pulmonary Nodules: Volumetrically Determined Growth Rates Based on CT Evaluation. Radiology 2000, 217, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.M.; van der Zaag-Loonen, H.J.; Oudkerk, M.; Wang, Y.; Vliegenthart, R.; Scholten, E.T.; Verschakelen, J.; Prokop, M.; de Koning, H.J.; van Klaveren, R.J. Smooth or attached solid indeter-minate nodules detected at baseline CT screening in the NELSON study: Cancer risk during 1 year of follow-up. Radiology 2009, 250, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Ucar, A.E.; Roel, M.D. Indication for VATS sublobar resections in early lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5 (Suppl. 3), S194. [Google Scholar]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E. NCCN Guidelines Version 3.2020 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer; National Comprehensive Cancer Network: Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–244. [Google Scholar]
- AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Amin, M.B., Edge, S.B., Greene, F.L., Byrd, D.R., Brookland, R.K., Washington, M.K., Gershenwald, J.E., Compton, C.C., Hess, K.R., Sullivan, D.C., et al., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, P.; Mazur, S.; Chan, E.; Awais, O.; Levy, R.; Pennathur, A.; Nason, K.; Luketich, J.; Schuchert, M. Segmentectomy vs Lobectomy for Pathological N1 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Chest 2017, 152, A662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, H.; Ozawa, Y. Definition of local and regional recurrence in the American College of Surgery Oncology Group Z0030 trial. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 146, 1306–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, A.S.; Das, A.; Naranje, P.; Irodi, A.; Raj, V.; Goyal, A. Imaging protocols for CT chest: A recommendation. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2019, 29, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Tan, Y.; Tsai, W.Y.; Schwartz, L.H.; Lu, L. Exploring Variability in CT Characterization of Tumors: A Preliminary Phantom Study. Transl. Oncol. 2014, 7, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, S.M.; Do, K.H.; Lee, J.G.; Bae, W.; Park, H.; Jung, K.H.; Seo, J.B. Deep learning algorithm for reducing CT slice thickness: Effect on re-producibility of radiomic features in lung cancer. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.-H.; Huang, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-C.; Huang, H.-K.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chang, H.; Wu, T.-H.; Sung, B.-Y.; Huang, T.-W. Benefit of Three-dimensional Image Simulation in Surgical Resection of Early-stage Lung Cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2021, 114, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Watanabe, S.-I.; Wakabayashi, M.; Saji, H.; Aokage, K.; Moriya, Y.; Yoshino, I.; Tsuboi, M.; Nakamura, S.; Nakamura, K.; et al. A single-arm study of sublobar resection for ground-glass opacity dominant peripheral lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 163, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altorki, N.; Wang, X.; Kozono, D.; Watt, C.; Landrenau, R.; Wigle, D.; Port, J.; Jones, D.R.; Conti, M.; Ashrafi, A.S.; et al. Lobar or Sublobar Resection for Peripheral Stage IA Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, X.H.; Lu, T.P.; Hsieh, M.S.; Tsai, T.M.; Liao, H.C.; Kao, T.N.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, M.W.; Hsu, H.H.; Chen, J.S. Thoracoscopic wedge resection versus segmentectomy for cT1N0 lung adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 8398–8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimae, T.; Saji, H.; Nakamura, H.; Okumura, N.; Tsuchida, M.; Sonobe, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Aokage, K.; Nakao, M.; Haruki, T.; et al. Survival of Octogenarians with Early-Stage Non-small Cell Lung Cancer is Comparable Between Wedge Resection and Lobectomy/Segmentectomy: JACS1303. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 7219–7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Lu, Z.; Li, D.; Pan, S.; Li, N.; Geng, Q. Survival after wedge resection versus lobectomy for stage IA second primary NSCLC with previous lung cancer-directed surgery. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 890033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRouen, M.C.; Canchola, A.J.; Thompson, C.A.; Jin, A.; Nie, S.; Wong, C.; Lichtensztajn, D.; Allen, L.; Patel, M.I.; Daida, Y.G.; et al. Incidence of lung cancer among never-smoking Asian American, Native Hawaiian, and Pacific Islander females. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, 114, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Henley, S.J.; Pollack, L.A.; Jemal, A. Proportion of Never Smokers Among Men and Women With Lung Cancer in 7 US States. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, G.; Maisonneuve, P.; Bellomi, M.; Rampinelli, C.; Durli, I.; Bertolotti, R.; Spaggiari, L. Estimating overdiagnosis in low-dose computed tomography screening for lung cancer: A cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setojima, Y.; Shimada, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Shigefuku, S.; Makino, Y.; Maehara, S.; Hagiwara, M.; Masuno, R.; Yamada, T.; Kakihana, M.; et al. Prognostic impact of solid-part tumour volume doubling time in patients with radiological part-solid or solid lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2019, 57, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Park, S.; Kim, H.; Goo, J.M.; Park, I.K.; Kang, C.H.; Kim, Y.T.; Yoon, S.H. Volume and Mass Doubling Time of Lung Adenocarcinoma according to WHO Histologic Classification. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, O.; Johkoh, T.; Sekiguchi, J.; Tomiyama, N.; Mihara, N.; Sumikawa, H.; Inoue, A.; Yanagawa, M.; Daimon, T.; Okumura, M.; et al. Doubling time of lung cancer determined using three-dimensional volumetric software: Comparison of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2009, 66, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frelinghuysen, M.; Fest, J.; Van der Voort Van, N.C.; Van der Holt, B.; Hoogeman, M.; Nuyttens, J. Consequences of Referral Time and Volume Doubling Time in Inoperable Patients With Early Stage Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, e403–e409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.G.; Choi, S.; Do, K.H.; Seo, J.B. Volume doubling times of lung adenocarcinomas: Correlation with pre-dominant histologic subtypes and prognosis. Radiology 2020, 295, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, M.A.; D’amico, T.A. Thoracoscopic Lobectomy for Non–small Cell Lung Cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 25, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, J.C.; Putnam, J.B., Jr.; Walsh, G.L.; Roth, J.A.; Mountain, C.F. Survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1995, 60, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijder, R.J.; de la Rivière, A.B.; Elbers, H.J.; Bosch, J.M.v.D. Survival in Resected Stage I Lung Cancer With Residual Tumor at the Bronchial Resection Margin. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1998, 65, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Ventura, A.; Cassivi, S.D.; Allen, M.S.; Wigle, D.A.; Nichols, F.C.; Pairolero, P.C.; Deschamps, C. Lung cancer in octogenarians: Factors affecting long-term survival following resection. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2007, 32, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienel, W.; Dango, S.; Kirschbaum, A.; Cucuruz, B.; Hörth, W.; Stremmel, C.; Passlick, B. Sublobar resections in stage IA non-small cell lung cancer: Segmentectomies result in significantly better cancer-related survival than wedge resections. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2008, 33, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divisi, D.; De Vico, A.; Zaccagna, G.; Crisci, R. Lobectomy versus sublobar resection in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 3357–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, G.; Li, J. Comparative Effectiveness of Lobectomy, Segmentectomy, and Wedge Resection for Pathological Stage I Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in Elderly Patients: A Population-Based Study. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 652770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Hamanaka, K.; Koizumi, T.; Kawakami, S.; Kobayashi, N.; Ito, K.-I. Solid component tumor doubling time is a prognostic factor in non-small cell lung cancer patients. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
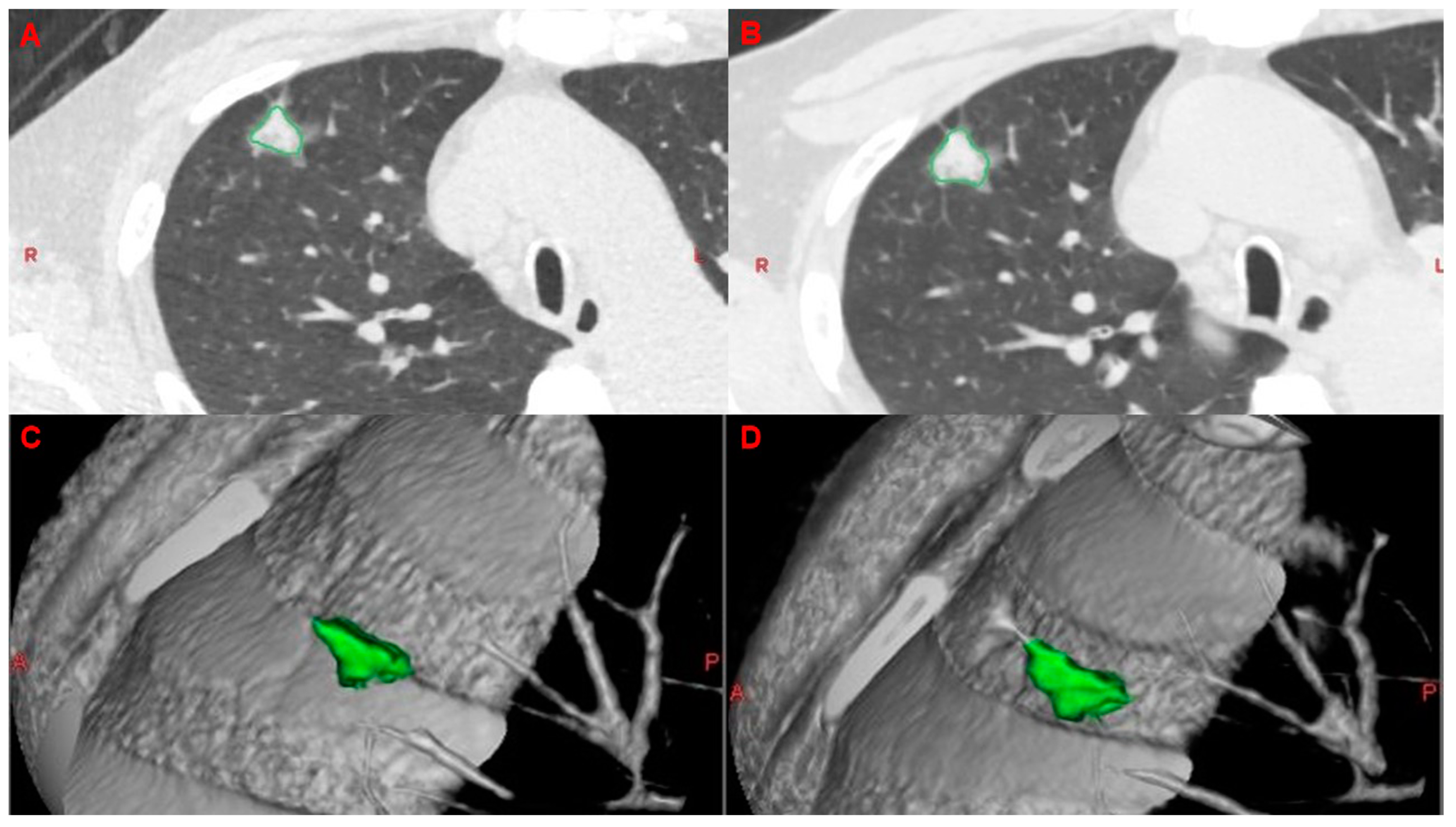
| Factors (Mean ± SD) | All Patients | VDT ≥ 133 Days | VDT < 133 Days | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 96 | 74 | 22 | |
| Age (years) (Mean ± SD) | 59.95 ± 11.38 | 59.53 ± 11.44 | 61.36 ± 11.35 | 0.36 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 39 (40.6%) | 26 (35.1%) | 13 (59.1%) | 0.01 |
| Female | 57 (59.4%) | 48 (64.9%) | 9 (40.9%) | 0.02 |
| Tumor size (cm) (Mean ± SD) | 0.96 ± 0.42 | 0.93 ± 0.40 | 1.06 ± 0.46 | 0.18 |
| C/D ratio (%) (Mean ± SD) | 11.67 ± 24.33 | 8.78 ± 22.19 | 21.41 ± 28.96 | 0.009 |
| Smoking | ||||
| Ever | 16 (16.7%) | 8 (10.8%) | 8 (36.4%) | <0.001 |
| Never | 80 (83.3%) | 66 (89.2%) | 14 (63.6%) | 0.04 |
| COPD | ||||
| Yes | 9 (9.4%) | 5 (6.8%) | 4 (18.2%) | 0.03 |
| No | 87 (90.6%) | 69 (93.2%) | 18 (81.8%) | 0.41 |
| EGFR mutation | ||||
| Positive | 10 (10.4%) | 4 (5.4%) | 6 (27.3%) | <0.001 |
| Negative | 86 (89.6%) | 70 (94.6%) | 16 (72.7%) | 0.09 |
| FEV1(%) (Mean ± SD) | 92.35 ± 16.78 | 93.79 ± 15.82 | 87.44 ± 19.36 | 0.53 |
| T stage | ||||
| Tis | 29 (30.2%) | 28 (37.8%) | 1 (4.5%) | <0.001 |
| T1 | 62 (64.6%) | 45 (60.8%) | 17 (77.3%) | 0.17 |
| T2 | 5 (5.2%) | 1 (1.4%) | 4 (18.2%) | <0.001 |
| TNM stage | ||||
| Stage 0 | 29 (30.2%) | 28 (37.8%) | 1 (4.5%) | <0.001 |
| Stage I | 67 (69.8%) | 46 (62.2%) | 21 (95.5%) | 0.007 |
| Tumor location | ||||
| Left | 44 (45.8%) | 36 (48.6%) | 8 (36.4%) | 0.16 |
| Right | 52 (54.2%) | 38 (51.4%) | 14 (63.6%) | 0.23 |
| Histological type | ||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 55 (57.3%) | 40 (54.1%) | 15 (68.2%) | 0.21 |
| SqCC | 7 (7.3%) | 2 (2.7%) | 5 (22.8%) | <0.001 |
| AIS | 21 (21.9%) | 21 (28.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | <0.001 |
| MIA | 10 (10.4%) | 9 (12.2%) | 1 (4.5%) | 0.09 |
| Other | 3 (3.1%) | 2 (2.7%) | 1 (4.5%) | 0.48 |
| Subtypes | ||||
| Lepidic | 5 (9.1%) | 3 (7.5%) | 2 (13.3%) | 0.275 |
| Non-lepidic | 50 (90.9%) | 37 (92.5%) | 13 (86.7%) | 0.655 |
| Surgical method | ||||
| Segmentectomy | 45 (46.9%) | 33 (44.6%) | 12 (54.5%) | 0.32 |
| Wedge resection | 51 (53.1%) | 41 (55.4%) | 10 (45.5%) | 0.37 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | p Value | Odds Ratio | p Value | |
| Age (years) | 1.10 | 0.009 | 1.11 | 0.17 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 14.45 | 0.01 | 2.59 | 0.59 |
| Female | 1 | |||
| Smoking | ||||
| Yes | 15.40 | <0.001 | 0.78 | 0.88 |
| No | 1 | |||
| COPD | ||||
| Yes | 13.12 | 0.002 | 69.45 | 0.09 |
| No | 1 | |||
| EGFR mutation | ||||
| Positive | 1.08 | 0.94 | 0.26 | 0.49 |
| Negative | 1 | |||
| FEV1(%) | −0.08 | 0.48 | 1.03 | 0.47 |
| TNM stage | ||||
| Stage 0 | 1 | |||
| Stage I | 2.51 × 108 | 0.99 | 2.88 × 107 | 0.99 |
| Tumor location | ||||
| Left | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.23 | 0.38 |
| Right | 1 | |||
| C/D ratio | ||||
| ≧50% | 14.29 | 0.001 | 7.16 | 0.22 |
| <50% | 1 | |||
| Surgery | ||||
| Wedge resection | 1 | |||
| Segmentectomy | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.23 | 0.35 |
| VDT | ||||
| ≥133 days | 1 | |||
| <133 days | 8.88 | 0.004 | 23.93 | 0.07 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | p Value | Odds Ratio | p Value | |
| Age (years) | 0.99 | 0.74 | 0.93 | 0.21 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 2.06 | 0.36 | 2.07 | 0.54 |
| Female | 1 | |||
| Smoking | ||||
| Yes | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.003 | 0.05 |
| No | 1 | |||
| COPD | ||||
| Yes | 1.69 | 0.65 | 262.29 | 0.09 |
| No | 1 | |||
| EGFR mutation | ||||
| Positive | 1.48 | 0.73 | 0.29 | 0.40 |
| Negative | 1 | |||
| FEV1(%) | 1.00 | 0.89 | 1.01 | 0.73 |
| TNM stage | ||||
| Stage 0 | 1 | |||
| Stage I | 2.75 | 0.36 | 0.75 | 0.85 |
| Tumor location | ||||
| Left | 1 | |||
| Right | 2.23 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.34 |
| C/D ratio | ||||
| ≧50% | 1 | |||
| <50% | 3.16 | 0.20 | 24.19 | 0.07 |
| Surgery | ||||
| Wedge resection | 1 | |||
| Segmentectomy | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.13 | 0.17 |
| VDT | ||||
| ≥133 days | 1 | |||
| <133 days | 10.59 | 0.007 | 55.63 | 0.008 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.-C.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Ke, P.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Lin, C.-M.; Wang, B.-Y. Prediction of Surgical Outcome by Tumor Volume Doubling Time via Stereo Imaging Software in Early Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3952. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153952
Liu C-C, Cheng Y-F, Ke P-C, Chen Y-L, Lin C-M, Wang B-Y. Prediction of Surgical Outcome by Tumor Volume Doubling Time via Stereo Imaging Software in Early Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(15):3952. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153952
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chia-Chi, Ya-Fu Cheng, Pei-Cing Ke, Yi-Ling Chen, Ching-Min Lin, and Bing-Yen Wang. 2023. "Prediction of Surgical Outcome by Tumor Volume Doubling Time via Stereo Imaging Software in Early Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 15: 3952. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153952
APA StyleLiu, C.-C., Cheng, Y.-F., Ke, P.-C., Chen, Y.-L., Lin, C.-M., & Wang, B.-Y. (2023). Prediction of Surgical Outcome by Tumor Volume Doubling Time via Stereo Imaging Software in Early Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers, 15(15), 3952. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153952







