Stereotactic Radiation Therapy of Single Brain Metastases: A Literature Review of Dosimetric Studies
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Selected Studies
| Study | Techniques | Study Type | Number of Metastases | Marge from GTV to PTV | Target Size | Prescription Dose | Prescription Isodose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brun et al., Cancer Radiother, 2021 [19] | NC DCA C VMAT NC VMAT C-NC VMAT | Retrospective In Silico | 10 | PTV = GTV + 2 mm | GTV: 5.7–13.6 cc—mean 8.7 cc PTV: 10.5–21.4 cc—mean 14.5 cc Mean diameter: 26 mm (25–30) | 33 Gy at the isocenter, 3 fr. | Isodose 70% (23.1 Gy) |
| Duan et al., Front Oncol, 2021 [28] | GK NC Cone-ARC (M)MLC-CRT | Retrospective In Silico | 11 | PTV = GTV + 2 mm | GTV: 0.18–0.76 cc—median 0.6 cc PTV: 0.92–2.24 cc—median 1.85 cc Median diameter: 13 mm (9.5–14.3) | 24 Gy, 1 fr. | NA |
| Torizuka et al., J Radiat Res, 2021 [21] | NC DCA C VMAT NC VMAT | Retrospective In Silico | 15 | PTV = GTV + 1 mm | PTV: 3.7–16.2 cc—median 6.4 cc Diameter: 20–30 mm | 20 Gy, 1 fr. | Isodose 70% |
| Ueda et al., Br J Radiol, 2019 [26] | CK C-NC VMAT | Retrospective In Silico | 31 singles (+14 multiple) | PTV = GTV | PTV: 0.01–4.4 cc—mean 0.7 cc | 25 Gy, 1 fr. | NA |
| Brun et al., Cancer Radiother, 2018 [20] | NC DCA C VMAT C-NC VMAT | Retrospective In Silico | 1 | PTV = GTV + 2 mm | PTV: 10.6 cc Diameter: 30 mm | 30 Gy at the isocenter, 3 fr. | Isodose 80% (24 Gy) |
| Greto et al., Radiol Med, 2017 [25] | CK TT | Retrospective In Silico | 19 | PTV = GTV + 2 mm | PTV: 0.69–18.35 cc—mean 6.32 cc and median 4.63 cc | 12–22 Gy | Isodose 80% for CK, 100% for TT |
| Calvo-Ortega et al., J Cancer Res Ther, 2016 [27] | NC DCA NC Fixed IMRT | Retrospective In Silico | 27 (+18 other cerebral lesions) | PTV = GTV + 2 mm | PTV: 0.44–29.18 cc Diameter: 9.4–38.2 mm | 12–24 Gy | NA |
| Molinier et al., J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2016 [22] | NC DCA C VMAT NC VMAT TR VMAT | Retrospective In Silico | 10 singles (+10 multiple; +5 close to OAR) | PTV = GTV + 2 mm | PTV: 1.5–13.7 cc—mean 5.2 cc | 20–25 Gy | Isodose 80% |
| Kumar et al., J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2010 [23] | TT GK | Retrospective In Silico | 8 (6 oblate spherical and 2 irregularly shaped lesions) | PTV = GTV | Largest diameters: 7 mm to 40 mm | 20 Gy, 1 fr. | Isodose 100% for TT, 50% for GK |
| Peñagarícano et al., Radiat Oncol, 2006 [24] | TT GK | Retrospective In Silico | 5 | PTV = GTV | PTV: 0.437–1.84 cc | 16–20 Gy, 1 fr. | Isodose 50% for GK |
| Yu et al., Neurosurgery, 2003 [29] | CK GK NC DCA MLC-CRT NC Fixed IMRT | Retrospective In Silico | 1 (ellipsoidal) | PTV = GTV + 1 mm | PTV: 11.5 cc Diameter: 25 mm | NA | Isodose 80% for CK, NC DCA, MLC-CRT, NC Fixed IMRT, 50% for GK |
3.2. Dosimetric Indexes
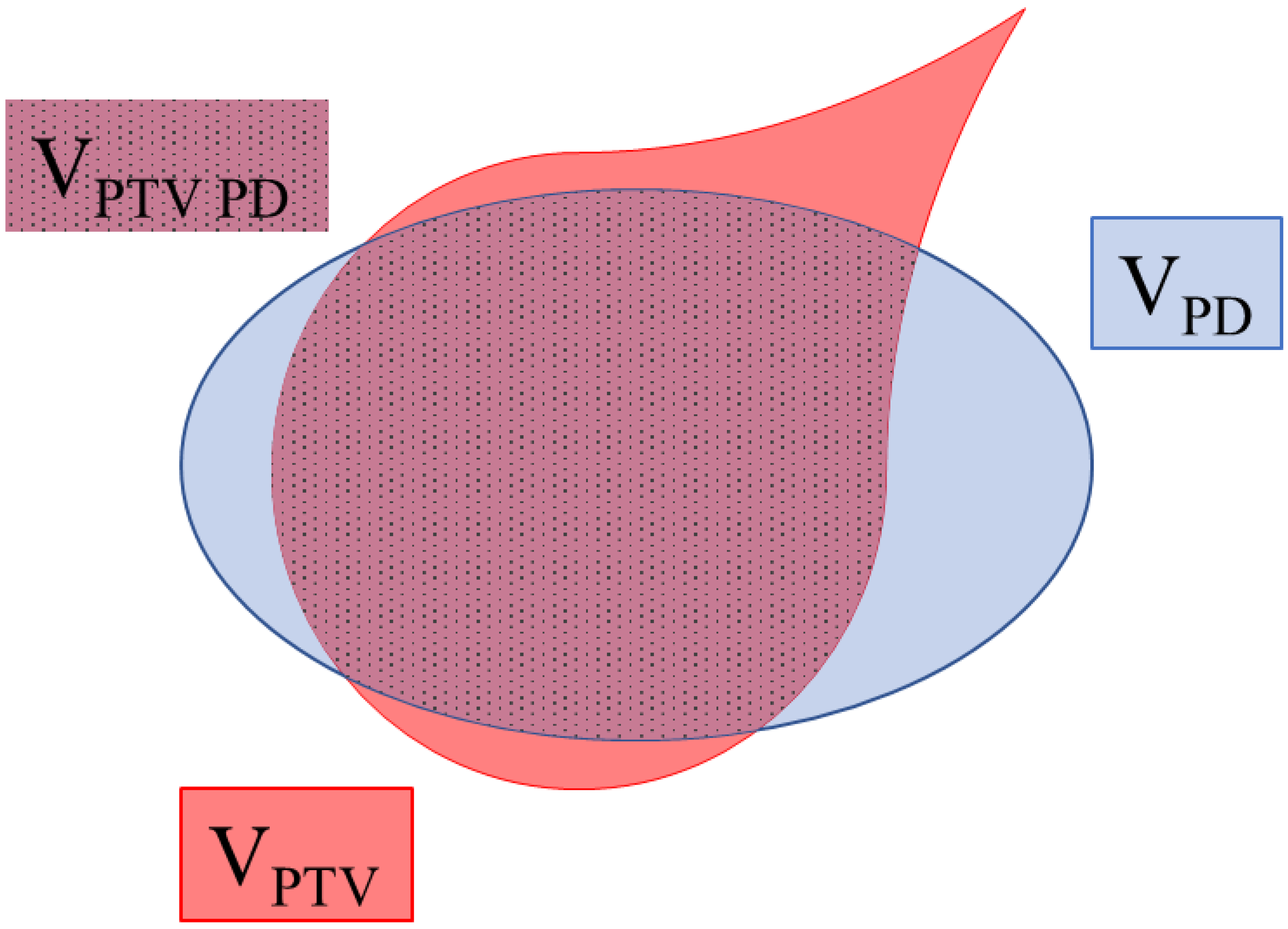
3.2.1. Conformity Index
3.2.2. Homogeneity Index
3.2.3. Gradient Index
3.3. Delivery Treatment Time
3.4. Dose-Volume of Normal Brain Tissue
| Study | Techniques | Conformity Index (CI)—Mean | Homogeneity Index (HI)—Mean | Gradient Index (GI)—Mean | Delivery Treatment Time—Mean (min) | Dose-Volume of Normal Brain Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brun et al., Cancer Radiother, 2021 [19] | NC DCA C VMAT NC VMAT C-NC VMAT | 1.28 vs. 1.04 vs. 1.07 vs. 1.05 (NC DCA vs. all VMAT < 0.01; between all VMAT ns) | NE | 2.41 vs. 3.02 vs. 2.45 vs. 3.02 (NC DCA vs. C-NC VMAT < 0.001; C-NC VMAT vs. NC VMAT < 0.001) | NE | Healthy brain-GTV Mean V23.1Gy, V20Gy, and V18Gy significantly lower for all VMAT techniques vs. NC DCA (respectively, <0.001 <0.05 and 0.04). Mean V10Gy and V5Gy lower for C-NC VMAT and NC-VMAT (respectively, ns and <0.05) |
| Duan et al., Front Oncol, 2021 [28] | GK NC Cone-ARC (M)MLC-CRT | 0.72 vs. 0.62 vs. 0.68 (GK vs. (M)MLC-CRT ns; GK and (M)MLC-CRT vs. NC Cone-ARC < 0.05) | 1.08 vs. 0.49 vs. 0.29 (<0.05 between any two plans) | 2.67 vs. 2.66 vs. 5.47 (GK vs. NC Cone-ARC ns; GK and NC Cone-ARC vs. (M)MLC-CRT < 0.05) | 26.67 vs. 3.88 vs. 3.14 (<0.05 between any two plans) | Healthy brain-PTV Mean V12Gy: GK vs. NC Cone-ARC ns; GK and NC Cone-ARC vs. (M)MLC-CRT < 0.05) Mean V3Gy and V6Gy: lower for GK (<0.05 between any two plans) |
| Torizuka et al., J Radiat Res, 2021 [21] | NC DCA C VMAT NC VMAT | RTOG-CI and IP-CI 0.73 and 0.72 vs. 0.76 and 0.78 vs. 0.82 and 0.83 (between all VMAT ns; NC DCA vs. NC VMAT < 0.05; NC DCA vs. C VMAT < 0.05 just for RTOG-CI) | NE | NE | 7.2 vs. 8.13 vs. 9.85 (NC VMAT vs. C VMAT and NC DCA < 0.05; C VMAT vs. NC DCA ns) | Healthy brain-PTV V20Gy, V15Gy, V12Gy, V10Gy, and V5Gy significantly lower for NC VMAT vs. C VMAT and NC DCA (<0.05) V15Gy, V12Gy, V10Gy, and V5Gy significantly lower for NC DCA vs. C VMAT (<0.05) |
| Ueda et al., Br J Radiol, 2019 [26] | CK C-NC VMAT | 0.6 vs. 0.8 (<0.01) | 1.1 vs. 1.1 (=0.55) | 14.6 vs. 14.1 (<0.01) | 15.6 vs. 5.6 (<0.01) | Healthy brain-PTV V21Gy, V18Gy, V15Gy, V12Gy, V6Gy, V3Gy significantly lower for C-NC VMAT vs. CK (<0.01) |
| Brun et al., Cancer Radiother, 2018 [20] | NC DCA C VMAT C-NC VMAT | 1.5 vs. 1.04 vs. 1.04 | NE | NE | NE | Healthy brain-PTV V24Gy, V18Gy, V10Gy, and V5Gy lower for C-NC VMAT |
| Greto et al., Radiol Med, 2017 [25] | CK TT | RTOG-CI and IP-CI 1.05 and 1.08 vs. 1.20 and 1.27 (p = 0.0001) | 1.25 vs. 1.06 (p = 0.0001) | 3.6 vs. 7.2 (p = 0.0001) | 33 vs. 22 (p = 0.0001) | NE |
| Calvo-Ortega et al., J Cancer Res Ther, 2016 [27] | NC DCA NC Fixed IMRT | 0.63 vs. 0.81 (<0.05) | 1.24 vs. 1.22 (ns) | 5.44 vs. 5.44 (ns) | NE | Healthy brain-PTV Mean V12Gy significantly lower for NC Fixed IMRT (p = 0.033) |
| Molinier et al., J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2016 [22] | NC DCA C VMAT NC VMAT TR VMAT | 0.77 vs. 0.84 vs. 0.84 vs. 0.85 | 0.27 vs. 0.21 vs. 0.17 vs. 0.20 | NE | NE | Healthy brain-PTV Mean V10Gy lower for NC DCA |
| Kumar et al., J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2010 [23] | TT GK | 0.59 vs. 0.57 | NE | 7.65 vs. 2.95 | 23.7 vs. 213.6 | NE |
| Peñagarícano et al., Radiat Oncol, 2006 [24] | TT GK | 0.59 vs. 0.60 | NE | NE | 38.4 vs. 28.7 | NE |
| Yu et al., Neurosurgery, 2003 [29] | CK GK NC DCA MLC-CRT NC Fixed IMRT | 1.16 vs. 1.15 vs. 1.19 vs. 1.16 vs. 1.27 | 1.25 vs. 2 vs. 1.25 vs. 1.25 vs. 1.26 | NE | NE | NE |
| Study | Conformity Index (CI) (Figure 2) | Homogeneity Index (HI) | Gradient Index (GI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paddick | Inverse Paddick | RTOG | Paddick | |||
| Brun et al., Cancer Radiother, 2021 [19] | X | NA | X | |||
| Duan et al., Front Oncol, 2021 [28] | X | X | ||||
| Torizuka et al., J Radiat Res, 2021 [21] | X | X | NA | NA | NA | |
| Ueda et al., Br J Radiol, 2019 [26] | X | X | ||||
| Brun et al., Cancer Radiother, 2018 [20] | X | NA | NA | NA | ||
| Greto et al., Radiol Med, 2017 [25] | X | X | X | |||
| Calvo-Ortega et al., J Cancer Res Ther, 2016 [27] | X | X | ||||
| Molinier et al., J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2016 [22] | X | NA | NA | |||
| Kumar et al., J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2010 [23] | X | NA | X | |||
| Peñagarícano et al., Radiat Oncol, 2006 [24] | X | NA | NA | NA | ||
| Yu et al., Neurosurgery, 2003 [29] | X | NA | NA | |||
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Study | Q.1 | Q.2 | Q.3 | Q.4 | Q.5 | Q.6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brun et al., Cancer Radiother, 2021 [19] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes |
| Duan et al., Front Oncol, 2021 [28] | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes |
| Torizuka et al., J Radiat Res, 2021 [21] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes |
| Ueda et al., Br J Radiol, 2019 [26] | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes |
| Brun et al., Cancer Radiother, 2018 [20] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes |
| Greto et al., Radiol Med, 2017 [25] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes |
| Calvo-Ortega et al., J Cancer Res Ther, 2016 [27] | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes |
| Molinier et al., J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2016 [22] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes |
| Kumar et al., J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2010 [23] | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes |
| Peñagarícano et al., Radiat Oncol, 2006 [24] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes |
| Yu et al., Neurosurgery, 2003 [29] | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes |
References
- Lamba, N.; Wen, P.Y.; Aizer, A.A. Epidemiology of brain metastases and leptomeningeal disease. Neuro.-Oncol. 2021, 23, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Mesko, S.; Li, J.; Cagney, D.; Aizer, A.; Lin, N.U.; Nesbit, E.; Kruser, T.J.; Chan, J.; Braunstein, S.; et al. Survival in Patients with Brain Metastases: Summary Report on the Updated Diagnosis-Specific Graded Prognostic Assessment and Definition of the Eligibility Quotient. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3773–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Wright, C.H.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. Brain metastases: Epidemiology. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 149, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, A.M.; Stöhring, C.; Hedderich, J.; Held-Feindt, J.; Mehdorn, H.M. Surgical treatment for brain metastases: Prognostic factors and survival in 309 patients with regard to patient age. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 18, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delattre, J.Y.; Krol, G.; Thaler, H.T.; Posner, J.B. Distribution of Brain Metastases. Arch. Neurol. 1988, 45, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, E.S.; Djalilian, H.R.; Cho, K.H.; Hall, W.A. Brain Metastases. Histology, Multiplicity, Surgery, and Survival. Cancer 1996, 78, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravan, M.J.; Fecci, P.E.; Anders, C.K.; Clarke, J.M.; Salama, A.K.S.; Adamson, J.D.; Floyd, S.R.; Torok, J.A.; Salama, J.K.; Sampson, J.H.; et al. Current multidisciplinary management of brain metastases. Cancer 2020, 126, 1390–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhermain, F.; Noël, G.; Antoni, D.; Tallet, A. Role of radiation therapy in brain metastases management. Cancer Radiother. 2020, 24, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorzeff, I.; Antoni, D.; Josset, S.; Noël, G.; Tallet-Richard, A. Radiation therapy for brain metastases. Cancer Radiother. 2021, 26, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SFPM-2019-RAPPORT N°35-Qualité et Sécurité des Radiochirurgies et des Radiothérapies Stéréotaxiques. Available online: https://www.calameo.com/read/00000613128590033b064 (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Andrevska, A.; Knight, K.A.; Sale, C.A. The feasibility and benefits of using volumetric arc therapy in patients with brain metastases: A systematic review. J. Med. Radiat. Sci. 2014, 61, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, E.; Kline, R.; Gillin, M.; Souhami, L.; Hirschfeld, A.; Dinapoli, R.; Martin, L. Radiation therapy oncology group: Radiosurgery quality assurance guidelines. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1993, 27, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuvret, L.; Noël, G.; Mazeron, J.-J.; Bey, P. Conformity index: A review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 64, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddick, I. A Simple Scoring Ratio to Index the Conformity of Radiosurgical Treatment Plans. Technical Note. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 93 (Suppl. 3), 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Rito, A.; Chaikh, A.; Troussier, I.; Darmon, I.; Thariat, J. Radiosurgery and stereotactic irradiation of multiple and contiguous brain metastases: A practical proposal of dose prescription methods and a literature review. Cancer Radiother. 2020, 25, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntz, L.; Le Fèvre, C.; Jarnet, D.; Keller, A.; Meyer, P.; Cox, D.G.; Bund, C.; Antoni, D.; Cebula, H.; Noel, G. Radionecrosis after repeated courses of radiotherapy under stereotactic conditions for brain metastases: Analysis of clinical and dosimetric data from a retrospective cohort of 184 patients. Cancer Radiother. 2022, 26, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aromataris, E.; Fernandez, R.; Godfrey, C.M.; Holly, C.; Khalil, H.; Tungpunkom, P. Summarizing systematic reviews: Methodological Development, Conduct and Reporting of an Umbrella Review Approach. Int. J. Evid.-Based Health 2015, 13, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brun, L.; Dupic, G.; Chassin, V.; Chautard, E.; Moreau, J.; Dedieu, V.; Khalil, T.; Verrelle, P.; Lapeyre, M.; Biau, J. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for large brain metastases: Optimizing the dosimetric parameters. Cancer/Radiothérapie 2021, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, L.; Dupic, G.; Chassin, V.; Verrelle, P.; Lapeyre, M.; Biau, J. Radionecrosis following stereotactic radiotherapy of a 3-cm brain metastasis: Can we improve the dosimetric results? Cancer Radiother. 2018, 22, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torizuka, D.; Uto, M.; Takehana, K.; Mizowaki, T. Dosimetric comparison among dynamic conformal arc therapy, coplanar and non-coplanar volumetric modulated arc therapy for single brain metastasis. J. Radiat. Res. 2021, 62, rrab092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinier, J.; Kerr, C.; Simeon, S.; Ailleres, N.; Charissoux, M.; Azria, D.; Fenoglietto, P. Comparison of volumetric-modulated arc therapy and dynamic conformal arc treatment planning for cranial stereotactic radiosurgery. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2016, 17, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, T.; Rakowski, J.; Zhao, B.; Alkhafaji, M.; Burmeister, J.; Austin, T.; Vlachaki, M. Helical TomoTherapy versus sterotactic Gamma Knife radiosurgery in the treatment of single and multiple brain tumors: A dosimetric comparison. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2010, 11, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñagarícano, J.A.; Yan, Y.; Shi, C.; Linskey, M.E.; Ratanatharathorn, V. Dosimetric comparison of Helical Tomotherapy and Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery for single brain metastasis. Radiat. Oncol. 2006, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greto, D.; Pallotta, S.; Masi, L.; Talamonti, C.; Marrazzo, L.; Doro, R.; Saieva, C.; Scoccianti, S.; Desideri, I.; Livi, L. A dosimetric comparison between CyberKnife and tomotherapy treatment plans for single brain metastasis. Radiol. Medica 2017, 122, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, Y.; Ohira, S.; Yamazaki, H.; Mabuchi, N.; Higashinaka, N.; Miyazaki, M.; Teshima, T. Dosimetric performance of two linear accelerator-based radiosurgery systems to treat single and multiplebrain metastases. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Ortega, J.F.; Delgado, D.; Moragues, S.; Pozo, M.; Casals, J. Dosimetric comparison of intensity modulated radiosurgery with dynamic conformal arc radiosurgery for small cranial lesions. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Cao, H.; Wu, B.; Wu, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhou, L.; Feng, A.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Gu, H.; et al. Dosimetric Comparison, Treatment Efficiency Estimation, and Biological Evaluation of Popular Stereotactic Radiosurgery Options in Treating Single Small Brain Metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 716152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Jozsef, G.; Apuzzo, M.L.J.; Petrovich, Z. Dosimetric Comparison of CyberKnife with Other Radiosurgical Modalities for an Ellipsoidal Target. Neurosurgery 2003, 53, 1155–1162; discussion 1162–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paddick, I.; Lippitz, B. A simple dose gradient measurement tool to complement the conformity index. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 105, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, R.M.; Benedict, S.H.; Wu, Q.; Zwicker, R.D.; Gaballa, H.E.; Mohan, R. A comparison of three stereotactic radiotherapy techniques; ARCS vs. noncoplanar fixed fields vs. intensity modulation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1998, 42, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Kim, D.G.; Chung, H.-T.; Paek, S.H.; Park, C.-K.; Jung, H.-W. Radiosurgery for Large Brain Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuvret, L.; Vinchon, S.; Martin, V.; Lamproglou, I.; Halley, A.; Calugaru, V.; Chea, M.; Valéry, C.; Simon, J.-M.; Mazeron, J.-J. Stereotactic radiotherapy for large solitary brain metastases. Cancer Radiother. 2014, 18, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, E.; Scott, C.; Souhami, L.; Dinapoli, R.; Bahary, J.-P.; Kline, R.; Wharam, M.; Schultz, C.; Davey, P.; Loeffler, J.; et al. Radiosurgery for the treatment of previously irradiated recurrent primary brain tumors and brain metastases: Initial report of radiation therapy oncology group protocol 90-05. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1996, 34, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, G.; Keller, A.; Antoni, D. Stereotactic radiotherapy of brain metastases in complex situations. Cancer Radiother. 2019, 23, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergalasova, I.; Liu, H.; Alonso-Basanta, M.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Nie, K.; Shi, W.; Teo, B.-K.K.; Yu, Y.; Yue, N.J.; et al. Multi-Institutional Dosimetric Evaluation of Modern Day Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) Treatment Options for Multiple Brain Metastases. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, A.; Puchades, V.; Mata, F.; Ramos, D.; Alcaraz, M. Influence of multi-leaf collimator leaf width in radiosurgery via volumetric modulated arc therapy and 3D dynamic conformal arc therapy. Phys. Medica 2015, 31, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leith, J.T.; Cook, S.; Chougule, P.; Calabresi, P.; Wahlberg, L.; Lindquist, C.; Epstein, M. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Characteristics of Human Tumors Relevant to Radiosurgery: Comparative Cellular Radiosensitivity and Hypoxic Percentages. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 1994, 62, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, W.A.; Fowler, J.F. Selective boosting of tumor subvolumes. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 48, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, F.; Key, S.; Dissaux, G.; Goasduff, G.; Lucia, A.-S.; Ollivier, L.; Pradier, O.; Schick, U. Inhomogeneous tumor dose distribution provides better local control than homogeneous distribution in stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 130, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohutek, Z.A.; Yamada, Y.; Chan, T.A.; Brennan, C.W.; Tabar, V.; Gutin, P.H.; Yang, T.J.; Rosenblum, M.K.; Ballangrud, Å.; Young, R.J.; et al. Long-term risk of radionecrosis and imaging changes after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2015, 125, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, I.J.; Ding, G.X.; Ahnesjö, A. Small fields: Nonequilibrium radiation dosimetry. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, R.; Shi, C.; Li, J.; Zhuang, H.; Tian, S.; Wang, J. Noncoplanar VMAT for Brain Metastases: A Plan Quality and Delivery Efficiency Comparison with Coplanar VMAT, IMRT, and CyberKnife. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819871621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lagerwaard, F.J.; Meijer, O.W.M.; van der Hoorn, E.A.P.; Verbakel, W.F.A.R.; Slotman, B.J.; Senan, S. Volumetric Modulated Arc Radiotherapy for Vestibular Schwannomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 74, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumert, B.G.; Norton, I.A.; Davis, J.B. Intensity-modulated stereotactic radiotherapy vs. stereotactic conformal radiotherapy for the treatment of meningioma located predominantly in the skull base. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 57, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uto, M.; Mizowaki, T.; Ogura, K.; Hiraoka, M. Non-coplanar volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for craniopharyngiomas reduces radiation doses to the bilateral hippocampus: A planning study comparing dynamic conformal arc therapy, coplanar VMAT, and non-coplanar VMAT. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Rhun, E.; Dhermain, F.; Vogin, G.; Reyns, N.; Metellus, P. Radionecrosis after stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2016, 16, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Clarke, E.; Lanzetta, G.; Osti, M.F.; Trasimeni, G.; Bozzao, A.; Romano, A.; Enrici, R.M. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: Analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blonigen, B.J.; Steinmetz, R.D.; Levin, L.; Lamba, M.A.; Warnick, R.E.; Breneman, J.C. Irradiated Volume as a Predictor of Brain Radionecrosis after Linear Accelerator Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doré, M.; Martin, S.; Delpon, G.; Clément, K.; Campion, L.; Thillays, F. Stereotactic radiotherapy following surgery for brain metastasis: Predictive factors for local control and radionecrosis. Cancer Radiother. 2017, 21, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Scaringi, C.; Paolini, S.; Lanzetta, G.; Romano, A.; Cicone, F.; Osti, M.; Enrici, R.M.; Esposito, V. Single-Fraction Versus Multifraction (3 × 9 Gy) Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Large (>2 cm) Brain Metastases: A Comparative Analysis of Local Control and Risk of Radiation-Induced Brain Necrosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.K.; Sato, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, J.-; Noda, S.; Seto, K.; Torikai, K.; Sakurai, H.; Nakano, T. Optimal hypofractionated conformal radiotherapy for large brain metastases in patients with high risk factors: A single-institutional prospective study. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loo, M.; Pin, Y.; Thierry, A.; Clavier, J.-B. Single-fraction radiosurgery versus fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases: A comparative study. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2020, 37, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chambrelant, I.; Jarnet, D.; Bou-Gharios, J.; Le Fèvre, C.; Kuntz, L.; Antoni, D.; Jenny, C.; Noël, G. Stereotactic Radiation Therapy of Single Brain Metastases: A Literature Review of Dosimetric Studies. Cancers 2023, 15, 3937. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153937
Chambrelant I, Jarnet D, Bou-Gharios J, Le Fèvre C, Kuntz L, Antoni D, Jenny C, Noël G. Stereotactic Radiation Therapy of Single Brain Metastases: A Literature Review of Dosimetric Studies. Cancers. 2023; 15(15):3937. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153937
Chicago/Turabian StyleChambrelant, Isabelle, Delphine Jarnet, Jolie Bou-Gharios, Clara Le Fèvre, Laure Kuntz, Delphine Antoni, Catherine Jenny, and Georges Noël. 2023. "Stereotactic Radiation Therapy of Single Brain Metastases: A Literature Review of Dosimetric Studies" Cancers 15, no. 15: 3937. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153937
APA StyleChambrelant, I., Jarnet, D., Bou-Gharios, J., Le Fèvre, C., Kuntz, L., Antoni, D., Jenny, C., & Noël, G. (2023). Stereotactic Radiation Therapy of Single Brain Metastases: A Literature Review of Dosimetric Studies. Cancers, 15(15), 3937. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153937





