PRO: Do We Still Need Whole-Brain Irradiation for Brain Metastases?
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy for Limited Brain Metastatic Disease
| Trial | Design | Patients | Oncological Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patchell et al., 1998 [16] | OP + WBRT vs. OP + Obs | 49 vs. 46 | Local recurrence: 10% vs. 46%, p < 0.001 * |
| Distant recurrence: 14% vs. 37%, p < 0.01 * | |||
| Median OS: 48 vs. 43 weeks, p = 0.39 | |||
| Neurological death: 14% vs. 44%, p = 0.003 * | |||
| Aoyama et al., 2006 [12] | WBRT + SRS vs. SRS | 65 vs. 67 | One-year recurrence: 46.8% vs. 76.4%, p < 0.001 * |
| Median OS: 7.5 vs. 8.0 months, p = 0.42 | |||
| Neurological death: 22.8% vs. 19.3%, p = 0.64 | |||
| Kocher et al., 2011 [17] | (SRS vs. OP) + WBRT vs. (SRS vs. OP) + Obs | (99 vs. 81) vs. (100 vs. 79) | Two-year local recurrence (OP): 59% vs. 27%, p < 0.001 * |
| Two -year local recurrence (SRS): 31% vs. 19%, p = 0.040 * | |||
| Two -year distant recurrence (OP): 42% vs. 23%, p = 0.008 * | |||
| Two -year distant recurrence (SRS): 48% vs. 33%, p = 0.023 * | |||
| Median OS: 10.9 v 10.7 months, p = 0.89 | |||
| Neurological death: 44% vs. 28%, p < 0.002 * | |||
| El Gantery et al., 2014 [13] | SRS vs. WBRT vs. SRS + WBRT | 18 vs. 21 vs. 21 | Median LTC: 6 vs. 5 vs. 10 months, p = 0.04 |
| Median OS: no significant difference | |||
| Median OS (BMs < 3 cm): 8 vs. 5 vs. 15 months, p = 0.002 | |||
| Kayama et al., 2018 [18] | OP + Obs + salvage SRS vs. WBRT | 134 vs. 137 | Median PFS: 4.0 vs. 10.4 months * |
| Median OS: 15.6 vs. 15.6 months, p = 0.027 | |||
| Neurological death: 21.0% vs. 21.9% | |||
| Brown et al., 2016 [14] | SRS vs. SRS + WBRT | 111 vs. 102 | Six-month LTC: 81.6% vs. 92.6%, p = 0.034 * |
| Twelve-month LTC: 72.8% vs. 90.1%, p = 0.003 * | |||
| Six-month DTC: 76.7% vs. 94.7%, p < 0.001 * | |||
| Twelve-month DTC: 69.9% vs. 92.3%, p < 0.001 * | |||
| Median OS: 7.4 vs. 10.4 months, p = 0.92 | |||
| Brown et al., 2017 [8] | OP + SRS vs. OP + WBRT | 98 vs. 96 | Six-month LTC: 80.4% vs. 87.1%, p = 0.00068 * |
| Median PFS: 6.4 vs. 27.5 months, p < 0.0001 * | |||
| Median OS: 12.2 vs. 11.6 months | |||
| Palmer et al., 2022 [19] | OP + SRS vs. OP + WBRT | 27 vs. 27 | Twelve-month LTC + DTC: 81.5% vs. 40.7% * |
3. Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy for Extensive Brain Metastatic Disease
3.1. Hippocampal Irradiation and Cognitive Impairment
3.2. Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy and Concomitant Memantine Administration
3.3. Hippocampus-Avoidance Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy
3.4. Hippocampus-Avoidance Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy with Simultaneous Integrated Boost to Metastases
| Trial | Design | Hippocampal Constraints | Patients | Neurocognitive Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gondi et al., 2014 [44] | HA-WBRT + memantine | D100% ≤ 9 Gy and Dmax ≤ 16 Gy in 10 Fx | 42 (analyzable) | Hopkins Verbal Learning Test—Revised: delayed recall decline at 4 mo—7% vs. 30% (historical control), p < 0.001 |
| Brown et al., 2020 [45] | HA-WBRT + memantine vs. WBRT + memantine | D100% ≤ 9 Gy and Dmax ≤ 16 Gy in 10 Fx | 261 vs. 257 | Cognitive failure: hazard ratio—0.76, p = 0.03 |
| Executive function at 4 mo: 23.3% vs. 40.4%, p = 0.01 | ||||
| Learning at 6 mo: 11.5% vs. 24.7%, p = 0.049 | ||||
| Memory at 6 mo: 16.4% vs. 33.3% p = 0.02 | ||||
| Grosu et al., 2020 [58] | HA-WBRT + SIB vs. WBRT + SIB | D98% ≤ 9 Gy and D2% ≤ 17 Gy in 12 Fx | 66 vs. 66 (planned) | Results pending |
| Redmond et al., 2017 [59] | HA-PCI | Dmean < 8 Gy in 10 Fx | 17 (analyzable) | Hopkins Verbal Learning Test—Revised: decline at 6 and 12 mo—no significant decline compared to baseline |
| Rodríguez de Dios et al., 2021 [60] | HA-PCI vs. PCI | D100% ≤ 9 Gy and Dmax ≤ 16 Gy in 10 Fx | 75 vs. 75 | Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test: delayed recall decline at 3 mo—5.8% vs. 23.5%, p = 0.003; |
| total recall decline at 3 mo—8.7% vs. 20.6%; | ||||
| delayed recall decline at 6 mo—11.1% vs. 33.3%; | ||||
| total recall decline at 6 mo—20.3% vs. 38.9%; | ||||
| total recall decline at 24 mo—14.2% vs. 47.6% | ||||
| Belderbos et al., 2021 [61] | HA-PCI vs. PCI | Dmean ≤ 8.5 Gy and D1% ≤ 10 Gy in 10 Fx | 84 vs. 84 | Hopkins Verbal Learning Test—Revised: total recall decline at 4 mo—28% vs. 29%, p = 1.000 |
4. Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer
4.1. Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation
4.2. Therapeutic Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lamba, N.; Wen, P.Y.; Aizer, A.A. Epidemiology of brain metastases and leptomeningeal disease. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelzer, K.J. Epidemiology and prognosis of brain metastases. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2013, 4, S192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Mesko, S.; Li, J.; Cagney, D.; Aizer, A.; Lin, N.U.; Nesbit, E.; Kruser, T.J.; Chan, J.; Braunstein, S.; et al. Survival in patients with brain metastases: Summary report on the updated diagnosis-specific graded prognostic assessment and definition of the eligibility quotient. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3773–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelbaum, M.A.; Brown, P.D.; Messersmith, H.; Brastianos, P.K.; Burri, S.; Cahill, D.; Dunn, I.F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gatson, N.T.N.; Gondi, V.; et al. Treatment for brain metastases: ASCO-SNO-ASTRO guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 492–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchell, R.A.; Tibbs, P.A.; Walsch, J.W.; Dempsey, R.J.; Maruyama, Y.; Kryscio, R.J.; Markesbery, W.R.; Macdonald, J.S.; Young, B. A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecht, C.J.; Haaxma-Reiche, H.; Noordijk, E.M.; Padberg, G.W.; Voormolen, J.H.; Hoekstra, F.H.; Tans, J.T.; Lambooij, N.; Metsaars, J.A.; Wattendorf, A.R.; et al. Treatment of single brain metastasis: Radiotherapy alone or combined with neurosurgery? Ann. Neurol. 1993, 33, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Ahmed, S.; McAleer, M.F.; Weinberg, J.S.; Li, J.; Brown, P.; Settle, S.; Prabhu, S.S.; Lang, F.F.; Levine, N.; et al. Post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery versus observation for completely resected brain metastases: A single-centre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2017, 18, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Ballman, K.V.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Whitton, A.C.; Greenspoon, J.; Parney, I.F.; Laack, N.N.I.; Ashman, J.B.; et al. Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC·3): A multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2017, 18, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanda, Z.Z.; Hong, W.; Nahavandi, S.; Haghighi, N.; Phillips, C.; Kok, D.L. Post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery following excision of brain metastases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 142, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilger, A.; Milanovic, D.; Lorenz, H.; Oehlke, O.; Urbach, H.; Schmucker, M.; Weyerbrock, A.; Nieder, C.; Grosu, A.L. Stereotactic fractionated radiotherapy of the resection cavity in patients with one to three brain metastases. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2016, 142, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Niyazi, M.; Andratschke, N.; Guckenberger, M.; Palmer, J.D.; Shih, H.A.; Lo, S.S.; Soltys, S.; Russo, I.; Brown, P.D.; et al. Current status and recent advances in resection cavity irradiation of brain metastases. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, H.; Shirato, H.; Tago, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Toyoda, T.; Hatano, K.; Kenjyo, M.; Oya, N.; Hirota, S.; Shioura, H.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2006, 295, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Gantery, M.M.; Abd El Baky, H.M.; El Hossieny, H.A.; Mahmoud, M.; Youssef, O. Management of brain metastases with stereotactic radiosurgery alone versus whole brain irradiation alone versus both. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Jaeckle, K.; Ballman, K.V.; Farace, E.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Barker, F.G., 2nd; Deming, R.; Burri, S.H.; et al. Effect of radiosurgery alone vs radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, M.N.; Xu, W.; Wong, R.K.; Lloyd, N.; Laperriere, N.; Sahgal, A.; Rakovitch, E.; Chow, E. Whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed multiple brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 1, CD003869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patchell, R.A.; Tibbs, P.A.; Regine, W.F.; Dempsey, R.J.; Mohiuddin, M.; Kryscio, R.J.; Markesbery, W.R.; Foon, K.A.; Young, B. Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: A randomized trial. JAMA 1998, 280, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, M.; Soffietti, R.; Abacioglu, U.; Villà, S.; Fauchon, F.; Baumert, B.G.; Fariselli, L.; Tzuk-Shina, T.; Kortmann, R.D.; Carrie, C.; et al. Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: Results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayama, T.; Sato, S.; Sakurada, K.; Mizusawa, J.; Nishikawa, R.; Narita, Y.; Sumi, M.; Miyakita, Y.; Kumabe, T.; Sonoda, Y.; et al. Effects of surgery with salvage sereotactic radiosurgery versus surgery with whole-brain radiation therapy in patients with one to four brain metastases (JCOG0504): A phase III, noninferiority, randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3282–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D.; Klamer, B.G.; Ballman, K.V.; Brown, P.D.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Whitton, A.C.; Greenspoon, J.; Parney, I.F.; et al. Association of long-term outcomes with stereotactic radiosurgery vs whole-brain radiotherapy for resected brain metastasis: A secondary analysis of the N107C/CEC.3 (Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology/Canadian Cancer Trials Group) randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1809–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTyre, E.R.; Soike, M.H.; Farris, M.; Ayala-Peacock, D.N.; Hepel, J.T.; Page, B.R.; Shen, C.; Kleinberg, L.; Contessa, J.N.; Corso, C.; et al. Multi-institutional validation of brain metastasis velocity, a recently defined predictor of outcomes following stereotactic radiosurgery. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 142, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.L.; Wefel, J.S.; Hess, K.R.; Allen, P.K.; Lang, F.F.; Kornguth, D.G.; Arbuckle, R.B.; Swint, J.M.; Shiu, A.S.; Maor, M.H.; et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2009, 10, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeAngelis, L.M.; Delattre, J.Y.; Posner, J.B. Radiation-induced dementia in patients cured of brain metastases. Neurology 1989, 39, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvenna, P.; Nankivell, M.; Barton, R.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Wilson, P.; McColl, E.; Moore, B.; Brisbane, I.; Ardron, D.; Holt, T.; et al. Dexamethasone and supportive care with or without whole brain radiotherapy in treating patients with non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases unsuitable for resection or stereotactic radio-therapy (QUARTZ): Results from a phase 3, non-inferiority, randomised trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popp, I.; Rau, S.; Hintz, M.; Schneider, J.; Bilger, A.; Fennell, J.T.; Heiland, D.H.; Rothe, T.; Egger, K.; Nieder, C.; et al. Hippocampus-avoidance whole-brain radiation therapy with a simultaneous integrated boost for multiple brain metastases. Cancer 2020, 126, 2694–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welzel, G.; Fleckenstein, K.; Schaefer, J.; Hermann, B.; Kraus-Tiefenbacher, U.; Mai, S.K.; Wenz, F. Memory function before and after whole brain radiotherapy in patients with and without brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 72, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliss, T.V.P.; Collingridge, G.L.; Morris, R.G.M.; Reymann, K.G. Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus: Discovery, mechanisms and function. Neuroforum 2018, 24, A103–A120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Jiménez, E.P.; Flor-García, M.; Terreros-Roncal, J.; Rábano, A.; Cafini, F.; Pallas-Bazarra, N.; Ávila, J.; Llorens-Martín, M. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.; Dhikav, V. Hippocampus in health and disease: An overview. Ann. Ind. Acad. Neurol. 2012, 15, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, T.M.; Karunamuni, R.; Kaifi, S.; Burkeen, J.; Connor, M.; Krishnan, A.P.; White, N.S.; Farid, N.; Bartsch, H.; Murzin, V.; et al. Cerebral cortex regions selectively vulnerable to radiation dose-dependent atrophy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 97, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monje, M.L.; Mizumatsu, S.; Fike, J.R.; Palmer, T.D. Irradiation induces neural precursor-cell dysfunction. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumatsu, S.; Monje, M.L.; Morhardt, D.R.; Rola, R.; Palmer, T.D.; Fike, J.R. Extreme sensitivity of adult neurogenesis to low doses of X-irradiation. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4021–4927. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Petersen, R.C.; Xu, Y.; O’Brien, P.C.; Smith, G.E.; Ivnik, R.J.; Boeve, B.F.; Tangalos, E.G.; Kokmen, E. Rates of hippocampal atrophy correlate with change in clinical status in aging and AD. Neurology 2000, 55, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawe, R.J.; Yu, L.; Arfanakis, K.; Schneider, J.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Boyle, P.A. Late-life cognitive decline is associated with hippocampal volume, above and beyond its associations with traditional neuropathologic indices. Alzheimer Dement. 2020, 16, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tringale, K.R.; Nguyen, T.T.; Karunamuni, R.; Seibert, T.; Huynh-Le, M.P.; Connor, M.; Moiseenko, V.; Gorman, M.K.; Marshall, A.; Tibbs, M.D.; et al. Quantitative imaging biomarkers of damage to critical memory regions are associated with post-radiation therapy memory performance in brain tumor patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; He, H.; Yang, Y.; Han, L.; Guo, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Qiu, Y.; Xie, C. Radiation-induced hippocampal atrophy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma early after radiotherapy: A longitudinal MR-based hippocampal subfield analysis. Brain Imaging Behav. 2019, 13, 1160–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagtegaal, S.H.J.; David, S.; Philippens, M.E.P.; Snijders, T.J.; Leemans, A.; Verhoeff, J.J.C. Dose-dependent volume loss in subcortical deep grey matter structures after cranial radiotherapy. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 26, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancelot, E.; Beal, M.F. Glutamate toxicity in chronic neurodegenerative disease. Prog. Brain Res. 1998, 116, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShane, R.; Westby, M.J.; Roberts, E.; Minakaran, N.; Schneider, L.; Farrimond, L.E.; Maayan, N.; Ware, J.; Debarros, J. Memantine for dementia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 3, CD003154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Pugh, S.; Laack, N.N.; Wefel, J.S.; Khuntia, D.; Meyers, C.; Choucair, A.; Fox, S.; Suh, J.H.; Roberge, D.; et al. Memantine for the prevention of cognitive dysfunction in patients receiving whole-brain radiotherapy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laack, N.N.; Pugh, S.L.; Brown, P.D.; Fox, S.; Wefel, J.S.; Meyers, C.; Choucair, A.; Khuntia, D.; Suh, J.H.; Roberge, D.; et al. The association of health-related quality of life and cognitive function in patients receiving memantine for the prevention of cognitive dysfunction during whole-brain radiotherapy. Neurooncol. Pract. 2019, 6, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, J.G.; Dinh, J.; Zhou, W.; Cham, H.; Mavratsas, V.C.; Paveškovic, M.; Mulherkar, S.; McGovern, S.L.; Tolias, K.F.; Grosshans, D.R. Memantine prevents acute radiation-induced toxicities at hippocampal excitatory synapses. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.; Leppert, I.R.; Roberge, D.; Boudam, K.; Brown, P.D.; Muanza, T.; Pike, G.B.; Chankowsky, J.; Mihalcioiu, C. A pilot study using dynamic contrast enhanced-MRI as a response biomarker of the radioprotective effect of memantine in patients receiving whole brain radiotherapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 50986–50996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondi, V.; Hermann, B.P.; Mehta, M.P.; Tomé, W.A. Hippocampal dosimetry predicts neurocognitive function impairment after fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for benign or low-grade adult brain tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, e487–e493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondi, V.; Pugh, S.L.; Tome, W.A.; Caine, C.; Corn, B.; Kanner, A.; Rowley, H.; Kundapur, V.; DeNittis, A.; Greenspoon, J.N.; et al. Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases (RTOG 0933): A phase II multi-institutional trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3810–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Gondi, V.; Pugh, S.; Tome, W.A.; Wefel, J.S.; Armstrong, T.S.; Bovi, J.A.; Robinson, C.; Konski, A.; Khuntia, D.; et al. Hippocampal avoidance during whole-brain radiotherapy plus memantine for patients with brain metastases: Phase III trial NRG Oncology CC001. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, V.; Deshmukh, S.; Brown, P.D.; Wefel, J.S.; Armstrong, T.S.; Tome, W.A.; Gilbert, M.R.; Konski, A.; Robinson, C.G.; Bovi, J.A.; et al. Sustained preservation of cognition and prevention of patient-reported symptoms with hippocampal avoidance during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases: Final results of NRG Oncology CC001. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, I.; Rau, A.; Kellner, E.; Reisert, M.; Fennell, J.T.; Rothe, T.; Nieder, C.; Urbach, H.; Egger, K.; Grosu, A.L.; et al. Hippocampus-avoidance whole-brain radiation therapy is efficient in the long-term preservation of hippocampal volume. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 714709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobis, L.; Manohar, S.G.; Smith, S.M.; Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Jenkinson, M.; Mackay, C.E.; Husain, M. Hippocampal volume across age: Nomograms derived from over 19,700 people in UK Biobank. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 23, 101904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Xu, H.; He, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Song, H.; Jiang, H. Distribution of metastasis in the brain in relation to the hippocampus: A retrospective single-center analysis of 565 metastases in 116 patients. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regine, W.F.; Scott, C.; Murray, K.; Curran, W. Neurocognitive outcome in brain metastases patients treated with accelerated-fractionation vs. accelerated-hyperfractionated radiotherapy: An analysis from Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Study 91-04. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 51, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, H.; Tago, M.; Kato, N.; Toyoda, T.; Kenjyo, M.; Hirota, S.; Shioura, H.; Inomata, T.; Kunieda, E.; Hayakawa, K.; et al. Neurocognitive function of patients with brain metastasis who received either whole brain radiotherapy plus stereotactic radiosurgery or radiosurgery alone. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Bentzen, S.M.; Renschler, M.; Mehta, M.P. Regression after whole-brain radiation therapy for brain metastases correlates with survival and improved neurocognitive function. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, C.A.; Smith, J.A.; Bezjak, A.; Mehta, M.P.; Liebmann, J.; Illidge, T.; Kunkler, I.; Caudrelier, J.M.; Eisenberg, P.D.; Meerwaldt, J.; et al. Neurocognitive function and progression in patients with brain metastases treated with whole-brain radiation and motexafin gadolinium: Results of a randomized phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, D.W.; Scott, C.B.; Sperduto, P.W.; Flanders, A.E.; Gaspar, L.E.; Schell, M.C.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Demas, W.; Ryu, J.; Bahary, J.P.; et al. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: Phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibamoto, Y.; Baba, F.; Oda, K.; Hayashi, S.; Kokubo, M.; Ishihara, S.; Itoh, Y.; Ogino, H.; Koizumi, M. Incidence of brain atrophy and decline in mini-mental state examination score after whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases: A prospective study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 72, 1168–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corn, B.W.; Yousem, D.M.; Scott, C.B.; Rotman, M.; Asbell, S.O.; Nelson, D.F.; Martin, L.; Curran, W.J., Jr. White matter changes are correlated significantly with radiation dose. Observations from a randomized dose-escalation trial for malignant glioma (Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 83-02). Cancer 1994, 74, 2828–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokic, V.; Wiedenmann, N.; Fels, F.; Schmucker, M.; Nieder, C.; Grosu, A.L. Whole brain irradiation with hippocampal sparing and dose escalation on multiple brain metastases: A planning study on treatment concepts. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 85, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosu, A.L.; Frings, L.; Bentsalo, I.; Oehlke, O.; Brenner, F.; Bilger, A.; Fennell, J.T.; Rothe, T.; Schneider-Fuchs, S.; Graf, E.; et al. Whole-brain irradiation with hippocampal sparing and dose escalation on metastases: Neurocognitive testing and biological imaging (HIPPORAD)—A phase II prospective randomized multicenter trial (NOA-14, ARO 2015-3, DKTK-ROG). BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, K.J.; Hales, R.K.; Anderson-Keightly, H.; Zhou, X.C.; Kummerlowe, M.; Sair, H.I.; Duhon, M.; Kleinberg, L.; Rosner, G.L.; Vannorsdall, T. Prospective study of hippocampal-sparing prophylactic cranial irradiation in limited-stage small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 98, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez de Dios, N.; Couñago, F.; Murcia-Mejía, M.; Rico-Oses, M.; Calvo-Crespo, P.; Samper, P.; Vallejo, C.; Luna, J.; Trueba, I.; Sotoca, A.; et al. Randomized phase III trial of prophylactic cranial irradiation with or without hippocampal avoidance for small-cell lung cancer (PREMER): A GICOR-GOECP-SEOR study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3118–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belderbos, J.S.A.; De Ruysscher, D.K.M.; De Jaeger, K.; Koppe, F.; Lambrecht, M.L.F.; Lievens, Y.N.; Dieleman, E.M.T.; Jaspers, J.P.M.; Van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Ubbels, F.; et al. Phase 3 randomized trial of prophylactic cranial irradiation with or without hippocampus avoidance in SCLC (NCT01780675). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aupérin, A.; Arriagada, R.; Pignon, J.P.; Le Péchoux, C.; Gregor, A.; Stephens, R.J.; Kristjansen, P.E.; Johnson, B.E.; Ueoka, H.; Wagner, H.; et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer in complete remission. Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Overview Collaborative Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, A.H.; Bae, K.; Komaki, R.; Meyers, C.; Movsas, B.; Le Pechoux, C.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Videtic, G.M.; Garces, Y.I.; Choy, H. Primary analysis of a phase II randomized trial Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 0212: Impact of different total doses and schedules of prophylactic cranial irradiation on chronic neurotoxicity and quality of life for patients with limited-disease small-cell lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotman, B.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Kramer, G.; Rankin, E.; Snee, M.; Hatton, M.; Postmus, P.; Collette, L.; Musat, E.; Senan, S.; et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation in extensive small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Seto, T.; Harada, H.; Nokihara, H.; Saka, H.; Nishio, M.; Kaneda, H.; Takayama, K.; Ishimoto, O.; et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation versus observation in patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosshans, D.R.; Meyers, C.A.; Allen, P.K.; Davenport, S.D.; Komaki, R. Neurocognitive function in patients with small cell lung cancer: Effect of prophylactic cranial irradiation. Cancer 2008, 112, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Bae, K.; Gore, E.M.; Movsas, B.; Wong, S.J.; Meyers, C.A.; Bonner, J.A.; Schild, S.E.; Gaspar, L.E.; Bogart, J.A.; et al. Phase III trial of prophylactic cranial irradiation compared with observation in patients with locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Neurocognitive and quality-of-life analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusthoven, C.G.; Yamamoto, M.; Bernhardt, D.; Smith, D.E.; Gao, D.; Serizawa, T.; Yomo, S.; Aiyama, H.; Higuchi, Y.; Shuto, T.; et al. Evaluation of first-line radiosurgery vs whole-brain radiotherapy for small cell lung cancer brain metastases: The FIRE-SCLC cohort study. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
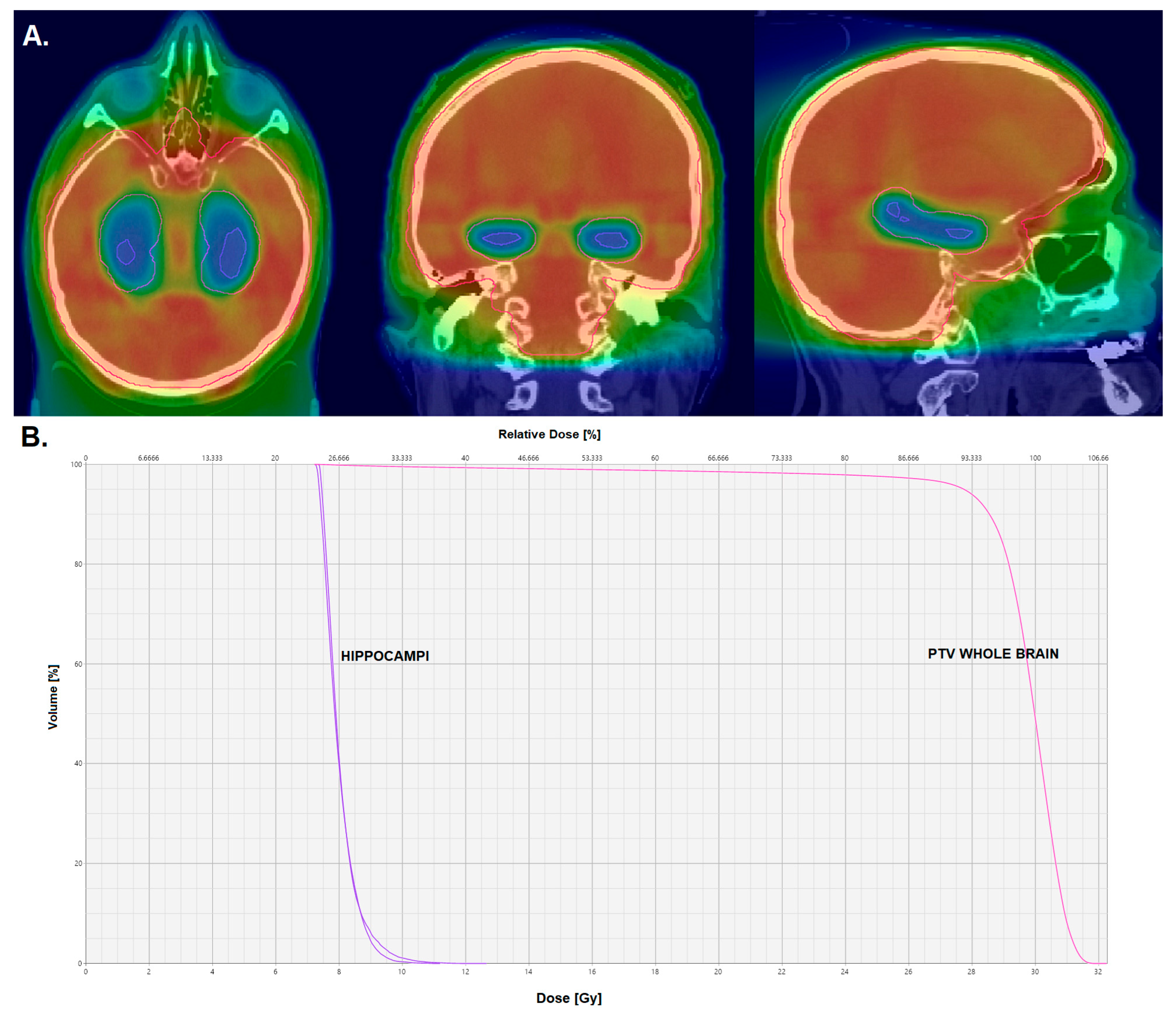
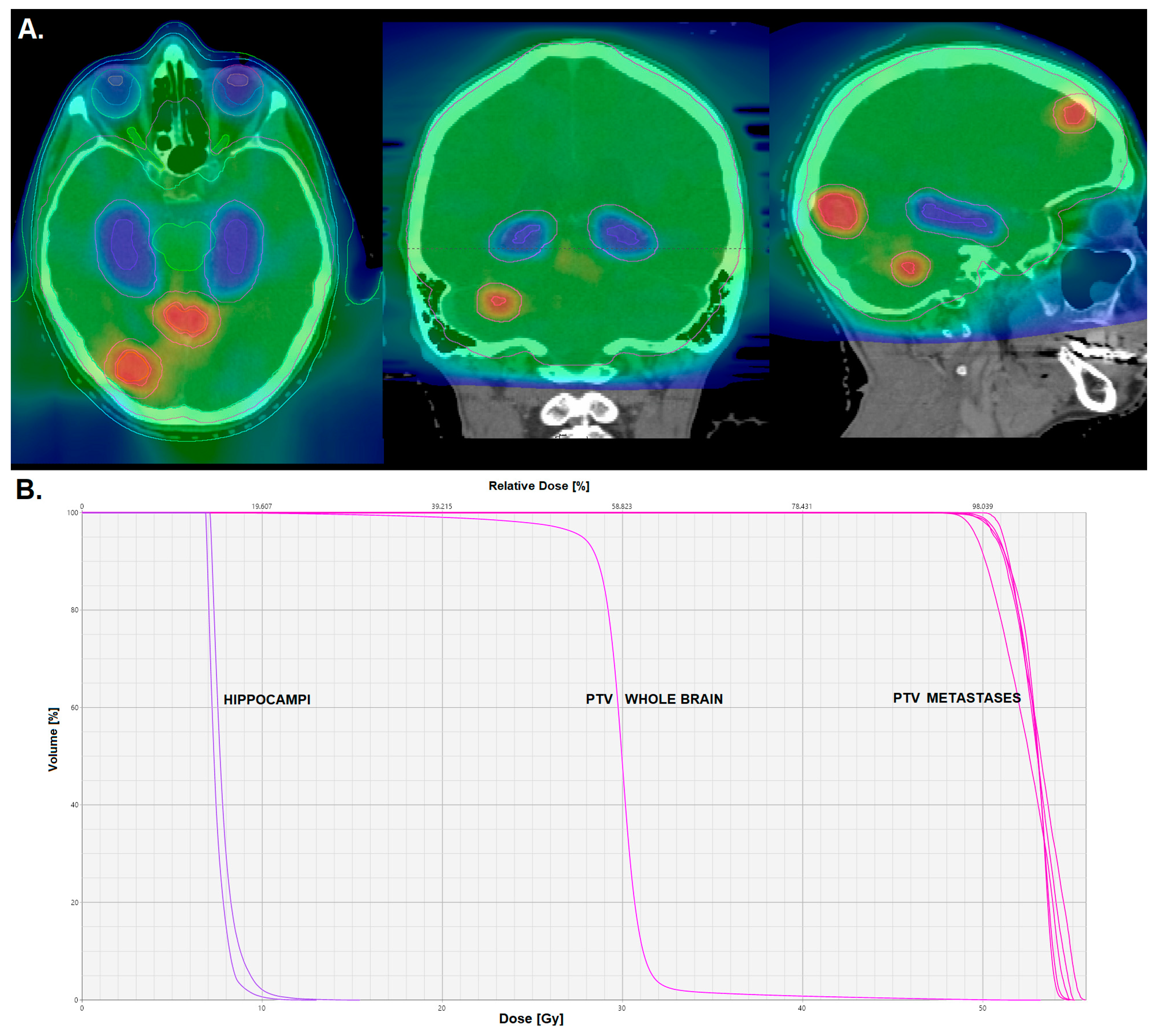
| Trial | Number of Brain Metastases | Study Arms |
|---|---|---|
| WHOBI-STER (NCT04891471) | ≥5 | SRS vs. WBRT |
| Sunnybrook (NCT03775330) | 5–30 | SRS vs. SRS + WBRT |
| MDACC (NCT01592968) | ≥5 | SRS vs. WBRT |
| HIPPORAD-RS (DRKS00025906) | 4–10 | SRS vs. HA-WBRT +/− SIB |
| HipSter (NCT04277403) | 4–15 | SRS vs. HA-WBRT + SIB |
| CCTG CE.7 (NCT03550391) | ≥5 | SRS vs. HA-WBRT |
| NRG Oncology (NCT04804644) | ≤10 (SCLC) | SRS vs. HA-WBRT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popp, I.; Hartong, N.E.; Nieder, C.; Grosu, A.-L. PRO: Do We Still Need Whole-Brain Irradiation for Brain Metastases? Cancers 2023, 15, 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123193
Popp I, Hartong NE, Nieder C, Grosu A-L. PRO: Do We Still Need Whole-Brain Irradiation for Brain Metastases? Cancers. 2023; 15(12):3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123193
Chicago/Turabian StylePopp, Ilinca, Nanna E. Hartong, Carsten Nieder, and Anca-L. Grosu. 2023. "PRO: Do We Still Need Whole-Brain Irradiation for Brain Metastases?" Cancers 15, no. 12: 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123193
APA StylePopp, I., Hartong, N. E., Nieder, C., & Grosu, A.-L. (2023). PRO: Do We Still Need Whole-Brain Irradiation for Brain Metastases? Cancers, 15(12), 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123193




