Extracellular-Vesicle-Based Cancer Panels Diagnose Glioblastomas with High Sensitivity and Specificity
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Isolation and Characterization of EVs
2.2.1. EV and RNA Isolation
2.2.2. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.3. Western Blotting
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. cDNA Synthesis
2.6. DNA Preparation
2.7. Pyrosequencing
2.8. IDH1 and IDH2
2.9. BRAF and H3F3A
2.10. TERT
2.11. MGMT
2.12. RNA Extraction from Serum EVs
2.13. Total RNA Sequencing
2.14. Analysis of RNA-seq Data
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Features of the Study Cohort and Transcriptome Analyses of EVs Derived from Glioblastoma Patient Serum
3.2. RNA Sequencing of Circulating EVs
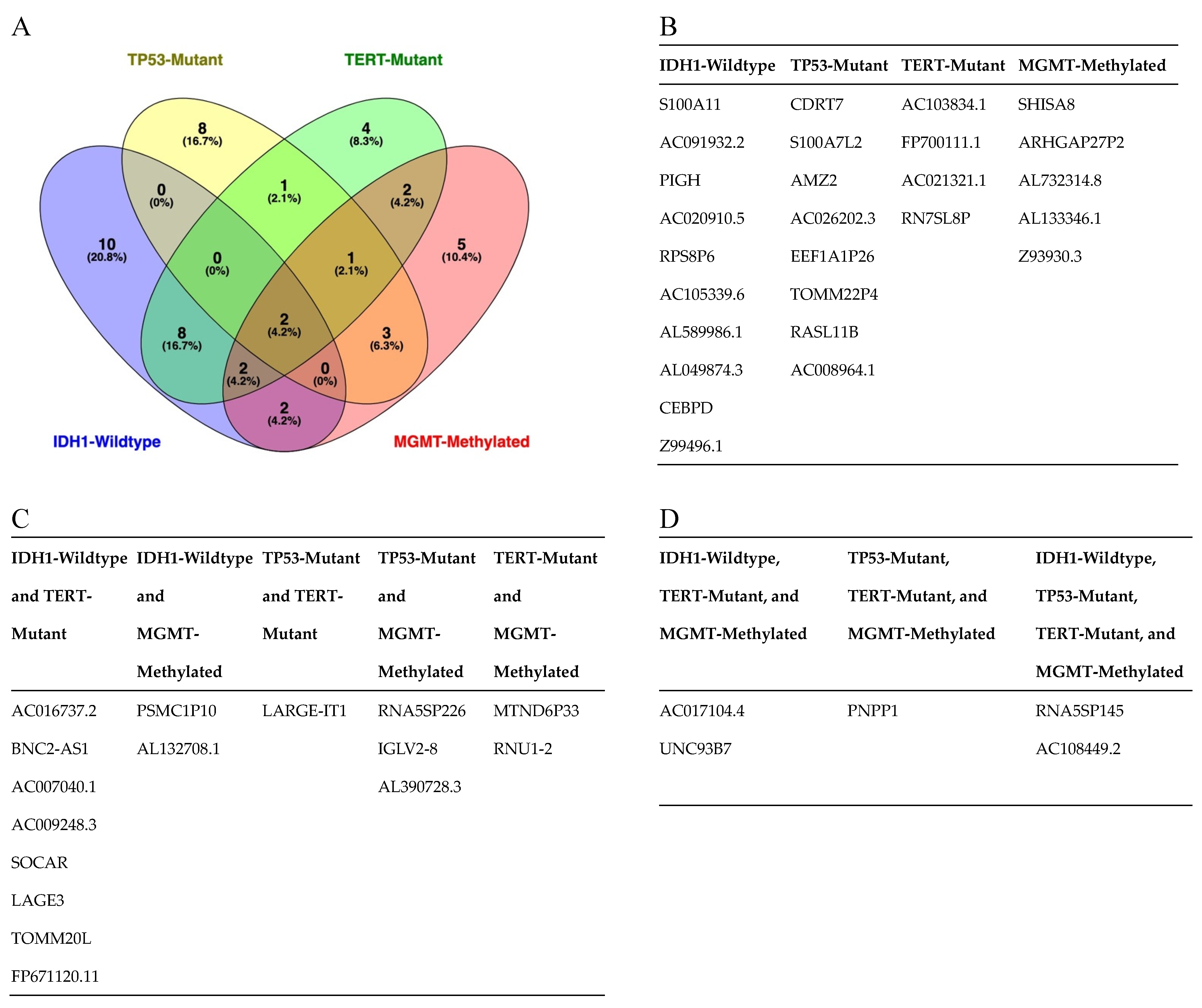
3.3. Serum-Derived EVs from Patients with IDH1-wt Glioblastoma Have Distinct Transcriptomic Features
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential Significance
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Patil, N.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2013–2017. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brat, D.J.; Aldape, K.; Colman, H.; Holland, E.C.; Louis, D.N.; Jenkins, R.B.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; Stupp, R.; et al. cIMPACT-NOW update 3: Recommended diagnostic criteria for “Diffuse astrocytic glioma, IDH-wildtype, with molecular features of glioblastoma, WHO grade IV”. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louis, D.N.; Wesseling, P.; Aldape, K.; Brat, D.J.; Capper, D.; Cree, I.A.; Eberhart, C.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Fouladi, M.; Fuller, G.N.; et al. cIMPACT-NOW update 6: New entity and diagnostic principle recommendations of the cIMPACT-Utrecht meeting on future CNS tumor classification and grading. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Parsons, D.W.; Jin, G.; McLendon, R.; Rasheed, B.A.; Yuan, W.; Kos, I.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Jones, S.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckel-Passow, J.E.; Lachance, D.H.; Molinaro, A.M.; Walsh, K.M.; Decker, P.A.; Sicotte, H.; Pekmezci, M.; Rice, T.; Kosel, M.L.; Smirnov, I.V.; et al. Glioma Groups Based on 1p/19q, IDH, and TERT Promoter Mutations in Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2499–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P. Genetic pathways to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hygino da Cruz, L.C.; Rodriguez, I.; Domingues, R.C.; Gasparetto, E.L.; Sorensen, A.G. Pseudoprogression and pseudoresponse: Imaging challenges in the assessment of posttreatment glioma. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strauss, S.B.; Meng, A.; Ebani, E.J.; Chiang, G.C. Imaging Glioblastoma Posttreatment: Progression, Pseudoprogression, Pseudoresponse, Radiation Necrosis. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 57, 1199–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Schwarzenbach, H.; Pantel, K. Circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. Annu. Rev. Med. 2012, 63, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucero, R.; Zappulli, V.; Sammarco, A.; Murillo, O.D.; Cheah, P.S.; Srinivasan, S.; Tai, E.; Ting, D.T.; Wei, Z.; Roth, M.E.; et al. Glioma-Derived miRNA-Containing Extracellular Vesicles Induce Angiogenesis by Reprogramming Brain Endothelial Cells. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 2065–2074.e2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Thery, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skog, J.; Wurdinger, T.; van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Curry, W.T.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesenberry, P.J.; Aliotta, J.; Camussi, G.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Wen, S.; Goldberg, L.; Zhang, H.G.; Tetta, C.; Franklin, J.; Coffey, R.J.; et al. Potential functional applications of extracellular vesicles: A report by the NIH Common Fund Extracellular RNA Communication Consortium. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yekula, A.; Minciacchi, V.R.; Morello, M.; Shao, H.; Park, Y.; Zhang, X.; Muralidharan, K.; Freeman, M.R.; Weissleder, R.; Lee, H.; et al. Large and small extracellular vesicles released by glioma cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1689784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.W.; Balaj, L.; Liau, L.M.; Samuels, M.L.; Kotsopoulos, S.K.; Maguire, C.A.; LoGuidice, L.; Soto, H.; Garrett, M.; Zhu, L.D.; et al. BEAMing and Droplet Digital PCR Analysis of Mutant IDH1 mRNA in Glioma Patient Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid Extracellular Vesicles. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, M.; Lamszus, K. Circulating biomarkers for gliomas. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, R.; Simon, T.; Vintu, M.; Solkin, B.; Koch, B.; Stewart, N.; Benstead-Hume, G.; Pearl, F.M.G.; Critchley, G.; Stebbing, J.; et al. Cell-derived extracellular vesicles can be used as a biomarker reservoir for glioblastoma tumor subtyping. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimkhani, S.; Vafaee, F.; Hallal, S.; Wei, H.; Lee, M.Y.T.; Young, P.E.; Satgunaseelan, L.; Beadnall, H.; Barnett, M.H.; Shivalingam, B.; et al. Deep sequencing of circulating exosomal microRNA allows non-invasive glioblastoma diagnosis. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osti, D.; Del Bene, M.; Rappa, G.; Santos, M.; Matafora, V.; Richichi, C.; Faletti, S.; Beznoussenko, G.V.; Mironov, A.; Bachi, A.; et al. Clinical Significance of Extracellular Vesicles in Plasma from Glioblastoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Romero, N.; Carrión-Navarro, J.; Esteban-Rubio, S.; Lázaro-Ibáñez, E.; Peris-Celda, M.; Alonso, M.M.; Guzmán-De-Villoria, J.; Fernández-Carballal, C.; de Mendivil, A.O.; García-Duque, S.; et al. DNA sequences within glioma-derived extracellular vesicles can cross the intact blood-brain barrier and be detected in peripheral blood of patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akers, J.C.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Kim, R.; Skog, J.; Nakano, I.; Pingle, S.; Kalinina, J.; Hua, W.; Kesari, S.; Mao, Y.; et al. MiR-21 in the extracellular vesicles (EVs) of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): A platform for glioblastoma biomarker development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manda, S.V.; Kataria, Y.; Tatireddy, B.R.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Ratnam, B.G.; Lath, R.; Ranjan, A.; Ray, A. Exosomes as a biomarker platform for detecting epidermal growth factor receptor-positive high-grade gliomas. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandran, V.I.; Welinder, C.; Mansson, A.S.; Offer, S.; Freyhult, E.; Pernemalm, M.; Lund, S.M.; Pedersen, S.; Lehtio, J.; Marko-Varga, G.; et al. Ultrasensitive Immunoprofiling of Plasma Extracellular Vesicles Identifies Syndecan-1 as a Potential Tool for Minimally Invasive Diagnosis of Glioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3115–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manterola, L.; Guruceaga, E.; Gallego Perez-Larraya, J.; Gonzalez-Huarriz, M.; Jauregui, P.; Tejada, S.; Diez-Valle, R.; Segura, V.; Sampron, N.; Barrena, C.; et al. A small noncoding RNA signature found in exosomes of GBM patient serum as a diagnostic tool. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vestad, B.; Llorente, A.; Neurauter, A.; Phuyal, S.; Kierulf, B.; Kierulf, P.; Skotland, T.; Sandvig, K.; Haug, K.B.F.; Øvstebø, R. Size and concentration analyses of extracellular vesicles by nanoparticle tracking analysis: A variation study. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1344087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ray, A. Liquid Biopsy in Gliomas—A Review. Neurol. India 2020, 68, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Siravegna, G.; Marsoni, S.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareen, H.; Garrett, C.; Lynch, D.; Powter, B.; Brungs, D.; Cooper, A.; Po, J.; Koh, E.S.; Vessey, J.Y.; McKechnie, S.; et al. The Role of Liquid Biopsies in Detecting Molecular Tumor Biomarkers in Brain Cancer Patients. Cancers 2020, 12, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, J.M.; Skog, J.; Akers, J.; Li, H.; Komotar, R.; Jensen, R.; Ringel, F.; Yang, I.; Kalkanis, S.; Thompson, R.; et al. Detection of wild-type EGFR amplification and EGFRvIII mutation in CSF-derived extracellular vesicles of glioblastoma patients. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maire, C.L.; Fuh, M.M.; Kaulich, K.; Fita, K.D.; Stevic, I.; Heiland, D.H.; Welsh, J.A.; Jones, J.C.; Görgens, A.; Ricklefs, T.; et al. Genome-wide methylation profiling of glioblastoma cell-derived extracellular vesicle DNA allows tumor classification. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.L.; Chung, J.; Lee, K.; Balaj, L.; Min, C.; Carter, B.S.; Hochberg, F.H.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lee, H.; Weissleder, R. Chip-based analysis of exosomal mRNA mediating drug resistance in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, A.L.; Wei, Z.Y.; Yan, W.; Yin, J.X.; Huang, X.X.; Zhou, X.; Li, R.; Shen, F.; Wu, W.N.; Wang, X.F.; et al. Exosomal transfer of miR-151a enhances chemosensitivity to temozolomide in drug-resistant glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2018, 436, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.; Alattar, A.A.; Akers, J.; Carter, B.S.; Heller, M.; Chen, C.C. A Pilot Proof-of-Principle Analysis Demonstrating Dielectrophoresis (DEP) as a Glioblastoma Biomarker Platform. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galanis, E.; Wen, P.Y.; de Groot, J.F.; Weller, M. Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Wild-type Glial Tumors, Including Glioblastoma. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 36, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.A.; Wood, M.D.; Tihan, T.; Bollen, A.W.; Gupta, N.; Phillips, J.J.; Perry, A. Diffuse Midline Gliomas with Histone H3-K27M Mutation: A Series of 47 Cases Assessing the Spectrum of Morphologic Variation and Associated Genetic Alterations. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, L.J.; Thornton, Z.A.; Saincher, S.S.; Yao, I.Y.; Dawson, S.; McGuinness, L.A.; Jones, H.E.; Jefferies, S.; Short, S.C.; Cheng, H.Y.; et al. Prevalence of BRAFV600 in glioma and use of BRAF Inhibitors in patients with BRAFV600 mutation-positive glioma: Systematic review. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baller, J.; Kono, T.; Herman, A.; Zhang, Y. CHURP: A Lightweight CLI Framework to Enable Novice Users to Analyze Sequencing Datasets in Parallel. In Proceedings of the Practice and Experience in Advanced Research Computing on Rise of the Machines (Learning) (PEARC ’19); Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 0.11.2, Released 6/6/14.
- Bolger, A.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. The R package Rsubread is easier, faster, cheaper and better for alignment and quantification of RNA sequencing reads. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bahin, M.; Noël, B.F.; Murigneux, V.; Bernard, C.; Bastianelli, L.; Le Hir, H.; Lebreton, A.; Genovesio, A. ALFA: Annotation landscape for aligned reads. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Version 4.0.4; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.Rproject.org/ (accessed on 14 February 2021).
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Controls | Male | Female | Total # | MGMT Status | Male | Female | Total # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 14 | 17 | 31 | Unmethylated | 22 | 15 | 37 |
| Age, years | 51.5 (27–86) | 47 (29–61) | Methylated | 24 | 18 | 42 | |
| Median (min.–max.) | NA | 6 | 6 | 12 | |||
| Glioblastoma | TERT promoter status C228T | ||||||
| Number of patients | 52 | 39 | 91 | Wild-type | 11 | 11 | 22 |
| Age, years | 55.02 (24–84) | 54.44 (24–81) | Mutant | 35 | 22 | 57 | |
| Median (min.–max.) | NA | 6 | 6 | 12 | |||
| IDH status (R132H) | ATRX status | ||||||
| Wild-type | 48 | 37 | 85 | Wild-type | 18 | 20 | 38 |
| Mutant | 4 | 2 | 6 | Mutant | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| NA | NA | ||||||
| IDH2 status (R172H) | BRAF status (600) | ||||||
| Wild-type | 52 | 39 | 79 | Wild-type | 46 | 33 | 79 |
| Mutant | 0 | 0 | 0 | Mutant | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TP53 status | H3F3A status (27/34) | ||||||
| Wild-type | 31 | 24 | 55 | Wild-type | 46 | 33 | 79 |
| Mutant | 21 | 15 | 36 | Mutant | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NA | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA | 6 | 6 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mut, M.; Adiguzel, Z.; Cakir-Aktas, C.; Hanalioğlu, Ş.; Gungor-Topcu, G.; Kiyga, E.; Isikay, I.; Sarac, A.; Soylemezoglu, F.; Strobel, T.; et al. Extracellular-Vesicle-Based Cancer Panels Diagnose Glioblastomas with High Sensitivity and Specificity. Cancers 2023, 15, 3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153782
Mut M, Adiguzel Z, Cakir-Aktas C, Hanalioğlu Ş, Gungor-Topcu G, Kiyga E, Isikay I, Sarac A, Soylemezoglu F, Strobel T, et al. Extracellular-Vesicle-Based Cancer Panels Diagnose Glioblastomas with High Sensitivity and Specificity. Cancers. 2023; 15(15):3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153782
Chicago/Turabian StyleMut, Melike, Zelal Adiguzel, Canan Cakir-Aktas, Şahin Hanalioğlu, Gamze Gungor-Topcu, Ezgi Kiyga, Ilkay Isikay, Aydan Sarac, Figen Soylemezoglu, Thomas Strobel, and et al. 2023. "Extracellular-Vesicle-Based Cancer Panels Diagnose Glioblastomas with High Sensitivity and Specificity" Cancers 15, no. 15: 3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153782
APA StyleMut, M., Adiguzel, Z., Cakir-Aktas, C., Hanalioğlu, Ş., Gungor-Topcu, G., Kiyga, E., Isikay, I., Sarac, A., Soylemezoglu, F., Strobel, T., Ampudia-Mesias, E., Cameron, C., Aslan, T., Tekirdas, E., Hayran, M., Oguz, K. K., Henzler, C., Saydam, N., & Saydam, O. (2023). Extracellular-Vesicle-Based Cancer Panels Diagnose Glioblastomas with High Sensitivity and Specificity. Cancers, 15(15), 3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153782






