Micro RNAs as a Diagnostic Marker between Glioma and Primary CNS Lymphoma: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
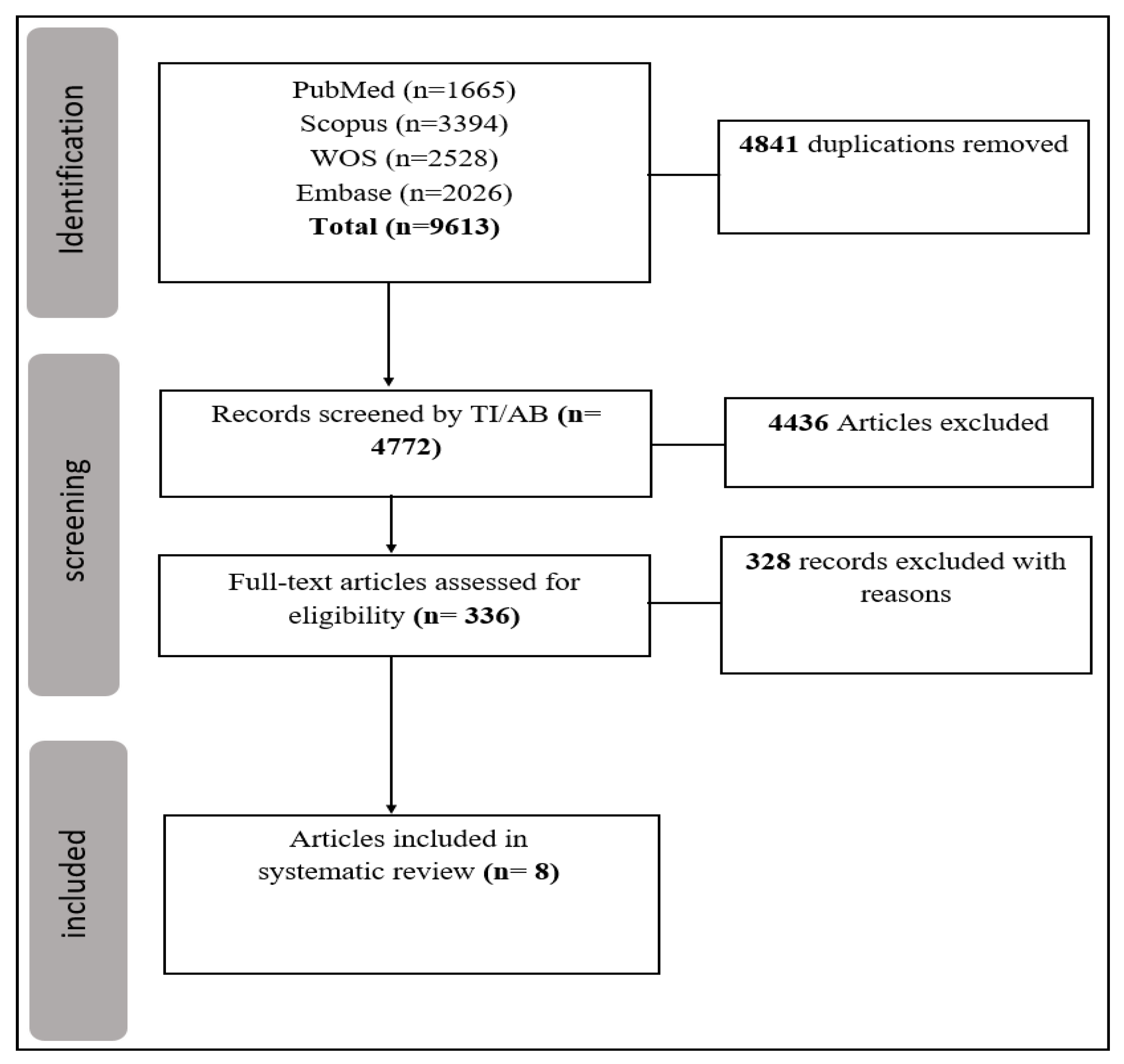
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction
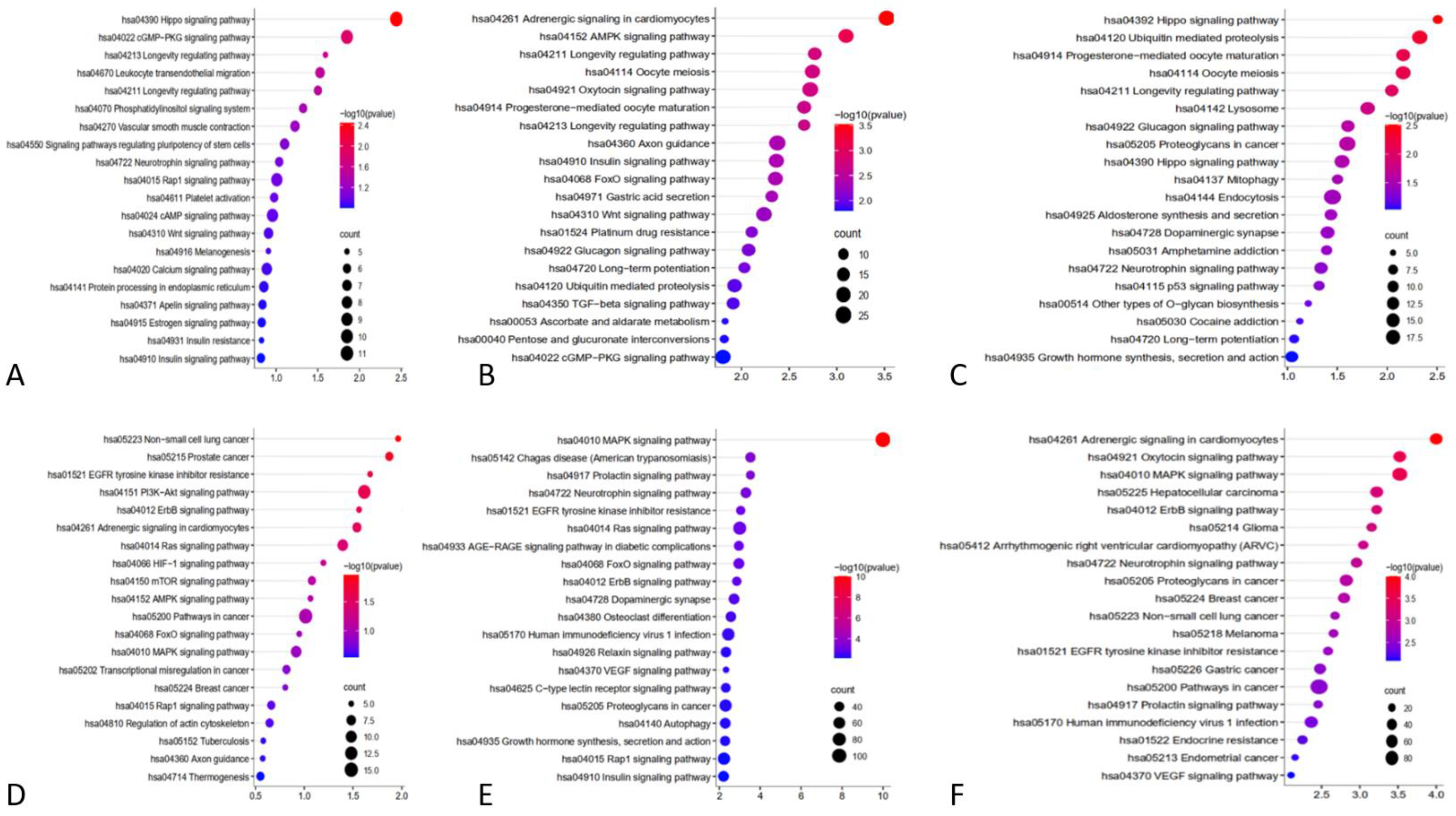
2.3. Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
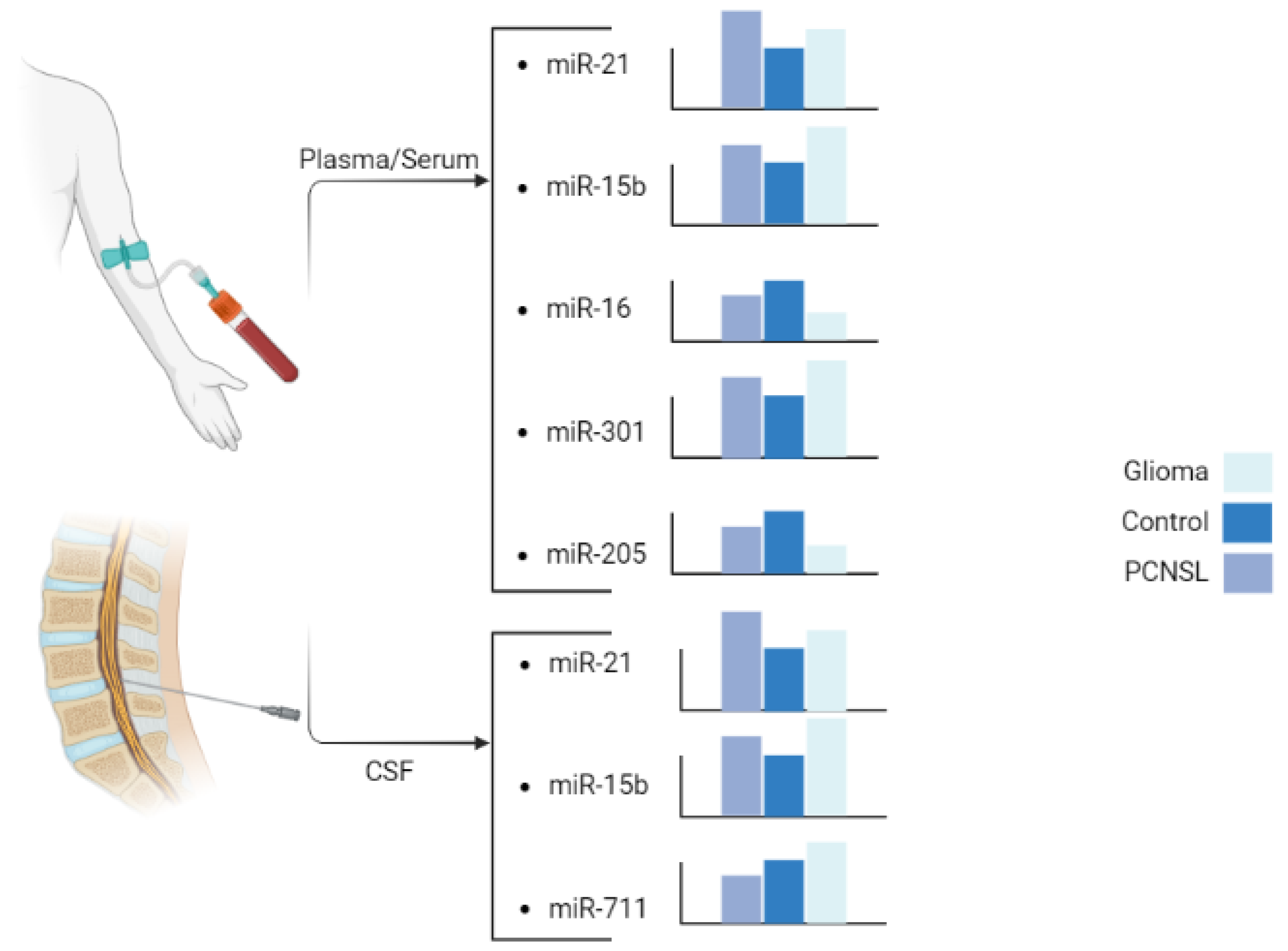
3.1. Serum
3.2. CSF
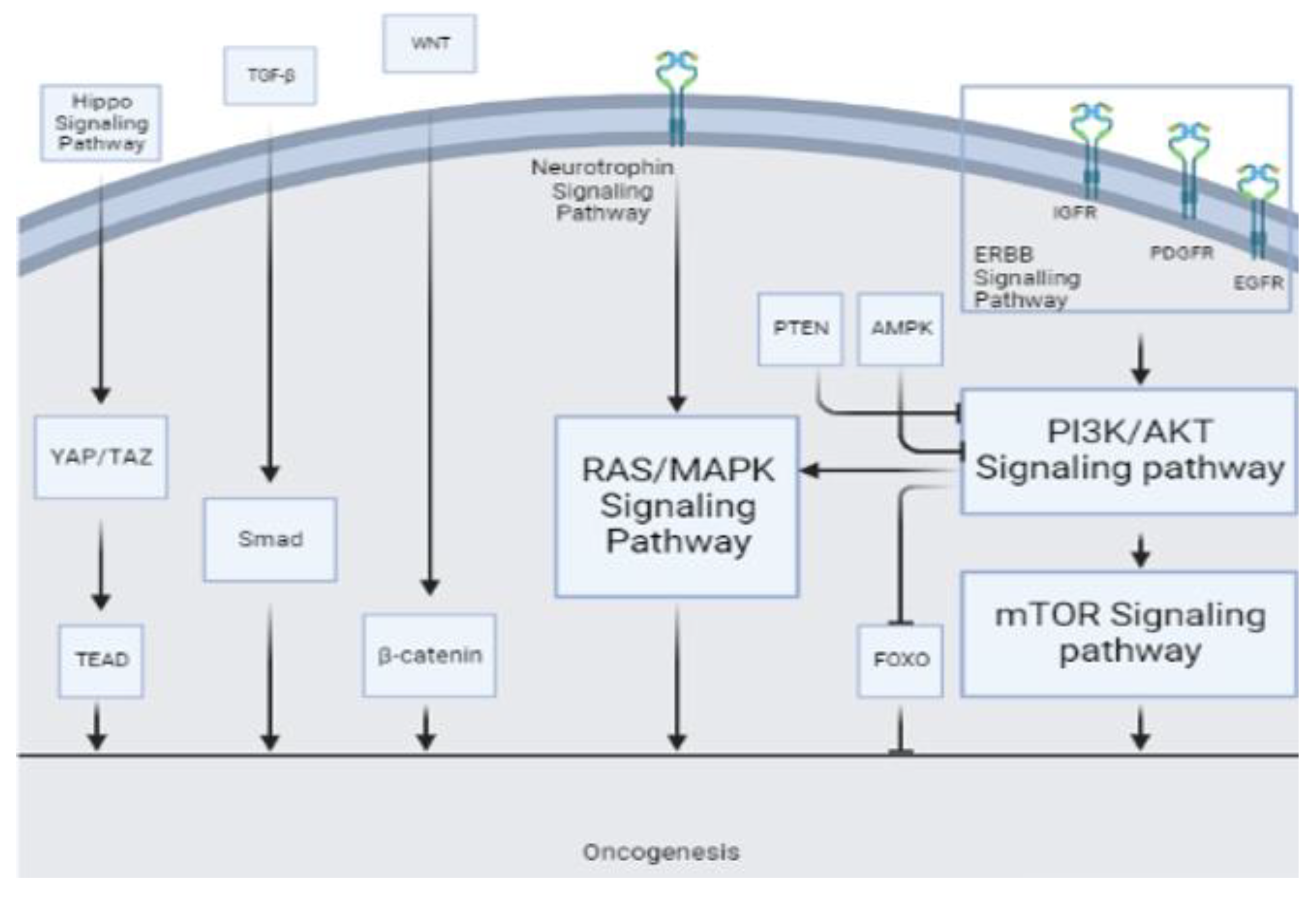
4. Discussion
4.1. miR-21
4.2. miR-15b
4.3. miR-16
4.4. miR-301a
4.5. miR-711
4.6. miR-205
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Surawicz, T.S.; McCarthy, B.J.; Kupelian, V.; Jukich, P.J.; Bruner, J.M.; Davis, F.G. Descriptive epidemiology of primary brain and CNS tumors: Results from the Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States, 1990–1994. Neuro-Oncol. 1999, 1, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posti, J.P.; Bori, M.; Kauko, T.; Sankinen, M.; Nordberg, J.; Rahi, M.; Frantzén, J.; Vuorinen, V.; Sipilä, J.O. Presenting symptoms of glioma in adults. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2015, 131, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Bauchet, L.; Davis, F.G.; Deltour, I.; Fisher, J.L.; Langer, C.E.; Pekmezci, M.; Schwartzbaum, J.A.; Turner, M.C.; Walsh, K.M.; et al. The epidemiology of glioma in adults: A “state of the science” review. Neuro-Oncol. 2014, 16, 896–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.Z.; Kim, C.Y.; Lim, D.H. The Overview of Practical Guidelines for Gliomas by KSNO, NCCN, and EANO. Brain Tumor Res. Treat. 2022, 10, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löw, S.; Han, C.H.; Batchelor, T.T. Primary central nervous system lymphoma. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2018, 11, 1756286418793562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, J.; Kumar Gupta, P.; Awasthi, A.; Pandey, C.M.; Singh, A.; Patir, R.; Ahlawat, S.; Sadashiva, N.; Mahadevan, A.; Kumar Gupta, R. Multiparametric imaging-based differentiation of lymphoma and glioblastoma: Using T1-perfusion, diffusion, and susceptibility-weighted MRI. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, e986–e987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Bjørnerud, A.; Park, J.E.; Lee, B.E.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Permeability measurement using dynamic susceptibility contrast magnetic resonance imaging enhances differential diagnosis of primary central nervous system lymphoma from glioblastoma. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 5539–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolburg, H.; Noell, S.; Fallier-Becker, P.; Mack, A.F.; Wolburg-Buchholz, K. The disturbed blood-brain barrier in human glioblastoma. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraniskin, A.; Kuhnhenn, J.; Schlegel, U.; Schmiegel, W.; Hahn, S.; Schroers, R. MicroRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid as biomarker for disease course monitoring in primary central nervous system lymphoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2012, 109, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajdel, M.; Rymkiewicz, G.; Sromek, M.; Cieslikowska, M.; Swoboda, P.; Kulinczak, M.; Goryca, K.; Bystydzienski, Z.; Blachnio, K.; Ostrowska, B.; et al. Tumor and Cerebrospinal Fluid microRNAs in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas. Cancers 2019, 11, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Leva, G.; Croce, C.M. miRNA profiling of cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2013, 23, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salarinia, R.; Sahebkar, A.; Peyvandi, M.; Mirzaei, H.R.; Jaafari, M.R.; Riahi, M.M.; Ebrahimnejad, H.; Nahand, J.S.; Hadjati, J.; Asrami, M.O.; et al. Epi-Drugs and Epi-miRs: Moving Beyond Current Cancer Therapies. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2016, 16, 773–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Lin, S.; Hu, D.; Feng, Y.; Tan, Y.; Peng, Y. Interactions of miR-323/miR-326/miR-329 and miR-130a/miR-155/miR-210 as prognostic indicators for clinical outcome of glioblastoma patients. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareev, I.; Beylerli, O.; Liang, Y.; Xiang, H.; Liu, C.; Xu, X.; Yuan, C.; Ahmad, A.; Yang, G. The Role of MicroRNAs in Therapeutic Resistance of Malignant Primary Brain Tumors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 740303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wan, Y.; Pan, T.; Gu, X.; Qian, C.; Sun, G.; Sun, L.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, L. MicroRNA-21 inhibitor sensitizes human glioblastoma U251 stem cells to chemotherapeutic drug temozolomide. J. Mol. Neurosci. MN 2012, 47, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Bardelli, A. Liquid biopsies: Genotyping circulating tumor DNA. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilié, M.; Hofman, P. Pros: Can tissue biopsy be replaced by liquid biopsy? Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Sun, Y.; Tang, J. Serum miR-21 is a diagnostic and prognostic marker of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 35, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Hou, J. Role of miRNA-21 in the diagnosis and prediction of treatment efficacy of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 3475–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, P.P.; Zhou, X.H.; Qu, Z.Z. Identification of Serum miRNAs as Effective Diagnostic Biomarkers for Distinguishing Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma from Glioma. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 5052609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, F.; Qing, Q.; Pan, Q.; Hu, M.; Yu, H.; Yue, X. Serum exosomal miR-301a as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 41, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Lan, F.; Hu, M.; Pan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J. Downregulation of serum microRNA-205 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivo D’Urso, P.; Fernando D’Urso, O.; Damiano Gianfreda, C.; Mezzolla, V.; Storelli, C.; Marsigliante, S. miR-15b and miR-21 as Circulating Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Glioma. Curr. Genom. 2015, 16, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniskin, A.; Kuhnhenn, J.; Schlegel, U.; Maghnouj, A.; Zöllner, H.; Schmiegel, W.; Hahn, S.; Schroers, R. Identification of microRNAs in the cerebrospinal fluid as biomarker for the diagnosis of glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drusco, A.; Bottoni, A.; Laganà, A.; Acunzo, M.; Fassan, M.; Cascione, L.; Antenucci, A.; Kumchala, P.; Vicentini, C.; Gardiman, M.P.; et al. A differentially expressed set of microRNAs in cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF) can diagnose CNS malignancies. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20829–20839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniskin, A.; Kuhnhenn, J.; Schlegel, U.; Chan, A.; Deckert, M.; Gold, R.; Maghnouj, A.; Zöllner, H.; Reinacher-Schick, A.; Schmiegel, W.; et al. Identification of microRNAs in the cerebrospinal fluid as marker for primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system. Blood 2011, 117, 3140–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, P.P.; Nolde, M.; Slack, F.J. OncomiR addiction in an in vivo model of microRNA-21-induced pre-B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2010, 467, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Wan, Q.; Li, L.; Jin, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G. MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Diagnosing Cancers of Central Nervous System: A Meta-analysis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, A.; Aguennouz, M.; La Torre, D.; Tomasello, C.; Cardali, S.; Angileri, F.F.; Maio, F.; Cama, A.; Germanò, A.; Vita, G.; et al. miR-21 and 221 upregulation and miR-181b downregulation in human grade II-IV astrocytic tumors. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2009, 93, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.A.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Kosik, K.S. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6029–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Chao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, X.; Gong, Y.; Qiang, B.; Yuan, J.; Sun, M.; Peng, X. MicroRNA-21 down-regulates the expression of tumor suppressor PDCD4 in human glioblastoma cell T98G. Cancer Lett. 2008, 272, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, K.C.; Wu, W.; Subramaniam, S.; Shyy, J.Y.; Chiu, J.J.; Li, J.Y.; Chien, S. MicroRNA-21 targets peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-alpha in an autoregulatory loop to modulate flow-induced endothelial inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10355–10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Ren, Y.; Moore, L.; Mei, M.; You, Y.; Xu, P.; Wang, B.; Wang, G.; Jia, Z.; Pu, P.; et al. Downregulation of miR-21 inhibits EGFR pathway and suppresses the growth of human glioblastoma cells independent of PTEN status. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Sun, M.; Zou, G.M.; Chen, J. MicroRNA and cancer: Current status and prospective. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannakopoulos, T.; Shapiro, A.; Kosik, K.S. MicroRNA-21 targets a network of key tumor-suppressive pathways in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8164–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Cai, X.; He, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, B. Microarray-based analysis of gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs in glioma. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Wang, P.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhang, C.G.; Jiang, T.; Li, W.B.; Ding, W.; et al. Exosomal levels of miRNA-21 from cerebrospinal fluids associated with poor prognosis and tumor recurrence of glioma patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 26971–26981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.E.; Suh, H.W.; Bahal, R.; Josowitz, A.; Zhang, J.; Song, E.; Cui, J.; Noorbakhsh, S.; Jackson, C.; Bu, T.; et al. Nanoparticle-mediated intratumoral inhibition of miR-21 for improved survival in glioblastoma. Biomaterials 2019, 201, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abels, E.R.; Maas, S.L.N.; Nieland, L.; Wei, Z.; Cheah, P.S.; Tai, E.; Kolsteeg, C.J.; Dusoswa, S.A.; Ting, D.T.; Hickman, S.; et al. Glioblastoma-Associated Microglia Reprogramming Is Mediated by Functional Transfer of Extracellular miR-21. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 3105–3119.e3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, A.B.; Holbeck, S.L.; Colburn, N.H.; Israel, M.A. Downregulation of Pdcd4 by mir-21 facilitates glioblastoma proliferation in vivo. Neuro Oncol. 2011, 13, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faragalla, H.; Youssef, Y.M.; Scorilas, A.; Khalil, B.; White, N.M.; Mejia-Guerrero, S.; Khella, H.; Jewett, M.A.; Evans, A.; Lichner, Z.; et al. The clinical utility of miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for renal cell carcinoma. J. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 14, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Song, L.J.; Han, S.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Li, M. MicroRNA-21 promotes glioma cell proliferation and inhibits senescence and apoptosis by targeting SPRY1 via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2018, 24, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yue, X.; Zhou, X.; Lan, F.M.; You, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, K.L.; Zhang, C.Z.; Cheng, J.Q.; Yu, S.Z.; et al. MicroRNA-21 expression is regulated by β-catenin/STAT3 pathway and promotes glioma cell invasion by direct targeting RECK. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2012, 18, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriely, G.; Wurdinger, T.; Kesari, S.; Esau, C.C.; Burchard, J.; Linsley, P.S.; Krichevsky, A.M. MicroRNA 21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase regulators. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 5369–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; He, C.; Hu, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; He, J.; Yu, H. MicroRNA-21 targets LRRFIP1 and contributes to VM-26 resistance in glioblastoma multiforme. Brain Res. 2009, 1286, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.G.; Grommes, C. Molecular profiling of primary central nervous system lymphomas—Predictive and prognostic value? Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2019, 32, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Gao, H.; Kadoch, C.; Lu, M.; Chen, L.; Anjum, R.; Drew, L.; Degorce, S.; Dillman, K.; Mayo, M.; et al. Targeting NF-KB Activation in Novel Intracranial Models of CNS Lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Chun, K.R.; Woo, Y.M.; Park, S.J.; Jeong, J.A.; Jo, S.H.; Kim, T.H.; Min, H.S.; Chae, J.S.; et al. Downregulation of Spry2 by miR-21 triggers malignancy in human gliomas. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2433–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Pan, Q.; Yu, H.; Yue, X. Sulforaphane enhances temozolomide-induced apoptosis because of down-regulation of miR-21 via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in glioblastoma. J. Neurochem. 2015, 134, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhang, J.X.; Han, L.; You, Y.P.; Jiang, T.; Pu, P.Y.; Kang, C.S. MicroRNA roles in beta-catenin pathway. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenquelli, M.; Tonon, G. WNT Signaling in Hematological Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 615190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nager, M.; Bhardwaj, D.; Cantí, C.; Medina, L.; Nogués, P.; Herreros, J. β-Catenin Signalling in Glioblastoma Multiforme and Glioma-Initiating Cells. Chemother. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 192362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farioli-Vecchioli, S.; Tanori, M.; Micheli, L.; Mancuso, M.; Leonardi, L.; Saran, A.; Ciotti, M.T.; Ferretti, E.; Gulino, A.; Pazzaglia, S.; et al. Inhibition of medulloblastoma tumorigenesis by the antiproliferative and pro-differentiative gene PC3. Faseb J. 2007, 21, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyan, P.; Zinn, P.O.; Marisetty, A.L.; Liu, B.; Kamal, M.M.; Singh, S.K.; Bady, P.; Lu, L.; Wani, K.M.; Veo, B.L.; et al. Mir-21-Sox2 Axis Delineates Glioblastoma Subtypes with Prognostic Impact. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 15097–15112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Luo, W.; Sun, X.; Lin, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; Zhang, Y. MicroRNA-21 promotes migration and invasion of glioma cells via activation of Sox2 and β-catenin signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masliantsev, K.; Karayan-Tapon, L.; Guichet, P.O. Hippo Signaling Pathway in Gliomas. Cells 2021, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Yan, S.; Shi, L.; Wan, Z.; Jiang, N.; Li, M.; Guo, J. Decreased Expression of miR-15b in Human Gliomas is Associated with Poor Prognosis. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2015, 30, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Formentini, A.; Chien, M.; Weir, D.B.; Russo, J.J.; Ju, J.; Kornmann, M.; Ju, J. Prognostic Values of microRNAs in Colorectal Cancer. Biomark. Insights 2006, 2, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, S.; Le, S.Y.; Lu, R.; Rader, J.S.; Meyers, C.; Zheng, Z.M. Aberrant expression of oncogenic and tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for cancer cell growth. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satzger, I.; Mattern, A.; Kuettler, U.; Weinspach, D.; Voelker, B.; Kapp, A.; Gutzmer, R. MicroRNA-15b represents an independent prognostic parameter and is correlated with tumor cell proliferation and apoptosis in malignant melanoma. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 2553–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhang, D.; Du, R.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Sun, S.; Hong, L.; Liu, J.; Fan, D. miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, G.E.; Yoon, J.H.; Myung, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, C.Y. High expression of microRNA-15b predicts a low risk of tumor recurrence following curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 23, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.P.; Zhang, N.N.; Ren, X.Q.; He, J.; Li, Y. miR-103/miR-195/miR-15b Regulate SALL4 and Inhibit Proliferation and Migration in Glioma. Molecules 2018, 23, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Shi, L.; Yan, S.; Wan, Z.; Jiang, N.; Fu, L.; Li, M.; Guo, J. MiR-15b targets cyclin D1 to regulate proliferation and apoptosis in glioma cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 687826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Pereira, C.; Suarez-Peñaranda, J.M.; Barros, F.; Sobrido, M.J.; Vazquez-Salvado, M.; Forteza, J. Analysis of 2 antiapoptotic factors in gliomas: Bcl-2 overexpression and p53 mutations. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2001, 125, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Saigo, K.; Urashima, T.; Toyoda, H.; Okanoue, T.; Shimotohno, K. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene 2006, 25, 2537–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashita, Y.; Osada, H.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yamada, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tomida, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Kawahara, K.; Sekido, Y.; Takahashi, T. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9628–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanaihara, N.; Caplen, N.; Bowman, E.; Seike, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.M.; Okamoto, A.; Yokota, J.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, E.; Tsuchiya, A.; Imoto, M. Functions of cyclin D1 as an oncogene and regulation of cyclin D1 expression. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, C.L.; Dong, Y.; Hou, L.; Hu, G.; Luo, C.; et al. Knockdown of cyclin D1 inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and attenuates the invasive capacity of human glioblastoma cells. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 106, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Yan, S.S.; Shi, L.; Wan, Z.Q.; Jiang, N.; Fu, L.S.; Li, M.; Guo, J. MicroRNA-15b suppresses the growth and invasion of glioma cells through targeted inhibition of cripto-1 expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 4897–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Chopp, M.; Lu, Y.; Buller, B.; Jiang, F. MiR-15b and miR-152 reduce glioma cell invasion and angiogenesis via NRP-2 and MMP-3. Cancer Lett. 2013, 329, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geretti, E.; Klagsbrun, M. Neuropilins: Novel targets for anti-angiogenesis therapies. Cell Adh Migr. 2007, 1, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedmirzaei, H.; Shobeiri, P.; Turgut, M.; Hanaei, S.; Rezaei, N. VEGF levels in patients with glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 32, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, T.; Song, Y.; Chai, L.; Li, Y. Low-expression of microRNA-107 inhibits cell apoptosis in glioma by upregulation of SALL4. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1962–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhipa, R.R.; Fan, Q.; Anderson, J.; Muraleedharan, R.; Huang, Y.; Ciraolo, G.; Chen, X.; Waclaw, R.; Chow, L.M.; Khuchua, Z.; et al. AMP kinase promotes glioblastoma bioenergetics and tumour growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, A.E.; Demanelis, K.; Fu, A.; Zheng, T.; Zhu, Y. Association of AMP-activated protein kinase with risk and progression of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. A Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2013, 22, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Alvarez-Breckenridge, C.A.; Wang, Q.E.; Yu, J. TGF-β signaling and its targeting for glioma treatment. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 945–955. [Google Scholar]
- Latour, M.; Her, N.G.; Kesari, S.; Nurmemmedov, E. WNT Signaling as a Therapeutic Target for Glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wu, A. FOXO1 is crucial in glioblastoma cell tumorigenesis and regulates the expression of SIRT1 to suppress senescence in the brain. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 2535–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sablon, A.; Bollaert, E.; Pirson, C.; Velghe, A.I.; Demoulin, J.B. FOXO1 forkhead domain mutants in B-cell lymphoma lack transcriptional activity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, C.; Guan, Y.; Zhao, K.; Chen, L.; Bao, Y.; Cui, R.; Li, G.; Wang, Y. Up-regulation of microRNA-15b correlates with unfavorable prognosis and malignant progression of human glioma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 4943–4952. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Mizoguchi, M.; Yoshimoto, K.; Hata, N.; Shono, T.; Suzuki, S.O.; Araki, Y.; Kuga, D.; Nakamizo, A.; Amano, T.; et al. MiRNA-196 is upregulated in glioblastoma but not in anaplastic astrocytoma and has prognostic significance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4289–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malzkorn, B.; Wolter, M.; Liesenberg, F.; Grzendowski, M.; Stühler, K.; Meyer, H.E.; Reifenberger, G. Identification and functional characterization of microRNAs involved in the malignant progression of gliomas. Brain Pathol. 2010, 20, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA-cancer connection: The beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7390–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, F. MicroRNA-16 inhibits the growth and metastasis of human glioma cells via modulation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway. Arch. Med. Sci. 2020, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.Q.; Lu, X.J.; Wu, T.F.; Ding, D.D.; Zhao, Z.H.; Chen, G.L.; Xie, X.S.; Li, B.; Wei, Y.X.; Guo, L.C.; et al. MicroRNA-16 inhibits glioma cell growth and invasion through suppression of BCL2 and the nuclear factor-κB1/MMP9 signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, P.; Han, G.; Xue, X.; Ma, D. CircRNA circPDSS1 promotes bladder cancer by down-regulating miR-16. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20191961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; He, S.B.; Li, D.C. Effects of miR-16 plus CA19-9 detections on pancreatic cancer diagnostic performance. Clin. Lab. 2014, 60, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Yu, H.; Jia, G.; Yu, J.; Su, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J. circZFR regulates thyroid cancer progression by the miR-16/MAPK1 axis. Env. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 2236–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wei, M.; Jiang, X.; Tan, J.; Xu, W.; Fan, X.; Zhang, R.; Ding, C.; Zhao, F.; Shao, X.; et al. lncRNA PVT1 Promotes Tumorigenesis of Colorectal Cancer by Stabilizing miR-16-5p and Interacting with the VEGFA/VEGFR1/AKT Axis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqeilan, R.I.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. miR-15a and miR-16-1 in cancer: Discovery, function and future perspectives. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondraganti, S.; Mohanam, S.; Chintala, S.K.; Kin, Y.; Jasti, S.L.; Nirmala, C.; Lakka, S.S.; Adachi, Y.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Ali-Osman, F.; et al. Selective suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human glioblastoma cells by antisense gene transfer impairs glioblastoma cell invasion. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6851–6855. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.S. Molecular mechanisms of glioma invasiveness: The role of proteases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Seiki, M. Regulatory mechanism of 92 kDa type IV collagenase gene expression which is associated with invasiveness of tumor cells. Oncogene 1993, 8, 395–405. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Li, H.; Qian, H.; Jiao, X.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, X.; Dai, G.; Huang, J. Upregulation of miR-301a correlates with poor prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, L.; Guo, B. Upregulated microRNA-301a in breast cancer promotes tumor metastasis by targeting PTEN and activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Gene 2014, 535, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, C.; Yu, B.; Su, L.; Li, J.; Ju, J.; Yu, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, B. Overexpressed miR-301a promotes cell proliferation and invasion by targeting RUNX3 in gastric cancer. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, G.; Feng, S. MicroRNA-301a modulates doxorubicin resistance in osteosarcoma cells by targeting AMP-activated protein kinase alpha 1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 459, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, Y.; Takwi, A.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Conklin, D.J.; Young, K.H.; Martin, R.; Li, Y. miR-301a as an NF-κB activator in pancreatic cancer cells. Embo J. 2011, 30, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, K.; Cen, G.; Jiang, T.; Cao, J.; Huang, K.; Huang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Qiu, Z. MicroRNA-301a-3p promotes pancreatic cancer progression via negative regulation of SMAD4. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21046–21063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Li, L.; Zhu, G.; Dang, Q.; Ma, Z.; He, D.; Chang, L.; Song, W.; Chang, H.C.; Krolewski, J.J.; et al. Correction: Infiltrated pre-adipocytes increase prostate cancer metastasis via modulation of the miR-301a/androgen receptor (AR)/TGF-β1/Smad/MMP9 signals. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83829–83830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Huang, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Xia, W.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Ding, H.; et al. Intronic miR-301 feedback regulates its host gene, ska2, in A549 cells by targeting MEOX2 to affect ERK/CREB pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 396, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Gerster, K.; Alajez, N.M.; Tsang, J.; Waldron, L.; Pintilie, M.; Hui, A.B.; Sykes, J.; P’ng, C.; Miller, N.; et al. MicroRNA-301 mediates proliferation and invasion in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2926–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralfkiaer, U.; Hagedorn, P.H.; Bangsgaard, N.; Løvendorf, M.B.; Ahler, C.B.; Svensson, L.; Kopp, K.L.; Vennegaard, M.T.; Lauenborg, B.; Zibert, J.R.; et al. Diagnostic microRNA profiling in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Blood 2011, 118, 5891–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, A.; Tan, G.; Chen, L.; Zhou, W.; Hu, H. RASSF1A inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation by miR-711- mediated downregulation of CDK4 expression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 5842–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.Y.; Yi, W.; Zhang, M.Y.; Xu, R.; Zeng, L.S.; Long, X.R.; Zhou, X.M.; Zheng, X.S.; Kang, Y.; Wang, H.Y. MicroRNA-711 is a prognostic factor for poor overall survival and has an oncogenic role in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabirzhanov, B.; Stoica, B.A.; Zhao, Z.; Loane, D.J.; Wu, J.; Dorsey, S.G.; Faden, A.I. miR-711 upregulation induces neuronal cell death after traumatic brain injury. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 654–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Ahmad, M.K.; Srivatava, V.K.; Rastogi, N.; Serajuddin, M.; Kumar, S.; Mishra, D.P.; Sankhwar, S.N.; Mahdi, A.A. Evaluation of miR-711 as Novel Biomarker in Prostate Cancer Progression. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.H.; Chang, C.C.; Wu, M.J.; Ko, H.W.; Wang, D.; Hung, M.C.; Yang, J.Y.; Chang, C.J. MicroRNA-205 signaling regulates mammary stem cell fate and tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3093–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liao, H.; Deng, Z.; Yang, P.; Du, N.; Zhanng, Y.; Ren, H. miRNA-205 affects infiltration and metastasis of breast cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yao, Y.; Meng, F.; Qian, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Gao, Z.; Gao, L. Predictive Value of Serum miR-10b, miR-29c, and miR-205 as Promising Biomarkers in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Screening. Medicine 2015, 94, e1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdoodt, B.; Neid, M.; Vogt, M.; Kuhn, V.; Liffers, S.T.; Palisaar, R.J.; Noldus, J.; Tannapfel, A.; Mirmohammadsadegh, A. MicroRNA-205, a novel regulator of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl2, is downregulated in prostate cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, P.; Lv, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G. MiR-205 functions as a tumor suppressor via targeting TGF-α in osteosarcoma. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2016, 100, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Dai, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Shen, C.; Ye, G.; Li, L. Circulating miR-205: A promising biomarker for the detection and prognosis evaluation of bladder cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 8075–8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, K.; Gong, G.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, X. Upregulation of MiR-205 transcriptionally suppresses SMAD4 and PTEN and contributes to human ovarian cancer progression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Liang, R. miR-205 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting AKT signaling in endometrial cancer cells. J. Obs. Gynaecol. Res. 2015, 41, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Wang, P.; Xu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, G.; Pang, Q.; Tao, R. MicroRNA-205 functions as a tumor suppressor in human glioblastoma cells by targeting VEGF-A. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.X.; Ding, B.J.; Li, H.Z.; Wang, L.; Xia, F.; Du, F.; Liu, L.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, X.D.; Jia, J.F.; et al. Identification of microRNA-205 as a potential prognostic indicator for human glioma. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 20, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Li, B.; Winer, J.; Armanini, M.; Gillett, N.; Phillips, H.S.; Ferrara, N. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature 1993, 362, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bacco, F.; Orzan, F.; Erriquez, J.; Casanova, E.; Barault, L.; Albano, R.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Bigatto, V.; Reato, G.; Patanè, M.; et al. ERBB3 overexpression due to miR-205 inactivation confers sensitivity to FGF, metabolic activation, and liability to ERBB3 targeting in glioblastoma. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, M.D.; Hopkins, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, Growth Disorders, and Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2052–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Hong, W. The emerging role of the hippo pathway in cell contact inhibition, organ size control, and cancer development in mammals. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Article | Method | Sample | Study Groups | MicroRNA Profile | Change Pattern | Assessments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mao 2014 [19] | qRT-PCR | Serum/Plasma | GBM: 32 HC: 47 PCNSL: 56 | miR-21 | HC < GBM, p < 0.0001 HC < PCNSL, p < 0.0001 GBM < PCNSL, p < 0.0001 | GBM vs. PCNSL AUC (CI) 0.883 (0.813–0.954), p < 0.0001 |
| qRT-PCR | Serum/Plasma | GBM: 23 HC: 35 PCNSL: 37 | miR-21 | HC < GBM, p < 0.0001 HC < PCNSL, p < 0.0001 GBM < PCNSL, p < 0.0001 | GBM vs. PCNSL AUC (CI) 0.851 (0.755–0.947) | |
| Yang 2019 [20] | RT-qPCR | Serum/Plasma | GBM: 25 HC: 25 PCNSL: 25 | miR-21 | HC < PCNSL, p < 0.05 GBM < PCNSL, p < 0.05 HC < GBM | - |
| Drusco 2015 [21] | RT-PCR | CSF | GBM: 4 (17 sample) PCNSL: 3 HC: 14 Glioma: 9 | miR-451 miR-711 miR-935 miR-125b miR-223 | HC < PCNSL < glioma PCNSL: downregulated < (glioma, Normal) PCNSL < GBM Not expressed in glioma and PCNSL < Normal HC < PCNSL < glioma HC < PCNSL < glioma | miR Concentration (HC/Glioma/PCNSL) miR-451: 4.20 ± 2.55/11.75 ± 5.74/10.23 ± 6.32 miR-711: 8.78 ± 4.97/9.54 ± 0.61/6.40 ± 0.53 miR-935: 10.25 ± 4.74/0/0 miR-125b: 3.89 ± 0.92/9.72 ± 2.42/7.82 ± 2.56 miR-223: 6.34 ± 5.48/13.24 ± 1.89/8.86 ± 0.97 Fold change (GBM/PCNSL): miR-711: 8.77, p < 0.001 |
| D’urso 2015 [22] | qRT-PCR | Serum/Plasma | GBM: 16 PCNSL: 36 VND: 30 | miR-16 | GBM < PCNSL < VND | - |
| qRT-PCR | Serum/Plasma | Glioma: 30 PCNSL: 36 VND: 30 | miR-15 bmiR-21 miR-16 | VND < PCNSL < Glioma VND < Glioma < PCNSL Glioma < PCNSL < VND | - | |
| Si 2022 [23] | - | Serum/Plasma | Glioma: 170 PCNSL: 42 | miR-6820-3p miR-6803-3p miR-4756-5p miR-30a-3p miR-548am-3p miR-487a-3p miR-3918 miR-4751 miR-371a-3p miR-146a-3p | Glioma < PCNSL, p = 0.00028 Glioma < PCNSL, p = 1.4 × 10−5 Glioma < PCNSL, p = 0.00068 Glioma < PCNSL, p = 1.9 × 10−6 Glioma < PCNSL, p = 0.0053 Glioma < PCNSL, p = 0.0003 Glioma < PCNSL, p = 0.00027 Glioma < PCNSL, p = 0.00011 Glioma < PCNSL, p = 0.0007 Glioma < PCNSL, p = 0.0017 | PCNSL vs. Glioma AUC (CI) 0.681 (0.579–0.774) 0.716 (0.646–0.786) 0.669 (0.578–0.755) 0.737 (0.660–0.810) 0.639 (0.531–0.743) 0.681 (0.593–0.762) 0.682 (0.586–0.766) 0.693 (0.602–0.778) 0.669 (0.578–0.757) 0.656 (0.551–0.754) |
| Lan 2018 [24] | qRT-PCR | Serum/Plasma | Glioma: 59 PCNSL: 7 HC: 28 | miR-301a | HC < Glioma p < 0.01 PCNSL < Glioma p < 0.01 HC < PCNSL | - |
| Yue 2016 [25] | qRT-PCR | Serum/Plasma | Glioma: 30 PCNSL: 6 HC: 20 | miR-205 | Glioma < PCNSL, p < 0.01 Glioma < HC, p < 0.01 Glioma < PCNSL < HC | - |
| Baraniskin 2012 [26] | qRT-PCR | CSF | Glioma: 10 PCNSL: 23 VND: 10 | miR-21 miR-15b | Control < Glioma < PCNSL, p < 0.05 Control < PCNSL < Glioma, p < 0.05 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dabbagh Ohadi, M.A.; Aleyasin, M.S.; Samiee, R.; Bordbar, S.; Maroufi, S.F.; Bayan, N.; Hanaei, S.; Smith, T.R. Micro RNAs as a Diagnostic Marker between Glioma and Primary CNS Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143628
Dabbagh Ohadi MA, Aleyasin MS, Samiee R, Bordbar S, Maroufi SF, Bayan N, Hanaei S, Smith TR. Micro RNAs as a Diagnostic Marker between Glioma and Primary CNS Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. Cancers. 2023; 15(14):3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143628
Chicago/Turabian StyleDabbagh Ohadi, Mohammad Amin, Mir Sajjad Aleyasin, Reza Samiee, Sanaz Bordbar, Seyed Farzad Maroufi, Nikoo Bayan, Sara Hanaei, and Timothy R. Smith. 2023. "Micro RNAs as a Diagnostic Marker between Glioma and Primary CNS Lymphoma: A Systematic Review" Cancers 15, no. 14: 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143628
APA StyleDabbagh Ohadi, M. A., Aleyasin, M. S., Samiee, R., Bordbar, S., Maroufi, S. F., Bayan, N., Hanaei, S., & Smith, T. R. (2023). Micro RNAs as a Diagnostic Marker between Glioma and Primary CNS Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. Cancers, 15(14), 3628. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143628






