Application of Radiomics in Prognosing Lung Cancer Treated with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview of Lung Cancer and Its Global Burden
1.2. Role of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Lung Cancer Treatment
1.3. Importance of Radiomics in Predicting Treatment Outcomes
1.4. Objectives of the Meta-Analysis
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.1.1. Databases and Search Terms
2.1.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.2.1. Data Extraction Process
2.2.2. Quality Assessment
2.3. Meta-Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
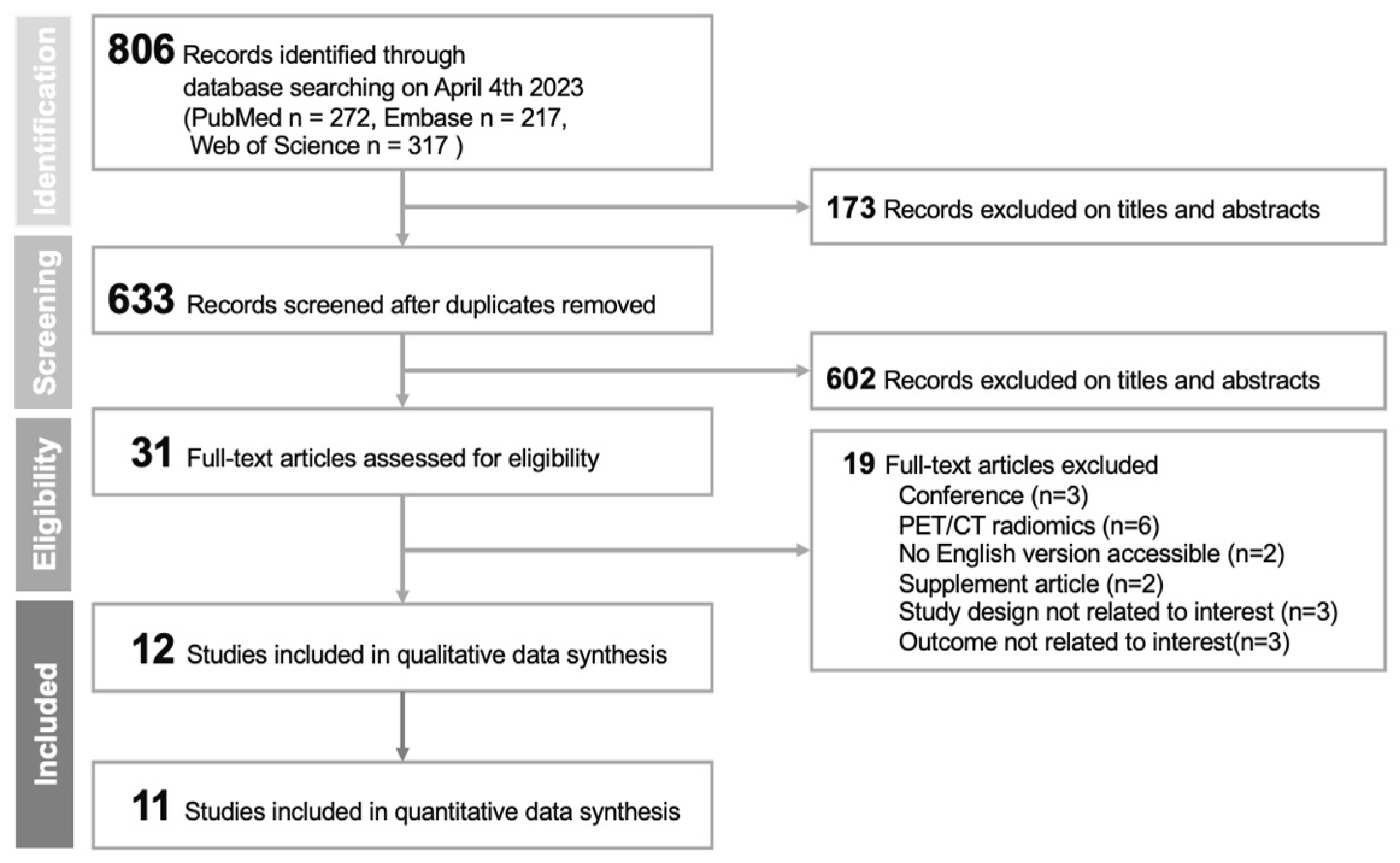
3.1. Study Selection and Characteristics
3.1.1. Flow Diagram of Study Selection
3.1.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
3.1.3. Radiomics and Image Analysis
3.2. Quality Assessment Results
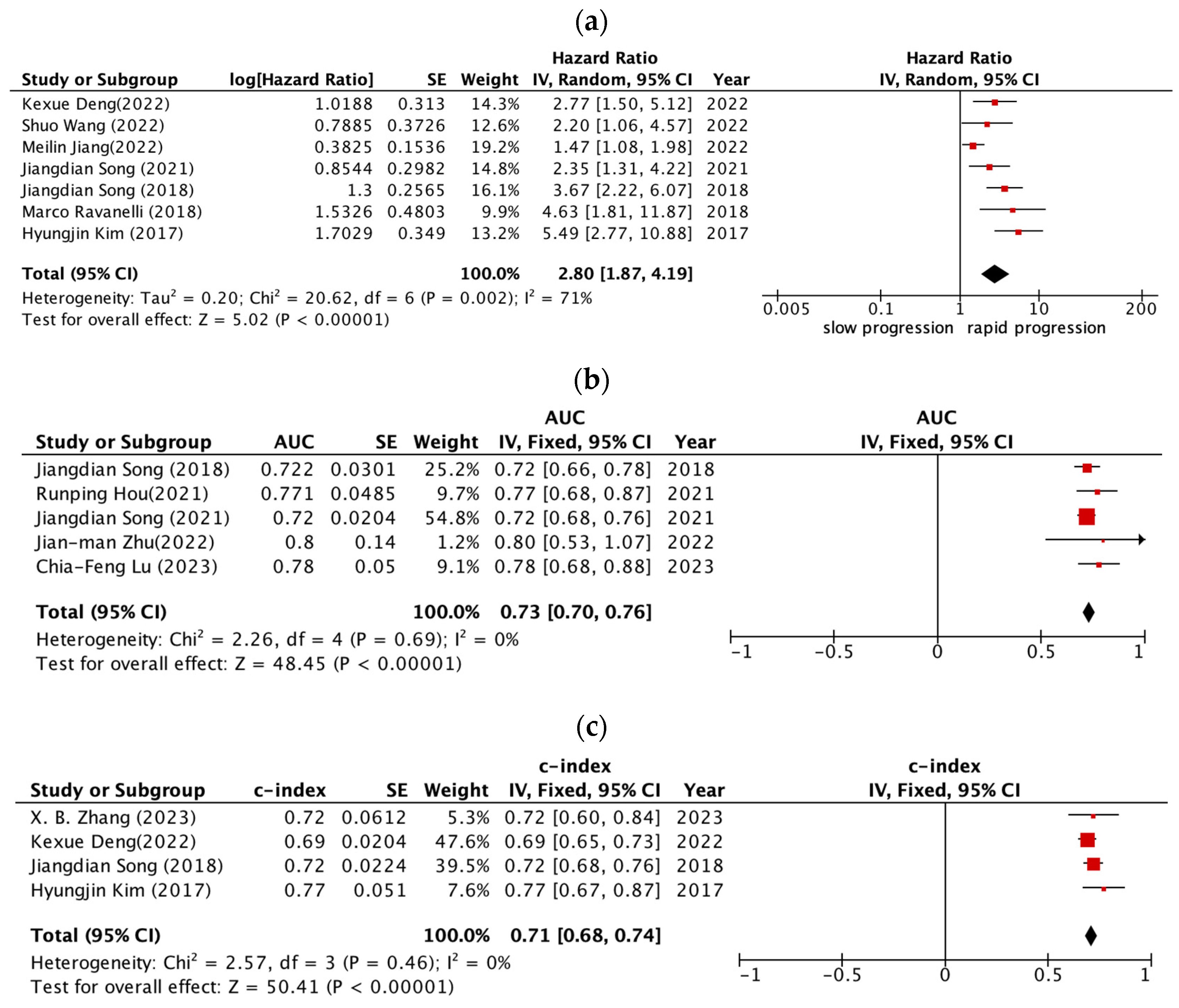
3.3. Radiomic Features and Prognostic Performance
4. Discussion
4.1. Quality of Radiomic Studies: QUIPS and RQS Evaluation
4.2. Summary of Main Findings of Meta-Analysis
4.3. Clinical Implications
4.4. Future Directions and Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Heymach, J.V.; Lippman, S.M. Lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Couraud, S.; Zalcman, G.; Milleron, B.; Morin, F.; Souquet, P. Lung cancer in never smokers—A review. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstraw, P.; Ball, D.; Jett, J.R.; Le Chevalier, T.; Lim, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Shepherd, F.A. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Nielsen, T.E.; Clausen, M.H. FDA-approved small-molecule kinase inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 422–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao, W.; Chmielecki, J. Rational, biologically based treatment of EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez, J.G.; Janne, P.A.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Meyerson, M.; et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.I.; Gee, J.M.; Harper, M.E. EGFR and cancer prognosis. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Abraham, R.T. The PI3K pathway in human disease. Cell 2017, 170, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuels, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bardelli, A.; Silliman, N.; Ptak, J.; Szabo, S.; Yan, H.; Gazdar, A.; Powell, S.M.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. High Frequency of Mutations of the PIK3CA Gene in Human Cancers. Science 2004, 304, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.-L.; Thongprasert, S.; Yang, C.-H.; Chu, D.-T.; Saijo, N.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Han, B.; Margono, B.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Gefitinib or Carboplatin–Paclitaxel in Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.H.I.; Bang, Y.J.; Camidge, D.R.; Solomon, B.J.; Salgia, R.; Iafrate, A.J. Crizotinib in ROS1-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rabe, K.F. Precision Diagnosis and Treatment for Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of Tumor Specimens at the Time of Acquired Resistance to EGFR-TKI Therapy in 155 Patients with EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, H.J. The potential of radiomic-based phenotyping in precision medicine: A review. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.S.; Ho, D.K.N.; Nguyen, N.N.; Tran, H.M.; Tam, K.-W.; Le, N.Q.K. Predicting EGFR Mutation Status in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Acad. Radiol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, S.S.F.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Applications and limitations of radiomics. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, R150–R166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tian, J.; Dong, D.; Gu, D.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lian, Z.; Liu, J.; Luo, X.; Pei, S.; et al. Radiomics Features of Multiparametric MRI as Novel Prognostic Factors in Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4259–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios Velazquez, E.; Parmar, C.; Liu, Y.; Coroller, T.P.; Cruz, G.; Stringfield, O.; Ye, Z.; Makrigiorgos, M.; Fennessy, F.; Mak, R.H.; et al. Somatic mutations drive distinct imaging phenotypes in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3922–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Limkin, E.J.; Vakalopoulou, M.; Dercle, L.; Champiat, S.; Han, S.R.; Verlingue, L.; Brandao, D.; Lancia, A.; Ammari, S.; et al. A radiomics approach to assess tumour-infiltrating CD8 cells and response to anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy: An imaging biomarker, retrospective multicohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, J.A.; Van Der Windt, D.A.; Cartwright, J.L.; Côté, P.; Bombardier, C. Assessing Bias in Studies of Prognostic Factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, A.; Schmid, M. Boosting the Concordance Index for Survival Data—A Unified Framework to Derive and Evaluate Biomarker Combinations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Sutton, A.J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Terrin, N.; Jones, D.R.; Lau, J.; Carpenter, J.; Rücker, G.; Harbord, R.M.; Schmid, C.H.; et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-F.; Liao, C.-Y.; Chao, H.-S.; Chiu, H.-Y.; Wang, T.-W.; Lee, Y.; Chen, J.-R.; Shiao, T.-H.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wu, Y.-T. A radiomics-based deep learning approach to predict progression free-survival after tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Imaging 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, B.; Yang, X.; Lan, D.; Lin, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, K.; Deng, D.; Peng, P.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Prognostic analysis and risk stratification of lung adenocarcinoma undergoing EGFR-TKI therapy with time-serial CT-based radiomics signature. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 33, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-M.; Sun, L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, T.-C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhen, X.; Liao, Z.-W. Radiomics combined with clinical characteristics predicted the progression-free survival time in first-line targeted therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR mutation. BMC Res. Notes 2022, 15, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, K.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Hou, Q.; Cao, M.; Ng, N.N.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Yeom, K.W.; et al. A deep learning-based system for survival benefit prediction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer patients: A multicenter, prognostic study. Eclinicalmedicine 2022, 51, 101541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yu, H.; Gan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, E.; Li, X.; Cao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Deng, H.; et al. Mining whole-lung information by artificial intelligence for predicting EGFR genotype and targeted therapy response in lung cancer: A multicohort study. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 4, e309–e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Yang, P.; Li, J.; Peng, W.; Pu, X.; Chen, B.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, L. Computed tomography-based radiomics quantification predicts epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status and efficacy of first-line targeted therapy in lung adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 985284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Li, X.; Xiong, J.; Shen, T.; Yu, W.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, J.; Fu, X. Predicting Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment Response in Stage IV Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients with EGFR Mutation Using Model-Based Deep Transfer Learning. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 679764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, W.-F.; Qian, W.-L.; Pang, T.; Gong, Y.-L.; Yang, Z.-G. Machine Learning-Based CT Radiomics Analysis for Prognostic Prediction in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients With EGFR-T790M Mutation Receiving Third-Generation EGFR-TKI Osimertinib Treatment. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 719919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, L.; Ng, N.N.; Zhao, M.; Shi, J.; Wu, N.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Yeom, K.W.; Tian, J. Development and Validation of a Machine Learning Model to Explore Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Response in Patients with Stage IV EGFR Variant–Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2030442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Shi, J.; Dong, D.; Fang, M.; Zhong, W.; Wang, K.; Wu, N.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; et al. A New Approach to Predict Progression-free Survival in Stage IV EGFR-mutant NSCLC Patients with EGFR-TKI Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3583–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanelli, M.; Agazzi, G.M.; Ganeshan, B.; Roca, E.; Tononcelli, E.; Bettoni, V.; Caprioli, A.; Borghesi, A.; Berruti, A.; Maroldi, R.; et al. CT texture analysis as predictive factor in metastatic lung adenocarcinoma treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 109, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Park, C.M.; Keam, B.; Park, S.J.; Kim, M.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, N.-W.; Heo, D.S.; Goo, J.M. The prognostic value of CT radiomic features for patients with pulmonary adenocarcinoma treated with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; van Stiphout, R.G.P.M.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.L.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coroller, T.P.; Grossmann, P.; Hou, Y.; Rios Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Hermann, G.; Lambin, P.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Mak, R.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. CT-based radiomic signature predicts distant metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 114, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, J.; Lee, S.M.; Do, K.-H.; Lee, G.; Lee, J.-G.; Seo, J.B. Deep Learning–based Image Conversion of CT Reconstruction Kernels Improves Radiomics Reproducibility for Pulmonary Nodules or Masses. Radiology 2019, 292, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, S.J.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Quality of science and reporting of radiomics in oncologic studies: Room for improvement according to radiomics quality score and TRIPOD statement. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 30, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B.; Reyes, M. Radiomics in medical imaging—“How-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author | Dataset | Study Duration | Country | Study Design | Patients | Age (Years) | Female (%) | Smoker (%) | Stage | Adeno (%) | EGFR-TKI | Median PFS (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chia-Feng L (2023) [30] | D | 2018~2019 | Taiwan | Retrospective | 270 | 67.5 | 158 (59) | 69 (26) | IIIB~IV | 263 (97.4) | First line First, second Gen | 11.5 |
| X. B. Z (2023) [31] | D | 2015~2020 | China | Retrospective | 131 | NR | 74 (57) | 33 (25) | II~IV | 131 (100) | First, second, third Gen | 11.1 |
| E | 2015~2020 | China | Retrospective | 41 | NR | 24 (59) | 9 (22) | II~IV | 41 (100) | First, second, third Gen | 13.1 | |
| Jian-man Z (2022) [32] | D | 2016~2019 | China | Retrospective | 100 | NR | 64 (64) | 23 (23) | IIIB~IV | 100 (100) | First line EGFR TKI | 10 |
| Kexue D (2022) [33] | D | 2010~2021 | China | Retrospective | 478 | 58 | 286 (60) | 112 (23) | IV | 451 (94) | First, second, third Gen | NA |
| E | 2010~2021 | China | Retrospective | 92 | 60 | 52 (57) | 22 (24) | IV | 86 (93) | First, second, third Gen | NA | |
| Shuo W (2022) [34] | D | 2009~2018 | China | Retrospective | 600 | 59 | 349 (58.2) | 150 (25) | I~IV | 574 (95.7) | First line First Gen | 11.42 |
| Meilin J (2022) [35] | D | 2013~2018 | China | Retrospective | 187 | 55 | 107 (57.2) | 57 (30.5) | III~IV | 187 (100) | First Generation | 12 |
| V | 2018~2019 | China | Retrospective | 38 | 57 | 23 (60.5) | 12 (31.6) | III~IV | 38 (100) | First Generation | 11.8 | |
| Runping H (2021) [36] | D | 2013~2017 | China | Retrospective | 239 | 61 | 142 (59.4) | 55 (23) | IIIA~ IVB | 239 (100) | First line EGFR TKI | 9 |
| V | 2013~2017 | China | Retrospective | 100 | 61 | 68 (68) | 17 (17) | IIIA~ IVB | 100 (100) | First line EGFR TKI | 9 | |
| Xin T (2021) [37] | D | 2017~2021 | China | Retrospective | 273 | 57 | 167 (61.2) | 55 (20.1) | IV | NA | Osimertinib | 13.3 |
| Jiangdian S (2021) [38] | D | 2010~2017 | China | Retrospective | 145 | NA | 87 (60) | 60 (41) | IV | 135 (93) | First, second, third Gen | 9.9 |
| E | 2010~2017 | China | Retrospective | 101 | NA | 60 (59) | 21 (21) | IV | 99 (98) | First, second, third Gen | 9.2 | |
| E | 2010~2017 | China | Retrospective | 96 | NA | 55 (57) | 17 (18) | IV | 92 (96) | First, second, third Gen | 8.2 | |
| Jiangdian S (2018) [39] | D | NA | China | Retrospective | 117 | NA | 73 (62) | 53 (45) | IV | NA | EGFR-TKI | 8.1 |
| E | NA | China | Retrospective | 101 | NA | 60 (59) | 21 (21) | IV | NA | EGFR-TKI | 9.2 | |
| E | NA | China | Retrospective | 96 | NA | 55 (57) | 17 (17) | IV | NA | EGFR-TKI | 8.2 | |
| Marco R (2018) [40] | D | 2008~2016 | Italy | Retrospective | 55 | 66 | 29 (58) | 23 (46) | IV | 55 (100) | First line EGFR TKI | 10.5 |
| Hyungjin K (2017) [41] | D | 2005~2015 | Korean | Retrospective | 48 | 61 | 25 (51.2) | 22 (45.8) | NA | NA | First line EGFR TKI | 9.7 |
| Author | Segmentation | VOI | Clinical Feature | Software | Radiomics | Validation | Classifier | Endpoints |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chia-Feng L (2023) [30] | Manual | Primary tumor | N, M, histology, TP, MCV | Multimodal Radiomics Platform | Radiomics | Split sample | DeepSurv | PFS |
| X. B. Z (2023) [31] | Semi-automatically | Primary tumor | None | Syngo.via Frontier, Radiomics, version 1.2.5, Siemens Healthineers | Delta Radiomics | External validation | Random survival forest | PFS |
| Jian-man Z (2022) [32] | Manual | ROI | age, sex, stage, smoking, mutations, TKI, outcome | Pyradiomics | Radiomics | Cross validation | logistic regression model | PFS |
| Kexue D (2022) [33] | Manual | Primary tumor | None | EfficientNetV2 architecture (deep learning) | Deep learning Radiomics | External validation | EfficientNetV2 architecture | PFS |
| Shuo W (2022) [34] | NA | Whole lung | None | FAIS (deep learning) | Deep learning Radiomics | Split sample | LASSO-Cox | PFS |
| Meilin J (2022) [35] | Manual | ROI | None | Pyradiomics | Radiomics | Split sample | Cox-proportional hazard | PFS |
| Runping H (2021) [36] | Manual | ROI | age, sex, smoking, clinical stages, molecular status | 3D CNN (deep learning) | Deep learning Radiomics | Split sample | 3D CNN | PFS |
| Xin T (2021) [37] | Manual | ROI | PS and M | NA | Radiomics | Cross validation | stepwise regression | PFS |
| Jiangdian S (2021) [38] | NA | Whole slice | None | BigBiGAN | Deep learning Radiomics | External validation | LASSO-Cox | PFS |
| Jiangdian S (2018) [39] | Manual | Primary tumor | smoke, N | programmed algorithms | Radiomics | External validation | LASSO-Cox | PFS |
| Marco R (2018) [40] | Manual | ROI | None | TexRAD | Radiomics | Cross validation | Cox-proportional hazard | PFS |
| Hyungjin K (2017) [41] | Manual | Primary tumor | age, baseline tumor diameter, and treatment response | Medical Imaging Solution for Segmentation and Texture Analysis | Delta Radiomics | Cross validation | Cox-proportional hazard | PFS |
| Domain 1 | Domain 2 | Domain 3 | Domain 4 | Domain 5 | Domain 6 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author | Image Protocol Quality | Multiple Segmentation | Phantom Study on All Scanner | Imaging at Multiple Time Points | Feature Reduction or Adjustment for Multiple Testing | Validation | Multivariable Analysis with Non Radiomics Features | Detect and Discuss Biological Correlates | Comparison to ‘Gold Standard’ | Potential Clinical utility | Cut-off Analyses | Discrimination Statistics | Calibration Statistics | Prospective Study Registered in a Trial Database | Cost-Effectiveness Analysis | Open Science and Data | Total |
| Chia-Feng L (2023) [30] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| X. B. Z (2023) [31] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 |
| Jian-man Z (2022) [32] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| Kexue D (2022) [33] | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 14 |
| Shuo W (2022) [34] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| Meilin J (2022) [35] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Runping H (2021) [36] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| Xin T (2021) [37] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 |
| Jiangdian S (2021) [38] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 14 |
| Jiangdian S (2018) [39] | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 15 |
| Marco R (2018) [40] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Hyungjin K (2017) [41] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.-W.; Hsu, M.-S.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chiu, H.-Y.; Chao, H.-S.; Liao, C.-Y.; Lu, C.-F.; Wu, Y.-T.; Huang, J.-W.; Chen, Y.-M. Application of Radiomics in Prognosing Lung Cancer Treated with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143542
Wang T-W, Hsu M-S, Lin Y-H, Chiu H-Y, Chao H-S, Liao C-Y, Lu C-F, Wu Y-T, Huang J-W, Chen Y-M. Application of Radiomics in Prognosing Lung Cancer Treated with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2023; 15(14):3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143542
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ting-Wei, Ming-Sheng Hsu, Yi-Hui Lin, Hwa-Yen Chiu, Heng-Sheng Chao, Chien-Yi Liao, Chia-Feng Lu, Yu-Te Wu, Jing-Wen Huang, and Yuh-Min Chen. 2023. "Application of Radiomics in Prognosing Lung Cancer Treated with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 15, no. 14: 3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143542
APA StyleWang, T.-W., Hsu, M.-S., Lin, Y.-H., Chiu, H.-Y., Chao, H.-S., Liao, C.-Y., Lu, C.-F., Wu, Y.-T., Huang, J.-W., & Chen, Y.-M. (2023). Application of Radiomics in Prognosing Lung Cancer Treated with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 15(14), 3542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143542






