Deep Learning Algorithm for Differentiating Patients with a Healthy Liver from Patients with Liver Lesions Based on MR Images
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
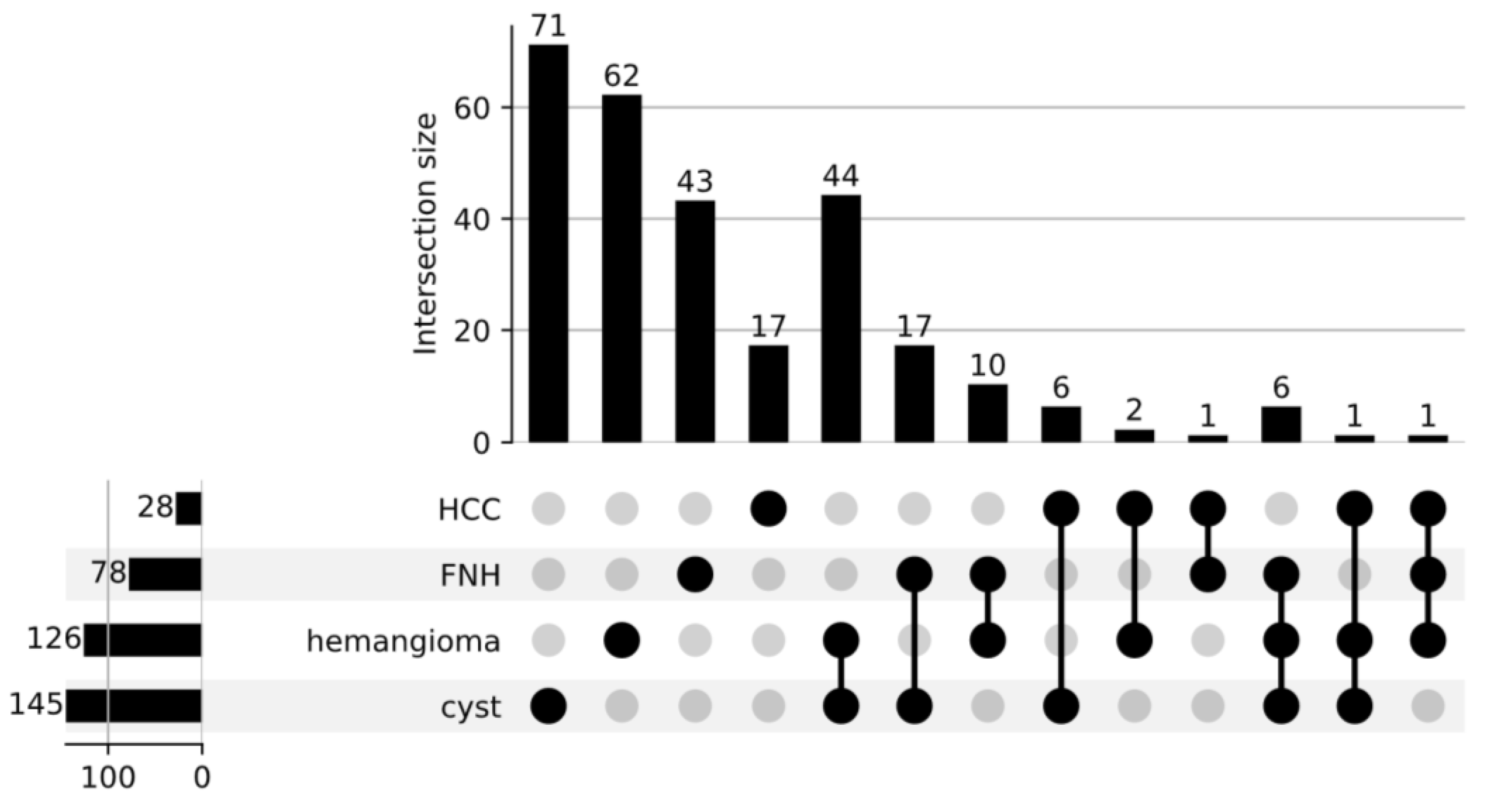
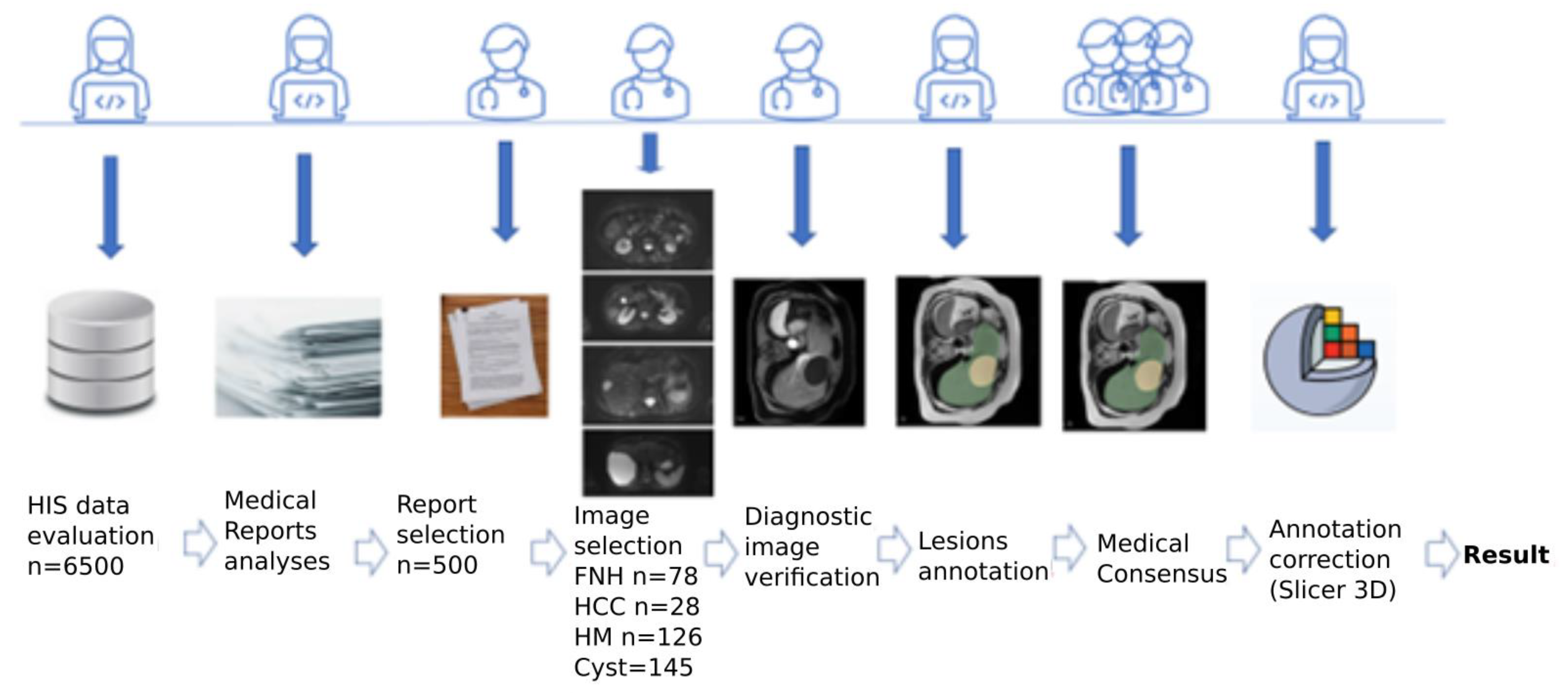
2.1. Materials
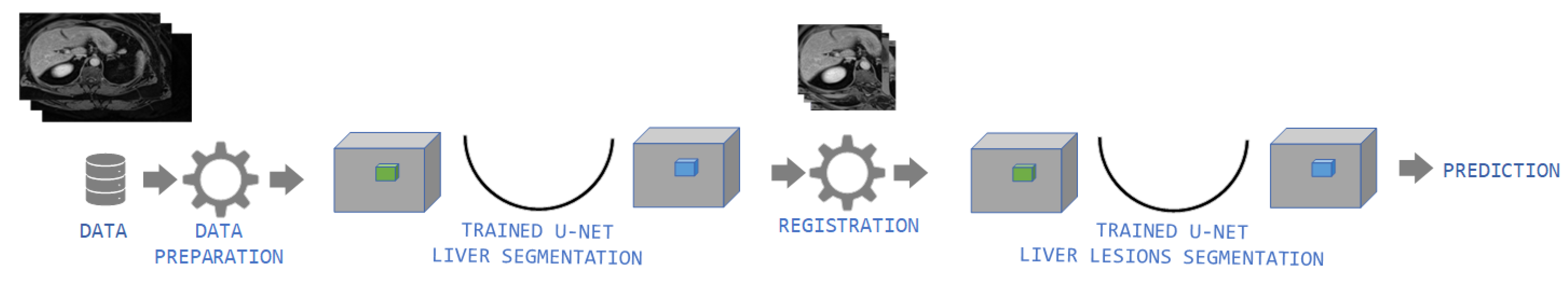
2.2. Methods
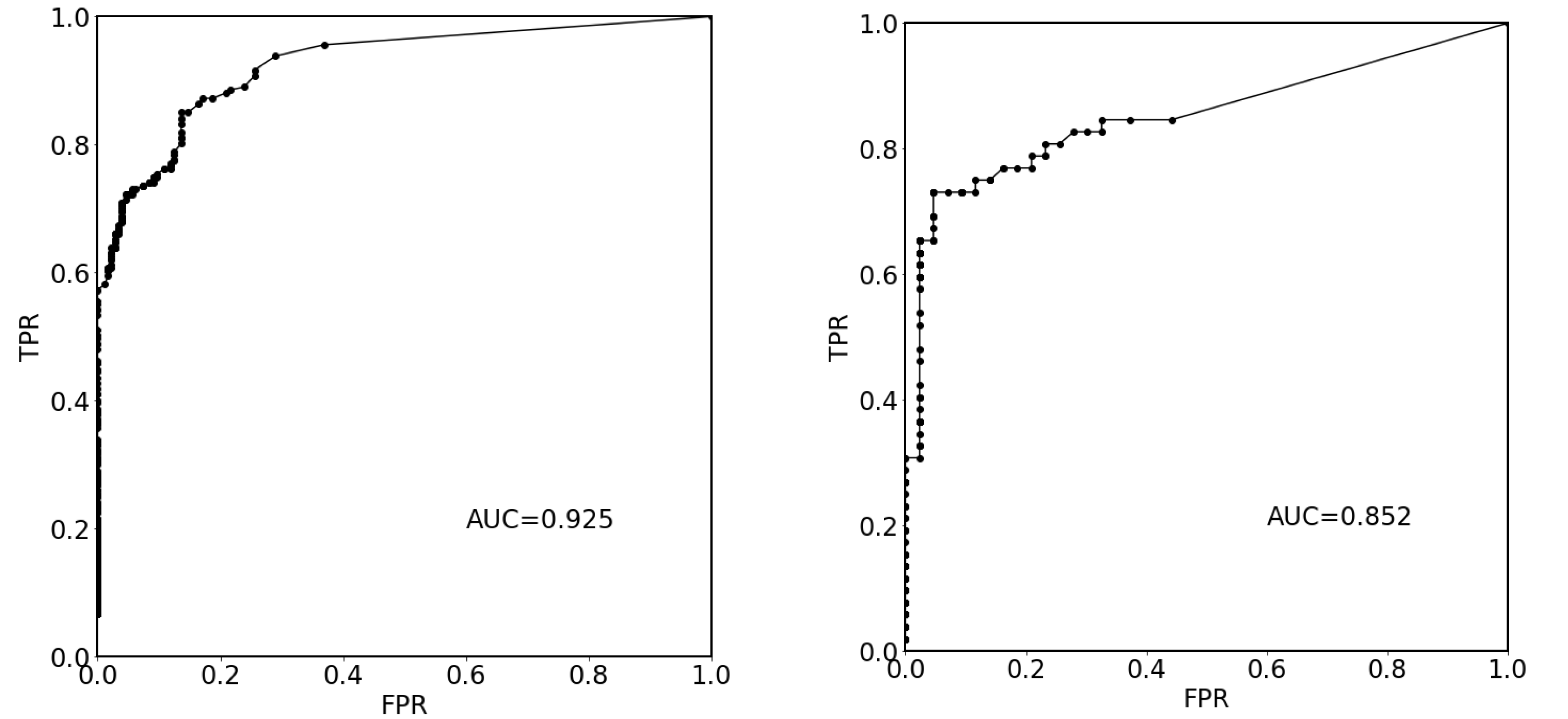
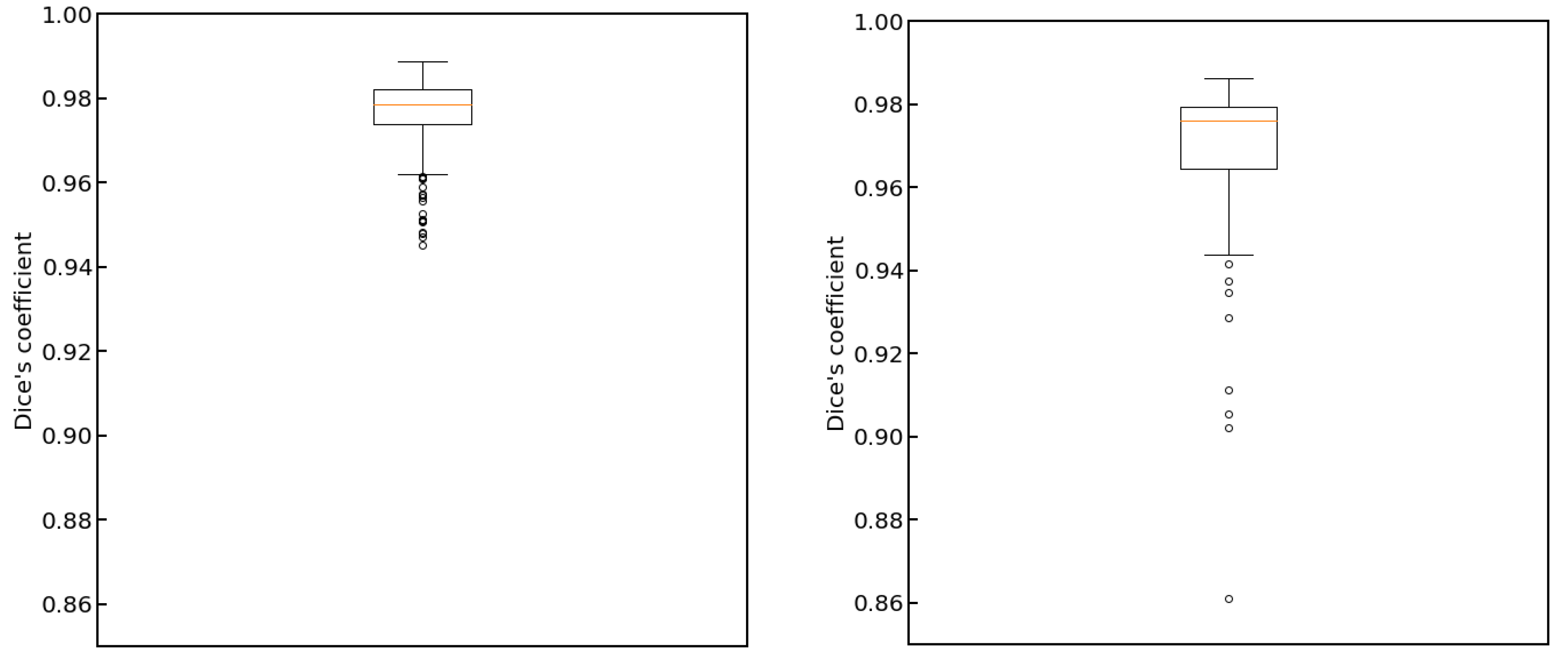
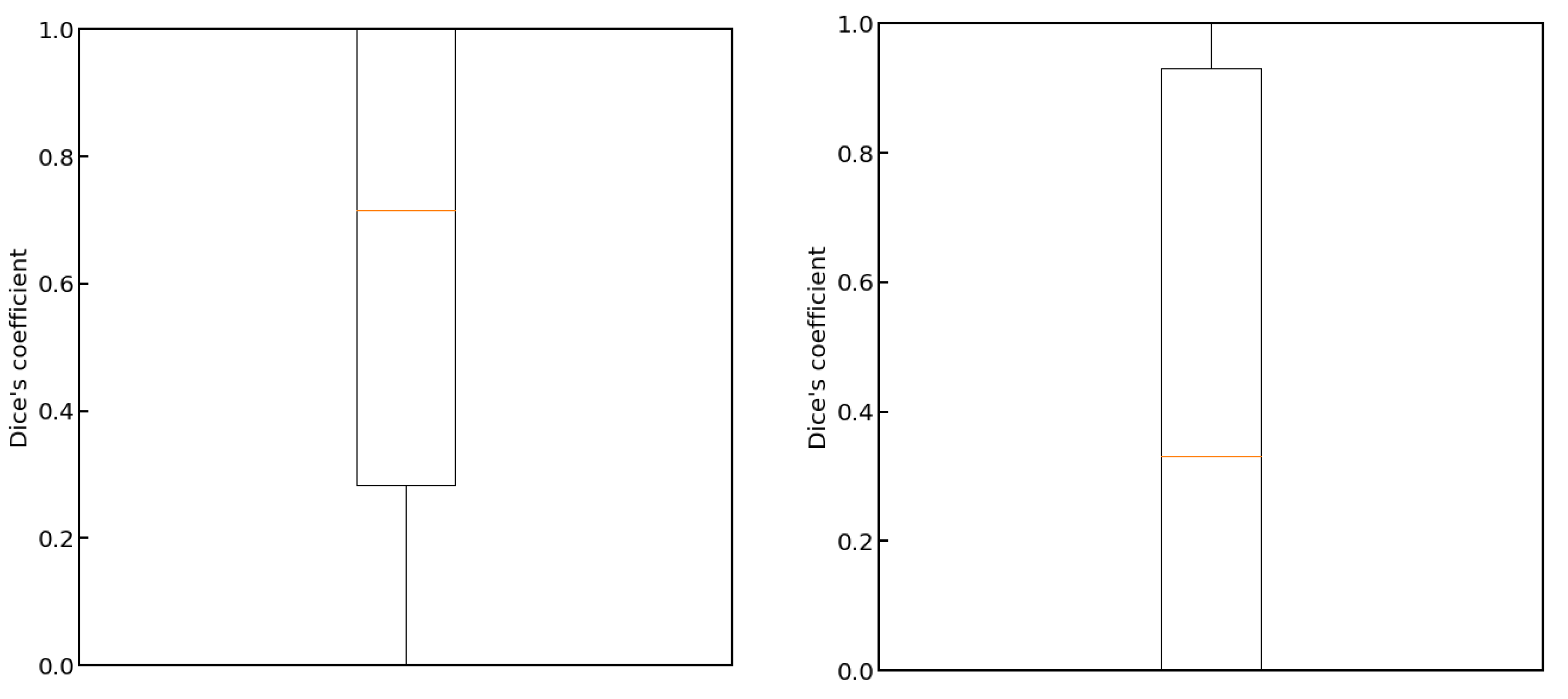
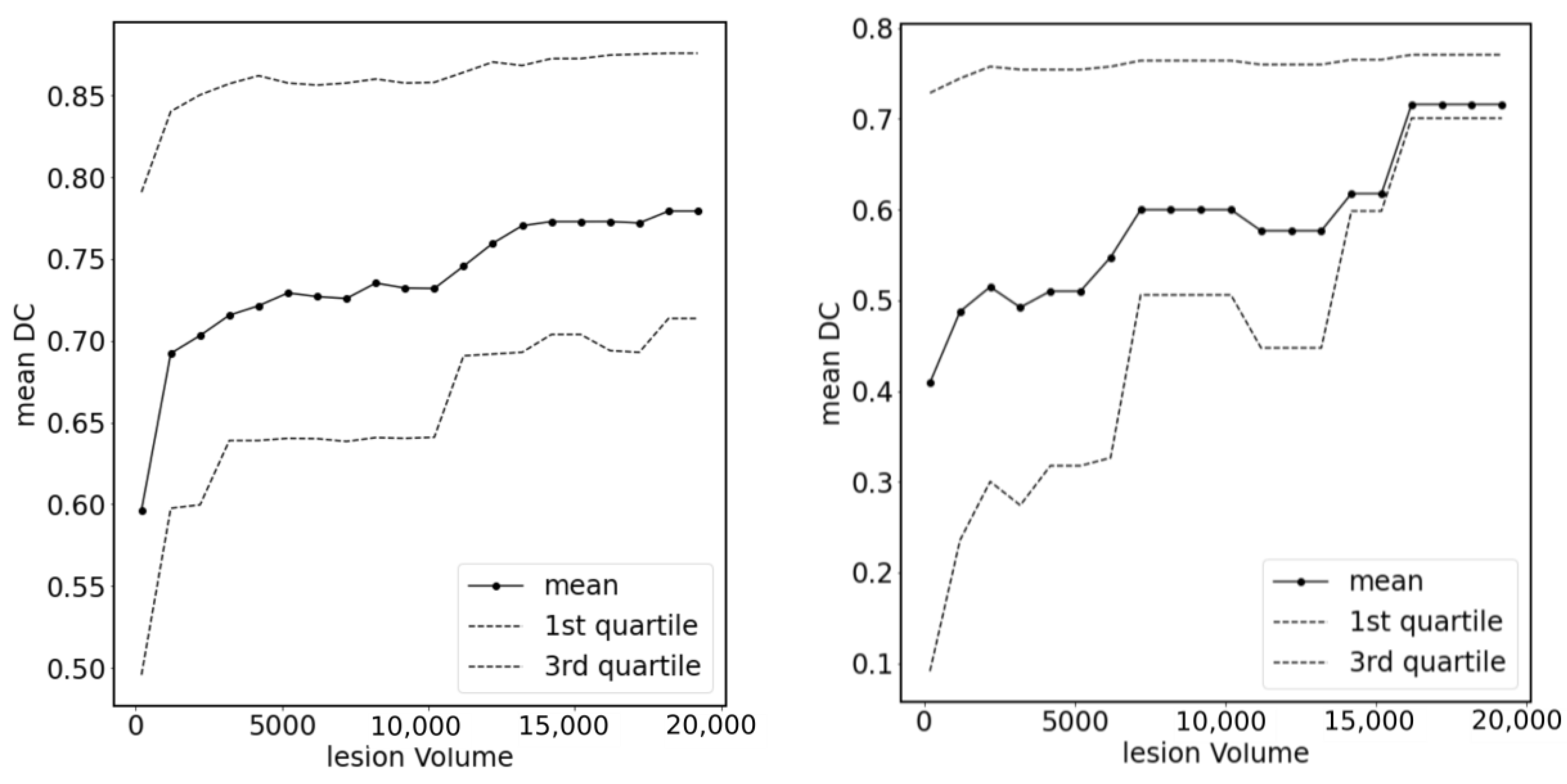
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giannitrapani, L.; Soresi, M.; La Spada, E.; Cervello, M.; D’Alessandro, N.; Montalto, G. Sex Hormones and Risk of Liver Tumor. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1089, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, F.; Zhai, M.; Long, J.; Gong, Y.; Ren, C.; Zhang, D.; Lin, X.; Liu, S. The Burden of Liver Cirrhosis in Mortality: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 909455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerecke, M.; Vafaei, A.; Hasan, O.S.M.; Chrystoja, B.R.; Cruz, M.; Lee, R.; Neuman, M.G.; Rehm, J. Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.-Y.; Chen, J.; Xia, C.-C.; Cao, L.-K.; Duan, T.; Song, B. Noninvasive Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Diagnosis to Prognosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2348–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, E.; Gores, G.J. When Should a Liver Mass Suspected of Being a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Be Biopsied? Liver Transpl. 2000, 6, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, A.; Pahwa, S.; Bonini, C.; Alcalá-Mata, L.; Wright, K.L.; Gulani, V. Multiparametric MR Imaging in Abdominal Malignancies. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. 2016, 24, 157–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taseva, A.; Tasev, V.; Bulanov, D.; Dimitrov, K.; Popov, V.; Zivkov, E.; Dimitrova, V. Diagnosis of liver hemangioma. Khirurgiia 2013, 3, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Caturelli, E.; Pompili, M.; Bartolucci, F.; Siena, D.A.; Sperandeo, M.; Andriulli, A.; Bisceglia, M. Hemangioma-like Lesions in Chronic Liver Disease: Diagnostic Evaluation in Patients. Radiology 2001, 220, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinkova, V.; Shevah, O.; Boaz, M.; Levine, A.; Shirin, H. Hepatic Haemangiomas: Possible Association with Female Sex Hormones. Gut 2004, 53, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantinga, M.A.; Gevers, T.J.; Drenth, J.P. Evaluation of Hepatic Cystic Lesions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 3543–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiin, N. MRI of Focal Liver Lesions. Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 2012, 8, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzulli, M.; Brandi, N.; Pecorelli, A.; Pastore, L.V.; Granito, A.; Martinese, G.; Tovoli, F.; Simonetti, M.; Dajti, E.; Colecchia, A.; et al. Segmental Distribution of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Livers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecorelli, A.; Franceschi, P.; Braccischi, L.; Izzo, F.; Renzulli, M.; Golfieri, R. MRI Appearance of Focal Lesions in Liver Iron Overload. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowlus, C.L.; Arrivé, L.; Bergquist, A.; Deneau, M.; Forman, L.; Ilyas, S.I.; Lunsford, K.E.; Martinez, M.; Sapisochin, G.; Shroff, R.; et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2023, 77, 659–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: Easloffice@easloffice.eu; European Association for the Study of the Liver EASL-ILCA Clinical Practice Guidelines on Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2023, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzulli, M.; Pecorelli, A.; Brandi, N.; Brocchi, S.; Tovoli, F.; Granito, A.; Carrafiello, G.; Ierardi, A.M.; Golfieri, R. The Feasibility of Liver Biopsy for Undefined Nodules in Patients under Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Is Biopsy Really a Useful Tool? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blonski, W.; Reddy, K.R. Evaluation of Nonmalignant Liver Masses. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2006, 8, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zviniene, K.; Zaboriene, I.; Basevicius, A.; Jurkiene, N.; Barauskas, G.; Pundzius, J. Comparative Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography, Computed Tomography, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Diagnosis of Hepatic Hemangiomas. Medicina 2010, 46, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilgrain, V. Focal Nodular Hyperplasia. Eur. J. Radiol. 2006, 58, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortelé, K.J.; Praet, M.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; de Hemptinne, B.; Zou, K.; Ros, P.R. Focal Nodular Hyperplasia of the Liver: Detection and Characterization with Plain and Dynamic-Enhanced MRI. Abdom. Imaging 2002, 27, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, B.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnostic Performance of Multidetector CT and MR Imaging-a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Radiology 2015, 275, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzulli, M.; Braccischi, L.; D’Errico, A.; Pecorelli, A.; Brandi, N.; Golfieri, R.; Albertini, E.; Vasuri, F. State-of-the-Art Review on the Correlations between Pathological and Magnetic Resonance Features of Cirrhotic Nodules. Histol. Histopathol. 2022, 37, 1151–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlacchio, A.; Chegai, F.; Fabiano, S.; Merolla, S.; Funel, V.; Di Giuliano, F.; Manuelli, M.; Tisone, G.; Francioso, S.; Angelico, M.; et al. Role of MRI with Hepatospecific Contrast Agent in the Identification and Characterization of Focal Liver Lesions: Pathological Correlation in Explanted Livers. Radiol. Med. 2016, 121, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Bindman, R.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Larson, E.B. Rising Use of Diagnostic Medical Imaging in a Large Integrated Health System. Health Aff. 2008, 27, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbey, C.K.; Barrett, H.H. Human- and Model-Observer Performance in Ramp-Spectrum Noise: Effects of Regularization and Object Variability. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2001, 18, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarrapico, A.M.; Ugenti, R.; Di Minco, L.; Santori, E.; Altobelli, S.; Coco, I.; D’Onofrio, S.; Simonetti, G. Diagnostic Imaging and Spending Review: Extreme Problems Call for Extreme Measures. Radiol. Med. 2017, 122, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in Medical Imaging—“How-to” Guide and Critical Reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binczyk, F.; Prazuch, W.; Bozek, P.; Polanska, J. Radiomics and Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer Screening. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkara, B.B.; Chen, M.M.; Federau, C.; Karabacak, M.; Briere, T.M.; Li, J.; Wintermark, M. Deep Learning for Detecting Brain Metastases on MRI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, C.; Linde, P.; Boda-Heggemann, J.; Baessler, B. Radiomics for Liver Tumours. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2020, 196, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Schabath, M.B. Radiomics Improves Cancer Screening and Early Detection. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 2556–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, P.S.; Janicas, C.; Veiga, J.; Matos, A.P.; Herédia, V.; Ramalho, M. Imaging Evaluation of the Liver in Oncology Patients: A Comparison of Techniques. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 1936–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Chun, J. A New Hyper Parameter of Hounsfield Unit Range in Liver Segmentation. J. Internet Comput. Serv. 2020, 21, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Stimper, V.; Bauer, S.; Ernstorfer, R.; Scholkopf, B.; Xian, R.P. Multidimensional Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 165437–165447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, S.; Luengo, J.; Herrera, F. Data Preprocessing in Data Mining; Intelligent Systems Reference Library; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 72, ISBN 978-3-319-10246-7. [Google Scholar]
- Dinc, I.; Dinc, S.; Sigdel, M.; Sigdel, M.; Aygun, R.; Pusey, M. Chapter 12—DT-Binarize: A Decision Tree Based Binarization for Protein Crystal Images. In Emerging Trends in Image Processing, Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 183–199. [Google Scholar]
- Tustison, N.J.; Avants, B.B.; Cook, P.A.; Zheng, Y.; Egan, A.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Gee, J.C. N4ITK: Improved N3 Bias Correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learned-Miller, E.G.; Jain, V. Many Heads Are Better Than One: Jointly Removing Bias from Multiple MRIs Using Nonparametric Maximum Likelihood. In Proceedings of the Information Processing in Medical Imaging; Christensen, G.E., Sonka, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 615–626. [Google Scholar]
- Isensee, F.; Petersen, J.; Klein, A.; Zimmerer, D.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.; Wasserthal, J.; Koehler, G.; Norajitra, T.; Wirkert, S.; et al. NnU-Net: Self-Adapting Framework for U-Net-Based Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.10486. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Isensee, F.; Jaeger, P.; Kohl, S.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K. NnU-Net: A Self-Configuring Method for Deep Learning-Based Biomedical Image Segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isensee, F.; Jäger, P.; Wasserthal, J.; Zimmerer, D.; Petersen, J.; Kohl, S.; Schock, J.; Klein, A.; Roß, T.; Wirkert, S.; et al. Batchgenerators—a Python Framework for Data Augmentation, Version 0.19.6; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Byrd, R.H.; Lu, P.; Nocedal, J.; Zhu, C. A Limited Memory Algorithm for Bound Constrained Optimization. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1995, 16, 1190–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Byrd, R.H.; Lu, P.; Nocedal, J. Algorithm 778: L-BFGS-B: Fortran Subroutines for Large-Scale Bound-Constrained Optimization. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 1997, 23, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assy, N.; Nasser, G.; Djibre, A.; Beniashvili, Z.; Elias, S.; Zidan, J. Characteristics of Common Solid Liver Lesions and Recommendations for Diagnostic Workup. World J. Gastroenterol 2009, 15, 3217–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grazioli, L.; Ambrosini, R.; Frittoli, B.; Grazioli, M.; Morone, M. Primary Benign Liver Lesions. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 95, 378–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa, K.; Bekiesińska-Figatowska, M. Artifacts in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Pol. J. Radiol. 2015, 80, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundel, H.L. Reader Error, Object Recognition, and Visual Search. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2004: Image Perception, Observer Performance, and Technology Assessment. SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–19 February 2004; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, D.J.; Gale, A.; Krupinski, E.A. Perception Research in Medical Imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2005, 78, 683–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupinski, E.A. Current Perspectives in Medical Image Perception. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2010, 72, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W. Quantitative Imaging in Oncology. Tomography 2022, 8, 1676–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Park, B.; Lee, S.S. Radiomics and Deep Learning: Hepatic Applications. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.; Chen, H.; Jin, Y.; Yu, L.; Qin, J.; Heng, P.-A. 3D Deeply Supervised Network for Automatic Liver Segmentation from CT Volumes. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2016: 19th International Conference, Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, C. Deep Supervision and Atrous Inception-Based U-Net Combining CRF for Automatic Liver Segmentation from CT. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Wu, F.; Hu, P.; Peng, Z.; Kong, D. Automatic 3D Liver Location and Segmentation via Convolutional Neural Network and Graph Cut. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, H.; Pham, C.; Franklin, D.; Walsum, T.; Luu, M. An Evaluation of CNN-Based Liver Segmentation Methods Using Multi-Types of CT Abdominal Images from Multiple Medical Centers. In Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 25–27 September 2019; pp. 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Jia, F.; Hu, Q. Automatic Segmentation of Liver Tumor in CT Images with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Comput. Commun. 2015, 3, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zou, B.; Liu, Q. A Deep Attention Network via High-Resolution Representation for Liver and Liver Tumor Segmentation. J. Appl. Biomed. 2021, 41, 1518–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taouli, B.; Ehman, R.L.; Reeder, S.B. Advanced MRI Methods for Assessment of Chronic Liver Disease. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 193, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitao, A.; Matsui, O.; Yoneda, N.; Kita, R.; Kozaka, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Gabata, T. Differentiation Between Hepatocellular Carcinoma Showing Hyperintensity on the Hepatobiliary Phase of Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced MRI and Focal Nodular Hyperplasia by CT and MRI. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 211, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonell, G.; Taouli, B. Abbreviated MR Protocols for Chronic Liver Disease and Liver Cancer. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. 2021, 29, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillman, B.G.; Gorman, J.D.; Hru, J.M.; Lee, M.H.; King, M.C.; Sirlin, C.B.; Marks, R.M. Diagnostic Per-Lesion Performance of a Simulated Gadoxetate Disodium-Enhanced Abbreviated MRI Protocol for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsing, R.L.; Fowler, K.J.; Yokoo, T.; Cunha, G.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Marks, R.M. Alternative Approach of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance: Abbreviated MRI. Hepatoma Res. 2020, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.V.; McDonald, S.J.; Ong, Y.-Y.; Mastrocostas, K.; Ho, E.; Huo, Y.R.; Santhakumar, C.; Lee, A.U.; Yang, J. HCC Screening: Assessment of an Abbreviated Non-Contrast MRI Protocol. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2019, 3, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzulli, M.; Mottola, M.; Coppola, F.; Cocozza, M.A.; Malavasi, S.; Cattabriga, A.; Vara, G.; Ravaioli, M.; Cescon, M.; Vasuri, F.; et al. Automatically Extracted Machine Learning Features from Preoperative CT to Early Predict Microvascular Invasion in HCC: The Role of the Zone of Transition (ZOT). Cancers 2022, 14, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogahed, M.M.; Zytoon, A.A.; Essa, B.; Abdellatif, W.; Ghanem, N.; ElWakeel, B. Natural History of Hepatic Hemangiomas as a Guide for Surgical Indication. Egypt. Liver J. 2020, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajenaru, N.; Balaban, V.; Săvulescu, F.; Campeanu, I.; Patrascu, T. Hepatic Hemangioma-Review. J. Med. Life 2015, 8, 4–11. [Google Scholar]


| TE | TR | FA | MX | VOX | FOV | CON | AV | PAT | DF | T | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2 (AX) | 100 | 4000 | 180 | 182 × 320 | 1.3 × 1.3 × 4 | 200 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 30 | 1.38 |
| T1 (AX) | 2.58 | 215 | 70 | 154 × 256 | 1.6 × 1.6 × 4 | 400 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 30 | 0.44 |
| DWI (AX) | 71 | 7800 | 0 | 118 × 192 | 2.1 × 2.1 × 4 | 400 | 4 | 2,4,8 | 2 | 30 | 5.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skwirczyński, M.; Tabor, Z.; Lasek, J.; Schneider, Z.; Gibała, S.; Kucybała, I.; Urbanik, A.; Obuchowicz, R. Deep Learning Algorithm for Differentiating Patients with a Healthy Liver from Patients with Liver Lesions Based on MR Images. Cancers 2023, 15, 3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123142
Skwirczyński M, Tabor Z, Lasek J, Schneider Z, Gibała S, Kucybała I, Urbanik A, Obuchowicz R. Deep Learning Algorithm for Differentiating Patients with a Healthy Liver from Patients with Liver Lesions Based on MR Images. Cancers. 2023; 15(12):3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123142
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkwirczyński, Maciej, Zbisław Tabor, Julia Lasek, Zofia Schneider, Sebastian Gibała, Iwona Kucybała, Andrzej Urbanik, and Rafał Obuchowicz. 2023. "Deep Learning Algorithm for Differentiating Patients with a Healthy Liver from Patients with Liver Lesions Based on MR Images" Cancers 15, no. 12: 3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123142
APA StyleSkwirczyński, M., Tabor, Z., Lasek, J., Schneider, Z., Gibała, S., Kucybała, I., Urbanik, A., & Obuchowicz, R. (2023). Deep Learning Algorithm for Differentiating Patients with a Healthy Liver from Patients with Liver Lesions Based on MR Images. Cancers, 15(12), 3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123142







