Hyperleukocytosis in Childhood Acute Leukemia: Early Complications and Survival Outcomes
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Hyperleukocytosis in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
3.3. Hyperleukocytosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
3.4. Survival Outcomes in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
3.5. Survival Outcomes in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bidwell, S.S.; Peterson, C.C.; Demanelis, K.; Zarins, K.R.; Meza, R.; Sriplung, H.; Wiangnon, S.; Chotsampancharoen, T.; Chitapanarux, I.; Pongnikorn, D.; et al. Childhood Cancer Incidence and Survival in Thailand: A Comprehensive Population-Based Registry Analysis, 1990–2011. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, E.; DeSantis, C.; Robbins, A.; Kohler, B.; Jemal, A. Childhood and Adolescent Cancer Statistics, 2014. Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Colombet, M.; Ries, L.A.G.; Moreno, F.; Dolya, A.; Bray, F.; Hesseling, P.; Shin, H.Y.; Stiller, C.A. IICC-3 contributors International Incidence of Childhood Cancer, 2001–2010: A Population-Based Registry Study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunin, N.J.; Pui, C.H. Differing Complications of Hyperleukocytosis in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic or Acute Nonlymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 1985, 3, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguiguren, J.M.; Schell, M.J.; Crist, W.M.; Kunkel, K.; Rivera, G.K. Complications and Outcome in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Hyperleukocytosis. Blood 1992, 79, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abla, O.; Angelini, P.; Di Giuseppe, G.; Kanani, M.F.; Lau, W.; Hitzler, J.; Sung, L.; Naqvi, A. Early Complications of Hyperleukocytosis and Leukapheresis in Childhood Acute Leukemias. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 38, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.G.; Seo, J.H.; Jun, S.E.; Lee, B.K.; Lim, Y.T. Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Hyperleukocytosis at Presentation. Blood Res. 2014, 49, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.M.; Yang, E.J.; Lee, J.M.; Hah, J.O.; Park, S.K.; Park, E.S.; Lim, J.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.; Shim, Y.J.; et al. Treatment Outcome in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Hyperleukocytosis in the Yeungnam Region of Korea: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 42, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, R.; Merkel, N.; Diwan, O.; Elsner, K.; Kramm, C.M. Leukapheresis and Exchange Transfusion in Children with Acute Leukemia and Hyperleukocytosis. A Single Center Experience. Klin. Padiatr. 2009, 221, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İrken, G.; Ören, H.; Öniz, H.; Çetingül, N.; Vergin, C.; Atabay, B.; Gülen, H.; Türker, M.; Kantar, M.; Yılmaz, Ş. Hyperleukocytosis in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Complications and Treatment Outcome. Turk. J. Haematol. 2006, 23, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, K.P.; Marwaha, R.K.; Trehan, A.; Bansal, D. Survival Outcome in Childhood ALL: Experience from a Tertiary Care Centre in North India. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2009, 53, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magrath, I.; Shanta, V.; Advani, S.; Adde, M.; Arya, L.S.; Banavali, S.; Bhargava, M.; Bhatia, K.; Gutiérrez, M.; Liewehr, D.; et al. Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia in Countries with Limited Resources; Lessons from Use of a Single Protocol in India over a Twenty Year Period. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 2005, 41, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creutzig, U.; Ritter, J.; Riehm, H.; Langermann, H.J.; Henze, G.; Kabisch, H.; Niethammer, D.; Jürgens, H.; Stollmann, B.; Lasson, U. Improved Treatment Results in Childhood Acute Myelogenous Leukemia: A Report of the German Cooperative Study AML-BFM-78. Blood 1985, 65, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, L.; Aplenc, R.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Gamis, A.S. AAML0531/PHIS Group Predictors and Short-Term Outcomes of Hyperleukocytosis in Children with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1770–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, H.; Fan, Y.; Pounds, S.; Geiger, T.L.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Pui, C.-H.; Razzouk, B.I. Clinical and Biologic Features and Treatment Outcome of Children with Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Hyperleukocytosis. Cancer 2008, 113, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creutzig, U.; Zimmermann, M.; Reinhardt, D.; Dworzak, M.; Stary, J.; Lehrnbecher, T. Early Deaths and Treatment-Related Mortality in Children Undergoing Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Analysis of the Multicenter Clinical Trials AML-BFM 93 and AML-BFM 98. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 4384–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcu, P.; Cripe, L.D.; Ng, E.W.; Bhatia, S.; Danielson, C.M.; Orazi, A.; McCarthy, L.J. Hyperleukocytic Leukemias and Leukostasis: A Review of Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation and Management. Leuk. Lymphoma 2000, 39, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, R.; Jeha, S.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, X.; Cheng, C.; Bhojwani, D.; Campbell, P.; Howard, S.C.; Rubnitz, J.; Ribeiro, R.C.; et al. The Role of Leukapheresis in the Current Management of Hyperleukocytosis in Newly Diagnosed Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1546–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demanelis, K.; Sriplung, H.; Meza, R.; Wiangnon, S.; Rozek, L.S.; Scheurer, M.E.; Lupo, P.J. Differences in Childhood Leukemia Incidence and Survival between Southern Thailand and the United States: A Population-Based Analysis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 1790–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laosombat, V.; Wongchanchailert, M.; Sattayasevana, B.; Wiriyasateinkul, A.; Watana-Arepornchai, S. The Treatment of Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Thailand. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 2002, 38, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubergen, D.G.; Gilchrist, G.S.; O’Brien, R.T.; Coccia, P.F.; Sather, H.N.; Waskerwitz, M.J.; Hammond, G.D. Improved Outcome with Delayed Intensification for Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Intermediate Presenting Features: A Childrens Cancer Group Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 1993, 11, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaynon, P.S.; Steinherz, P.G.; Bleyer, W.A.; Ablin, A.R.; Albo, V.C.; Finklestein, J.Z.; Grossman, N.J.; Novak, L.J.; Pyesmany, A.F.; Reaman, G.H. Improved Therapy for Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Unfavorable Presenting Features: A Follow-up Report of the Childrens Cancer Group Study CCG-106. J. Clin. Oncol. 1993, 11, 2234–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creutzig, U.; Ritter, J.; Schellong, G. Identification of Two Risk Groups in Childhood Acute Myelogenous Leukemia after Therapy Intensification in Study AML-BFM-83 as Compared with Study AML-BFM-78. AML-BFM Study Group. Blood 1990, 75, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creutzig, U.; Zimmermann, M.; Ritter, J.; Reinhardt, D.; Hermann, J.; Henze, G.; Jürgens, H.; Kabisch, H.; Reiter, A.; Riehm, H.; et al. Treatment Strategies and Long-Term Results in Paediatric Patients Treated in Four Consecutive AML-BFM Trials. Leukemia 2005, 19, 2030–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seksarn, P.; Wiangnon, S.; Veerakul, G.; Chotsampancharoen, T.; Kanjanapongkul, S.; Chainansamit, S.O. Outcome of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated Using the Thai National Protocols. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 4609–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, S.J.; Shuster, J.J.; Mahoney, D.H.; Winick, N.; Toledano, S.; Munoz, L.; Kiefer, G.; Pullen, J.D.; Steuber, C.P.; Camitta, B.M. A Comparison of Early Intensive Methotrexate/Mercaptopurine with Early Intensive Alternating Combination Chemotherapy for High-Risk B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Pediatric Oncology Group Phase III Randomized Trial. Leukemia 2001, 15, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, T.M.; Franklin, J.; Gerbing, R.B.; Alonzo, T.A.; Hurwitz, C.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hirsch, B.; Smith, F.O.; Mathew, P.; Arceci, R.J.; et al. AAML03P1, a Pilot Study of the Safety of Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin in Combination with Chemotherapy for Newly Diagnosed Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer 2012, 118, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chotsampancharoen, T.; Songthawee, N.; Chavananon, S.; Sripornsawan, P.; McNeil, E.B. Relapsed Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Experience from a Single Tertiary Center in Thailand. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 3517–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songthawee, N.; Sripornsawan, P.; Chavananon, S.; McNeil, E.B.; Chotsampancharoen, T. Relapsed Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Experience from a Single Tertiary Center in Thailand. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 4079–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairo, M.S.; Bishop, M. Tumour Lysis Syndrome: New Therapeutic Strategies and Classification. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 127, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; Aspelin, P.; Barsoum, R.S.; Burdmann, E.A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Herzog, C.A.; Joannidis, M.; Kribben, A.; Levey, A.S.; et al. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, B.; Giroir, B.; Randolph, A. Definitions for Sepsis and Organ Dysfunction in Pediatrics. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 6, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, F.B.; Toh, C.H.; Hoots, W.K.; Wada, H.; Levi, M. Scientific Subcommittee on Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH). Towards Definition, Clinical and Laboratory Criteria, and a Scoring System for Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 86, 1327–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaventure, A.; Harewood, R.; Stiller, C.A.; Gatta, G.; Clavel, J.; Stefan, D.C.; Carreira, H.; Spika, D.; Marcos-Gragera, R.; Peris-Bonet, R.; et al. Worldwide Comparison of Survival from Childhood Leukaemia for 1995–2009, by Subtype, Age, and Sex (CONCORD-2): A Population-Based Study of Individual Data for 89,828 Children from 198 Registries in 53 Countries. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e202–e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ssenyonga, N.; Stiller, C.; Nakata, K.; Shalkow, J.; Redmond, S.; Bulliard, J.-L.; Girardi, F.; Fowler, C.; Marcos-Gragera, R.; Bonaventure, A.; et al. Worldwide Trends in Population-Based Survival for Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults Diagnosed with Leukaemia, by Subtype, during 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of Individual Data from 258 Cancer Registries in 61 Countries. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2022, 6, 409–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, H.S.; Steinherz, P.G.; Gaynon, P.S.; Finklestein, J.Z.; Sather, H.N.; Reaman, G.H.; Bleyer, W.A.; Hammond, G.D. The Effect of Initial Management of Hyperleukocytosis on Early Complications and Outcome of Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 1988, 6, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, H.; Mullighan, C.G. Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2524–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, A.M.; Weinstein, H.J. The Role of Prognostic Features in the Treatment of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Oncologist 2000, 5, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möricke, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Reiter, A.; Gadner, H.; Odenwald, E.; Harbott, J.; Ludwig, W.-D.; Riehm, H.; Schrappe, M. Prognostic Impact of Age in Children and Adolescents with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Data from the Trials ALL-BFM 86, 90, and 95. Klin. Padiatr. 2005, 217, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrooman, L.M.; Silverman, L.B. Treatment of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Prognostic Factors and Clinical Advances. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2016, 11, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Arthur, D.; Camitta, B.; Carroll, A.J.; Crist, W.; Gaynon, P.; Gelber, R.; Heerema, N.; Korn, E.L.; Link, M.; et al. Uniform Approach to Risk Classification and Treatment Assignment for Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creutzig, U.; Ritter, J.; Budde, M.; Sutor, A.; Schellong, G. Early Deaths Due to Hemorrhage and Leukostasis in Childhood Acute Myelogenous Leukemia. Associations with Hyperleukocytosis and Acute Monocytic Leukemia. Cancer 1987, 60, 3071–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
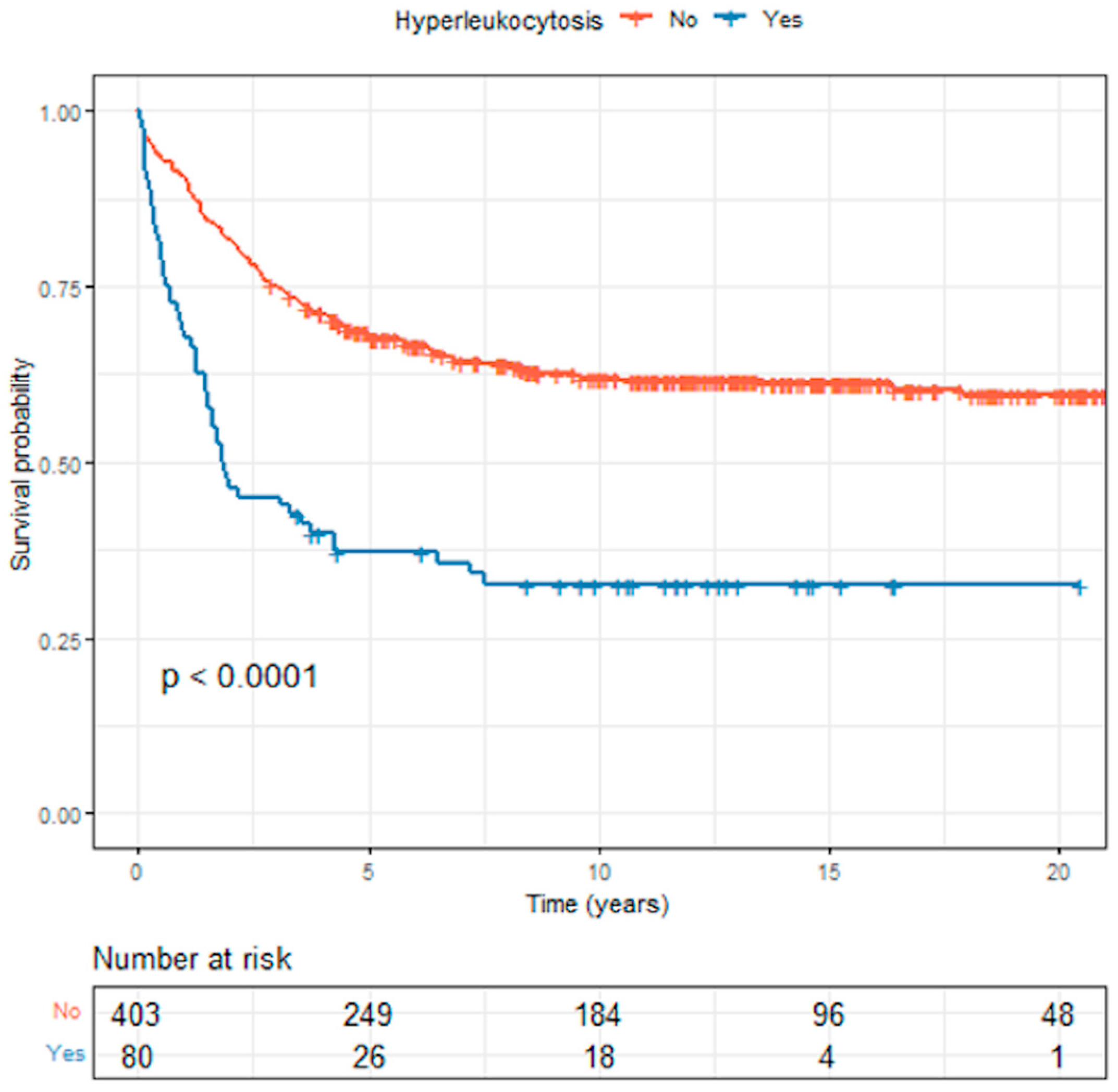
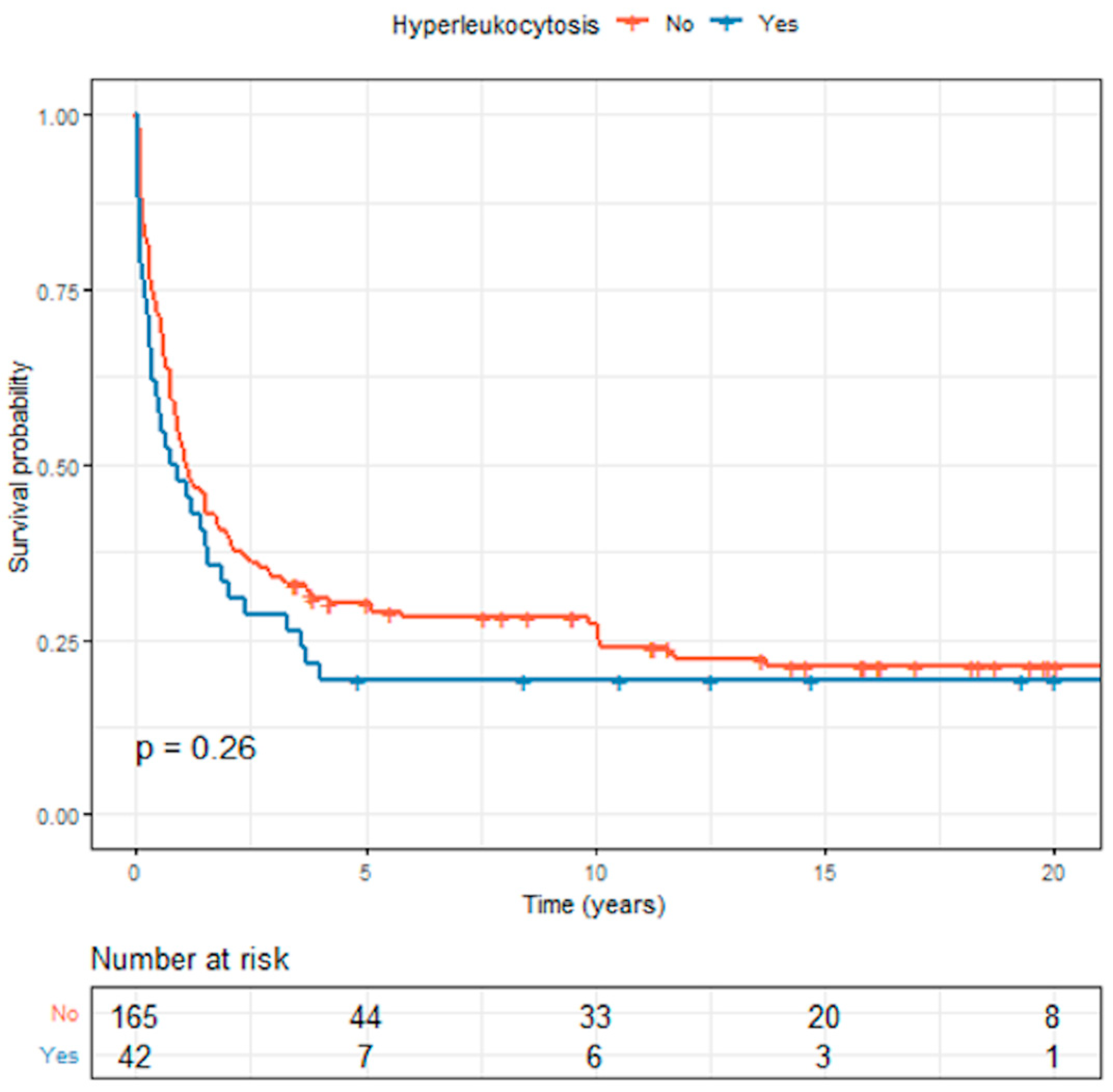
| Variables | Total (N = 483) | Hyperleukocytosis (N = 80) | No Hyperleukocytosis (N = 403) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic and clinical characteristics, n (%) | ||||
| Age (months), median (IQR) | 54.0 (36.0–97.0) | 91.0 (34.0–137.0) | 52.0 (36.0–86.0) | 0.013 |
| Sex | 0.171 | |||
| Male | 272 (56.3) | 39 (48.8) | 233 (57.8) | |
| Female | 211 (43.7) | 41 (51.2) | 170 (42.2) | |
| Immunophenotype | <0.001 | |||
| T-cell | 63 (13.0) | 25 (31.2) | 38 (9.4) | |
| B-cell | 376 (77.9) | 51 (63.8) | 325 (80.7) | |
| FAB classification | 44 (9.1) | 4 (5.0) | 40 (9.9) | |
| Fever | 360 (74.5) | 62 (77.5) | 298 (73.9) | 0.599 |
| Mediastinal mass | 23 (4.8) | 8 (10.0) | 15 (3.7) | 0.037 |
| Hepatomegaly | 448 (92.8) | 80 (100.0) | 368 (91.3) | 0.012 |
| Splenomegaly | 332 (68.7) | 72 (90.0) | 260 (64.5) | <0.001 |
| Laboratory parameters, mean (SD) | ||||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 7.5 (3.5) | 7.0 (2.7) | 7.6 (3.7) | 0.223 |
| Platelet count (×109/L) | 75.5 (92.3) | 38.0 (29.9) | 82.9 (98.5) | <0.001 |
| Blast cells (%) | 50.2 (34.8) | 90.4 (11.5) | 42.2 (32.2) | <0.001 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 9.6 (1.1) | 9.3 (0.9) | 9.6 (1.1) | 0.018 |
| Phosphorus (mmol/L) | 4.8 (1.3) | 4.1 (1.5) | 5 (1.3) | <0.001 |
| Uric acid (mmol/L) | 6.1 (3.5) | 7.5 (4.1) | 5.9 (3.3) | <0.001 |
| Lactate dehydrogenase (U/L) | 2776.3 (5339.4) | 4971.5 (7105.8) | 2350.3 (4820.7) | <0.001 |
| Treatment-related complications, n (%) | ||||
| Tumor lysis syndrome | 67 (13.9) | 24 (30.0) | 43 (10.7) | <0.001 |
| Seizure | 21 (4.3) | 9 (11.3) | 12 (3.0) | 0.003 |
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 6 (1.2) | 3 (3.8) | 3 (0.7) | 0.056 |
| Acute kidney injury | 27 (5.6) | 9 (11.3) | 18 (4.5) | 0.025 |
| Septic shock | 106 (21.9) | 26 (32.5) | 80 (19.9) | 0.009 |
| DIC | 65 (13.5) | 21 (26.3) | 44 (10.9) | <0.001 |
| ETT intubation | 38 (7.9) | 14 (17.5) | 24 (6.0) | <0.001 |
| ICU admission | 50 (10.4) | 22 (27.5) | 28 (6.9) | <0.001 |
| Treatment outcomes, n (%) | ||||
| Induction of remission | 428 (96.8) | 63 (91.3) | 365 (97.9) | 0.011 |
| Relapse | 162 (33.5) | 31 (38.8) | 131 (32.5) | 0.342 |
| Mortality | 207 (42.9) | 53 (66.3) | 154 (38.2) | <0.001 |
| Variables | Total (N = 207) | Hyperleukocytosis (N = 42) | No Hyperleukocytosis (N = 165) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic and clinical characteristics, n (%) | ||||
| Age (months), median (IQR) | 65.0 (25.5–133.5) | 137.0 (34.0–150.5) | 58.0 (25.0–116.0) | 0.021 |
| Sex | 0.268 | |||
| Male | 125 (60.4) | 29 (69.0) | 96 (58.2) | |
| Female | 82 (39.6) | 13 (31.0) | 69 (41.8) | |
| Fever | 157 (75.8) | 39 (92.9) | 118 (71.5) | 0.007 |
| Hepatomegaly | 165 (79.7) | 37 (88.1) | 128 (77.6) | 0.194 |
| Splenomegaly | 119 (57.5) | 31 (73.8) | 88 (53.3) | 0.026 |
| Lymphadenopathy | 142 (68.6) | 35 (83.3) | 107 (64.8) | 0.034 |
| Laboratory parameters, mean (SD) | ||||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 7.3 (2.2) | 7.1 (1.6) | 7.3 (2.3) | 0.585 |
| Platelet count (×109/L) | 64.1 (93.1) | 50.0 (35.3) | 67.7 (102.5) | 0.272 |
| Blast cells (%) | 43.4 (34.7) | 80.5 (24.7) | 33.9 (30.3) | <0.001 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 9.3 (0.7) | 9.0 (0.9) | 9.3 (0.7) | 0.021 |
| Phosphorus (mmol/L) | 4.6 (1.2) | 4.1 (1.4) | 4.8 (1.0) | <0.001 |
| Uric acid (mmol/L) | 5.0 (2.1) | 6.0 (2.6) | 4.8 (1.9) | <0.001 |
| Lactate dehydrogenase (U/L) | 2035.6 (2210.0) | 2619.7 (2425.5) | 1888.6 (2135.3) | 0.058 |
| Treatment-related complications, n (%) | ||||
| Tumor lysis syndrome | 11 (5.3) | 4 (9.5) | 7 (4.2) | 0.276 |
| Seizure | 8 (3.9) | 1 (2.4) | 7 (4.2) | 1 |
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 2 (1.0) | 2 (4.8) | 0 (0) | 0.037 |
| Acute kidney injury | 14 (6.8) | 2 (4.8) | 12 (7.3) | 1 |
| Septic shock | 59 (28.5) | 11 (26.2) | 48 (29.1) | 1 |
| DIC | 49 (23.7) | 13 (31.0) | 36 (21.8) | 0.219 |
| ETT intubation | 41 (19.8) | 8 (19.0) | 33 (20.0) | 1 |
| ICU admission | 46 (22.2) | 11 (26.2) | 35 (21.2) | 0.504 |
| Treatment outcomes, n (%) | ||||
| Induction of remission | 109 (67.3) | 19 (59.3) | 90 (69.2) | 0.289 |
| Relapse | 63 (30.4) | 12 (28.6) | 51 (30.9) | 0.915 |
| Mortality | 160 (77.3) | 34 (81.0) | 126 (76.4) | 0.669 |
| Risk Factor | Crude HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||
| 1–9 | Reference | Reference | |
| <1 | 3.51 (1.79–6.89) | 3.05 (1.57–5.96) | 0.001 |
| ≥10 | 1.80 (1.29–2.52) | 1.64 (1.15–2.32) | 0.006 |
| Male sex | 1.11 (0.84–1.47) | 1.37 (1.05–1.79) | 0.021 |
| Immunophenotype | |||
| T-cell | Reference | Reference | |
| B-cell | 0.79 (0.55–1.15) | 1.37 (0.90–2.08) | 0.14 |
| FAB classification | 0.56 (0.31–1.01) | 0.85 (0.46–1.56) | 0.6 |
| Initial WBC count (×109/L) | |||
| <50 | Reference | Reference | |
| 50–<100 | 1.47 (0.97–2.23) | 1.59 (1.07–2.36) | 0.022 |
| ≥100–<200 | 2.45 (1.60–4.61) | 2.04 (1.33–3.14) | <0.001 |
| ≥200 | 3.04 (2.00–4.61) | 2.71 (1.74–4.21) | <0.001 |
| Early complication | 1.16 (0.79–1.71) | 0.88 (0.62–1.26) | 0.5 |
| Risk Factor | Crude HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||
| 1–9 | Reference | Reference | |
| <1 | 1.43 (0.80–2.55) | 1.82 (1.00–3.32) | 0.049 |
| ≥10 | 0.84 (0.59–1.20) | 0.70 (0.48–1.02) | 0.064 |
| Male sex | 1.06 (0.77–1.47) | 1.03 (0.74–1.42) | 0.9 |
| Initial WBC count (×109/L) | |||
| <50 | Reference | Reference | |
| 50–<100 | 1.13 (0.70–1.82) | 1.25 (0.76–2.03) | 0.4 |
| ≥100–<200 | 0.83 (0.48–1.43) | 0.81 (0.46–1.44) | 0.5 |
| ≥200 | 2.16 (1.32–3.53) | 2.63 (1.56–4.43) | <0.001 |
| Early complication | 0.83 (0.50–1.40) | 0.89 (0.53–1.50) | 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kittivisuit, S.; Jongthitinon, N.; Sripornsawan, P.; Songthawee, N.; Chavananon, S.; Limratchapong, C.; McNeil, E.B.; Chotsampancharoen, T. Hyperleukocytosis in Childhood Acute Leukemia: Early Complications and Survival Outcomes. Cancers 2023, 15, 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123072
Kittivisuit S, Jongthitinon N, Sripornsawan P, Songthawee N, Chavananon S, Limratchapong C, McNeil EB, Chotsampancharoen T. Hyperleukocytosis in Childhood Acute Leukemia: Early Complications and Survival Outcomes. Cancers. 2023; 15(12):3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123072
Chicago/Turabian StyleKittivisuit, Sirinthip, Nichanan Jongthitinon, Pornpun Sripornsawan, Natsaruth Songthawee, Shevachut Chavananon, Chompoonut Limratchapong, Edward B. McNeil, and Thirachit Chotsampancharoen. 2023. "Hyperleukocytosis in Childhood Acute Leukemia: Early Complications and Survival Outcomes" Cancers 15, no. 12: 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123072
APA StyleKittivisuit, S., Jongthitinon, N., Sripornsawan, P., Songthawee, N., Chavananon, S., Limratchapong, C., McNeil, E. B., & Chotsampancharoen, T. (2023). Hyperleukocytosis in Childhood Acute Leukemia: Early Complications and Survival Outcomes. Cancers, 15(12), 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123072






