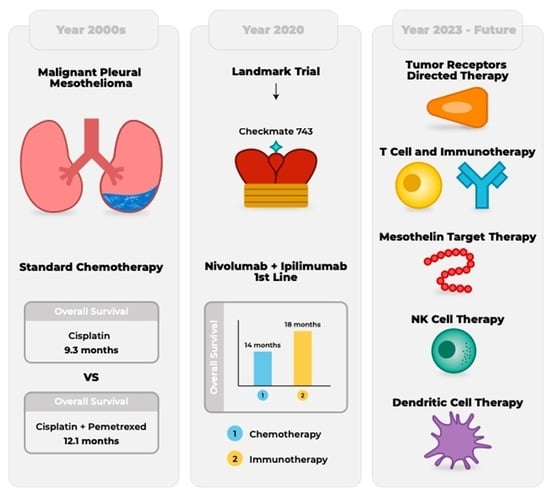
Success of Checkpoint Blockade Paves the Way for Novel Immune Therapy in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Early Immunotherapy Trials for MPM
2.1. Interferon-Based Therapy
2.2. Checkpoint Inhibitors
| Trial | Agent | Phase | Target | Patients | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DETERMINE | Tremelimumab | II | CTLA-4 | 571 | Median OS 1 7.7 months |
| NIVOMES | Nivolumab | II | PD-1 | 38 | DCR 2 50% |
| MERIT | Nivolumab | II | PD-1 | 34 | Median OS 1 17.3 and PFS 3 6.1 months |
| CONFIRM | Nivolumab | III | PD-1 | 332 | Median OS 1 10.1 and PFS 3 3.0 months |
| KEYNOTE-028 | Pembrolizumab | IB | PD-1 | 25 | ORR 4 20%. |
| Chicago group: NCT02399371 | Pembrolizumab | II | PD-1 | 65 | Median OS 1 11.5 and median PFS 3 4.5 months |
| PROMISE-MESO | Pembrolizumab | III | PD-1 | 144 | OS 1 10.7, PFS 3 2.4 months. ORR 4 22% |
| JAVELIN | Avelumab | IB | PDL-1 | 53 | ORR 4 9% |
| DREAM | Durvalumab | II | PDL-1 | 55 | ORR 4 61% and PFS 3 71% |
| MAPS 2 | Nivolumab/ ipilimumab | II | PD-1/ CTLA-4 | 125 | DCR 2 52% and ORR 4 28%. OS 1 15.9 months |
| INITIATE | Nivolumab/ ipilimumab | II | PD-1/ CTLA-4 | 38 | DCR 2 68% and ORR 4 29% |
| NIBIT-MESO-1 | Tremelimumab/ Durvalumab | II | CTLA-4/ PDL-1 | 40 | Median OS 1 16.6 and median PFS 3 5.7 months |
3. Immunotherapy in the Frontline
| Trial | Year | Phase | Intervention | Size | Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEYNOTE-A17 | 2022 | IB | Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy 1 | 19 | Drug limiting toxicity/AE 4 |
| NCT05324436 | 2022 | Cohort | Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab | 50 | Safety/AEs 4 |
| DREAM3R | 2021 | III | Durvalumab plus chemotherapy 1 | 480 | OS 3 |
| BEAT-Meso | 2019 | III | Atezolizumab, Bevacizumab plus chemotherapy 2 | 401 | OS 3 |
| NCT02784171 | 2016 | II/III | Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy 1 | 520 | PFS 5 and OS 3 |
| Checkmate743 | 2016 | III | Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab | 605 | OS 3 |
| PrE0505 | 2016 | II | Durvalumab plus chemotherapy 1 | 55 | OS 3 |
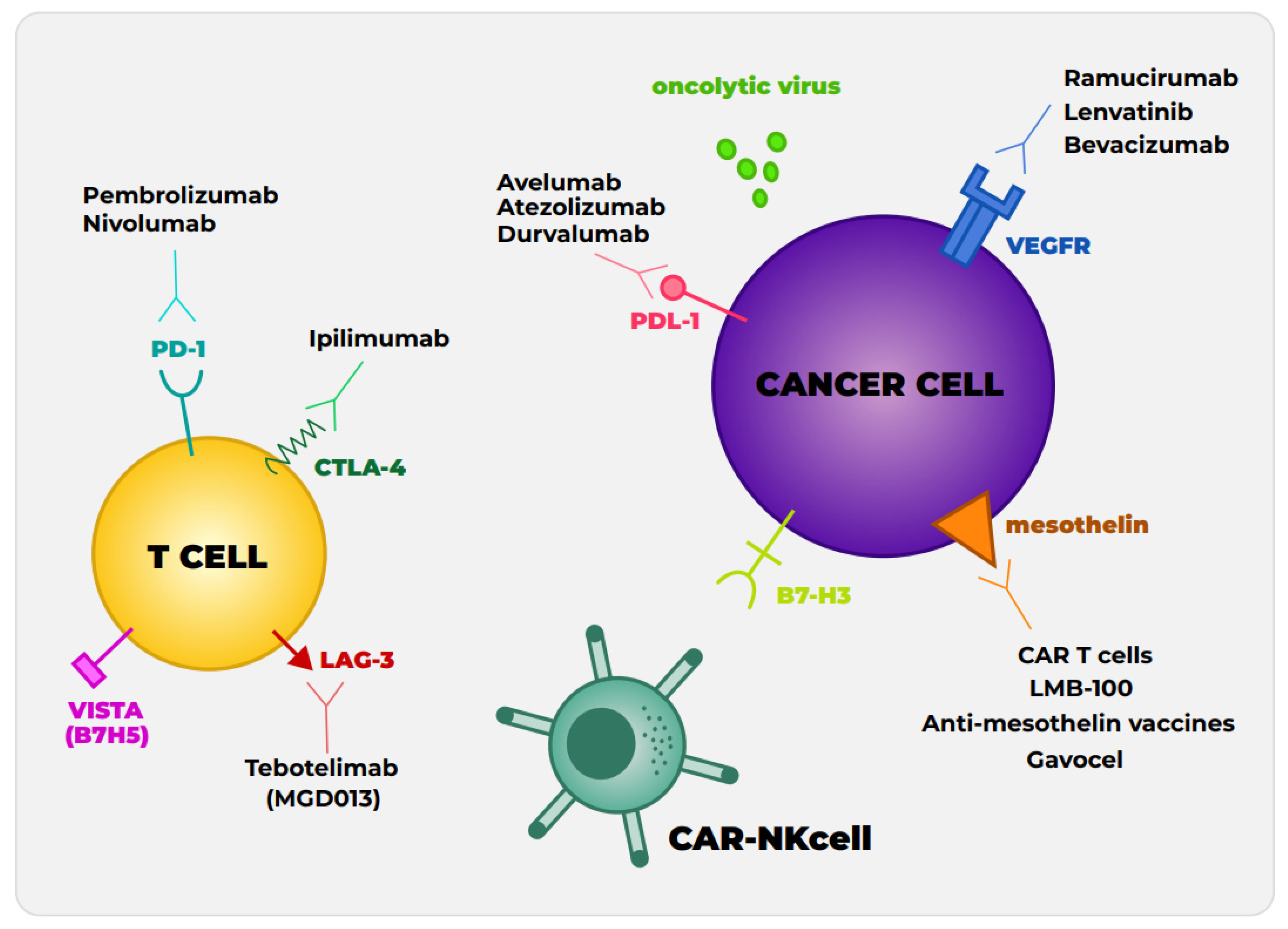
4. Alternative Checkpoint Inhibitors and Novel Combinations
4.1. Other Immune Checkpoint Protein
4.2. Antiangiogenic Therapies and Checkpoint Inhibitors
5. Mesothelin-Targeted Therapy
5.1. Immunotoxin Therapy
5.2. Vaccine Therapy
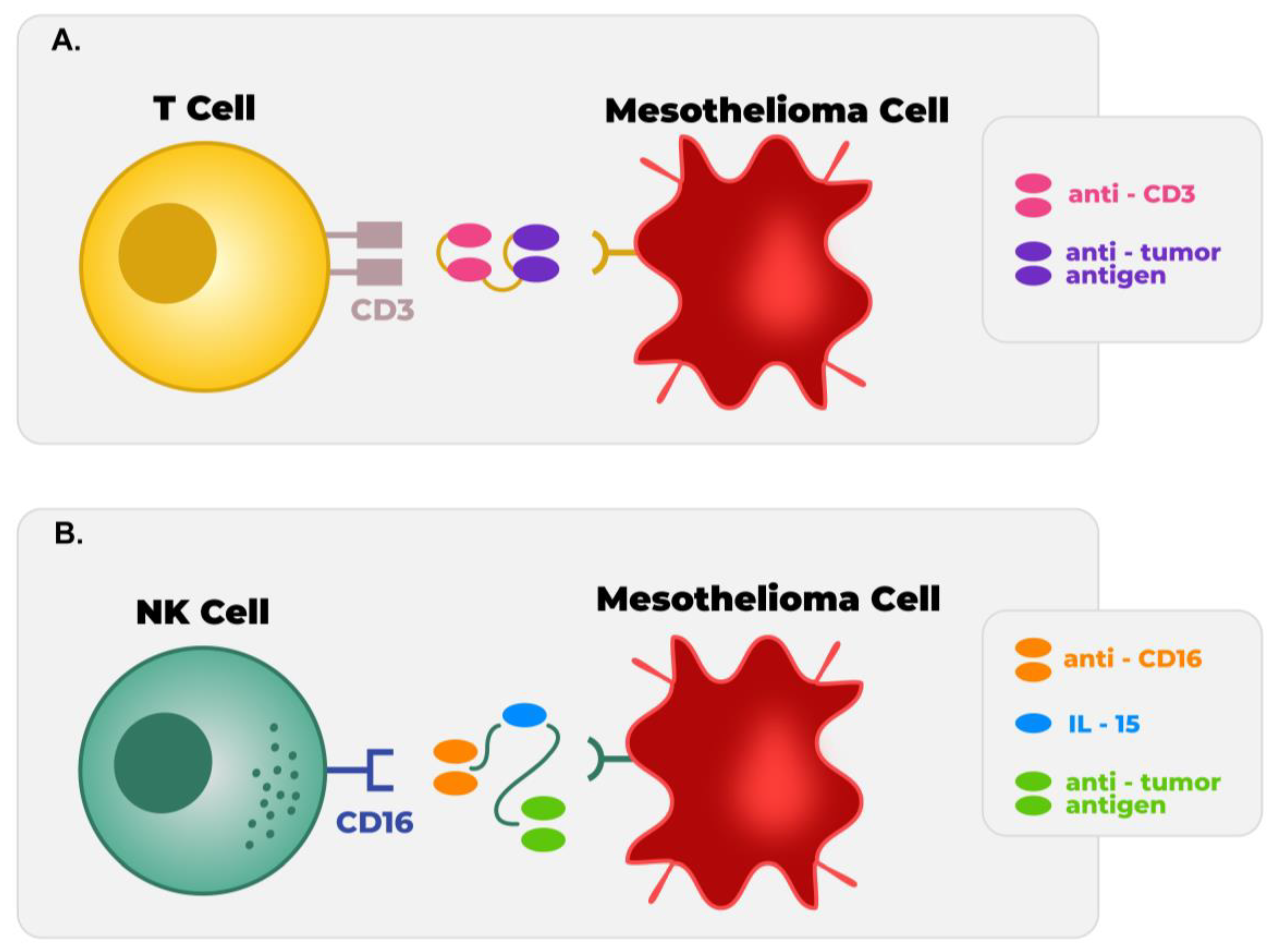
5.3. Chimeric Antigen Receptor Therapy
5.4. Targeted T Cell Receptor Fusion Construct
6. Other Novel Immunotherapy Approaches
6.1. NK Cell
6.2. Dendritic Cells
6.3. Oncolytic Virus Therapy
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bibby, A.C.; Maskell, N.A. Current treatments and trials in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 2161–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCambridge, A.J.; Napolitano, A.; Mansfield, A.S.; Fennell, D.A.; Sekido, Y.; Nowak, A.K.; Reungwetwattana, Y.; Mao, W.; Pass, H.; Carbone, M.; et al. Progress in the Management of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma in 2017. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, S.G. Emerging avenues in immunotherapy for the management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuss, J.E.; Forde, P.M. Immunotherapy for mesothelioma: Rationale and new approaches. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 18, 562–572. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, A.K.; Jackson, A.; Sidhu, C. Management of Advanced Pleural Mesothelioma—At the Crossroads. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2022, 18, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelzang, N.J.; Rusthoven, J.J.; Symanowski, J.; Denham, C.; Kaukel, E.; Ruffie, P.; Gatzemeier, U.; Boyer, M.; Emri, S.; Manegold, C.; et al. Phase III Study of Pemetrexed in Combination with Cisplatin Versus Cisplatin Alone in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucali, P.A. Target therapy: New drugs or new combinations of drugs in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S311–S321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Désage, A.L.; Karpathiou, G.; Peoc’h, M.; Froudarakis, M.E. The Immune Microenvironment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Literature Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterman, D.H.; Recio, A.; Carroll, R.G.; Gillespie, C.T.; Haas, A.; Vachani, A.; Kapoor, V.; Sun, J.; Hodinka, R.; Brown, J.; et al. A phase I clinical trial of single-dose intrapleural IFN-beta gene transfer for malignant pleural mesothelioma and metastatic pleural effusions: High rate of antitumor immune responses. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13 (15 Pt 1), 4456–4466. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17671130/ (accessed on 15 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Al, G.; Boldrini, L.; Lucchi, M.; Picchi, A.; Dell’Omodarme, M.; Prati, M.C.; Mussi, A.; Corsi, V.; Fontanini, G. Treatment with interleukin-2 in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Immunological and angiogenetic assessment and prognostic impact. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 1869–1875. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19935800/ (accessed on 15 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, L.; Morra, A.; Fonsatti, E.; Cutaia, O.; Amato, G.; Giannarelli, D.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; Danielli, R.; Altomonte, M.; Mutti, L.; et al. Tremelimumab for patients with chemotherapy-resistant advanced malignant mesothelioma: An open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maio, M.; Scherpereel, A.; Calabrò, L.; Aerts, J.; Perez, S.C.; Bearz, A.; Nackaerts, K.; Fennel, D.; Kowalski, D.; Tsao, A.; et al. Tremelimumab as second-line or third-line treatment in relapsed malignant mesothelioma (DETERMINE): A multicentre, international, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, D.A.; Ewings, S.; Ottensmeier, C.; Califano, R.; Hanna, G.G.; Hill, K.; Danson, S.; Steele, N.; Nye, M.; Johnson, L.; et al. Nivolumab versus placebo in patients with relapsed malignant mesothelioma (CONFIRM): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Kijima, T.; Aoe, K.; Kato, T.; Fujimoto, N.; Nakagawa, K.; Takeda, Y.; Hida, T.; Kanai, K.; Imamura, F.; et al. Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab: Results of a Multicenter, Open-label, Single-arm, Japanese Phase II study in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MERIT). Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5485–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispel-Janssen, J.; Zago, G.; Schouten, R.; Buikhuisen, W.; Monkhorst, K.; Thunissen, E.; Baas, P. OA13.01 A Phase II Study of Nivolumab in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (NivoMes): With Translational Research (TR) Biopies. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, S292–S293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghav, K.; Liu, S.; Overman, M.; Morani, A.; Willette, A.; Fournier, K.; Varadhachary, G. Clinical Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Advanced Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2119934. Available online: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2782760 (accessed on 15 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Menis, J.; Pasello, G.; Remon, J. Immunotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma: A review of literature data. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 2988–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alley, E.W.; Lopez, J.; Santoro, A.; Morosky, A.; Saraf, S.; Piperdi, B.; Brummelen, E. Clinical safety and activity of pembrolizumab in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma (KEYNOTE-028): Preliminary results from a non-randomised, open-label, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Karrison, T.; Rose, B.; Tan, Y.; Hill, B.; Pemberton, E.; Straus, C.M.; Seiwert, T.; Kindler, H. OA08.03 Phase II Trial of Pembrolizumab (NCT02399371) In Previously Treated Malignant Mesothelioma (MM): Final Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, S339. Available online: http://www.jto.org/article/S1556086418312358/fulltext (accessed on 15 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Popat, S.; Curioni-Fontecedro, A.; Dafni, U.; Shah, R.; O’Brien, M.; Pope, A.; Fishes, P.; Spicer, J.; Roy, A.; Gilligan, D.; et al. A multicentre randomised phase III trial comparing pembrolizumab versus single-agent chemotherapy for advanced pre-treated malignant pleural mesothelioma: The European Thoracic Oncology Platform (ETOP 9-15) PROMISE-meso trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1734–1745. Available online: http://www.annalsofoncology.org/article/S0923753420424597/fulltext (accessed on 15 May 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.; Thomas, A.; Nemunaitis, J.J.; Patel, M.R.; Bennouna, J.; Chen, F.L.; Delord, J.P.; Dowlati, A.; Kochuparambil, S.T.; Taylor, M.H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Avelumab Treatment in Patients with Advanced Unresectable Mesothelioma: Phase 1b Results from the JAVELIN Solid Tumor Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 351–357. Available online: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaoncology/fullarticle/2719756 (accessed on 15 May 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, A.; Kok, P.; Lesterhuis, W.; Hughes, B.; Brown, C.; Kao, S.; Karikios, D.; John, T.; Pavlakis, N.; O’Byrne, K.; et al. OA08.02 DREAM—A Phase 2 Trial of Durvalumab with First Line Chemotherapy in Mesothelioma: Final Result. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, S338–S339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, A.; Mazieres, J.; Greillier, L.; Lantuejoul, S.; Dô, P.; Bylicki, O.; Monnet, I.; Corre, R.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Locatelli-Sanchez, M.; et al. Nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with relapsed malignant pleural mesothelioma (IFCT-1501 MAPS2): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, non-comparative, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disselhorst, M.J.; Quispel-Janssen, J.; Lalezari, F.; Monkhorst, K.; de Vries, J.F.; Van der Noort, V.; Harms, E.; Burgers, S.; Baas, P. Ipilimumab and nivolumab in the treatment of recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma (INITIATE): Results of a prospective, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 260–270. Available online: http://www.thelancet.com/article/S221326001830420X/fulltext (accessed on 15 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, L.; Morra, A.; Giannarelli, D.; Amato, G.; D’Incecco, A.; Covre, A.; Lewis, A.; Rebelatto, M.; Danielli, R.; Altomonte, M.; et al. Tremelimumab combined with durvalumab in patients with mesothelioma (NIBIT-MESO-1): An open-label, non-randomised, phase 2 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 451–460. Available online: http://www.thelancet.com/article/S2213260018301516/fulltext (accessed on 15 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Yu, Y.; Mei, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Jia, Y.; Kong, F. Advances in Immunotherapy of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Onco Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 4477–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, P.; Scherpereel, A.; Nowak, A.K.; Fujimoto, N.; Peters, S.; Tsao, A.S.; Mansfiels, A.S.; Popat, S.; Jahan, T.; Antonia, S.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, K.; Fujimoto, N. Current evidence and future perspectives of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socinski, M.A.; Nishio, M.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Thomas, C.; et al. IMpower150 Final Overall Survival Analyses for Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Chemotherapy in First-Line Metastatic Nonsquamous NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1909–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forde, P.M.; Nowak, A.K.; Kok, P.S.; Brown, C.; Sun, Z.; Anagnostou, V.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Yip, S.; Cook, A.; Joost, W.; et al. DREAM3R: Durvalumab with chemotherapy as first-line treatment in advanced pleural mesothelioma—A phase 3 randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S15), TPS8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pembrolizumab in Patients with Advanced Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02784171 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- A Study of Pembrolizumab in Combination with Cisplatin and Pemetrexed in Advanced Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM) (MK-3475-A17). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04153565 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- A Study of Yervoy and Opdivo Combination Therapy in Participants with Unresectable Advanced/Recurrent Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05324436 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- BEAT-Meso: Bevacizumab and Atezolizumab in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03762018 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Forde, P.M.; Anagnostou, V.; Sun, Z.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Kindler, H.L.; Niknafs, N.; Purcell, T.; Santana-Davila, R.; Dudek, A.; Borghaei, H.; et al. Durvalumab with platinum-pemetrexed for unresectable pleural mesothelioma: Survival, genomic and immunologic analyses from the phase 2 PrE0505 trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1910–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.S.; Righi, L.; Koeppen, H.; Zou, W.; Izzo, S.; Grosso, F.; Libener, R.; Loiacono, M.; Monica, V.; Buttigliero, C.; et al. Molecular and Histopathological Characterization of the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Advanced Stage of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, M.A.; Fumarola, C.; La Monica, S.; Alfieri, R. New therapeutic strategies for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 123, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, L.; Duregon, E.; Vatrano, S.; Izzo, S.; Giorcelli, J.; Rondón-Lagos, M.; Ascoli, V.; Ruffini, E.; Ventura, L.; Volante, M.; et al. BRCA1-Associated Protein 1 (BAP1) Immunohistochemical Expression as a Diagnostic Tool in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Classification: A Large Retrospective Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.G.; Mutti, L. Immunotherapy for mesothelioma: A critical review of current clinical trials and future perspectives. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, S100–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Study of MGD013 in Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic Neoplasms. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03219268 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- SL-279252 (PD1-Fc-OX40L) in Subjects with Advanced Solid Tumors or Lymphomas. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03894618 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Study of the Efficacy and Safety of the Bintrafusp Alfa in Previously Treated Advanced Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05005429 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Pembrolizumab Plus Lenvatinib in Second Line and Third Line Malignant Pleural mesothelioma Patients. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04287829 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Douma, L.A.H.; de Gooijer, C.J.; Noort, V.v.d.; Lalezari, F.; de Vries, J.F.; Vermeulen, M.; Schilder, B.; Smesseim, I.; Baas, O.; Burgers, J.A. OA04.06 PEMbrolizumab Plus Lenvatinib in Second and Third Line Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Patients: A Single Arm Phase II Study (PEMMELA). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haakensen, V.D.; Nowak, A.K.; Ellingsen, E.B.; Farooqi, S.J.; Bjaanæs, M.M.; Horndalsveen, H.; Mcculloch, T.; Grundberg, O.; Cedres, S.; Helland, A. NIPU: A randomised, open-label, phase II study evaluating nivolumab and ipilimumab combined with UV1 vaccination as second line treatment in patients with malignant mesothelioma. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nivolumab and Ipilimumab +/− UV1 Vaccination as Second Line Treatment in Patients with Malignant Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04300244 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- MTG201 Plus Nivolumab in Patients with Relapsed Pleural Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04013334 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Using a Targeted Cancer Vaccine (Galinpepimut-S) With Immunotherapy (Nivolumab) in Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04040231 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Pembrolizumab and Hypofractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04166734 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Phase II Nivolumab and Ramucirumab for Patients with Previously-Treated Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03502746 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Atezolizumab and Bevacizumab in Treating Patients with Rare Solid Tumors. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03074513 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Kennedy, P.P.; Kile, Q.; Jacobson, B.; Ettestad, B.; Zorko, N.; Hallstrom, C.; Kodal, B.; Todhunter, D.; Vallera, D.; Berk, G.; et al. 1202 Tri-specific killer engagers target natural killer cells towards mesothelioma. In Regular and Young Investigator Award Abstracts; BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.: London, UK, 2022; p. A1244. [Google Scholar]
- Safety Study of MGD009 in B7-H3-expressing Tumors. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02628535 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Aggarwal, C.; Joshua, A.; Ferris, R.; Antonia, S.; Rahma, O.; Tolcher, A.; Cohen, R.; Lou, Y.; Hauke, R.; Vogelzang, N.; et al. Rhode Island Hospital. Peninsula and Southeast Oncology. Available online: http://ir.macrogenics.com/events.cfm (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Safety Study of Enoblituzumab (MGA271) in Combination with Pembrolizumab or MGA012 in Refractory Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02475213 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Zalcman, G.; Mazieres, J.; Margery, J.; Greillier, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Molinier, O.; Corre, R.; Monnet, I.; Gounat, V.; et al. Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed pleural mesothelioma in the Mesothelioma Avastin Cisplatin Pemetrexed Study (MAPS): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scagliotti, G.V.; Gaafar, R.; Nowak, A.K.; Nakano, T.; van Meerbeeck, J.; Popat, S.; Vogelzang, N.; Gross, F.; Aboelhassan, R.; Jakopovic, M.; et al. Nintedanib in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin for chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced malignant pleural mesothelioma (LUME-Meso): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makker, V.; Colombo, N.; Casado Herráez, A.; Santin, A.D.; Colomba, E.; Miller, D.S.; Fujiwara, K.; Pignata, S.; Baron-Hay, S.; Ray-Coquard, I.; et al. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab for Advanced Endometrial Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reckamp, K.L.; Redman, M.W.; Dragnev, K.H.; Minichiello, K.; Villaruz, L.C.; Faller, B.; Al Baghdadi, T.; Hines, S.; Everhart, L.; Highleyman, L.; et al. Phase II Randomized Study of Ramucirumab and Pembrolizumab Versus Standard of Care in Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Previously Treated with Immunotherapy—Lung-MAP S1800A. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2295–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Thomas, A.; Alewine, C.; Le, D.T.; Jaffee, E.M.; Pastan, I. Mesothelin Immunotherapy for Cancer: Ready for Prime Time? J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4171–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anti-Mesothelin Immunotoxin LMB-100 Followed by Pembrolizumab in Malignant Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03644550 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Safety and Efficacy of Listeria in Combination with Chemotherapy as Front-line Treatment for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01675765 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Evaluation of CRS-207 with Pembrolizumab in Previously Treated Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03175172 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Hassan, R.; Alley, E.; Kindler, H.; Antonia, S.; Jahan, T.; Honarmand, S.; Nair, N.; Whiting, C.; Enstrom, A.; Lemmens, E.; et al. Clinical Response of Live-Attenuated, Listeria monocytogenes Expressing Mesothelin (CRS-207) with Chemotherapy in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5787–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study of CRS-207, Nivolumab, and Ipilimumab with or without GVAX Pancreas Vaccine (with Cy) in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03190265 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Klampatsa, A.; Dimou, V.; Albelda, S.M. Mesothelin-targeted CAR-T cell therapy for solid tumors. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2021, 21, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klampatsa, A.; Haas, A.; Moon, E.; Albelda, S. Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cell Therapy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM). Cancers 2017, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusumilli, P.S.; Zauderer, M.G.; Rivière, I.; Solomon, S.B.; Rusch, V.W.; O’Cearbhaill, R.E.; Zhu, A.; Cheema, W.; Chintala, N.; Halton, E.; et al. A Phase I Trial of Regional Mesothelin-Targeted CAR T-cell Therapy in Patients with Malignant Pleural Disease, in Combination with the Anti–PD-1 Agent Pembrolizumab. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2748–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morello, A.; Sadelain, M.; Adusumilli, P.S. Mesothelin-Targeted CARs: Driving T Cells to Solid Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldea, M.; Benitez, J.C.; Chaput, N.; Besse, B. New Immunotherapy Combinations Enter the Battlefield of Malignant Mesothelioma. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2674–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phase 1/2 Trial of Gavo-cel (TC-210) in Patients with Advanced Mesothelin-Expressing Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03907852 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- A Phase 1/2 Trial of TC-510 In Patients with Advanced Mesothelin-Expressing Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05451849 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Intratumor Injection of Anti-Mesothelin Immunotoxin LMB-100 with Ipilimumab in Malignant Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04840615 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Mesothelin-Targeted CAR T-Cell Therapy in Patients with Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04577326 (accessed on 23 May 2023).
- Autologous CAR-T/TCR-T Cell Immunotherapy for Malignancies. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03638206 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- CAR T Cells in Mesothelin Expressing Cancers. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03054298 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Pembrolizumab with or without Anetumab Ravtansine in Treating Patients with Mesothelin-Positive Pleural Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03126630 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Malignant Pleural Disease Treated with Autologous T Cells Genetically Engineered to Target the Cancer-Cell Surface Antigen Mesothelin—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02414269 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Nishimura, Y.; Kumagai-Takei, N.; Matsuzaki, H.; Lee, S.; Maeda, M.; Kishimoto, T.; Fukuoka, K.; Nakano, T.; Otsuki, T. Functional Alteration of Natural Killer Cells and Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes upon Asbestos Exposure and in Malignant Mesothelioma Patients. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 238431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai-Takei, N.; Nishimura, Y.; Matsuzaki, H.; Lee, S.; Yoshitome, K.; Ito, T.; Otsuki, T. Effect of IL-15 addition on asbestos-induced suppression of human cytotoxic T lymphocyte induction. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2021, 26, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.P.; Kile, Q.; Jacobson, B.; Ettestad, B.; Miller, S.; Miller, J.; Patel, M.; Felices, M. 465 Synergistic approaches to overcome the solid tumor microenvironment of mesothelioma with natural killer cell-focused immunotherapy. In Regular and Young Investigator Award Abstracts; BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.: London, UK, 2022; p. A485. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, S.S.; Carol, H.; Biro, M. TriKEs and BiKEs join CARs on the cancer immunotherapy highway. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2016, 12, 2790–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DENdritic Cell Immunotherapy for Mesothelioma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03610360238431 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Pembrolizumab Plus Autologous Dendritic Cell Vaccine in Patients with PD-L1 Negative Advanced Mesothelioma Who Have Failed Prior Therapies. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03546426238431 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Silberhumer, G.R.; Brader, P.; Wong, J.; Serganova, I.S.; Gönen, M.; Gonzalez, S.J.; Blasberg, R.; Zamarin, D.; Fong, Y. Genetically Engineered Oncolytic Newcastle Disease Virus Effectively Induces Sustained Remission of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2761–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Peng, K.W.; Dingli, D.; Kratzke, R.A.; Russell, S.J. Oncolytic measles viruses encoding interferon β and the thyroidal sodium iodide symporter gene for mesothelioma virotherapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmon, C.L.; Saloura, V.; Fridlender, Z.G.; Wongthida, P.; Diaz, R.M.; Thompson, J.; Kottke, T.; Federspiel, M.; Barber, G.; Albelda, S.; et al. Expression of IFN-β Enhances Both Efficacy and Safety of Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus for Therapy of Mesothelioma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7713–7720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, D.F.; Kratzke, R.A. Oncolytic Viral Therapy for Mesothelioma. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecora, A.L.; Rizvi, N.; Cohen, G.I.; Meropol, N.J.; Sterman, D.; Marshall, J.L.; Gross, P.; O’Neil, J.; Groene, W.; Roberts, M.; et al. Phase I Trial of Intravenous Administration of PV701, an Oncolytic Virus, in Patients with Advanced Solid Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2251–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, R.; Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh, H.; Farzanehpour, M.; Dorostkar, R.; Ranjbar, R.; Bolandian, M.; Nodooshan, M.M.; Alvanegh, A.G. Combination therapy with CAR T cells and oncolytic viruses: A new era in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Luo, Y.; Da, T.; Guedan, S.; Ruella, M.; Scholler, J.; Keith, B.; Young, R.; Engels, B.; Sorsa, S.; et al. Pancreatic cancer therapy with combined mesothelin-redirected chimeric antigen receptor T cells and cytokine-armed oncolytic adenoviruses. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e99573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trial | Year | Phase | Intervention | Size | Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05005429 | 2021 | II | Bintrafusp alfa | 47 | PFS 4 |
| PEMMELA | 2020 | II | Pembrolizumab and Lenvatinib | 36 | ORR 5 |
| NIPU | 2020 | II | Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab with UV1 vaccine | 118 | PFS 8 |
| NCT04013334 | 2019 | II | MTG201 1 plus Nivolumab | 12 | ORR 5 |
| NCT04040231 | 2019 | I | Galinpepimut-S 1 plus Nivolumab | 10 | MTD 6 |
| MESO-PRIME | 2019 | I | Pembrolizumab plus HSR 2 | 18 | DLT 7 |
| NCT03894618 | 2019 | I | SL-279252 (PD1-Fc-OX40L) 3 | 87 | MTD 6/Safety |
| NCT03502746 | 2018 | II | Nivolumab plus Ramucirumab | 35 | ORR 5 |
| NCT03074513 | 2017 | II | Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab | 137 | ORR 5 |
| NCT03219268 | 2017 | I | MGD013 | 353 | MTD 6AEs 8 |
| Trial | Year | Phase | Intervention | Size | Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05451849 | 2022 | I/II | Mesothelin TruC T cells | 115 | RP2D 1 (Phase I)/ORR 4 and DCR 6 (Phase II) |
| NCT04840615 | 2021 | I | LMB-100 plus Ipilimumab | 20 | AEs 2/DLT 3 |
| NCT04577326 | 2020 | I | Mesothelin CAR T engineered with anti-PD-1 | 30 | MTD 5 |
| NCT03907852 | 2019 | I/II | Mesothelin targeted T cells: Gavo-cel | 175 | DLT 3/ORR 4 |
| NCT03638206 | 2018 | I/II | Mesothelin targeted T cells | 73 | AEs 2 |
| NCT03054298 | 2017 | I | Mesothelin targeted T cells: huCART-mesocells | 27 | AEs 1/Clinical benefit |
| NCT03126630 | 2017 | I/II | Pembrolizumab plus anetumab ravtansine 2 | 110 | DLT 3/ORR 4 |
| NCT02414269 | 2015 | I/II | Mesothelin targeted T cells Plus Pembrolizumab | 113 | AEs 2/Clinical benefit |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rondon, L.; Fu, R.; Patel, M.R. Success of Checkpoint Blockade Paves the Way for Novel Immune Therapy in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers 2023, 15, 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15112940
Rondon L, Fu R, Patel MR. Success of Checkpoint Blockade Paves the Way for Novel Immune Therapy in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers. 2023; 15(11):2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15112940
Chicago/Turabian StyleRondon, Lizbeth, Roberto Fu, and Manish R. Patel. 2023. "Success of Checkpoint Blockade Paves the Way for Novel Immune Therapy in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma" Cancers 15, no. 11: 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15112940
APA StyleRondon, L., Fu, R., & Patel, M. R. (2023). Success of Checkpoint Blockade Paves the Way for Novel Immune Therapy in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers, 15(11), 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15112940