Cross-Resistance between Platinum-Based Chemotherapy and PARP Inhibitors in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
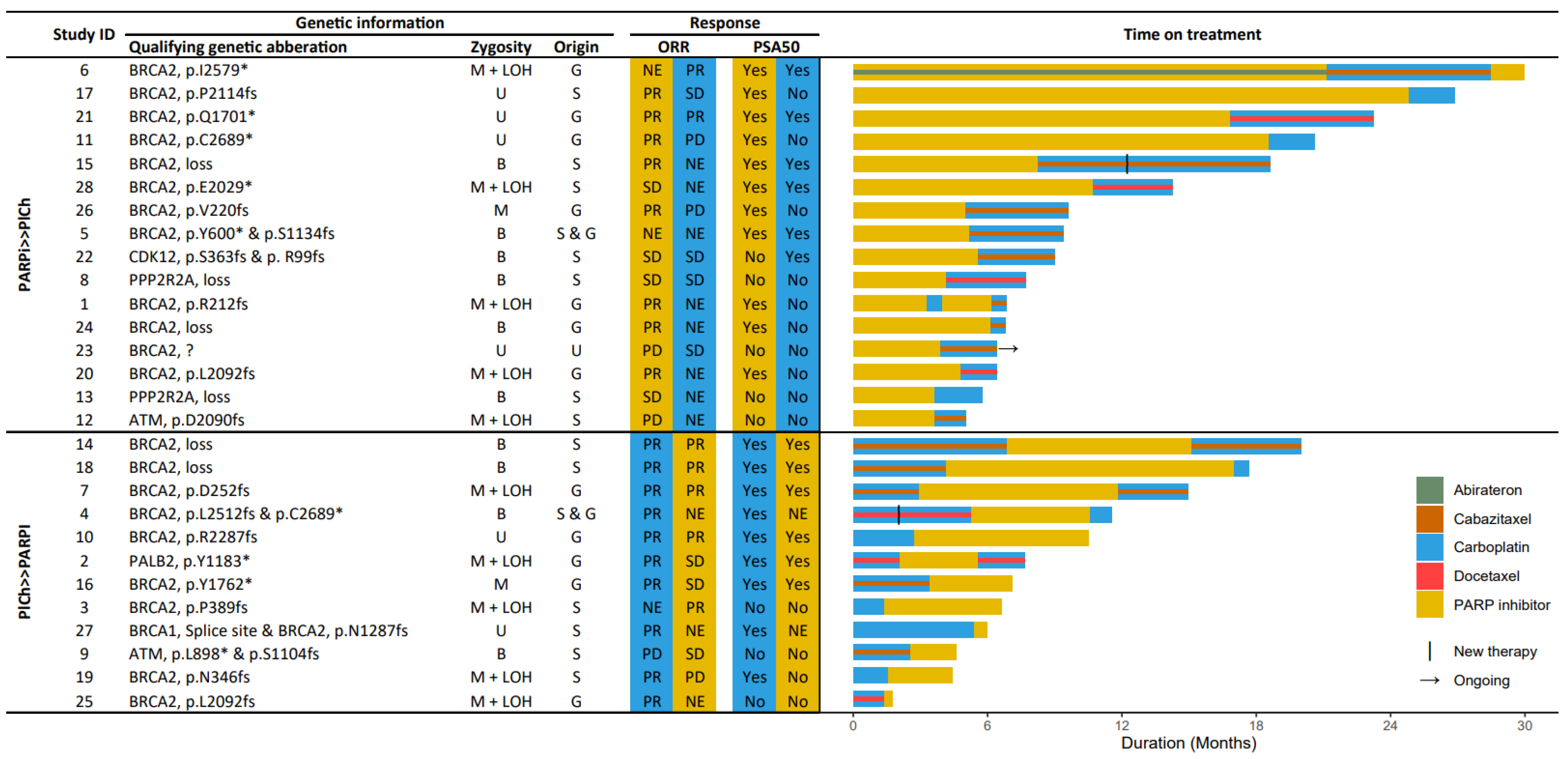
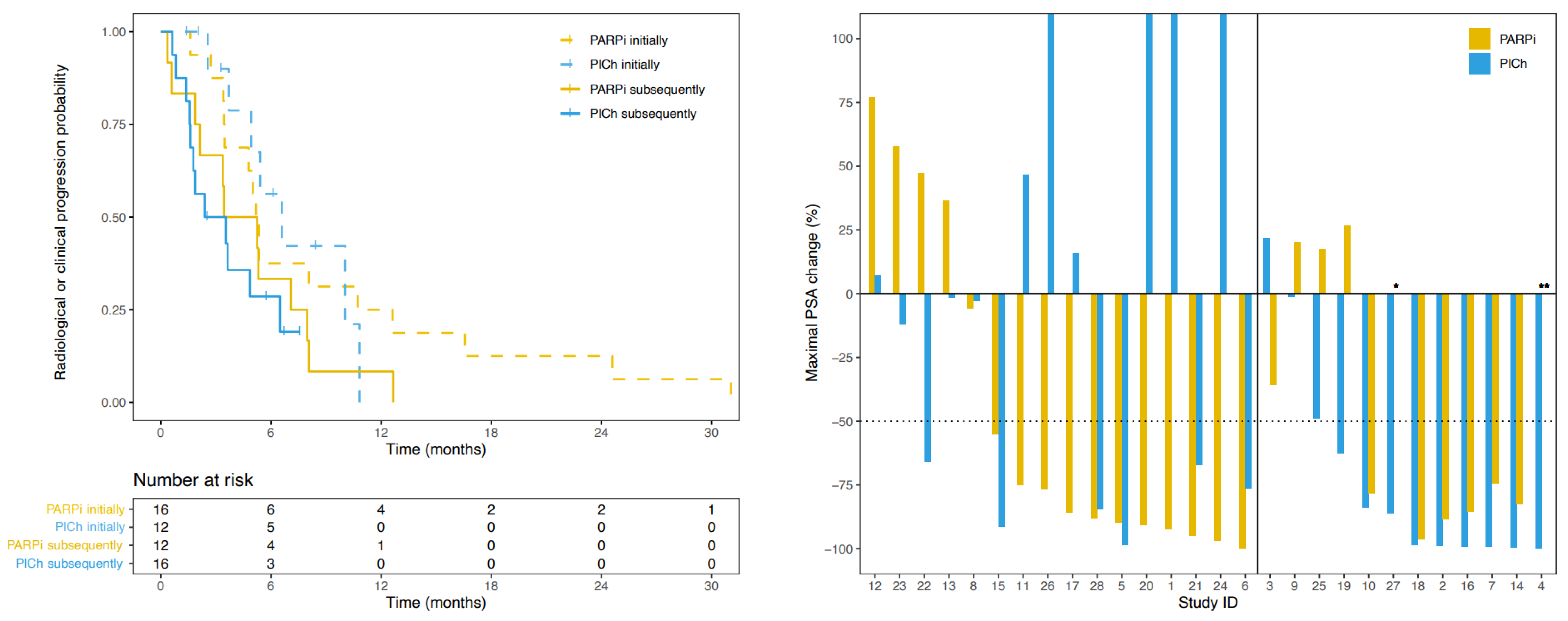
3.2. HRR-Targeting Agents
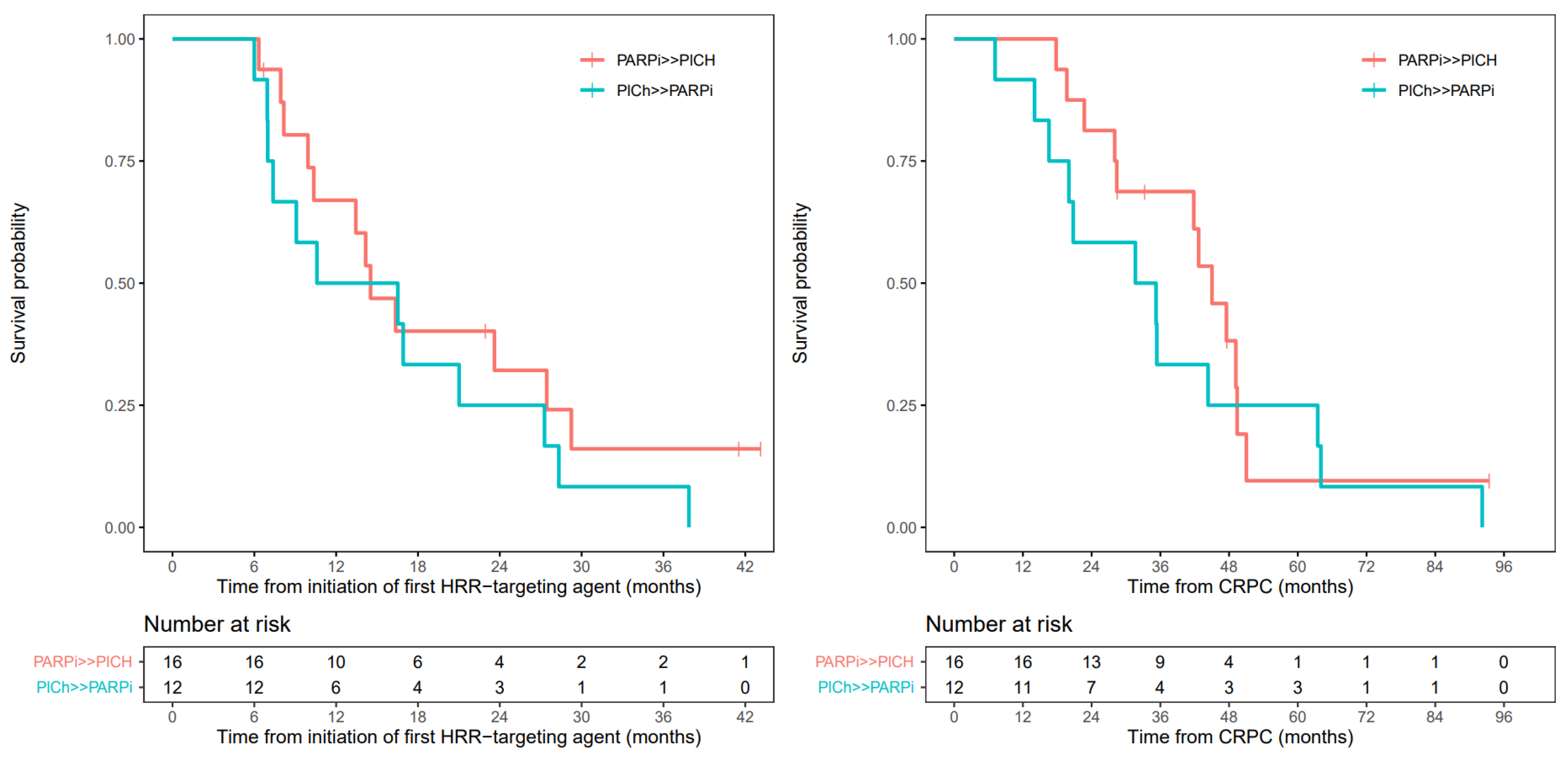
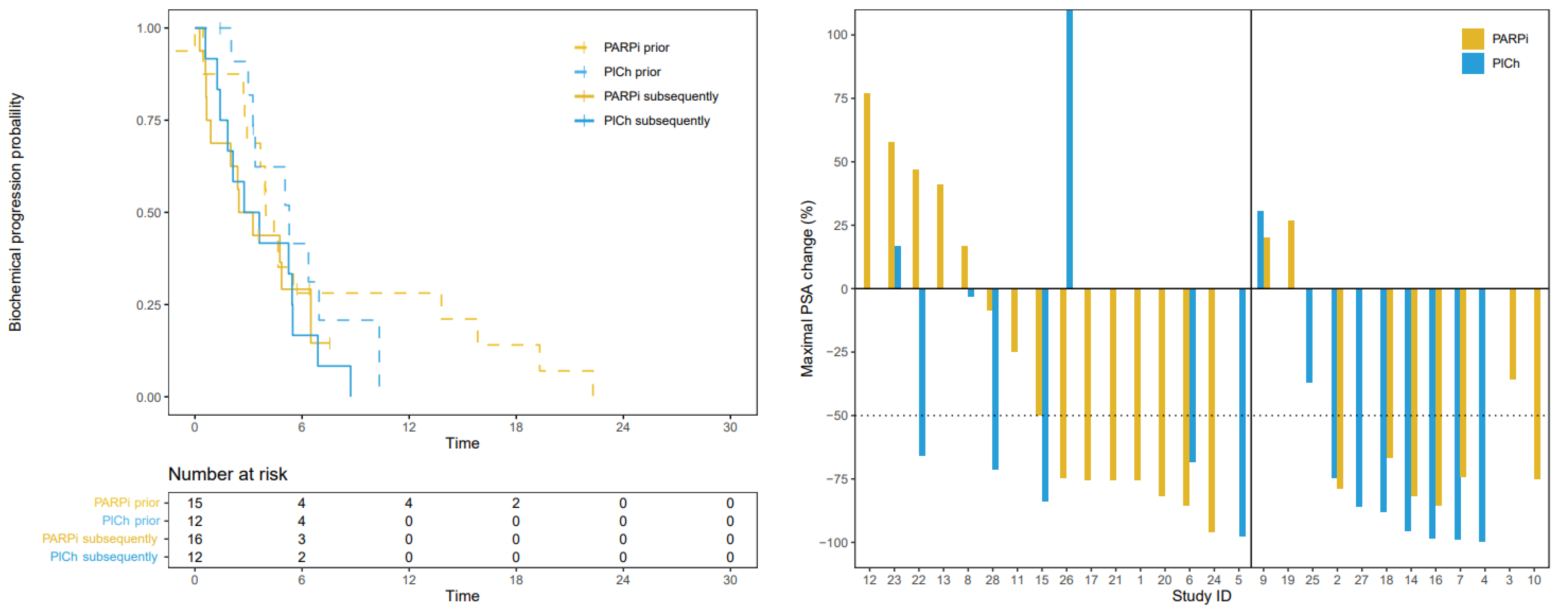
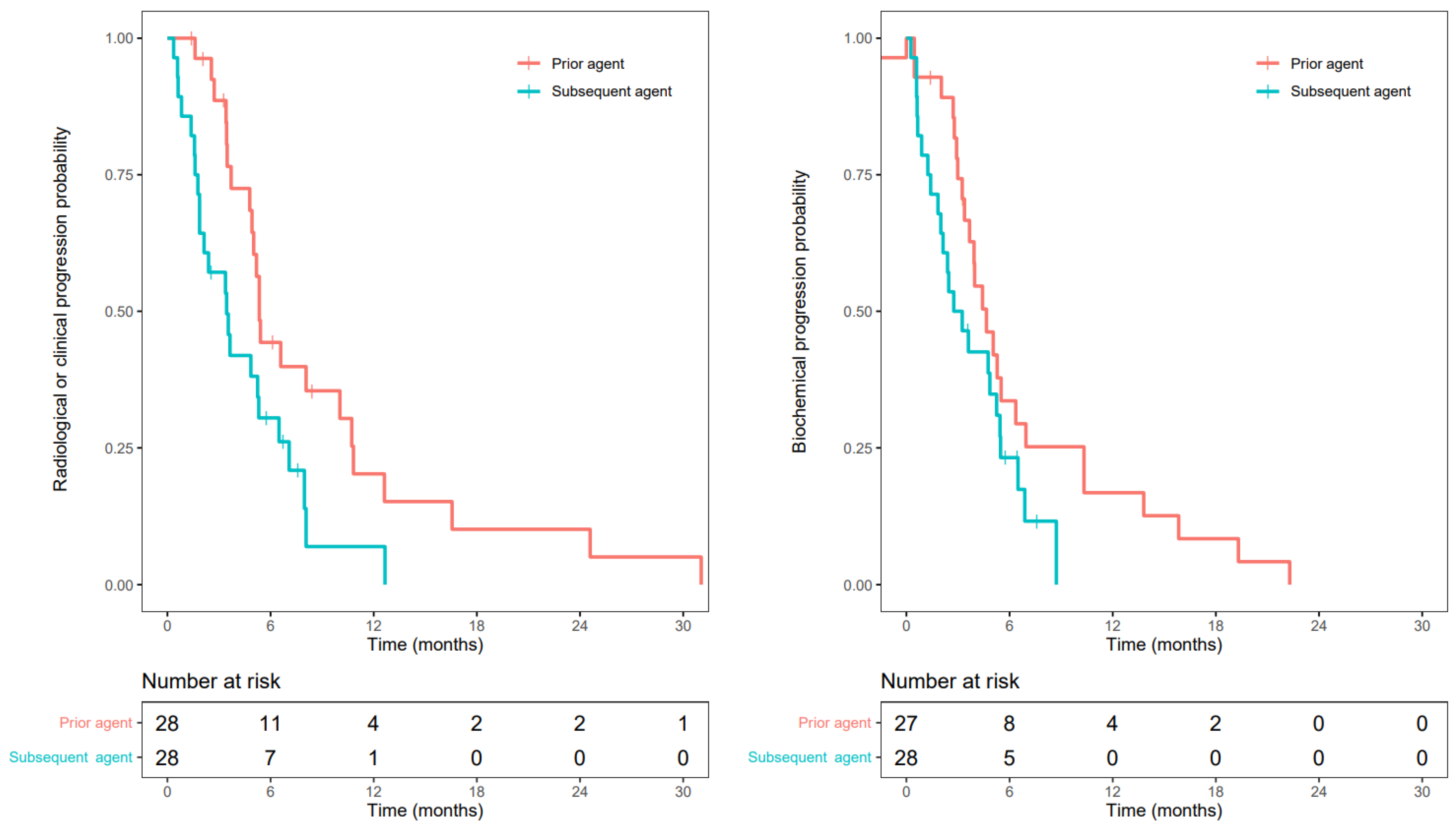
3.3. Progression-Free Survival
3.4. Prostate Specific Antigen Response
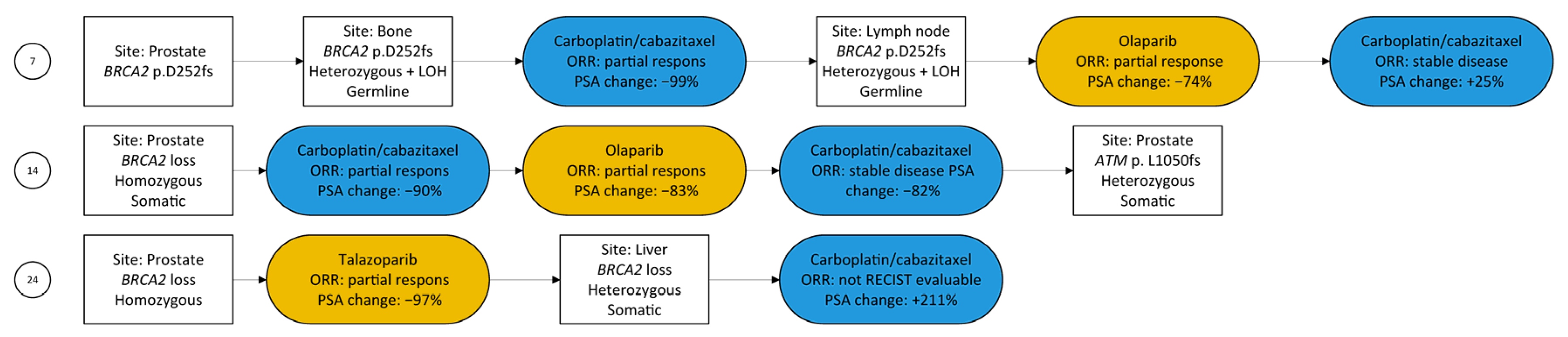
3.5. Radiographic Response
3.6. Overall Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| PARPi | PlCh | Hazard Ratio | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median [95%-CI] | |||||
| Initial HRR-targeting agent | PFS, months | 5.3 [3.5–16.6] | 6.6 [4.9–NA] | 0.98 | 0.962 |
| bPFS, months | 4.0 [2.9–19.3] | 5.3 [3.4–NA] | 1.22 | 0.658 | |
| Subsequent HRR-targeting agent | PFS, months | 4.3 [2.1–NA] | 3.0 [1.6–NA] | 1.33 | 0.524 |
| bPFS, months | 3.2 [1.8–NA] | 2.9 [0.9–NA] | 0.97 | 0.944 | |


References
- de Bono, J.; Mateo, J.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Shore, N.; Sandhu, S.; Chi, K.N.; Sartor, O.; Agarwal, N.; Olmos, D.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, N.W.; Armstrong, A.J.; Thiery-Vuillemin, A.; Oya, M.; Shore, N.; Loredo, E.; Procopio, G.; de Menezes, J.; Girotto, G.; Arslan, C.; et al. Abiraterone and Olaparib for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2200043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizazi, K.; Piulats, J.M.; Reaume, M.N.; Ostler, P.; McDermott, R.; Gingerich, J.R.; Pintus, E.; Sridhar, S.S.; Bambury, R.M.; Emmenegger, U.; et al. Rucaparib or Physician’s Choice in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abida, W.; Campbell, D.; Patnaik, A.; Shapiro, J.D.; Sautois, B.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Voog, E.G.; Bryce, A.H.; McDermott, R.; Ricci, F.; et al. Non-BRCA DNA Damage Repair Gene Alterations and Response to the PARP Inhibitor Rucaparib in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Analysis from the Phase II TRITON2 StudyRucaparib in mCRPC with a Non-BRCA DDR Gene Alteration. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2487–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Scher, H.I.; Sandhu, S.; Efstathiou, E.; Lara, P.N.; Yu, E.Y.; George, D.J.; Chi, K.N.; Saad, F.; Ståhl, O.; et al. Niraparib in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer and DNA repair gene defects (GALAHAD): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bono, J.S.; Mehra, N.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Castro, E.; Dorff, T.; Stirling, A.; Stenzl, A.; Fleming, M.T.; Higano, C.S.; Saad, F.; et al. Talazoparib monotherapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with DNA repair alterations (TALAPRO-1): An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1250–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.M.; Barnett, E.; Nauseef, J.T.; Nguyen, B.; Stopsack, K.H.; Wibmer, A.; Flynn, J.R.; Heller, G.; Danila, D.C.; Rathkopf, D.; et al. Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Metastatic Prostate Cancer with DNA Repair Gene Alterations. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.; Omlin, A.; Higano, C.; Sweeney, C.; Chanza, N.M.; Mehra, N.; Kuppen, M.C.P.; Beltran, H.; Conteduca, V.; De Almeida, D.V.P.; et al. Activity of Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer with and without DNA Repair Gene Aberrations. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2021692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Ear, U.S.; Koller, B.H.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Bishop, D.K. The breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 is required for subnuclear assembly of Rad51 and survival following treatment with the DNA cross-linking agent cisplatin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23899–23903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slootbeek, P.H.J.; Duizer, M.L.; van der Doelen, M.J.; Kloots, I.S.H.; Kuppen, M.C.P.; Westgeest, H.M.; Groot, C.A.U.; Naga, S.P.; Ligtenberg, M.J.L.; van Oort, I.M.; et al. Impact of DNA damage repair defects and aggressive variant features on response to carboplatin-based chemotherapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopsack, K.H. Efficacy of PARP Inhibition in Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer is Very Different with Non-BRCA DNA Repair Alterations: Reconstructing Prespecified Endpoints for Cohort B from the Phase 3 PROfound Trial of Olaparib. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerantz, M.M.; Spisák, S.; Jia, L.; Cronin, A.M.; Csabai, I.; Ledet, E.; Sartor, A.O.; Rainville, I.; O’Connor, E.P.; Herbert, Z.T.; et al. The association between germline BRCA2 variants and sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy among men with metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer 2017, 123, 3532–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.H.; Pritchard, C.C.; Boyd, T.; Nelson, P.S.; Montgomery, B. Biallelic inactivation of BRCA2 in platinum-sensitive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loehr, A.; Hussain, A.; Patnaik, A.; Bryce, A.H.; Castellano, D.; Font, A.; Shapiro, J.; Zhang, J.; Sautois, B.; Vogelzang, N.J.; et al. Emergence of BRCA Reversion Mutations in Patients with Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer After Treatment with Rucaparib. Eur. Urol. 2022, 83, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, J.; Mateo, J.; Yuan, W.; Mossop, H.; Porta, N.; Miranda, S.; Perez-Lopez, R.; Dolling, D.; Robinson, D.R.; Sandhu, S.; et al. Circulating Cell-Free DNA to Guide Prostate Cancer Treatment with PARP Inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtishak, K.; Attard, G.; Kanno, T.; Thomas, S.; Mason, G.E.; Espina, B.; Zhu, E.; Hutnick, N.; Guckert, M.; del Corral, A.; et al. High prevalence and heterogeneity of emergence of BRCA reversion mutations at progression on niraparib treatment in BRCA-mutant metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) patients. Cancer Res. 2022, 82 (Suppl. S12), 4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, B.A.; Collier, K.A.; Nagy, R.J.; Pamarthy, S.; Sagar, V.; Fairclough, S.; Odegaard, J.; Lanman, R.B.; Costa, R.; Taxter, T.; et al. Acquired resistance to poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor olaparib in BRCA2-associated prostate cancer resulting from biallelic BRCA2 reversion mutations restores both germline and somatic loss-of-function mutations. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.H.; Salipante, S.J.; Nelson, P.S.; Montgomery, B.; Pritchard, C.C. Polyclonal BRCA2 reversion mutations detected in circulating tumor DNA after platinum chemotherapy in a patient with metastatic prostate cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, PO.17.00169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A.D.; Nguyen, M.; Pintus, E. Polyclonal BRCA2 mutations following carboplatin treatment confer resistance to the PARP inhibitor rucaparib in a patient with mCRPC: A case report. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.M.; Datto, M.; Duncavage, E.J.; Kulkarni, S.; Lindeman, N.I.; Roy, S.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Wolff, D.J.; Younes, A.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation and reporting of sequence variants in cancer: A joint consensus recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and College of American Pathologists. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, H.I.; Morris, M.J.; Stadler, W.M.; Higano, C.; Basch, E.; Fizazi, K.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Beer, T.M.; Carducci, M.A.; Chi, K.N.; et al. Trial design and objectives for castration-resistant prostate cancer: Updated recommendations from the Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials Working Group 3. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanti, S.; Goffin, K.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Herrmann, K.; Maurer, T.; MacLennan, S.; Oprea-Lager, D.E.; Oyen, W.J.; Rouvière, O.; Mottet, N.; et al. Consensus statements on PSMA PET/CT response assessment criteria in prostate cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.L.; Kiedrowski, L.A.; Chae, Y.K. The dynamic landscape of BRCA1 reversion mutations from indel to SNV in a patient with ovarian cancer treated with PARP-inhibitors and immunotherapy. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, S.L.; Brough, R.; Lord, C.J.; Natrajan, R.; Vatcheva, R.; Levine, D.A.; Boyd, J.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Ashworth, A. Resistance to therapy caused by intragenic deletion in BRCA2. Nature 2008, 451, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bernhardy, A.J.; Cruz, C.; Krais, J.J.; Nacson, J.; Nicolas, E.; Peri, S.; van der Gulden, H.; van der Heijden, I.; O’Brien, S.W.; et al. The BRCA1-Δ11q alternative splice isoform bypasses germline mutations and promotes therapeutic resistance to PARP inhibition and cisplatin. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2778–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelt, B.; Comino-Méndez, I.; de Bruijn, I.; Tian, L.; Meisel, J.L.; García-Murillas, I.; Fribbens, C.; Cutts, R.; Martelotto, L.G.; Ng, C.K.; et al. Diverse BRCA1 and BRCA2 Reversion Mutations in Circulating Cell-Free DNA of Therapy-Resistant Breast or Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6708–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helleday, T. The underlying mechanism for the PARP and BRCA synthetic lethality: Clearing up the misunderstandings. Mol. Oncol. 2011, 5, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Peer, C.J.; Yu, M.; Amable, L.; Gordon, N.; Annunziata, C.M.; Houston, N.; Goey, A.K.; Sissung, T.M.; Parker, B.; et al. Sequence-Specific Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Phase I/Ib Study of Olaparib Tablets and Carboplatin in Women’s Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peer, C.J.; Lee, J.-M.; Roth, J.; Rodgers, L.; Nguyen, J.; Annunziata, C.M.; Minasian, L.; Kohn, E.C.; Figg, W.D. Population pharmacokinetic analyses of the effect of carboplatin pretreatment on olaparib in recurrent or refractory women’s cancers. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total Cohort | PARPi >> PlCh | PlCh >> PARPi | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median [IQR] or N (Valid %) | ||||
| Age at initial diagnosis, years | 61.0 [55.5–64.7] | 60.7 [55.5–64.7] | 61.3 [55.0–65.5] | 0.833 |
| Initial PSA, ng/mL 1 | 91 [11.0–247.0] | 68 [15.0–234.0] | 98 [9.8–237.0] | 0.768 2 |
| Time from start ADT tot CRPC, months | 13.5 [8.8–21.9] | 17.9 [11.7–25.5] | 9.6 [7.3–15.9] | 0.040 3 |
| Age at CRPC, years | 62.7 [60.5–66.2] | 62.7 [60.5–66.2] | 63.1 [56.4–66.2] | 0.693 |
| ISUP classification | ||||
| 1 | 1 (3.7) | 1 (6.7) | 0 | 1.000 |
| 2 | 1 (3.7) | 1 (6.7) | 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4 | 5 (18.5) | 3 (20.0) | 2 (16.7) | |
| 5 | 20 (74.1) | 10 (66.7) | 10 (83.3) | |
| Missing | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| Synchronous metastasis | ||||
| Yes | 18 (64.3) | 7 (43.8) | 11 (91.7) | 0.016 |
| No | 10 (35.7) | 9 (56.3) | 1 (8.3) | |
| Treatment before first HRRtA | ||||
| Treatment lines for CRPC | 3 [2–4] | 3 [2–4] | 3 [2–3.3] | 0.753 |
| Prior taxane | 27 (96.4) | 15 (93.8) | 12 (100) | 1.000 |
| Prior ARSI | 27 (96.4) | 15 (93.8) | 12 (100) | 1.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slootbeek, P.H.J.; Kloots, I.S.H.; van Oort, I.M.; Kroeze, L.I.; Schalken, J.A.; Bloemendal, H.J.; Mehra, N. Cross-Resistance between Platinum-Based Chemotherapy and PARP Inhibitors in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102814
Slootbeek PHJ, Kloots ISH, van Oort IM, Kroeze LI, Schalken JA, Bloemendal HJ, Mehra N. Cross-Resistance between Platinum-Based Chemotherapy and PARP Inhibitors in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(10):2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102814
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlootbeek, Peter H. J., Iris S. H. Kloots, Inge M. van Oort, Leonie I. Kroeze, Jack A. Schalken, Haiko J. Bloemendal, and Niven Mehra. 2023. "Cross-Resistance between Platinum-Based Chemotherapy and PARP Inhibitors in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 10: 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102814
APA StyleSlootbeek, P. H. J., Kloots, I. S. H., van Oort, I. M., Kroeze, L. I., Schalken, J. A., Bloemendal, H. J., & Mehra, N. (2023). Cross-Resistance between Platinum-Based Chemotherapy and PARP Inhibitors in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancers, 15(10), 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102814







