Simple Summary
Penile squamous cell carcinomas harbouring mutations of TP53 have an increased risk of lymph node metastases and an impaired prognosis, but the mutational analysis of the TP53 gene is not available in many pathology laboratories. Although p53 immunohistochemistry (IHC) has been proposed as an alternative to the molecular analysis, the current method of evaluation of p53 IHC has many inaccuracies. The aim of our study was to determine, in a series of 40 penile tumours, if a recently described pattern-based framework of p53 IHC evaluation correlates better than the classical method with the TP53 mutational status. Our results show that the new method has a very good correlation with TP53 mutations (95% sensitivity; 92% specificity), higher than that of the classical method, and can be considered as a reliable surrogate of the TP53 mutational status. This new framework can help clinicians to better define risk groups and refine treatment strategies.
Abstract
p53 immunohistochemistry (IHC) has been proposed as a surrogate for TP53 mutations in penile squamous cell carcinomas (PSCC). We aimed to evaluate the performance of a pattern-based evaluation of p53 IHC in PSCC. Human papilloma virus (HPV) DNA testing, p16 and p53 IHC, and whole exome sequencing were performed in a series of 40 PSCC. p53 IHC was evaluated following a pattern-based framework and conventional p53 IHC evaluation. Out of 40 PSCC, 12 (30.0%) were HPV-associated, and 28 (70.0%) were HPV-independent. The agreement between the p53 IHC pattern-based evaluation and TP53 mutational status was almost perfect (k = 0.85). The sensitivity and accuracy of the pattern-based framework for identifying TP53 mutations were 95.5% and 92.5%, respectively, which were higher than the values of conventional p53 IHC interpretation (54.5% and 70.0%, respectively), whereas the specificity was the same (88.9%). In conclusions, the pattern-based framework improves the accuracy of detecting TP53 mutations in PSCC compared to the classical p53 IHC evaluation.
1. Introduction
Penile squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC) is an unusual neoplasm, with incidence rates that range from 0.5 to 1.6 per 100,000 inhabitants in different European regions [1]. Several risk factors have been identified as possibly implicated in the development of PSCC, including local chronic inflammatory conditions and sexual behaviour, especially exposure to human papillomavirus (HPV) [2].
Two distinct pathways seem to be involved in the carcinogenesis of PSCC: one driven by HPV (HPV-associated) and another independent of HPV infection (HPV-independent) [1]. In keeping with this etiological categorization, the current version of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of urological tumours [2] divides PSCC according to the presence or absence of HPV. As a consequence, the use of immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for p16, a surrogate marker of the presence of HPV, has become a recommended biomarker to accurately classify these tumours [3]. In Western Europe, a marked predominance of HPV-independent and a low frequency of HPV-associated tumours (70% vs. 30%) has been reported in most studies [4].
The molecular mechanisms involved in HPV-associated PSCC are characterized by genomic instability secondary to the overexpression of the oncoproteins E6 and E7, which lead to uncontrolled activation of the cell cycle [5,6]. In contrast, the pathogenesis of HPV-independent PSCC is less well understood [1]. TP53 mutations [7,8,9,10] have frequently been reported in this HPV-independent subset of PSCC. Moreover, several studies [11,12] have suggested that TP53 mutations might be associated with a high frequency of nodal metastases, a factor known to be strongly correlated with impaired prognosis [13,14]. These studies have suggested that TP53 mutational status could add relevant prognostic information in PSCC [8,11]. However, molecular analysis of the TP53 gene is technically challenging and not available in many pathology laboratories. Thus, the evaluation of p53 IHC has been proposed as a more feasible alternative [15]. Although a few studies have shown a correlation between p53 IHC overexpression and impaired prognosis in PSCC [16,17], unfortunately, there is a lack of standardization in the evaluation of p53 IHC. Indeed, in most published studies, the assessment of p53 IHC has been based on the percentage of positive nuclei at the basal and parabasal layers [15], and p53 is considered abnormal when diffuse overexpression is identified. However, the cut-off levels have not been clearly established, and thus, the actual meaning of these percentages is not known. Not surprisingly, the studies analysing the correlation between p53 IHC expression and TP53 mutational status in PSCC have shown discrepant results [18].
Interestingly, the histological features of PSCC as well as the two pathogenic pathways are very similar to the pathology and etiopathogenesis of vulvar carcinomas [19]. Recently, a well-defined, pattern-based framework of p53 IHC evaluation showing a close correlation with TP53 mutational status has been described in vulvar tumours [20,21]. This pattern-based framework includes four main abnormal p53 IHC patterns that strongly correlate with TP53 mutations and two normal patterns that reflect a wild-type protein [20,21]. Moreover, based on a combination of HPV status and p53 IHC, three prognostic subtypes of tumours have recently been identified in vulvar squamous cell carcinomas [22].
Due to the marked similarities between PSCC and vulvar carcinoma [23], we hypothesized that this pattern-based framework of p53 IHC interpretation [21] could also be applied to PSCC and have similar implications to those defined in the vulva. Thus, we aimed to explore the correlation between p53 IHC evaluated as described in vulva [21] and the TP53 mutational status in a series of PSCC from a single institution in Spain, comparing its performance with the conventional interpretation of p53 IHC that generally includes only diffuse overexpression.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Case Selection
All PSCCs diagnosed and surgically treated at the Hospital Clinic de Barcelona from 2000 to 2021 were retrieved, and all the available material was reviewed. The initial inclusion criteria for this study were: (1) the presence of invasive PSCC, (2) sufficient material available for HPV testing and IHC evaluation, and (3) available tissue for whole-exome sequencing of the invasive carcinoma. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Hospital Clinic de Barcelona (ref HCB/2020/1207).
A total of 51 PSCC complied with the initial inclusion criteria.
2.2. Histological Revision
All of the haematoxylin and eosin sections of the 51 tumours were carefully reviewed. The histological revision aimed to confirm the presence of invasive carcinoma, which was further classified according to the 2022 WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs [2].
In the histological review, a block of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue including both the PSCC, and the adjacent skin was selected for HPV testing and IHC staining. In this evaluation, two blocks were also selected for whole-exome sequencing, one representative of the invasive tumour, containing at least 50% of tumour cells (tumour purity estimated by morphology), and another of normal skin or a reactive lymph node, which was selected as control tissue.
2.3. HPV Testing, p16 IHC, and Criteria for Classifying a Tumour as HPV-Associated or HPV-Independent
DNA extraction was performed on 10-µm whole tissue sections using a commercial kit (QIAamp DNA FFPE Tissue Kit; Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) as previously described [24]. HPV DNA genotyping was performed using the short polymerase chain reaction (PCR) fragment (SPF10) amplified through the INNO-LiPA HPV Genotyping Extra II Amplification (Fujirebio, Gent, Belgium) [25].
All IHC analyses were performed with the Roche platform. p16 IHC was conducted with the CINtec Histology Kit (clone E6H4). Only the “block” staining pattern with diffuse and intense positivity (nuclear and cytoplasmic) in a group of contiguous cells located in basal and parabasal layers, except in the areas of keratosis and parakeratosis, were considered positive [2].
To categorise a tumour as HPV-associated or -independent, both p16 IHC staining and HPV testing were considered. Any tumour showing a positive p16 IHC and/or HPV DNA testing result was considered as HPV-associated. Tumours negative for both techniques were considered as HPV-independent [2].
2.4. p53 IHC Staining and Evaluation
p53 IHC was performed with the anti-p53 (DO-7) monoclonal antibody (Roche, Vienna, Austria), a widely used antibody that detects both wild-type and mutant p53 [21,22]. Staining in the invasive tumour was evaluated according to the p53 pattern-based interpretation framework recently described for vulvar tumours [21,26]. This framework consists of six patterns grouped into two major categories: normal and abnormal. The “normal” category, which is suggestive of wild-type protein, includes two patterns: (1) occasional positive nuclei in the basal and/or parabasal layer (scattered pattern), and (2) moderate to strong nuclear p53 IHC staining in the parabasal layers with an absence of expression in the basal cells (mid-epithelial pattern). The “abnormal” category, suggestive of mutant protein, includes four p53 IHC staining patterns: (1) continuous, strong nuclear staining of the basal layer (basal overexpression pattern), (2) continuous and strong nuclear basal staining with suprabasal extension of the positive cells (diffuse overexpression pattern), (3) cytoplasmic staining with or without nuclear positivity (cytoplasmic pattern), and (4) complete absence of staining in the tumour, with evidence of intrinsic positive control in the adjacent skin, stromal, or inflammatory cells (null pattern). Figure 1 shows a representative example of the six staining patterns of PSCC.

Figure 1.
Examples of the six evaluated patterns of p53 immunohistochemical expression in penile squamous cell carcinoma: two normal (wild-type) patterns include scattered and mid-epithelial pattern. Four abnormal (mutant) patterns comprise basal (continuous, strong staining of the nuclei in the basal layer) and diffuse overexpression (continuous and strong nuclear basal staining with suprabasal extension) patterns, null pattern (complete absence of staining in the tumour with positivity in the background inflammatory and stromal cells), and cytoplasmic pattern (with or without nuclear staining).
p53 IHC slides were independently evaluated by three pathologists (I.T., C.M. and N.R.) blind to the molecular results. All pathologists were asked to assign the p53 IHC status (normal vs. abnormal) and pattern for each PSCC. Discordant cases were reviewed between the three evaluators in a meeting where consensus was reached.
In addition to this six-pattern framework, we evaluated the performance of the conventional interpretation of p53 IHC (only diffuse overexpression considered as abnormal) conducted blindly to the molecular results by a fourth pathologist (A.S.) not involved in the evaluations described above.
2.5. Whole Exome Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
DNA was isolated as described above from invading tumour and matched normal tissue (skin or lymph node). For the DNA isolation, between 20 and 200 ng of gDNA were sheared using a Covaris™ LE220-Plus (MA, USA) and underwent quality control on an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (CA, USA). The adaptor-modified end library was amplified by 10, 15 or 18 cycles of pre-capture PCR with the 2x KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix PCR Kit (Roche). Pools of eight indexed libraries of a combined mass of 1.5 microgram were set up for hybridization (55 °C; 16 h). After washes, the pooled libraries were PCR-amplified. The libraries were sequenced on NovaSeq 6000 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) in paired-end mode with a read length of 2 × 151 bp.
Reads were mapped to the human genome (hs37d5) using the Burrows-Wheeler Alignment and processed using Picard tools version 1.110. The Genome Analysis Tool Kit [27] was used for local indel realignment and base recalibration. Somatic variant calling was performed with GATK v4.1.9.0 Mutect2 and Strelka2 v2.8.3, and annotation with SnpEff v.4.3.e and SnpSift. Copy number variants were predicted with Control-FREEC [28] and annotated with SnpEff.
Cases with tumour and/or non-tumour samples with low coverage depth (<20×) were excluded from the analysis.
2.6. Attribution of TP53 Mutational Status
TP53 was considered mutated if a somatic mutation/s and/or loss in copy number were identified. Only the variants with an allele frequency >4% [29], predicted by both the Mutect2 and Strelka2 databases, and that had passed the quality filters of each program were considered as driver mutations. Tumours with no identified TP53 somatic mutations or variants with allele frequency <4%, and tumours showing only gains in the TP53 gene, in the absence of somatic mutations, were classified as TP53 wild-type [30]. The pathogenicity level (clinical significance) for each identified TP53 somatic variant was retrieved from the National Centre of Biotechnology Information ClinVar database [31].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
StataC/v15.0.591 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA) was used for all the data analyses. The clinical and histopathological data were compared using Chi-square tests (categorical data) and analysis of variance (numerical data). The diagnostic test performance of p53 IHC evaluation against TP53 mutational status (gold standard), as well as inter-observer agreement, was calculated using the Fleiss’ kappa test. The strength of agreement of kappa values was evaluated following the Landis-defined categories: 0, none beyond chance; 0–0.20, slight; 0.21–0.40, fair; 0.41–0.60, moderate; 0.61–0.80, substantial; and 0.81–1.00, almost perfect [32]. The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and accuracy of p53 IHC evaluation, with 95% confidence intervals (95%CI), were also calculated. A two-sided p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Cases Included in the Study and Association with HPV
Eleven tumours were excluded from the study due to insufficient coverage depth (<20×) of the tumour or the matched control tissue (8 and 3 samples, respectively). Forty tumours fulfilled the inclusion criteria and were included in the study. Twelve out of the 40 PSCC (30.0%) were classified as HPV-associated PSCC, with seven cases showing p16 overexpression and HPV-DNA and five cases being only positive for p16 IHC with a negative HPV testing result. In all seven HPV-DNA positive cases, HPV16 was the only type identified. Twenty-eight out of 40 tumours (70.0%) were negative for p16 and HPV testing and were classified as HPV-independent.
3.2. Characteristics of the Overall Series
Table 1 shows the main clinic-pathological characteristics of the PSCC patients, categorised into the two major groups, HPV-associated and HPV-independent, as well as their stage at diagnosis. Patients with HPV-associated PSCC were slightly younger (mean 65.2 years; range 45–94) than the HPV-independent patients (mean 69.1 years; range 40–86) (p = 0.23).

Table 1.
Clinical and pathological characteristics of the penile squamous cell carcinomas (PSCC) included in the study categorized in the two main pathological types.
3.3. TP53 Mutations
The mean percentage of tumoral cells in the samples (tumour purity) was 58% (range 0.50–0.89). The average tumour sequencing depth was 81×, ranging from 23× to 314×. TP53 mutations (somatic and/or copy number alterations) were identified in 22 PSCC (52.5%), whereas 18 tumours (47.5%) were TP53 wild-type. Nineteen PSCC harboured 21 somatic variants, with two of them additionally showing TP53 copy number alterations. Three tumours showed only TP53 copy number loss. The mean allele frequency of the 21 identified somatic TP53 variants was 0.21 (range 0.04–0.79). TP53 missense variants were the most prevalent (14/21; 66.6%), followed by nonsense (4/21; 19.0%), splice-site (2/40; 5.0%) and frameshift (1/4; 2.5%).
3.4. Agreement between p53 IHC and TP53 Mutational Status and Interobserver Agreement
The agreement between the p53 IHC status and TP53 mutational status was substantial for two observers, and moderate for the third observer (k = 0.64, 0.75 and 0.50, respectively; p < 0.0001 for each). After the consensus meeting, in which the twelve discordant cases were discussed, the agreement between the final p53 IHC pattern-based evaluation and the TP53 mutational status increased to almost perfect (k = 0.85; 95% CI = 0.68–1). In this consensus evaluation of p53 IHC, 17 tumours (42.5%) were classified as normal. Fifteen of them showed scattered and two mid-epithelial staining. Twenty-three tumours were classified as showing an abnormal p53 IHC pattern. Of these, 14 (60.8%) showed diffuse overexpression, six (26.0%) null pattern, two (8.6%) cytoplasmic staining, and one (4.3%) basal overexpression. All but one tumour assigned as p53 IHC normal were TP53 wild-type (16/17; agreement: 94.1%), and all but two tumours evaluated as p53 IHC abnormal in the consensus were TP53-mutant (21/23; agreement: 91.3%). The agreement of the p53 IHC pattern-based evaluation (normal vs. abnormal) between three observers was moderate (k = 0.59). A flowchart showing the results of the pattern-based framework evaluation of p53 IHC, their correlation with the classic IHC evaluation of p53, and with the results of the genomic analysis of TP53 are shown in Figure 2. The differences between the pattern-based and the conventional p53 IHC evaluation were related to a misclassification as abnormal expression of the mid-epithelial pattern and a misclassification as normal expression of the cases showing cytoplasmic, null, or basal overexpression.
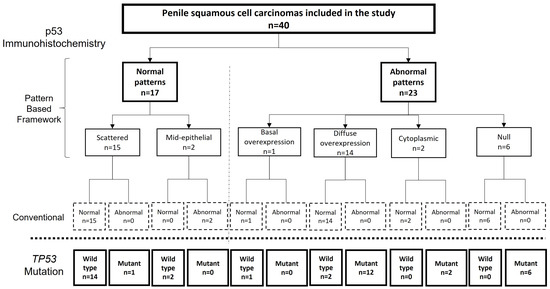
Figure 2.
Flow chart showing the results of the pattern-based framework evaluation of p53 immunohistochemistry (IHC), their correlation with the classic IHC evaluation of p53 and with the results of the genetic analysis.
The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of each ratter and of the consensus evaluation, as well as the figures for the evaluation using conventional criteria are shown in Table 2. The final p53 IHC pattern-based evaluation sensitivity, specificity and accuracy were 95.5% (95%CI 77.2–99.9%), 88.9% (95%CI 65.3–98.6%) and 92.5% (95%CI 79.6–98.4%), respectively.

Table 2.
The p53 immunohistochemical (IHC) evaluation in penile squamous cell carcinomas (PSCC) for each of the observers and after consensus meeting.
A detailed description of the p53 IHC patterns and TP53 mutational status of the 40 PSCC and their relationship with HPV status is shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Summary of immunohistochemical (IHC) and molecular features for each of the 40 penile squamous cell carcinomas.
Frequencies and numbers of TP53 variants in other type of cancers (found to be discordant with pattern-based p53 IHC evaluation for at least one of the three observers) are shown in the Supplementary Table S1.
3.5. p53 IHC Patterns and TP53 Status in HPV-Associated PSCC
Ten out of 12 (83.3%) HPV-associated tumours showed normal p53 IHC pattern. All of them were TP53 wild-type. Eight tumours showed scattered p53 staining, and two showed a mid-epithelial pattern. In seven tumours, the p53 IHC normal pattern was unanimously assigned by the three observers, whereas in three cases, at least one of the observers diagnosed a p53 IHC abnormal pattern.
An abnormal p53 IHC pattern was identified in 2/12 (16.7%) HPV-associated tumours, the two of them showing diffuse p53 overexpression pattern, which was independently assigned by each of the three pathologists. In the sequencing analysis, one tumour showed a pathogenic TP53 c.637C>T nonsense mutation (p.Arg213Ter) with a variant allele frequency of 0.05 accompanied by a loss in the TP53 copy number. Figure 3 shows the histological and IHC features of this tumour.

Figure 3.
The case of Human Papillomavirus (HPV)-associated penile squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC) with basaloid features (A). Immunohistochemistry for p16 is positive (B) and p53 staining shows an abnormal pattern of diffuse overexpression (C). However, in some areas, the tumour shows scattered p53 staining (D). A pathogenic TP53 nonsense mutation (c.637C>T [R213*]) and a loss in TP53 copy number have been identified in this tumour.
Contrarily, in the second case, the exome sequencing did not reveal any TP53 alteration. Figure 4A,A’ illustrates the latter discordant case. None of the HPV-associated PSCC tumours showed cytoplasmic, null, or basal overexpression pattern.
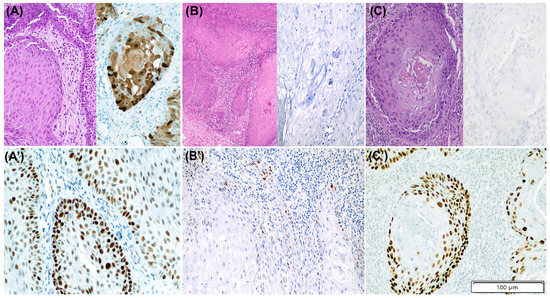
Figure 4.
Three discordant cases between p53 immunohistochemistry (IHC) and TP53 mutational status in penile squamous cell carcinomas (PSCC). (A–C) show H/E staining together with p16 IHC staining and (A’–C’) outline p53 IHC staining for each case. (A,A’): HPV-associated PSCC with p53 abnormal pattern (diffuse overexpression) and no evidence of TP53 alterations. (B,B’): HPV-independent tumour with normal (scattered) p53 IHC pattern and presence of likely benign missense TP53 mutation (c.251C>T [A84V]). (C,C’): HPV-independent PSCC with p53 abnormal pattern (diffuse overexpression) and no evidence of TP53 alterations.
3.6. p53 IHC Patterns and TP53 Status in HPV-Independent PSCC
Seven out of the 28 (25.0%) HPV-independent tumours showed normal p53 IHC; all of them displayed scattered pattern. Six showed TP53 wild-type status in the sequencing analysis and one harboured a likely benign TP53 c.251C>T missense mutation (p. Ala84Val), with a variant allele frequency of 0.04. Figure 4B,B’ illustrates the latter case. In four cases, the normal p53 IHC status was assigned by the three observers (full concordance), whereas in three cases, including the TP53-mutated case, one of the observers suggested an abnormal p53 pattern. No tumours with mid-epithelial pattern were identified in the HPV-independent PSCC group.
An abnormal p53 IHC pattern was identified in 21/28 (75.0%) HPV-independent tumours. Twelve of them (57.1%) showed a diffuse overexpression pattern, six (28.6%) a null pattern, two tumours (9.5%) showed cytoplasmic and one (4.8%) basal staining. Twenty out of the 21 (95.2%) PSCC with abnormal p53 IHC were TP53-mutant. Of them, 17 tumours (85.0%) showed at least one somatic TP53 alteration and three (15.0%) only TP53 copy number loss. In 15/21 tumours (71.4%), all three observers assigned p53 abnormal IHC (including a TP53 wild-type tumour), whereas in six cases, an abnormal p53 IHC was diagnosed by at least one observer. Figure 4C,C’ shows the PSCC with abnormal p53 IHC and absence of TP53 mutations.
Of the 17 cases with TP53 somatic mutations and abnormal p53 IHC, 11 (64.7%) harboured at least one pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant, five (29.4%) showed only a variant of uncertain significance and in one (5.9%) case the mutational variant was not found in ClinVar database (frameshift c.273dupT codifying p.Glu131fs protein). Eight out of 10 (80.0%) PSCC with diffuse overexpression pattern were enriched in pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants of TP53, followed by those with null pattern (2/4; 50.0%), cytoplasmic pattern (1/2; 50.0%), while the only tumour with basal overexpression harboured the variant of uncertain significance.
Among the three tumours with only TP53 copy number loss, two showed p53 IHC null pattern and one diffuse overexpression p53 IHC pattern. Finally, the tumour with abnormal p53 IHC and TP53 wild-type status showed diffuse overexpression (with full concordance between 3 observers).
4. Discussion
In this study, we evaluated the correlation between p53 IHC expression and TP53 mutations in PSCC, using for the first time the pattern-based p53 IHC evaluation framework recently described in vulvar tumours. In keeping with the data reported in the vulva [21,26], this pattern-based p53 IHC evaluation framework reliably predicted the TP53 mutational status of the PSCC (95.7% sensitivity, 88.9% specificity, 92.5% accuracy).
Several studies have shown that TP53 mutational status is clinically relevant in patients with PSCC because mutations are associated with an increased risk of lymph node metastases and impaired prognosis [8,10,11,12,13]. However, TP53 sequencing is technically challenging to implement in the routine. Consequently, several investigators have proposed using p53 IHC staining as a surrogate of TP53 [14], with conflicting results in the correlation between both techniques [8,18]. This poor correlation can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, previous studies have considered diffuse p53 IHC overexpression as the only abnormal pattern suggestive of TP53 mutation, which has shown a limited sensitivity in most series [8]. Secondly, there is a lack of standardisation in the evaluation of p53 staining: although p53 IHC assessment is usually based on the percentage of positive nuclei at the basal and parabasal layers [14], the threshold of positivity suggesting mutation has not been clearly defined. While some studies consider as abnormal p53 staining a positivity in at least 20% of the nuclei [33], other investigators have used a combination of intensity and extent of the positivity [34]. Remarkably, the sensitivity and accuracy of the pattern-based framework of p53 IHC expression to detect TP53 mutation (95.5% and 92.5%, respectively) were much higher than the classical criteria considering only diffuse positive staining as abnormal (9) (54.5% and 70.0%, respectively). However, the specificity did not vary at all between the two methods of evaluation (88.9%).
The correlation between normal p53 IHC using the pattern-based evaluation framework and wild-type TP53 status was excellent in our study (16/17; 94.1%). Interestingly, the only tumour with normal p53 IHC staining but TP53-mutated status harboured a TP53 mutation classified as likely benign, probably not involved in the pathogenesis of this neoplasm. Thus, if only the pathogenic variants were used to define TP53-mutated status, this case would have been reclassified as p53 IHC-TP53 concordant, which would increase the correlation between normal p53 IHC and TP53 wild-type status to 100%. The two p53 IHC patterns described as normal in vulvar carcinomas, scattered and mid-epithelial pattern [21], were identified in our series. The mid-epithelial pattern, previously described in HPV-associated vulvar cancers [21,26,35,36], and identified in two HPV-associated PSCC, is of particular interest. This type of staining probably reflects senescence of high-risk HPV-infected neoplastic cells and represents a potential diagnostic pitfall with p53 overexpression [36], if the pathologist only notices the strong staining in the centre of the tumoral nests.
The excellent correlation between normal p53 IHC and wild-type TP53 status is in contrast with the data reported by Kashofer et al. [8], who, applying the conventional p53 IHC evaluation criteria, showed high frequency of TP53-mutated tumours with normal p53 staining. It should be noted that some of the p53 patterns considered as abnormal in the pattern-based p53 IHC evaluation framework, especially the cytoplasmic and the null patterns, are considered as normal in the conventional evaluation.
We also observed an excellent correlation between abnormal p53 IHC using the pattern-based evaluation framework and TP53-mutant status (21/23; 91.3%). However, if only pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants were considered to define TP53 mutant status, the correlation would drop to 65.2% (15/23). The most frequent abnormal p53 IHC pattern was diffuse overexpression (61%), the only pattern previously considered as abnormal in previous studies on PSCC [8]. It is also the most frequent pattern in vulvar tumours [20,21,26], stomach [37], and ovary [38], usually associated with a missense TP53 mutation. In addition to this common pattern, two additional abnormal patterns of p53 IHC expression (null and cytoplasmic) were identified in as many as one-third of HPV-independent tumours. These two patterns have been identified in HPV-independent vulvar tumours [21,39] but, to our knowledge, have not been previously described in PSCC. Finally, basal overexpression pattern was the most uncommon pattern in our series, observed in only one tumour. As reported in the vulva [21] the distinction between wild-type expression and basal overexpression is often challenging. In addition, this case had a TP53 variant with uncertain pathogenicity and thus might as well be classified as wild-type if only pathogenic variants had been used to define TP53-mutated status.
The findings of our study are consistent with previously reported data [29], showing that TP53 mutations are much more frequent in HPV-independent than in HPV-associated PSCC [7]. Indeed, 75% of the HPV-independent and 8.3% of the HPV-associated PSCC in our series had TP53 alterations (p < 0.001). These differences were also observed for p53 IHC using the pattern-based framework: abnormal patterns were identified in 75% of the HPV-independent and 16.6% of the HPV-associated PSCC (p = 0.005).
The case of HPV-associated tumour with diffuse p53 overexpression and a pathogenic nonsense TP53 variant (c.637C>T codifying for p.Arg213Ter protein) is certainly interesting, as TP53 mutations are highly uncommon in HPV-related neoplasm [7,29,40]. Remarkably, the same mutational variant of TP53 was identified in two additional cases in our series, both HPV-independent, one with diffuse overexpression and one with null p53 pattern. The mutation has been reported to cause a truncated or absent TP53 protein [31], thus correlating with diffuse overexpression and null IHC patterns identified in our study, respectively. The variant was occasionally reported in PSCC [7,41] but was never correlated with p53 IHC staining.
The main strength of our study is that we analysed the TP53 gene by exome sequencing, targeting both somatic mutations and copy number alterations, which has allowed us to obtain an accurate correlation between the findings of IHC and the molecular analysis. In addition, we have used a well-defined pattern-based framework of p53 IHC evaluation that has shown a good correlation in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma, a neoplasm with similar etiopathogenic background [21]. This framework allowed the identification of several abnormal patterns of expression not previously identified in PSCC and showed better correlation with the TP53 molecular status than the conventional criteria. The main limitation is the small sample size, particularly of HPV-associated tumours, which precludes obtaining a reliable distribution of p53 IHC patterns. A second limitation is the use of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue for sequencing, which might have resulted in under- or over-identification of TP53 alterations. Finally, the tumour purity of the samples was relatively low (58%), which could have impacted the somatic variant calling conducted in this study. Lastly, although we obtained strong correlation between p53 IHC and mutational status, we identified a proportion of tumours with TP53 variants of uncertain significance, which introduced a challenge in attribution of TP53 mutational status.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study shows that the pattern-based framework of p53 IHC evaluation accurately predicts TP53 mutational status in PSCC, improving the performance of previously reported methods of p53 IHC evaluation. This new framework recognises three new patterns (mid-epithelial, null and cytoplasmic) in PSCC that would be misclassified by conventional criteria, while the existence of basal pattern is questionable. Further molecular studies are warranted to validate our findings in larger cohorts of PSCC.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers15102719/s1, Table S1: Frequencies of identified TP53 variant among other TP53 mutations and number and types of cancers in which the variant was reported for five penile squamous carcinomas (PSCC) in which there was discordance between p53 immunohistochemistry (IHC) evaluation (for at least one of the three observers) and TP53 mutational status.
Author Contributions
I.T.: study design, investigation, methodology, writing of the first draft, writing and editing; A.S.: investigation, methodology, writing of the first draft, writing and editing; M.d.P.: investigation, writing and editing, software, statistical analysis; F.M.P.: investigation, writing and editing; R.L.d.C.: investigation, writing and editing; C.M.: investigation, writing and editing; O.O.: investigation, writing and editing; N.V.: investigation, writing and editing; S.A.: investigation, writing and editing, L.M.: investigation, methodology, writing and editing; L.R.-C.: investigation, writing and editing; A.M.: study supervision, investigation, writing and editing; P.J.: investigation, methodology, writing and editing; O.R.: study design, resources, investigation, methodology, writing and editing, project management; C.T.: investigation, methodology, writing and editing; T.A.: investigation, methodology, writing and editing; J.M.C.-M.: investigation, resources, writing and editing; F.A.: study design, investigation, resources, writing and editing; M.J.R.: study design, investigation, resources, writing and editing; I.R.-C.: study design, investigation, methodology, writing of the first draft, writing and editing, project management; N.R.: study design, resources, investigation, methodology, statistical analysis, writing of the first draft, writing and editing, project management. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The institutional ethical approval for this study was obtained (registry reference HCB/2020/1207).
Informed Consent Statement
Written study consent was obtained from all the patients enrolled in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All data used in this study are available and can be accessed upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Emmanuel, A.; Nettleton, J.; Watkin, N.; Berney, D.M. The molecular pathogenesis of penile carcinoma—Current developments and understanding. Virchows Arch. 2019, 475, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Moch, H. Tumours of the penis and scrotum: Introduction. In WHO Classification of Tumours: Urinary and Male Genital Tumours; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cubilla, A.L.; Velazquez, E.F.; Amin, M.B.; Epstein, J.; Berney, D.M.; Corbishley, C.M. Members of the ISUP Penile Tumor Panel The World Health Organisation 2016 classification of penile carcinomas: A review and update from the International Society of Urological Pathology expert-driven recommendations. Histopathology 2018, 72, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemany, L.; Cubilla, A.; Halec, G.; Kasamatsu, E.; Quirós, B.; Masferrer, E.; Tous, S.; Lloveras, B.; Hernández-Suarez, G.; Lonsdale, R.; et al. Role of Human Papillomavirus in Penile Carcinomas Worldwide. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaux, A.; Velazquez, E.F.; Algaba, F.; Ayala, G.; Cubilla, A.L. Developments in the pathology of penile squamous cell carcinomas. Urology 2010, 76, S7–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, G.; Pfister, H. Role of human papillomavirus in penile cancer, penile intraepithelial squamous cell neoplasias and in genital wartsitle. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 193, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, A.S.; Hovelson, D.H.; Cani, A.K.; Liu, C.-J.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Weizer, A.Z.; Mehra, R.; Feng, F.Y.; Alva, A.S.; et al. Genomic Profiling of Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma Reveals New Opportunities for Targeted Therapy. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 5219–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashofer, K.; Winter, E.; Halbwedl, I.; Thueringer, A.; Kreiner, M.; Sauer, S.; Regauer, S. HPV-negative penile squamous cell carcinoma: Disruptive mutations in the TP53 gene are common. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feber, A.; Worth, D.C.; Chakravarthy, A.; de Winter, P.; Shah, K.; Arya, M.; Saqib, M.; Nigam, R.; Malone, P.R.; Tan, W.S.; et al. CSN1 Somatic Mutations in Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4720–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, D.; Luo, L.; et al. Mutational landscape of penile squamous cell carcinoma in a Chinese population. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoehr, R.; Weisser, R.; Wendler, O.; Giedl, J.; Daifalla, K.; Gaisa, N.T.; Richter, G.; Campean, V.; Burger, M.; Wullich, B.; et al. P53 codon 72 polymorphism and risk for squamous cell carcinoma of the penis: A Caucasian case-control study. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 4234–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.; Bezerra AL, R.; Pinto CA, L.; Serrano, S.V.; de Mello, C.A.; Villa, L.L. p53 as a new prognostic factor for lymph node metastasis in penile carcinoma: Analysis of 82 patients treated with amputation and bilateral lymphadenectomy. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficarra, V.; Akduman, B.; Bouchot, O.; Palou, J.; Tobias- Machado, M. Prognostic factors in penile cancer. Urology 2010, 76, S66–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horenblas, S.; van Tinteren, H. Squamous cell carcinoma of the penis. IV. Prognostic factors of survival: Analysis of tumor, nodes and metastasis classification system. J. Urol. 1994, 151, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.M.; Ignácio, J.A.; Jordán, J.; Carraro, D.M.; Lisboa, B.; Lopes, A.; Carvalho, K.C.; Da Cunha, I.W.; Cubilla, A.; Guimarães, G.C.; et al. A clinical, pathologic, and molecular study of p53 and murine double minute 2 in penile carcinogenesis and its relation to prognosis. Hum. Pathol 2012, 43, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunia, S.; Kakies, C.; Erbersdobler, A.; Hakenberg, O.W.; Koch, S.; May, M. Expression of p53, p21 and cyclin D1 in penile cancer: p53 predicts poor prognosis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 65, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prapiska, F.F.; Warli, S.M. P53 and survival rate in penile cancer. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 1170–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, N.; Osakabe, M.; Hayashi, M.; Tamura, G.; Motoyama, T. Detection of HPV-DNA, p53 alterations, and methylation in penile squamous cell carcinoma in Japanese men. Pathol. Int. 2008, 58, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Pino, M.; Rodriguez-Carunchio, L.; Ordi, J. Pathways of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2013, 62, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakislova, N.; Alemany, L.; Clavero, O.; Saco, A.; Torné, A.; Del Pino, M.; Munmany, M.; Rodrigo-calvo, M.T.; Guerrero, J.; Marimon, L.; et al. P53 immunohistochemical patterns in HPV- independent squamous cell carcinomas of the vulva and the associated skin lesions: A study of 779 cases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier-Cloutier, B.; Kortekaas, K.E.; Thompson, E.; Pors, J.; Chen, J.; Ho, J.; Prentice, L.M.; McConechy, M.K.; Chow, C.; Proctor, L.; et al. Major p53 immunohistochemical patterns in in situ and invasive squamous cell carcinomas of the vulva and correlation with TP53 mutation status. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortekaas, K.E.; Bastiaannet, E.; van Doorn, H.C.; van Steenwijk, P.J.D.V.; Ewing-Graham, P.C.; Creutzberg, C.L.; Akdeniz, K.; Nooij, L.S.; van der Burg, S.H.; Bosse, T.; et al. Vulvar cancer subclassification by HPV and p53 status results in three clinically distinct subtypes. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 159, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darragh, T.M.; Colgan, T.J.; Cox, J.T.; Heller, D.S.; Henry, M.R.; Luff, R.D.; McCalmont, T.; Nayar, R.; Palefsky, J.M.; Stoler, M.H.; et al. The Lower Anogenital Squamous Terminology Standardization Project for HPV-Associated Lesions: Background and consensus recommendations from the College of American Pathologists and the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2012, 36, 1266–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzotti, C.; Chulo, L.; López del Campo, R.; Trias, I.; del Pino, M.; Saúde, O.; Basílio, I.; Tchamo, N.; Lovane, L.; Lorenzoni, C.; et al. Penile Squamous Cell Carcinomas in Sub-Saharan Africa and Europe: Differential Etiopathogenesis. Cancers 2022, 14, 5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, E.L.; Lambie, N.; Donoghoe, M.W.; Naing, Z.; Hacker, N.F. The Clinical Relevance of p16 and p53 Status in Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Vulva. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 3739075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortekaas, K.E.; Solleveld-Westerink, N.; Tessier-Cloutier, B.; Rutten, T.A.; van Poelgeest, M.I.E.; Gilks, C.B.; Hoang, L.N.; Bosse, T. Performance of the Pattern Based Interpretation of p53 Immunohistochemistry as a Surrogate for TP53 Mutations in Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Histopathology 2020, 77, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeva, V.; Popova, T.; Bleakley, K.; Chiche, P.; Cappo, J.; Schleiermacher, G.; Janoueix-Lerosey, I.; Delattre, O.; Barillot, E. Control-FREEC: A tool for assessing copy number and allelic content using next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahoud, J.; Gleber-Netto, F.O.; McCormick, B.Z.; Rao, P.; Lu, X.; Guo, M.; Morgan, M.B.; Chu, R.A.; Martinez-Ferrer, M.; Eterovic, A.K.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing in penile squamous cell carcinoma uncovers novel prognostic categorization and drug targets similar to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma A C. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 2560–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Xu, Z.; Scuoppo, C.; Rillahan, C.D.; Gao, J.; Spitzer, B.; Bosbach, B.; Kastenhuber, E.R.; Baslan, T.; et al. Deletions linked to TP53 loss drive cancer through p53-independent mechanisms. Nature 2016, 531, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinVar National Center for Biotechnology Information: ClinVar entry NM_000546.6(TP53):c.637C>T (p.Arg213Ter). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/variation/43590/?new_evidence=true (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Yao, K.; Ye, Y.-L.; Xie, D.; Han, H.; Liu, Z.-W.; Qin, Z.-K.; Zhou, F.-J. The risk factors for the presence of pelvic lymph node metastasis in penile squamous cell carcinoma patients with inguinal lymph node dissection. World J. Urol. 2013, 31, 2519–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar-Shoshtari, K.; Spiess, P.E.; Berglund, A.E.; Sharma, P.; Powsang, J.M.; Giuliano, A.; Magliocco, A.M.; Dhillon, J. Clinical Significance of p53 and p16ink4a Status in a Contemporary North American Penile Carcinoma Cohort. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2016, 14, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, J.C.; Yang, E.; Crum, C.P.; Herfs, M.; Gheit, T.; Tommasino, M.; Nucci, M.R. Classic Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia with Superimposed Lichen Simplex Chronicus: A Unique Variant Mimicking Differentiated Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2019, 38, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffreys, M.; Jeffus, S.K.; Herfs, M.; Quick, C.M. Accentuated p53 staining in usual type vulvar dysplasia-A potential diagnostic pitfall. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.J.; Nam, S.K.; Park, H.; Park, Y.; Koh, J.; Na, H.Y.; Kwak, Y.; Kim, W.H.; Lee, H.S. Prediction of TP53 mutations by p53 immunohistochemistry and their prognostic significance in gastric cancer. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2020, 54, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, S.; D’Andrea, D.; Vetterlein, M.W.; Cole, A.P.; Fletcher, S.A.; Krimphove, M.J.; Marchese, M.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Sonpavde, G.; Noldus, J.; et al. Impact of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with adverse features and variant histology at radical cystectomy for muscle-invasive carcinoma of the bladder: Does histologic subtype matter? Cancer 2019, 125, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Leen, S.L.; Han, G.; Faruqi, A.; Kokka, F.; Rosenthal, A.; Jiang, X.R.; Kim, R.; McAlpine, J.N.; Gilks, C.B. Expanding the morphologic spectrum of differentiated VIN (dVIN) through detailed mapping of cases with p53 loss. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribera-Cortada, I.; Guerrero-Pineda, J.; Trias, I.; Veloza, L.; Garcia, A.; Marimon, L.; Diaz-mercedes, S.; Alamo, J.R.; Rodrigo-calvo, M.T.; Vega, N.; et al. Pathogenesis of penile squamous cell carcinoma: Molecular update and systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehir, A.; Benayed, R.; Shah, R.H.; Syed, A.; Middha, S.; Kim, H.R.; Srinivasan, P.; Gao, J.; Chakravarty, D.; Devlin, S.M.; et al. Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).