Electrochemical Biosensors in the Diagnosis of Acute and Chronic Leukemias
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
General Considerations on Electrochemical Biosensors
2. Bioreceptor Molecules as Biorecognition Elements
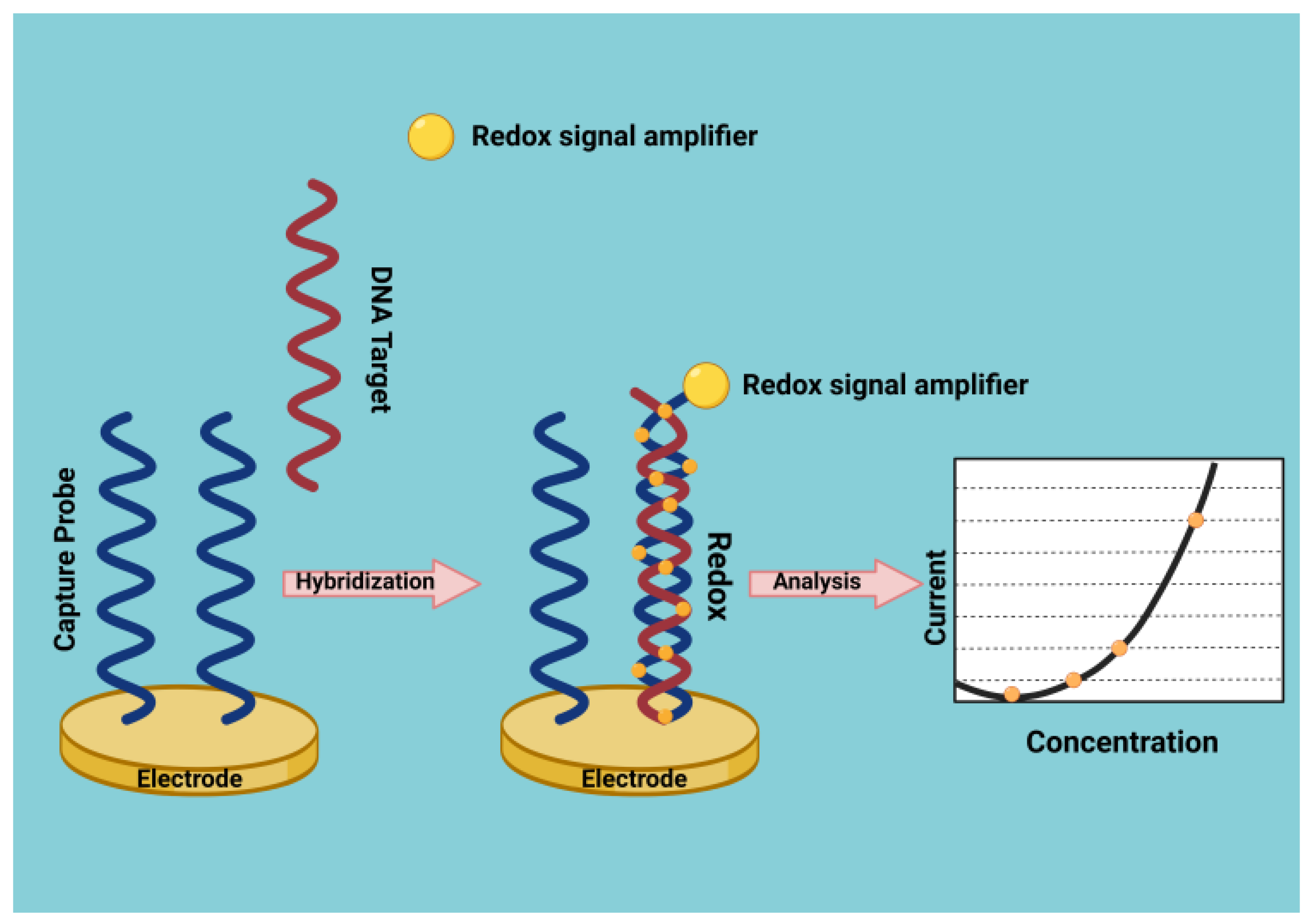
DNA Biosensors
3. Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
4. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Electrochemical Biosensors and Chemoresistance
5. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Monitoring of the Efficacy of the Therapy through Biosensors
6. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brancato, V.; Reis, R.L.; Kundu, S.C. Coupling Micro-Physiological Systems and Biosensors for Improving Cancer Biomarkers Detection. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1379, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Xia, Y.; Lu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Shu, Y.; Hu, X. Recent advances in inorganic functional nanomaterials based flexible electrochemical sensors. Talanta 2022, 244, 123419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulanicki, A.; Glab, S.; Ingman, F. Chemical sensors: Definitions and classification. Pure Appl. Chem. 1991, 63, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.K.; Saha, S.; Ramirez-Vick, J.E.; Gupta, V.; Bhansali, S.; Singh, S.P. Recent advances in ZnO nanostructures and thin films for biosensor applications: Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 737, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.M.; Rao, S.; Yang, X.; Dubey, S.; Mays, J.; Cao, H.; Chiao, J.C. Sol-gel deposition of iridium oxide for biomedical micro-devices. Sensors 2015, 15, 4212–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Sol–gel materials for electrochemical biosensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 399, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, S.; Xu, F.; Chen, S.; Jia, J.; Tan, H.; Hou, H.; Song, Y. Electrochemical sensing and biosensing platform based on biomass-derived macroporous carbon materials. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, A.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Y.; Shi, G.; Tian, Y. A two-channel ratiometric electrochemical biosensor for in vivo monitoring of copper ions in a rat brain using gold truncated octahedral microcages. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 8129–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravalli, A.; Rivas, L.; De la Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Pons, J.; Merkoçi, A.; Marrazza, G. A DNA Aptasensor for Electrochemical Detection of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 3411–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, P.; Su, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yang, S.; Lu, J.; Gao, J.; Fan, C.; Huang, Q. Ultrasensitive electrochemical DNA sensor based on the target induced structural switching and surface-initiated enzymatic polymerization. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Yan, F.; Ju, H. A facile strategy for quantitative sensing of glycans on cell surface using organic electrochemical transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 175, 112878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Kawde, A.N.; Polsky, R. Metal nanoparticle based electrochemical stripping potentiometric detection of DNA hybridization. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5576–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegra, A.; Penna, G.; Alonci, A.; Rizzo, V.; Russo, S.; Musolino, C. Nanoparticles in oncology: The new theragnostic molecules. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentini, G.; Fazio, E.; Calabrese, F.; De Plano, L.M.; Puliafico, M.; Franco, D.; Nicolò, M.S.; Carnazza, S.; Trusso, S.; Allegra, A.; et al. Phage-AgNPs complex as SERS probe for U937 cell identification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, N.; Yu, H.; Niu, Y.; Sun, C. Covalent attachment of glucose oxidase to an Au electrode modified with gold nanoparticles for use as glucose biosensor. Bioelectrochemistry 2005, 67, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Carbon–nanotube based electrochemical biosensors: A review. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.S.; Upadhaya, P.G.; Patravale, V.B. Quantum Dots: Novel Realm in Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Industry. In Handbook of Nanomaterials for Industrial Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 621–637. [Google Scholar]
- Bakirhan, N.K.; Ozkan, S.A. Quantum Dots as a New Generation Nanomaterials and Their Electrochemical Applications. In: Pharmaceutical Industry. In Handbook of Nanomaterials for Industrial Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 520–529. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, S. Nanobiosensors: The future for diagnosis of disease. Nanobiosen. Dis. Dig. 2014, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, T.; Li, Z.; Gu, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, J. Synthesis of palladium@gold nanoalloys/nitrogen and sulphur-functionalized multiple graphene aerogel for electrochemical detection of dopamine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 954, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduraiveeran, G.; Sasidharan, M.; Ganesan, V. Electrochemical sensor and biosensor platforms based on advanced nanomaterials for biological and biomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 103, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.; Julkapli, N.M.; Yehye, W.A.; Basirun, W.J.; Bhargava, S.K. Graphene-Gold Nanoparticles Hybrid-Synthesis, Functionalization, and Application in a Electrochemical and Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Biosensor. Materials 2016, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.H.; Lee, C.S.; Kim, T.H. Electrochemical Detection of Ultratrace Lead Ion through Attaching and Detaching DNA Aptamer from Electrochemically Reduced Graphene Oxide Electrode. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.; Luo, L.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X. A novel nitrite sensor based on graphene/polypyrrole/chitosan nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. Analyst 2011, 136, 4563–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Yu, S.H.; Kim, T.H. One-Step Electrochemical Fabrication of Reduced Graphene Oxide/Gold Nanoparticles Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode for Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine, Ascorbic Acid, and Uric Acid. Nanomaterials 2017, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zhao, N.; Hou, S.; Zhang, C. Electrochemical Synthesis of Polypyrrole, Reduced Graphene Oxide, and Gold Nanoparticles Composite and Its Application to Hydrogen Peroxide Biosensor. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, D.W.; LeBlanc, G.; Meschievitz, M.E.; Cliffel, D.E. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2011, 84, 685–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.X.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.M.; Ni, Z.Z.; Yu, H.Q.; Luo, C.N.; Wei, Q.; Du, B. Label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on graphene/methylene blue nanocomposite. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 422, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Chen, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. A graphene functionalized electrochemical aptasensor for selective label-free detection of cancer cell. Biomaterial 2011, 32, 2930–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Electrochemically synthesized polymers in molecular imprinting for chemical sensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3177–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Hou, B. Impedimetric immunosensor doped with reduced graphene sheets fabricated by controllable electrodeposition for the non-labelled detection of bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, D.; Jordaan, J. Advances in enzyme immobilisation. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjami, E.; Clima, L.; Gothelf, K.; Ferapontova, E.E. “Off–On” electrochemical hairpin-dna-based genosensor for cancer diagnostics. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkoci, A.; Aldavert, M.; Marın, S.; Alegret, S. New materials for electrochemical sensing v: Nanoparticles for DNA labelling. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, L.; Jin, H.; Yang, T.; Bao, W.; Huang, S.; Wang, J. Electrochemical detection of hepatitis B and papilloma virus DNAs using SWCNT array coated with gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.M.; Ju, H.Q.; Ding, C.F.; Zhang, S.S. Nucleic acid biosensor for detection of hepatitis B virus using 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline copper complex as electrochemical indicator. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 582, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccardi Cdos, S.; Dahmouche, K.; Santilli, C.V.; da Costa, P.I.; Yamanaka, H. Immobilization of streptavidin in sol-gel films: Application on the diagnosis of hepatitis C virus. Talanta 2006, 70, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, T.; Feng, Y.; Jiao, K. A DNA electrochemical sensor based on nanogold-modified poly-2,6-pyridinedicarboxylic acid film and detection of PAT gene fragment. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 365, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarova, E.; Aldissi, M.; Bogomolova, A. Direct electrochemical sensor for fast reagent-free DNA detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, C.; Joubert, A.; Tardy, C.; Maestre, N.; Cacho, M.; Braña, M.F.; Bailly, C. DNA sequence recognition by bispyrazinonaphthalimides antitumor agents. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 11751–11761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.H.; Wu, P.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xia, X.H. Electrochemical DNA biosensor for the detection of short DNA species of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia by using methylene blue. Talanta 2007, 72, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meric, B.; Kerman, K.; Ozkan, D.; Kara, P.; Erensoy, S.; Akarca, U.S.; Mascini, M.; Ozsoz, M. Electrochemical DNA biosensor for the detection of TT and Hepatitis B virus from PCR amplified real samples by using methylene blue. Talanta 2002, 56, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Mishima, Y.; Minagawa, K.; Motonaka, J. DNA sensor with a dipyridophenazine complex of osmium(lI) as an electrochemical probe. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 3698–76703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Niu, S.Y.; Qu, B.; Jie, G.F.; Xu, H.; Ding, C.F. Studies on the interaction mechanism between hexakis(imidazole) manganese(II) terephthalate and DNA and preparation of DNA electrochemical sensor. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 2340–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shen, Z.; Li, D.; He, X.; Lin, B. Study of interactions between actinomycin D and oligonucleotides by microchip electrophoresis and ESI-MS. Talanta 2007, 72, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinauskas, A.; Ruzgas, T.; Gorton, L. Tuning the redox potential of riboflavin by zirconium phosphate in carbon paste electrodes. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1999, 49, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole-based synthetic receptor for direct detection of bovine leukemia virus glycoproteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynor, B.W.; Filocamo, S.F.; Grinstaff, M.W.; Liu, J. Direct-writing of polymer nanostructures: Poly(thiophene) nanowires on semiconducting and insulating surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 522–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.G.; Bein, T. Conducting polyaniline filaments in a mesoporous channel host. Science 1994, 264, 1757–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozer, J.P.; Brañas, G.; Laíz, J. Electrochemical DNA hybridization sensors applied to real and complex biological samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Wang, J.; Liao, W.; Zimmermann, B.G.; Wong, D.T.; Ho, C.M. Electrochemical detection of low-copy number salivary RNA based on specific signal amplification with a hairpin probe. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallman, M.S.; Nabhan, C.; Feusner, J.H.; Rowe, J.M. Acute promyelocytic leukemia: Evolving therapeutic strategies. Blood 2002, 99, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.J.; Seo, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, Y.H.; Park, P.W.; Ahn, J.Y. A complex, four-way variant t(15;17) in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2006, 167, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, P.S.; Baisane, C.; Saikia, T.; Nair, R.; Gawade, H.; Advani, S. Fluorescence in situ hybridization: A highly efficient technique of molecular diagnosis and predication for disease course in patients with myeloid leukemias. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2001, 131, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado, C.A.; Golembiewski-Ruiz, V.; Horvatinovich, J.; Moore, J.O.; Buckley, P.J.; Stenzel, T.T.; Goodman, B.K. Cytogenetic and molecular analysis of an unusual case of acute promyelocytic leukemia with a t(15;17;17)(q22;q23;q21). Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2003, 145, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Kim, K.E.; Kim, K.H.; Park, J.I.; Kim, J.S. Identification of PML-RARA rearrangement by RT-PCR and sequencing in an acute promyelocytic leukemia without t(15;17) on G-banding and FISH. Leuk. Res. 2007, 31, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamero, M.; Pariente, F.; Lorenzo, E.; Alonso, C. Nanostructured rough gold electrodes for the development of lactate oxidase-based biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2038–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Liu, A.; Chen, X.; Wang, K.; Lian, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Du, M.; Lin, X. Electrochemical biosensor based on nanoporous gold electrode for detection of PML/RARα fusion gene. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3812–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, C.B.; Peairs, M.J.; Venton, B.J. Review: Carbon nanotube based electrochemical sensors for biomolecules. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 662, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zong, P.; Zheng, X.; Wang, L. An enhanced sensing platform for ultrasensitive impedimetric detection of target genes based on ordered FePt nanoparticles decorated carbon nanotubes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.S.; Hola, K.; Ambrosi, A.; Zboril, R.; Pumera, M. Graphene and carbon quantum dots electrochemistry. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 52, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Li, X.; Ying, Z.; Chai, Y.Q.; Yuan, R. Synthesizing anode electrochemiluminescent self-catalyzed carbon dots-based nanocomposites and its application in sensitive ECL biosensor for microRNA detection. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2020, 305, 127490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, V.C.; Dave, K.; Gomes, V.G. Carbon quantum dot-based composites for energy storage and electrocatalysis: Mechanism, applications and future prospects. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarra, M.; Gonzalez-Calabuig, A.; Radotic, K.; Mutavdzic, D.; Ania, C.O.; Lázaro-Martínez, J.M.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Del Valle, M. Enhanced electrochemical response of carbon quantum dot modified electrodes, applications and future prospects. Talanta 2018, 178, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.T.; Ye, Y.B.; Wan, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Xia, Y.; Li, G.; He, Q. Morphology-dependent electrochemical sensing properties of iron oxide-graphene oxide nanohybrids for dopamine and uric acid. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.Y.; Zhu, H.Y.; Li, Z.J.; Liu, J.K. Electrochemical determination of acetaminophen using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a hybrid material consisting of graphene aerogel and octadecylamine-functionalized carbon quantum dots. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Q.; Huang, N.; Lu, Q.J.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. A quadruplet electrochemical platform for ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and acetaminophen based on a ferrocene derivative functional Au NPs/carbon dots nanocomposite and graphene. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 903, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.D.; Zhuang, X.M.; Zhai, J.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Lua, H.; Chen, L.X. Preparation of highly sensitive Pt nanoparticles-carbon quantum dots/ionic liquid functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposites and application for H2O2 detection. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 255, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Huang, L.-X.; Xu, Z.-W.; Wang, P.; Lei, Y.; Liu, A.-L. Efficient Determination of PML/RARα Fusion Gene by the Electrochemical DNA Biosensor Based on Carbon Dots/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 3497–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K.; Xu, X.; Lin, J.; Li, G.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y. An electrochemical biosensor for detection of PML/RARA fusion gene using capture probe covalently immobilized onto poly-calcon carboxylic acid modified glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 2009, 78, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, T.; Tian, G.; Cao, H.; Liu, Q.; Ito, Y. Preparative isolation and purification of hydroxyanthraquinones from Rheum officinale Baill by high-speed counter-current chromatography using pH-modulated stepwise elution. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 858, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.H.; Wan, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chen, J.H. Studies of the interaction between Aloe-emodin and DNA and preparation of DNA biosensor for detection of PML-RAR fusion gene in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Talanta 2008, 74, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Kim, Y.; Medley, C.D.; Lin, H.; Tan, W. Synthesis and investigation of deoxyribonucleic acid/locked nucleic acid chimeric molecular beacons. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 4030–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K.; Lin, X.; Huang, L.; Chen, G. Electrochemical biosensor for detection of BCR/ABL fusion gene using locked nucleic acids on 4-aminobenzenesulfonic acid-modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8028–8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obika, S.; Uneda, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Nanbu, D.; Minami, T.; Doi, T.; Imanishi, T. 2′-O,4′-C-Methylene bridged nucleic acid (2′,4′-BNA): Synthesis and triplex-forming properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, A.; Weng, S.; Lei, Y.; Chen, W.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y. Enzyme-amplified electrochemical biosensor for detection of PML-RARα fusion gene based on hairpin LNA probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Lei, Y.; Zhong, G.X.; Zheng, Y.J.; Sun, Z.L.; Peng, H.P.; Chen, W.; Liu, A.L.; Chen, Y.Z.; Lin, X.H. Dual-probe electrochemical DNA biosensor based on the “Y” junction structure and restriction endonuclease assisted cyclic enzymatic amplification for detection of double-strand DNA of PML/RARα related fusion gene. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Wang, K.; Wu, S.Y.; Huang, D.D.; Dai, M.; Zheng, Y.J.; Sun, Z.L.; Chen, Y.Z.; Lin, X.H.; Liu, A.L. 2’-Fluoro ribonucleic acid modified DNA dual-probe sensing strategy for enzyme-amplified electrochemical detection of double-strand DNA of PML/RARα related fusion gene. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 112, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, H.; Mullighan, C.G. Pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2524–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshfetrat, S.M.; Mehrgardi, M.A. Amplified detection of leukemia cancer cells using an aptamer-conjugated gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles on a nitrogen-doped graphene modified electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 2017, 114, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heltemes-Harris, L.M.; Willette, M.J.; Ramsey, L.B.; Qiu, Y.H.; Neeley, E.S.; Zhang, N.; Thomas, D.A.; Koeuth, T.; Baechler, E.C.; Kornblau, S.M.; et al. Ebf1 or Pax5 haploinsufficiency synergizes with STAT5 activation to initiate acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebral, K.; Denk, D.; Attarbaschi, A.; König, M.; Mann, G.; Haas, O.A.; Strehl, S. Incidence and diversity of PAX5 fusion genes in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2009, 23, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, D.; Hayakawa, F.; Yasuda, T.; Tange, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Kojima, Y.; Morishita, T.; Imoto, N.; Tsuzuki, S.; Mano, H.; et al. Chromosomal translocation-mediated evasion from miRNA induces strong MEF2D fusion protein expression, causing inhibition of PAX5 transcriptional activity. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2263–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochman, M.L.; Paeschke, K.; Zakian, V.A. DNA secondary structures: Stability and function of G-quadruplex structures. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Hurley, L.H.; Neidle, S. Targeting G-quadruplexes in gene promoters: A novel anticancer strategy? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Tu, W.; Bao, J.; Dai, Z. Versatile biosensing platform for DNA detection based on a DNAzyme and restriction-endonuclease-assisted recycling. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Dou, B.; Yang, J.; Yuan, R.; Xiang, Y. Cascaded strand displacement for non-enzymatic target recycling amplification and label-free electronic detection of microRNA from tumor cells. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 916, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Tang, S.; Kong, R.M.; Yu, R. Ultra-sensitive label-free electrochemical detection of the acute leukaemia gene Pax-5a based on enzyme-assisted cycle amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 143, 111593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, P.; Cai, J. An efficient nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensor for sensitive recognition of drug-resistant leukemia cells. Analyst 2014, 139, 3629–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apperley, J.F. Chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2015, 385, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Wang, Z.J.; Jiang, J.H.; Shen, G.L.; Yu, R.Q. A nano-porous CeO(2)/Chitosan composite film as the immobilization matrix for colorectal cancer DNA sequence-selective electrochemical biosensor. Talanta 2006, 70, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassee, F.R.; van Balen, E.C.; Singh, C.; Green, D.; Muijser, H.; Weinstein, J.; Dreher, K. Exposure, health and ecological effects review of engineered nanoscale cerium and cerium oxide associated with its use as a fuel additive. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2011, 41, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhong, L.; Lu, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, B.; Xie, G.; Feng, W. Electrochemical determination of BCR/ABL fusion gene based on in situ synthesized gold nanoparticles and cerium dioxide nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avelino, K.Y.P.S.; Oliveira, L.S.; Santos, M.R.; Lucena-Silva, N.; Andrade, C.A.S.; Oliveira, M.D.L. Electrochemical DNA biosensor for chronic myelocytic leukemia based on hybrid nanostructure. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 147, 108176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Li, Z.; Lin, J.; Han, G.; Huang, P. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5109–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hui, Z.; Zhou, J.; Huang, X.; Sun, G.; Huang, W. Ti3C2TX MXene for sensing applications: Recent progress, design principles, and future perspectives. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3996–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Xue, J.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, A.; Xue, J. Novel Ti3C2TX MXene nanozyme with manageable catalytic activity and application to electrochemical biosensor. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sumana, G.; Sapra, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Quantum dots self assembly based interface for blood cancer detection. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8753–8762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencer, E.B.; Ural, A.U.; Avcu, F.; Baran, Y. A novel mechanism of dasatinib-induced apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia; ceramide synthase and ceramide clearance genes. Ann. Hematol. 2011, 90, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Fu, J.J.; Hu, L.; Qiu, F.; Hu, M.; Zhu, J.J.; Hua, Z.C.; Wang, H. Nanoarchitectured electrochemical cytosensors for selective detection of leukemia cells and quantitative evaluation of death receptor expression on cell surfaces. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5609–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. The promise of cancer therapeutics targeting the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and TRAIL receptor pathway. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6207–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zheng, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Lu, F.; Zhu, J.J. Toward therapeutic effects evaluation of chronic myeloid leukemia drug: Electrochemical platform for caspase-3 activity sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banikazemi, Z.; Farshadi, M.; Rajabi, A.; Homayoonfal, M.; Sharifi, N.; Chaleshtori, R.S. Nanoplastics: Focus on the role of microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs. Chemosphere 2022, 308 Pt 1, 136299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-X.; Huang, K.-J.; Niu, K.-X. Recent advances in signal amplification strategy based on oligonucleotide and nanomaterials for microRNA detection—A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujica, M.L.; Gallay, P.A.; Perrachione, F.; Montemerlo, A.E.; Tamborelli, L.A.; Vaschetti, V.M.; Reartes, D.F.; Bollo, S.; Rodríguez, M.C.; Dalmasso, P.R.; et al. New trends in the development of electrochemical biosensors for the quantification of microRNAs. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 189, 113478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, H.; Yammouri, G.; Amine, A. Current advances in electrochemical genosensors for detecting microRNA cancer markers. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 16, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshpour, M.; Omidfar, K.; Ghanbarian, H. A novel electrochemical nanobiosensor for the ultrasensitive and specific detection of femtomolar-level gastric cancer biomarker miRNA-106a. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 2023–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, E.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Ma, C.; Sun, Y.; Lei, M.; Lu, B.; Han, R. Retracted Article: Graphene oxide/DNA-decorated electrode for the fabrication of microRNA biosensor. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69334–69338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, S.; Fang, X.; Kong, J. Double signal amplification strategy for ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor based on nuclease and quantum dot-DNA nanocomposites in the detection of breast cancer 1 gene mutation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, H.; Motovali-Bashi, M.; Radfar, S. An enzyme-free electrochemical biosensor for simultaneous detection of two hemophilia A biomarkers: Combining target recycling with quantum dots-encapsulated metal-organic frameworks for signal amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1092, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Ning, W.; Chen, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Bai, J. High performance electrochemical biosensor based on 3D nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide electrode and tetrahedral DNA nanostructure. Talanta 2019, 194, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Huang, W.; Qin, C.; Yu, A.; Lai, G. Exonuclease-assisted target recycling for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of microRNA at vertically aligned carbon nanotubes. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 11262–11269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yammouri, G.; Mohammadi, H.; Amine, A. A Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Carbon Black and Gold Nanoparticles Modified Pencil Graphite Electrode for microRNA-21 Detection. Chem. Afr. 2019, 2, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Aamri, M.; Yammouri, G.; Mohammadi, H.; Amine, A.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. Electrochemical Biosensors for Detection of MicroRNA as a Cancer Biomarker: Pros and Cons. Biosensors 2020, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinani, H.S.; Pourmadadi, M.; Yazdian, F.; Rashedi, H.; Ebrahimi, S.A.S.; Shayeh, J.S.; Ghorbani, M. Fabrication of Au/Fe3O4/RGO based aptasensor for measurement of miRNA-128, a biomarker for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Eng. Life Sci. 2022, 22, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr-Phillipsa, T.E.; Aydemira, N.; Chi Chana, E.W.; Barkera, D.; Malmstroma, J.; Plessec, C.; Sejdic, J.T. Conducting electrospun fibres with polyanionic grafts as highly selective, label-free, electrochemical biosensor with a low detection limit for non-Hodgkin lymphoma gene. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegra, A.; Cancemi, G.; Mirabile, G.; Tonacci, A.; Musolino, C.; Gangemi, S. Circulating tumour cells, cell free DNA and tumour-educated platelets as reliable diagnostic and management biomarkers for the liquid biopsy in multiple myeloma. Cancers 2022, 14, 4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yea, M.; Zhang, W.; Tan, D.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Yang, X.; Guo, Z. Liquid biopsy of circulating tumor DNA and biosensor applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Measurable Residual Disease Testing in Acute Leukemia: Technology and Clinical Significance. In Leukemia; Li, W., Ed.; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2022; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Rhouati, A.; Marty, J.L.; Vasilescu, A. Electrochemical biosensors combining aptamers and enzymatic activity: Challenges and analytical opportunities. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 390, 138863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chupradit, S.; Km Nasution, M.; Rahman, H.S.; Suksatan, W.; Turki Jalil, A.; Abdelbasset, W.K.; Bokov, D.; Markov, A.; Fardeeva, I.N.; Widjaja, G.; et al. Various types of electrochemical biosensors for leukemia detection and therapeutic approaches. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 654, 114736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disease | Sensor | Detection Limit | Ref.f. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute promyelocytic leukemia | Gold nanoparticles | 6.7 pM | [58] |
| target DNA (22-base sequence S2)-5′-CGG GGA GGC AGC CAT TGA GAC C-3′ | |||
| immobilized probe (22-base sequence S1)-5′-SH-GGT CTC AAT GGC TGC CTC CCC G-3′ | |||
| Carbon nanotubes | 2.1 mol/L | [60] | |
| probe DNA (ssDNA): 5′-TCT CAA TGG CTG CCT CCC-3′; | |||
| target DNA (cDNA): 5′-GGG AGG CAG CCA TTG AGA-3′; | |||
| Quantum dots/Graphene oxide | 83 pM | [69] | |
| capture probe DNA (22-base sequence): 5′-NH2-GGTCTCAATGGCTGCCTCCCCG-3′ | |||
| complementary target DNA (22-base sequence): 5′-CGGGGAGGCAGCCATTGAGACC-3′ | |||
| Poly-calcon carboxylic acid | 6.7 × 10−13 M | [70] | |
| immobilized probe (18-base sequence, S1)-5′-NH2-TCT CAA TGG CTG CCT CCC-3′ | |||
| target (S2)-5′-GGG AGG CAG CCA TTG AGA-3′; | |||
| Aloe-amodin/Glassy carbon electrode | 6.7 × 10−8 M | [72] | |
| immobilized probe(18-base sequence S1)-5′-NH3 TCT CAA TGG CTG CCT CCC-3′ | |||
| target (18-base sequence S2)-5′-GGG AGG CAG CCA TTG AGA-3′ | |||
| Gold nanoparticles | 84 fM | [78] | |
| Disease | Sensor | Detection Limit | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic Myeloid leukemia | Cerium dioxide, Carbon nanotubes, Chitosan | 5 × 10−13 M | [93] |
| Immobilized probe HS-ssDNA (S1): 5′-HS-AGA GTT CAA AAG CCC TTC-3′ | |||
| Target ssDNA (S2, complementary to S1): 5′-GAA GGG CTT TTG AAC TCT-3′ | |||
| Chitosan, Zinc oxide nanoparticles | 1.84 fM | [94] | |
| Recombinant plasmid containing the BCR/ABL fusion gene: 5′-AGCTTCTCCCTGACATCCGTG-3′ | |||
| MXene, Gold nanoparticles | 0.05 fM | [98] | |
| Capture probe SH-TTTCCGGAGGAGCTACCTACGATCAATCCA | |||
| Detection probe ACCACACGCTCCTCCGGCTTT-Biotin | |||
| Quantum dots | 1.0 pM | [99] | |
| Patent Publication n. | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101928767A | 2010-12-29 | Electrochemical DNA biosensor for detecting BCR/ABL fusion gene of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) |
| CN101705279A | 2010-05-12 | Nano biosensor for detecting PML/RAR alpha fusion gene of acute promyelocytic leukemia |
| US5871918A | 1996-06-20–1999-02-16 | The University Of North Carolina At Chapel Hill Electrochemical detection of nucleic acid hybridization |
| CN102676638A | 2011-03-08–2012-09-19 | Method and kit for detecting drug-resistance mutation site of ABL kinase domain of BCR/ABL fusion gene |
| WO2017114008A1 | 2015-12-30–2017-07-06 | BCR gene and ABL gene detection probe, preparation method, and reagent kit |
| CN103063715A | 2012-11-03–2013-04-24 | Method for detecting surviving gene based on graphene-gold composite material electrochemical DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) biosensor |
| CN101928767A | 2010-12-29 | Electrochemical DNA biosensor for detecting BCR/ABL fusion gene of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) |
| CN101705279A | 2010-05-12 | Nano biosensor for detecting PML/RAR alpha fusion gene of acute promyelocytic leukemia |
| CN2009101120902A | 2009-06-29 | Electrochemical DNA biosensor for detecting BCR/ABL fusion gene of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) |
| US20210048405A1 | 2021-02-18 | Binding probe circuits for molecular sensors |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Allegra, A.; Petrarca, C.; Di Gioacchino, M.; Mirabile, G.; Gangemi, S. Electrochemical Biosensors in the Diagnosis of Acute and Chronic Leukemias. Cancers 2023, 15, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010146
Allegra A, Petrarca C, Di Gioacchino M, Mirabile G, Gangemi S. Electrochemical Biosensors in the Diagnosis of Acute and Chronic Leukemias. Cancers. 2023; 15(1):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010146
Chicago/Turabian StyleAllegra, Alessandro, Claudia Petrarca, Mario Di Gioacchino, Giuseppe Mirabile, and Sebastiano Gangemi. 2023. "Electrochemical Biosensors in the Diagnosis of Acute and Chronic Leukemias" Cancers 15, no. 1: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010146
APA StyleAllegra, A., Petrarca, C., Di Gioacchino, M., Mirabile, G., & Gangemi, S. (2023). Electrochemical Biosensors in the Diagnosis of Acute and Chronic Leukemias. Cancers, 15(1), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010146








