System for the Recognizing of Pigmented Skin Lesions with Fusion and Analysis of Heterogeneous Data Based on a Multimodal Neural Network
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
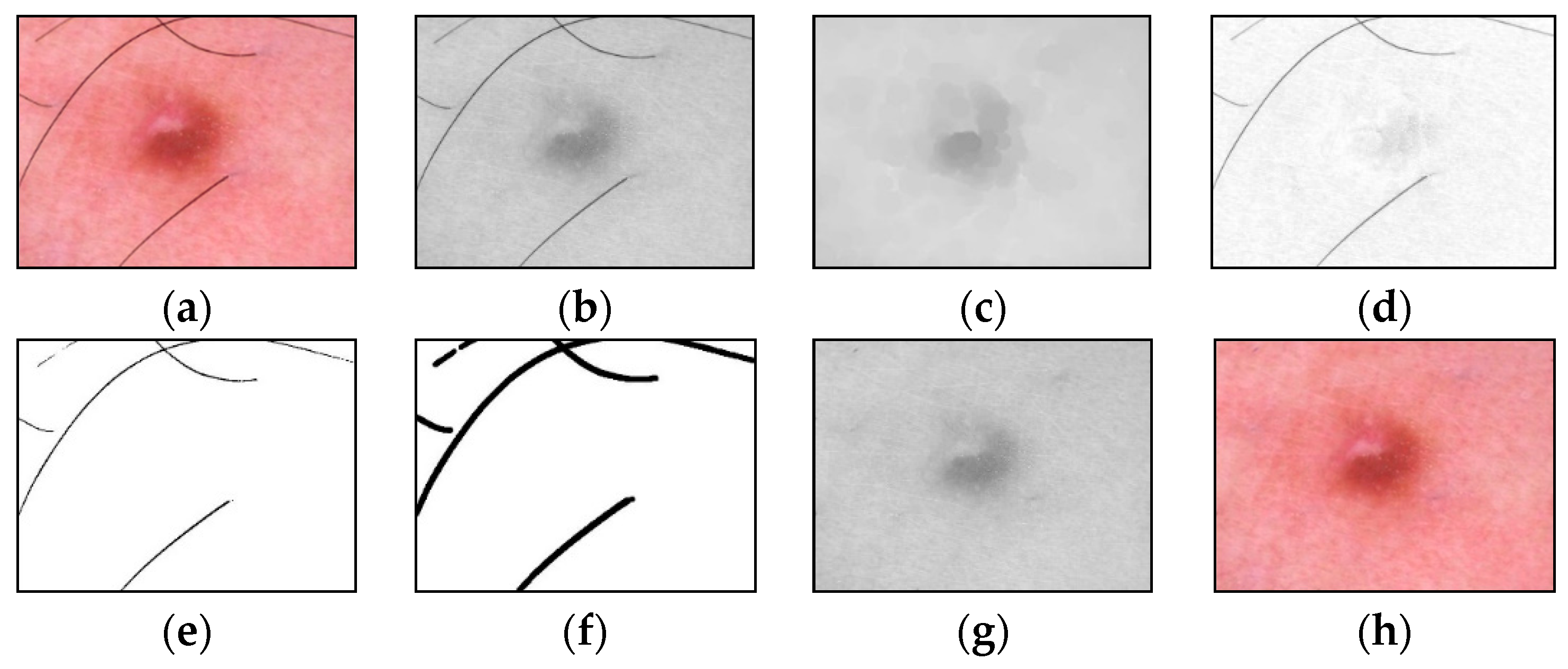
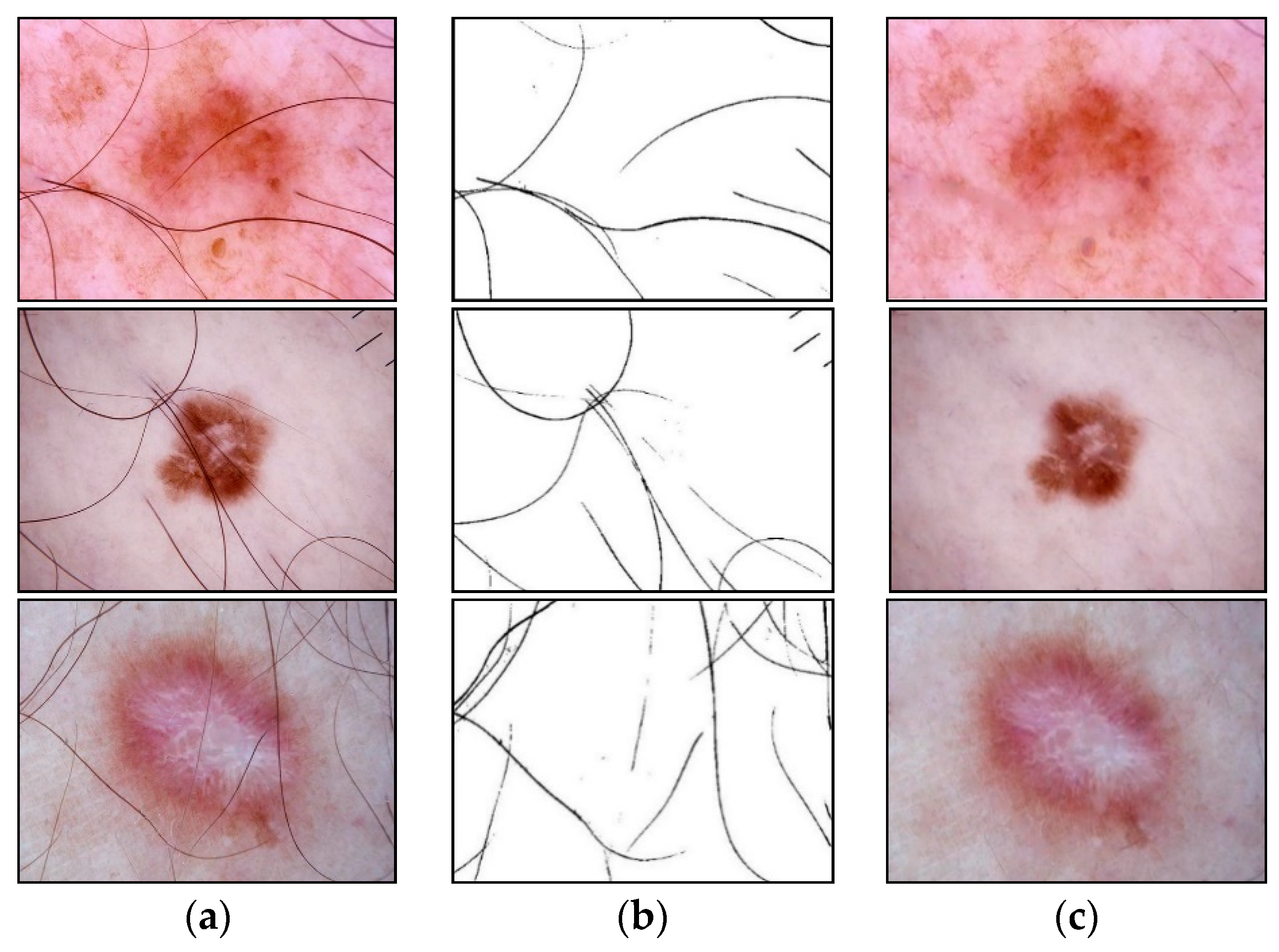
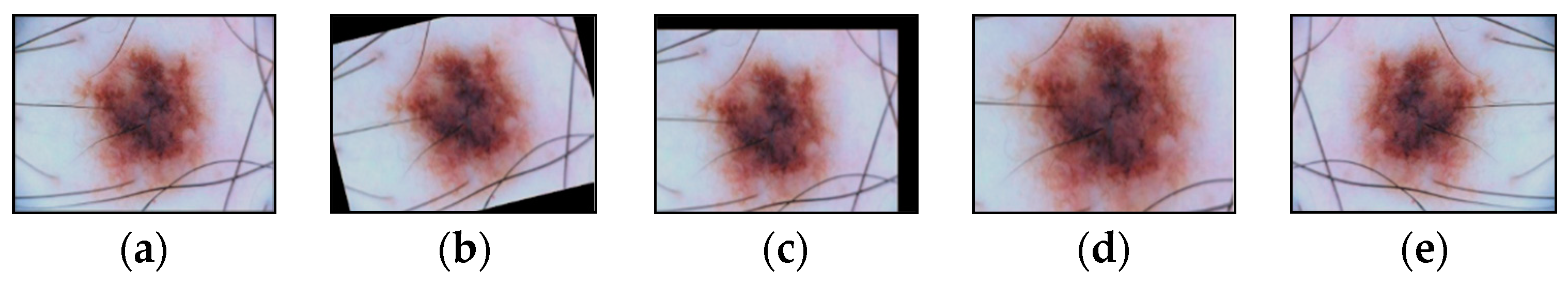
2.1. Hair Removal
2.2. Metadata Pre-Processing
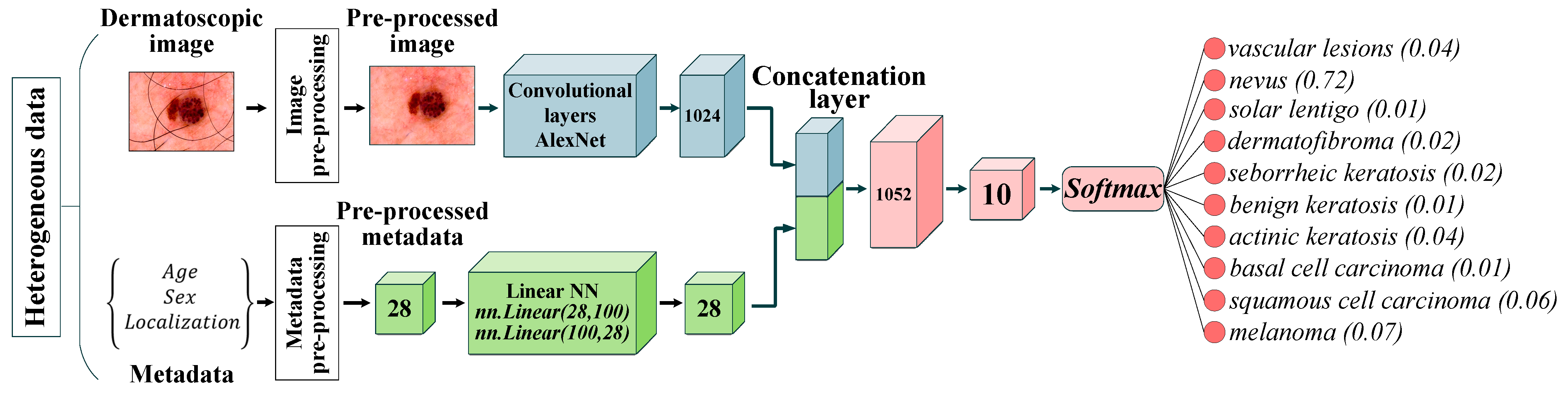
2.3. Multimodal Neural Network
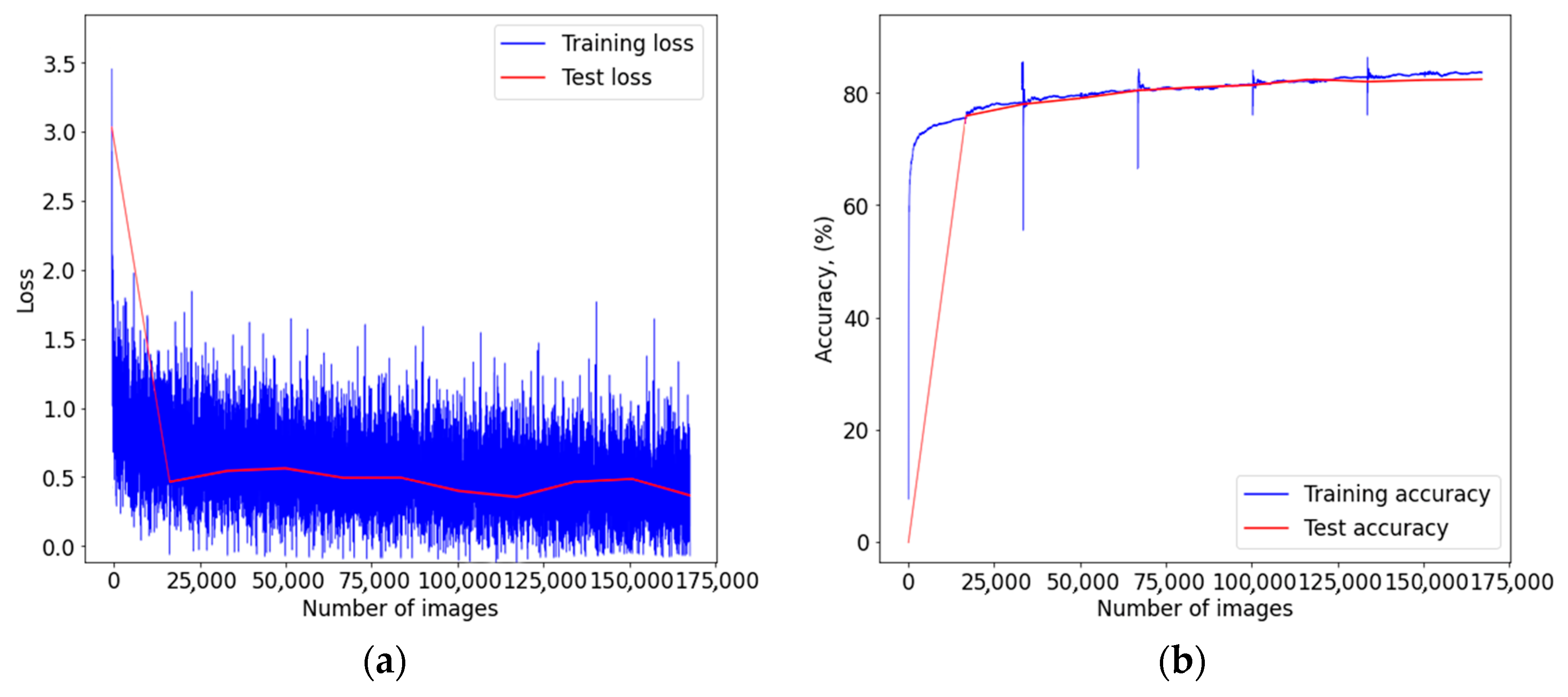
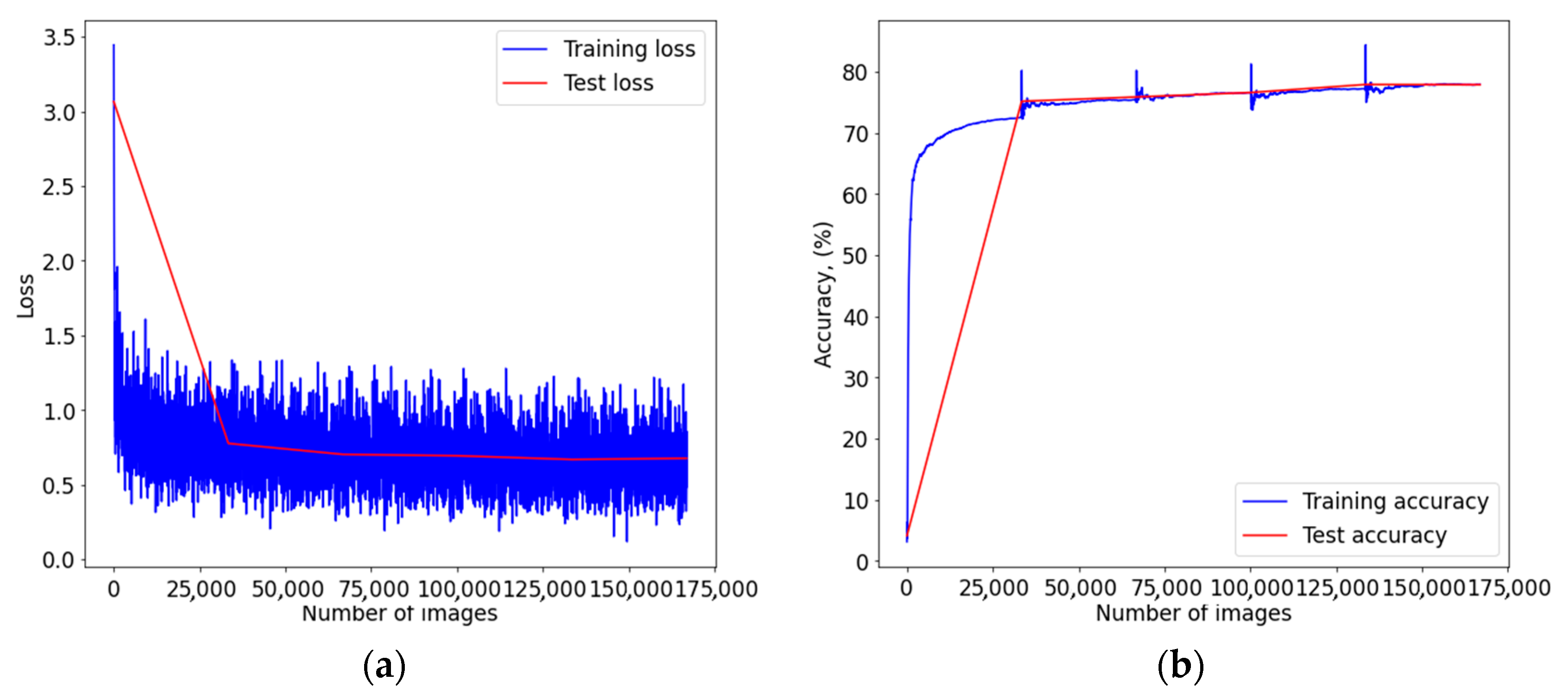
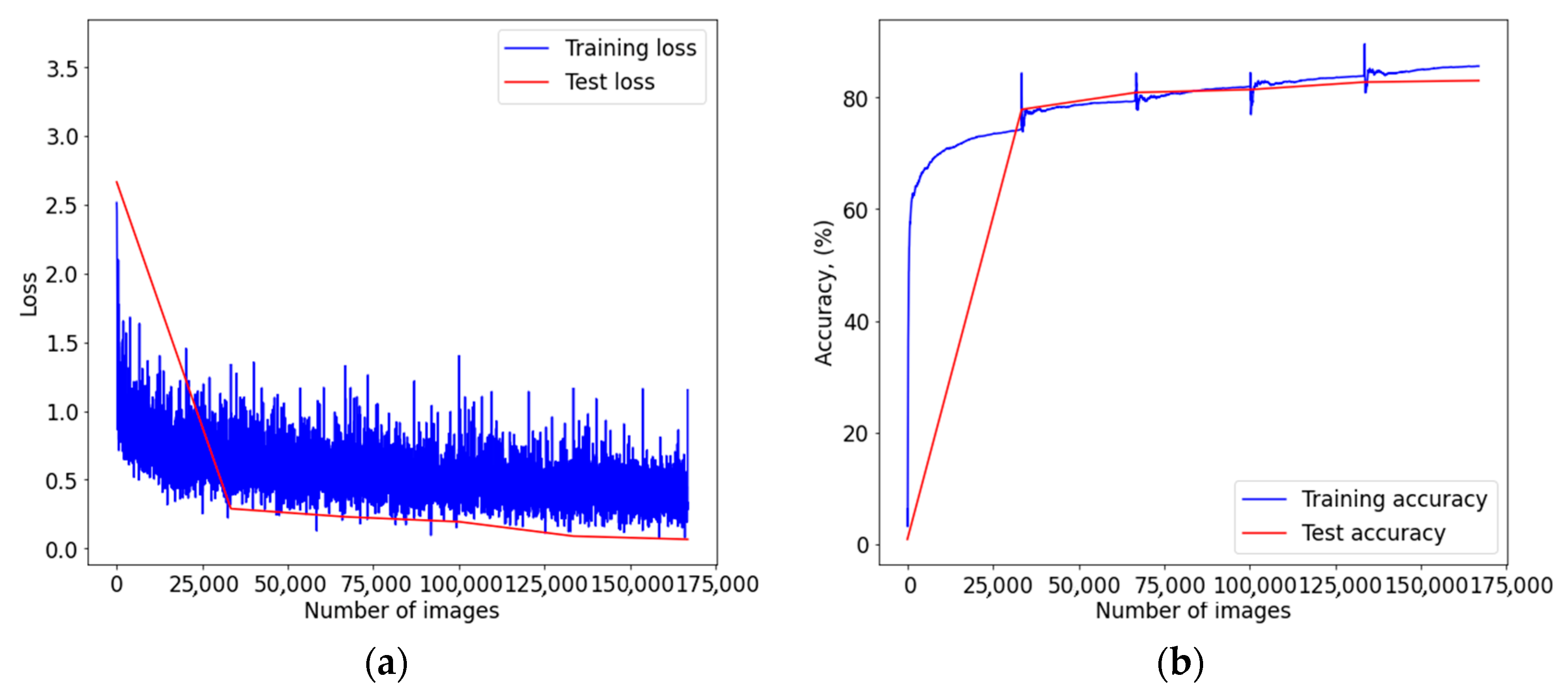
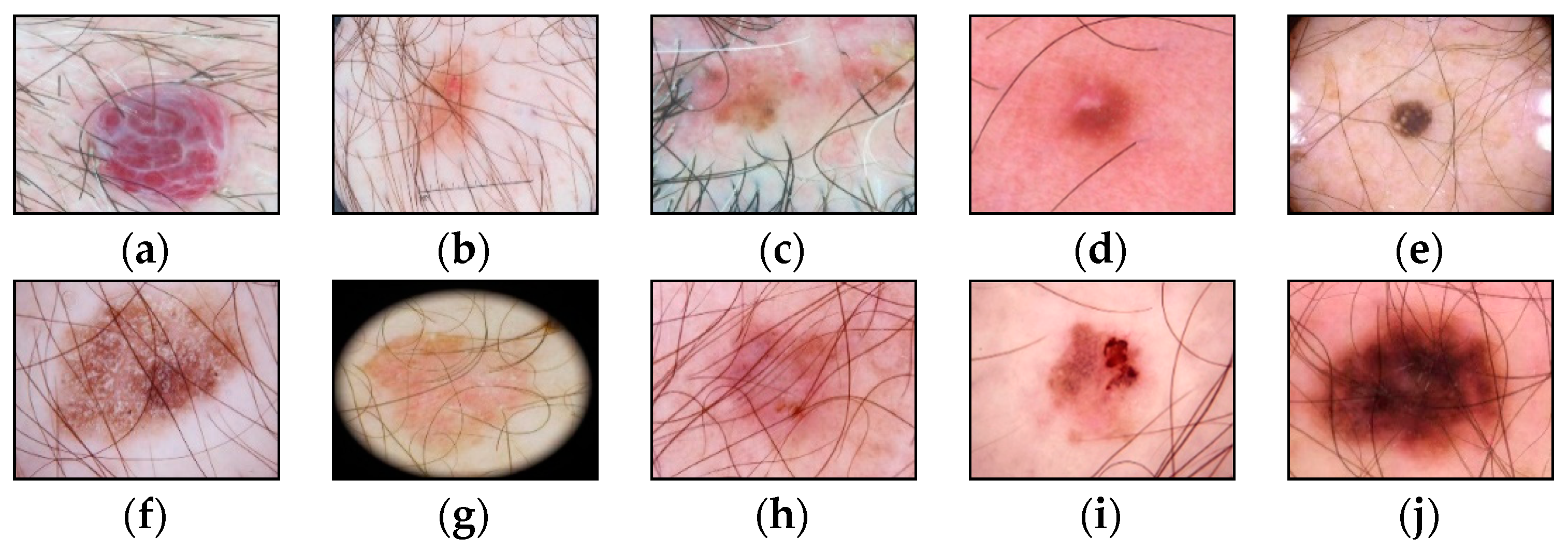
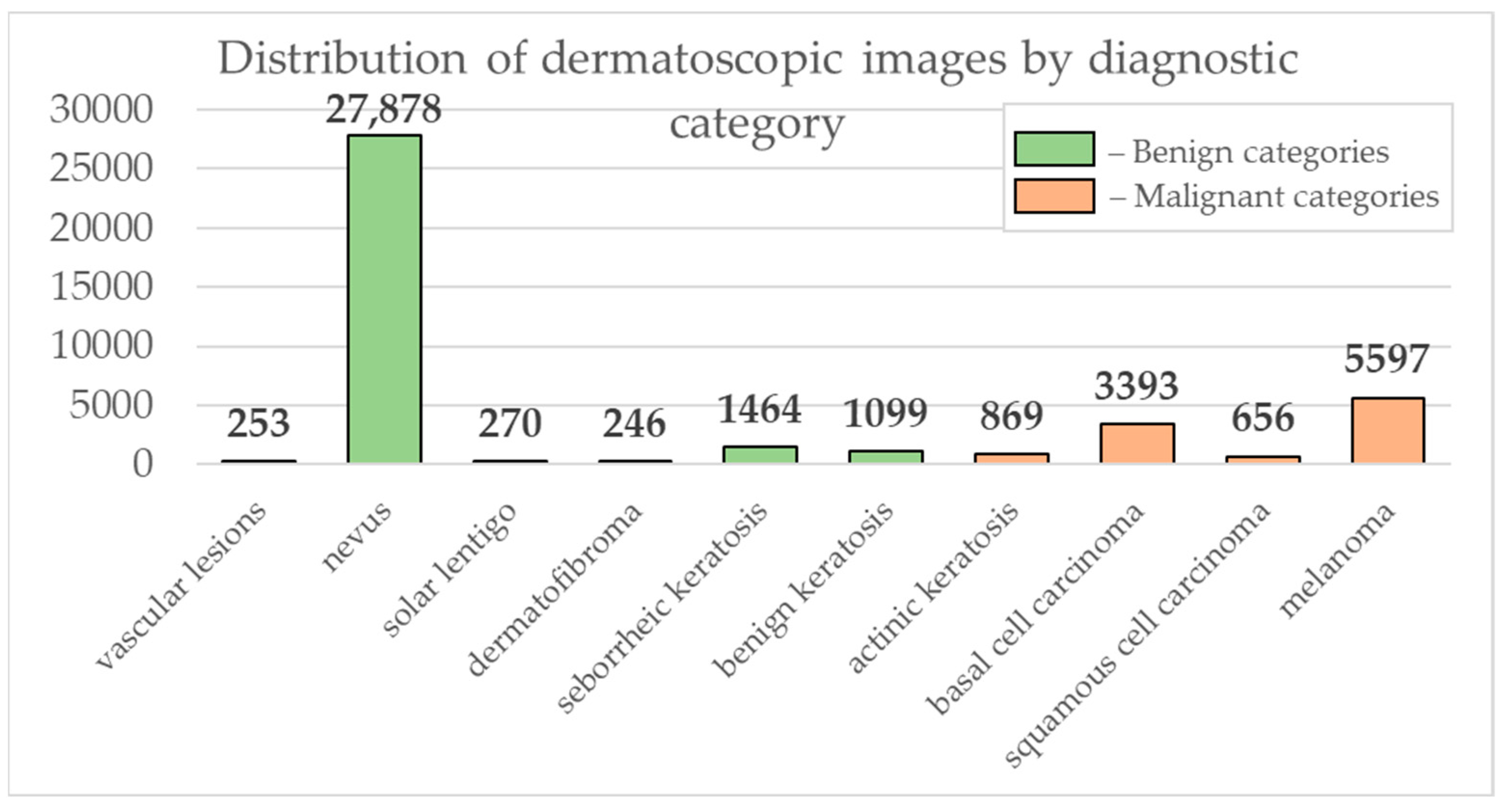
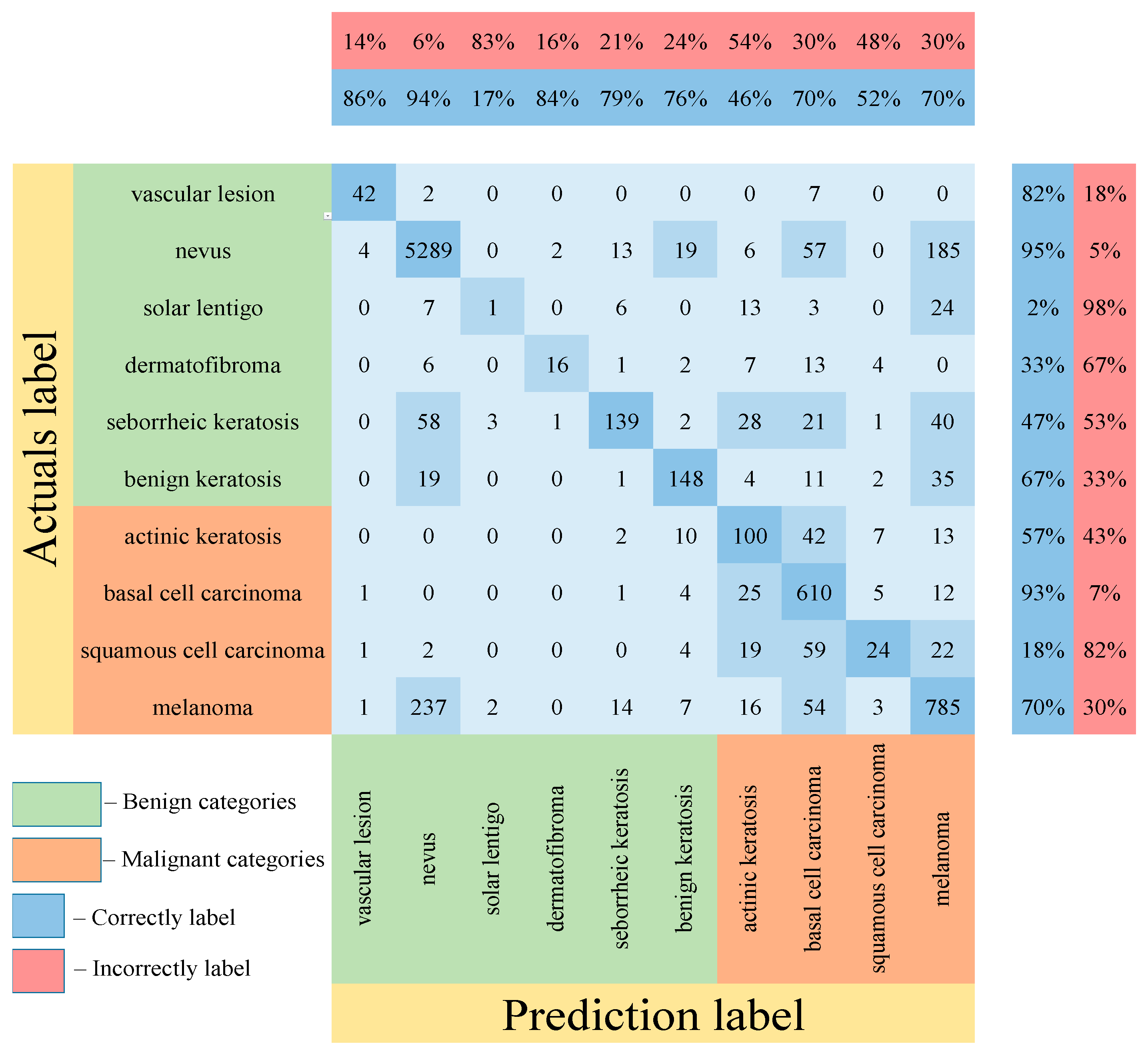
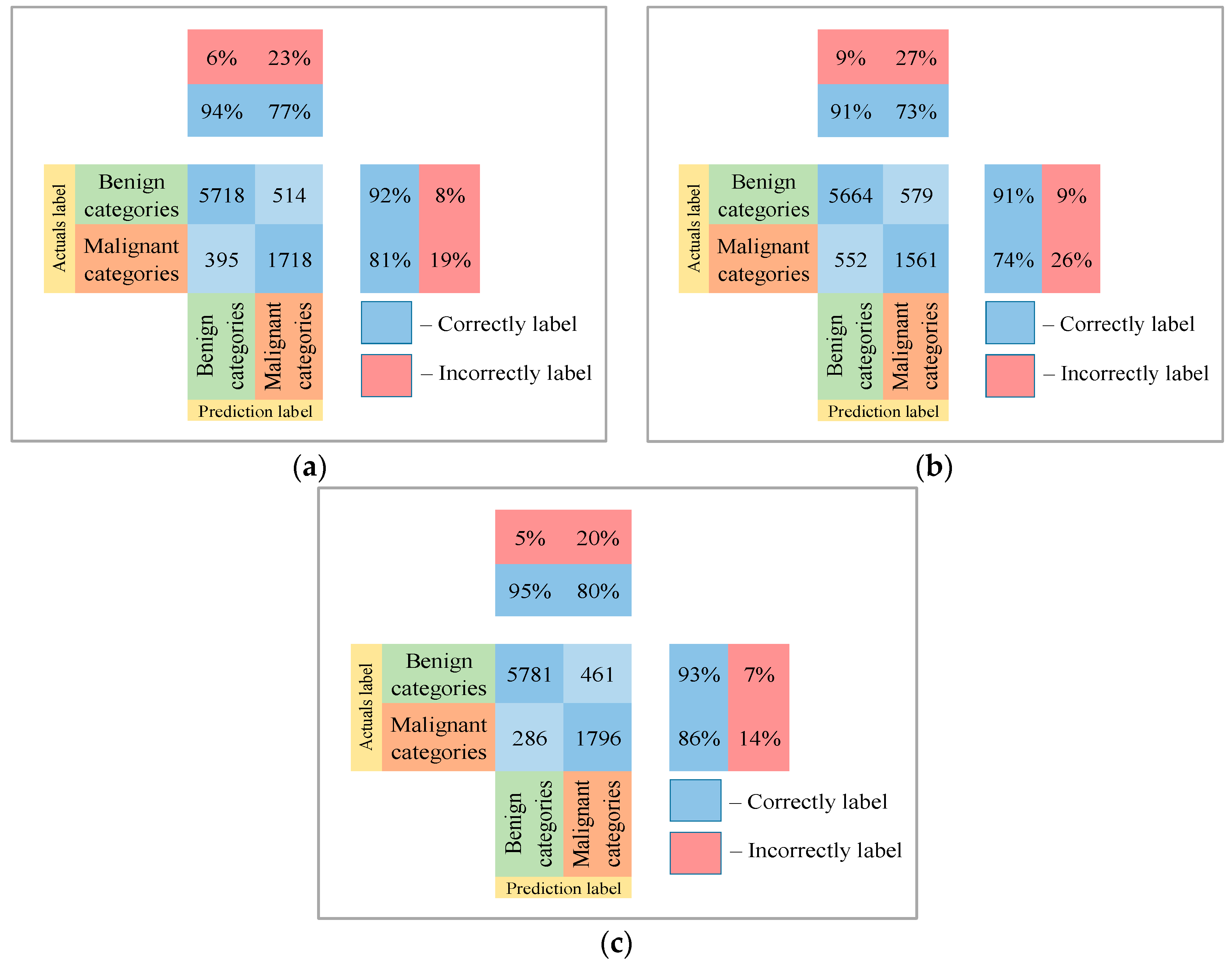
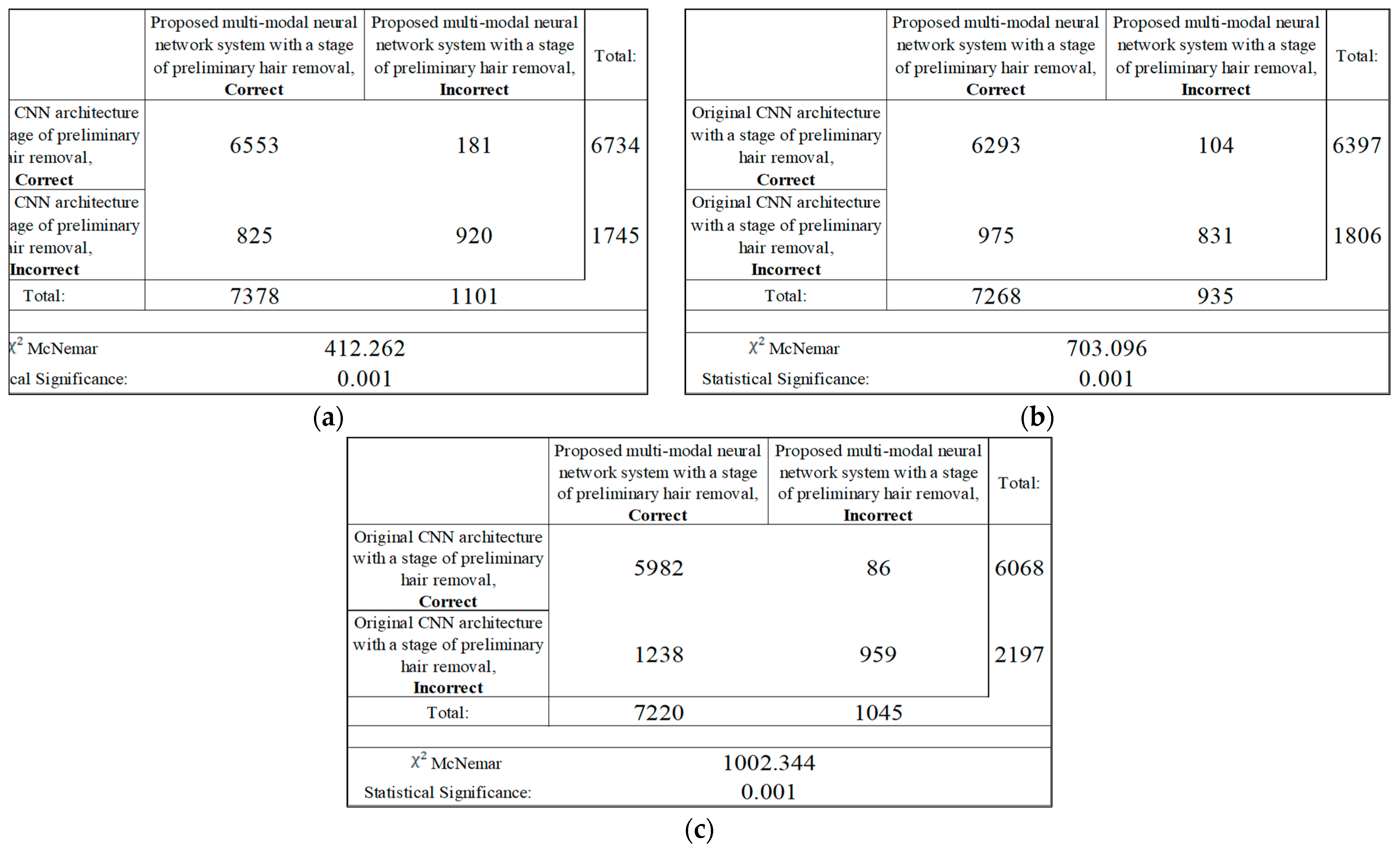
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Health Consequences of Excessive Solar UV Radiation. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/25-07-2006-health-consequences-of-excessive-solar-uv-radiation (accessed on 18 October 2021).
- Rogers, H.W.; Weinstock, M.A.; Harris, A.R.; Hinckley, M.R.; Feldman, S.R.; Fleischer, A.B.; Coldiron, B.M. Incidence Estimate of Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer in the United States, 2006. Arch. Dermatol. 2010, 146, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madan, V.; Lear, J.T.; Szeimies, R.-M. Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. Lancet 2010, 375, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Skin Cancer Foundation. Skin Cancer Facts & Statistics. Available online: https://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/skin-cancer-facts/ (accessed on 21 October 2021).
- Stern, R.S. Prevalence of a History of Skin Cancer in 2007: Results of an Incidence-Based Model. Arch. Dermatol. 2010, 146, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, T.B. Pathophysiology of Hypermelanoses. Clin. Drug Investig. 2012, 10, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, T.B. The Validity and Practicality of Sun-Reactive Skin Types I Through VI. Arch. Dermatol. 1988, 124, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, M.A.; Jimbow, K.; Szabo, G.; Fitzpatrick, T.B. Sunlight and Melanin Pigmentation. Photochem. Photobiol. Rev. 1976, 1, 211–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, H.W.; Weinstock, M.A.; Feldman, S.R.; Coldiron, B.M. Incidence Estimate of Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer (Keratinocyte Carcinomas) in the US Population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoey, S.E.H.; Devereux, C.E.J.; Murray, L.; Catney, D.; Gavin, A.; Kumar, S.; Donnelly, D.; Dolan, O.M. Skin Cancer Trends in Northern Ireland and Consequences for Provision of Dermatology Services. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diepgen, T.L.; Mahler, V. The Epidemiology of Skin Cancer. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 146, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, S.; Al-Bander, B.; Al-Nuaimy, W. A Comprehensive Evaluation and Benchmarking of Convolutional Neural Networks for Melanoma Diagnosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics for Hispanics/Latinos, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nami, N.; Giannini, E.; Burroni, M.; Fimiani, M.; Rubegni, P. Teledermatology: State-of-the-Art and Future Perspectives. Expert Rev. Dermatol. 2012, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bratchenko, I.A.; Alonova, M.v.; Myakinin, O.O.; Moryatov, A.A.; Kozlov, S.V.; Zakharov, V.P. Hyperspectral Visualization of Skin Pathologies in Visible Region. Comput. Opt. 2016, 40, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, P.; Wu, D.; Hu, L.; Hassan, M.M.; Alamri, A. AI-Skin: Skin Disease Recognition Based on Self-Learning and Wide Data Collection through a Closed-Loop Framework. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreu-Perez, J.; Poon, C.C.Y.; Merrifield, R.D.; Wong, S.T.C.; Yang, G.Z. Big Data for Health. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2015, 19, 1193–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, C. Evaluation of Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1998, 9, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, T.J.; Hekler, A.; Enk, A.H.; Klode, J.; Hauschild, A.; Berking, C.; Schilling, B.; Haferkamp, S.; Schadendorf, D.; Holland-Letz, T.; et al. Deep Learning Outperformed 136 of 157 Dermatologists in a Head-to-Head Dermoscopic Melanoma Image Classification Task. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 113, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-Level Classification of Skin Cancer with Deep Neural Networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, T.J.; Hekler, A.; Enk, A.H.; Berking, C.; Haferkamp, S.; Hauschild, A.; Weichenthal, M.; Klode, J.; Schadendorf, D.; Holland-Letz, T.; et al. Deep Neural Networks Are Superior to Dermatologists in Melanoma Image Classification. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 119, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, M.; Benning, L.; Peintner, A.; Peintner, L. Advances in and the Applicability of Machine Learning-Based Screening and Early Detection Approaches for Cancer: A Primer. Cancers 2022, 14, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, J.; Sharif, A.; Gul, N.; Anjum, M.A.; Nisar, M.W.; Azam, F.; Bukhari, S.A.C. Integrated Design of Deep Features Fusion for Localization and Classification of Skin Cancer. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 131, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Akram, T.; Sharif, M.; Javed, K.; Rashid, M.; Bukhari, S.A.C. An Integrated Framework of Skin Lesion Detection and Recognition through Saliency Method and Optimal Deep Neural Network Features Selection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 15929–15948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Akram, T.; Bukhari, S.A.C.; Nayak, R.S. Developed Newton-Raphson Based Deep Features Selection Framework for Skin Lesion Recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 129, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, K.; Majeed, F.; Siddique, A.; Meraj, T.; Rauf, H.T.; El-Meligy, M.A.; Sharaf, M.; Abd Elgawad, A.E.E. A Lightweight Approach for Skin Lesion Detection through Optimal Features Fusion. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 70, 1617–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Garcia, A.M.; McLaren, C.E.; Meyskens, F.L. Melanoma: Is Hair the Root of the Problem? Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2011, 24, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaqout, I.S. Image Processing, Pattern Recognition: An Efficient Block-Based Algorithm for Hair Removal in Dermoscopic Images. Comput. Opt. 2017, 41, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, M.; Gass, R.; Rehg, J.M.; Ferris, L.; Ho, J.; Drogowski, L. Feature-preserving artifact removal from dermoscopy images. In Medical Imaging 2008: Image Processing; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2008; Volume 6914, p. 69141B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Ng, V.; Gallagher, R.; Coldman, A.; McLean, D. Dullrazor®: A Software Approach to Hair Removal from Images. Comput. Biol. Med. 1997, 27, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Q.; Celebi, M.E.; Garcia, I.F. Hair Removal Methods: A Comparative Study for Dermoscopy Images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2011, 6, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, C.A.Z.; Pires, V.B. An Automatic Based Nonlinear Diffusion Equations Scheme for Skin Lesion Segmentation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2009, 215, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.Y.; Qin, S.Y.; Jiang, Z.G.; Meng, R.S. PDE-Based Unsupervised Repair of Hair-Occluded Information in Dermoscopy Images of Melanoma. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2009, 33, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessert, N.; Nielsen, M.; Shaikh, M.; Werner, R.; Schlaefer, A. Skin Lesion Classification Using Ensembles of Multi-Resolution EfficientNets with Meta Data. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yin, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y. Interpretability-Based Multimodal Convolutional Neural Networks for Skin Lesion Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, J.; Yolland, W.; Tschandl, P. Multimodal Skin Lesion Classification Using Deep Learning. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, L.; Feng, D.D.; Fulham, M.; Kim, J. Multi-Label Classification of Multi-Modality Skin Lesion via Hyper-Connected Convolutional Neural Network. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 107, 107502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Castilla, J.-S.; Rangel-Cortes, J.-J.; Garcia-Lamont, F.; Trueba-Espinosa, A.; Zumpango, J.; Tejocote, E.; de Mexico, E. CNN and Metadata for Classification of Benign and Malignant Melanomas. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 11644, pp. 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellacani, G.; Seidenari, S. Comparison between Morphological Parameters in Pigmented Skin Lesion Images Acquired by Means of Epiluminescence Surface Microscopy and Polarized-Light Videomicroscopy. Clin. Dermatol. 2002, 20, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinz, C.; Tschandl, P.; Rosendahl, C.; Akay, B.N.; Argenziano, G.; Blum, A.; Braun, R.P.; Cabo, H.; Gourhant, J.Y.; Kreusch, J.; et al. Accuracy of Dermatoscopy for the Diagnosis of Nonpigmented Cancers of the Skin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Joseph Raj, A.N.; Tjahjadi, T.; Zhuang, Z. Digital Hair Removal by Deep Learning for Skin Lesion Segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 117, 107994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorese, M.; Peserico, E.; Silletti, A. VirtualShave: Automated Hair Removal from Digital Dermatoscopic Images. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 5145–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, P. Approximate Bayesian Neural Networks in Genomic Prediction. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atrey, P.K.; Hossain, M.A.; El Saddik, A.; Kankanhalli, M.S. Multimodal Fusion for Multimedia Analysis: A Survey. Multimedia Syst. 2010, 16, 345–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Q. Multi-Modal Bioelectrical Signal Fusion Analysis Based on Different Acquisition Devices and Scene Settings: Overview, Challenges, and Novel Orientation. Inf. Fusion 2022, 79, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Luo, J.; Yan, J.; Pulya, R.; Li, X.; Wells, W.; Jagadeesan, J. Adversarial Uni- and Multi-Modal Stream Networks for Multimodal Image Registration. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 12263, pp. 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas-Tato, J.; Martin, A.; Fierrez, J.; Camacho, D. Fusing CNNs and Statistical Indicators to Improve Image Classification. Inf. Fusion 2022, 79, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L. Skin Disease Diagnosis with Deep Learning: A Review. Neurocomputing 2021, 464, 364–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISIC Archive. Available online: https://www.isic-archive.com/#!/topWithHeader/wideContentTop/main (accessed on 18 November 2021).
- Tschandl, P.; Rosendahl, C.; Kittler, H. The HAM10000 Dataset, a Large Collection of Multi-Source Dermatoscopic Images of Common Pigmented Skin Lesions. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaphy, M.R.; Ackerman, A.B. The nature of solar keratosis: A critical review in historical perspective. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2000, 43, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, J.A.; Korgavkar, K.; Weinstock, M.A. Current perspective on actinic keratosis: A review. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffes, E.W.B.; Tang, E.H. Actinic keratosis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2000, 1, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-Level Accuracy with 50x Fewer Parameters and <0.5 MB Model Size. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, A.; Balakrishnan, G.; Durand, F.; Guttag, J.V.; Dalca, A.V. Data Augmentation Using Learned Transformations for One-Shot Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 8543–8553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisla, D.; Choromanska, A.; Berman, R.S.; Stein, J.A.; Polsky, D. Towards Automated Melanoma Detection with Deep Learning: Data Purification and Augmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 2720–2728. [Google Scholar]
- Hosny, K.M.; Kassem, M.A.; Foaud, M.M. Classification of Skin Lesions Using Transfer Learning and Augmentation with Alex-Net. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynn, N.C.; Kyu, Z.M. Segmentation and Classification of Skin Cancer Melanoma from Skin Lesion Images. In Proceedings of the Parallel and Distributed Computing, Applications and Technologies, PDCAT, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–20 December 2017; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, A. A Color-Based Approach for Melanoma Skin Cancer Detection. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Secure Cyber Computing and Communications, ICSCCC 2018, Jalandhar, India, 15–17 December 2018; pp. 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagrouba, E.; Barhoumi, W. A Prelimary Approach for the Automated Recognition of Malignant Melanoma. Image Anal. Stereol. 2004, 23, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




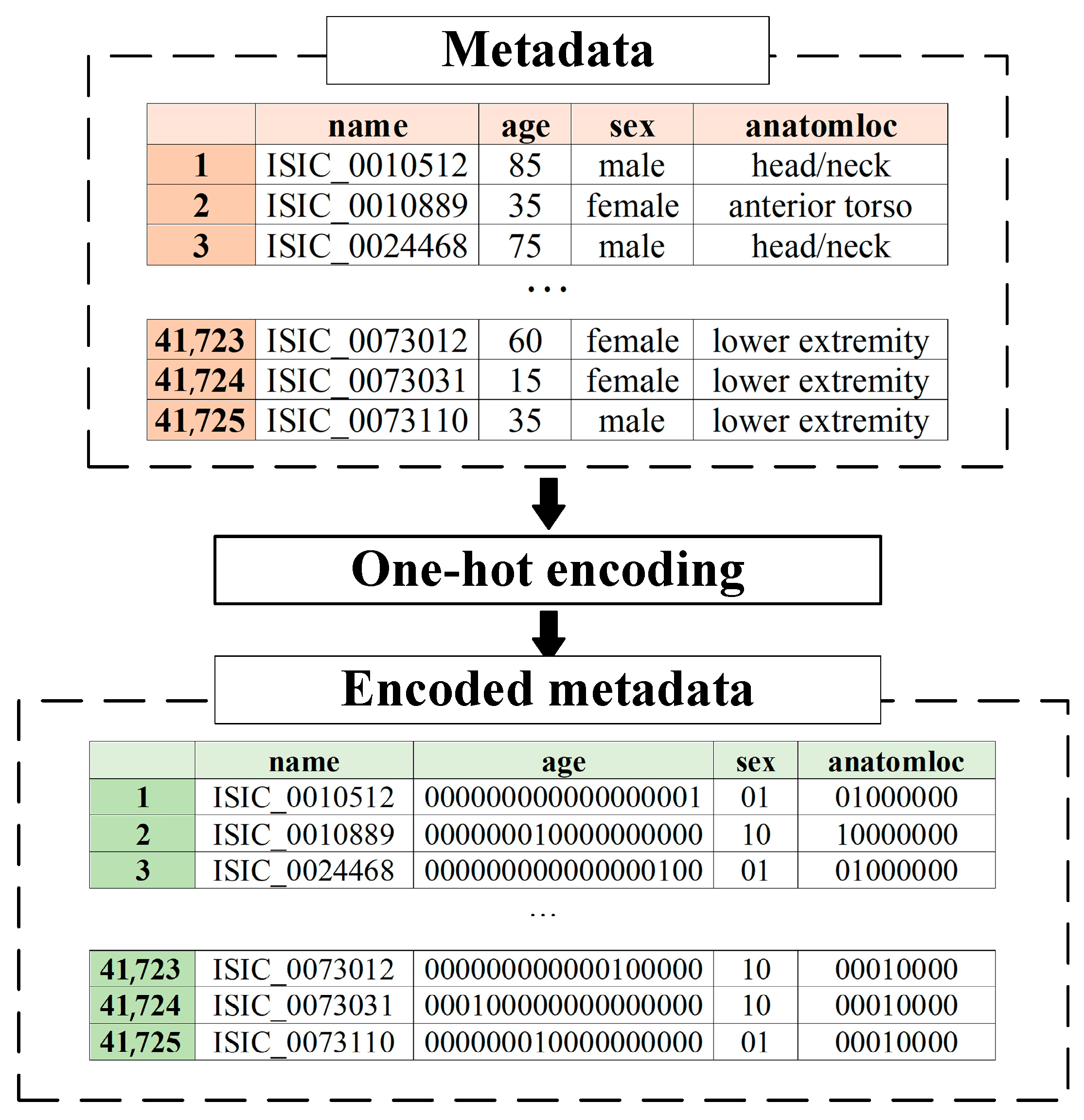



| Patient Gender (Sex) | One-Hot Code | |
|---|---|---|
| male | 0 | 1 |
| female | 1 | 0 |
| Localization of Pigmented Lesion on the Patient Body (Anatomloc) | One-Hot Code | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| anterior torso | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| head/neck | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| lateral torso | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| lower extremity | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| oral/genital | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| palms/soles | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| posterior torso | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| upper extremity | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| The Age of the Patient (Age) | One-Hot Code | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 35 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 45 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 55 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 65 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 70 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 75 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 80 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 85 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| CNN Architecture | Results of Recognition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original CNN Architecture, % | Original CNN Architecture with a Stage of Preliminary Hair Removal, % | Proposed Multimodal Neural Network System with a Stage of Preliminary Hair Removal, % | Different in Recognition Accuracy between Original and Proposed Neural Network Systems, % | |
| AlexNet [54] | 78.63 | 80.81 | 83.56 | 4.93 |
| SqueezeNet [55] | 71.63 | 73.76 | 77.87 | 6.24 |
| ResNet-101 [56] | 76.75 | 79.92 | 83.03 | 6.28 |
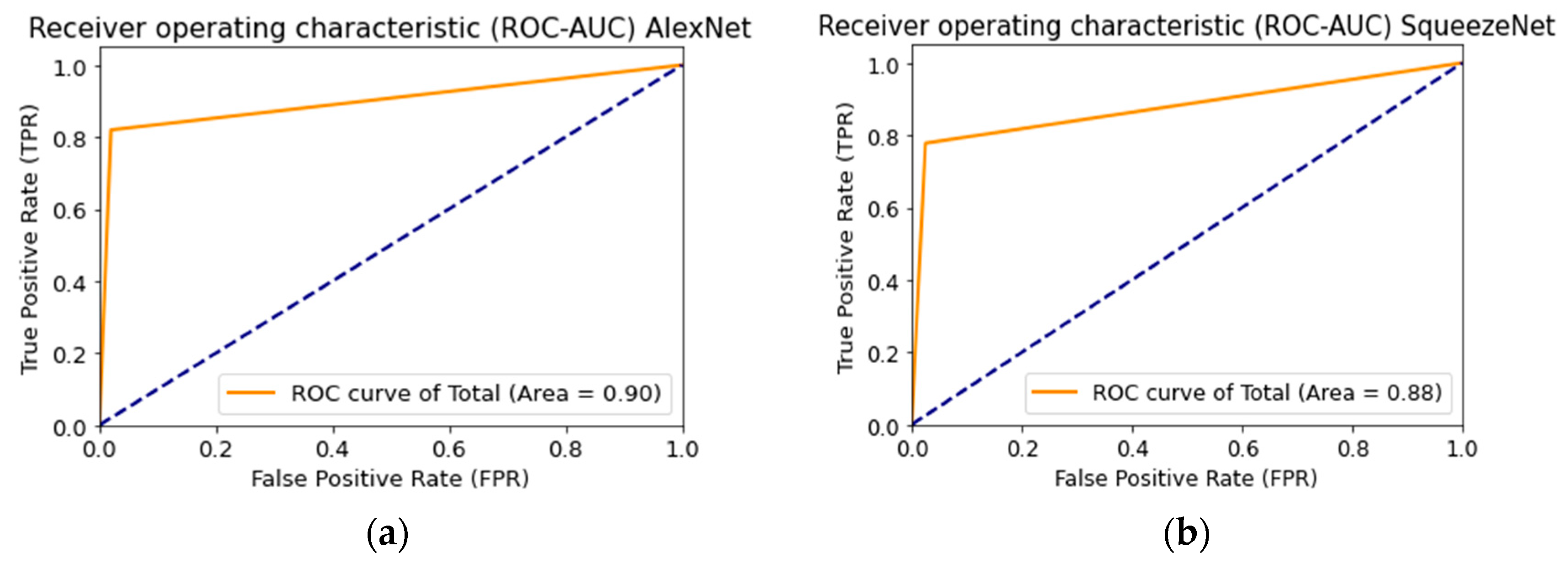
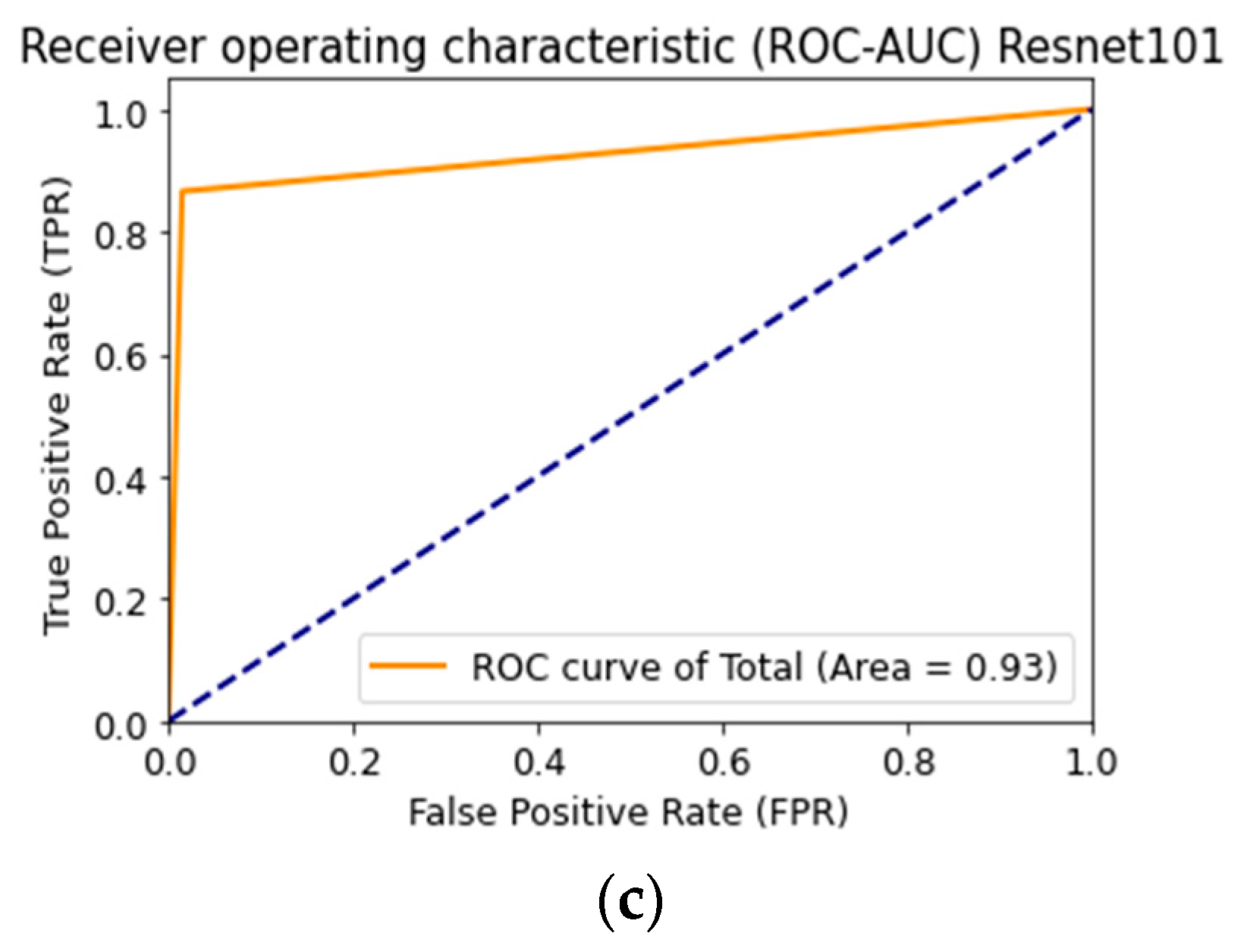
| CNN Architecture | Recognition Accuracy, % | Loss Function | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|
| AlexNet [54] | 83.56 | 0.47 | 0.90 |
| SqueezeNet [55] | 77.87 | 0.67 | 0.88 |
| ResNet-101 [56] | 83.03 | 0.66 | 0.93 |
| Multimodal Neural Network Systems for the Classification of Skin Pigmentation Lesions | Accuracy of Detection of Pigmented Skin Lesions, % | |
|---|---|---|
| Known neural network systems | [34] | 63.4 |
| [35] | 72.0 | |
| [36] | 72.9 | |
| [38] | 79.0 | |
| Proposed neural network system | 83.6 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyakhov, P.A.; Lyakhova, U.A.; Nagornov, N.N. System for the Recognizing of Pigmented Skin Lesions with Fusion and Analysis of Heterogeneous Data Based on a Multimodal Neural Network. Cancers 2022, 14, 1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071819
Lyakhov PA, Lyakhova UA, Nagornov NN. System for the Recognizing of Pigmented Skin Lesions with Fusion and Analysis of Heterogeneous Data Based on a Multimodal Neural Network. Cancers. 2022; 14(7):1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071819
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyakhov, Pavel Alekseevich, Ulyana Alekseevna Lyakhova, and Nikolay Nikolaevich Nagornov. 2022. "System for the Recognizing of Pigmented Skin Lesions with Fusion and Analysis of Heterogeneous Data Based on a Multimodal Neural Network" Cancers 14, no. 7: 1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071819
APA StyleLyakhov, P. A., Lyakhova, U. A., & Nagornov, N. N. (2022). System for the Recognizing of Pigmented Skin Lesions with Fusion and Analysis of Heterogeneous Data Based on a Multimodal Neural Network. Cancers, 14(7), 1819. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071819







