Planar Proton Minibeam Irradiation Elicits Spatially Confined DNA Damage in a Human Epidermis Model
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reconstructed Human Epidermis Model
2.2. Irradiation and Dosimetry
2.3. Tissue Processing
2.4. Immunofluorescence Staining (IF)
2.5. Microscopy and Quantitative Image Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
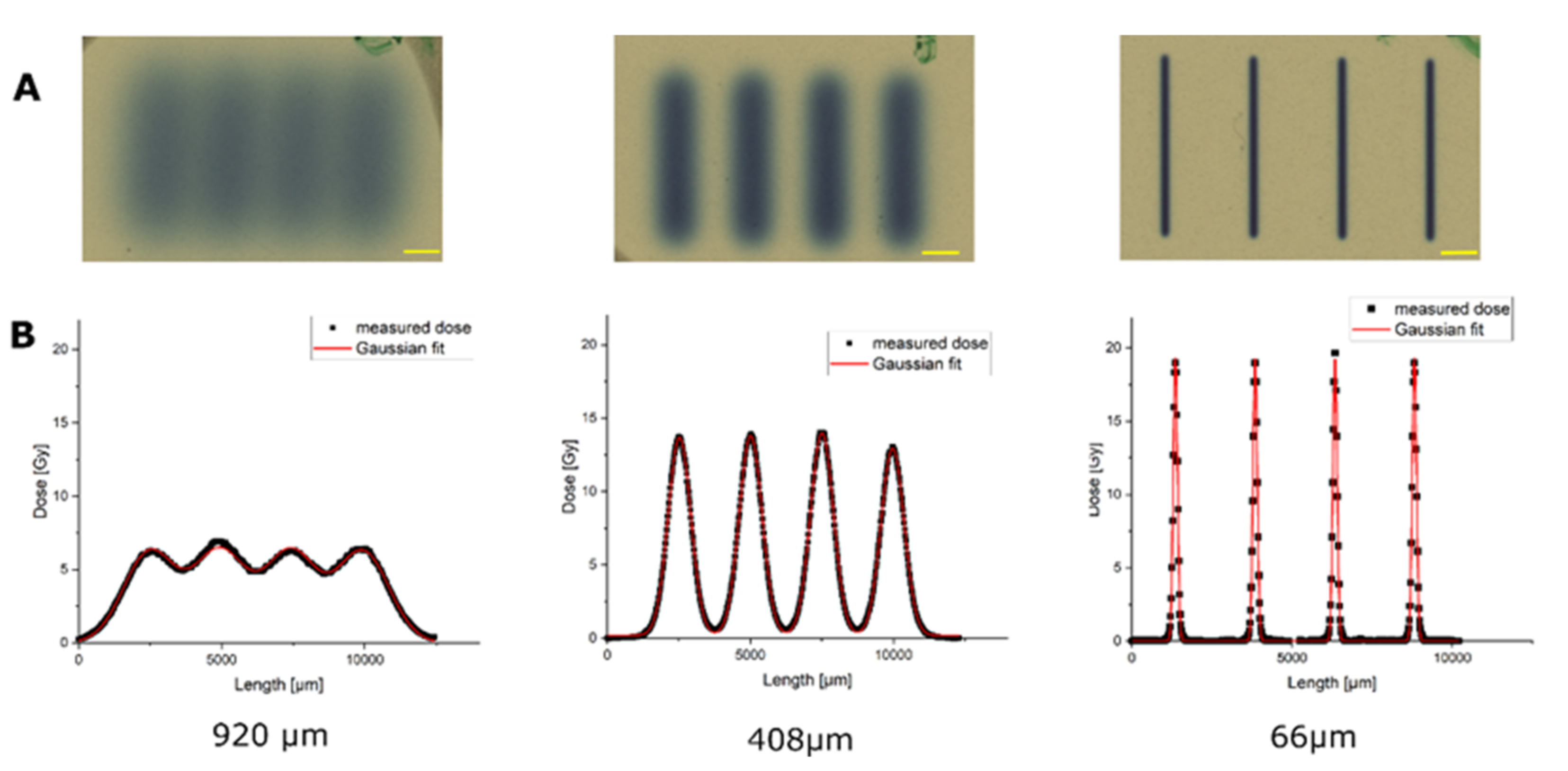
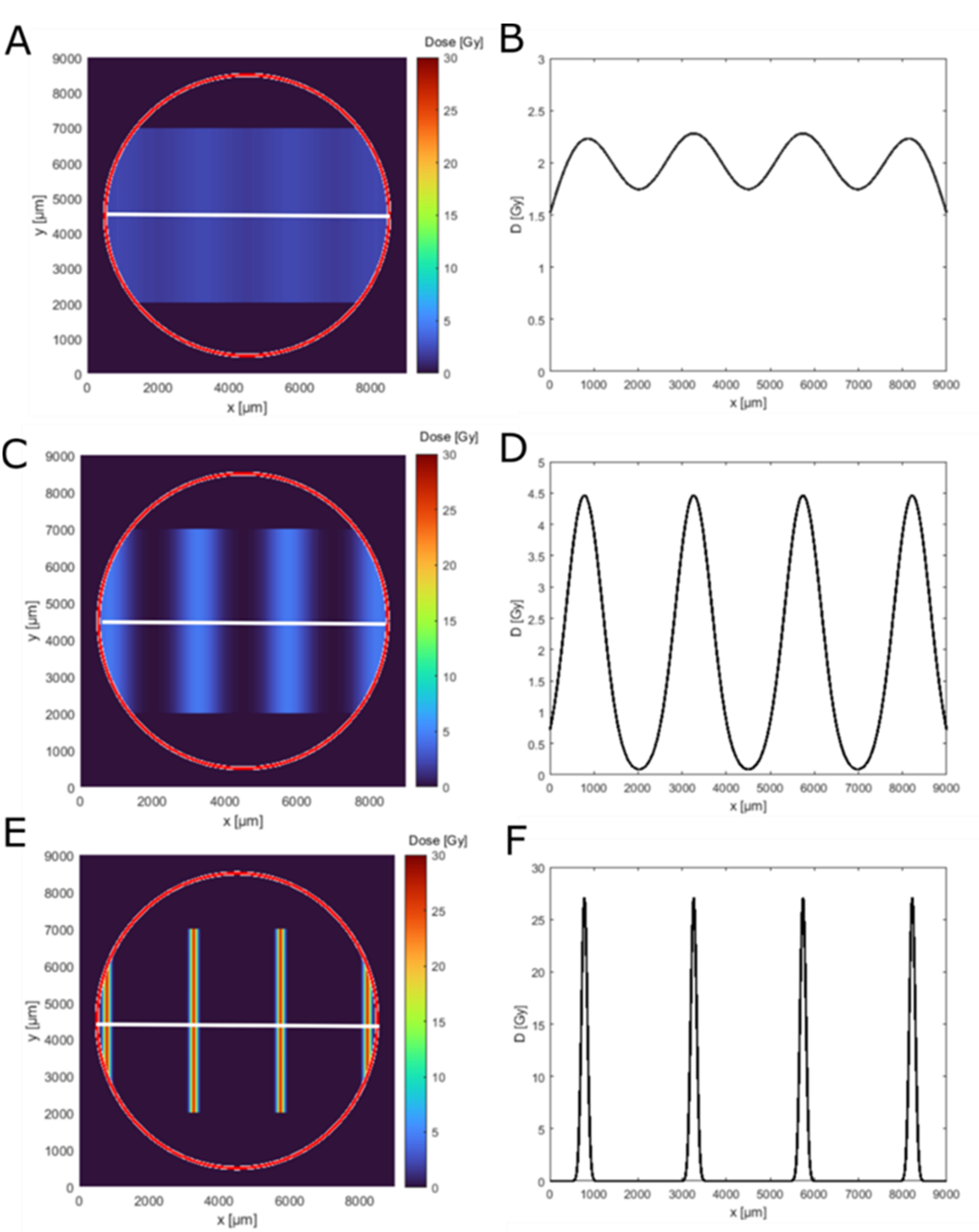
3.1. Dose Distributions
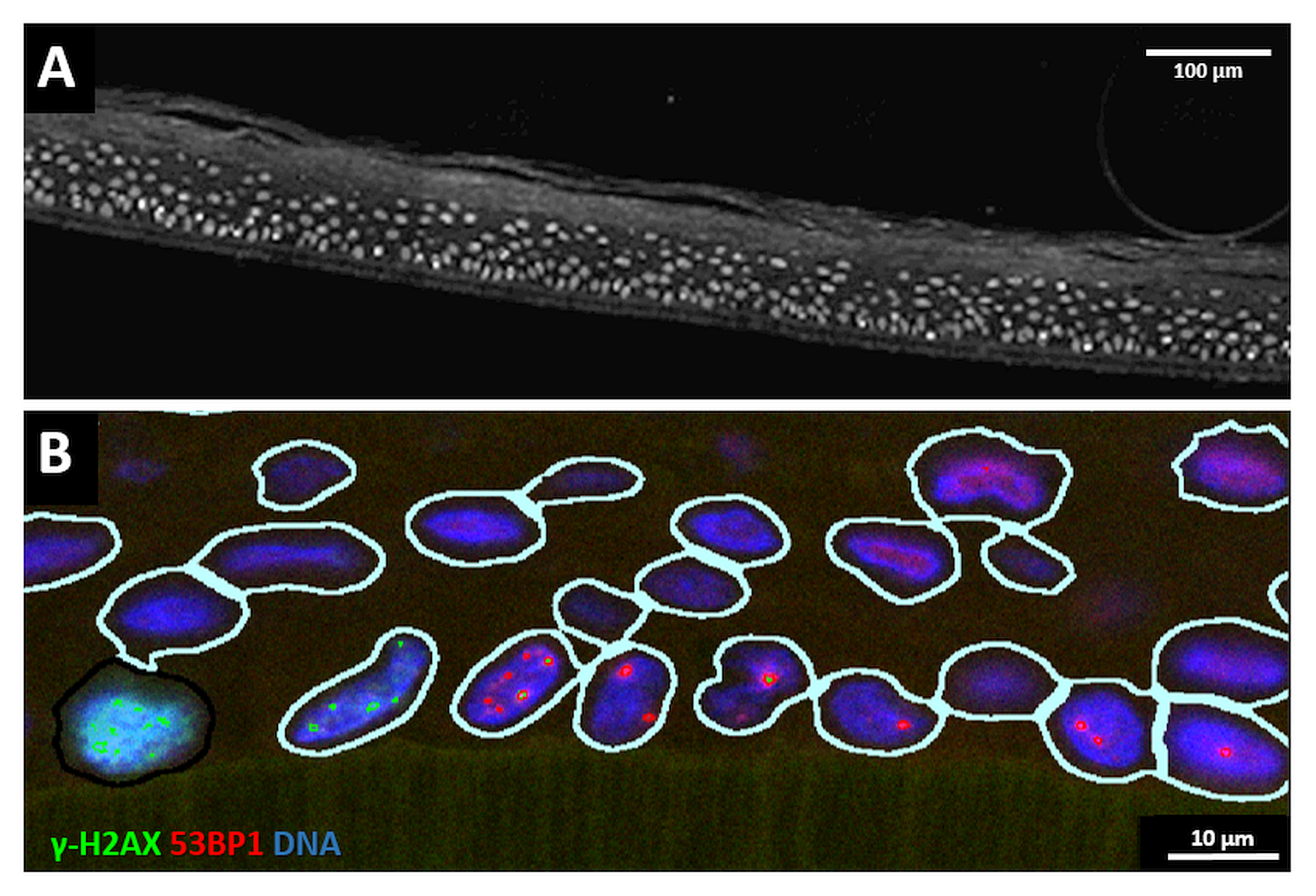
3.2. Narrow Minibeams Induce Spatially Limited Damage
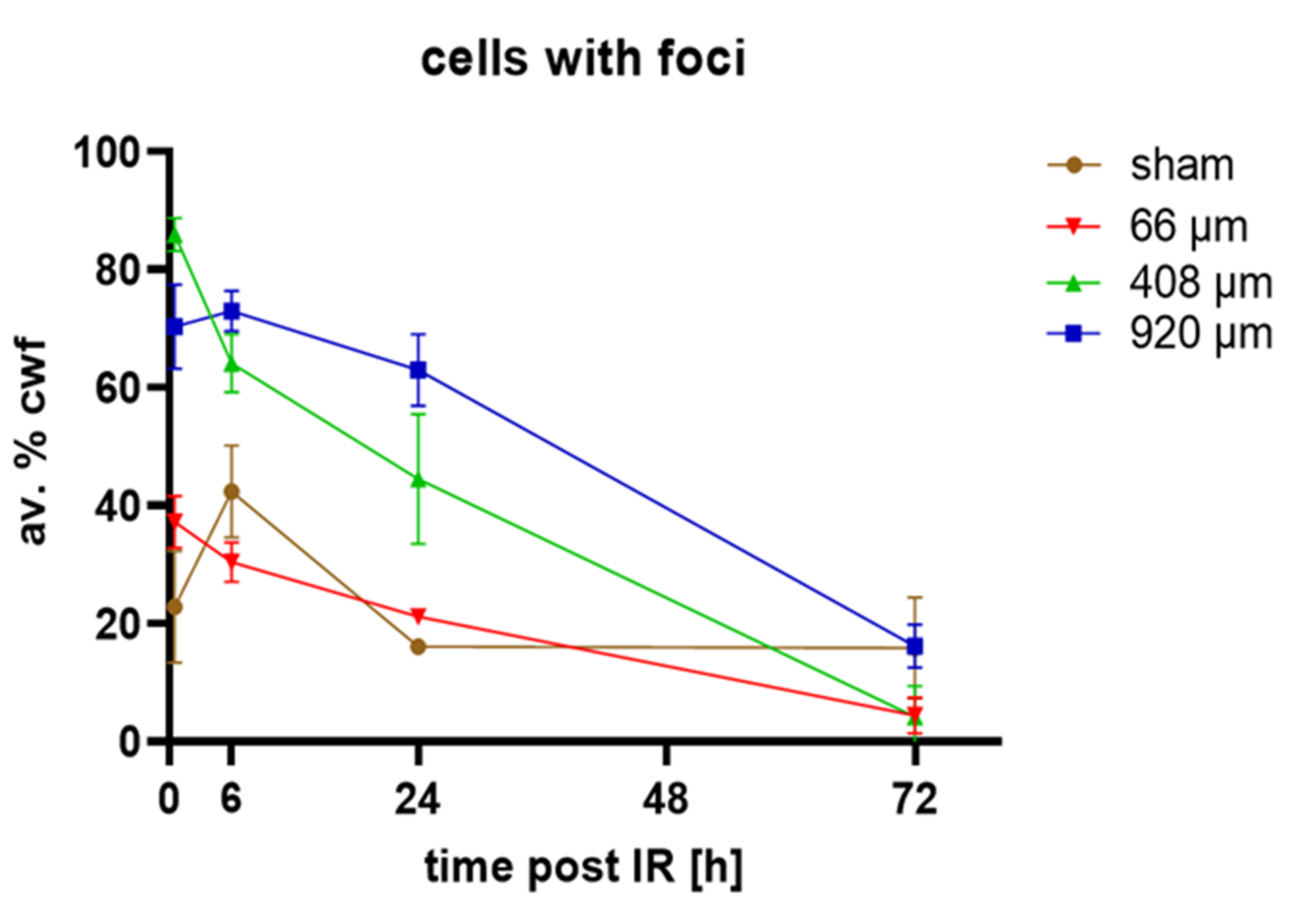
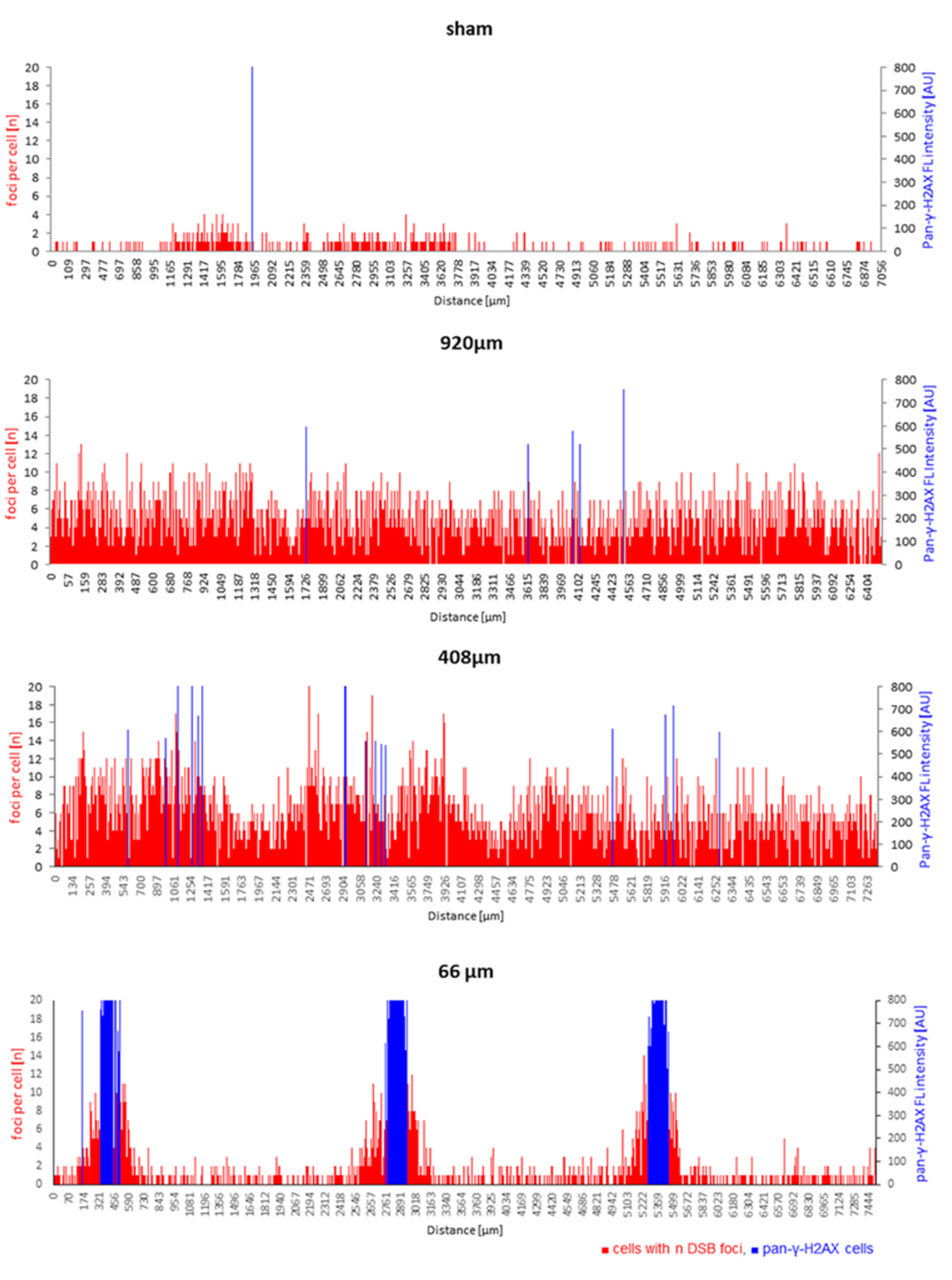
3.3. Spatial Distribution of DNA Damage across Epidermis Models
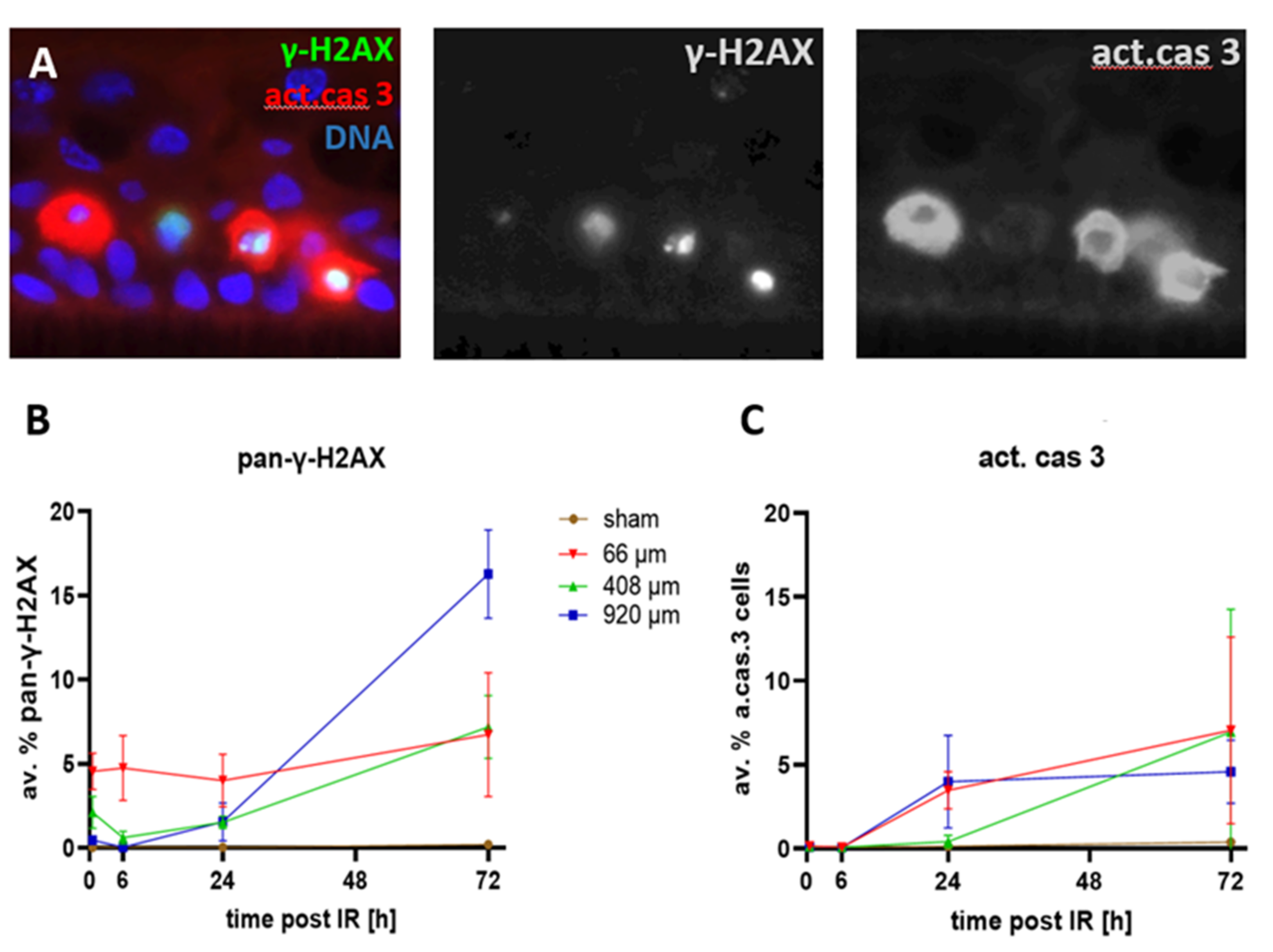
3.4. Cell Death after Proton Minibeam Irradiation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salvo, N.; Barnes, E.; van Draanen, J.; Stacey, E.; Mitera, G.; Breen, D.; Giotis, A.; Czarnota, G.; Pang, J.; De Angelis, C. Prophylaxis and management of acute radiation-induced skin reactions: A systematic review of the literature. Curr. Oncol. 2010, 17, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köhler, A. A Method of Deep Roentgen Irradiation without Injury to the Skin. Arch. Roentgen Ray 1909, 14, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatkin, D.N.; Dilmanian, F.A.; Spanne, P.O. Method for Microbeam Radiation Therapy. U.S. Patent 5,339,347, 1 January 1994. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/doepatents/biblio/869455-method-microbeam-radiation-therapy (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Laissue, J.A.; Geiser, G.; Spanne, P.O.; Dilmanian, F.A.; Gebbers, J.-O.; Geiser, M.; Wu, X.-Y.; Makar, M.S.; Micca, P.L.; Nawrocky, M.M.; et al. Neuropathology of ablation of rat gliosarcomas and contiguous brain tissues using a microplanar beam of synchrotron-wiggler-generated X rays. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 78, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezado, Y.; Fois, G.R. Proton-minibeam radiation therapy: A proof of concept. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 031712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlobinskaya, O.; Girst, S.; Greubel, C.; Hable, V.; Siebenwirth, C.; Walsh, D.W.; Multhoff, G.; Wilkens, J.J.; Schmid, T.E.; Dollinger, G. Reduced side effects by proton microchannel radiotherapy: Study in a human skin model. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2013, 52, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, J.; Hartmann, J.T.; Dorr, W.; Ugurel, S. Skin toxicity of anti-cancer therapy. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2008, 6, 959–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girst, S.; Reindl, J. pMB FLASH - Status and Perspectives of Combining Proton Minibeam with FLASH Radiotherapy. J. Cancer Immunol. 2019, 1, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sammer, M.; Dombrowsky, A.C.; Schauer, J.; Oleksenko, K.; Bicher, S.; Schwarz, B.; Rudigkeit, S.; Matejka, N.; Reindl, J.; Bartzsch, S.; et al. Normal Tissue Response of Combined Temporal and Spatial Fractionation in Proton Minibeam Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammer, M.; Zahnbrecher, E.; Dobiasch, S.; Girst, S.; Greubel, C.; Ilicic, K.; Reindl, J.; Schwarz, B.; Siebenwirth, C.; Walsh, D.W.M.; et al. Proton pencil minibeam irradiation of an in-vivo mouse ear model spares healthy tissue dependent on beam size. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girst, S.; Greubel, C.; Reindl, J.; Siebenwirth, C.; Zlobinskaya, O.; Walsh, D.W.M.; Ilicic, K.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; Wilkens, J.J.; et al. Proton Minibeam Radiation Therapy Reduces Side Effects in an In Vivo Mouse Ear Model. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamirault, C.; Doyère, V.; Juchaux, M.; Pouzoulet, F.; Labiod, D.; Dendale, R.; Patriarca, A.; Nauraye, C.; Le Dudal, M.; Jouvion, G.; et al. Short and long-term evaluation of the impact of proton minibeam radiation therapy on motor, emotional and cognitive functions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezado, Y.; Jouvion, G.; Patriarca, A.; Nauraye, C.; Guardiola, C.; Juchaux, M.; Lamirault, C.; Labiod, D.; Jourdain, L.; Sebrie, C.; et al. Proton minibeam radiation therapy widens the therapeutic index for high-grade gliomas. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prezado, Y.; Jouvion, G.; Hardy, D.; Patriarca, A.; Nauraye, C.; Bergs, J.; González, W.; Guardiola, C.; Juchaux, M.; Labiod, D.; et al. Proton minibeam radiation therapy spares normal rat brain: Long-Term Clinical, Radiological and Histopathological Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withers, H.R.; Thames, H.D. Dose fractionation and volume effects in normal tissues and tumors. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1988, 11, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straile, W.E.; Chase, H.B. The use of elongate microbeams of x-rays for simulating the effects of cosmic rays on tissues: A study of wound healing and hair follicle regeneration. Radiat. Res. 1963, 18, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilmanian, F.A.; Qu, Y.; Feinendegen, L.E.; Pena, L.A.; Bacarian, T.; Henn, F.A.; Kalef-Ezra, J.; Liu, S.; Zhong, Z.; McDonald, J.W. Tissue-sparing effect of x-ray microplanar beams particularly in the CNS: Is a bystander effect involved? Exp. Hematol. 2007, 35, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyakov, O.V.; Mitchell, S.A.; Parikh, D.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Marino, S.A.; Amundson, S.A.; Geard, C.R.; Brenner, D.J. Biological effects in unirradiated human tissue induced by radiation damage up to 1 mm away. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14203–14208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauptner, A.; Dietzel, S.; Drexler, G.A.; Reichart, P.; Krucken, R.; Cremer, T.; Friedl, A.A.; Dollinger, G. Microirradiation of cells with energetic heavy ions. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2004, 42, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, C.M.; do Nascimento Pedrosa, T.; Pennacchi, P.C.; de Assis, S.R.; Gimenes, F.; Consolaro, M.E.L.; de Moraes Barros, S.B.; Maria-Engler, S.S. Skin corrosion test: A comparison between reconstructed human epidermis and full thickness skin models. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 125, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 439: In Vitro Skin Irritation: Reconstructed Human Epidermis Test Method. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; Section 4; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, T.; Shimada, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Okino, A. DNA Damage Response After Ionizing Radiation Exposure in Skin Keratinocytes Derived from Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redon, C.E.; Dickey, J.S.; Bonner, W.M.; Sedelnikova, O.A. γ-H2AX as a biomarker of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation in human peripheral blood lymphocytes and artificial skin. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 43, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakashima, M.; Yamashita, S. Dynamics of ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage response in reconstituted three-dimensional human skin tissue. Radiat. Res. 2010, 174, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Meador, J.A.; Geard, C.R.; Balajee, A.S. Analysis of ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage and repair in three-dimensional human skin model system. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, e16–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Girst, S.; Greubel, C.; Reindl, J.; Siebenwirth, C.; Zlobinskaya, O.; Dollinger, G.; Schmid, T.E. The influence of the channel size on the reduction of side effects in microchannel proton therapy. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2015, 54, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hable, V.; Greubel, C.; Bergmaier, A.; Reichart, P.; Hauptner, A.; Krücken, R.; Strickfaden, H.; Dietzel, S.; Cremer, T.; Drexler, G.A.; et al. The live cell irradiation and observation setup at SNAKE. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2009, 267, 2090–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girst, S.; Marx, C.; Brauer-Krisch, E.; Bravin, A.; Bartzsch, S.; Oelfke, U.; Greubel, C.; Reindl, J.; Siebenwirth, C.; Zlobinskaya, O.; et al. Improved normal tissue protection by proton and X-ray microchannels compared to homogeneous field irradiation. Phys. Med. 2015, 31, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinhardt, S.; Hillbrand, M.; Wilkens, J.J.; Assmann, W. Comparison of Gafchromic EBT2 and EBT3 films for clinical photon and proton beams. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 5257–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, R.C.; Steiner, G.E. Microscopy-based multicolor tissue cytometry at the single-cell level. Cytometry A 2004, 59, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.F. DNA damage and repair. Basic Life Sci. 1991, 58, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.A.; Agay, D.; Schrock, G.; Drouet, M.; Meineke, V.; Scherthan, H. Persistent DNA damage after high dose in vivo gamma exposure of minipig skin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.; Voss, K.O.; Tobias, F.; Jakob, B.; Durante, M.; Taucher-Scholz, G. Clustered DNA damage induces pan-nuclear H2AX phosphorylation mediated by ATM and DNA-PK. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 6109–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Yu, K.N.; Hou, J.; Liu, Q.; Han, W. Radiation-induced bystander effect: Early process and rapid assessment. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, M.V.; Smilenov, L.B.; Hall, E.J.; Panyutin, I.G.; Bonner, W.M.; Sedelnikova, O.A. Ionizing radiation induces DNA double-strand breaks in bystander primary human fibroblasts. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7257–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heib, M.; Weiss, J.; Saggau, C.; Hoyer, J.; Fuchslocher Chico, J.; Voigt, S.; Adam, D. Ars moriendi: Proteases as sculptors of cellular suicide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamkowski, A.; Forcheron, F.; Agay, D.; Ahmed, E.A.; Drouet, M.; Meineke, V.; Scherthan, H. DNA damage focus analysis in blood samples of minipigs reveals acute partial body irradiation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Xu, Q.; Martin, T.D.; Li, M.Z.; Demaria, M.; Aron, L.; Lu, T.; Yankner, B.A.; Campisi, J.; Elledge, S.J. The DNA damage response induces inflammation and senescence by inhibiting autophagy of GATA4. Science 2015, 349, aaa5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olivieri, F.; Albertini, M.C.; Orciani, M.; Ceka, A.; Cricca, M.; Procopio, A.D.; Bonafe, M. DNA damage response (DDR) and senescence: Shuttled inflamma-miRNAs on the stage of inflamm-aging. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 35509–35521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furuta, T.; Takemura, H.; Liao, Z.Y.; Aune, G.J.; Redon, C.; Sedelnikova, O.A.; Pilch, D.R.; Rogakou, E.P.; Celeste, A.; Chen, H.T.; et al. Phosphorylation of histone H2AX and activation of Mre11, Rad50, and Nbs1 in response to replication-dependent DNA double-strand breaks induced by mammalian DNA topoisomerase I cleavage complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20303–20312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moeglin, E.; Desplancq, D.; Conic, S.; Oulad-Abdelghani, M.; Stoessel, A.; Chiper, M.; Vigneron, M.; Didier, P.; Tora, L.; Weiss, E. Uniform Widespread Nuclear Phosphorylation of Histone H2AX Is an Indicator of Lethal DNA Replication Stress. Cancers 2019, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogakou, E.P.; Nieves-Neira, W.; Boon, C.; Pommier, Y.; Bonner, W.M. Initiation of DNA fragmentation during apoptosis induces phosphorylation of H2AX histone at serine 139. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9390–9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harfouche, G.; Martin, M.T. Response of normal stem cells to ionizing radiation: A balance between homeostasis and genomic stability. Mutat. Res. 2010, 704, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirman, Z.; de Lange, T. 53BP1: A DSB escort. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santivasi, W.L.; Xia, F. Ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage, response, and repair. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackford, A.N.; Jackson, S.P. ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK: The Trinity at the Heart of the DNA Damage Response. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 801–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horn, S.; Brady, D.; Prise, K. Alpha particles induce pan-nuclear phosphorylation of H2AX in primary human lymphocytes mediated through ATM. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismail, F.; Ikram, M.; Purdie, K.; Harwood, C.; Leigh, I.; Storey, A. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and the DNA damage response: pATM expression patterns in pre-malignant and malignant keratinocyte skin lesions. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granzotto, A.; Benadjaoud, M.A.; Vogin, G.; Devic, C.; Ferlazzo, M.L.; Bodgi, L.; Pereira, S.; Sonzogni, L.; Forcheron, F.; Viau, M.; et al. Influence of Nucleoshuttling of the ATM Protein in the Healthy Tissues Response to Radiation Therapy: Toward a Molecular Classification of Human Radiosensitivity. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 94, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Caër, S. Water Radiolysis: Influence of Oxide Surfaces on H2 Production under Ionizing Radiation. Water 2011, 3, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scherthan, H.; Wagner, S.-Q.; Grundhöfer, J.; Matejka, N.; Müller, J.; Müller, S.; Rudigkeit, S.; Sammer, M.; Schoof, S.; Port, M.; et al. Planar Proton Minibeam Irradiation Elicits Spatially Confined DNA Damage in a Human Epidermis Model. Cancers 2022, 14, 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14061545
Scherthan H, Wagner S-Q, Grundhöfer J, Matejka N, Müller J, Müller S, Rudigkeit S, Sammer M, Schoof S, Port M, et al. Planar Proton Minibeam Irradiation Elicits Spatially Confined DNA Damage in a Human Epidermis Model. Cancers. 2022; 14(6):1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14061545
Chicago/Turabian StyleScherthan, Harry, Stephanie-Quinta Wagner, Jan Grundhöfer, Nicole Matejka, Jessica Müller, Steffen Müller, Sarah Rudigkeit, Matthias Sammer, Sarah Schoof, Matthias Port, and et al. 2022. "Planar Proton Minibeam Irradiation Elicits Spatially Confined DNA Damage in a Human Epidermis Model" Cancers 14, no. 6: 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14061545
APA StyleScherthan, H., Wagner, S.-Q., Grundhöfer, J., Matejka, N., Müller, J., Müller, S., Rudigkeit, S., Sammer, M., Schoof, S., Port, M., & Reindl, J. (2022). Planar Proton Minibeam Irradiation Elicits Spatially Confined DNA Damage in a Human Epidermis Model. Cancers, 14(6), 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14061545






