Mechanisms, Mediators, and Moderators of the Effects of Exercise on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
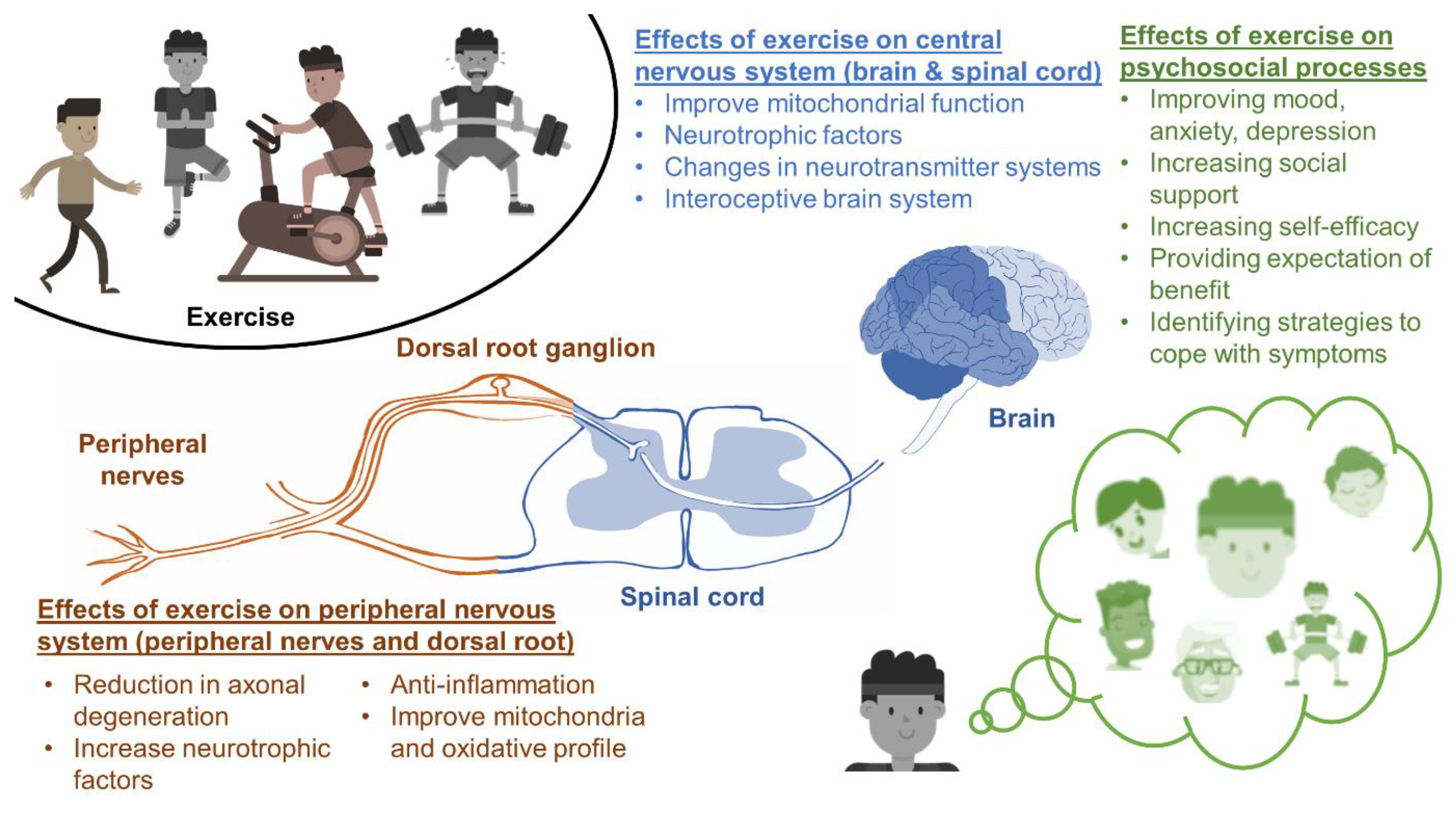
2. Neurophysiological Mechanisms
2.1. Neurotrophic Factors
2.2. Inflammation
2.3. CIPN and the Brain
2.4. Mitochondrial Function
2.5. Axonal Integrity and Outgrowth
3. Psychosocial Mechanisms
3.1. Improving Mood, Anxiety, Depression, and Fatigue
3.2. Increasing Social Support and Self-Efficacy
3.3. Expectation of Benefit
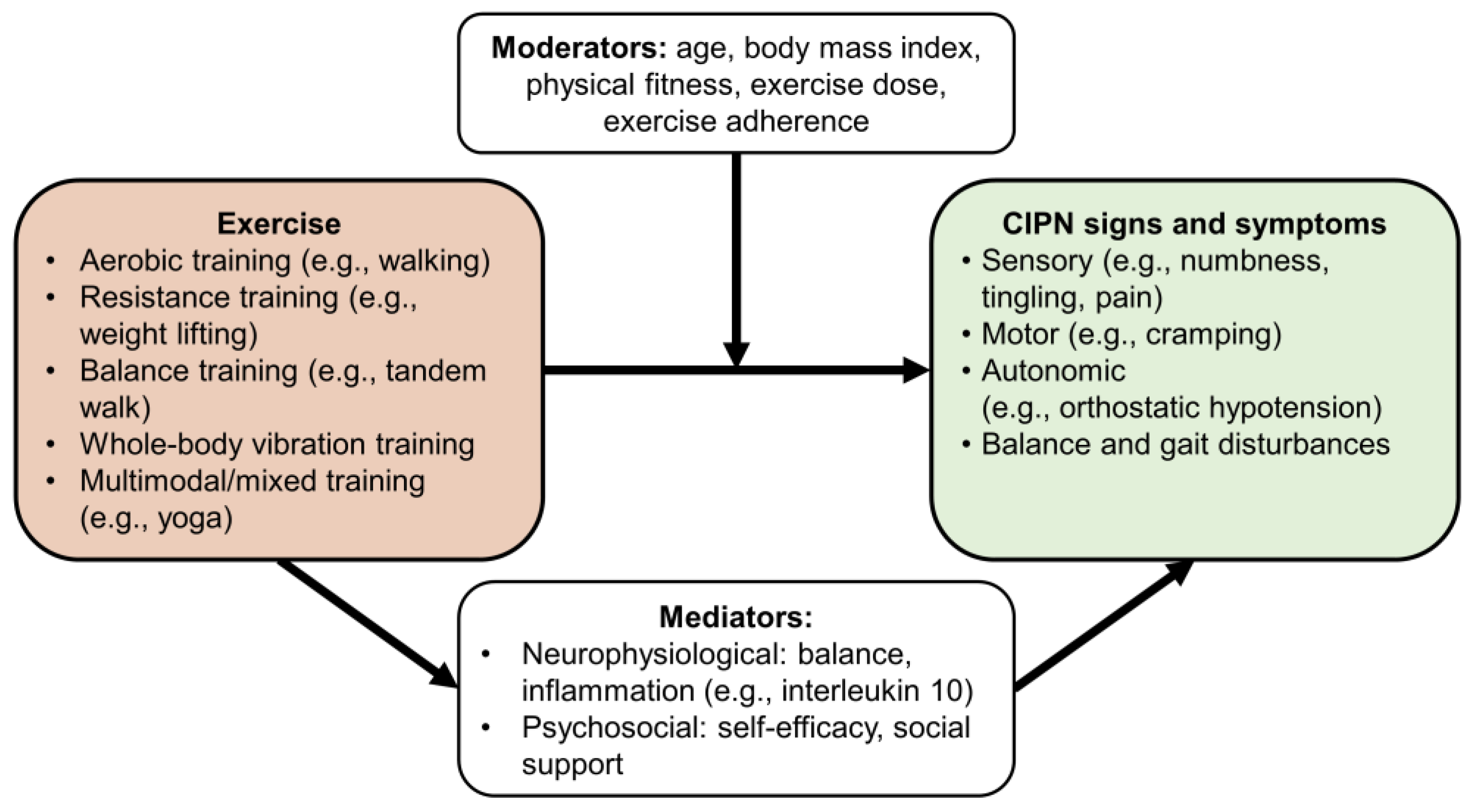
4. Mediators and Moderators
4.1. Mediators of the Effects of Exercise on CIPN
4.2. Moderators of the Effects of Exercise on CIPN
5. Biomarkers
6. Clinical Implications
7. Summary and Future Work
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, A.; Hertz, D.L.; Morales, M.; Adams, E.J.; Gordon, S.; Tan, C.J.; Staff, N.P.; Kamath, J.; Oh, J.; Shinde, S.; et al. Biological predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): MASCC neurological complications working group overview. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 3729–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staff, N.P.; Grisold, A.; Grisold, W.; Windebank, A.J. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A current review. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seretny, M.; Currie, G.L.; Sena, E.S.; Ramnarine, S.; Grant, R.; MacLeod, M.R.; Colvin, L.A.; Fallon, M. Incidence, prevalence, and predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 2014, 155, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hershman, D.L.; Unger, J.M.; Crew, K.D.; Till, C.; Greenlee, H.; Minasian, L.M.; Moinpour, C.M.; Lew, D.L.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Wade, J.L., 3rd; et al. Two-Year Trends of Taxane-Induced Neuropathy in Women Enrolled in a Randomized Trial of Acetyl-L-Carnitine (SWOG S0715). J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandos, H.; Melnikow, J.; Rivera, D.R.; Swain, S.M.; Sturtz, K.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Wade, J.L., 3rd; Brufsky, A.M.; Julian, T.B.; Margolese, R.G.; et al. Long-term Peripheral Neuropathy in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Adjuvant Chemotherapy: NRG Oncology/NSABP B-30. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajaczkowska, R.; Kocot-Kepska, M.; Leppert, W.; Wrzosek, A.; Mika, J.; Wordliczek, J. Mechanisms of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, C.W.; Cheng, H.; Au, S.K.; Leung, K.T.; Li, Y.C.; Wong, K.H.; Molassiotis, A. Living with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Uncovering the symptom experience and self-management of neuropathic symptoms among cancer survivors. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2018, 36, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfort, S.M.; Pan, X.; Patrick, R.; Ramaswamy, B.; Wesolowski, R.; Naughton, M.J.; Loprinzi, C.L.; Chaudhari, A.M.W.; Lustberg, M.B. Gait, balance, and patient-reported outcomes during taxane-based chemotherapy in early-stage breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 164, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewski, A.; Mohile, N. Meet the expert: How I treat chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, N.A.; Smith, A.G.; Singleton, J.R.; Beck, S.L.; Stoddard, G.J.; Brown, S.; Mooney, K. The Association of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms and the Risk of Falling. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gewandter, J.S.; Fan, L.; Magnuson, A.; Mustian, K.; Peppone, L.; Heckler, C.; Hopkins, J.; Tejani, M.; Morrow, G.R.; Mohile, S.G. Falls and functional impairments in cancer survivors with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): A University of Rochester CCOP study. Support. Care Cancer 2013, 21, 2059–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hershman, D.L.; Lacchetti, C.; Dworkin, R.H.; Lavoie Smith, E.M.; Bleeker, J.; Cavaletti, G.; Chauhan, C.; Gavin, P.; Lavino, A.; Lustberg, M.B.; et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1941–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loprinzi, C.L.; Lacchetti, C.; Bleeker, J.; Cavaletti, G.; Chauhan, C.; Hertz, D.L.; Kelley, M.R.; Lavino, A.; Lustberg, M.B.; Paice, J.A.; et al. Prevention and Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Survivors of Adult Cancers: ASCO Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3325–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzawa-Lee, G.A.; Larson, J.L.; Resnicow, K.; Smith, E.M.L. Exercise Effects on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Comprehensive Integrative Review. Cancer Nurs. 2020, 43, E172–E185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleckner, I.R.; Park, S.B.; Streckmann, F.; Wiskemann, J.; Hardy, S.; Mohile, N.A. Systematic review of exercise for prevention and managment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. In Diagnosis, Management, and Emerging Strategies for Chemotherapy Induced Neuropathy; Lustberg, M.B., Loprinzi, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 183–241. [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner, I.R.; SB, P.; Streckmann, F.; Wiskemann, J.; Hardy, S.; Mohile, N.A. Clinical and practical recommendations in the use of exercise, physical therapy, and occupational therapy for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. In Diagnosis, Managment and Emerging Strategies for Chemotherapy Induced Neuropathy; Lustberg, M.B., Loprinzi, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 243–252. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, K.L.; Winters-Stone, K.M.; Wiskemann, J.; May, A.M.; Schwartz, A.L.; Courneya, K.S.; Zucker, D.S.; Matthews, C.E.; Ligibel, J.A.; Gerber, L.H.; et al. Exercise Guidelines for Cancer Survivors: Consensus Statement from International Multidisciplinary Roundtable. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Streckmann, F.; Balke, M.; Cavaletti, G.; Toscanelli, A.; Bloch, W.; Decard, B.F.; Lehmann, H.C.; Faude, O. Exercise and Neuropathy: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett Whalen, L.; Zachary Wright, W.; Kundur, P.; Angadi, S.; Modesitt, S.C. Beneficial effects of exercise on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and sleep disturbance: A review of literature and proposed mechanisms. Gynecol. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 39, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courneya, K.S.; McKenzie, D.C.; Mackey, J.R.; Gelmon, K.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Yasui, Y.; Reid, R.D.; Vallerand, J.R.; Adams, S.C.; Proulx, C.; et al. Subgroup effects in a randomised trial of different types and doses of exercise during breast cancer chemotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleckner, I.R.; Kamen, C.; Gewandter, J.S.; Mohile, N.A.; Heckler, C.E.; Culakova, E.; Fung, C.; Janelsins, M.C.; Asare, M.; Lin, P.J.; et al. Effects of exercise during chemotherapy on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A multicenter, randomized controlled trial. Support. Care Cancer 2018, 26, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, J.; Kreutz, C.; Ringhof, S.; Koeppel, M.; Kleindienst, N.; Sam, G.; Schneeweiss, A.; Wiskemann, J.; Weiler, M. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Longitudinal analysis of predictors for postural control. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedenreich, C.M.; Neilson, H.K.; Farris, M.S.; Courneya, K.S. Physical activity and cancer outcomes: A precision medicine approach. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4766–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ross, R.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Koch, L.G.; Sarzynski, M.A.; Kohrt, W.M.; Johannsen, N.M.; Skinner, J.S.; Castro, A.; Irving, B.A.; Noland, R.C. Precision exercise medicine: Understanding exercise response variability. Br. J. Sports Med. 2019, 53, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, M.A.; Kluding, P.M.; Wright, D.E. Emerging Relationships between Exercise, Sensory Nerves, and Neuropathic Pain. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.S.; Kim, S.; Hoke, A. An exercise regimen prevents development paclitaxel induced peripheral neuropathy in a mouse model. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. JPNS 2015, 20, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Höke, A. Treadmill exercise induced functional recovery after peripheral nerve repair is associated with increased levels of neurotrophic factors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilhelm, J.C.; Xu, M.; Cucoranu, D.; Chmielewski, S.; Holmes, T.; Lau, K.S.; Bassell, G.J.; English, A.W. Cooperative roles of BDNF expression in neurons and Schwann cells are modulated by exercise to facilitate nerve regeneration. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 5002–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cobianchi, S.; Arbat-Plana, A.; Lopez-Alvarez, V.M.; Navarro, X. Neuroprotective Effects of Exercise Treatments after Injury: The Dual Role of Neurotrophic Factors. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 495–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.M.; Lehky, T.J.; Brell, J.M.; Dorsey, S.G. Discovering cytokines as targets for chemotherapy-induced painful peripheral neuropathy. Cytokine 2012, 59, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleckner, I.R.; Jusko, T.; Culakova, E.; Chung, K.; Asare, M.; Inglis, J.E.; Loh, K.P.; Peppone, L.J.; Miller, J.; Melnik, M.; et al. Longitudinal study of Inflammatory, Behavioral, Clinical and Psychosocial Risk Factors for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 189, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, M.; Bishop, N.C.; Stensel, D.J.; Lindley, M.R.; Mastana, S.S.; Nimmo, M.A. The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: Mechanisms and implications for the prevention and treatment of disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.P. Interleukin-6 in acute exercise and training: What is the biological relevance? Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 12, 6–33. [Google Scholar]
- Steensberg, A.; Fischer, C.P.; Keller, C.; Moller, K.; Pedersen, B.K. IL-6 enhances plasma IL-1ra, IL-10, and cortisol in humans. Am. J. Physiology. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, E433–E437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleckner, I.R.; Kamen, C.; Cole, C.; Fung, C.; Heckler, C.E.; Guido, J.J.; Culakova, E.; Onitilo, A.A.; Conlin, A.; Kuebler, J.P. Effects of exercise on inflammation in patients receiving chemotherapy: A nationwide NCORP randomized clinical trial. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 4615–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, L.F. The theory of constructed emotion: An active inference account of interoception and categorization. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2017, 12, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boland, E.G.; Selvarajah, D.; Hunter, M.; Ezaydi, Y.; Tesfaye, S.; Ahmedzai, S.H.; Snowden, J.A.; Wilkinson, I.D. Central pain processing in chronic chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omran, M.; Belcher, E.K.; Mohile, N.A.; Kesler, S.R.; Janelsins, M.C.; Hohmann, A.G.; Kleckner, I.R. Review of the Role of the Brain in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 693133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleckner, I.R.; Zhang, J.; Touroutoglou, A.; Chanes, L.; Xia, C.; Simmons, W.K.; Quigley, K.S.; Dickerson, B.C.; Barrett, L.F. Evidence for a Large-Scale Brain System Supporting Allostasis and Interoception in Humans. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalsa, S.S.; Adolphs, R.; Cameron, O.G.; Critchley, H.D.; Davenport, P.W.; Feinstein, J.S.; Feusner, J.D.; Garfinkel, S.N.; Lane, R.D.; Mehling, W.E.; et al. Interoception and Mental Health: A Roadmap. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleckner, I.R.; Gewandter, J.S.; Heckler, C.E.; Staples, S.; Colasurdo, A.; Lin, P.J.; Shayne, M.; Huston, A.; Magnuson, A.; Tejani, M.A.; et al. The effect of structured exercise during chemotherapy on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): A role for interoceptive brain circuitry. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 11590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleckner, I.R. A pilot randomized controlled trial of exercise during chemotherapy on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) and the interoceptive brain system. In Proceedings of the 2021 NIH Pain Consortium Symposium, Virtual Meeting, 24–25 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Canta, A.; Pozzi, E.; Carozzi, V.A. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN). Toxics 2015, 3, 198–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toyama, S.; Shimoyama, N.; Szeto, H.H.; Schiller, P.W.; Shimoyama, M. Protective Effect of a Mitochondria-Targeted Peptide against the Development of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforgia, M.; Laface, C.; Calabro, C.; Ferraiuolo, S.; Ungaro, V.; Tricarico, D.; Gadaleta, C.D.; Nardulli, P.; Ranieri, G. Peripheral Neuropathy under Oncologic Therapies: A Literature Review on Pathogenetic Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podratz, J.L.; Knight, A.M.; Ta, L.E.; Staff, N.P.; Gass, J.M.; Genelin, K.; Schlattau, A.; Lathroum, L.; Windebank, A.J. Cisplatin induced mitochondrial DNA damage in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 41, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rangaraju, V.; Lewis, T.L., Jr.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Bergami, M.; Motori, E.; Cartoni, R.; Kwon, S.K.; Courchet, J. Pleiotropic Mitochondria: The Influence of Mitochondria on Neuronal Development and Disease. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 8200–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorriento, D.; Di Vaia, E.; Iaccarino, G. Physical Exercise: A Novel Tool to Protect Mitochondrial Health. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 660068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steib, K.; Schaffner, I.; Jagasia, R.; Ebert, B.; Lie, D.C. Mitochondria modify exercise-induced development of stem cell-derived neurons in the adult brain. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 6624–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, T.C.; Marques-Aleixo, I.; Beleza, J.; Oliveira, P.J.; Ascensao, A.; Magalhaes, J. Physical Exercise and Brain Mitochondrial Fitness: The Possible Role Against Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 648–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Aleixo, I.; Santos-Alves, E.; Balca, M.M.; Moreira, P.I.; Oliveira, P.J.; Magalhaes, J.; Ascensao, A. Physical exercise mitigates doxorubicin-induced brain cortex and cerebellum mitochondrial alterations and cellular quality control signaling. Mitochondrion 2016, 26, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatier, M.J.; Redmon, N.; Schwartz, G.; English, A.W. Treadmill training promotes axon regeneration in injured peripheral nerves. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 211, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bobinski, F.; Martins, D.F.; Bratti, T.; Mazzardo-Martins, L.; Winkelmann-Duarte, E.C.; Guglielmo, L.G.; Santos, A.R. Neuroprotective and neuroregenerative effects of low-intensity aerobic exercise on sciatic nerve crush injury in mice. Neuroscience 2011, 194, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobianchi, S.; Marinelli, S.; Florenzano, F.; Pavone, F.; Luvisetto, S. Short- but not long-lasting treadmill running reduces allodynia and improves functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, J.R.; Marcus, R.L.; Jackson, J.E.; Lessard, M.K.; Graham, T.E.; Smith, A.G. Exercise increases cutaneous nerve density in diabetic patients without neuropathy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2014, 1, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kluding, P.M.; Pasnoor, M.; Singh, R.; Jernigan, S.; Farmer, K.; Rucker, J.; Sharma, N.K.; Wright, D.E. The effect of exercise on neuropathic symptoms, nerve function, and cutaneous innervation in people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2012, 26, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muller, J.; Weiler, M.; Schneeweiss, A.; Haag, G.M.; Steindorf, K.; Wick, W.; Wiskemann, J. Preventive effect of sensorimotor exercise and resistance training on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A randomised-controlled trial. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Jung, D.; Hwang, H.; Son, K.L.; Kim, T.Y.; Im, S.A.; Lee, K.H.; Hahm, B.J. Pre-treatment anxiety is associated with persistent chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in women treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. J. Psychosom. Res. 2018, 108, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhof, C.S.; van de Poll-Franse, L.V.; Vissers, P.A.; Wasowicz, D.K.; Wegdam, J.A.; Révész, D.; Vreugdenhil, G.; Mols, F. Anxiety and depression mediate the association between chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and fatigue: Results from the population-based PROFILES registry. Psycho-oncology 2019, 28, 1926–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandola, A.; Ashdown-Franks, G.; Hendrikse, J.; Sabiston, C.M.; Stubbs, B. Physical activity and depression: Towards understanding the antidepressant mechanisms of physical activity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 107, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, S.J.H.; Mutrie, N.; Gorely, T. Psychology of Physical Activity: Determinants, Well-Being and Interventions; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wegner, M.; Helmich, I.; Machado, S.; Nardi, A.E.; Arias-Carrion, O.; Budde, H. Effects of exercise on anxiety and depression disorders: Review of meta- analyses and neurobiological mechanisms. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mustian, K.M.; Alfano, C.M.; Heckler, C.; Kleckner, A.S.; Kleckner, I.R.; Leach, C.R.; Mohr, D.; Palesh, O.G.; Peppone, L.J.; Piper, B.F.; et al. Comparison of Pharmaceutical, Psychological, and Exercise Treatments for Cancer-Related Fatigue: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, T.J.; Middleton, K.R.; Winner, L.; Janelle, C.M. Physical activity interventions differentially affect exercise task and barrier self-efficacy: A meta-analysis. Health Psychol. 2014, 33, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, D.; Baum, G.; Jovanovic, J.; Carmack, C.; Greisinger, A.; Basen-Engquist, K. An acute exercise session increases self-efficacy in sedentary endometrial cancer survivors and controls. J. Phys. Act. Health 2010, 7, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, S.; Jaremka, L.M.; Alfano, C.M.; Glaser, R.; Povoski, S.P.; Lipari, A.M.; Agnese, D.M.; Farrar, W.B.; Yee, L.D.; Carson, W.E., III. Social support predicts inflammation, pain, and depressive symptoms: Longitudinal relationships among breast cancer survivors. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 42, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gellert, P.; Ziegelmann, J.P.; Warner, L.M.; Schwarzer, R. Physical activity intervention in older adults: Does a participating partner make a difference? Eur. J. Ageing 2011, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scarapicchia, T.M.F.; Amireault, S.; Faulkner, G.; Sabiston, C.M. Social support and physical activity participation among healthy adults: A systematic review of prospective studies. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2017, 10, 50–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, M.; Kaczmarek, L.D. Successful performance and cardiovascular markers of challenge and threat: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2018, 130, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colloca, L.; Barsky, A.J. Placebo and Nocebo Effects. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wager, T.D.; Atlas, L.Y. The neuroscience of placebo effects: Connecting context, learning and health. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindheimer, J.B.; O’Connor, P.J.; Dishman, R.K. Quantifying the placebo effect in psychological outcomes of exercise training: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 693–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubert, C.; Hannan, A.J. Exercise mimetics: Harnessing the therapeutic effects of physical activity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 862–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.J.; Kleckner, I.R.; Loh, K.P.; Inglis, J.E.; Peppone, L.J.; Janelsins, M.C.; Kamen, C.S.; Heckler, C.E.; Culakova, E.; Pigeon, W.R.; et al. Influence of Yoga on Cancer-Related Fatigue and on Mediational Relationships between Changes in Sleep and Cancer-Related Fatigue: A Nationwide, Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial of Yoga in Cancer Survivors. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bao, T.; Zhi, I.; Baser, R.; Hooper, M.; Chen, C.; Piulson, L.; Li, Q.S.; Galantino, M.L.; Blinder, V.; Robson, M.; et al. Yoga for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy and Fall Risk: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galantino, M.L.; Brooks, J.; Tiger, R.; Jang, S.; Wilson, K. Effectiveness of Somatic Yoga and Meditation: A Pilot Study in a Multicultural Cancer Survivor Population with Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Int. J. Yoga Ther. 2020, 30, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colloca, L.; Corsi, N.; Fiorio, M. The interplay of exercise, placebo and nocebo effects on experimental pain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, N.M.; Gucalp, A.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Hudis, C.A. Obesity and Cancer Mechanisms: Tumor Microenvironment and Inflammation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalter, J.; Buffart, L.M.; Korstjens, I.; van Weert, E.; Brug, J.; Verdonck-de Leeuw, I.M.; Mesters, I.; van den Borne, B.; Hoekstra-Weebers, J.E.; Ros, W.J.; et al. Moderators of the effects of group-based physical exercise on cancer survivors’ quality of life. Support. Care Cancer 2015, 23, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwenk, M.; Grewal, G.S.; Holloway, D.; Muchna, A.; Garland, L.; Najafi, B. Interactive Sensor-Based Balance Training in Older Cancer Patients with Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Gerontology 2016, 62, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selleck, M.J.; Senthil, M.; Wall, N.R. Making Meaningful Clinical Use of Biomarkers. Biomark. Insights 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freidlin, B.; McShane, L.M.; Korn, E.L. Randomized clinical trials with biomarkers: Design issues. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandolini, L.; d’Angelo, M.; Antonosante, A.; Allegretti, M.; Cimini, A. Chemokine Signaling in Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bujalska, M.; Tatarkiewicz, J.; Gumulka, S.W. Effect of bradykinin receptor antagonists on vincristine- and streptozotocin-induced hyperalgesia in a rat model of chemotherapy-induced and diabetic neuropathy. Pharmacology 2008, 81, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujalska, M.; Makulska-Nowak, H. Bradykinin receptors antagonists and nitric oxide synthase inhibitors in vincristine and streptozotocin induced hyperalgesia in chemotherapy and diabetic neuropathy rat model. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2009, 30, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Leitzelar, B.N.; Koltyn, K.F. Exercise and Neuropathic Pain: A General Overview of Preclinical and Clinical Research. Sports Med. Open 2021, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szudy-Szczyrek, A.; Mlak, R.; Bury-Kaminska, M.; Mielnik, M.; Podgajna, M.; Kusmierczuk, K.; Mazurek, M.; Homa-Mlak, I.; Szczyrek, M.; Krawczyk, J.; et al. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) concentration predicts polyneuropathy and overall survival in multiple myeloma patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 191, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azoulay, D.; Giryes, S.; Nasser, R.; Sharon, R.; Horowitz, N.A. Prediction of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Lymphoma and Myeloma: The Roles of Brain-Derived Neurotropic Factor Protein Levels and A Gene Polymorphism. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 15, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaletti, G.; Bogliun, G.; Marzorati, L.; Zincone, A.; Piatti, M.; Colombo, N.; Franchi, D.; La Presa, M.T.; Lissoni, A.; Buda, A.; et al. Early predictors of peripheral neurotoxicity in cisplatin and paclitaxel combination chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 1439–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudelman, K.N.; McDonald, B.C.; Wang, Y.; Smith, D.J.; West, J.D.; O’Neill, D.P.; Zanville, N.R.; Champion, V.L.; Schneider, B.P.; Saykin, A.J. Cerebral Perfusion and Gray Matter Changes Associated with Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prinsloo, S.; Novy, D.; Driver, L.; Lyle, R.; Ramondetta, L.; Eng, C.; McQuade, J.; Lopez, G.; Cohen, L. Randomized controlled trial of neurofeedback on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A pilot study. Cancer 2017, 123, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agalave, N.M.; Mody, P.H.; Szabo-Pardi, T.A.; Jeong, H.S.; Burton, M.D. Neuroimmune Consequences of eIF4E Phosphorylation on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 642420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasabova, I.A.; Khasabov, S.G.; Olson, J.K.; Uhelski, M.L.; Kim, A.H.; Albino-Ramirez, A.M.; Wagner, C.L.; Seybold, V.S.; Simone, D.A. Pioglitazone, a PPARgamma agonist, reduces cisplatin-evoked neuropathic pain by protecting against oxidative stress. Pain 2019, 160, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Xiao, W.H.; Bennett, G.J. Mitotoxicity and bortezomib-induced chronic painful peripheral neuropathy. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 238, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent-Roberge, H.; Fontvieille, A.; Maréchal, R.; Wagner, R.; Fülöp, T.; Pavic, M.; Riesco, E. Effects of combined exercise training on the inflammatory profile of older cancer patients treated with systemic therapy. Brain Behav. Immun.-Health 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, T.; Mazzoni, A.S.; Henriksson, A.; Demmelmaier, I.; Berntsen, S.; Raastad, T.; Nordin, K.; Pedersen, B.K.; Christensen, J.F. Exercise intensity and markers of inflammation during and after (neo-) adjuvant cancer treatment. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szuhany, K.L.; Bugatti, M.; Otto, M.W. A meta-analytic review of the effects of exercise on brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 60, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smoak, P.; Flores, V.; Harman, N.; Lisano, J.; Hayward, R.; Stewart, L.K. Structured Exercise in Cancer Survivors: Is it Enough for Neural, Mental Health and Well-being? Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2021, 14, 162–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ellingson, L.D.; Stegner, A.J.; Schwabacher, I.J.; Koltyn, K.F.; Cook, D.B. Exercise Strengthens Central Nervous System Modulation of Pain in Fibromyalgia. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voss, M.W.; Prakash, R.S.; Erickson, K.I.; Basak, C.; Chaddock, L.; Kim, J.S.; Alves, H.; Heo, S.; Szabo, A.N.; White, S.M.; et al. Plasticity of brain networks in a randomized intervention trial of exercise training in older adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2010, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Zhao, Z.W.; Zhou, H.Y.; Chen, G.Q.; Yang, H.J. Effects of exercise intensity on copy number and mutations of mitochondrial DNA in gastrocnemus muscles in mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigelso, A.; Anderson, N.B.; Dela, F. The relationship between skeletal muscle mitochondrial citrate synthase activity and whole body oxygen uptake adaptations in response to exercise training. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 6, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mijwel, S.; Cardinale, D.A.; Norrbom, J.; Chapman, M.; Ivarsson, N.; Wengstrom, Y.; Sundberg, C.J.; Rundqvist, H. Exercise training during chemotherapy preserves skeletal muscle fiber area, capillarization, and mitochondrial content in patients with breast cancer. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 5495–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, L.L. Redefining the role of mitochondria in exercise: A dynamic remodeling. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1201, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balan, E.; Schwalm, C.; Naslain, D.; Nielens, H.; Francaux, M.; Deldicque, L. Regular Endurance Exercise Promotes Fission, Mitophagy, and Oxidative Phosphorylation in Human Skeletal Muscle Independently of Age. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purohit, S.; Tran, P.M.H.; Tran, L.K.H.; Satter, K.B.; He, M.; Zhi, W.; Bai, S.; Hopkins, D.; Gardiner, M.; Wakade, C.; et al. Serum Levels of Inflammatory Proteins Are Associated with Peripheral Neuropathy in a Cross-Sectional Type-1 Diabetes Cohort. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 654233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, N.E.; Cotter, M.A. Pro-inflammatory mechanisms in diabetic neuropathy: Focus on the nuclear factor kappa B pathway. Curr. Drug Targets 2008, 9, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendrell, I.; Macedo, D.; Alho, I.; Dionisio, M.R.; Costa, L. Treatment of Cancer Pain by Targeting Cytokines. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 984570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nitta, A.; Murai, R.; Suzuki, N.; Ito, H.; Nomoto, H.; Katoh, G.; Furukawa, Y.; Furukawa, S. Diabetic neuropathies in brain are induced by deficiency of BDNF. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2002, 24, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Guan, S.; Shen, Y.; Sun, M.; Hao, Y.; He, L.; Liu, L.; Yin, C.; Huang, R.; Xiong, W.; et al. Dihydromyricetin affects BDNF levels in the nervous system in rats with comorbid diabetic neuropathic pain and depression. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harte, S.E.; Ichesco, E.; Hampson, J.P.; Peltier, S.J.; Schmidt-Wilcke, T.; Clauw, D.J.; Harris, R.E. Pharmacologic attenuation of cross-modal sensory augmentation within the chronic pain insula. Pain 2016, 157, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Miesen, M.M.; Lindquist, M.A.; Wager, T.D. Neuroimaging-based biomarkers for pain: State of the field and current directions. Pain Rep. 2019, 4, e751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascensao, A.; Oliveira, P.J.; Magalhaes, J. Exercise as a beneficial adjunct therapy during Doxorubicin treatment—Role of mitochondria in cardioprotection. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 156, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filler, K.; Lyon, D.; Bennett, J.; McCain, N.; Elswick, R.; Lukkahatai, N.; Saligan, L.N. Association of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Fatigue: A Review of the Literature. BBA Clin. 2014, 1, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, E.; Chia, C.W.; Spencer, R.G.; Fishbein, K.W.; Reiter, D.A.; Cameron, D.; Zane, A.C.; Moore, Z.A.; Gonzalez-Freire, M.; Zoli, M.; et al. Insulin resistance is associated with reduced mitochondrial oxidative capacity measured by 31P-magnetic resonance spectroscopy in participants without diabetes from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Diabetes 2017, 66, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chirles, T.J.; Reiter, K.; Weiss, L.R.; Alfini, A.J.; Nielson, K.A.; Smith, J.C. Exercise Training and Functional Connectivity Changes in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Healthy Elders. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A.; Zhao, K.; Jin, S.; Ding, W.X. New methods for monitoring mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, H.C. Messages for Clinicians: Moderators and Mediators of Treatment Outcome in Randomized Clinical Trials. Am. J. Psychiatry 2016, 173, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploeger, H.E.; Takken, T.; de Greef, M.H.; Timmons, B.W. The effects of acute and chronic exercise on inflammatory markers in children and adults with a chronic inflammatory disease: A systematic review. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 15, 6–41. [Google Scholar]
- Sellami, M.; Gasmi, M.; Denham, J.; Hayes, L.D.; Stratton, D.; Padulo, J.; Bragazzi, N. Effects of Acute and Chronic Exercise on Immunological Parameters in the Elderly Aged: Can Physical Activity Counteract the Effects of Aging? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleckner, I.R.; Dunne, R.F.; Asare, M.; Cole, C.; Fleming, F.; Fung, C.; Lin, P.J.; Mustian, K.M. Exercise for Toxicity Management in Cancer—A Narrative Review. Oncol. Hematol. Rev. 2018, 14, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biomarker | Citation | Population | Methods | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation | Kleckner et al., 2021 [32] | 116 women with breast cancer |
|
|
| Inflammation | Bujalska et al., 2008 and 2009 [85,86] | Rat model of chemo- and diabetic neuropathy |
|
|
| Inflammation | Leitzelar et al., 2021 [87] | Review article |
|
|
| Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) | Szudy-Szczyrek et al., 2020 [88] | 91 patients with multiple myeloma |
|
|
| BDNF | Azoulay et al., 2019 [89] | 45 patients with multiple myeloma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma with CIPN |
|
|
| BDNF | Cavaletti et al., 2004 [90] | 62 women with squamous cervical carcinoma |
|
|
| Brain structure and function | Nudelman et al., 2016 [91] | 47 patients with nonmetastatic breast cancer |
|
|
| Brain structure and function | Boland et al., 2014 [38] | 12 patients with multiple myeloma or CIPN and 12 healthy volunteers |
|
|
| Brain structure and function | Prinsloo et al., 2017 [92] | 62 cancer survivors with CIPN |
|
|
| Mitochondria | Agalave et al., 2021 [93] | 3 male mice and 3 female mice in multiple experimental groups |
|
|
| Mitochondria | Khasabova et al., 2019 [94] | Murine model of cisplatin-induced hyperalgesia |
|
|
| Mitochondria | Zheng et al., 2012 [95] | Mouse model of bortezomib-induced peripheral neuropathy |
|
|
| Biomarker | Citation | Population | Methods | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation | Gleeson et al., 2011 [33] | Review article of healthy and patient populations |
| Exercise has potent anti-inflammatory effects on the body by:
|
| Inflammation | Kleckner et al., 2019 [36] | 293 patients with cancer undergoing chemotherapy Exploratory/hypothesis-generating secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial |
|
|
| Inflammation | Parent-Roberge et al., 2020 [96] | 20 non-metastatic cancer patients initiating chemotherapy and/or hormone therapy |
|
|
| Inflammation | Schauer et al., 2021 [97] | Secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial n = 600 breast, prostate, colorectal cancer patients undergoing primary adjuvant cancer treatment |
|
|
| Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) | Szuhany et al., 2015 [98] | Meta-analysis focusing on 29 studies (n = 1111 participants in total in healthy, multiple sclerosis, mild cognitive impairment, or major depressive disorder populations) |
|
|
| BDNF | Smoak et al., 2021 [99] | Correlational study n = 32 participants either receiving chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy or not receiving therapy |
|
|
| Brain structure and function | Ellingson et al., 2016 [100] | Case–control correlational + crossover interventional study with acute exercise and a control condition (quiet rest) n = 9 fibromyalgia (FM) patients and n = 9 non-FM controls |
|
|
| Brain structure and function | Voss et al., 2010 [101] | Randomized controlled trial n = 97 older adults and younger adults (older adults: 55 < x < 80; younger adults: 18 < x < 35) |
|
|
| Mitochondria | Cao et al., 2012 [102] | Randomized preclinical experimental study n = 50 male mice |
|
|
| Mitochondria | Vigelsø et al., 2014 [103] | Review article |
|
|
| Mitochondria | Mijwel et al., 2018 [104] | Randomized controlled trial n = 23 women with breast cancer |
|
|
| Mitochondria | Balan et al., 2019 (for review see Bo et al., 2020) [105,106] | Cohort correlational study of 33 young sedentary, old sedentary, young active, and old active men |
|
|
| Biomarker | Citation | Population | Methods | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation | Purohit et al., 2021 [107] | Case–control correlational study n = 694 type 1 diabetes patients (n = 507 patients without peripheral neuropathy (nDPN) and n = 187 patients with peripheral neuropathy) |
|
|
| Inflammation | Cameron et al., 2008 [108] | Review article |
|
|
| Inflammation | Vendrell et al., 2015 [109] | Review article |
|
|
| Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) | Nitta et al., 2002 [110] | Randomized preclinical interventional study Rats with diabetes induced by streptozotocin |
|
|
| Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) | Ge et al., 2019 [111] | Randomized preclinical interventional study Rats with comorbid diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP) and depression (DP) |
|
|
| Brain structure and function | Harte et al., 2016 [112] | Randomized controlled trial/case–control correlational study n = 17 patients with fibromyalgia (FM) and n = 17 healthy controls |
|
|
| Brain structure and function | Van der Miesen et al., 2019 [113] | Review article |
|
|
| Brain structure and function | Omran et al., 2021 [39] | Review article |
|
|
| Mitochondria | Ascensao et al., 2021 [114] | Review article |
|
|
| Mitochondria | Filler et al., 2014 [115] | Review article |
|
|
| Mitochondria | Fabbri et al., 2017 [116] | 248 participants without diabetes |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, K.H.; Park, S.B.; Streckmann, F.; Wiskemann, J.; Mohile, N.; Kleckner, A.S.; Colloca, L.; Dorsey, S.G.; Kleckner, I.R. Mechanisms, Mediators, and Moderators of the Effects of Exercise on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Cancers 2022, 14, 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051224
Chung KH, Park SB, Streckmann F, Wiskemann J, Mohile N, Kleckner AS, Colloca L, Dorsey SG, Kleckner IR. Mechanisms, Mediators, and Moderators of the Effects of Exercise on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Cancers. 2022; 14(5):1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051224
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Kaitlin H., Susanna B. Park, Fiona Streckmann, Joachim Wiskemann, Nimish Mohile, Amber S. Kleckner, Luana Colloca, Susan G. Dorsey, and Ian R. Kleckner. 2022. "Mechanisms, Mediators, and Moderators of the Effects of Exercise on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy" Cancers 14, no. 5: 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051224
APA StyleChung, K. H., Park, S. B., Streckmann, F., Wiskemann, J., Mohile, N., Kleckner, A. S., Colloca, L., Dorsey, S. G., & Kleckner, I. R. (2022). Mechanisms, Mediators, and Moderators of the Effects of Exercise on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Cancers, 14(5), 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051224







