Non-Invasive Monitoring of Increased Fibrotic Tissue and Hyaluronan Deposition in the Tumor Microenvironment in the Advanced Stages of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Strains
2.2. MRI Protocol
2.2.1. Anatomical Images
2.2.2. T1 Weighted Imaging
2.2.3. T2 Weighted Imaging
2.2.4. Magnetization Transfer (MT)
2.2.5. Diffusion Weighted Images (DWI)
2.2.6. Chemical Exchange Transfer Saturation (CEST) Imaging
2.3. Tissue Preparation and Histology
2.4. Image Analysis
2.4.1. MR Image Analysis
2.4.2. Histological Image Analysis
3. Results
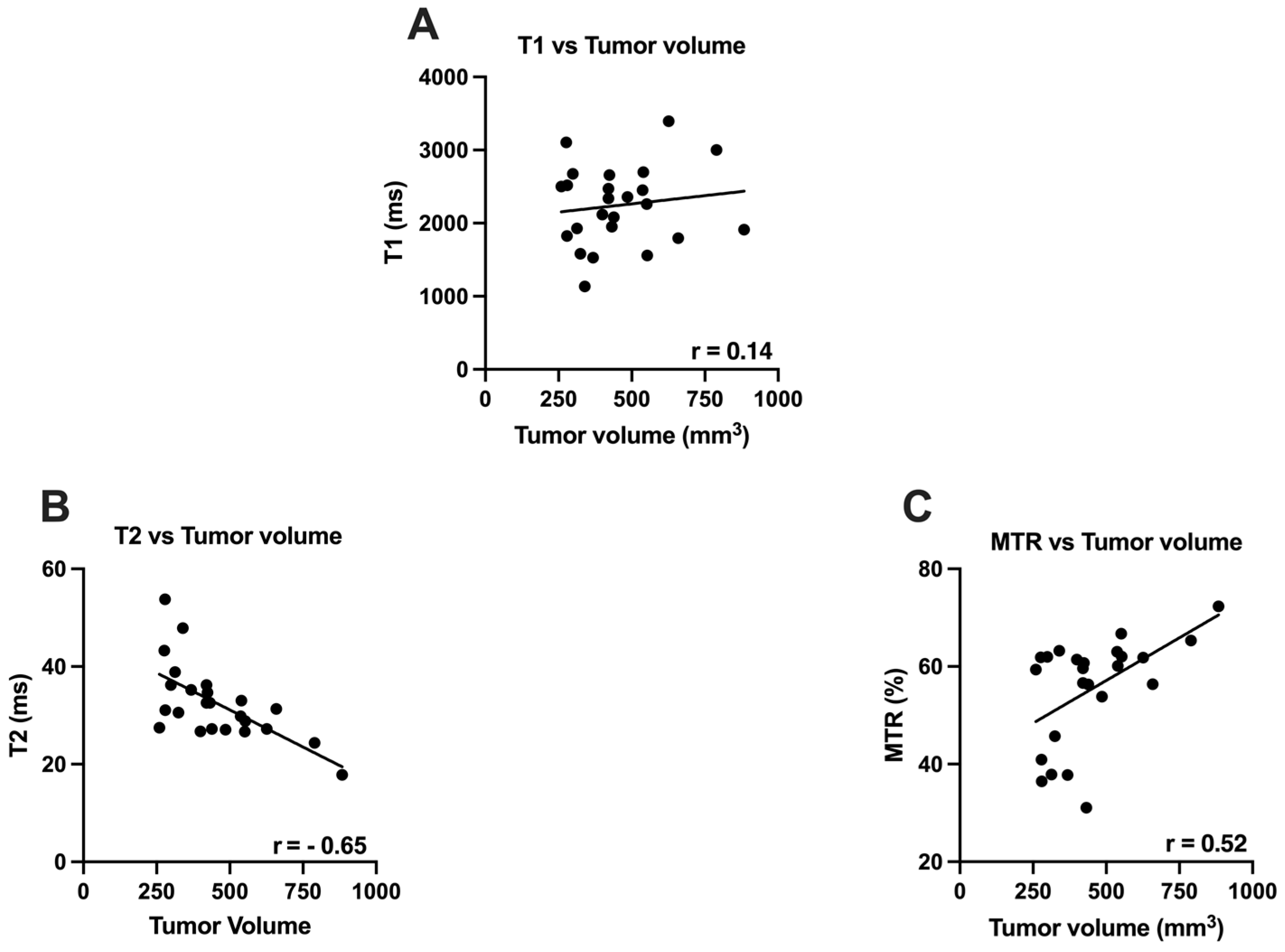
3.1. T1, T2 and MTR vs. Tumor Volume
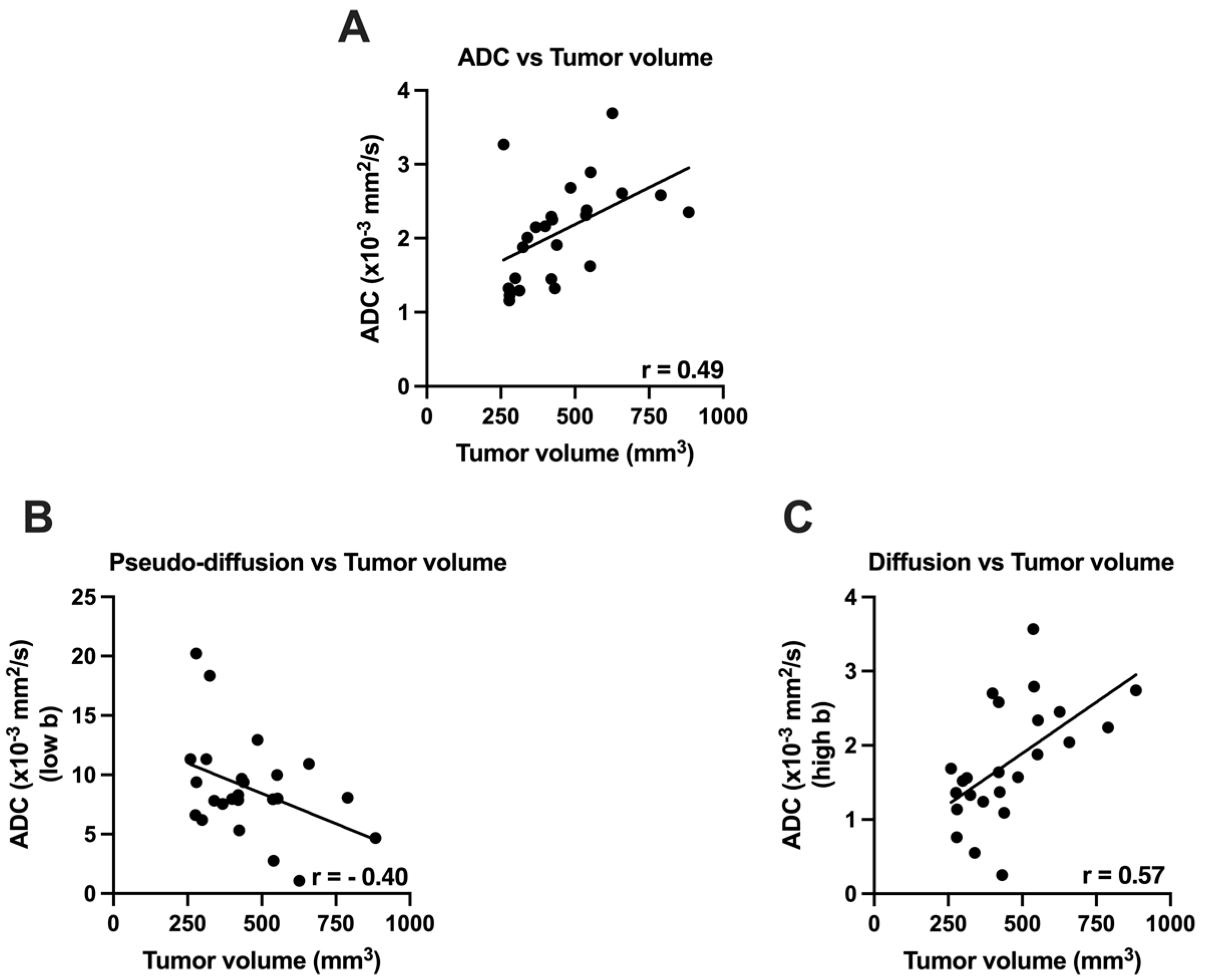
3.2. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) vs. Tumor Volume
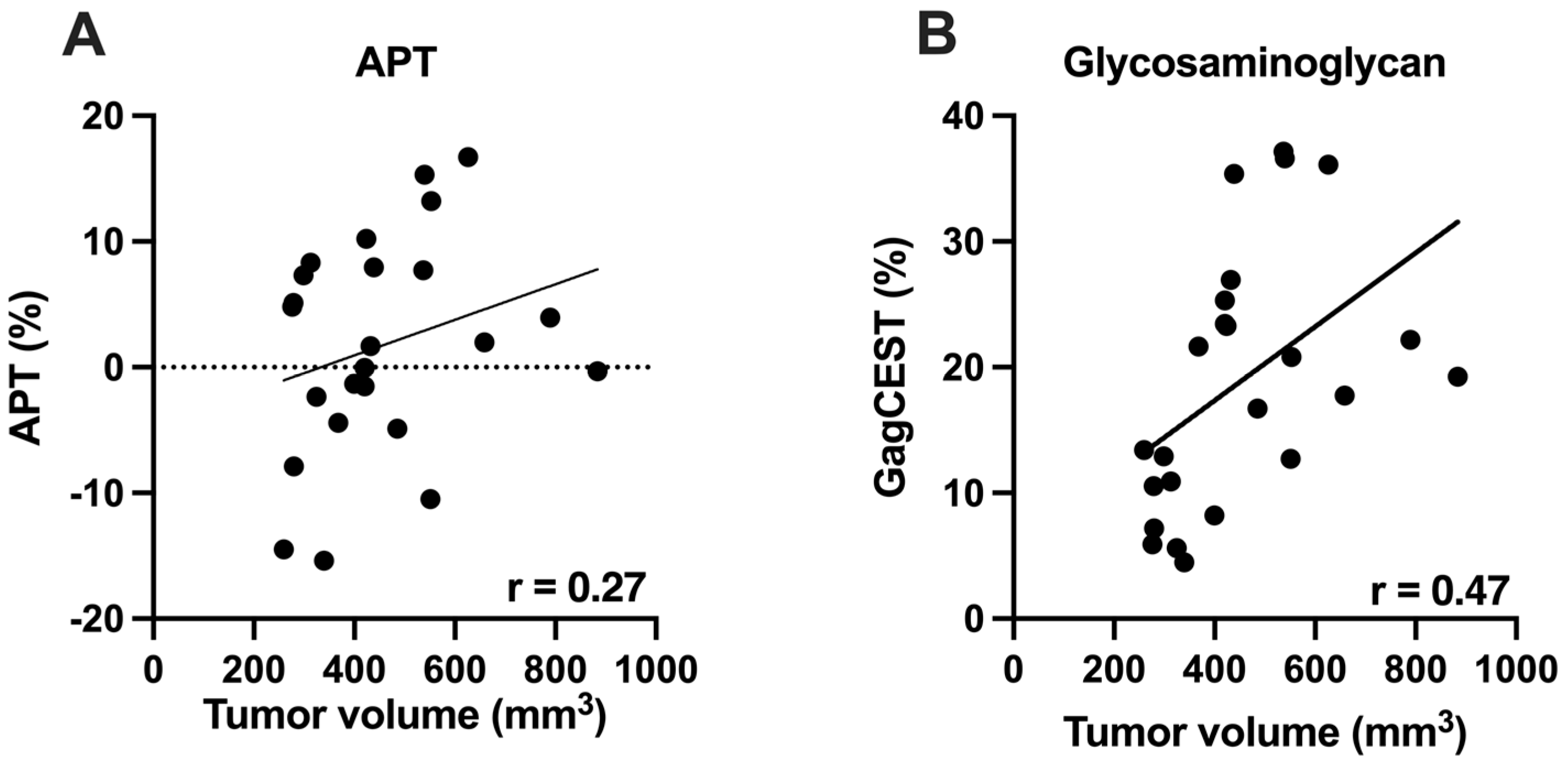
3.3. Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST) Imaging vs. Tumor Volume
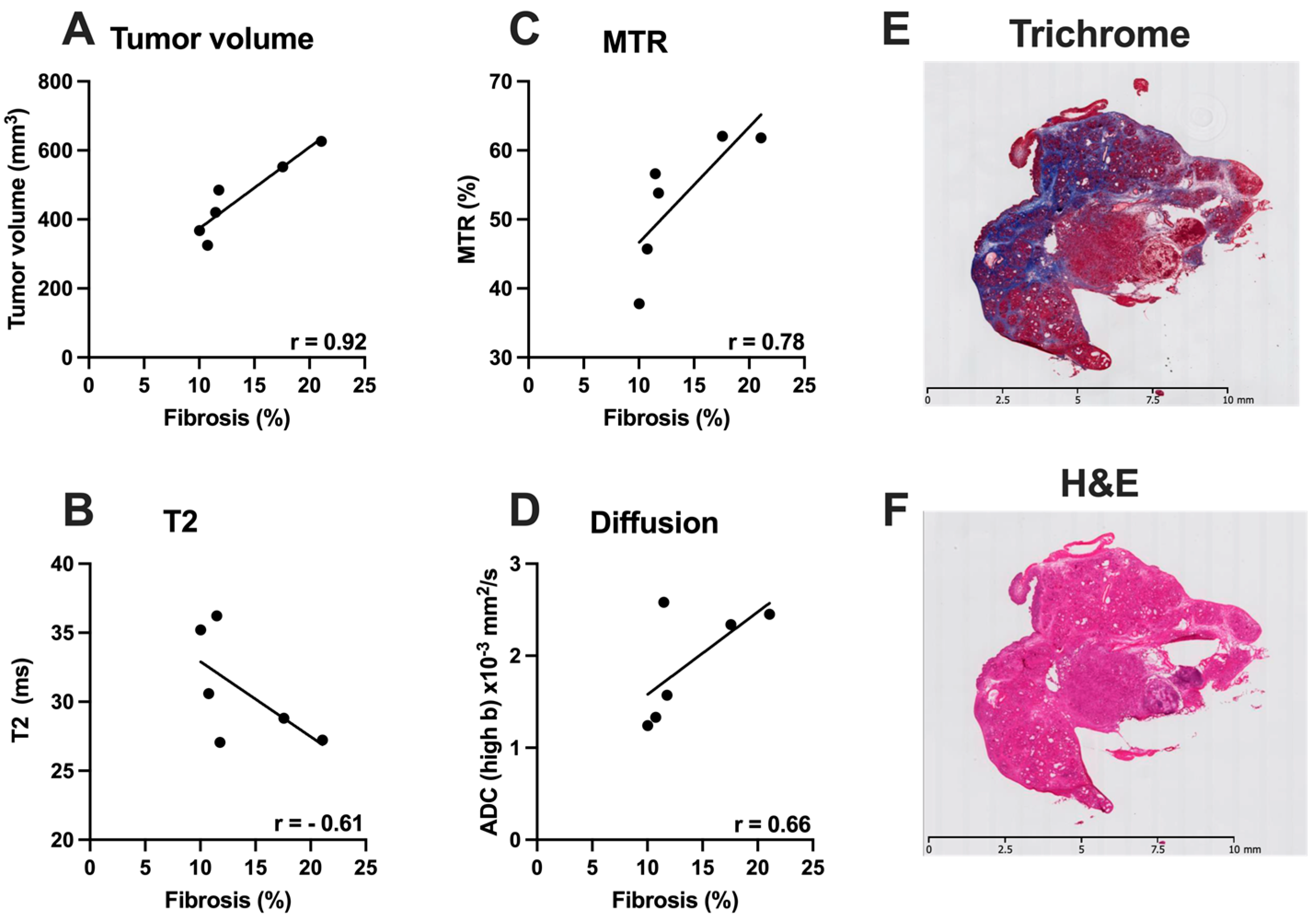
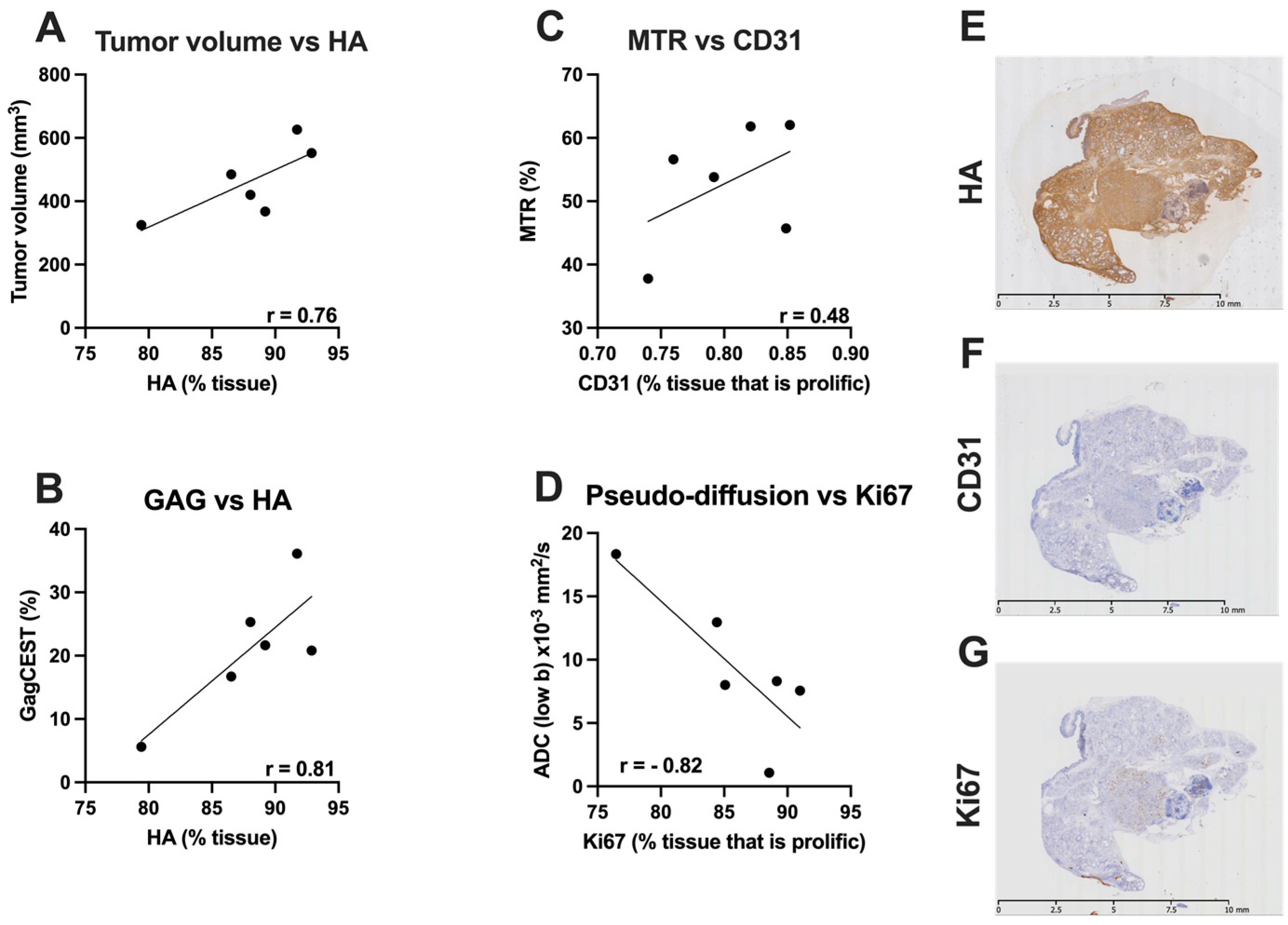
3.4. Correlative Histological Measures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufort, C.C.; DelGiorno, K.E.; Carlson, M.A.; Osgood, R.J.; Zhao, C.; Huang, Z.; Thompson, C.B.; Connor, R.J.; Thanos, C.D.; Brockenbrough, J.S.; et al. Interstitial Pressure in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Is Dominated by a Gel-Fluid Phase. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 2106–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Provenzano, P.; Hingorani, S. Hyaluronan, fluid pressure, and stromal resistance in pancreas cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DuFort, C.C.; DelGiorno, K.E.; Hingorani, S.R. Mounting Pressure in the Microenvironment: Fluids, Solids, and Cells in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1545–1557.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vachiranubhap, B.; Kim, Y.H.; Balci, N.C.; Semelka, R.C. Magnetic resonance imaging of adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 20, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, C.B.; Mitchell, D.G.; Cutwater, E.K.; Ehrlich, S.M. Pancreatic signal intensity on T1-weighted fat saturation MR images: Clinical correlation. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 1995, 5, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, E.; Wang, Y.-N.; Vohra, R.; Son, H.; Whang, S.; Khokhlova, T.; Park, J.; Gravelle, K.; Totten, S.; Hwang, J.H.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers for pulsed focused ultrasound treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, R.; Park, J.; Wang, Y.-N.; Gravelle, K.; Whang, S.; Hwang, J.-H.; Lee, D. Evaluation of pancreatic tumor development in KPC mice using multi-parametric MRI. Cancer Imaging 2018, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Nicolai, J.; Yang, G.-Y.; Omary, R.A.; Larson, A.C. Quantitative magnetization transfer MRI of desmoplasia in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma xenografts. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 1688–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraoka, N.; Uematsu, H.; Kimura, H.; Imamura, Y.; Rt, Y.F.; Murakami, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Itoh, H. Apparent diffusion coefficient in pancreatic cancer: Characterization and histopathological correlations. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 27, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmond, K.L.; Moosvi, F.; Stanisz, G.J. Mapping of amide, amine, and aliphatic peaks in the CEST spectra of murine xenografts at 7 T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 1841–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, W.; Regatte, R.R.; Navon, G.; Jerschow, A. Assessment of glycosaminoglycan concentration in vivo by chemical exchange-dependent saturation transfer (gagCEST). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2266–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Payen, J.-F.; Wilson, D.A.; Traystman, R.J.; Van Zijl, P.C.M. Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect pH effects in MRI. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmand, A.; Tsipouras, M.G.; Tzallas, A.T.; Forlano, R.; Manousou, P.; Giannakeas, N. Quantification of liver fibrosis—A comparative study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giannakeas, N.; Tsipouras, M.G.; Tzallas, A.T.; Kyriakidi, K.; Tsianou, Z.E.; Manousou, P.; Hall, A.; Karvounis, E.C.; Tsianos, V.; Tsianos, E. A clustering based method for collagen proportional area extraction in liver biopsy images. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 3097–3100. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Decarlo, L.; Cho, G.Y.; Jensen, J.; Sodickson, D.; Moy, L.; Formenti, S.C.; Schneider, R.; Goldberg, J.D.; Sigmund, E. Interstitial fluid pressure correlates with intravoxel incoherent motion imaging metrics in a mouse mammary carcinoma model. NMR Biomed. 2012, 25, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Bihan, D.; Breton, E.; Lallemand, D.; Aubin, M.L.; Vignaud, J.; Laval-Jeantet, M. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 1988, 168, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagiyama, K.; Mashimo, T.; Togao, O.; Vemireddy, V.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Maher, E.A.; Mickey, B.E.; Pan, E.; Sherry, D.; Bachoo, R.M.; et al. In vivo chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging allows early detection of a therapeutic response in glioblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4542–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Lal, B.; Wilson, D.A.; Laterra, J.; van Zijl, P.C. Amide proton transfer (APT) contrast for imaging of brain tumors. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 50, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisen, A.M.; Doi, K.; Swanson, S.D. Detection of liver fibrosis with magnetic cross-relaxation. Magn. Reson. Med. 1994, 31, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, T.; Peeters, R.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Dymarkowski, S.; Himmelreich, U.; Oyen, R.; Ni, Y. Characterization of a rat orthotopic pancreatic head tumor model using three-dimensional and quantitative multi- parametric MRI. NMR Biomed. 2017, 30, e3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beall, P.T.; Asch, B.B.; Chang, D.C.; Medina, D.; Hazlewood, C.F. Distinction of normal, preneoplastic, and neoplastic mouse mammary primary cell cultures by water nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation times. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1980, 64, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullino, P.M. Considerations on blood supply and fluid exchange in tumors. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1982, 107, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rofstad, E.; Steinsland, E.; Kaalhus, O.; Chang, Y.; Høvik, B.; Lyng, H. Magnetic resonance imaging of human melanoma xenografts in vivo: Proton spin-lattice and spin-spin relaxation times versus fractional tumour water content and fraction of necrotic tumour tissue. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1994, 65, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, J.V.; Mulkern, R.V.; Panych, L.P.; Fennessy, F.M.; Fedorov, A.; Maier, S.E.; Tempany, C.M. Multiparametric MRI of prostate cancer: An update on state-of-the-art techniques and their performance in detecting and localizing prostate cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 37, 1035–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Nicolai, J.; Yang, G.-Y.; Omary, R.A.; Larson, A.C. Magnetization transfer MRI in pancreatic cancer xenograft models. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farr, N.; Wang, Y.; D’Andrea, S.; Gravelle, K.M.; Hwang, J.H.; Lee, D. Noninvasive characterization of pancreatic tumor mouse models using magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Bihan, D.; Turner, R.; Moonen, C.T.W.; Pekar, J. Imaging of diffusion and microcirculation with gradient sensitization: Design, strategy, and significance. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1991, 1, 7–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, D.; Breton, E.; Lallemand, D.; Grenier, P.; Cabanis, E.; Laval-Jeantet, M. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: Application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 1986, 161, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemke, A.; Laun, F.B.; Klau, M.; Re, T.J.; Simon, D.; Delorme, S.; Schad, L.R.; Stieltjes, B. Differentiation of pancreas carcinoma from healthy pancreatic tissue using multiple b-values: Comparison of apparent diffusion coefficient and intravoxel incoherent motion derived parameters. Investig. Radiol. 2009, 44, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.-Z.; Yun, H.; Zeng, M.-S.; Wang, H.; Sun, F.; Rao, S.-X.; Ji, Y. Evaluation of ADC measurements among solid pancreatic masses by respiratory-triggered diffusion-weighted MR imaging with inversion-recovery fat-suppression technique at 3.0 T. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 31, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Li, W.; Gordon, A.C.; Huan, Y.; Shangguan, J.; Procissi, D.; Bentrem, D.J.; Larson, A.C. Quantitative functional MRI in a clinical orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer in immunocompetent Lewis rats. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, H.; Kanematsu, M.; Tanaka, K.; Osada, S.; Tomita, H.; Hara, A.; Goshima, S.; Kondo, H.; Kawada, H.; Noda, Y.; et al. Fibrosis and postoperative fistula of the pancreas: Correlation with MR imaging findings—Preliminary results. Radiology 2014, 270, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Kawamitsu, H.; Mitchell, D.G.; Ohno, Y.; Ku, Y.; Seo, Y.; Fujii, M.; Sugimura, K. ADC measurement of abdominal organs and lesions using parallel imaging technique. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 187, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.E.; Nikolaidis, P.; McCarthy, R.J.; Merrick, L.; Sternick, L.A.; Horowitz, J.M.; Yaghmai, V.; Miller, F.H. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of pancreatic adenocarcinomas: Association with histopathology and tumor grade. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 33, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.S.; Byun, J.H.; Park, B.J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, N.; Park, B.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, M.-G. Quantitative analysis of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas: Usefulness in characterizing solid pancreatic masses. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 28, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.M.; Lee, J.M.; Yoon, J.H.; Kiefer, B.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging for characterization of focal pancreatic lesions. Radiology 2014, 270, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barral, M.; Sebbag-Sfez, D.; Hoeffel, C.; Chaput, U.; Dohan, A.; Eveno, C.; Boudiaf, M.; Soyer, P. Characterization of focal pancreatic lesions using normalized apparent diffusion coefficient at 1.5-Tesla: Preliminary experience. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2013, 94, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hao, J.-G.; Wang, J.-P.; Gu, Y.-L.; Lu, M.-L. Importance of b value in diffusion weighted imaging for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 6651–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukukura, Y.; Takumi, K.; Kamimura, K.; Shindo, T.; Kumagae, Y.; Tateyama, A.; Nakajo, M. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Variability of diffusion-weighted MR imaging findings. Radiology 2012, 263, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.-M.; Collins, D.; Orton, M.R. Intravoxel incoherent motion in body diffusion-weighted MRI: Reality and challenges. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klau, M.; Lemke, A.; Grünberg, K.; Simon, D.; Re, T.J.; Wente, M.N.; Laun, F.B.; Kauczor, H.U.; Delorme, S.; Grenacher, L.; et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion MRI for the differentiation between mass forming chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma. Investig. Radiol. 2011, 46, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klau, M.; Gaida, M.M.; Lemke, A.; Grünberg, K.; Simon, D.; Wente, M.N.; Delorme, S.; Kauczor, H.U.; Grenacher, L.; Stieltjes, B. Fibrosis and pancreatic lesions: Counterintuitive behavior of the diffusion imaging-derived structural diffusion coefficient D. Investig. Radiol. 2013, 48, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Arnoletti, P.J.; Christein, J.; Heslin, M.J.; Posey, J.A., III; Pednekar, A.; Mark Beasley, T.; Morgan, D.E. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A pilot study of quantitative perfusion and diffusion-weighted breath-hold magnetic resonance imaging. Abdom. Imaging 2014, 39, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, S.D.; Balaban, R.S. NMR imaging of labile proton exchange. J. Magn. Reson. 1990, 86, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tryggestad, E.; Wen, Z.-B.; Lal, B.; Zhou, T.; Grossman, R.; Wang, S.; Yan, K.; Fu, D.-X.; Ford, E.; et al. Differentiation between glioma and radiation necrosis using molecular magnetic resonance imaging of endogenous proteins and peptides. Nat. Med. 2010, 17, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glunde, K.; Jacobs, M.A.; Pathak, A.P.; Artemov, D.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Molecular and functional imaging of breast cancer. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damadian, R. Tumor detection by nuclear magnetic resonance. Science 1971, 171, 1151–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, J.M.; Woods, A.E. Structural and functional characteristics of the microcirculation in neoplasms. J. Pathol. 1975, 116, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.K.; Schlosser, M.J.; van Zijl, P.C.; Pomper, M.G.; Golay, X.; Zhou, J. Amide proton transfer imaging of human brain tumors at 3T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 56, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomp, D.W.J.; Dula, A.N.; Arlinghaus, L.; Italiaander, M.; Dortch, R.; Zu, Z.; Williams, J.M.; Gochberg, D.F.; Luijten, P.R.; Gore, J.C.; et al. Amide proton transfer imaging of the human breast at 7T: Development and reproducibility. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dula, A.N.; Arlinghaus, L.; Dortch, R.; Dewey, B.E.; Whisenant, J.G.; Ayers, G.D.; Yankeelov, T.; Smith, S.A. Amide proton transfer imaging of the breast at 3 T: Establishing reproducibility and possible feasibility assessing chemotherapy response. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 70, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Blakeley, J.O.; Hua, J.; Kim, M.; Laterra, J.; Pomper, M.G.; van Zijl, P.C. Practical data acquisition method for human brain tumor amide proton transfer (APT) imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maloney, E.; Dufort, C.C.; Provenzano, P.P.; Farr, N.; Carlson, M.A.; Vohra, R.; Park, J.; Hingorani, S.R.; Lee, D. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Stromal Biophysics with Targeted Depletion of Hyaluronan in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vohra, R.; Wang, Y.-N.; Son, H.; Totten, S.; Arora, A.; Maxwell, A.; Lee, D. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Increased Fibrotic Tissue and Hyaluronan Deposition in the Tumor Microenvironment in the Advanced Stages of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040999
Vohra R, Wang Y-N, Son H, Totten S, Arora A, Maxwell A, Lee D. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Increased Fibrotic Tissue and Hyaluronan Deposition in the Tumor Microenvironment in the Advanced Stages of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2022; 14(4):999. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040999
Chicago/Turabian StyleVohra, Ravneet, Yak-Nam Wang, Helena Son, Stephanie Totten, Akshit Arora, Adam Maxwell, and Donghoon Lee. 2022. "Non-Invasive Monitoring of Increased Fibrotic Tissue and Hyaluronan Deposition in the Tumor Microenvironment in the Advanced Stages of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 14, no. 4: 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040999
APA StyleVohra, R., Wang, Y.-N., Son, H., Totten, S., Arora, A., Maxwell, A., & Lee, D. (2022). Non-Invasive Monitoring of Increased Fibrotic Tissue and Hyaluronan Deposition in the Tumor Microenvironment in the Advanced Stages of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 14(4), 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040999






