A Multi-Disciplinary Approach to Diagnosis and Treatment of Radionecrosis in Malignant Gliomas and Cerebral Metastases
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Current Evidence
3.1. Treatment Response
3.2. Predictive Factors for Radionecrosis
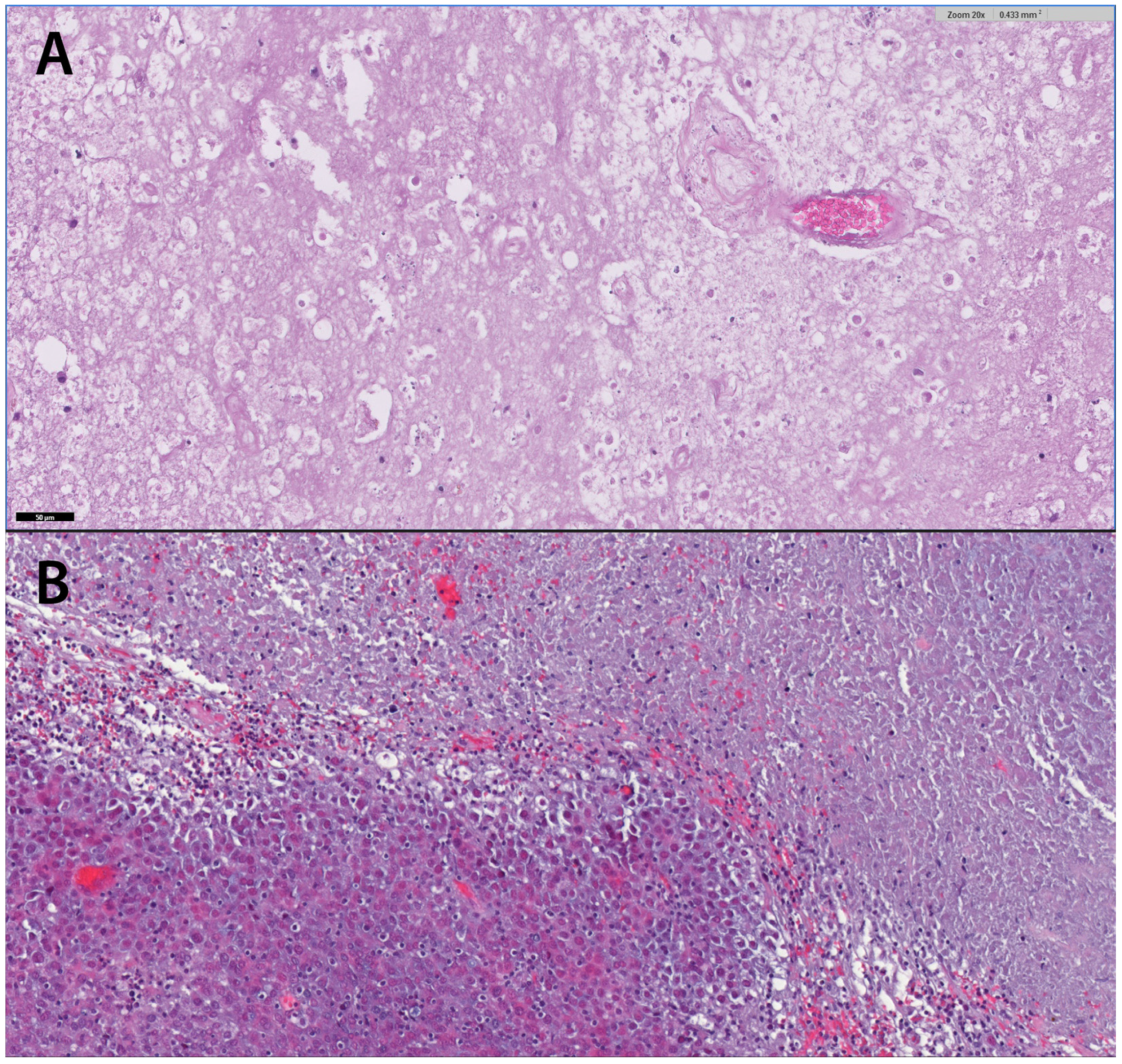
3.3. Evaluation of Treatment Response by MRI
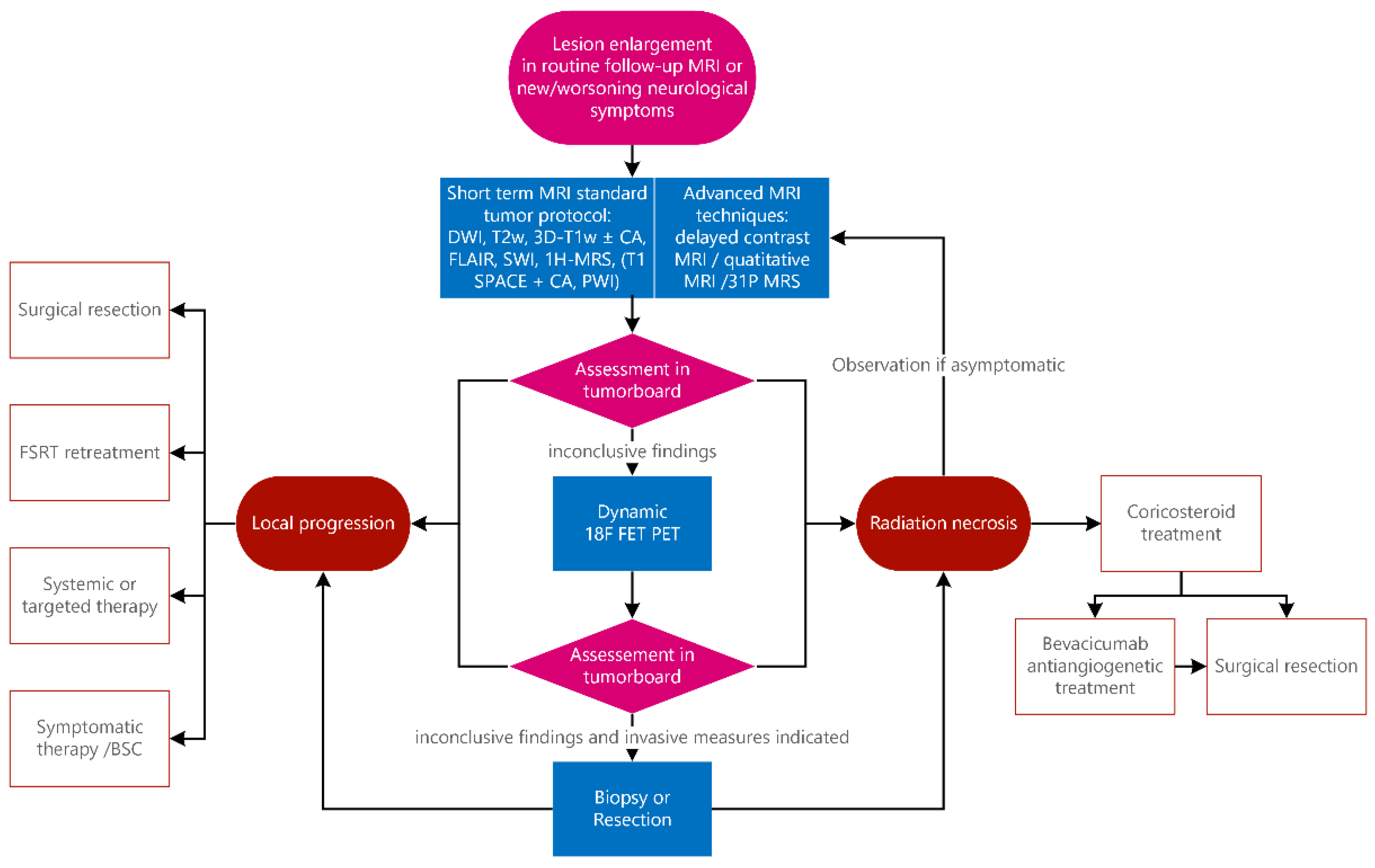
4. Institutional Practice
4.1. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protocol
4.1.1. Structural MRI—Glioma
4.1.2. Structural MRI—Metastases
4.1.3. Diffusion-Weighted MRI
4.1.4. Perfusion-Weighted Imaging—Glioma
4.1.5. Perfusion-Weighted Imaging—Metastases
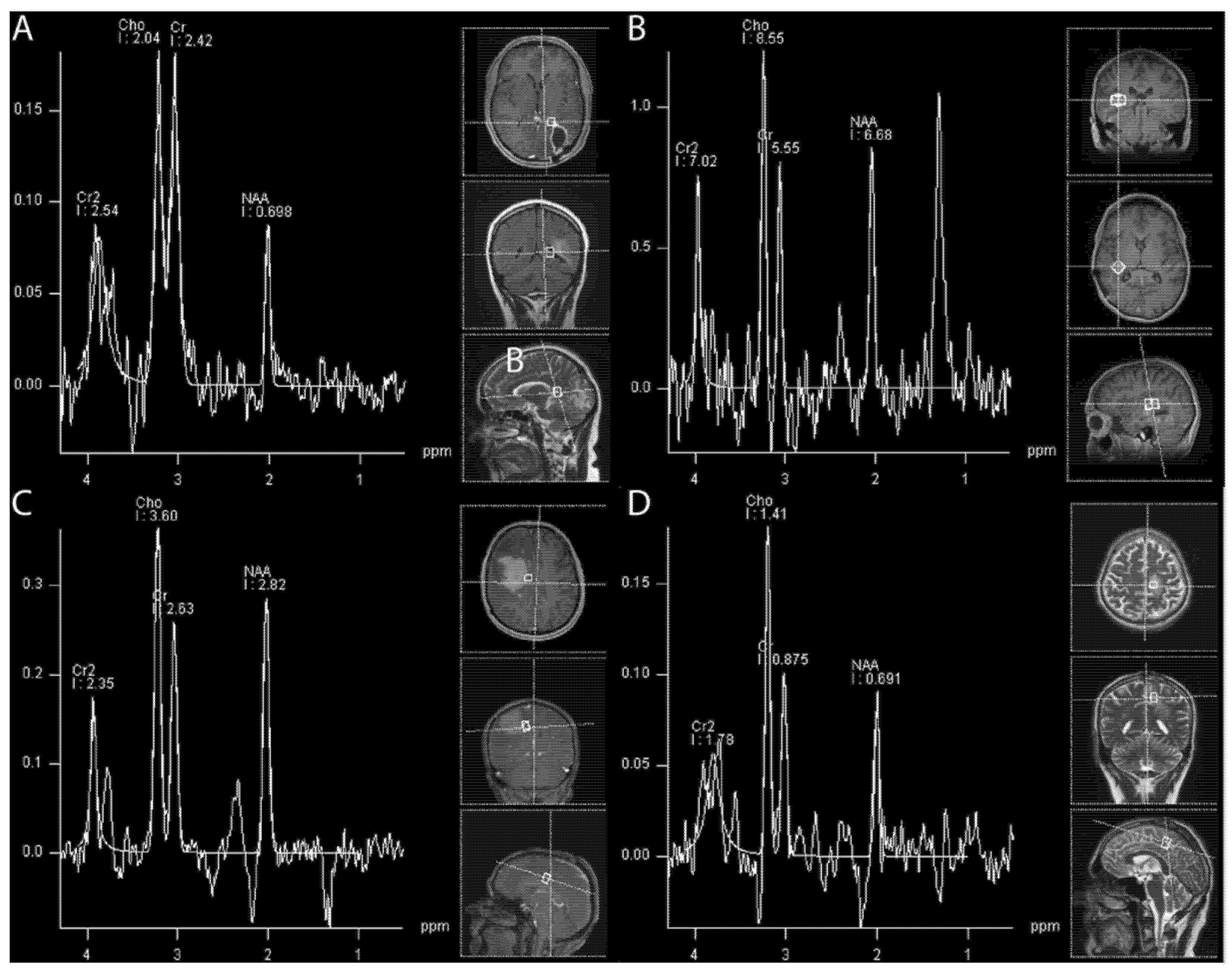
4.1.6. (1H) Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
4.1.7. When the Difficult Becomes Even more Challenging: Bevacizumab and Systemic Therapies
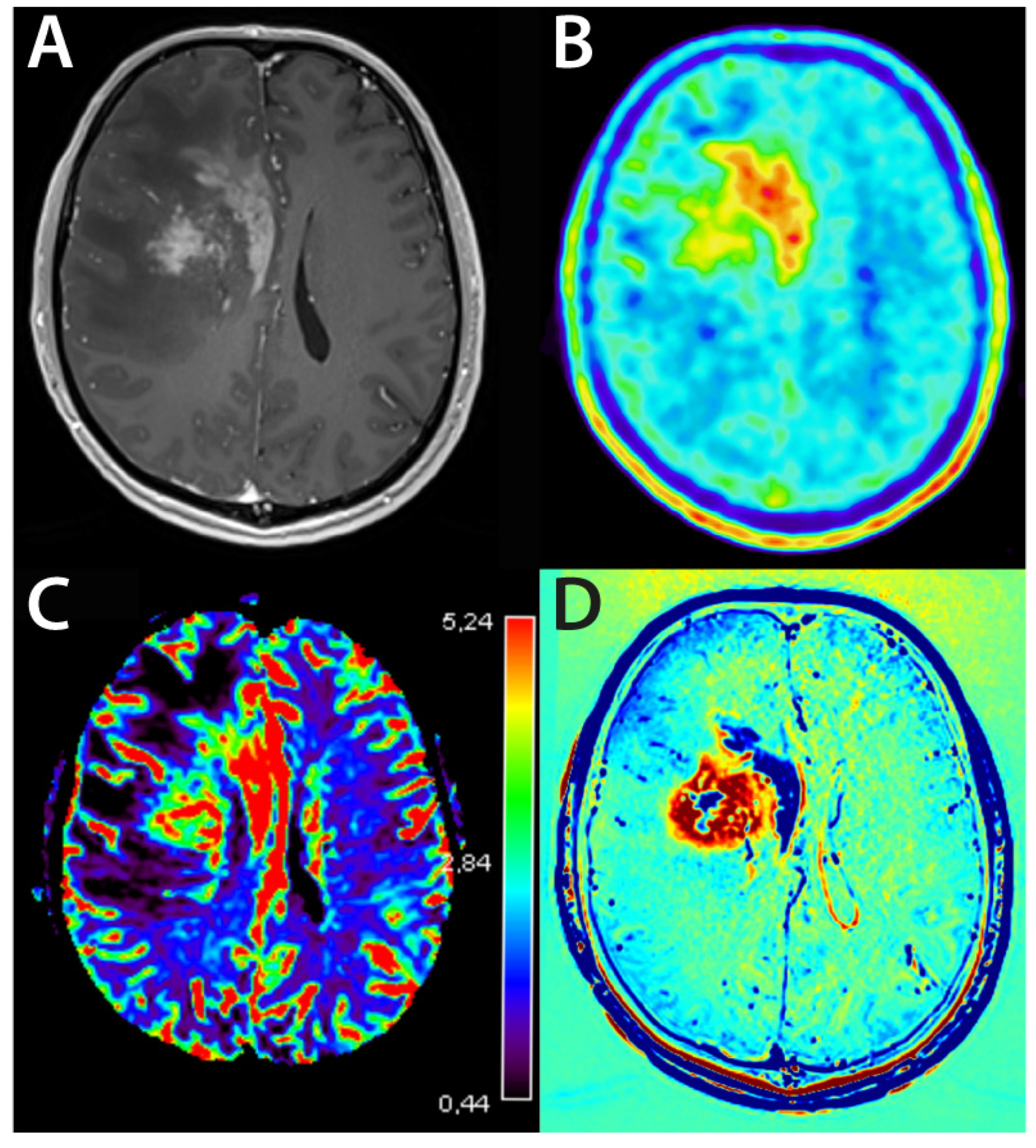
4.2. Evolving MRI Techniques
4.2.1. Delayed Contrast Extravasation MRI and Quantitative Imaging
4.2.2. (31P) Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
4.2.3. Deep Neural Networks
4.3. Nuclear Medicine—PET
4.3.1. PET Tracers
4.3.2. 18F-FET—PET
5. Treatment Strategies
5.1. Medical Treatment
5.2. Surgical Treatment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Sato, Y.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Patients with Multiple Brain Metastases (Jlgk0901): A Multi-Institutional Prospective Observational Study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerschbaumer, J.; Demetz, M.; Krigers, A.; Nevinny-Stickel, M.; Thomé, C.; Freyschlag, C.F. Risk Factors for Radiation Necrosis in Patients Undergoing Cranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Cancers 2021, 13, 4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, E.; Scott, C.; Souhami, L.; Dinapoli, R.; Kline, R.; Loeffler, J.; Farnan, N. Single Dose Radiosurgical Treatment of Recurrent Previously Irradiated Primary Brain Tumors and Brain Metastases: Final Report of Rtog Protocol 90-05. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 47, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minniti, G.; Clarke, E.; Lanzetta, G.; Osti, M.F.; Trasimeni, G.; Bozzao, A.; Romano, A.; Enrici, R.M. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases: Analysis of Outcome and Risk of Brain Radionecrosis. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovich, Z.; Yu, C.; Giannotta, S.L.; O’Day, S.; Apuzzo, M.L. Survival and Pattern of Failure in Brain Metastasis Treated with Stereotactic Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonigen, B.J.; Steinmetz, R.D.; Levin, L.; Lamba, M.A.; Warnick, R.E.; Breneman, J.C. Irradiated Volume as a Predictor of Brain Radionecrosis after Linear Accelerator Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneed, P.K.; Mendez, J.; den Hoek, J.G.V.; Seymour, Z.A.; Ma, L.; Molinaro, A.M.; Fogh, S.E.; Nakamura, J.L.; McDermott, M.W. Adverse Radiation Effect after Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases: Incidence, Time Course, and Risk Factors. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, A.; Wind, J.J.; Iorgulescu, J.B.; Chan, T.A.; Yamada, Y.; Sherman, J.H. Radiation Necrosis Following Treatment of High Grade Glioma—A Review of the Literature and Current Understanding. Acta Neurochir. 2012, 154, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easaw, J.C.; Mason, W.P.; Perry, J.; Laperriere, N.; Eisenstat, D.D.; del Maestro, R.; Belanger, K.; Fulton, D.; Macdonald, D.; Committee Canadian Glioblastoma Recommendations. Canadian Recommendations for the Treatment of Recurrent or Progressive Glioblastoma Multiforme. Curr. Oncol. 2011, 18, e126–e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandsma, D.; Stalpers, L.; Taal, W.; Sminia, P.; van den Bent, M.J. Clinical Features, Mechanisms, and Management of Pseudoprogression in Malignant Gliomas. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruben, J.D.; Dally, M.; Bailey, M.; Smith, R.; McLean, C.A.; Fedele, P. Cerebral Radiation Necrosis: Incidence, Outcomes, and Risk Factors with Emphasis on Radiation Parameters and Chemotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 65, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, M.C.; Glantz, M.J.; Chalmers, L.; van Horn, A.; Sloan, A.E. Early Necrosis Following Concurrent Temodar and Radiotherapy in Patients with Glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2007, 82, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, A.A.; Franceschi, E.; Tosoni, A.; Blatt, V.; Pession, A.; Tallini, G.; Bertorelle, R.; Bartolini, S.; Calbucci, F.; Andreoli, A.; et al. Mgmt Promoter Methylation Status Can Predict the Incidence and Outcome of Pseudoprogression after Concomitant Radiochemotherapy in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2192–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubimova, N.; Hopewell, J.W. Experimental Evidence to Support the Hypothesis That Damage to Vascular Endothelium Plays the Primary Role in the Development of Late Radiation-Induced Cns Injury. Br. J. Radiol. 2004, 77, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korytko, T.; Radivoyevitch, T.; Colussi, V.; Wessels, B.W.; Pillai, K.; Maciunas, R.J.; Einstein, D.B. 12 Gy Gamma Knife Radiosurgical Volume Is a Predictor for Radiation Necrosis in Non-Avm Intracranial Tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 64, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minniti, G.; Anzellini, D.; Reverberi, C.; Cappellini, G.C.A.; Marchetti, L.; Bianciardi, F.; Bozzao, A.; Osti, M.; Gentile, P.C.; Esposito, V. Stereotactic Radiosurgery Combined with Nivolumab or Ipilimumab for Patients with Melanoma Brain Metastases: Evaluation of Brain Control and Toxicity. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.A.; Bennett, E.E.; Xiao, R.; Kotecha, R.; Chao, S.T.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Barnett, G.H.; Angelov, L.; Murphy, E.S.; Yu, J.S.; et al. Association between Radiation Necrosis and Tumor Biology after Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastasis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Scaringi, C.; Paolini, S.; Lanzetta, G.; Romano, A.; Cicone, F.; Osti, M.; Enrici, R.M.; Esposito, V. Single-Fraction Versus Multifraction (3 X 9 Gy) Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Large (>2 Cm) Brain Metastases: A Comparative Analysis of Local Control and Risk of Radiation-Induced Brain Necrosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putz, F.; Weissmann, T.; Oft, D.; Schmidt, M.A.; Roesch, J.; Siavooshhaghighi, H.; Filimonova, I.; Schmitter, C.; Mengling, V.; Bert, C.; et al. Fsrt Vs. Srs in Brain Metastases-Differences in Local Control and Radiation Necrosis-a Volumetric Study. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 559193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, R.E.; Leeman, J.E.; Kabolizadeh, P.; Rwigema, J.C.; Mintz, A.H.; Burton, S.A.; Heron, D.E. Fractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Large Brain Metastases. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 38, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minniti, G.; D’Angelillo, R.M.; Scaringi, C.; Trodella, L.E.; Clarke, E.; Matteucci, P.; Osti, M.F.; Ramella, S.; Enrici, R.M.; Trodella, L. Fractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Patients with Brain Metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 117, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colaco, R.J.; Martin, P.; Kluger, H.M.; Yu, J.B.; Chiang, V.L. Does Immunotherapy Increase the Rate of Radiation Necrosis after Radiosurgical Treatment of Brain Metastases? J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.M.; Cagney, D.N.; Catalano, P.J.; Alexander, B.M.; Redig, A.J.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Aizer, A.A. Immunotherapy and Symptomatic Radiation Necrosis in Patients with Brain Metastases Treated with Stereotactic Radiation. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, K.; Bian, S.X.; Routman, D.M.; Yu, C.; Kim, P.E.; Wagle, N.A.; Wong, M.K.; Zada, G.; Chang, E.L. Combination Ipilimumab and Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases: Tumor, Edema, and Adverse Radiation Effects. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, P.; Jiang, W.; Allen, P.; Glitza, I.; Guha, N.; Hwu, P.; Ghia, A.; Phan, J.; Mahajan, A.; Tawbi, H.; et al. Radiation Necrosis with Stereotactic Radiosurgery Combined with Ctla-4 Blockade and Pd-1 Inhibition for Treatment of Intracranial Disease in Metastatic Melanoma. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Miller, J.A.; Kotecha, R.; Xiao, R.; Juloori, A.; Ward, M.C.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Mohammadi, A.M.; Peereboom, D.M.; Murphy, E.S.; et al. The Risk of Radiation Necrosis Following Stereotactic Radiosurgery with Concurrent Systemic Therapies. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 133, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asao, C.; Korogi, Y.; Kitajima, M.; Hirai, T.; Baba, Y.; Makino, K.; Kochi, M.; Morishita, S.; Yamashita, Y. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Radiation-Induced Brain Injury for Differentiation from Tumor Recurrence. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, P.Y.; Macdonald, D.R.; Reardon, D.A.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Sorensen, A.G.; Galanis, E.; Degroot, J.; Wick, W.; Gilbert, M.R.; Lassman, A.B.; et al. Updated Response Assessment Criteria for High-Grade Gliomas: Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology Working Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, D.M.; Bell, M.A.; Challa, V.R. Features of the Cerebral Vascular Pattern That Predict Vulnerability to Perfusion or Oxygenation Deficiency: An Anatomic Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1990, 11, 431–439. [Google Scholar]
- Dequesada, I.M.; Quisling, R.G.; Yachnis, A.; Friedman, W.A. Can Standard Magnetic Resonance Imaging Reliably Distinguish Recurrent Tumor from Radiation Necrosis after Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases? A Radiographic-Pathological Study. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, 898–904; discussion 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, A.M.; Shetty, A.; Maitz, A.H.; Yan, D.; Doyle, D.; Richey, K.; Park, S.; Pieper, D.R.; Chen, P.Y.; et al. Differentiation between Intra-Axial Metastatic Tumor Progression and Radiation Injury Following Fractionated Radiation Therapy or Stereotactic Radiosurgery Using Mr Spectroscopy, Perfusion Mr Imaging or Volume Progression Modeling. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 29, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.J.; Leeds, N.E.; Fuller, G.N.; van Tassel, P.; Maor, M.H.; Sawaya, R.E.; Levin, V.A. Malignant Gliomas: Mr Imaging Spectrum of Radiation Therapy- and Chemotherapy-Induced Necrosis of the Brain after Treatment. Radiology 2000, 217, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullins, M.E.; Barest, G.D.; Schaefer, P.W.; Hochberg, F.H.; Gonzalez, R.G.; Lev, M.H. Radiation Necrosis Versus Glioma Recurrence: Conventional Mr Imaging Clues to Diagnosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 1967–1972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.; Westerly, D.; Chen, C. Mri Patterns of T1 Enhancing Radiation Necrosis Versus Tumour Recurrence in High-Grade Gliomas. J. Med. Imaging. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 57, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.L.; Leung, S.F.; King, A.D.; Choi, P.H.; Metreweli, C. Late Radiation Injury to the Temporal Lobes: Morphologic Evaluation at Mr Imaging. Radiology 1999, 213, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.S.; Kang, X.S.; Li, C.F.; Zhou, G.Y. Detection of Hemorrhagic Hypointense Foci in Radiation Injury Region Using Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging. Acta Radiol. 2011, 52, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimbault, A.; Cazals, X.; Lauvin, M.A.; Destrieux, C.; Chapet, S.; Cottier, J.P. Radionecrosis of Malignant Glioma and Cerebral Metastasis: A Diagnostic Challenge in Mri. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2014, 95, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.R.; McHugh, B.J.; Bi, W.L.; Minja, F.J.; Knisely, J.P.; Chiang, V.L. A Comprehensive Review of Mr Imaging Changes Following Radiosurgery to 500 Brain Metastases. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamai, A.; Benlalam, H.; Meslin, F.; Hasmim, M.; Carre, T.; Akalay, I.; Janji, B.; Berchem, G.; Noman, M.Z.; Chouaib, S. Immune Surveillance of Human Cancer: If the Cytotoxic T-Lymphocytes Play the Music, Does the Tumoral System Call the Tune? Tissue Antigens 2010, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.E.; Yun, T.J.; Hwang, I.; Hong, E.K.; Kang, K.M.; Choi, S.H.; Park, C.K.; Won, J.K.; Kim, J.H.; Sohn, C.H. Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion-Weighted Imaging Aids in Prediction of Molecular Biomarkers and Survival in Glioblastomas. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, J.E.; Clump, D.A.; Flickinger, J.C.; Mintz, A.H.; Burton, S.A.; Heron, D.E. Extent of Perilesional Edema Differentiates Radionecrosis from Tumor Recurrence Following Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy Plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N. Engl J Med 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hein, P.A.; Eskey, C.J.; Dunn, J.F.; Hug, E.B. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the Follow-up of Treated High-Grade Gliomas: Tumor Recurrence Versus Radiation Injury. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castillo, M.; Smith, J.K.; Kwock, L.; Wilber, K. Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-Grade Cerebral Gliomas. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.L.; Yeung, D.K.; Leung, S.F.; Chan, P.N. Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Radiation-Induced Cerebral Necrosis. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Lesion Components. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2003, 27, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundgren, P.C.; Fan, X.; Weybright, P.; Welsh, R.C.; Carlos, R.C.; Petrou, M.; McKeever, P.E.; Chenevert, T.L. Differentiation of Recurrent Brain Tumor Versus Radiation Injury Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Patients with New Contrast-Enhancing Lesions. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 24, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.S.; Li, C.F.; Liu, H.; Zhen, J.H.; Feng, D.C. Distinction between Recurrent Glioma and Radiation Injury Using Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Combination with Diffusion-Weighted Imaging. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobek-Billewicz, B.; Stasik-Pres, G.; Majchrzak, H.; Zarudzki, L. Differentiation between Brain Tumor Recurrence and Radiation Injury Using Perfusion, Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Mr Spectroscopy. Folia Neuropathol. 2010, 48, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Sundgren, P.C. Mr Spectroscopy in Radiation Injury. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronen, H.J.; Perkio, J. Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Mri of Gliomas. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2002, 12, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellika, S.K.; Jain, R.; Patel, S.C.; Scarpace, L.; Schultz, L.R.; Rock, J.P.; Mikkelsen, T. Role of Perfusion Ct in Glioma Grading and Comparison with Conventional Mr Imaging Features. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.K. Normalizing Tumor Vasculature with Anti-Angiogenic Therapy: A New Paradigm for Combination Therapy. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 987–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuya, K.; Nakasu, Y.; Horiguchi, S.; Harada, H.; Nishimura, T.; Bando, E.; Okawa, H.; Furukawa, Y.; Hirai, T.; Endo, M. Perfusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Distinguish the Recurrence of Metastatic Brain Tumors from Radiation Necrosis after Stereotactic Radiosurgery. J. Neurooncol. 2010, 99, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas, R.F.; Chang, J.S.; Sneed, P.K.; Segal, M.R.; McDermott, M.W.; Cha, S. Distinguishing Recurrent Intra-Axial Metastatic Tumor from Radiation Necrosis Following Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Using Dynamic Susceptibility-Weighted Contrast-Enhanced Perfusion Mr Imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemura, Y.; Wang, D.; Peck, K.K.; Flynn, J.; Zhang, Z.; Fatovic, R.; Anderson, E.S.; Beal, K.; Shoushtari, A.N.; Kaley, T.; et al. Dce-Mri Perfusion Predicts Pseudoprogression in Metastatic Melanoma Treated with Immunotherapy. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 146, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walecki, J.; Sokól, M.; Pieniążek, P.; Maciejewski, B.; Tarnawski, R.; Krupska, T.; Wydmański, J.; Brzeziński, J.; Grieb, P. Role of Short Te 1h-Mr Spectroscopy in Monitoring of Post-Operation Irradiated Patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 1999, 30, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.; Moustafa, H.; Ahmed, E.; El-Toukhy, M. Glioma Residual or Recurrence Versus Radiation Necrosis: Accuracy of Pentavalent Technetium-99m-Dimercaptosuccinic Acid [Tc-99m (V) Dmsa] Brain Spect Compared to Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1h-Mrs): Initial Results. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2012, 106, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, J.P.; Hearshen, D.; Scarpace, L.; Croteau, D.; Gutierrez, J.; Fisher, J.L.; Rosenblum, M.L.; Mikkelsen, T. Correlations between Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Image-Guided Histopathology, with Special Attention to Radiation Necrosis. Neurosurgery 2002, 51, 912–919; discussion 919–920. [Google Scholar]
- Weybright, P.; Sundgren, P.C.; Maly, P.; Hassan, D.G.; Nan, B.; Rohrer, S.; Junck, L. Differentiation between Brain Tumor Recurrence and Radiation Injury Using Mr Spectroscopy. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 185, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas, R.F., Jr.; Chang, J.S.; Segal, M.R.; Parsa, A.T.; McDermott, M.W.; Berger, M.S.; Cha, S. Differentiation of Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme from Radiation Necrosis after External Beam Radiation Therapy with Dynamic Susceptibility-Weighted Contrast-Enhanced Perfusion Mr Imaging. Radiology 2009, 253, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galijasevic, M.; Steiger, R.; Mangesius, S.; Mangesius, J.; Kerschbaumer, J.; Freyschlag, C.F.; Gruber, N.; Janjic, T.; Gizewski, E.R.; Grams, A.E. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Diagnosis and Follow-up of Gliomas: State-of-the-Art. Cancers 2022, 14, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grams, A.E.; Mangesius, S.; Steiger, R.; Radovic, I.; Rietzler, A.; Walchhofer, L.M.; Galijasevic, M.; Mangesius, J.; Nowosielski, M.; Freyschlag, C.F.; et al. Changes in Brain Energy and Membrane Metabolism in Glioblastoma Following Chemoradiation. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 5041–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hygino da Cruz, L.C., Jr.; Rodriguez, I.; Domingues, R.C.; Gasparetto, E.L.; Sorensen, A.G. Pseudoprogression and Pseudoresponse: Imaging Challenges in the Assessment of Posttreatment Glioma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandsma, D.; van den Bent, M.J. Pseudoprogression and Pseudoresponse in the Treatment of Gliomas. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2009, 22, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, J.L.; Chang, S. Pseudoprogression and Pseudoresponse: Challenges in Brain Tumor Imaging. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2009, 9, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Gufler, H.; Eichner, G.; Lanfermann, H. Characterisation of Lesions after Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases: Impact of Delayed Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Clin. Oncol. R Coll Radiol. 2017, 29, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zach, L.; Guez, D.; Last, D.; Daniels, D.; Grober, Y.; Nissim, O.; Hoffmann, C.; Nass, D.; Talianski, A.; Spiegelmann, R.; et al. Delayed Contrast Extravasation Mri: A New Paradigm in Neuro-Oncology. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 17, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescher, S.; Jurcoane, A.; Veit, A.; Bahr, O.; Deichmann, R.; Hattingen, E. Quantitative T1 and T2 Mapping in Recurrent Glioblastomas under Bevacizumab: Earlier Detection of Tumor Progression Compared to Conventional Mri. Neuroradiology 2015, 57, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppu, T.; Sato, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Terasaki, K.; Yamashita, F.; Sasaki, M.; Ogasawara, K. Comparisons between Pet with 11c-Methyl-L-Methionine and Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion Imaging in Recurrent Glioblastomas Treated with Bevacizumab. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, T.; Ahmeti, H.; Juhasz, J.; Helle, M.; Jansen, O.; Synowitz, M.; Ulmer, S. A Comparison of Arterial Spin Labeling and Dynamic Susceptibility Perfusion Imaging for Resection Control in Glioblastoma Surgery. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 18570–18577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsunar, Y.; Mullins, M.E.; Kwong, K.; Hochberg, F.H.; Ament, C.; Schaefer, P.W.; Gonzalez, R.G.; Lev, M.H. Glioma Recurrence Versus Radiation Necrosis? A Pilot Comparison of Arterial Spin-Labeled, Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Enhanced Mri, and Fdg-Pet Imaging. Acad. Radiol. 2010, 17, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, P.; Ge, M.; Gao, M.; Ding, F.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y. Postcontrast T1 Mapping for Differential Diagnosis of Recurrence and Radionecrosis after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Metastasis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.; Choi, S.; Oh, J.Y.; Yoon, S.K.; Kang, M.J.; Kim, K. Application of 31p Mr Spectroscopy to the Brain Tumors. Korean J. Radiol. 2013, 14, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattingen, E.; Bähr, O.; Rieger, J.; Blasel, S.; Steinbach, J.; Pilatus, U. Phospholipid Metabolites in Recurrent Glioblastoma: In Vivo Markers Detect Different Tumor Phenotypes before and under Antiangiogenic Therapy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maintz, D.; Heindel, W.; Kugel, H.; Jaeger, R.; Lackner, K.J. Phosphorus-31 Mr Spectroscopy of Normal Adult Human Brain and Brain Tumours. NMR Biomed. 2002, 15, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulakbasi, N.; Kocaoglu, M.; Sanal, H.T.; Tayfun, C. Efficacy of in Vivo 31phosphorus Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Differentiation and Staging of Adult Human Brain Tumors. Neuroradiol. J. 2007, 20, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, R.B.; Jayakumar, P.N.; Shivashankar, R. Energy Status and Metabolism in Intracranial Space Occupying Lesions: A Prospective 31p Spectroscopic Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2014, 8, RC05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, K.J.; Hattingen, E.; Franz, K.; Steinbach, J.P.; Bähr, O.; Pilatus, U. Intracellular Ph Measured by (31) P-Mr-Spectroscopy Might Predict Site of Progression in Recurrent Glioblastoma under Antiangiogenic Therapy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnilicova, P.; Richterova, R.; Zelenak, K.; Kolarovszki, B.; Majercikova, Z.; Hatok, J. Noninvasive Study of Brain Tumours Metabolism Using Phosphorus-31 Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2020, 121, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattingen, E.; Jurcoane, A.; Bähr, O.; Rieger, J.; Magerkurth, J.; Anti, S.; Steinbach, J.P.; Pilatus, U. Bevacizumab Impairs Oxidative Energy Metabolism and Shows Antitumoral Effects in Recurrent Glioblastomas: A 31p/1h Mrsi and Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Neuro-Oncology 2011, 13, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walchhofer, L.M.; Steiger, R.; Rietzler, A.; Kerschbaumer, J.; Freyschlag, C.F.; Stockhammer, G.; Gizewski, E.R.; Grams, A.E. Phosphorous Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy to Detect Regional Differences of Energy and Membrane Metabolism in Naïve Glioblastoma Multiforme. Cancers 2021, 13, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galijašević, M.; Steiger, R.; Radović, I.; Birkl-Toeglhofer, A.M.; Birkl, C.; Deeg, L.; Mangesius, S.; Rietzler, A.; Regodić, M.; Stockhammer, G.; et al. Phosphorous Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Molecular Markers in Idh1 Wild Type Glioblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietzler, A.; Steiger, R.; Mangesius, S.; Walchhofer, L.M.; Gothe, R.M.; Schocke, M.; Gizewski, E.R.; Grams, A.E. Energy Metabolism Measured by 31p Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in the Healthy Human Brain. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 49, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Paek, S.; Yeo, J.S.; Jeong, J.M.; Lee, D.S.; Jung, H.W.; Lee, M.C. Usefulness of 11c-Methionine Pet in the Evaluation of Brain Lesions That Are Hypo- or Isometabolic on 18f-Fdg Pet. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2002, 29, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Witte, O.; Goldberg, I.; Wikler, D.; Rorive, S.; Damhaut, P.; Monclus, M.; Salmon, I.; Brotchi, J.; Goldman, S. Positron Emission Tomography with Injection of Methionine as a Prognostic Factor in Glioma. J. Neurosurg. 2001, 95, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.A.; Frey, K.A.; Schwaiger, M. Discordance between F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose Uptake and Contrast Enhancement in a Brain Abscess. Clin. Nucl. Med. 1993, 18, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Laere, K.; Ceyssens, S.; van Calenbergh, F.; de Groot, T.; Menten, J.; Flamen, P.; Bormans, G.; Mortelmans, L. Direct Comparison of 18f-Fdg and 11c-Methionine Pet in Suspected Recurrence of Glioma: Sensitivity, Inter-Observer Variability and Prognostic Value. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2005, 32, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopa, B.M.; Juhasz, C.; Mittal, S. Comparison of Amino Acid Pet to Advanced and Emerging Mri Techniques for Neurooncology Imaging: A Systematic Review of the Recent Studies. Mol. Imaging 2021, 2021, 8874078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmo, P.; Quartuccio, N.; Rossetti, V.; Celli, M.; Alongi, P.; Boero, M.; Arnone, G.; Baldari, S.; Matteucci, F.; Laudicella, R. [(18)F] Fluorothymidine Positron Emission Tomography Imaging in Primary Brain Tumours: A Systematic Review. Curr. Med. Imaging 2022, 18, 363–371. [Google Scholar]
- Hutterer, M.; Nowosielski, M.; Putzer, D.; Jansen, N.L.; Seiz, M.; Schocke, M.; McCoy, M.; Gobel, G.; la Fougere, C.; Virgolini, I.J.; et al. [18f]-Fluoro-Ethyl-L-Tyrosine Pet: A Valuable Diagnostic Tool in Neuro-Oncology, but Not All That Glitters Is Glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinot, O.L.; Macdonald, D.R.; Abrey, L.E.; Zahlmann, G.; Kerloeguen, Y.; Cloughesy, T.F. Response Assessment Criteria for Glioblastoma: Practical Adaptation and Implementation in Clinical Trials of Antiangiogenic Therapy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2013, 13, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Bent, M.J.; Wefel, J.S.; Schiff, D.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Jaeckle, K.; Junck, L.; Armstrong, T.; Choucair, A.; Waldman, A.D.; Gorlia, T.; et al. Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (a Report of the Rano Group): Assessment of Outcome in Trials of Diffuse Low-Grade Gliomas. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, H.; Weller, M.; Huang, R.; Finocchiaro, G.; Gilbert, M.R.; Wick, W.; Ellingson, B.M.; Hashimoto, N.; Pollack, I.F.; Brandes, A.A.; et al. Immunotherapy Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology: A Report of the Rano Working Group. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e534–e542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.; King, A.D.; Zhou, H.; Leung, S.F.; Abrigo, J.; Chan, Y.L.; Hu, C.W.; Yeung, D.K.; Ahuja, A.T. Evolution of Radiation-Induced Brain Injury: Mr Imaging-Based Study. Radiology 2010, 254, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drappatz, J.; Schiff, D.; Kesari, S.; Norden, A.D.; Wen, P.Y. Medical Management of Brain Tumor Patients. Neurol. Clin. 2007, 25, 1035–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.J.; Bates, D. Conservative Treatment of Delayed Cerebral Radiation Necrosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1984, 47, 1338–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glantz, M.J.; Burger, P.C.; Friedman, A.H.; Radtke, R.A.; Massey, E.W.; Schold, S.C., Jr. Treatment of Radiation-Induced Nervous System Injury with Heparin and Warfarin. Neurology 1994, 44, 2020–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuba, P.J.; Aronin, P.; Bhambhani, K.; Eichenhorn, M.; Zamarano, L.; Cianci, P.; Muhlbauer, M.; Porter, A.T.; Fontanesi, J. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Radiation-Induced Brain Injury in Children. Cancer 1997, 80, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohshi, K.; Imada, H.; Nomoto, S.; Yamaguchi, R.; Abe, H.; Yamamoto, H. Successful Treatment of Radiation-Induced Brain Necrosis by Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2003, 209, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leber, K.A.; Eder, H.G.; Kovac, H.; Anegg, U.; Pendl, G. Treatment of Cerebral Radionecrosis by Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 1998, 70 (Suppl. 1), 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohguri, T.; Imada, H.; Kohshi, K.; Kakeda, S.; Ohnari, N.; Morioka, T.; Nakano, K.; Konda, N.; Korogi, Y. Effect of Prophylactic Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment for Radiation-Induced Brain Injury after Stereotactic Radiosurgery of Brain Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 67, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, J.; Kumar, A.J.; Conrad, C.A.; Levin, V.A. Effect of Bevacizumab on Radiation Necrosis of the Brain. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 67, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arratibel-Echarren, I.; Albright, K.; Dalmau, J.; Rosenfeld, M.R. Use of Bevacizumab for Neurological Complications during Initial Treatment of Malignant Gliomas. Neurologia 2011, 26, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torcuator, R.; Zuniga, R.; Mohan, Y.S.; Rock, J.; Doyle, T.; Anderson, J.; Gutierrez, J.; Ryu, S.; Jain, R.; Rosenblum, M.; et al. Initial Experience with Bevacizumab Treatment for Biopsy Confirmed Cerebral Radiation Necrosis. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 94, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, V.A.; Bidaut, L.; Hou, P.; Kumar, A.J.; Wefel, J.S.; Bekele, B.N.; Grewal, J.; Prabhu, S.; Loghin, M.; Gilbert, M.R.; et al. Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial of Bevacizumab Therapy for Radiation Necrosis of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubelski, D.; Abdullah, K.G.; Weil, R.J.; Marko, N.F. Bevacizumab for Radiation Necrosis Following Treatment of High Grade Glioma: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 115, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.G.; Sai, K.; Wang, Z.N.; Zhang, X.H.; Lu, Y.C.; Wei, D.N.; Yang, Q.Y.; Chen, Z.P. Surgical Management of Radiation-Induced Temporal Lobe Necrosis in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Report of 14 Cases. Head Neck 2011, 33, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonoguchi, N.; Miyatake, S.; Fukumoto, M.; Furuse, M.; Hiramatsu, R.; Kawabata, S.; Kuroiwa, T.; Tsuji, M.; Fukumoto, M.; Ono, K. The Distribution of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Producing Cells in Clinical Radiation Necrosis of the Brain: Pathological Consideration of Their Potential Roles. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 105, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gempt, J.; Buchmann, N.; Ryang, Y.M.; Krieg, S.; Kreutzer, J.; Meyer, B.; Ringel, F. Frameless Image-Guided Stereotaxy with Real-Time Visual Feedback for Brain Biopsy. Acta Neurochir. 2012, 154, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sequence | TA (mins) | Voxel Size (mm³) | TR (ms) | TE (ms) | FA | FOV (mm²) | AM | ST (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native | ||||||||
| Transverse diffusion-weighted sequence (DTI) † | 5:28 | 2.0 × 2.0 × 2.0 | 9600 | 92 | 90° | 250 × 250 | 128 × 100% | 2 |
| Native transverse T1-weighted magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo sequence (T1-MPRAGE) | 3:37 | 0.9 × 0.9 × 1.0 | 2210 | 3 | 8° | 220 × 179 | 256 × 100% | 1 |
| Coronal T2-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) | 3:14 | 0.7 × 0.7 × 3.0 | 8000 | 87 | 150° | 220 × 172 | 320 × 70% | 3 |
| Transverse gradient-echo susceptibility-weighted imaging sequence (SWI) | 3:04 | 0.9 × 0.9 × 1.8 | 27 | 20 | 15° | 220 × 172 | 256 × 90% | 1.8 |
| Transverse Hydrogen 1 magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) †† | 6:53 | 10.0 × 10.0 × 15.0 | 1700 | 135 | 90 | 160 × 160 | n.a. | 15 |
| Gadolinium contrast agent application | ||||||||
| Transverse dynamic T2*-weighted susceptibility contrast (DSC) perfusion (in case of glioblastoma) ††† | 1:42 | 0.9 × 0.9 × 4.0 | 1600 | 30 | 90° | 220 × 220 | 128 × 100% | 4 |
| Transverse T2-weighted turbo-spin echo sequence (T2 TSE) | 3:13 | 0.6 × 0.6 × 2.0 | 5800 | 95 | 150° | 220 × 179 | 384 × 70% | 2 |
| Post-contrast transverse T1-weighted magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo sequence (MPRAGE) | 3:37 | 0.9 × 0.9 × 1.0 | 2210 | 3 | 8° | 220 × 179 | 256 × 100% | 1 |
| Post-contrast sagittal T1 SPACE fat sat dark blood sequences (in case of metastases) | 5:55 | 1.0 × 1.0 × 1.6 | 600 | 9.5 | variable | 256 × 256 | 256 × 90% | 1 |
| 80 min after contrast agent application | ||||||||
| Post-contrast transverse T1-weighted magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo sequence (MPRAGE) †††† | 3:37 | 0.9 × 0.9 × 1.0 | 2210 | 3 | 8° | 220 × 179 | 256 × 100% | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mangesius, J.; Mangesius, S.; Demetz, M.; Uprimny, C.; Di Santo, G.; Galijasevic, M.; Minasch, D.; Gizewski, E.R.; Ganswindt, U.; Virgolini, I.; et al. A Multi-Disciplinary Approach to Diagnosis and Treatment of Radionecrosis in Malignant Gliomas and Cerebral Metastases. Cancers 2022, 14, 6264. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246264
Mangesius J, Mangesius S, Demetz M, Uprimny C, Di Santo G, Galijasevic M, Minasch D, Gizewski ER, Ganswindt U, Virgolini I, et al. A Multi-Disciplinary Approach to Diagnosis and Treatment of Radionecrosis in Malignant Gliomas and Cerebral Metastases. Cancers. 2022; 14(24):6264. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246264
Chicago/Turabian StyleMangesius, Julian, Stephanie Mangesius, Matthias Demetz, Christian Uprimny, Gianpaolo Di Santo, Malik Galijasevic, Danijela Minasch, Elke R. Gizewski, Ute Ganswindt, Irene Virgolini, and et al. 2022. "A Multi-Disciplinary Approach to Diagnosis and Treatment of Radionecrosis in Malignant Gliomas and Cerebral Metastases" Cancers 14, no. 24: 6264. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246264
APA StyleMangesius, J., Mangesius, S., Demetz, M., Uprimny, C., Di Santo, G., Galijasevic, M., Minasch, D., Gizewski, E. R., Ganswindt, U., Virgolini, I., Thomé, C., Freyschlag, C. F., & Kerschbaumer, J. (2022). A Multi-Disciplinary Approach to Diagnosis and Treatment of Radionecrosis in Malignant Gliomas and Cerebral Metastases. Cancers, 14(24), 6264. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246264







