Analysis of High-Risk Extramedullary Relapse Factors in Newly Diagnosed MM Patients
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Research Patients
2.2. Treatment
2.3. Efficacy assessment
2.4. Data Acquisition
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
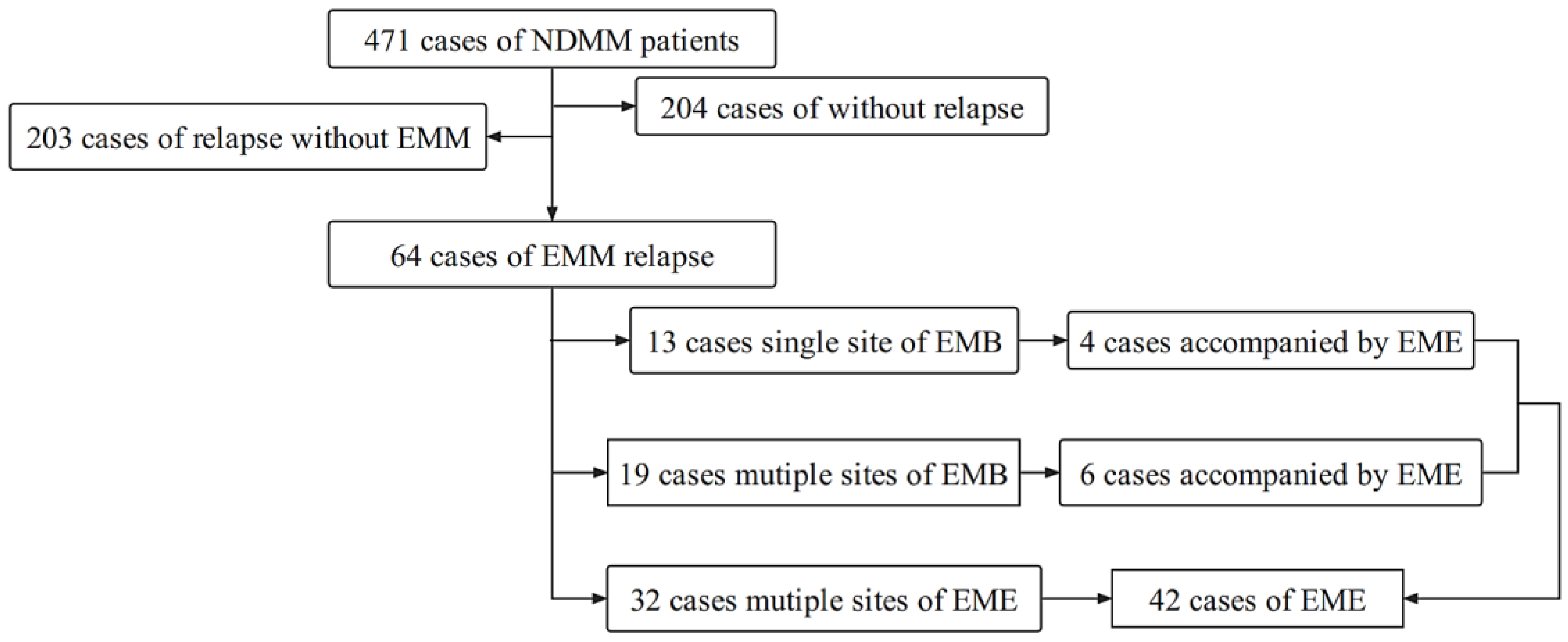
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Extramedullary Relapse
3.2. Effect of Extramedullary Relapse on the Prognosis of MM Patients
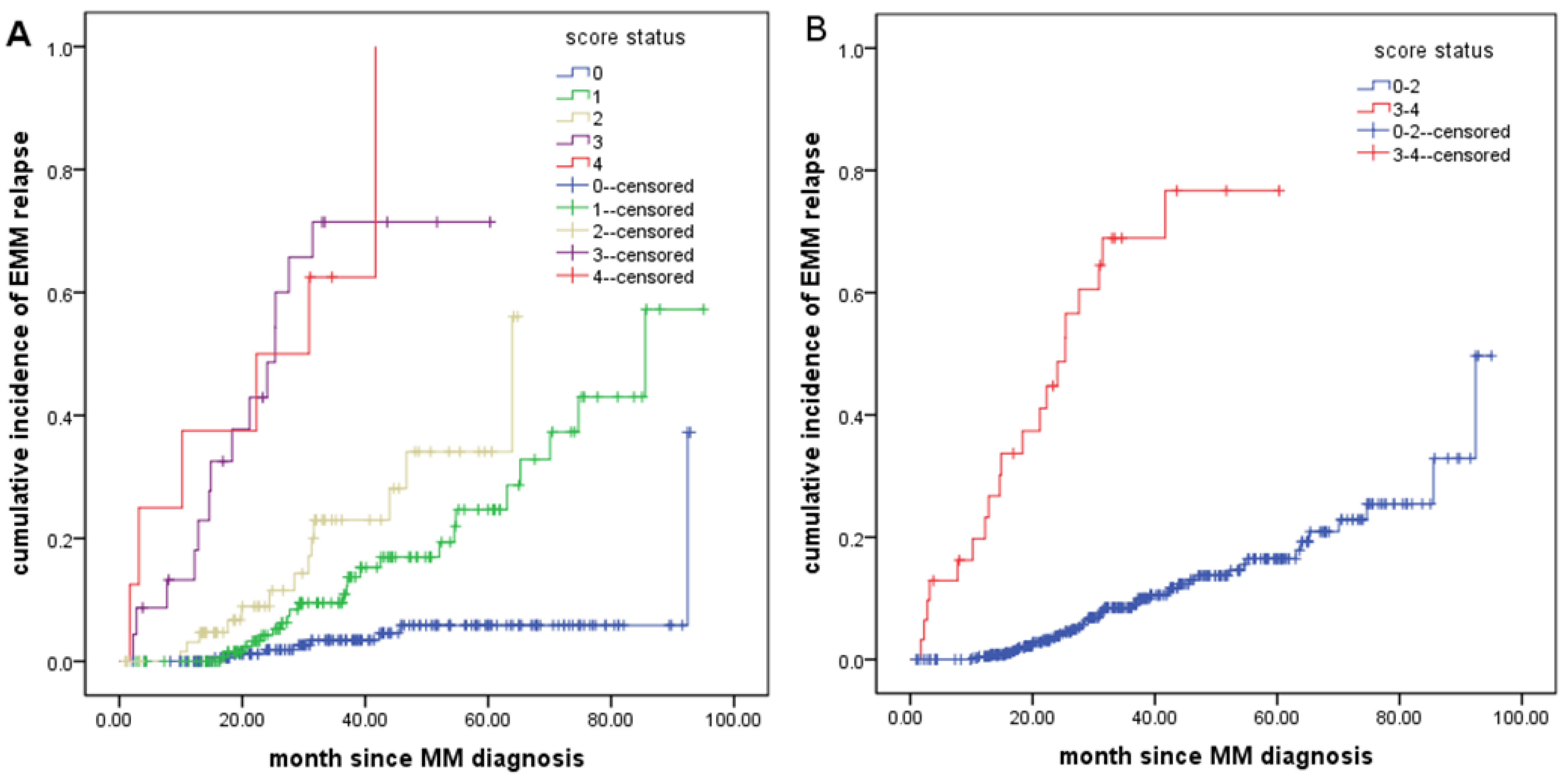
3.3. Risk Factors for Extramedullary Relapse in NDMM Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.; Paiva, B.; Anderson, K.C.; Durie, B.; Landgren, O.; Moreau, P.; Munshi, N.; Lonial, S.; Blade, J.; Mateos, M.V.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group consensus criteria for response and minimal residual disease assessment in multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e328–e346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, A.; Anderson, K. Multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1046–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, R.A.; Gertz, M.A.; Witzig, T.E.; Lust, J.A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Dispenzieri, A.; Fonseca, R.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Offord, J.R.; Larson, D.R.; et al. Review of 1027 patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2003, 78, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.K.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Hayman, S.R.; Buadi, F.K.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Dingli, D.; Russell, S.J.; Lust, J.A.; et al. Improved survival in multiple myeloma and the impact of novel therapies. Blood 2008, 111, 2516–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.E.; Kim, J.H.; Jeon, Y.W.; Yoon, J.H.; Shin, S.H.; Eom, K.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.; Cho, S.G.; et al. Impact of extramedullary plasmacytomas on outcomes according to treatment approach in newly diagnosed symptomatic multiple myeloma. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhutani, M.; Foureau, D.M.; Atrash, S.; Voorhees, P.M.; Usmani, S.Z. Extramedullary multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touzeau, C.; Moreau, P. How I treat extramedullary myeloma. Blood 2016, 127, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blade, J.; Fernandez de Larrea, C.; Rosinol, L.; Cibeira, M.T.; Jimenez, R.; Powles, R. Soft-tissue plasmacytomas in multiple myeloma: Incidence, mechanisms of extramedullary spread, and treatment approach. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3805–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stork, M.; Sevcikova, S.; Minarik, J.; Krhovska, P.; Radocha, J.; Pospisilova, L.; Brozova, L.; Jarkovsky, J.; Spicka, I.; Straub, J.; et al. Identification of patients at high risk of secondary extramedullary multiple myeloma development. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, L.; Sevcikova, S.; Greslikova, H.; Kupska, R.; Majkova, P.; Zahradova, L.; Sandecka, V.; Adam, Z.; Krejci, M.; Kuglik, P.; et al. Soft-tissue extramedullary multiple myeloma prognosis is significantly worse in comparison to bone-related extramedullary relapse. Haematologica 2014, 99, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.Z.; Heuck, C.; Mitchell, A.; Szymonifka, J.; Nair, B.; Hoering, A.; Alsayed, Y.; Waheed, S.; Haider, S.; Restrepo, A.; et al. Extramedullary disease portends poor prognosis in multiple myeloma and is over-represented in high-risk disease even in the era of novel agents. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varettoni, M.; Corso, A.; Pica, G.; Mangiacavalli, S.; Pascutto, C.; Lazzarino, M. Incidence, presenting features and outcome of extramedullary disease in multiple myeloma: A longitudinal study on 1003 consecutive patients. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevcikova, S.; Minarik, J.; Stork, M.; Jelinek, T.; Pour, L.; Hajek, R. Extramedullary disease in multiple myeloma—Controversies and future directions. Blood Rev. 2019, 36, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; He, D.; Han, X.; Zheng, G.; Wei, G.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W.; Fu, J.; Shou, L.; et al. Bortezomib-Based Regimens for Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma in China: A Report of 12-Year Real-World Data. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 561601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagelmann, N.; Eikema, D.J.; Iacobelli, S.; Koster, L.; Nahi, H.; Stoppa, A.M.; Masszi, T.; Caillot, D.; Lenhoff, S.; Udvardy, M.; et al. Impact of extramedullary disease in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma undergoing autologous stem cell transplantation: A study from the Chronic Malignancies Working Party of the EBMT. Haematologica 2018, 103, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durie, B.G.; Harousseau, J.L.; Miguel, J.S.; Blade, J.; Barlogie, B.; Anderson, K.; Gertz, M.; Dimopoulos, M.; Westin, J.; Sonneveld, P.; et al. International uniform response criteria for multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2006, 20, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpos, E.; Rezvani, K.; Basu, S.; Milne, A.E.; Rose, P.E.; Scott, G.L.; Rahemtulla, A.; Samson, D.; Apperley, J.F. Plasmacytoma relapses in the absence of systemic progression post-high-dose therapy for multiple myeloma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2005, 75, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avivi, I.; Cohen, Y.C.; Suska, A.; Shragai, T.; Mikala, G.; Garderet, L.; Seny, G.M.; Glickman, S.; Jayabalan, D.S.; Niesvizky, R.; et al. Hematogenous extramedullary relapse in multiple myeloma—A multicenter retrospective study in 127 patients. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oriol, A. Multiple myeloma with extramedullary disease. Adv. Ther. 2011, 28 (Suppl. S7), 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosinol, L.; Beksac, M.; Zamagni, E.; Van de Donk, N.; Anderson, K.C.; Badros, A.; Caers, J.; Cavo, M.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Dispenzieri, A.; et al. Expert review on soft-tissue plasmacytomas in multiple myeloma: Definition, disease assessment and treatment considerations. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 194, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzetti, A.; Papini, G.; Defina, M.; Bocchia, M. Extramedullary myeloma relapses. Ann. Hematol. 2012, 91, 1511–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Fluchter, P.; Nickel, K.; Meckel, K.; Messerschmidt, J.; Bockle, D.; Knorz, S.; Steinhardt, M.J.; Krummenast, F.; Danhof, S.; et al. Carfilzomib Based Treatment Strategies in the Management of Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma with Extramedullary Disease. Cancers 2020, 12, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tao, S.; Zheng, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, K.; He, Z.; Wang, C.; Yu, L. Research progress on treatment of extramedullary multiple myeloma. Hematology 2021, 26, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alegre, A.; Granda, A.; Martinez-Chamorro, C.; Diaz-Mediavilla, J.; Martinez, R.; Garcia-Larana, J.; Lahuerta, J.J.; Sureda, A.; Blade, J.; de la Rubia, J.; et al. Different patterns of relapse after autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma: Clinical results of 280 cases from the Spanish Registry. Haematologica 2002, 87, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perez-Simon, J.A.; Sureda, A.; Fernandez-Aviles, F.; Sampol, A.; Cabrera, J.R.; Caballero, D.; Martino, R.; Petit, J.; Tomas, J.F.; Moraleda, J.M.; et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic transplantation is associated with a high incidence of extramedullary relapses in multiple myeloma patients. Leukemia 2006, 20, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiser, R.; Deschler, B.; Bertz, H.; Finke, J.; Engelhardt, M. Extramedullary vs medullary relapse after autologous or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) in multiple myeloma (MM) and its correlation to clinical outcome. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004, 34, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonial, S.; Weiss, B.M.; Usmani, S.Z.; Singhal, S.; Chari, A.; Bahlis, N.J.; Belch, A.; Krishnan, A.; Vescio, R.A.; Mateos, M.V.; et al. Daratumumab monotherapy in patients with treatment-refractory multiple myeloma (SIRIUS): An open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonial, S.; Dimopoulos, M.; Palumbo, A.; White, D.; Grosicki, S.; Spicka, I.; Walter-Croneck, A.; Moreau, P.; Mateos, M.V.; Magen, H.; et al. Elotuzumab Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facon, T.; Kumar, S.; Plesner, T.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Moreau, P.; Bahlis, N.; Basu, S.; Nahi, H.; Hulin, C.; Quach, H.; et al. Daratumumab plus Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone for Untreated Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2104–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinek, T.; Sevcikova, T.; Zihala, D.; Popkova, T.; Kapustova, V.; Broskevicova, L.; Capkova, L.; Rihova, L.; Bezdekova, R.; Sevcikova, S.; et al. Limited efficacy of daratumumab in multiple myeloma with extramedullary disease. Leukemia 2022, 36, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.Z.; Weiss, B.M.; Plesner, T.; Bahlis, N.J.; Belch, A.; Lonial, S.; Lokhorst, H.M.; Voorhees, P.M.; Richardson, P.G.; Chari, A.; et al. Clinical efficacy of daratumumab monotherapy in patients with heavily pretreated relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2016, 128, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.H.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Cao, X.M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, F.X.; Zhang, P.Y.; Lei, B.; et al. A phase 1, open-label study of LCAR-B38M, a chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy directed against B cell maturation antigen, in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, T.; Kang, Y. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for multiple myeloma. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 108007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiacavalli, S.; Pompa, A.; Ferretti, V.; Klersy, C.; Cocito, F.; Varettoni, M.; Cartia, C.S.; Cazzola, M.; Corso, A. The possible role of burden of therapy on the risk of myeloma extramedullary spread. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schavgoulidze, A.; Lauwers-Cances, V.; Perrot, A.; Cazaubiel, T.; Chretien, M.L.; Moreau, P.; Facon, T.; Leleu, X.; Karlin, L.; Stoppa, A.M.; et al. Heterogeneity in long term outcomes for R-ISS stage II in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients. Haematologica 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamagni, E.; Barbato, S.; Cavo, M. How I treat high-risk multiple myeloma. Blood 2022, 139, 2889–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkumar, S.V. Multiple myeloma: 2022 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 1086–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, A.J.; Green, D.J.; Kwok, M.; Lee, S.; Coffey, D.G.; Holmberg, L.A.; Tuazon, S.; Gopal, A.K.; Libby, E.N. Diagnosis and Management of Multiple Myeloma: A Review. JAMA 2022, 327, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yue, X.; He, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, E.; Han, X.; Wu, W.; Yang, L.; et al. Multiple Extramedullary-Bone Related and/or Extramedullary Extraosseous Are Independent Poor Prognostic Factors in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 668099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Without Relapse N = 204(%) | Relapse Without EMM N = 203(%) | Relapse With EMM N = 64(%) | p Value 1 | p Value 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.075 | 0.037 | |||
| ≤65 years | 118 (57.8) | 112 (55.2) | 45 (70.3) | ||
| >65 years | 86 (42.2) | 91 (44.8) | 19 (29.7) | ||
| Gender | 0.386 | 0.302 | |||
| Male | 115 (56.4) | 112 (55.2) | 40 (62.5) | ||
| Female | 89 (43.6) | 91 (44.8) | 24 (37.5) | ||
| Type of M protein, n (%) | <0.001 | 0.095 | |||
| Non-IgD | 200 (98.5) | 191 (94.6) | 55 (87.3) | ||
| IgD | 3 (1.5) | 11 (5.4) | 8 (12.7) | ||
| D-S stage, n (%) | 0.207 | 0.915 | |||
| 1 + 2 | 56 (27.5) | 39 (19.2) | 11 (17.2) | ||
| 3A | 117 (57.4) | 134 (66.0) | 14 (68.8) | ||
| 3B | 31 (15.2) | 30 (14.8) | 9 (14.1) | ||
| ISS, n (%) | 0.510 | 0.639 | |||
| 1 | 64 (31.4) | 57 (28.1) | 17 (26.6) | ||
| 2 | 64 (31.4) | 67 (33.0) | 18 (28.1) | ||
| 3 | 76 (37.3) | 79 (38.9) | 29 (45.3) | ||
| R-ISS, n (%) | 0.025 | 0.516 | |||
| 1 + 2 | 124 (70.9) | 100 (59.5) | 30 (54.5) | ||
| 3 | 51 (29.1) | 68 (40.5) | 25 (45.5) | ||
| Unknow | 29 | 30 | 14 | ||
| Hb (g/L), median(range) | 94 (49–160) | 89 (42–161) | 99 (49–159) | 0.841 | 0.100 |
| ≥100 | 96 (51.8) | 71 (35.1) | 34 (53.1) | 0.849 | 0.092 |
| <100 | 103 (51.8) | 131 (64.9) | 30 (46.9) | ||
| Plt (×109/L), median(range) | 198 (31–597) | 158 (36–397) | 155 (23–354) | 0.002 | 0.870 |
| ≥150 × 10 | 142 (72.1) | 115 (57.8) | 34 (54.0) | 0.007 | 0.594 |
| <150 × 10 | 55 (27.9) | 84 (42.2) | 29 (46.0) | ||
| CRP (g/L), median(range) | 1.8 (0–34.2) | 2.2 (0–8.1) | 2.1 (0–20.4) | 0.282 | 0.865 |
| ≤8 | 152 (81.2) | 139 (47.7) | 45 (71.4) | 0.102 | 0.606 |
| >8 | 35 (18.8) | 47 (25.3) | 18 (28.6) | ||
| LDH (U/L), median(range) | 171.5 (85–605) | 188 (79–848) | 218 (83–5785) | <0.001 | 0.012 |
| <245 | 163 (85.5) | 156 (78.9) | 38 (60.3) | <0.001 | 0.003 |
| ≥245 | 27 (14.2) | 41 (21.1) | 25 (39.7) | ||
| Ca2+ (mmol/L) | |||||
| ≤2.65 | 124 (63.6) | 131 (66.8) | 31 (50.0) | 0.057 | 0.017 |
| >2.65 | 71 (36.4) | 65 (33.2) | 31 (50.0) | ||
| BMPCs (%), median(range) | 22.0 (0–96) | 31.0 (0–97) | 30.8 (1–99) | 0.003 | 0.954 |
| ≤30 | 128 (63.4) | 98 (48.8) | 31 (48.4) | 0.034 | 0.965 |
| >30 | 74 (36.6) | 103 (51.2) | 33 (51.6) | ||
| EMM at diagnosed | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| Non-EMM | 162 (79.4) | 167 (82.3) | 32 (50.0) | ||
| EMM | 42 (20.6) | 36 (17.7) | 32 (50.0) | ||
| EMB | 40 (19.6) | 34 (16.7) | 20 (31.3) | ||
| EME | 2 (1.0) | 2 (1.0) | 12 (18.8) | ||
| Osteolytic lesions | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| ≤2 lesions | 177 (86.8) | 172 (84.7) | 32 (50.0) | ||
| >2 lesions | 27 (13.2) | 31 (15.2) | 32 (50.0) | ||
| Spleen | <0.001 | 0.006 | |||
| Normal | 171 (83.3) | 156 (76.8) | 38 (59.4) | ||
| Enlarged | 33 (16.2) | 47 (23.2) | 26 (40.6) | ||
| Treatment efficacy | <0.001 | 0.334 | |||
| ≥PR | 200 (100) | 173 (90.1) | 54 (85.7) | ||
| <PR | 0 | 19 (9.9) | 9 (14.3) | ||
| Therapy received | 0.286 | 0.234 | |||
| PD | 38 (19.7) | 48 (24.9) | 8 (13.3) | ||
| PAD | 19 (8.8) | 23 (11.9) | 8 (13.3) | ||
| PCD | 99 (51.3) | 106 (54.9) | 36 (60.0) | ||
| PTD or PRD | 39 (20.2) | 16 (8.3) | 8 (13.3) | ||
| ASCT | 0.008 | 0.280 | |||
| No | 161 (79.3) | 181(89.2) | 60 (93.8) | ||
| Yes | 42 (20.7) | 22 (10.8) | 4 (6.3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, X.; He, D.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, E.; et al. Analysis of High-Risk Extramedullary Relapse Factors in Newly Diagnosed MM Patients. Cancers 2022, 14, 6106. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246106
Yue X, He D, Zheng G, Yang Y, Han X, Li Y, Zhao Y, Wu W, Chen Q, Zhang E, et al. Analysis of High-Risk Extramedullary Relapse Factors in Newly Diagnosed MM Patients. Cancers. 2022; 14(24):6106. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246106
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Xiaoyan, Donghua He, Gaofeng Zheng, Yang Yang, Xiaoyan Han, Yi Li, Yi Zhao, Wenjun Wu, Qingxiao Chen, Enfang Zhang, and et al. 2022. "Analysis of High-Risk Extramedullary Relapse Factors in Newly Diagnosed MM Patients" Cancers 14, no. 24: 6106. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246106
APA StyleYue, X., He, D., Zheng, G., Yang, Y., Han, X., Li, Y., Zhao, Y., Wu, W., Chen, Q., Zhang, E., Cai, Z., & He, J. (2022). Analysis of High-Risk Extramedullary Relapse Factors in Newly Diagnosed MM Patients. Cancers, 14(24), 6106. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246106




