Prognostic Indicators of EIF1AX-Mutated Thyroid Tumor Malignancy and Cancer Aggressiveness
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patient Population
2.3. Tumor Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
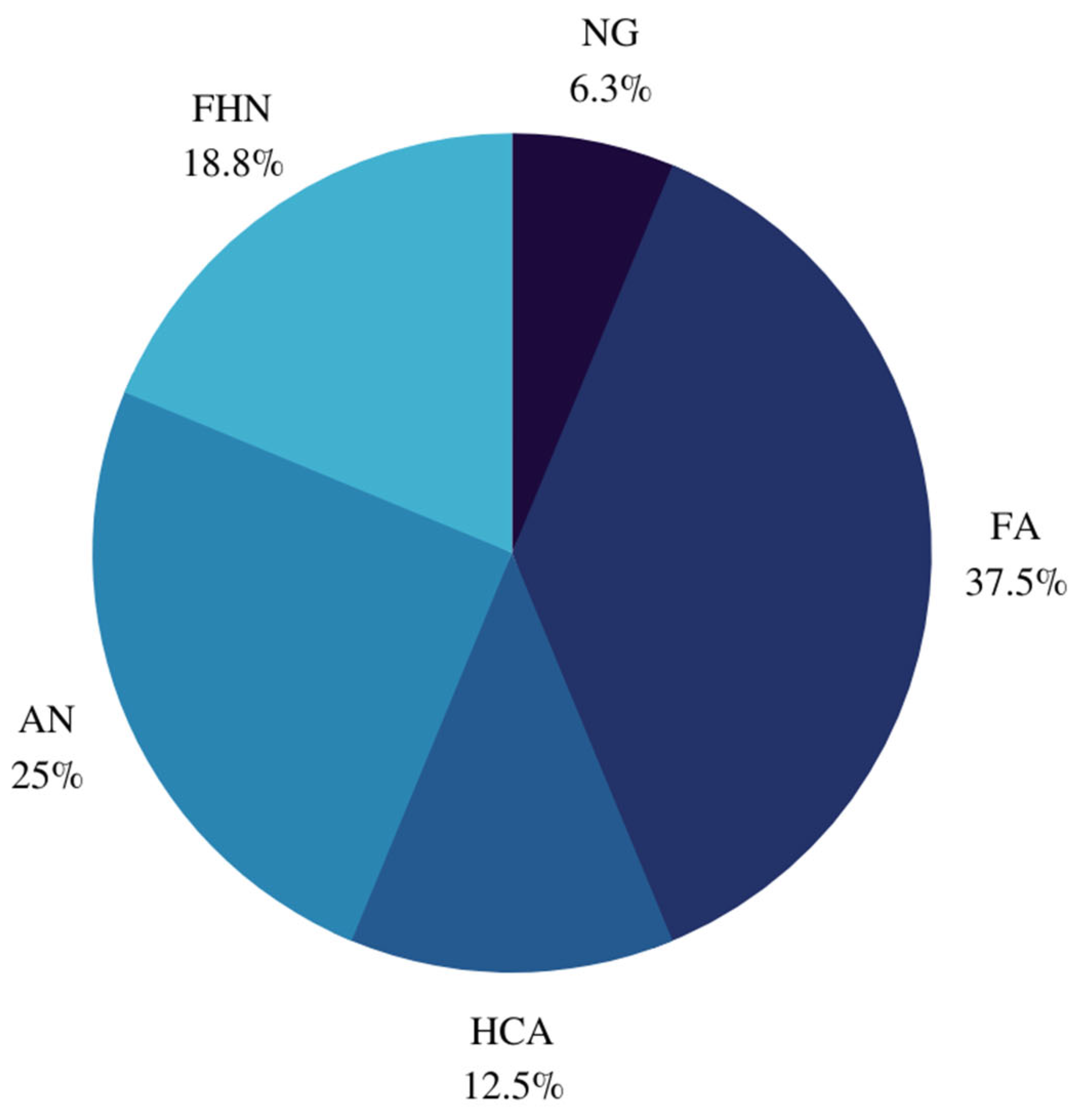
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Tumor Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rossi, E.D.; Pantanowitz, L.; Hornick, J.L. A worldwide journey of thyroid cancer incidence centred on tumour histology. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canadian Cancer Statistics 2021; Canadian Cancer Society: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2021.
- VanderLaan, P.A.; Marqusee, E.; Krane, J.F. Clinical outcome for atypia of undetermined significance in thyroid fine-needle aspirations: Should repeated fna be the preferred initial approach? Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 135, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cibas, E.S.; Ali, S.Z.; NCI Thyroid FNA State of the Science Conference. The Bethesda System For Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 132, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyeon, J.; Ahn, S.; Shin, J.H.; Oh, Y.L. The prediction of malignant risk in the category “atypia of undetermined significance/follicular lesion of undetermined significance” of the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology using subcategorization and BRAF mutation results. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014, 122, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarella, M.A.; Peeva, M.; Forest, V.I.; Pusztaszeri, M.P.; Avior, G.; Tamilia, M.; Mlynarek, A.M.; Hier, M.P.; Payne, R.J. Association of Bethesda category and molecular mutation in patients undergoing thyroidectomy. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2022, 47, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.I.; Junit, S.M.; Ng, K.L.; Jayapalan, J.J.; Karikalan, B.; Hashim, O.H. Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Genetic Alterations and Molecular Biomarker Investigations. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell 2014, 159, 676–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinnebusch, A.G. The scanning mechanism of eukaryotic translation initiation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2014, 83, 779–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestova, T.V.; Kolupaeva, V.G.; Lomakin, I.B.; Pilipenko, E.V.; Shatsky, I.N.; Agol, V.I.; Hellen, C.U. Molecular mechanisms of translation initiation in eukaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7029–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, G.P.; Davidson, N.R.; Leach, S.D.; Zhao, Z.; Lowe, S.W.; Lee, G.; Landa, I.; Nagarajah, J.; Saqcena, M.; Singh, K.; et al. EIF1AX and RAS Mutations Cooperate to Drive Thyroid Tumorigenesis through ATF4 and c-MYC. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 264–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões-Pereira, J.; Moura, M.M.; Marques, I.J.; Rito, M.; Cabrera, R.A.; Leite, V.; Cavaco, B.M. The role of EIF1AX in thyroid cancer tumourigenesis and progression. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunamurthy, A.; Panebianco, F.; JHsiao, S.; Vorhauer, J.; Nikiforova, M.N.; Chiosea, S.; Nikiforov, Y.E. Prevalence and phenotypic correlations of EIF1AX mutations in thyroid nodules. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Liu, X.; Ren, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Liang, Z. Mutation profiles of follicular thyroid tumors by targeted sequencing. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiforova, M.N.; Mercurio, S.; Wald, A.I.; Barbi de Moura, M.; Callenberg, K.; Santana-Santos, L.; Gooding, W.E.; Yip, L.; Ferris, R.L.; Nikiforov, Y.E. Analytical performance of the ThyroSeq v3 genomic classifier for cancer diagnosis in thyroid nodules. Cancer 2018, 124, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Gilfix, B.M.; Rivera, J.; Sadeghi, N.; Richardson, K.; Hier, M.P.; Forest, V.I.; Fishman, D.; Caglar, D.; Pusztaszeri, M.; et al. The Role of the ThyroSeq v3 Molecular Test in the Surgical Management of Thyroid Nodules in the Canadian Public Health Care Setting. Thyroid 2020, 30, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugen, B.R.; Alexander, E.K.; Bible, K.C.; Doherty, G.M.; Mandel, S.J.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Pacini, F.; Randolph, G.W.; Sawka, A.M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloch, Z.W.; Asa, S.L.; Barletta, J.A.; Ghossein, R.A.; Juhlin, C.C.; Jung, C.K.; LiVolsi, V.A.; Papotti, M.G.; Sobrinho-Simões, M.; Tallini, G.; et al. Overview of the 2022 WHO Classification of Thyroid Neoplasms. Endocr. Pathol. 2022, 33, 27–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiforov, Y.E.; Nikiforova, M.N. Molecular genetics and diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, M.; Ricarte-Filho, J.; Knauf, J.; Shaha, A.; Tuttle, M.; Fagin, J.A.; Ghossein, R.A. Molecular genotyping of papillary thyroid carcinoma follicular variant according to its histological subtypes (encapsulated vs. infiltrative) reveals distinct BRAF and RAS mutation patterns. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asa, S.L.; Mete, O. Oncocytic Change in Thyroid Pathology. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 678119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asa, S.L. My approach to oncocytic tumours of the thyroid. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 57, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landa, I.; Ibrahimpasic, T.; Boucai, L.; Sinha, R.; Knauf, J.A.; Shah, R.H.; Dogan, S.; Ricarte-Filho, J.C.; Krishnamoorthy, G.P.; Xu, B.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic hallmarks of poorly differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancers. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsherbini, N.; Kim, D.H.; Payne, R.J.; Hudson, T.; Forest, V.I.; Hier, M.P.; Payne, A.E.; Pusztaszeri, M.P. EIF1AX mutation in thyroid tumors: A retrospective analysis of cytology, histopathology and co-mutation profiles. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 51, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karslioglu French, E.; Nikitski, A.V.; Yip, L.; Nikiforova, M.N.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Carty, S.E. Clinicopathological features and outcomes of thyroid nodules with EIF1AX mutations. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2022, 29, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargano, S.M.; Badjatia, N.; Nikolaus, Y.; Peiper, S.C.; Wang, Z.X. Characterization and Clinical Significance of EIF1AX Mutations and Co-Mutations in Cytologically Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules: A 5-Year Retrospective Analysis. Acta Med. Acad. 2021, 50, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Case | Sex | Age (Year) | Cytologic Diagnosis (Bethesda Score) | Histopathologic Diagnosis | Nodule Size (cm) | Co-Existing Mutation(s) | Type of EIF1AX Mutation | EIF1AX Mutation AF (%) | Co-Existing Mutation(s) AF (%) | Aggressive Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 60 | 4 | FA | 0.9 | - | A113_splice site | 15 | - | - |
| 2 | F | 69 | 3 | NG | 1.8 | - | R13L | 38 | - | - |
| 3 | F | 55 | 3 | AN | 0.8 | - | A113_splice site | 8 | - | - |
| 4 | F | 55 | 3 | FA | 1.4 | - | G9V | 28 | - | - |
| 5 | F | 62 | 3 | AN | 1.5 | TP53 | G15D | 2 | 9 | - |
| 6 | F | 63 | 3 | FA | 1.5 | - | G9R | 28 | - | - |
| 7 | F | 58 | 3 | FHN | 1 | - | A113_splice site | 36 | - | - |
| 8 | M | 66 | 3 | AN | 1.8 | - | A113_splice site | 59 | - | - |
| 9 | F | 70 | 3 | FA | 2.6 | CNAs | G9R | 27 | - | - |
| 10 | F | 46 | 3 | FA | 3 | - | N11_E20dup | 14 | - | - |
| 11 | F | 82 | 3 | FHN | - | - | G6V | 12 | - | - |
| 12 | M | 43 | 3 | FA | 5 | - | A113_splice site | 14 | - | - |
| 13 | F | 68 | 3 | HCA | 1 | - | G124L | 14 | - | - |
| 14 | F | 78 | 3 | HCA | 3.4 | - | K10_N11insKPSGKGGK | 10 | - | - |
| 15 | F | 85 | 4 | FHN | - | - | G9R | 40 | - | - |
| 16 | M | 52 | 3 | AN | 4 | - | G8E | 62 | - | - |
| 17 | F | 72 | 3 | FVPTC | 1.3 | NRAS | R13P | 11 | 10 | - |
| 18 | F | 75 | 4 | PDTC | 2.5 | - | A113_splice site | 12 | - | PDTC |
| 19 | F | 68 | 3 | HCC | 3 | TP53 | A113_splice site | 30 | 45 | 40% component PDTC |
| 20 | F | 88 | 3 | IFVPTC | 2.8 | - | G9V | 22 | - | - |
| 21 | F | 51 | 4 | IFVPTC | 1.8 | NRAS | G9D | 26 | 23 | - |
| 22 | F | 77 | 4 | OVPTC | 0.6 | - | A113_splice site | 18 | - | - |
| 23 | F | 75 | 4 | PDTC | 3.5 | - | A113_splice site | 19 | - | PDTC |
| 24 | F | 44 | 4 | EFVPTC | 3.9 | - | A113_splice site | 24 | - | Positive SLNB |
| 25 | F | 77 | 3 | HCC | 4 | PIK3CA, TERT | N17_K23dup | 11 | 16, 16 | - |
| 26 | F | 45 | 3 | PTC | 0.55 | - | A113_splice site | 6 | - | - |
| 27 | M | 60 | 4 | HCC | - | TP53, NRAS, CNAs | A113_splice site | 57 | 40, 7 | 30% component PDTC |
| 28 | M | 74 | 4 | EFVPTC | 5 | HRAS, GEAs | A113_splice site | 32 | 19 | 10% component PDTC |
| 29 | F | 58 | 4 | PTC | 2 | - | A113_splice site | 37 | - | - |
| 30 | F | 44 | 3 | PMTC | 0.3 | - | G8R | 17 | - | - |
| 31 | M | 33 | 3 | EFVPTC | 5 | HRAS | A113_splice site | 61 | 29 | - |
| 32 | F | 77 | 3 | OVPTC | 3.5 | - | A113_splice site | 20 | - | - |
| 33 | M | 55 | 3 | PMTC | 0.3 | - | G5V | 23 | - | - |
| 34 | F | 49 | 3 | EFVPTC | 2 | - | A113_splice site | 32 | - | - |
| 35 | F | 64 | 4 | FVPTC | - | CNAs | G8V | 29 | - | - |
| 36 | F | 66 | 3 | PMTC | 0.1 | - | R13P | 15 | - | - |
| 37 | M | 58 | 3 | WDT-UMP | 3.2 | - | K16E | 29 | - | - |
| 38 | F | 48 | 3 | NIFTP | 1.3 | - | G9D | 15 | - | - |
| 39 | F | 46 | 3 | WDT-UMP | 2.5 | - | G9D | 10 | - | - |
| 40 | F | 26 | 4 | WDT-UMP | 2.1 | GNAS | G15D | 11 | 10 | - |
| 41 | F | 66 | 5 | NIFTP | 2 | - | R13H | 29 | - | - |
| 42 | F | 68 | 3 | NIFTP | 0.7 | G9V | 31 | - | - |
| Type of EIF1AX Mutation | ROM (%) | ROM or NIFTPs/WDT-UMPs (%) | ROM for Nodules with ≥1 Additional Molecular Alteration (%) | ROM for Nodules with Concurrent RAS (%) | ROM for Nodules with TP53 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 47.6 | 61.9 | 72.7 | 100 | 66.7 |
| non-A113_splice site | 36 | 56 | – | 100 | 0 |
| A113_splice site | 70.6 | 70.6 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Study | Sample Size n (%) | Mutation Frequency (%) | Benign Disease n (%) | NIFTPs/WDT-UMPs n (%) | Malignancy n (%) | A113_Splice Site Mutation (%) | Nodules with ≥1 Additional Molecular Alterations (%) | Co-Existing Genetic Mutations Present | Nodules with Concurrent RAS (%) | Nodules with Concurrent TP53 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current study Sensitivity Specificity PPV | 42 (5.5) | 5.5 | 16 (38.1) | 6 (14.3) | 20 (47.6) | 40.5 57.2 76.2 70.6 | 26.2 53.4 81.8 77.8 | TP53, NRAS, PIK3CA, TERT, HRAS, GNAS | 11.9 23.8 100 100 | 7.14 9.5 95.2 66.7 |
| Elsherbini et al., 2022 [24] PPV | 31 (5) | 5 | 17 (55) | 2 (6.5) | 12 (38.7) | 48.4 53 | 22.6 85.7 | NRAS, HRAS, TP53, TERT, PIK3CA | 12.9 100 | 9.7 66.7 |
| Karslioglu et al., 2022 [25] PPV | 31 (5) | - | 17 (55) | 2 (6) | 12 (39) | 45 33.3 | 48 80 | - | - | - |
| Gargano et al., 2021 [26] * PPV | 26 (4.5) | 4.5 | 6 (23) | 3 (11.5) | 17 (65.4) | 65.4 85 | 57.7 93 | KRAS, NRAS, TERT, HRAS, TP53, YWHAG-BRAF | 46.2 91.7 | 7.7 100 |
| Karunamurthy et al., 2016 [13] * PPV | 11 (4.2) | 4.2 | 7 (63.6) | 0 | 4 (36.4) | 54.5 83.3 | 27.3 100 | NRAS, TP53, TERT | 27.3 100 | 9.1 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bandargal, S.; Chen, T.; Pusztaszeri, M.P.; Forest, V.-I.; da Silva, S.D.; Payne, R.J. Prognostic Indicators of EIF1AX-Mutated Thyroid Tumor Malignancy and Cancer Aggressiveness. Cancers 2022, 14, 6097. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246097
Bandargal S, Chen T, Pusztaszeri MP, Forest V-I, da Silva SD, Payne RJ. Prognostic Indicators of EIF1AX-Mutated Thyroid Tumor Malignancy and Cancer Aggressiveness. Cancers. 2022; 14(24):6097. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246097
Chicago/Turabian StyleBandargal, Saruchi, Tanya Chen, Marc Philippe Pusztaszeri, Véronique-Isabelle Forest, Sabrina Daniela da Silva, and Richard J. Payne. 2022. "Prognostic Indicators of EIF1AX-Mutated Thyroid Tumor Malignancy and Cancer Aggressiveness" Cancers 14, no. 24: 6097. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246097
APA StyleBandargal, S., Chen, T., Pusztaszeri, M. P., Forest, V.-I., da Silva, S. D., & Payne, R. J. (2022). Prognostic Indicators of EIF1AX-Mutated Thyroid Tumor Malignancy and Cancer Aggressiveness. Cancers, 14(24), 6097. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246097







