Multi-Stage Classification-Based Deep Learning for Gleason System Grading Using Histopathological Images
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
Related Work
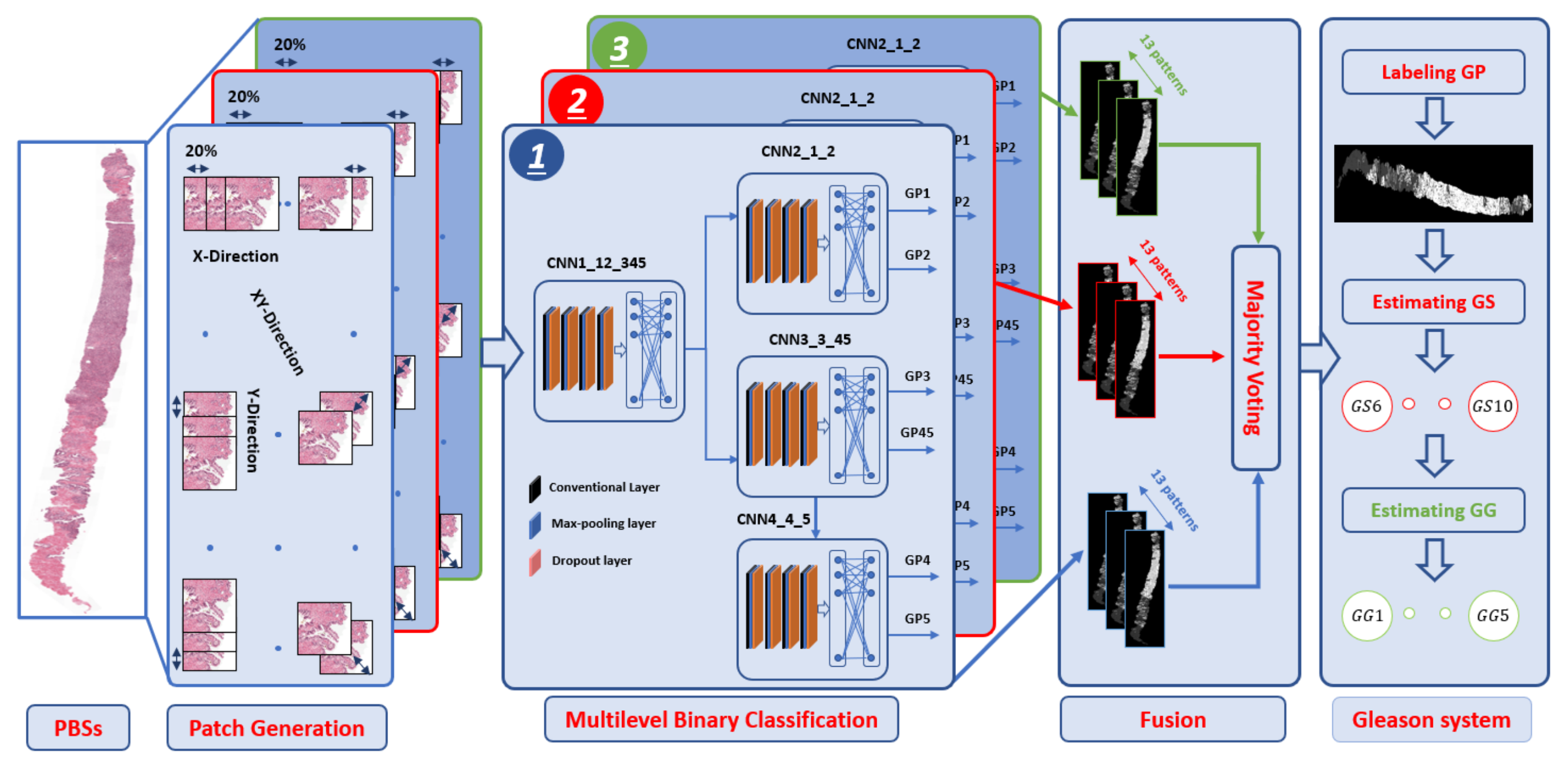
2. Methods
2.1. Dataset Description
2.2. Preprocessing Step
| Algorithm 1: Preprocessing step and selecting training patches, the value of S is 100, 75, or 50. |
Input: Whole slide images (WSIs) of the digitized prostate biopsy specimens (PBSs). Output: Label the choice patches into the Gleason pattern (GP) classes.
|
2.3. Multilevel Binary Classification
2.4. Estimating the Gleason System
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures. 2020. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2020.html (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Litwin, M.S.; Tan, H.J. The diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer: A review. JAMA 2017, 317, 2532–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottke, D.; Golz, R.; Störkel, S.; Hinke, A.; Siegmann, A.; Hertle, L.; Miller, K.; Hinkelbein, W.; Wiegel, T. Phase 3 study of adjuvant radiotherapy versus wait and see in pT3 prostate cancer: Impact of pathology review on analysis. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvåle, R.; Møller, B.; Wahlqvist, R.; Fosså, S.D.; Berner, A.; Busch, C.; Kyrdalen, A.E.; Svindland, A.; Viset, T.; Halvorsen, O.J. Concordance between Gleason scores of needle biopsies and radical prostatectomy specimens: A population-based study. BJU Int. 2009, 103, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veloso, S.G.; Lima, M.F.; Salles, P.G.; Berenstein, C.K.; Scalon, J.D.; Bambirra, E.A. Interobserver agreement of Gleason score and modified Gleason score in needle biopsy and in surgical specimen of prostate cancer. Int. Braz j Urol 2007, 33, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melia, J.; Moseley, R.; Ball, R.; Griffiths, D.; Grigor, K.; Harnden, P.; Jarmulowicz, M.; McWilliam, L.; Montironi, R.; Waller, M.; et al. A UK-based investigation of inter-and intra-observer reproducibility of Gleason grading of prostatic biopsies. Histopathology 2006, 48, 644–654. [Google Scholar]
- Egevad, L.; Ahmad, A.S.; Algaba, F.; Berney, D.M.; Boccon-Gibod, L.; Compérat, E.; Evans, A.J.; Griffiths, D.; Grobholz, R.; Kristiansen, G.; et al. Standardization of Gleason grading among 337 European pathologists. Histopathology 2013, 62, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, K.; Foote, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.H.C.; Wulczyn, E.; Tan, F.; Olson, N.; Smith, J.L.; Mohtashamian, A.; Wren, J.H.; et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for improving Gleason scoring of prostate cancer. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoso, A.; Epstein, J.I. Defining clinically significant prostate cancer on the basis of pathological findings. Histopathology 2019, 74, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Amin, M.B.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Humphrey, P.A. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) consensus conference on Gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouda, K.; Khalifa, F.; El-Melegy, M.; Ghazal, M.; Darwish, H.E.; El-Ghar, M.A.; El-Baz, A. A Deep Learning Pipeline for Grade Groups Classification Using Digitized Prostate Biopsy Specimens. Sensors 2021, 21, 6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Hammouda, K.; Khalifa, F.; Abdeltawab, H.; Elnakib, A.; Giridharan, G.; Zhu, M.; Ng, C.; Dassanayaka, S.; Kong, M.; Darwish, H.; et al. A new framework for performing cardiac Strain Analysis from cine MRi imaging in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayana, G.; Park, J.; Choe, S.W. Patchless Multi-Stage Transfer Learning for Improved Mammographic Breast Mass Classification. Cancers 2022, 14, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayana, G.; Choe, S.w. BUViTNet: Breast Ultrasound Detection via Vision Transformers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouda, K.; Khalifa, F.; Soliman, A.; Ghazal, M.; Abou El-Ghar, M.; Haddad, A.; Elmogy, M.; Darwish, H.; Khalil, A.; Elmaghraby, A.; et al. A CNN-based framework for bladder wall segmentation using MRI. In Proceedings of the 2019 Fifth International Conference on Advances in Biomedical Engineering (ICABME), Tripoli, Lebanon, 17–19 October 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hammouda, K.; Khalifa, F.; Soliman, A.; Abdeltawab, H.; Ghazal, M.; Abou El-Ghar, M.; Haddad, A.; Darwish, H.E.; Keynton, R.; El-Baz, A. A 3D CNN with a Learnable Adaptive Shape Prior for Accurate Segmentation of Bladder Wall Using MR Images. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Iowa City, IA, USA, 3–7 April 2020; pp. 935–938. [Google Scholar]
- Hammouda, K.; Khalifa, F.; Soliman, A.; Ghazal, M.; Abou El-Ghar, M.; Badawy, M.; Darwish, H.; Khelifi, A.; El-Baz, A. A multiparametric MRI-based CAD system for accurate diagnosis of bladder cancer staging. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 90, 101911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Rodríguez, J.; Payá-Bosch, E.; García, G.; Colomer, A.; Naranjo, V. Prostate Gland Segmentation in Histology Images via Residual and Multi-resolution U-NET. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning, Guimaraes, Portugal, 4–6 November 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bulten, W.; Bándi, P.; Hoven, J.; Loo, R.v.d.; Lotz, J.; Weiss, N.; Laak, J.v.d.; Ginneken, B.v.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.; Litjens, G. Epithelium segmentation using deep learning in H&E-stained prostate specimens with immunohistochemistry as reference standard. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 864. [Google Scholar]
- Bulten, W.; Pinckaers, H.; van Boven, H.; Vink, R.; de Bel, T.; van Ginneken, B.; van der Laak, J.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.; Litjens, G. Automated deep-learning system for Gleason grading of prostate cancer using biopsies: A diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilovic, M.; Azar, J.C.; Lindblad, J.; Wählby, C.; Bengtsson, E.; Busch, C.; Carlbom, I.B. Blind color decomposition of histological images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, A.; Bonthu, S.; Singhal, N. Carcino-Net: A deep learning framework for automated Gleason grading of prostate biopsies. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 1380–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Arvaniti, E.; Fricker, K.S.; Moret, M.; Rupp, N.; Hermanns, T.; Fankhauser, C.; Wey, N.; Wild, P.J.; Rueschoff, J.H.; Claassen, M. Automated Gleason grading of prostate cancer tissue microarrays via deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Website for the Dataset. 2021. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/c/prostate-cancer-grade-assessment (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Kaur, M.; Kaur, J.; Kaur, J. Survey of contrast enhancement techniques based on histogram equalization. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Wang, Z.; Yi, P.; Wang, G.; Lu, T.; Jiang, J. Edge-enhanced GAN for remote sensing image superresolution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5799–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshed, M.S.; Murphy, C.; Hou, D.; Khan, N.; Ananthanarayanan, G.; Hussain, F. Machine learning at the network edge: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. CSUR 2021, 54, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadon, S. A survey of loss functions for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB), Via del Mar, Chile, 27–29 October 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Feurer, M.; Hutter, F. Hyperparameter optimization. In Automated Machine Learning; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstra, J.; Bengio, Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 281–305. [Google Scholar]
- Hossin, M.; Sulaiman, M.N. A review on evaluation metrics for data classification evaluations. Int. J. Data Min. Knowl. Manag. Process 2015, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- McNee, S.M.; Riedl, J.; Konstan, J.A. Being accurate is not enough: How accuracy metrics have hurt recommender systems. In Proceedings of the CHI’06 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors In Computing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 22–27 April 2006; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1097–1101. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, J.A.; Donovan, J.L.; Davis, M.; Walsh, E.; Dedman, D.; Down, L.; Turner, E.L.; Mason, M.D.; Metcalfe, C.; Peters, T.J.; et al. Active monitoring, radical prostatectomy, or radiotherapy for localised prostate cancer: Study design and diagnostic and baseline results of the ProtecT randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.C.; Rumble, R.B.; Loblaw, D.A.; Finelli, A.; Ehdaie, B.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Morgan, S.C.; Tyldesley, S.; Haluschak, J.J.; Tan, W.; et al. Active surveillance for the management of localized prostate cancer (Cancer Care Ontario guideline): American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline endorsement. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2182–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimo, F.; Schultz, L.; Epstein, J.I. The value of mandatory second opinion pathology review of prostate needle biopsy interpretation before radical prostatectomy. J. Urol. 2010, 184, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, D.F.; MacDonald, R.; Liu, Y.; Truszkowski, P.; Hipp, J.D.; Gammage, C.; Thng, F.; Peng, L.; Stumpe, M.C. Impact of deep learning assistance on the histopathologic review of lymph nodes for metastatic breast cancer. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kohlberger, T.; Norouzi, M.; Dahl, G.E.; Smith, J.L.; Mohtashamian, A.; Olson, N.; Peng, L.H.; Hipp, J.D.; Stumpe, M.C. Artificial intelligence—Based breast cancer nodal metastasis detection: Insights into the black box for pathologists. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislén, A.; Dacke, M.; Kröger, R.H.; Abrahamsson, M.; Nilsson, D.E.; Warrant, E.J. Superior underwater vision in a human population of sea gypsies. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allsbrook Jr, W.C.; Mangold, K.A.; Johnson, M.H.; Lane, R.B.; Lane, C.G.; Epstein, J.I. Interobserver reproducibility of Gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma: General pathologist. Hum. Pathol. 2001, 32, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, M.; Potosky, A.L.; Penson, D.; Freedman, A.N. A 22 gene-expression assay, Decipher®(GenomeDx Biosciences) to predict five-year risk of metastatic prostate cancer in men treated with radical prostatectomy. PLoS Curr. 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Courtiol, P.; Maussion, C.; Moarii, M.; Pronier, E.; Pilcer, S.; Sefta, M.; Manceron, P.; Toldo, S.; Zaslavskiy, M.; Le Stang, N.; et al. Deep learning-based classification of mesothelioma improves prediction of patient outcome. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulczyn, E.; Steiner, D.F.; Xu, Z.; Sadhwani, A.; Wang, H.; Flament-Auvigne, I.; Mermel, C.H.; Chen, P.H.C.; Liu, Y.; Stumpe, M.C. Deep learning-based survival prediction for multiple cancer types using histopathology images. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweldam, C.F.; Kümmerlin, I.P.; Nieboer, D.; Verhoef, E.I.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Van der Kwast, T.H.; Roobol, M.J.; van Leenders, G.J. Disease-specific survival of patients with invasive cribriform and intraductal prostate cancer at diagnostic biopsy. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
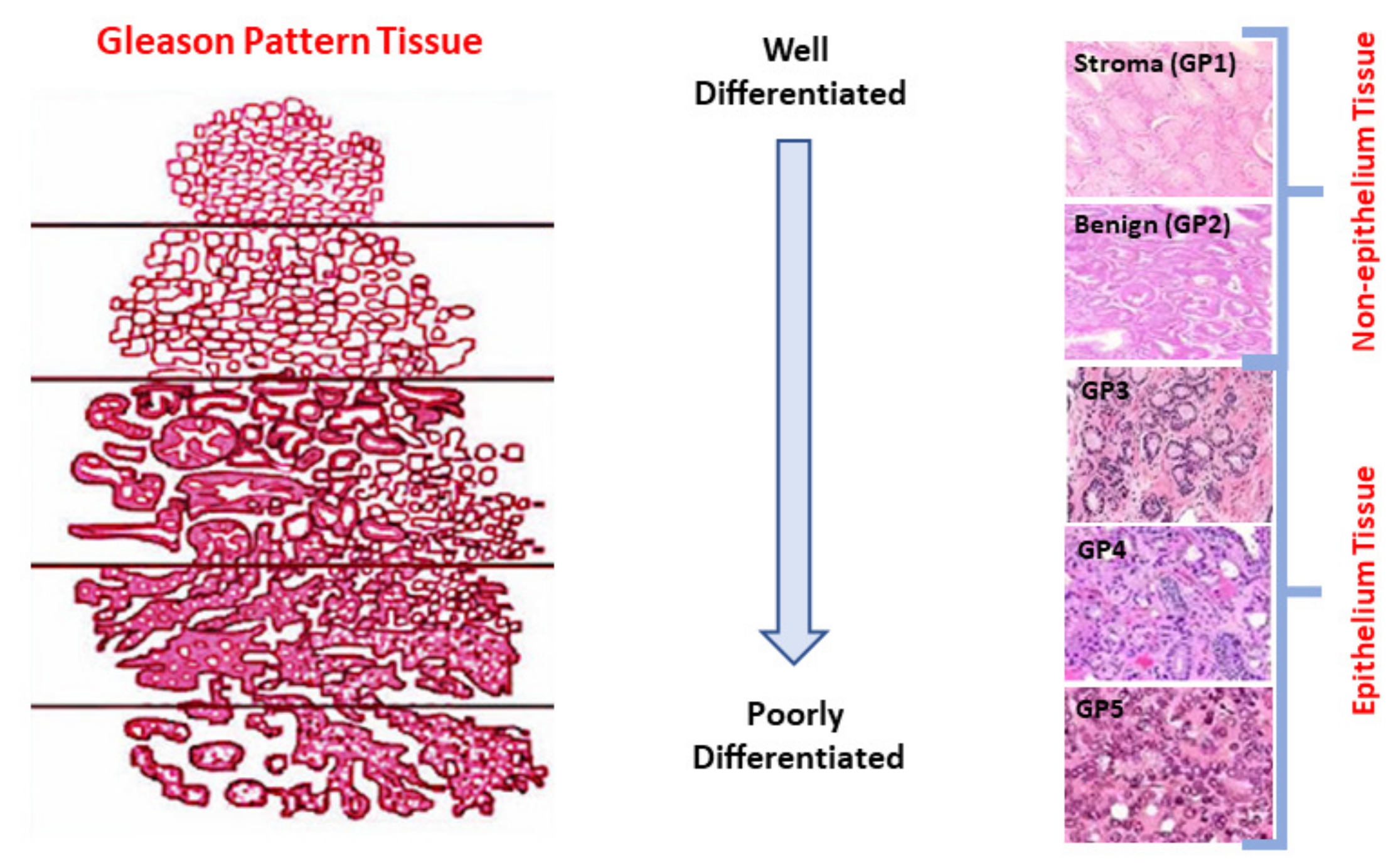






| GP | Risk Level | GS | GG |
|---|---|---|---|
| GP1 | Stroma | - | - |
| GP2 | Benign | - | - |
| GP3 | Low | GP3 + GP3 = GS6 | GG1 |
| Favorable | GP3 + GP4 = GS7 | GG2 | |
| GP4 | Unfavorable | GP4 + GP3 = GS7 | GG3 |
| High | GP4 + GP4 = GS8 GP3 + GP5 = GS8 GP5 + GP3 = GS8 | GG4 | |
| GP5 | High | GP4 + GP5 = GS9 GP5 + GP4 = GS9 GP5 + GP5 = GS10 | GG5 |
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class1 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.58 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.66 |
| Class2 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.66 | 0.86 | 0.75 | 0.83 | 0.66 | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.67 |
| Performance Across Classes | ||||||||||||
| Macro-averaged | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.71 | 0.72 | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.66 |
| Weighted-average | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.74 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.66 |
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class1 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 0.90 | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.86 | 0.55 | 0.77 | 0.64 | 0.68 | 0.62 | 0.65 |
| Class2 | 0.54 | 0.87 | 0.66 | 0.92 | 0.75 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.61 | 0.70 | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.68 |
| Performance Across Classes | ||||||||||||
| Macro-averaged | 0.75 | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.66 |
| Weighted-average | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.66 |
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class1 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.53 | 0.63 | 0.57 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.66 |
| Class2 | 0.76 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.75 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.60 | 0.63 |
| Performance Across Classes | ||||||||||||
| Macro-averaged | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.64 |
| Weighted-average | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.64 |
| Our Model | Bulten et al. [21] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | Precision | Recall | |
| Benign | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.94 |
| GG1 | 0.64 | 0.69 | 0.65 | 0.70 |
| GG2 | 0.50 | 0.60 | 0.44 | 0.51 |
| GG3 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.40 | 0.52 |
| GG4 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.34 | 0.33 |
| GG5 | 0.81 | 0.68 | 0.89 | 0.67 |
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class1 | 0.68 | 0.79 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.59 | 0.92 | 0.72 | 0.53 | 0.63 | 0.75 |
| Class2 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.91 | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 0.75 |
| Performance Across Classes | ||||||||||||
| Macro-averaged | 0.78 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.67 |
| Weighted-average | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hammouda, K.; Khalifa, F.; Alghamdi, N.S.; Darwish, H.; El-Baz, A. Multi-Stage Classification-Based Deep Learning for Gleason System Grading Using Histopathological Images. Cancers 2022, 14, 5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235897
Hammouda K, Khalifa F, Alghamdi NS, Darwish H, El-Baz A. Multi-Stage Classification-Based Deep Learning for Gleason System Grading Using Histopathological Images. Cancers. 2022; 14(23):5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235897
Chicago/Turabian StyleHammouda, Kamal, Fahmi Khalifa, Norah Saleh Alghamdi, Hanan Darwish, and Ayman El-Baz. 2022. "Multi-Stage Classification-Based Deep Learning for Gleason System Grading Using Histopathological Images" Cancers 14, no. 23: 5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235897
APA StyleHammouda, K., Khalifa, F., Alghamdi, N. S., Darwish, H., & El-Baz, A. (2022). Multi-Stage Classification-Based Deep Learning for Gleason System Grading Using Histopathological Images. Cancers, 14(23), 5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235897








