Simple Summary
Abnormal expression of miRNA is often observed in cancer. MiR-101 is closely associated with tumor initiation and progression. In this review, we summarized new findings regarding the role of miR-101 in cancer and the potential mechanisms of targeted gene degradation and microenvironmental regulation.
Abstract
MiRNAs are small single-stranded non-coding RNAs. MiRNA contributes to the transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA in different cell types, including mRNA transcription inhibition and mRNA decay and phenotypes via the effect of several essential oncogenic processes and tumor microenvironment. MiR-101 is a highly conserved miRNA that was found to alter the expression in various human cancers. MiR-101 has been reported to have tumor oncogenic and suppressive effects to regulate tumorigenesis and tumor progression. In this review, we summarize the new findings about the roles of miR-101 in cancers and the underlying mechanisms of targeting genes degradation and microenvironment regulation, which will improve biological understanding and design of novel therapeutics.
Keywords:
miR-101; microenvironment; suppressor; proliferation; migration; invasion; apoptosis; therapy 1. Introduction
MiRNAs were found in 1993 by Lee et al. [1], who identified a class of small molecule RNAs named Lin-4 [1], and the discovery of this new biomolecule provides a new way of thinking about the regulation of cell fate in physiology and pathophysiology in eukaryotes. The latest released miRBase database (v22) contains 48,860 mature miRNAs, of which 2654 miRNAs are human miRNAs [2].
MiRNAs are a class of small (18–25 nucleotides) non-coding single-stranded RNAs [3,4]. Studies have revealed that miRNAs share common biologic characteristics, such as evolutionarily conservation, stage, and tissue-specific expression. The mature miRNA can recognize specific target mRNA sequences utilizing the Watson–Crick base pairing principle, which ultimately leads to the degradation or translation inhibition of target mRNA, thus regulating the expression of target genes at the transcriptional or post-transcriptional level [5]. More than 5300 human genes, which represent 30% of all known genes, are regulated by miRNAs.
In cancers, as negative regulatory factors of gene expression, miRNAs regulate tumorigenesis and cancer progression by affecting numerous biological signaling pathways [6,7,8,9,10,11].
MiR-101 is highly conserved in various species. There are two gene loci producing miR-101 in humans, which are located in regions 1p31.3 and 9p24.1. MiR-101 contains two precursor RNAs: miR-101-1 and miR-101-2, with length of 75 bp and 79 bp, respectively [12]. MiR-101-3p is one of the most dominant members of mature miR-101, which is named because the dicer enzyme binds to the 3‘arm of pre-miR-101.
Recent studies have shown that miRNA-101 plays important regulatory roles in the occurrence and development of fibrosis in pulmonary or liver, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, cancer, and other diseases. MiR-101 has become the focus and hotspot of cancer research [13,14]. Wang et al. [15] summarized the function of miR-101 in cancer cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis via SRY-box transcription factor 9 (SOX9), enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit (EZH2), Rac family small GTPase 1 (Rac1) etc. in 2018 [15]. Since then, a lot of new findings have been published. In this review, we review ongoing efforts to understand the roles of miR-101 in tumor development and progression and discuss the challenges and future steps to clarify the conflicting results of miR-101 as an oncogene and tumor suppressor, which provide approaches to leverage these discoveries for translational studies.
2. MiR-101 Regulates Cancer Growth, Metastasis, and Therapeutic Resistance via Several Essential Oncogenic Processes
As described above, the genes producing miR-101 are in the 1p31.3 region and 9p24.1 region of the human genome. By using genomic quantitative polymerase chain reaction, Sooryanarayana et al. [16] found that 1p31.3 region loss is a common phenomenon in many cancers, such as breast, gastric, and prostate cancers. Further, they observed genomic losses of one or both miR-101 loci in a subset of glioblastoma multiforme, lung adenocarcinoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia, which resulted in a deficiency of miR-101 expression in cancer tissues [16]. The downregulated miR-101 is proven to play important roles in cancer cell phenotype regulation, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and therapy resistance [17,18]. However, certain research finds that miR-101 affects tumor development as an oncogene, especially the in vivo studies. It was reported that increased miR-101 level predicts poor overall survival and disease-free survival in ovarian cancer patients [19].
2.1. The Role of miR-101 in Cell Proliferation
One of the cancer hallmarks is disruptions of negative feedback mechanisms that attenuate proliferative signaling and the consequent malignant growth of tumor cells. MiR-101 expression deficiency impairs negative feedback of proliferative signaling. Previous studies have confirmed that miR-101 inhibits cell proliferation in multiple tumors, and it exists as a tumor suppressor by affecting several essential oncogenic pathways.
Consistent with previous studies, the discoveries also confirm that miR-101 expression is decreased in a wide variety of cancers [20]. The decreased miR-101 promotes cancer cell proliferation by increasing the expression of numerous oncogenes. In hepatocellular carcinoma, miR-101 is proven to specifically bind to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) to decrease protein levels of VEGFA (one of the main isotypes of VEGF) [21] and inhibit VEGFR2 signaling pathway thereby impair the malignant behavior of HCC cells. MiR-101 could also inhibit the proliferation of liver cancer cells by targeting zinc finger protein 217 (ZNF217), mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathways, and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/c-MET axis [22,23,24]. The expression level of miR-101 is decreased in liver cancer which loses the inhibition effect on the above target genes acting as on–off switches of particular mRNAs or by modulating the relationship between effector and target mRNAs. Similarly, miR-101 was found to regulate downstream targets of growth factor signaling in other cancers. MiR-101 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by regulating the expression of proto-oncogene serine/threonine protein kinase (PIM 1) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Mechanistically, the expression of AMPK is regulated by lncRNA SPRY4-IT1 via sponging miR-101 [25,26]. In melanoma, miR-101 regulated by lncRNA SNHG6 is negatively correlated with Ras-related protein Rap-2b (RAP2B) expression, which is a member of the RAS oncogene family. RAP2B overexpression reversed the inhibitory effect on melanoma cell proliferation induced by miR-101 [27]. MiR-101 is downregulated in NSCLC tissues, and overexpression of miR-101 inhibits the proliferation of NSCLC cells by targeting several essential proliferative genes, including ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 1 (ABCC1), zinc finger E-Box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1), chromodomain Y-like (CDYL), myeloid cell leukemia-1 (Mcl-1) and metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT-1) [28,29,30,31,32]. MiR-101 suppression also accelerates cervical cancer cell proliferation by promoting the expression of methionine adenosyltransferase II Alpha (MAT2A) [33]. Med19 enhances breast cancer cell proliferation, which is negatively correlated with miR-101 expression [34]. Furthermore, miR-101 mimics can reduce the proliferation rate of breast cancer cells by reducing the mRNA level of nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) [35]. In colon cancer cell lines, silencing of stanniocalcin 1 (STC1) reverses the tumor-promoting effects of miR-101 down-regulation [36], and overexpression of miR-101 generates anti-tumor effects by targeting the cAMP-responsive element binding protein 1 (CREB1) and Notch signaling pathway [37,38]. In pancreatic cancer, miR-101 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting STMN1 [39]. It was also announced that miR-101 reduces the expression of other RAS oncogenic family members, such as Rap1A, in prostate cancer and thereby inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion [40]. Additionally, miR-101 inhibits the proliferation of retinoblastoma cells by targeting EZH2 and histone deacetylase 9 (HDAC9) [41]. Although many new target genes of miR-101 were identified, how miR-101 regulates these genes is not fully understood. It is important to clarify the intracellular mechanisms associated with miR-101 regulation as we harness this knowledge for therapeutic benefits.
MiR-101 regulates proliferation by affecting metabolism. CDGSH iron sulfur domain 1(CISD1) plays a key role in regulating maximal electron transport capacity and oxidative phosphorylation. CISD1 is up-regulated in lung adenocarcinoma, and CISD1 knockdown is noted to significantly inhibit lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation. The miR-101 is identified to be upstream of CISD1 [42]. MiR-101 disrupts the transcription of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) via down-regulating mitochondrial transcription initiation complex proteins transcription factor B2, mitochondrial (TFB2M), and mitofilin to inhibit cancer cell proliferation in osteosarcoma [43]. MiR-101 directly interacted with the 3′-UTR of KRAS mRNA to weaken glycolytic metabolism in NSCLC [44]. Overexpression of miR-101 could inhibit the growth of liver cancer stem cells xenograft tumors, which works through targeting annexin A2 (ANXA2) [45].
Studies also revealed that miR-101 could control proliferation by affecting the protein degradation process. Ubiquitin-specific protease 47 is a deubiquitinating enzyme that removes ubiquitin conjugates from their substrates, thereby altering their stabilities, localizations, or activities. MiR-101 regulates ribosomal protein L11 (RPL11) localization and its interaction with MDM2pProto-oncogene (MDM2) by inhibiting the ubiquitin-specific peptidase 47 (USP47)-induced deubiquitylation of RPL11. MiR-101 was found to bind directly to the 3′-UTR region of the USP47 mRNA and inhibit its expression [46]. Cullin 4B (CUL4B) encodes a scaffold protein that organizes the cullin-RING (an interesting new gene) ubiquitin ligase (E3) complex during ubiquitylation. In non-small cell lung cancer and prostate cancer, CUL4B is confirmed as a functional target of miR-101, and its knockdown results in a strong alleviation of cell proliferation, which is enhanced by the silencing of miR-101 [47,48]. MiR-101 may regulate protein intracellular distribution and decay. MiR-101 expression is low in cervical squamous cell carcinoma, while importin karyopherin subunit alpha 2 (KPNA2) expression is high MiR-101 suppresses the progression of cervical squamous cell carcinoma by targeting and down-regulating KPNA2 [49].
Together, miR-101 inhibits tumor cell proliferation by targeting many essential oncogenic targets. However, some controversial studies have shown that miR-101 promotes cell growth and acts as an oncogene. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are important cellular components in the tumor microenvironment which protect tumor cells from the attack of the immune system and promote tumor progression [50]. Cui et al. show that MDSCs stimulate the expression of miR-101 in ovarian cancer cells by targeting C-terminal binding protein 2 (CTBP2) and promoting the formation of tumor stem cells [19]. Therefore, it is necessary to further study whether the controversial discovery is caused by tissue specificity, tumor grade, subtype, or other reasons.
2.2. The Role of miR-101 in Migration
MiR-101 has been identified as a key regulator in several stages of metastasis. Epigenetic changes, particularly histone and DNA methylation, play an important role in tumor progression, especially metastasis. Trimethylation refers to the methylation of histone H3K9me3, H3K27me3, and H3K79me3, which can inhibit transcription from regulating phenotype, in which H3K27me3 is the most frequent modification that regulates transcription [51]. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is an essential nuclear transcription regulator that encodes the core catalytic subunit of polycomb polysive complex 2 (PRC2) that directly trimethylates the 27th lysine residue of histone 3. EZH2 promotes cell migration, thus promoting tumor progression. Studies have demonstrated that miR-101 negatively regulates EZH2 expression in breast cancer, prostate cancer, and glioma [52,53,54]. Huang et al. revealed two-way negative feedback between EZH2 and miR-101. The imbalance of this negative feedback pathway continuously increases the expression level of EZH2, thus promoting the proliferation of tumor cells [55]. In bladder cancer cells, lncRNA SPRY4-IT1 could directly interact with miR-101 acting as a miRNA sponge, and miR-101 inhibition leads to increased EZH2 expression. EZH2 inhibits the E-cadherin promoter activity through methylating of H3K27me3 and promotes bladder cancer cell invasion and metastasis [56]. Methylation in the gene promoter locus is catalyzed by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs). DNMT3A (DNA Methyltransferase 3 Alpha) is a de novo methyltransferase that can methylate 5-methylcytosine methylation [57]. Wei et al. [58] found that miR-101 directly inhibited the mRNA expression and protein level of DNMT3A by complementary binding with the 3′-UTR region, leading to increased methylation level in the promoter regions of tumor suppressor genes, thus suppressing tumor growth and invasion, but the miR-101 expression was frequently down-regulated in HBV-related HCC tissues [58]. The negative correlation between miR-101 and DNMT3A expression has been confirmed in breast cancer, lung cancer, brain glioma, and other tumors [15]. MiR-101 has been proven to inhibit cell migration and invasion by inhibiting the expression of DNMT3A and up-regulating the expression of E-cadherin in breast cancer cells [59]. MiR-101 is also closely related to the prognosis of glioma. Low miR-101 expression informs poor prognosis in glioma patients. MiR-101 inhibits the expression of EZH2 and DNMT3A, which leads to increased levels of H3K4me3 and H4K20me3 in the core promoter region of LIM domain only 3 (LMO3), thereby inhibiting the expression of LMO3 and metastasis of glioma cells [60].
Except for EZH2 and DNMT3A, attenuation of miR-101 is also required for other genes expression and metastasis. Ectopic overexpression of miR-101 suppressed cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) activation and abrogated the promoting effect of CAFs on migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells (NSCLC) through attenuating CAFs’ effect on epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) process, metastasis-related genes matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP9), twist family BHLH transcription factor 1(TWIST1-), and AKT/endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) signaling pathway. Further study indicates that vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) is a novel target of miR-101, and CAFs-derived VEGFA mediates the effect of miR-101 on migration and invasion of lung cancer cells [61], suggesting a new combination of VEGF and miR-101 for metastasis therapy. Ceramide synthesis by Ceramide Synthase 6 (CERS6) is required for cell migration and metastasis in lung cancer. MiR-101 can reduce CERS6 expression in lung cancer [62]. In both cervical cancer and NSCLC, miR-101 inhibits metastasis by inhibiting CXCL6 expression [63,64]. Moreover, in NSCLC cells, miR-101 also shows an inhibitory effect on migration by targeting CUL4B, CISD1, MALAT-1, and DNMT3A [32,42,47,65]. In papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), CLDN1 is the target of miR-101, and overexpression of CLDN1 can reverse the inhibitory effect of miR-101 on cell migration and invasion [66]. MiR-101 could also suppress colorectal cancer cell migration by negatively regulating Rap1b [67]. The previous description mentioned that the expression level of miR-101 declines in hepatocellular carcinoma, and miR-101 suppresses migration by targeting the HGF/c-Met pathway [23]. MiR-101 could inhibit metastasis of liver cancer, and it was downregulated in liver cancer stem cells. ANXA2 is a novel target of miR-101, which mediates the role of miR-101 in the migration and invasion ability of liver cancer stem cells [45]. Additionally, miR-101 is downregulated in colorectal cancer tissues, lower expression of miR-101 results in overexpression of ZEB1, which promotes the migration of colorectal cancer cells [68]. MiR-101 is discovered to repress cell metastasis of ovarian cancer via decreasing Fibronectin 1(FN1) expression [69]. It is also found that downregulation of miR-101 increases the transmigration of breast cancer cells through the brain endothelium in vitro by inducing prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase-2 (PTGS2, also known as COX-2), expression in cancer cells and miR-101 mediates its effect by modulating COX-2-MMP1 (Matrix Metalloproteinase-1) signaling pathway [70]. Like other cancers, the expression of miR-101 is significantly reduced in bladder cancer tissue compared with that in adjacent non-tumor tissue, and miR-101 can inhibit bladder cancer cell migration and invasion via directly targeting frizzled class receptor 4 (FZD4) [71]. Additionally, it was recognized that miR-101 could suppress the expression of tripartite motif containing 44 (TRIM44) by directly targeting its 3′-UTR, thereby reducing proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioblastoma cells [72]. Those studies support the use of miR-101 restoration treatment for aggressive cancers.
2.3. MiR-101 and Invasion
Tumor invasion is considered one of the prime reasons for tumor progression. Epithelial–mesenchymal transformation is a biological process that allows cancers to gain metastatic capacity. E-cadherin is a key molecule of EMT. Down-regulation of E-Cadherin is a typical hallmark during EMT in cancer progression. Down-regulation or inhibition of E-cadherin leads to the release of β-catenin, which can be transferred into the nucleus and acts as a transcriptional activator to initiate EMT. MiR-101 up-regulates the expression of E-cadherin and inhibits EMT [56,73]. Zeb1/2 binds to the E-box in the E-cadherin promoter region and acts as a transcriptional repressor to inhibit the expression of E-cadherin [74,75]. Guo et al. found miR-101 directly binds to the seed sequence on the 3′-UTR of ZEB1 or ZEB2, resulting in the inhibition of ZEB1 and ZEB2 expression and thus inhibiting EMT [76]. Kailash et al. also confirmed that miR-101 inhibits the expression of ZEB1, ZEB2, RAS homolog family member A(RhoA), and Rac family small GTPase 1 (RAC1), and a significant negative correlation between miR-101 expression and lymph node metastasis was confirmed in clinical specimens [77]. Additionally, miR-101 is significantly down-regulated in osteosarcoma and could inhibit the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma by targeting ZEB2 [78]. It was recognized that miR-101 could suppress the invasion ability of cervical cancer cells by inhibiting the expression of MAT2A [33]. Furthermore, miR-101 could inhibit the invasion of NSCLC cells by targeting CDYL [30]. It was also elucidated that miR-101 suppresses cell invasion and proliferation in gastric cancer by targeting PIM-1 and serum response factor (SRF) [25,79]. As described above, the expression level of miR-101 was decreased and acted as a negative regulator of ZNF217 in liver cancer, which could not only suppress proliferation but also inhibit the invasion of liver cancer cells [24]. Moreover, miR-101 was found to suppress the invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting VEGF-C (another member of the VEGF family) and Girdin [80,81]. These studies support the importance of miR-101 loss in tumor metastasis.
2.4. MiR-101 in Apoptosis
In addition to affecting the proliferation, migration, and invasion of tumor cells, miR-101 is also involved in the regulation of programmed cell death, such as apoptosis in a variety of tumors. Wang et al. summarized the function of miR-101 in apoptosis via SOX2, a mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR), VEGF-2, etc., in 2018 [15]. Since then, many new target genes have been identified. In oral cancer, the increased level of miR-101 promotes apoptosis by suppressing BicC family RNA binding protein 1 (BICC1) [82]. MiR-101 could promote cell apoptosis in medulloblastoma targeting forkhead box P4 (FOXP4) and EZH2 [83]. Furthermore, in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), miR-101 regulates cell apoptosis by targeting lysine demethylase 1A (KDM1A) and MAPK kinase 1 (MEK1). This reveals that miR-101 may be a useful tool for the treatment of DLBCL patients [84,85]. Additionally, miR-101 also promotes cell apoptosis by inhibiting the RAS/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma [86]. MiR-101 also has a pro-apoptotic role in breast cancer via Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2) [11]. Zhu et al. revealed overexpression of miR-101 promotes TRAIL-induced mitochondrial apoptosis in papillary thyroid carcinoma by targeting c-met and MCL-1 [87]. MiR-101 ‘drug’ represents a promise for cancer therapy.
2.5. miR-101 and Tumor Chemoresistance
Chemotherapy is one of the main options for cancer patients’ therapy. Patients no longer benefit from chemotherapy because of drug resistance. MiR-101 is involved in the regulation of drug resistance in a variety of cancers. MiR-101 affects the sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapy drugs by regulating relevant processes, including drug transporters, apoptosis regulation, cell cycle regulation, autophagy, etc.
In 2009, researchers from Scripps Research Institute discovered a protein called glycoprotein, P-gp (P-Glycoprotein). This protein blocks many chemotherapeutic drugs from entering cells, which is one of the main reasons cancer cells become resistant to them. However, overexpression of miR-101 leads to decreased P-gp expression in gastric cancer cells and enhances the sensitivity of tumor cells to cisplatin or vincristine [88]. Chai et al. confirm that up-regulated miR-101 can also increase the sensitivity of liver cancer to cisplatin by negatively regulating DNA-PKCs/Akt/NF-κB signals [89]. Negative regulation of EZH2 by miR-101 can enhance the sensitivity of bladder urothelial carcinoma to cisplatin [90]. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promoted the chemoresistance to temozolomide by suppressing the miR-101 signaling pathway via directly binding it in glioblastoma cells [91]. MiR-101 acts as a tumor suppressor in HER2-positive breast cancer cells, improving targeted therapy of lapatinib and trastuzumab [92].
Autophagy is a highly conserved cell metabolic process that plays a dual role in tumor procession, including therapy resistance. Studies have shown that autophagy protects tumor cells from the attack of chemotherapeutic drugs by cleaning up large molecules or organelles damaged by chemotherapy and ionizing radiation. MiR-101 enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis of HepG2 cells by inhibiting autophagy of targets such as member RAS oncogene family (RAB5A), STMN1, and autophagy-related 4D cysteine peptidase (AtG4D) in HCC [93]. Inhibition of miR-101 expression can increase the expression of autophagy-related proteins such as Rab5a and Atg4d and enhance the resistance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDCA) to gemcitabine [94]. MiR-101 can block autophagy-characterized acidic vesicle organelles (AVOs) and enhance the sensitivity of osteosarcoma cells U-2OS to doxorubicin [95]. Re-expressing miR-101 has great promise for cancer therapy. As the therapeutic potential of miR-101 is explored, the combination of miR-101 and chemical therapy will probably follow.
2.6. miR-101 and Radiosensitivity
Radiation therapy is another important available approach for tumor therapy, which kills tumor cells by inducing double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs). Some tumors, such as nasopharynx cancer, can be cured by radiation therapy. However, radiation resistance also occurs in tumor development, and effective repair of tumor cells is a key factor hindering the success of radiation therapy. DNA double-strand breaks induced by radiation can be repaired by non-homologous end-source ligation repair (NHEJ) and homologous recombination repair (HRR). Cells lacking AT mutated (ATM) enzyme—a member of the phophatidylinositol-3-OH kinase (PI(3)K) family—are sensitive to ionizing radiation (IR) due to inefficient DNA DSB repair [96]. It has been proved in lung cancer cell lines and glioblastoma cell lines that miR-101 can bind to the 3′-UTR of DNA-PKCs or ATM mRNA to negatively regulate DNA-PKCs and ATM mRNA. Upregulation of miR-101 can reduce the protein levels of DNA-PKCs and ATM, which leads to acquiring radiosensitivity in tumor cells to radiation [97]. Chen et al. confirmed that miR-101 could sensitize HCC cells through negative modulation of WEE1 G2 checkpoint kinase (WEE1) [98].
Ectopic expression of miR-101 can increase the radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by targeting STMN1 inhibition [99]. MiR-101 can also negatively regulate the mTOR signaling pathway to increase the radiosensitivity of A549 cells [100]. Decreased expression of miR-101 can increase the expression levels of downstream target proteins ATM and mTOR and increase the radiation resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [101]. In lung adenocarcinoma cells, miR-101 can enhance LUAD cell sensitivity to radiotherapy by regulating the expression of baculoviral IAP repeat containing 5 (BIRC5) [102]. These data suggest that the loss of miR-101 plays a significant role in cancer therapy, showing potential value as a therapeutic tool in the future. The advancement of such studies will help to guide the development of miR-101-based treatment for sensitization to radiotherapy.
Overall, the miR-101 regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis, and therapy resistance via regulates numerous targets (Figure 1) in transcriptional and post-transcriptional manners (Table 1).
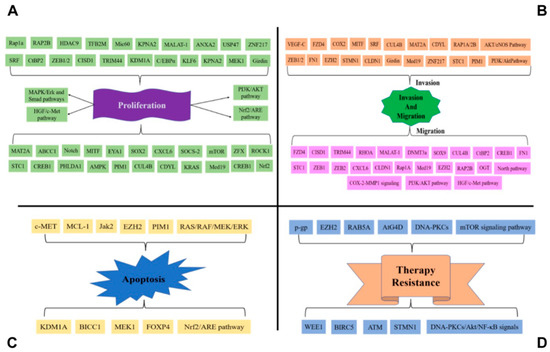
Figure 1.
MiR-101 regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis, and therapy resistance via regulates numerous targets. (A) MiR-101 targets important oncogenes such as SOX2 and AKT to suppress tumor growth. (B) MiR-101 directly targets the mRNAs encoding the ZEB1 and ZEB2 et al. in cancers; as such, when miR-101 level is reduced, the expression of ZEB1 et al. becomes elevated, which suppresses the expression of epithelial genes to promote the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) to promote cancer cell local invasion, migration, and metastatic tumors. (C) MiR-101 targets apoptosis-related genes MCL-1 et al. to promote cancer cell apoptosis. (D) MiR-101 affects therapy resistance in cancers via NF-kb signaling and other pathways.

Table 1.
New target genes and dysregulation of miR-101 in proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, drug resistance.
3. MiR-101 Inhibits Cancer by Remodeling the Tumor Ecosystem
Tumor microenvironment refers to the occurrence, growth, and metastasis of tumors and the internal and external environment in which tumor cells are located. Tumor cells and tumor microenvironments are closely related. Tumor cells can improve their developmental conditions through autocrine and paracrine promotion. Systemic and local tissues can also limit and affect the development of tumors through immune secretion changes.
3.1. Crosstalk between MiR-101 and Microenvironment
Interactions between cancer cells and their microenvironment can greatly influence tumor progression and metastasis. Previous studies confirmed that miR-101 inhibited the growth of breast cancer cell line MCF-7 in the presence of estrogen in the medium, but it promotes cell growth in the estradiol-free medium [121]. This suggests that miR-101 may inhibit breast cancer growth by affecting estrogen secretion. However, we still do not know whether the regulation is causal.
Hypoxia is present in many malignant tissues. The hypoxic environment increases the expression of miR-101 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), astrocytes, HeLa, and U937, which is dependent on HIF-α expression [122]. Similarly, our research demonstrates that hypoxia promotes the expression of miR-101 in breast cancer cells [123]. This evidence shows that the microenvironment regulates tumor progression mediates by miR-101. Understanding these interactions is important for the therapies development in cancers.
3.2. MiR-101 and Tumor Angiogenesis
The typical manifestation of early tumors is little or no vascularization. As the tumor grows, tumor cells stimulate the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis to meet the needs of nutrients.
To date, the role of miR-101 in angiogenesis is contradictory. VEGF is one of the most essential factors in angiogenesis. MiR101 is known as a key regulator of angiogenesis via post-transcriptional regulation of VEGF. It has also been confirmed that miR-101 inhibits angiogenesis in gastric cancer by down-regulating the expression of VEGF-C [124]. By using the liver cancer model, Wang et al. found that overexpression of miR-101 could significantly reduce the level of VEGF, and further studies confirmed that miR-101 affected the secretion of VEGF by inhibiting the expression of junB proto-oncogene/AP-1 transcription factor subunit (JunB) [73]. MiR-101 was found to target VEGF mRNA 3′-UTR to regulate its expression in hepatocellular carcinoma [21]. Moreover, the VEGF mRNA is also identified as the target of miR-101 in cholangiocarcinoma cells. MiR-101 could inhibit VEGF or COX-2 expression by directly targeting the 3′-UTR of VEGF or COX-2 mRNA by which inhibits angiogenesis [125].
However, in breast cancer cells, we found that miR-101 can target and down-regulate VHL expression, which is a negative regulator of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 subunit alpha (HIF1α) to increase HIF-1α expression and HIF-1α downstream target VEGFA expression. MiR-101 could promote angiogenesis by indirectly promoting VEGFA gene expression [21]. As described above, miR-101 can improve blood perfusion in the ischemic hind limbs of mice, confirming that hypoxia-induced miR-101 plays an important role in angiogenesis and vascular remodeling after ischemia [122]. As mentioned above, hypoxia induces miR-101 expression in multiple cancers. Therefore, the relationship between miR-101 and angiogenesis needs to be further studied.
3.3. miR-101 and Tumor Immunology
Different from the roles in proliferation, migration etc. in vitro, miR-101 may play oncogenic and suppressive roles in vivo via regulating the immune response. However, this is still new research filed for miR-101.
MiR-101 regulates the differentiation of immune cells. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are related to tumor development [126]. Currently, TAMs have become valuable targets for cancer therapy. TAMs are divided into two phenotypes based on their activation status and function, M1 and M2. M1 acts as a tumor suppressor, while M2 plays a protumorigenic role in tumor development and progression. Zhao et al. revealed that overexpression of miR-101 in M1 could induce M1-to-M2 macrophage-type conversion, which leads to promoting cell proliferation and migration of breast and ovarian cancer cells by inhibiting CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP)α, and kruppel-like factor 6 (KLF6) expression [127]. MiR-101 binds to the 3′-UTR of tribbles pseudokinase 1 (TRIB1) mRNA, leading to increased transcription and secretion of interleukin-8 to regulate macrophage 2 differentiation in prostate cancer and control the inflammatory profile of human primary macrophages and prostate cancer cells [128]. Wu et al. suggest that miR-101, targeting dual specificity phosphatase 1 (DUSP1), regulates MAPKs activation during sorafenib-mediated inhibition of macrophage-induced hepatocarcinoma growth [129]. Gao also found that miR-101 affects macrophage polarization and might be an important factor associated with HCC prognosis and immune infiltration [130]. MiR-101 also could regulate the innate immune responses of macrophages to LPS by targeting MAPK phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) [12]. Yasuo Takashima et al. revealed that in primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL), miR-101 regulates Th-1/Th-2 status, Treg status, and immune checkpoints [131].
Emerged evidence indicated that miR-101 might promote tumorigenesis by suppressing immune infiltration and promoting immune escape. Kinesin family member 14 (KIF14) was up-regulated in a variety of cancers, including lung adenocarcinoma. GSEC/TYMSOS inhibited miR-101-3P to increase KIF14 expression in lung adenocarcinoma to promote immune checkpoint-related gene expression, immune cell biomarkers, and tumor immune cell infiltration [132]. Calmodulin-regulated spectrin-associated protein 1 (CAMSAP1) suppresses immune cell infiltration in liver hepatocellular carcinoma, and the LINC01748-miR-101-3p axis is specifically responsible for CAMSAP1 overexpression [133]. Furthermore, M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages transfer miR-101 to cancer cells to increase ZEB1 and PD-L1 expression, thereby stimulating the immune escape of ovarian cancer cells [134]. MiR-101 is considered one of the useful markers for cancer immunotherapy (Figure 2).
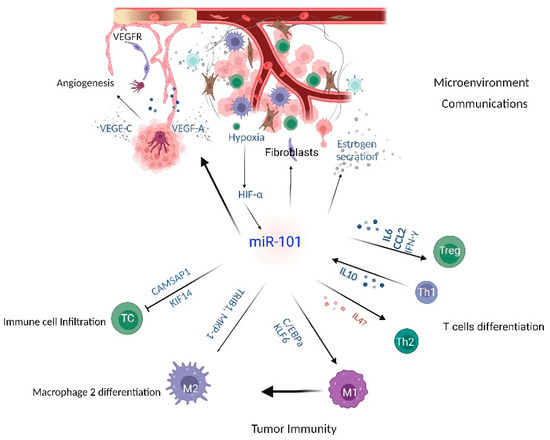
Figure 2.
MiR-101 in context: tumor microenvironmental inputs.
4. Conclusions
Cancer-associated change in miR-101 expression patterns is emerging as promising diagnostic markers that often correlate with histological stage, tumor progression, and patient survival [34,56,88,94,98,125,135,136,137,138,139]. MiR-101 has key roles in cancer initiation, progression, and metastasis as miR-101 is a critical regulator of gene expression by binding to complementary sequences in the 3′-UTR of mRNAs to target them for degradation or prevent the target gene translation. Genetic loss of tumor suppressor miR-101 is associated with human cancers via affecting a lot of signaling pathways in cancers.
Although miR-101 can have either an oncogenic or tumor-suppressive role, research has shown that miRNA expression is globally suppressed in tumor cells compared with normal tissue, suggesting that miR-101 may be a suppressor [140]. Therefore, it is important to figure out whether miR-101 is an oncogene or suppressor, and it is essential to clarify whether these contradictory results are caused by methodology and technology. However, it is interesting that miR-101 is proven to be a tumor suppressor in vitro studies, while more and more in vivo results show that miR-101 promotes tumor progression. A key factor in vivo is the tumor microenvironment, especially the presence of immune cells. In addition to genomic alterations, hypermethylation of CpG islands at the gene promoters of tumor-suppressive miRNAs, disruption of miRNA production by depletion of any of the miRNA processing factors [141], the miR-101 secretion by exosome may aggravate the deficiency of miR-101 in cancer cells. Moreover, the secreted miR-101 inhibits immune response [142,143], such as Th-1/2 differentiation and killer T cell infiltration. A question may arise regarding how tumor cells survive in the secreted miR-101 microenvironment. The cancer stem cell, responsible for maintaining tumor heterogeneity, fueling tumor growth, and therapy resistance, may be one reason. Research reports that miR-101 promotes ovarian stem cell self-renewal and proliferation [19]. MiR-101 is closely related to the tumor microenvironment in a two-way communication manner. On the one hand, oxygen is essential for tumor growth and metastasis. Hypoxia can increase miR-101 expression in tumor cells. On the other hand, miR-101 stimulates angiogenesis by activating the HO-1/VEGF/eNOS axis via Cul3 targeting. In addition to indirectly participating in angiogenesis, miR-101 can also directly participate in the regulation of angiogenesis in tumor tissues by binding with the 3UTR of VEGF mRNA.
Overall, in this review, we summarized new findings regarding the role of miR-101 in cancer and the potential mechanisms of targeted gene degradation and microenvironmental regulation, which will bring insight into miR-101 research and cancer treatment. Consequently, the roles of miR-101 in cancer and the underlying mechanisms are still needed to be further explored to better reveal its clinical potential.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.L. and D.L.; Writing—original draft preparation, N.L., C.Y. and A.G.; Writing—review and editing, N.L., D.L. and M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Tai’an Technological Innovation and Development (2020NS279), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2020QH210). And the APC was funded by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2020QH210).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzi, L.; Chiu, H.S.; Avila Cobos, F.; Gross, S.; Volders, P.J.; Cannoodt, R.; Nuytens, J.; Vanderheyden, K.; Anckaert, J.; Lefever, S.; et al. The RNA Atlas expands the catalog of human non-coding RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jens, M.; Rajewsky, N. Competition between target sites of regulators shapes post-transcriptional gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X. MicroRNA in the pathogenesis and prognosis of esophageal cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Volinia, S.; Galasso, M.; Sana, M.E.; Wise, T.F.; Palatini, J.; Huebner, K.; Croce, C.M. Breast cancer signatures for invasiveness and prognosis defined by deep sequencing of microRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3024–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeri, M.; Verri, C.; Conte, D.; Roz, L.; Modena, P.; Facchinetti, F.; Calabrò, E.; Croce, C.M.; Pastorino, U.; Sozzi, G. MicroRNA signatures in tissues and plasma predict development and prognosis of computed tomography detected lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3713–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Dutta, A. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev. Pathol. 2009, 4, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, K.; Hu, F.; Qian, C.; Guan, H.; Feng, K.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z. MicroRNA-101 protects cardiac fibroblasts from hypoxia-induced apoptosis via inhibition of the TGF-beta signaling pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 65, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, L.; Guo, R.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Guan, X.; Gitau, S.C.; Xu, C.; Yang, B.; Shan, H. miR-101 promotes breast cancer cell apoptosis by targeting Janus kinase 2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.X.; Lan, K.; Ge, B.X. MicroRNA-101 targets MAPK phosphatase-1 to regulate the activation of MAPKs in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7435–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, H.; Li, H.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Li, Q.; Wang, S. MicroRNA-101 Inhibits Growth, Proliferation and Migration and Induces Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting Sex-Determining Region Y-Box 2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Dai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. MicroRNA-101 inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting EYA1 in breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Deng, F.; Li, H.; Wang, D.D.; Zhang, W.; Ding, L.; Tang, J.H. MiR-101: A potential therapeutic target of cancers. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 3310–3321. [Google Scholar]
- Varambally, S.; Cao, Q.; Mani, R.S.; Shankar, S.; Wang, X.; Ateeq, B.; Laxman, B.; Cao, X.; Jing, X.; Ramnarayanan, K.; et al. Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Science 2008, 322, 1695–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Liu, C.G.; Veronese, A.; Spizzo, R.; Sabbioni, S.; Magri, E.; Pedriali, M.; Fabbri, M.; Campiglio, M.; et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7065–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanaihara, N.; Caplen, N.; Bowman, E.; Seike, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.M.; Okamoto, A.; Yokota, J.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.X.; Kryczek, I.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, E.; Kuick, R.; Roh, M.H.; Vatan, L.; Szeliga, W.; Mao, Y.; Thomas, D.G.; et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells enhance stemness of cancer cells by inducing microRNA101 and suppressing the corepressor CtBP2. Immunity 2013, 39, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calastri, M.C.J.; Ferreira, R.F.; Tenani, G.D.; Spinola, L.P.; Vieira, G.F.; Rabaca Roque Botelho, M.F.; Abrantes, A.M.C.; Tralhao, J.; De Brito, A.F.M.; Da Silva, R.F.; et al. Investigating VEGF. miR-145-3p, and miR-101-3p Expression in Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Liao, H.; He, Y.; Zheng, Q. CCDC88A Post-Transcriptionally Regulates VEGF via miR-101 and Subsequently Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 859331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Shi, Y.; Xiang, X.; Li, C.; Ge, X.; Pan, K.; Liang, Y. Influence of miR-101 on proliferation of liver cancer cells through the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, J.; Ou, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, L. MicroRNA-101-3p suppresses proliferation and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting the HGF/c-Met pathway. Invest. N. Drugs 2020, 38, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y. The coordination between ZNF217 and LSD1 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma progress and is negatively regulated by miR-101. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 379, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Huang, W.; Yang, L.; Xu, F. MicroRNA-101-3p regulates gastric cancer cell proliferation, invasion and apoptosis by targeting PIM 1 expression. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 65, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Lin, L.; Xia, X.; Wu, H. lncRNA SPRY4-IT1 Regulates Cell Proliferation and Migration by Sponging miR-101-3p and Regulating AMPK Expression in Gastric Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 17, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. Long non-coding RNA SNHG6 promotes tumorigenesis in melanoma cells via the microRNA-101-3p/RAP2B axis. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Song, L.; Sun, X. Exosomal circ_PIP5K1A regulates the progression of non-small cell lung cancer and cisplatin sensitivity by miR-101/ABCC1 axis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 2253–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Chen, W.; Xia, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, T. MiR-101 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer by targeting zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Jiang, Y.; Xiang, X.; Gong, Q.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Q.; Zhuang, L. Long non-coding RNA SNHG6 promotes the growth and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by downregulating miR-101-3p. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahverdi, M.; Amri, J.; Karami, H.; Baazm, M. Knockdown of Myeloid Cell Leukemia-1 by MicroRNA-101 Increases Sensitivity of A549 Lung Cancer Cells to Etoposide. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 46, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Guo, S.; Liang, Y. MiR-101-3p inhibits the growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through blocking PI3K/AKT signal pathway by targeting MALAT-1. Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 93, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Gu, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Huo, S.; Liu, X.; Lu, H. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007364 increases cervical cancer progression through activating methionine adenosyltransferase II alpha (MAT2A) expression by restraining microRNA-101-5p. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, D.; Fang, K.; Guo, Z.; Li, L. Med19 is targeted by miR-101-3p/miR-422a and promotes breast cancer progression by regulating the EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2019, 444, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Huang, W.Z.; Wen, Y.Q.; Yi, Y.C. Effect of miR-101 on proliferation and oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of breast cancer cells via Nrf2 signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 8931–8939. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, C. Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 Promotes the Development of Colon Cancer by Regulating miR-101-3p/STC1 Axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 3653–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yu, W.; Han, X. Overexpression of microRNA101 causes antitumor effects by targeting CREB1 in colon cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3159–3167. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.B.; Huang, S.S.; Lu, C.G.; Tian, S.D.; Chen, M. CircAPLP2 regulates the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting miR-101-3p to activate the Notch signalling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 2554–2569. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Nie, K.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, H. MiR-101 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer through targeting STMN1. Cancer Biomark 2018, 23, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Tong, W.; Pu, X.F.; Wang, J.Z. Long noncoding RNA CRNDE promotes proliferation, migration and invasion in prostate cancer through miR-101/Rap1A. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; He, W.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Shi, K.; You, Z. MicroRNA-101-3p inhibits proliferation in retinoblastoma cells by targeting EZH2 and HDAC9. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Duan, L. Systematic Analysis and Validation of the Prognosis, Immunological Role and Biology Function of the Ferroptosis-Related lncRNA GSEC/miRNA-101-3p/CISD1 Axis in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 793732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemann, M.; Lim, S.C.; Kang, Y.; Samuel, S.; Sanchez, I.L.; Gantier, M.; Stojanovski, D.; McKenzie, M. MicroRNA-101-3p Modulates Mitochondrial Metabolism via the Regulation of Complex II Assembly. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Xi, G.; Wang, G.; Cui, D.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Jiang, G.; Song, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, J. Exosomal Circ-MEMO1 Promotes the Progression and Aerobic Glycolysis of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Through Targeting MiR-101-3p/KRAS Axis. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Ding, N.; Zhou, F.; Ji, R.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, C.; Pan, Y. A novel regulatory loop miR-101/ANXA2/EGR1 mediates malignant characteristics of liver cancer stem cells. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Cho, M.; Cho, J.; Kim, E.E.; Song, E.J. MicroRNA-101-3p Suppresses Cancer Cell Growth by Inhibiting the USP47-Induced Deubiquitination of RPL11. Cancers 2022, 14, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.W.; Liu, J.C. LncRNA SNHG12 regulates the miR-101-3p/CUL4B axis to mediate the proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; You, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ding, R.; Wang, M.; Pu, J.; Chen, J. Inhibition of MicroRNA miR-101-3p on prostate cancer progression by regulating Cullin 4B (CUL4B) and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 4719–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, R.; Yang, B. MiR-101-3p Suppresses Progression of Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting and Down-Regulating KPNA2. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211055948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesi, R.J. MDSC; The Most Important Cell You Have Never Heard Of. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, A.; Cross, N.C. Aberrations of EZH2 in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2613–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, M.; Nilsson, J.; Mir, S.E.; van der Stoop, P.M.; Hulleman, E.; Niers, J.M.; de Witt Hamer, P.C.; Marquez, V.E.; Cloos, J.; Krichevsky, A.M.; et al. miR-101 is down-regulated in glioblastoma resulting in EZH2-induced proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis. Oncotarget 2010, 1, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Liu, G.; Tang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, X. The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 interacted with miR-101 modulates breast cancer growth by targeting EZH2. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 615, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarthi, B.V.; Goswami, M.T.; Pathi, S.S.; Robinson, A.D.; Cieslik, M.; Chandrashekar, D.S.; Agarwal, S.; Siddiqui, J.; Daignault, S.; Carskadon, S.L.; et al. MicroRNA-101 regulated transcriptional modulator SUB1 plays a role in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6330–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, C.; Shi, W.; Liu, M.; Tu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Hu, L. Reciprocal negative feedback loop between EZH2 and miR-101-1 contributes to miR-101 deregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Luo, G.; Xiao, X.; Tao, D.; Wu, X.; Wang, M.; Huang, C.; Wang, L.; Zeng, F.; et al. LncRNA SPRY4-IT1 sponges miR-101-3p to promote proliferation and metastasis of bladder cancer cells through up-regulating EZH2. Cancer Lett. 2017, 388, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Li, E. Structure and function of eukaryotic DNA methyltransferases. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2004, 60, 55–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Xiang, T.; Ren, G.; Tan, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z. miR-101 is down-regulated by the hepatitis B virus x protein and induces aberrant DNA methylation by targeting DNA methyltransferase 3A. Cell Signal. 2013, 25, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Xu, F.; Ren, H.; Liu, D. miR-101 inhibits the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells via downregulating the expression of DNA methyltransferase 3a. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2016, 32, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Lei, Q.; Yu, Z.; Xu, G.; Tang, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Wu, M. MiR-101 reverses the hypomethylation of the LMO3 promoter in glioma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7930–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Chen, M.; Cao, L.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Wu, X.; Meng, Z.; Xu, K. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promote Migration and Invasion of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells via miR-101-3p Mediated VEGFA Secretion and AKT/eNOS Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 764151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Cao, K.; Kato, S.; Mizutani, N.; Tanaka, K.; Arima, C.; Tai, M.C.; Nakatani, N.; Yanagisawa, K.; Takeuchi, T.; et al. CERS6 required for cell migration and metastasis in lung cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 11949–11959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Xie, X.Y.; Liu, M.R.; Wang, L.L. MicroRNA-101-5p inhibits the growth and metastasis of cervical cancer cell by inhibiting CXCL6. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, D.; Hu, Z.; Luo, C.; Zheng, S.L. miRNA-101-5p inhibits the growth and aggressiveness of NSCLC cells through targeting CXCL6. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Shen, N.; Pang, J.; Xie, D.; Deng, B.; Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Liu, S. Restoration of miR-101 suppresses lung tumorigenesis through inhibition of DNMT3a-dependent DNA methylation. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.L.; Liang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Shi, G.Q. LncRNA XIST Promotes Migration and Invasion of Papillary Thyroid Cancer Cell by Modulating MiR-101-3p/CLDN1 Axis. Biochem. Genet. 2021, 59, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, H.; Duan, Y.; Liu, B. MicroRNA-101 suppresses colorectal cancer progression by negative regulation of Rap1b. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 2225–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.C.; Han, N.; Wu, N.; Zhao, K.L.; Han, C.; Wang, H.X.; Ping, G.F.; Zheng, P.F.; Feng, H.; Qin, L.; et al. Interplay between long noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 and miR-101/ZEB1 axis regulates proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Yu, M.; Yang, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.; Luo, H.; Hong, Y.; Yu, T.; Sun, J.; Shan, H.; et al. A PTAL-miR-101-FN1 Axis Promotes EMT and Invasion-Metastasis in Serous Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Ther. -Oncolytics 2020, 16, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harati, R.; Mohammad, M.G.; Tlili, A.; El-Awady, R.A.; Hamoudi, R. Loss of miR-101-3p Promotes Transmigration of Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells through the Brain Endothelium by Inducing COX-2/MMP1 Signaling. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Long, Y.; Han, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, W.; Yang, F.; Li, T.; Shu, L.; Zhong, Y. MicroRNA-101 inhibits cell migration and invasion in bladder cancer via targeting FZD4. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Shao, M.Y.; Zou, S.C.; Xiao, Z.F.; Chen, Z.C. MiR-101-3p inhibits EMT to attenuate proliferation and metastasis in glioblastoma by targeting TRIM44. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 141, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Jia, L.T.; Hu, S.J.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J.D.; Wen, W.H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, R.A.; et al. c-Myc-mediated epigenetic silencing of MicroRNA-101 contributes to dysregulation of multiple pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1850–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aigner, K.; Dampier, B.; Descovich, L.; Mikula, M.; Sultan, A.; Schreiber, M.; Mikulits, W.; Brabletz, T.; Strand, D.; Obrist, P.; et al. The transcription factor ZEB1 (deltaEF1) promotes tumour cell dedifferentiation by repressing master regulators of epithelial polarity. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6979–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakopoulos-Soares, I.; Chartoumpekis, D.V.; Kyriazopoulou, V.; Zaravinos, A. EMT Factors and Metabolic Pathways in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Cogdell, D.; Hu, L.; Yang, D.; Sood, A.K.; Xue, F.; Zhang, W. MiR-101 suppresses the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2 in ovarian carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 2021–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra Mangalhara, K.; Manvati, S.; Saini, S.K.; Ponnusamy, K.; Agarwal, G.; Abraham, S.K.; Bamezai, R.N.K. ERK2-ZEB1-miR-101-1 axis contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell migration in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 391, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Zheng, X.; Lu, T.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Yan, H. The proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma are inhibited by miR-101 via targetting ZEB2. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, G.; Zhai, J.; Liu, F.; Li, G. miR-101-3p Suppresses HOX Transcript Antisense RNA (HOTAIR)-Induced Proliferation and Invasion Through Directly Targeting SRF in Gastric Carcinoma Cells. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Mao, Y.; Zou, B.; Fan, X. MicroRNA-101 suppresses migration and invasion via targeting vascular endothelial growth factor-C in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, K.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, Q.; He, S.; Yu, L.; Zhou, J.; Cao, P. miR-101 Inhibiting Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Downregulating Girdin. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Mi, N.; Zhou, L. miR-101-3p and miR-199b-5p promote cell apoptosis in oral cancer by targeting BICC1. Mol. Cell. Probes 2020, 52, 101567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, P.; Huang, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L.; Xiao, W.; Fu, J.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y. Exosomal miR-101-3p and miR-423-5p inhibit medulloblastoma tumorigenesis through targeting FOXP4 and EZH2. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Lin, L.; Ma, X.; Zheng, R. miR-101 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting KDM1A in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 2739–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Lin, L.; Ma, X.; Zheng, R. miR101 regulates the cell proliferation and apoptosis in diffuse large Bcell lymphoma by targeting MEK1 via regulation of the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.S.; Qiu, E.H.; Zhu, J.J.; Wang, J.R.; Lin, H.L. MiR-101 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell apoptosis through inhibiting Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 8240. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Z. Overexpression of miR-101 promotes TRAIL-induced mitochondrial apoptosis in papillary thyroid carcinoma by targeting c-met and MCL-1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 108665–108675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Li, J. miR-101 alleviates chemoresistance of gastric cancer cells by targeting ANXA2. Biomed. Pharmacother 2017, 92, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Z.; Yin, X.; Chen, J.; Shi, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, F.; Cheng, S. MicroRNA-101 modulates cisplatin chemoresistance in liver cancer cells via the DNA-PKcs signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3655–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Xie, D.; Zhang, H. MicroRNA-101-3p advances cisplatin sensitivity in bladder urothelial carcinoma through targeted silencing EZH2. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2628–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, J. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 knockdown reverses chemoresistance to temozolomide via promoting microRNA-101 in glioblastoma. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 1404–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normann, L.S.; Haugen, M.H.; Aure, M.R.; Kristensen, V.N.; Maelandsmo, G.M.; Sahlberg, K.K. miR-101-5p Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Cells and Improves Targeted Therapy. Breast Cancer 2022, 14, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; An, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, X. miR-101 inhibits autophagy and enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 2019–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, P.; Wang, C.; Xin, B. SNHG14 enhances gemcitabine resistance by sponging miR-101 to stimulate cell autophagy in pancreatic cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 510, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Z.; Huo, L.; Li, K.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Z. Blocked autophagy by miR-101 enhances osteosarcoma cell chemosensitivity in vitro. Sci. World J. 2014, 794756, 9. [Google Scholar]
- van Gent, D.C.; Hoeijmakers, J.H.; Kanaar, R. Chromosomal stability and the DNA double-stranded break connection. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Ng, W.L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Mo, Y.Y.; Mao, H.; Hao, C.; Olson, J.J.; Curran, W.J.; et al. Targeting DNA-PKcs and ATM with miR-101 sensitizes tumors to radiation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 0011397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, N. Downregulation of lncRNA NEAT1_2 radiosensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells through regulation of miR-101-3p/WEE1 axis. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhang, T.; Du, S.; Xie, G.X.; Lin, X.; Chen, L.; Yuan, Y. MiR-101 sensitizes human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to radiation by targeting stathmin 1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 3330–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Qu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qin, M.; Zhang, H. miR-101-3p sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to irradiation. Open Med. 2020, 15, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, P.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shen, M.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, A.; Lin, Y.; Yang, R.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA FAM201A Mediates the Radiosensitivity of Esophageal Squamous Cell Cancer by Regulating ATM and mTOR Expression via miR-101. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Mu, Y. miR-101-3p sensitizes lung adenocarcinoma cells to irradiation via targeting BIRC5. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.J.; Zou, Y.H.; He, P.J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.M.; Li, C.Z. Long non-coding RNA SPRY4-IT1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical cancer by regulating the miR-101-3p/ZEB1 axis. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Jia, H. MicroRNA-101 inhibits angiogenesis via COX-2 in endometrial carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 448, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Lu, C.; Chu, H.; Yang, R.; Zhao, G. MALAT1/miR-101-3p/MCL1 axis mediates cisplatin resistance in lung cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7501–7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Tao, Z.; Hou, M.; Ma, H. Overexpression of HIF-2alpha-Dependent NEAT1 Promotes the Progression of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer through miR-101-3p/SOX9/Wnt/beta-Catenin Signal Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 2019, 52, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, F.; Wei, H.; Li, L. Circular RNA ZFR accelerates non-small cell lung cancer progression by acting as a miR-101-3p sponge to enhance CUL4B expression. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3410–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Yu, T.; Han, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C.; You, T.; Zhao, X.; Shan, H.; Yang, R.; Yang, L.; et al. LncRNA PTAR promotes EMT and invasion-metastasis in serous ovarian cancer by competitively binding miR-101-3p to regulate ZEB1 expression. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Jin, H.; Yang, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Jia, Y.; Cui, M. MicroRNA-101 inhibits growth and metastasis of human ovarian cancer cells by targeting PI3K/AKT. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 17, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Yu, Y. MiR-101-3p and Syn-Cal14.1a Synergy in Suppressing EZH2-Induced Progression of Breast Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 9599–9609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, J. miR-101 suppresses colon cancer cell migration through the regulation of EZH2. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2021, 113, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Han, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, M.; Chen, Y. ERO1alpha mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis via microRNA-101/EZH2 axis in colon cancer RKO and HT-29 cells. Hum. Cell 2021, 34, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, S.K.; Miao, E.Y.; Jia, C.Q.; Fan, Y.Z.; Li, Y.B. Eicosapentaenoic acid’s metabolism of 15-LOX-1 promotes the expression of miR-101 thus inhibits Cox2 pathway in colon cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 5605–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Shang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, D.; Wu, N.; Hu, S.; Zhang, S.; et al. O-GlcNAcylation promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via the miR-101-O-GlcNAc/EZH2 regulatory feedback circuit. Oncogene 2019, 38, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Xu, C.; Shen, W.; Tan, J.; Li, L.; Fan, M.; Sun, D.; Lai, Y.; Cheng, H. HIPK3 Inhibition by Exosomal hsa-miR-101-3p Is Related to Metabolic Reprogramming in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 758336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ma, L.; Tang, J.; Yu, Q.; Shen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, C.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, W. LncRNA00518 promotes cell proliferation through regulating miR-101 in bladder cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, X.; Cui, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Zu, X. LncRNA-MALAT1 mediates cisplatin resistance via miR-101-3p/VEGF-C pathway in bladder cancer. Acta Biochim. Et Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Xu, Y.; Du, K.; Mi, C.; Yang, C.; Xiang, L.; Xie, Y.; Liu, W. LINC01303 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate EZH2 expression by sponging miR-101-3p in gastric cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7342–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, A.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Effects of miR-101, miR-345 on HBV replication regulation and on the growth of liver cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, B.Q.; Lin, X.H.; Ye, X.D.; Huang, W.; Pei, X.; Xiong, D.; Long, X.; Zhu, S.Q.; Lu, F.; Lin, K.; et al. Long non-coding RNA PSMA3-AS1 promotes malignant phenotypes of esophageal cancer by modulating the miR-101/EZH2 axis as a ceRNA. Aging 2020, 12, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, M.; Wu, H.; Ru, P.; Hwang, L.; Trieu, V.; Mo, Y.Y. MicroRNA-101-mediated Akt activation and estrogen-independent growth. Oncogene 2011, 30, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, D.K.; Kim, J.; Kwak, S.N.; Ha, K.S.; Choe, J.; Won, M.H.; Cho, B.R.; Jeoung, D.; et al. Hypoxia-responsive microRNA-101 promotes angiogenesis via heme oxygenase-1/vascular endothelial growth factor axis by targeting cullin 3. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 2469–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Xia, W.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Chen, H.Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, M.Y.; Li, L.F.; Lu, H.M.; Fu, Y.J.; Wang, P.; et al. MicroRNA-101 targets von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor (VHL) to induce HIF1α mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in normoxia condition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Xing, A.Y.; Chen, X.; Ma, R.R.; Wang, Y.W.; Shi, D.B.; Zhang, H.; Li, P.; Chen, H.F.; Li, Y.H.; et al. MicroRNA-27b, microRNA-101 and microRNA-128 inhibit angiogenesis by down-regulating vascular endothelial growth factor C expression in gastric cancers. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37458–37470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, C.; Zhu, H.; Song, K.; Wu, T. miR-101 inhibits cholangiocarcinoma angiogenesis through targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanmee, T.; Ontong, P.; Konno, K.; Itano, N. Tumor-associated macrophages as major players in the tumor microenvironment. Cancers 2014, 6, 1670–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, Z.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yan, Y.; Lv, X.; Zhang, L.; Su, P.; Bi, J.; et al. lncRNA-Xist/miR-101-3p/KLF6/C/EBPalpha axis promotes TAM polarization to regulate cancer cell proliferation and migration. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niespolo, C.; Johnston, J.M.; Deshmukh, S.R.; Satam, S.; Shologu, Z.; Villacanas, O.; Sudbery, I.M.; Wilson, H.L.; Kiss-Toth, E. Tribbles-1 Expression and Its Function to Control Inflammatory Cytokines, Including Interleukin-8 Levels are Regulated by miRNAs in Macrophages and Prostate Cancer Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 574046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Tang, C.; Lu, X.; Liu, R.; Zhou, M.; He, D.; Zheng, D.; Sun, C.; Wu, Z. MiR-101 targets DUSP1 to regulate the TGF-beta secretion in sorafenib inhibits macrophage-induced growth of hepatocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18389–18405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Zhang, J.; Guo, G.; Zhang, L.; Dai, J.; Gao, Y. Comprehensive analysis of GSEC/miR-101-3p/SNX16/PAPOLG axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashima, Y.; Kawaguchi, A.; Iwadate, Y.; Hondoh, H.; Fukai, J.; Kajiwara, K.; Hayano, A.; Yamanaka, R. miR-101, miR-548b, miR-554, and miR-1202 are reliable prognosis predictors of the miRNAs associated with cancer immunity in primary central nervous system lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Tang, F.; Tang, P.; Zhang, L.; Gan, Q.; Li, Y. Noncoding RNAs-mediated overexpression of KIF14 is associated with tumor immune infiltration and unfavorable prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Aging 2022, 14, 8013–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S. Non-coding ribonucleic acid-mediated CAMSAP1 upregulation leads to poor prognosis with suppressed immune infiltration in liver hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 916847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Wang, Y. Extracellular vesicles derived from M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages promote immune escape in ovarian cancer through NEAT1/miR-101-3p/ZEB1/PD-L1 axis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yang, D.; Ru, Y.; Cao, S.; Gao, A. MicroRNA-101 Targets CXCL12-Mediated Akt and Snail Signaling Pathways to Inhibit Cellular Proliferation and Invasion in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Oncol. Res. 2019, 27, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semaan, A.; Qazi, A.M.; Seward, S.; Chamala, S.; Bryant, C.S.; Kumar, S.; Morris, R.; Steffes, C.P.; Bouwman, D.L.; Munkarah, A.R.; et al. MicroRNA-101 inhibits growth of epithelial ovarian cancer by relieving chromatin-mediated transcriptional repression of p21(waf¹/cip¹). Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 3079–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Zhu, P. MiR-101 reduces cell proliferation and invasion and enhances apoptosis in endometrial cancer via regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 21, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Pan, J.J.; Deng, Y.H.; Liang, M.R.; Yao, L.H. Down-regulated serum microRNA-101 is associated with aggressive progression and poor prognosis of cervical cancer. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 28, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ge, Q.; Yu, L.; Yao, M.; Sun, X.; Ren, Z.; Ding, C. Long non-coding RNA Malat1 activated autophagy, hence promoting cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis by sponging miR-101 in colorectal cancer. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 019–0175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.S.; Lu, J.; Mercer, K.L.; Golub, T.R.; Jacks, T. Impaired microRNA processing enhances cellular transformation and tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solinas, G.; Germano, G.; Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) as major players of the cancer-related inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Qu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Gao, X.; et al. Prognostic significance of tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer: A meta-analysis of the literature. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30576–30586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).