Exosomal and Soluble Programed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Predicts Responses to Pembrolizumab in Patients with Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. RNA Stability Assay and Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Isolation and Characterization of Exosome
2.7. Measurement of Soluble PD-L1 and Exosomal PD-L1
2.8. Flow Cytometry
2.9. Immunohistochemistry
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
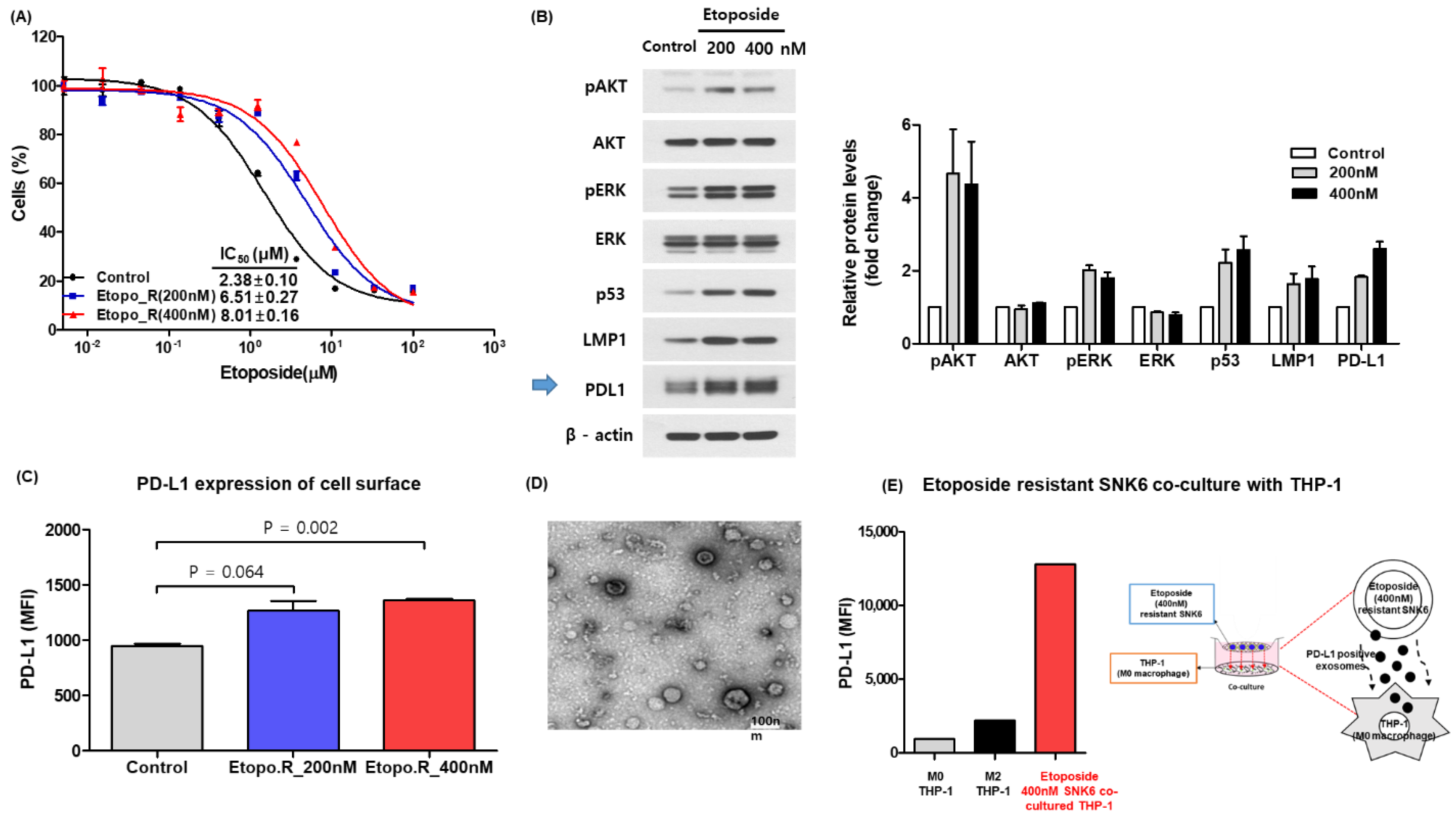
3.1. Increase of Soluble and Exosomal PD-L1 in Etoposide-Resistant Cells
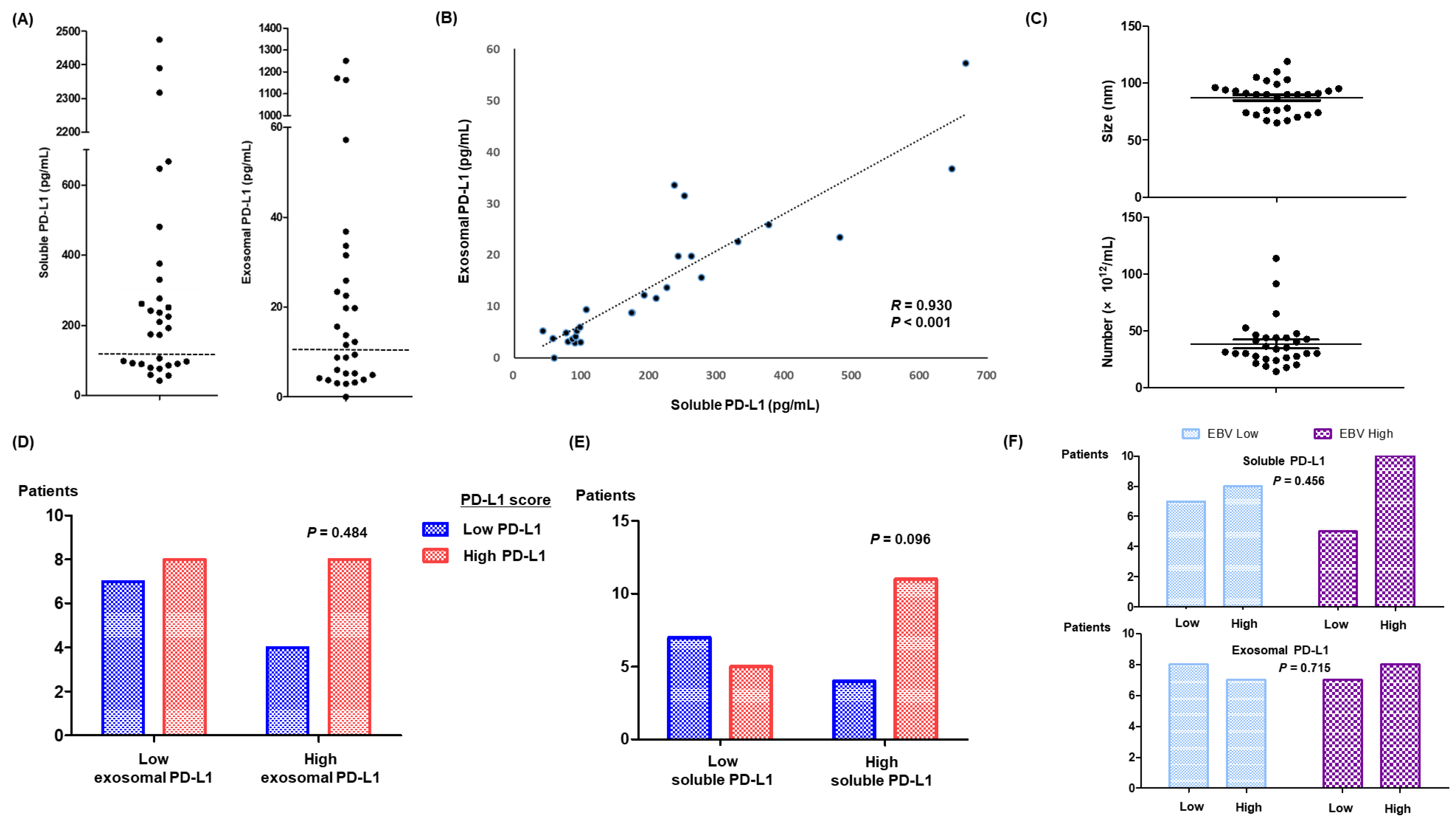
3.2. Soluble and Exosomal PD-L1 in Relapsed or Refractory ENKTL Patients
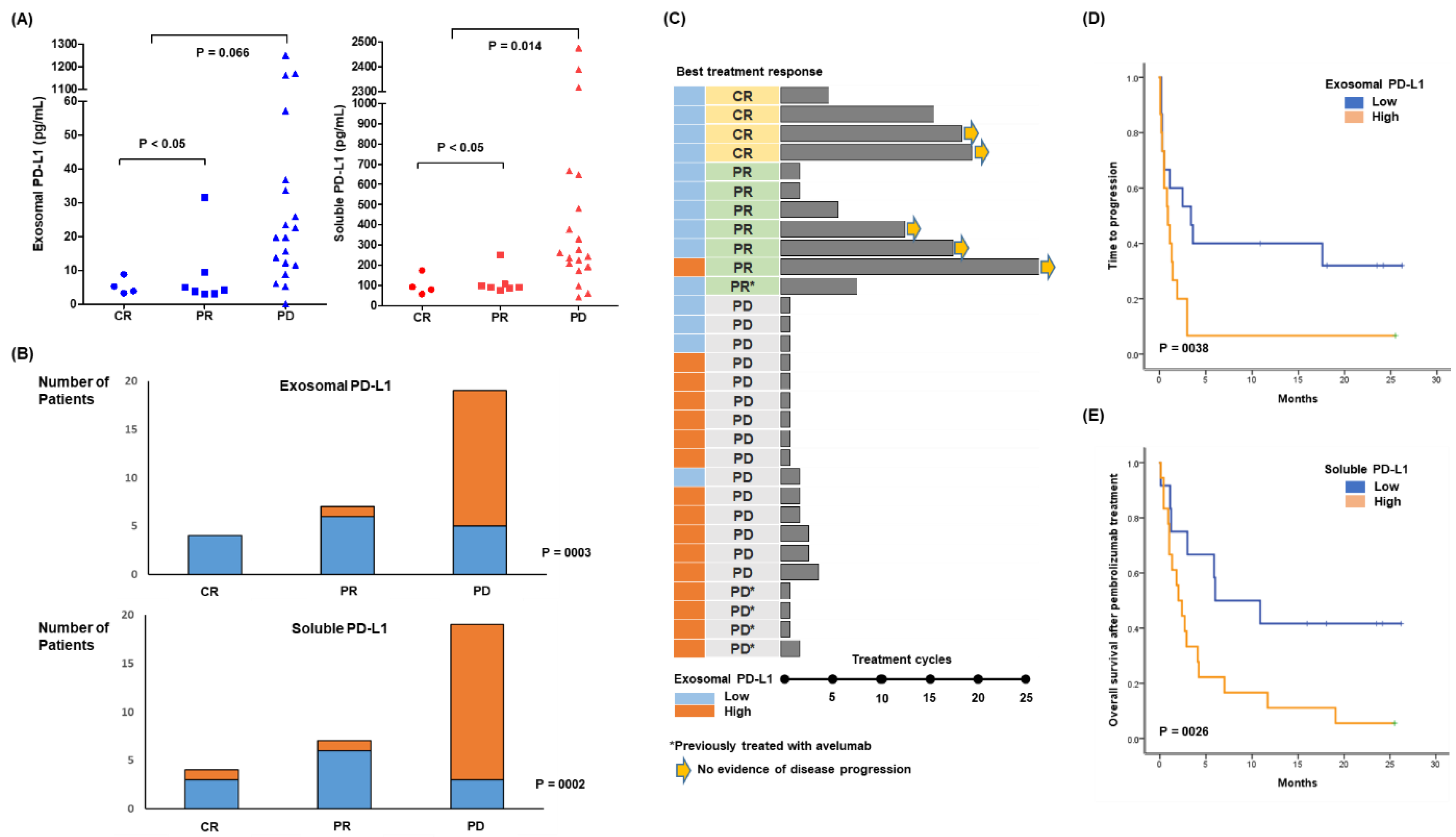
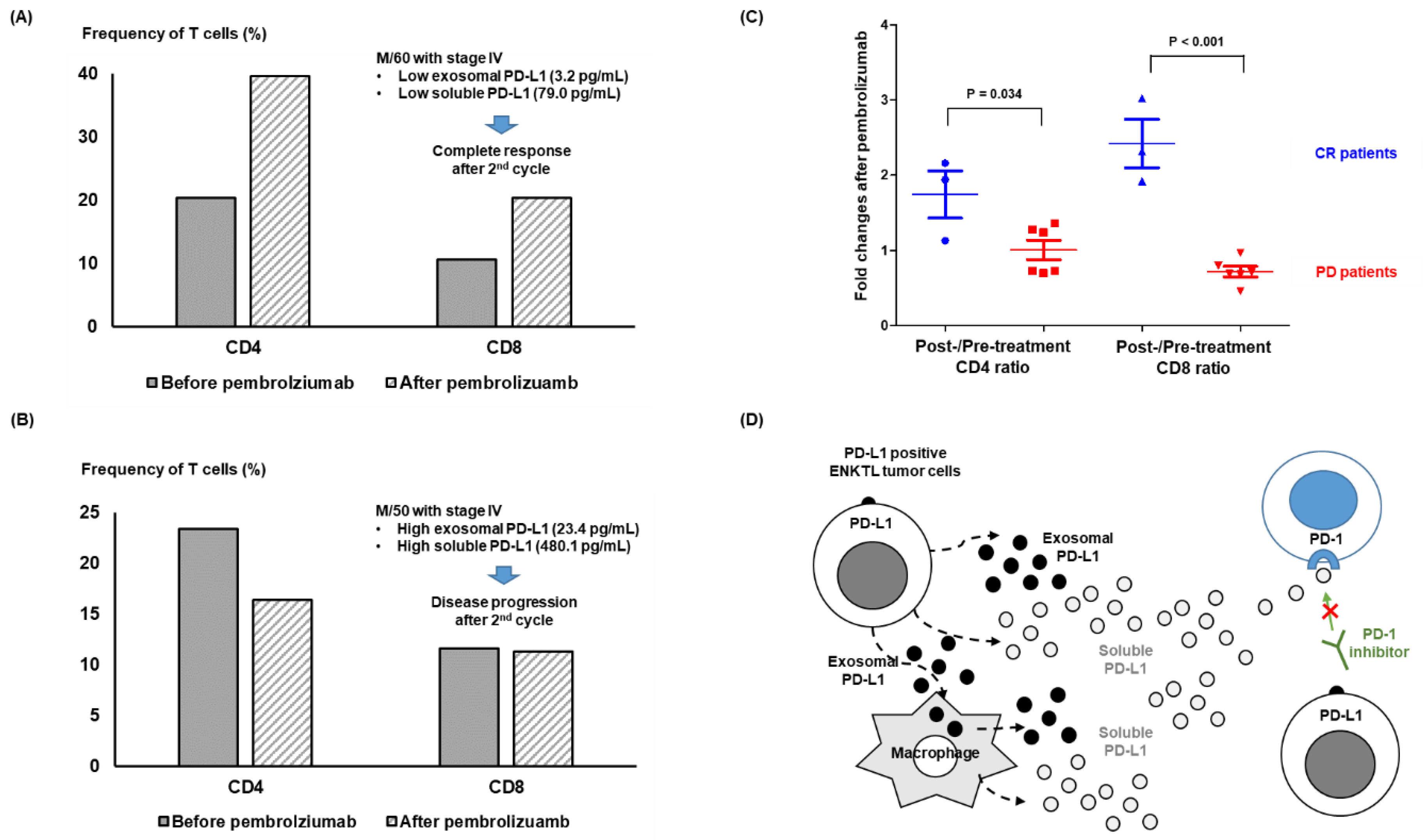
3.3. Response to Pembrolizumab and Levels of Soluble and Exosomal PD-L1
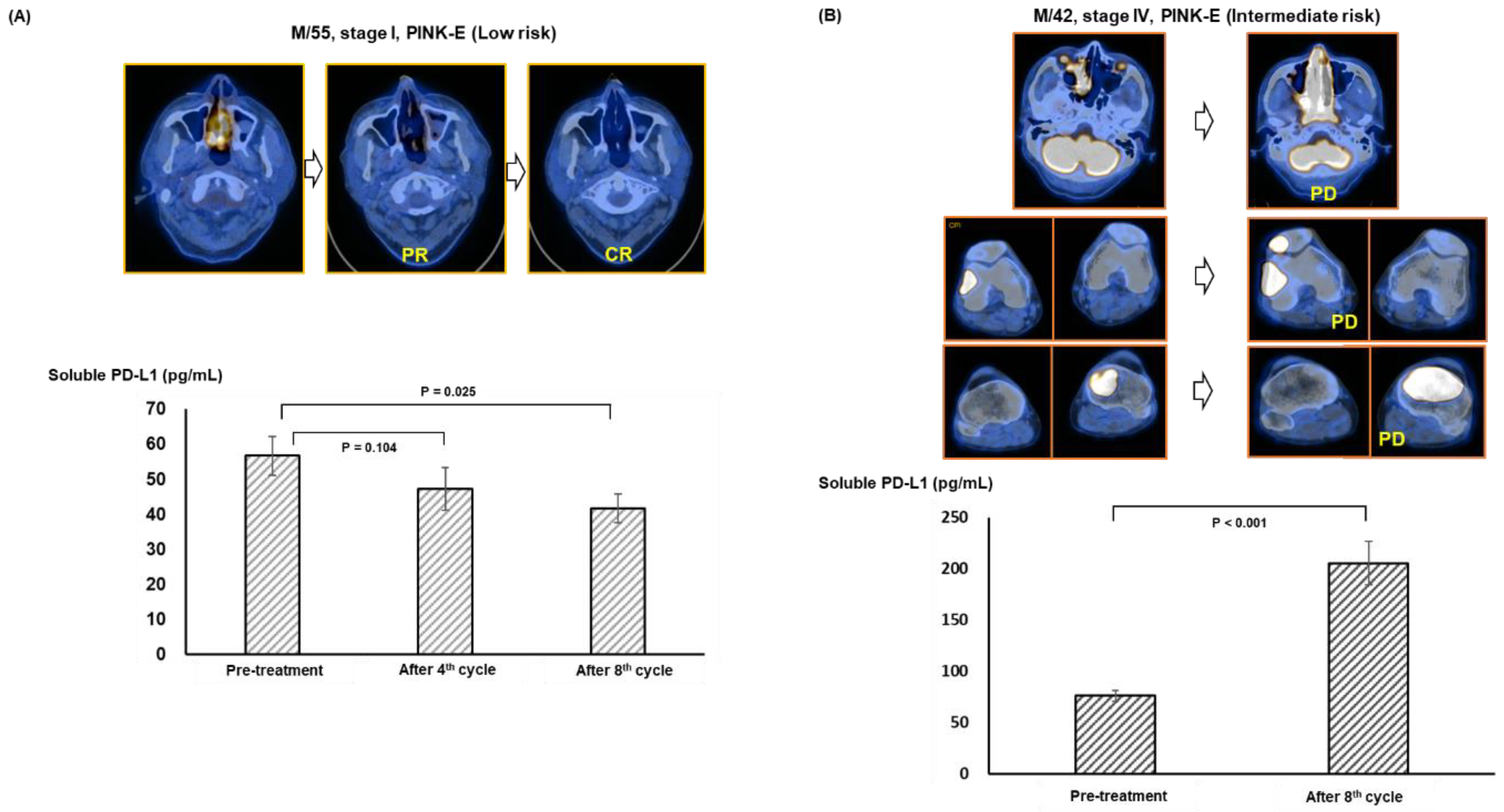
3.4. Longitudinal Analysis before and after Pembrolizumab Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weber, J. Immune Checkpoint Proteins: A New Therapeutic Paradigm for Cancer—Preclinical Background: CTLA-4 and PD-1 Blockade. Semin. Oncol. 2010, 37, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Flies, D.B. Molecular mechanisms of T cell co-stimulation and co-inhibition. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darvin, P.; Toor, S.M.; Sasidharan Nair, V.; Elkord, E. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: Recent progress and potential biomarkers. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C. A decade of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hude, I.; Sasse, S.; Engert, A.; Bröckelmann, P.J. The emerging role of immune checkpoint inhibition in malignant lymphoma. Haematologica 2017, 102, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, Y.-L.; Chan, T.S.Y.; Tan, D.; Kim, S.J.; Poon, L.-M.; Mow, B.; Khong, P.-L.; Loong, F.; Au-Yeung, R.; Iqbal, J.; et al. PD1 blockade with pembrolizumab is highly effective in relapsed or refractory NK/T-cell lymphoma failing l-asparaginase. Blood 2017, 129, 2437–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Hyeon, J.; Cho, I.; Ko, Y.H.; Kim, W.S. Comparison of Efficacy of Pembrolizumab between Epstein-Barr Virus Positive and Negative Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 51, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossille, D.; Gressier, M.; Damotte, D.; Maucort-Boulch, D.; Pangault, C.; Semana, G.; Le Gouill, S.; Haioun, C.; Tarte, K.; Lamy, T.; et al. High level of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 in blood impacts overall survival in aggressive diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma: Results from a French multicenter clinical trial. Leukemia 2014, 28, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Ji, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W. Soluble programmed death-ligand 1 are highly expressed in peripheral T-cell lymphoma: A biomarker for prognosis. Hematology 2019, 24, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.; Lee, H.; Yoon, S.E.; Ryu, K.J.; Ko, Y.H.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, S.J. Serum levels of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1) in patients with primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, C.-W.; Chan, L.-C.; Wei, Y.; Hsu, J.-M.; Xia, W.; Cha, J.-H.; Hou, J.; Hsu, J.L.; Sun, L.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 harbors active defense function to suppress T cell killing of breast cancer cells and promote tumor growth. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 862–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodoraki, M.-N.; Yerneni, S.S.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Gooding, W.E.; Whiteside, T.L. Clinical Significance of PD-L1+ Exosomes in Plasma of Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Huang, A.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Xu, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, H.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 2018, 560, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.W.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, W.J.; Xia, Z.J.; Huang, H.Q.; Jiang, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, L. PD-L1 is upregulated by EBV-driven LMP1 through NF-kappaB pathway and correlates with poor prognosis in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-W.; Wei, P.; Guo, Y.; Shi, D.; Yu, B.-H.; Su, Y.-F.; Li, X.-Q.; Zhou, X.-Y. Clinical significance of circulating exosomal PD-L1 and soluble PD-L1 in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 4498–4512. [Google Scholar]
- Nagato, T.; Ohkuri, T.; Ohara, K.; Hirata, Y.; Kishibe, K.; Komabayashi, Y.; Ueda, S.; Takahara, M.; Kumai, T.; Ishibashi, K.; et al. Programmed death-ligand 1 and its soluble form are highly expressed in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: A potential rationale for immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Jing, C.; Yu, X.; Cao, X.; Xu, C. Predicting treatment response of patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma based on levels of PD-L1 mRNA and soluble PD-L1. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 38, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, M.E.; Yoon, S.E.; Cho, J.; Ko, Y.H.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, W.S.; Park, C.; Kim, S.J. Serum-Derived Exosomal MicroRNA Profiles Can Predict Poor Survival Outcomes in Patients with Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D.; Fisher, R.I.; Barrington, S.F.; Cavalli, F.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Lister, T.A.; Alliance, A.L.; Lymphoma, G.; Eastern Cooperative Oncology, G.; et al. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: The Lugano classification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3059–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Yoon, D.H.; Jaccard, A.; Chng, W.J.; Lim, S.T.; Hong, H.; Park, Y.; Chang, K.M.; Maeda, Y.; Ishida, F.; et al. A prognostic index for natural killer cell lymphoma after non-anthracycline-based treatment: A multicentre, retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, E.W.; Graham, A.E.; Re, N.A.; Carr, I.M.; Robinson, J.I.; Mackie, S.L.; Morgan, A.W. Standardized protocols for differentiation of THP-1 cells to macrophages with distinct M(IFNgamma+LPS), M(IL-4) and M(IL-10) phenotypes. J. Immunol. Methods 2020, 478, 112721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, W.-Y.; Kim, J.; Woo, J.; Kim, G.; Yoon, S.E.; Ko, Y.H.; Kim, W.S. Immune subtyping of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: A new biomarker and an immune shift during disease progression. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schemper, M.; Smith, T.L. A note on quantifying follow-up in studies of failure time. Control. Clin. Trials 1996, 17, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lim, J.Q.; Laurensia, Y.; Cho, J.; Yoon, S.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Ryu, K.J.; Ko, Y.H.; Koh, Y.; Cho, D.; et al. Avelumab for the treatment of relapsed or refractory extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: An open-label phase 2 study. Blood 2020, 136, 2754–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-H.; Miao, F.-A.; Xu, J.-G.; Zhang, Y. Angiotensin II enhances the proliferation of Natural Killer/T-cell lymphoma cells via activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Cui, B.-W.; Wang, N.; Dai, Y.-T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.-F.; Zhong, H.-J.; Cheng, S.; Ou-Yang, B.-S.; Hu, Y.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Characterization of Natural Killer T Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 403–419.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Han, H.; Gong, M.; Song, Y. The role of exosomal miR-181b in the crosstalk between NSCLC cells and tumor-associated macrophages. Genes Genom. 2022, 44, 1243–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezutter-Dambuyant, C.; Durand, I.; Alberti, L.; Bendriss-Vermare, N.; Valladeau-Guilemond, J.; Duc, A.; Magron, A.; Morel, A.-P.; Sisirak, V.; Rodriguez, C.; et al. A novel regulation of PD-1 ligands on mesenchymal stromal cells through MMP-mediated proteolytic cleavage. OncoImmunology 2016, 5, e1091146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hira-Miyazawa, M.; Nakamura, H.; Hirai, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kitahara, H.; Bou-Gharios, G.; Kawashiri, S. Regulation of programmed-death ligand in the human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma microenvironment is mediated through matrix metalloproteinase-mediated proteolytic cleavage. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Su, Y.; Zhong, S.; Cong, L.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Tao, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y. Exosomes: Key players in cancer and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrissey, S.M.; Yan, J. Exosomal PD-L1: Roles in Tumor Progression and Immunotherapy. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzo, B.M.; Ludwig, N.; Hong, C.-S.; Sharma, P.; Fabian, K.P.; Fecek, R.J.; Storkus, W.J.; Whiteside, T.L. Tumor-derived exosomes promote carcinogenesis of murine oral squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.M.; Lee, C.; Son, S.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, J.A.; Ko, H.; Shin, S.; Song, S.H.; Park, S.; Bae, J.; et al. Sulfisoxazole Elicits Robust Antitumour Immune Response Along with Immune Checkpoint Therapy by Inhibiting Exosomal PD-L1. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Total (n = 30) | Exosomal PD-L1 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | |||
| Age (years) | ||||
| ≤60 | 23 (77) | 11 (73) | 12 (80) | >0.99 |
| >60 | 7 (23) | 4 (27) | 3 (20) | |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 21 (70) | 13 (87) | 8 (53) | 0.109 |
| Female | 9 (30) | 2 (13) | 7 (47) | |
| Performance status | ||||
| ECOG 0 or 1 | 13 (43) | 10 (67) | 3 (20) | 0.025 |
| ECOG ≥ 2 | 17 (57) | 5 (33) | 12 (80) | |
| Serum LDH | ||||
| Normal | 10 (33) | 6 (40) | 4 (27) | 0.700 |
| Increased | 20 (67) | 9 (60) | 11 (73) | |
| Stage | ||||
| I/II | 5 (17) | 4 (27) | 1 (7) | 0.330 |
| III/IV | 25 (83) | 11 (73) | 14 (93) | |
| Disease status | ||||
| Relapsed | 10 (33) | 8 (53) | 2 (13) | 0.050 |
| Refractory | 20 (67) | 7 (47) | 13 (87) | |
| PINK-E risk | ||||
| Low | 3 (10) | 2 (13) | 1 (7) | 0.135 |
| Intermediate | 3 (10) | 3 (20) | 0 (0) | |
| High | 24 (80) | 10 (67) | 14 (93) | |
| Number of previous treatments | ||||
| <2 | 18 (60) | 10 (67) | 8 (53) | 0.710 |
| ≥2 | 12 (40) | 5 (33) | 7 (47) | |
| Previous treatment with avelumab | ||||
| Yes | 5 (17) | 1 (7) | 4 (27) | 0.330 |
| No | 25 (83) | 14 (93) | 11 (73) | |
| Autologous SCT | ||||
| Done | 13 (43) | 6 (40) | 7 (47) | >0.99 |
| Not done | 17 (57) | 9 (60) | 8 (53) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.J.; Ryu, K.J.; Park, B.; Yoon, S.E.; Cho, J.; Park, Y.; Kim, W.S. Exosomal and Soluble Programed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Predicts Responses to Pembrolizumab in Patients with Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 5618. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225618
Kim SJ, Ryu KJ, Park B, Yoon SE, Cho J, Park Y, Kim WS. Exosomal and Soluble Programed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Predicts Responses to Pembrolizumab in Patients with Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma. Cancers. 2022; 14(22):5618. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225618
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seok Jin, Kyung Ju Ryu, Bon Park, Sang Eun Yoon, Junhun Cho, Yoon Park, and Won Seog Kim. 2022. "Exosomal and Soluble Programed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Predicts Responses to Pembrolizumab in Patients with Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma" Cancers 14, no. 22: 5618. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225618
APA StyleKim, S. J., Ryu, K. J., Park, B., Yoon, S. E., Cho, J., Park, Y., & Kim, W. S. (2022). Exosomal and Soluble Programed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Predicts Responses to Pembrolizumab in Patients with Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma. Cancers, 14(22), 5618. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225618






