CRISPR/Cas9 Edited RAS & MEK Mutant Cells Acquire BRAF and MEK Inhibitor Resistance with MEK1 Q56P Restoring Sensitivity to MEK/BRAF Inhibitor Combo and KRAS G13D Gaining Sensitivity to Immunotherapy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
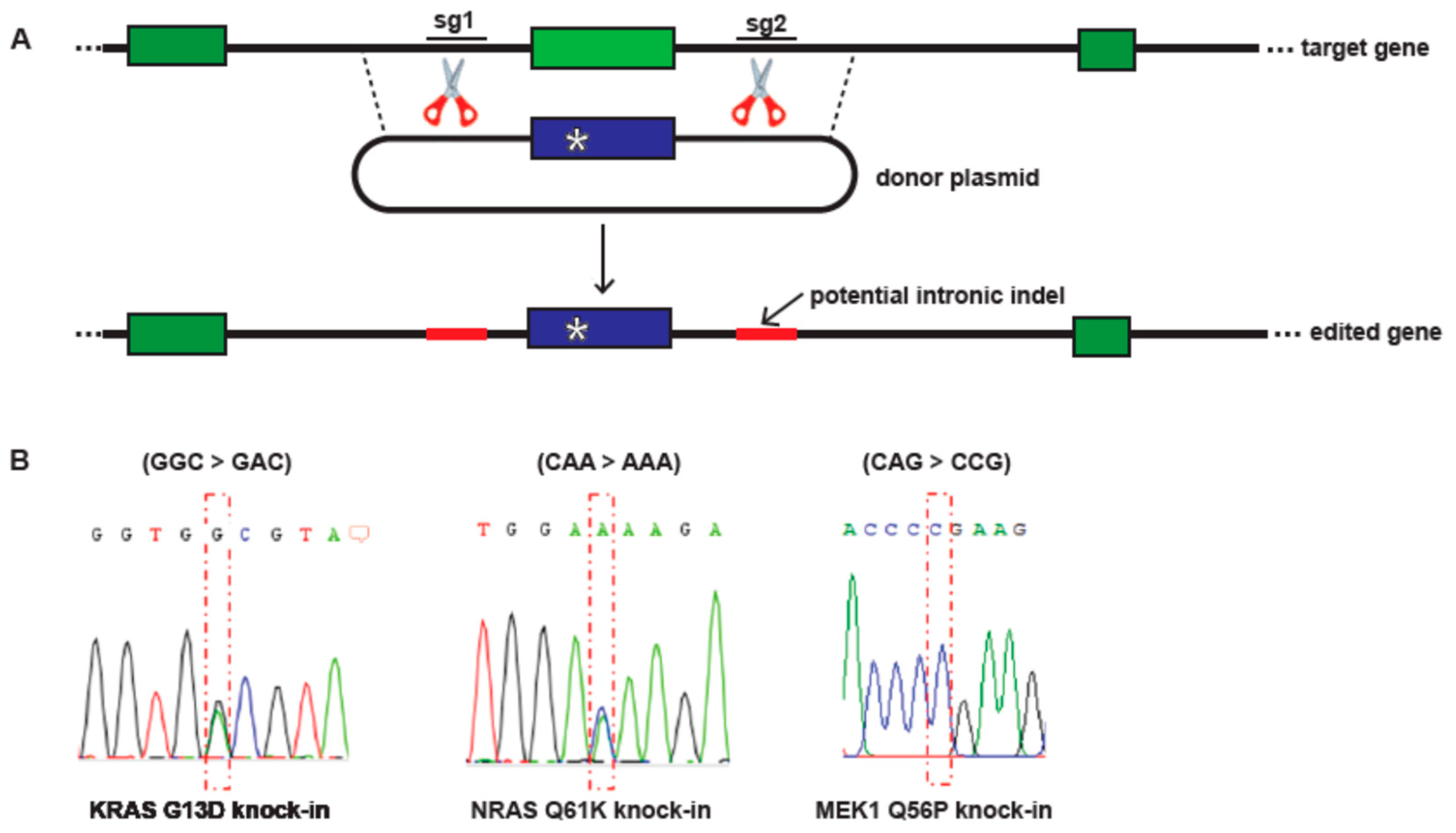
2.1. CRISPR/Cas9 Engineering of Ras and MEK1 Point Mutations
2.2. Cell Culture and Single Cell Cloning
2.3. Genotyping for Positive KI Mutant Clones
2.4. Immunoblots
2.5. D Cell Culture Dose-Response Curves
2.6. D Spheroid Formation, Drug Treatment, and Imaging
2.7. Flow Cytometry
3. Results
3.1. CRISPR/Cas9 Engineering of KRAS G13D, NRAS Q61K and MEK1 Q56P A375 Melanoma Models
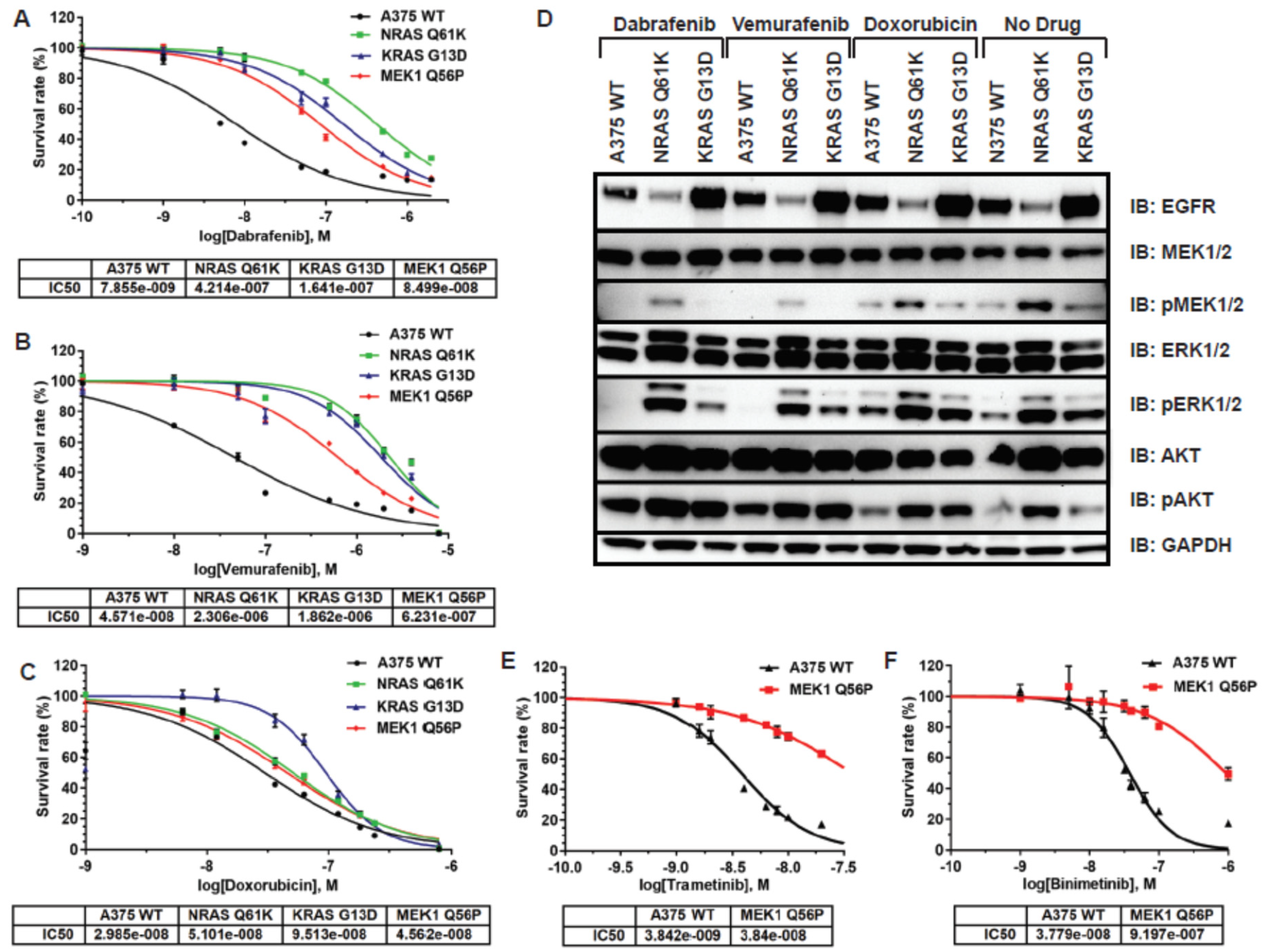
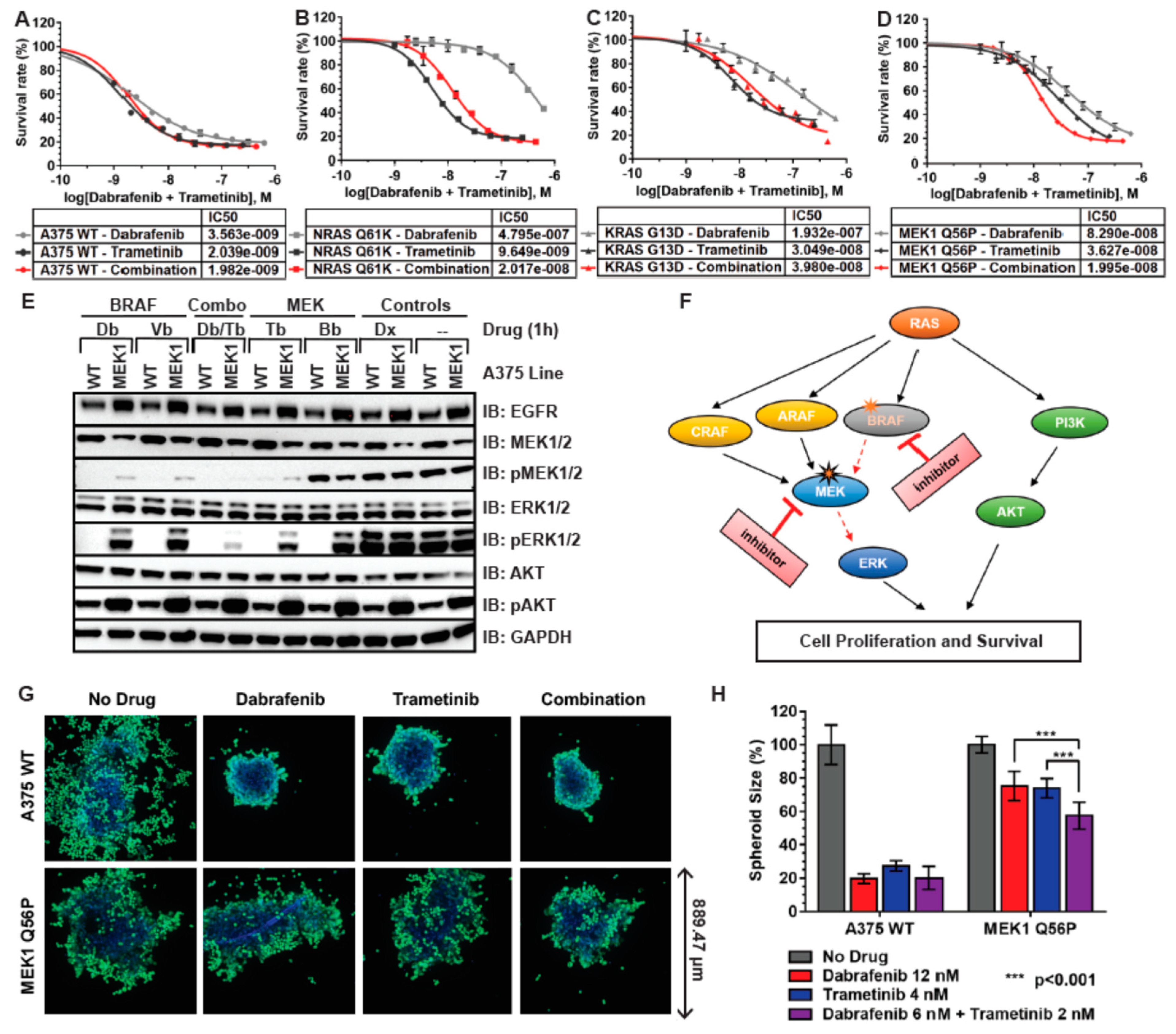
3.2. RAS and MEK Mutant A375 Melanoma Models Are Resistant to BRAF and MEK Inhibitors in 2D Tissue Culture
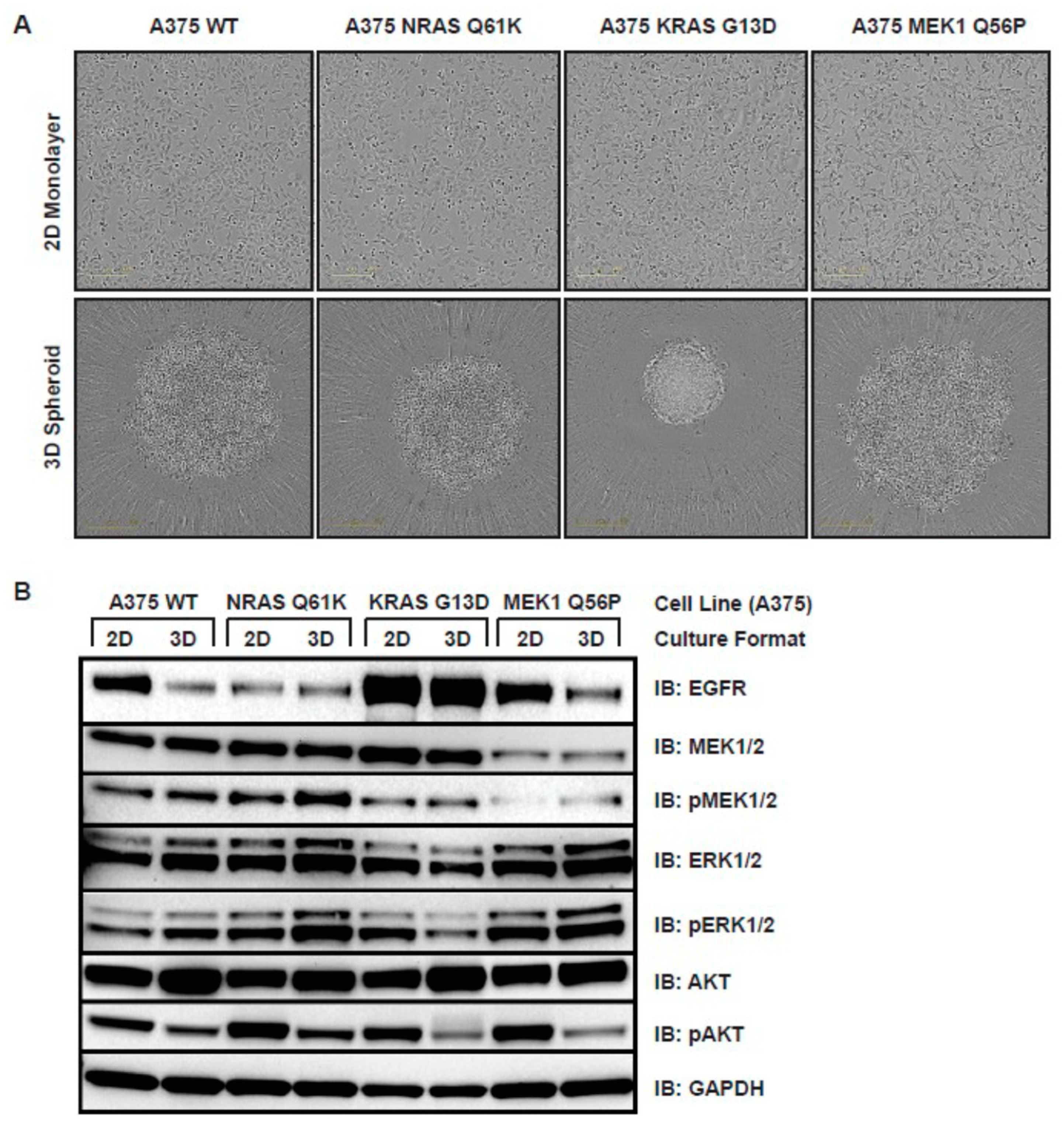
3.3. Ras and MEK1 Mutant Melanoma Models Display Differential Ras/RAF/MEK/ERK Pathway Perturbations in 2D vs. 3D Tissue Culture
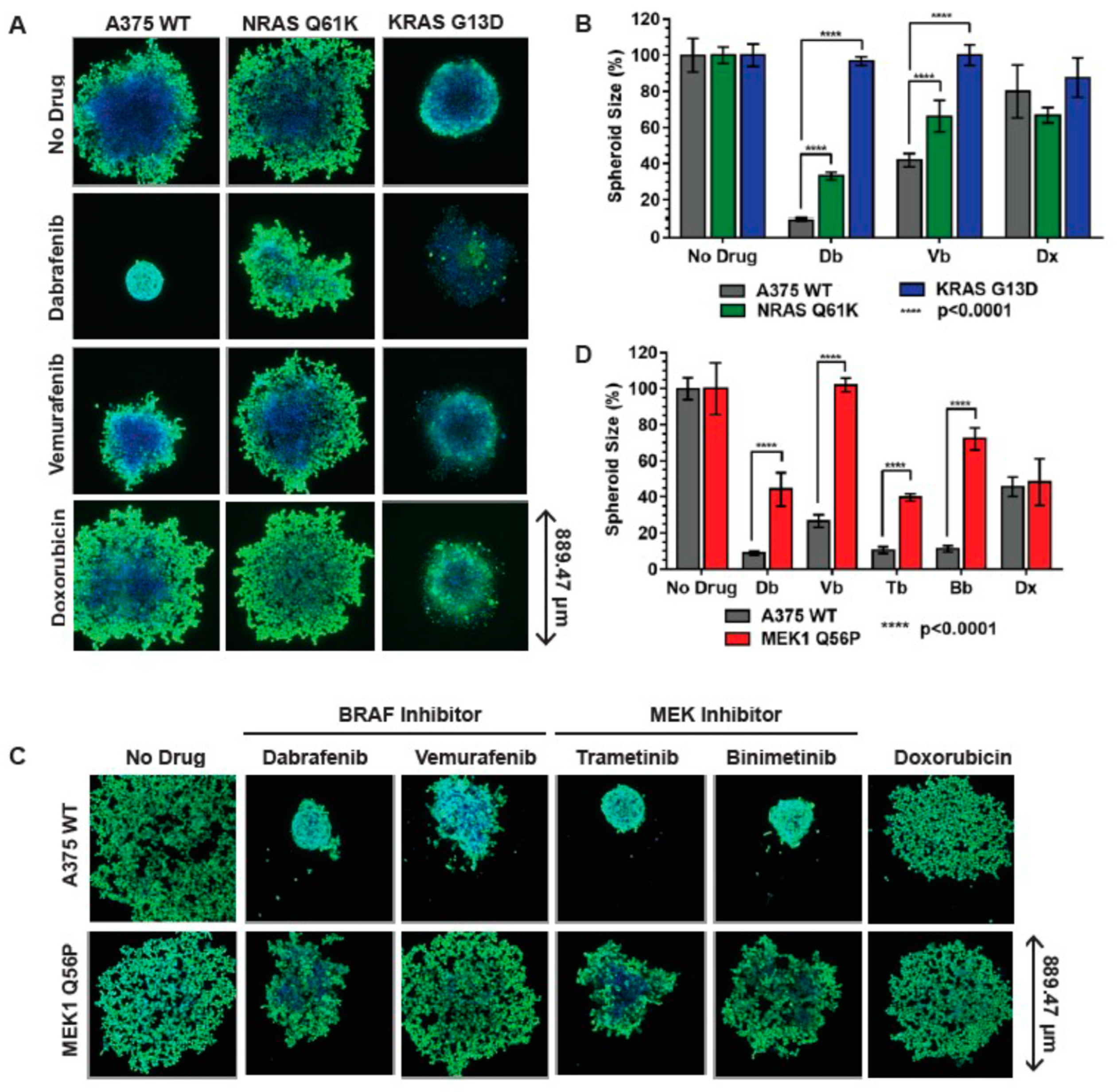
3.4. RAS and MEK1 Mutant A375 Isogenic Melanoma Models Are Resistant to BRAF Inhibitors in 3D Tissue Culture
3.5. MEK1 Q56P A375 Cells Are Sensitive to Combination BRAF/MEK Inhibitor Treatment in 2D and 3D Tissue Culture
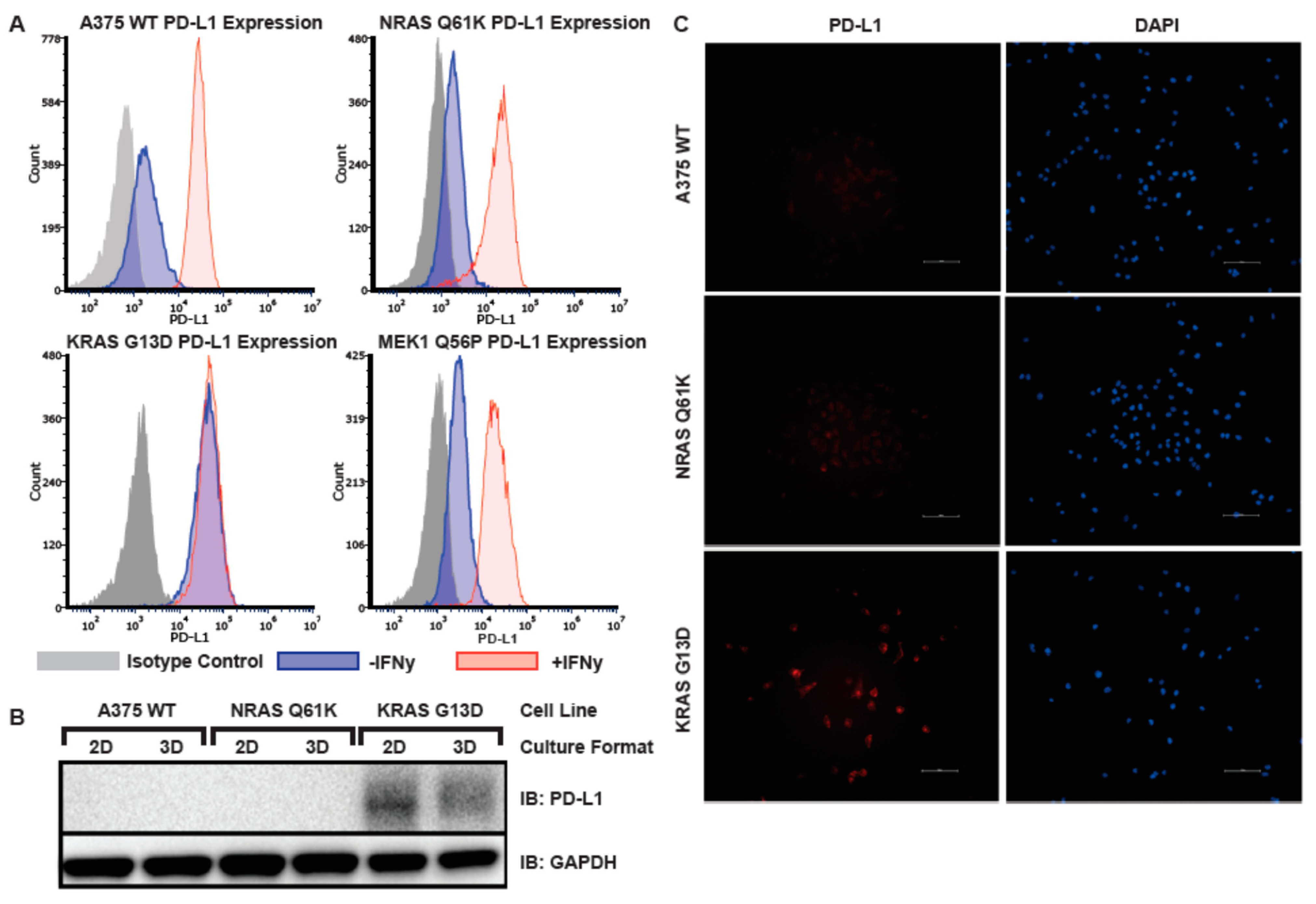
3.6. Elevated Basal PD-L1 Expression in A375 KRAS G13D Isogenic Melanoma Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smalley, K.S. A pivotal role for ERK in the oncogenic behaviour of malignant melanoma? Int. J. Cancer 2003, 104, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, H.; Bignell, G.R.; Cox, C.; Stephens, P.; Edkins, S.; Clegg, S.; Teague, J.; Woffendin, H.; Garnett, M.J.; Bottomley, W.; et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 2002, 417, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solit, D.B.; Garraway, L.A.; Pratilas, C.A.; Sawai, A.; Getz, G.; Basso, A.; Ye, Q.; Lobo, J.M.; She, Y.; Osman, I.; et al. BRAF mutation predicts sensitivity to MEK inhibition. Nature 2006, 439, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, P.B.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.B.; Ascierto, P.; Larkin, J.; Dummer, R.; Garbe, C.; Testori, A.; Maio, M.; et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.T.; Puzanov, I.; Kim, K.B.; Ribas, A.; McArthur, G.A.; Sosman, J.A.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Lee, R.J.; Grippo, J.F.; Nolop, K.; et al. Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. New Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschild, A.; Grob, J.-J.; Demidov, L.V.; Jouary, T.; Gutzmer, R.; Millward, M.; Rutkowski, P.; Blank, C.U.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; Kaempgen, E.; et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: A multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosman, J.A.; Kim, K.B.; Schuchter, L.; Gonzalez, R.; Pavlick, A.C.; Weber, J.S.; McArthur, G.A.; Hutson, T.E.; Moschos, S.J.; Flaherty, K.T.; et al. Survival in BRAF V600–Mutant Advanced Melanoma Treated with Vemurafenib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Hugo, W.; Kong, X.; Hong, A.; Koya, R.C.; Moriceau, G.; Chodon, T.; Guo, R.; Johnson, D.B.; Dahlman, K.B.; et al. Acquired Resistance and Clonal Evolution in Melanoma during BRAF Inhibitor Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaviva, J.; Smith, D.L.; Jimenez, J.-P.; Zhang, C.; Sequeira, M.; He, S.; Sang, J.; Bates, R.C.; Proia, D.A. Overcoming Acquired BRAF Inhibitor Resistance in Melanoma via Targeted Inhibition of Hsp90 with Ganetespib. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greger, J.G.; Eastman, S.D.; Zhang, V.; Bleam, M.R.; Hughes, A.M.; Smitheman, K.N.; Dickerson, S.H.; Laquerre, S.G.; Liu, L.; Gilmer, T.M. Combinations of BRAF, MEK, and PI3K/mTOR Inhibitors Overcome Acquired Resistance to the BRAF Inhibitor GSK2118436 Dabrafenib, Mediated by NRAS or MEK Mutations. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.J.; Jha, S.; Restaino, C.R.; Dayananth, P.; Zhu, H.; Cooper, A.; Carr, D.; Deng, Y.; Jin, W.; Black, S.; et al. Discovery of a Novel ERK Inhibitor with Activity in Models of Acquired Resistance to BRAF and MEK Inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-P.; Li, X.-L.; Li, G.-H.; Chen, W.; Arakaki, C.; Botimer, G.D.; Baylink, D.; Zhang, L.; Wen, W.; Fu, Y.-W.; et al. Efficient precise knockin with a double cut HDR donor after CRISPR/Cas9-mediated double-stranded DNA cleavage. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orchard, R.C.; Wilen, C.B.; Doench, J.G.; Baldridge, M.T.; McCune, B.T.; Lee, Y.-C.J.; Lee, S.; Pruett-Miller, S.M.; Nelson, C.A.; Fremont, D.H.; et al. Discovery of a proteinaceous cellular receptor for a norovirus. Science 2016, 353, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holderfield, M.; Deuker, M.M.; McCormick, F.; McMahon, M. Targeting RAF kinases for cancer therapy: BRAF-mutated melanoma and beyond. Nat. Cancer 2014, 14, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murali, R.; Menzies, A.M.; Long, G. Dabrafenib and its potential for the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2012, 6, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Fung, C.; Menzies, A.M.; Pupo, G.M.; Carlino, M.S.; Hyman, J.; Shahheydari, H.; Tembe, V.; Thompson, J.F.; Saw, R.P.; et al. Increased MAPK reactivation in early resistance to dabrafenib/trametinib combination therapy of BRAF-mutant metastatic melanoma. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trunzer, K.; Pavlick, A.C.; Schuchter, L.; Gonzalez, R.; McArthur, G.A.; Hutson, T.E.; Moschos, S.J.; Flaherty, K.T.; Kim, K.B.; Weber, J.S.; et al. Pharmacodynamic Effects and Mechanisms of Resistance to Vemurafenib in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, C.M.; Vijayendran, K.G.; Zipser, M.C.; Sawyer, A.M.; Niu, L.; Kim, J.J.; Hatton, C.; Chopra, R.; Oberholzer, P.A.; Karpova, M.B.; et al. MEK1 mutations confer resistance to MEK and B-RAF inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20411–20416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarian, R.; Shi, H.; Wang, Q.; Kong, X.; Koya, R.C.; Lee, H.; Chen, Z.; Lee, M.-K.; Attar, N.; Sazegar, H.; et al. Melanomas acquire resistance to B-RAF(V600E) inhibition by RTK or N-RAS upregulation. Nature 2010, 468, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misale, S.; Yaeger, R.; Hobor, S.; Scala, E.; Janakiraman, M.; Liska, D.; Valtorta, E.; Schiavo, R.; Buscarino, M.; Siravegna, G.; et al. Emergence of KRAS mutations and acquired resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. Nature 2012, 486, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, R.; Broglie, J.J.; Adcock, A.F.; Yang, L. Three-Dimensional Cell Culture Systems and Their Applications in Drug Discovery and Cell-Based Biosensors. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.B. Three-dimensional tissue culture models in cancer biology. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2005, 15, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, G.; Hsiao, A.Y.; Ingram, M.; Luker, G.D.; Takayama, S. Opportunities and challenges for use of tumor spheroids as models to test drug delivery and efficacy. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederick, D.T.; Piris, A.; Cogdill, A.P.; Cooper, Z.A.; Lezcano, C.; Ferrone, C.R.; Mitra, D.; Boni, A.; Newton, L.P.; Liu, C.; et al. BRAF Inhibition Is Associated with Enhanced Melanoma Antigen Expression and a More Favorable Tumor Microenvironment in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Smalley, K.S.; Sosman, J.A. Molecular pathways: Targeting NRAS in melanoma and acute myelogenous leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4186–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lito, P.; Pratilas, C.A.; Joseph, E.W.; Tadi, M.; Halilovic, E.; Zubrowski, M.; Huang, A.; Wong, W.L.; Callahan, M.K.; Merghoub, T.; et al. Relief of Profound Feedback Inhibition of Mitogenic Signaling by RAF Inhibitors Attenuates Their Activity in BRAFV600E Melanomas. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Suyama, K.; Baba, H. Recent Advances in Targeting the EGFR Signaling Pathway for the Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, K.; Ota, K.; Kawahara, A.; Hattori, S.; Iwama, E.; Harada, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Takayama, K.; Takamori, S.; Kage, M.; et al. Association of PD-L1 overexpression with activating EGFR mutations in surgically resected nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1935–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, R.; Maeda, A.; Shimizu, K.; Nojima, Y.; Saisho, S.; Nakata, M. PD-L1 overexpression is partially regulated by EGFR/HER2 signaling and associated with poor prognosis in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2017, 66, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Fang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, S.; Kang, S.; Yan, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhan, J.; He, X.; Qin, T.; et al. The association between PD-L1 and EGFR status and the prognostic value of PD-L1 in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with EGFR-TKIs. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14209–14219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Cho, E.N.; Park, H.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Lim, S.; Ypun, J.P.; Hwang, S.Y.; Chang, Y.S. Compound EGFR mutation is frequently detected with co-mutations of actionable genes and associated with poor clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Shi, X.; Le, X.; Feng, F.; Chen, J.; Zhou, C.; Chen, Y.; Wen, S.; Zeng, H.; et al. A systematic and genome-wide correlation meta-analysis of PD-L1 expression and targetable NSCLC driver genes. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 2560–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischmann, T.O.; Smith, C.K.; Mayhood, T.W.; Myers, J.J.E.; Reichert, P.; Mannarino, A.; Carr, D.; Zhu, H.; Wong, J.; Yang, R.-S.; et al. Crystal Structures of MEK1 Binary and Ternary Complexes with Nucleotides and Inhibitors. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 2661–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordan, M.; Pallara, C.; Maik-Rachline, G.; Hanoch, T.; Gervasio, F.L.; Glaser, F.; Fernandez-Recio, J.; Seger, R. Intrinsically active MEK variants are differentially regulated by proteinases and phosphatases. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turner, E.; Chen, L.; Foulke, J.G.; Gu, Z.; Tian, F. CRISPR/Cas9 Edited RAS & MEK Mutant Cells Acquire BRAF and MEK Inhibitor Resistance with MEK1 Q56P Restoring Sensitivity to MEK/BRAF Inhibitor Combo and KRAS G13D Gaining Sensitivity to Immunotherapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215449
Turner E, Chen L, Foulke JG, Gu Z, Tian F. CRISPR/Cas9 Edited RAS & MEK Mutant Cells Acquire BRAF and MEK Inhibitor Resistance with MEK1 Q56P Restoring Sensitivity to MEK/BRAF Inhibitor Combo and KRAS G13D Gaining Sensitivity to Immunotherapy. Cancers. 2022; 14(21):5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215449
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurner, Elizabeth, Luping Chen, John G. Foulke, Zhizhan Gu, and Fang Tian. 2022. "CRISPR/Cas9 Edited RAS & MEK Mutant Cells Acquire BRAF and MEK Inhibitor Resistance with MEK1 Q56P Restoring Sensitivity to MEK/BRAF Inhibitor Combo and KRAS G13D Gaining Sensitivity to Immunotherapy" Cancers 14, no. 21: 5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215449
APA StyleTurner, E., Chen, L., Foulke, J. G., Gu, Z., & Tian, F. (2022). CRISPR/Cas9 Edited RAS & MEK Mutant Cells Acquire BRAF and MEK Inhibitor Resistance with MEK1 Q56P Restoring Sensitivity to MEK/BRAF Inhibitor Combo and KRAS G13D Gaining Sensitivity to Immunotherapy. Cancers, 14(21), 5449. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215449







