Nuclear Membrane Protein SUN5 Is Highly Expressed and Promotes Proliferation and Migration in Colorectal Cancer by Regulating the ERK Pathway
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.2. Collection of Tissue Samples
2.3. Overexpression of SUN5
2.4. Knockdown of SUN5
2.5. Silencing of Nesprin2
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.8. Cell-Proliferation Assays
2.9. Colony-Formation Assays
2.10. Wound-Healing Assay
2.11. Transwell Assay
2.12. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) Using RNA-Seq
2.13. Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analyses
2.14. Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Fractionation
2.15. Cell Immunofluorescence Assay
2.16. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
2.17. Inhibition of pERK1/2 Level with PD0325901
2.18. Tumor Xenograft
3. Results
3.1. SUN5 Is Highly Expressed in Colorectal Cancer Tissues and Cells
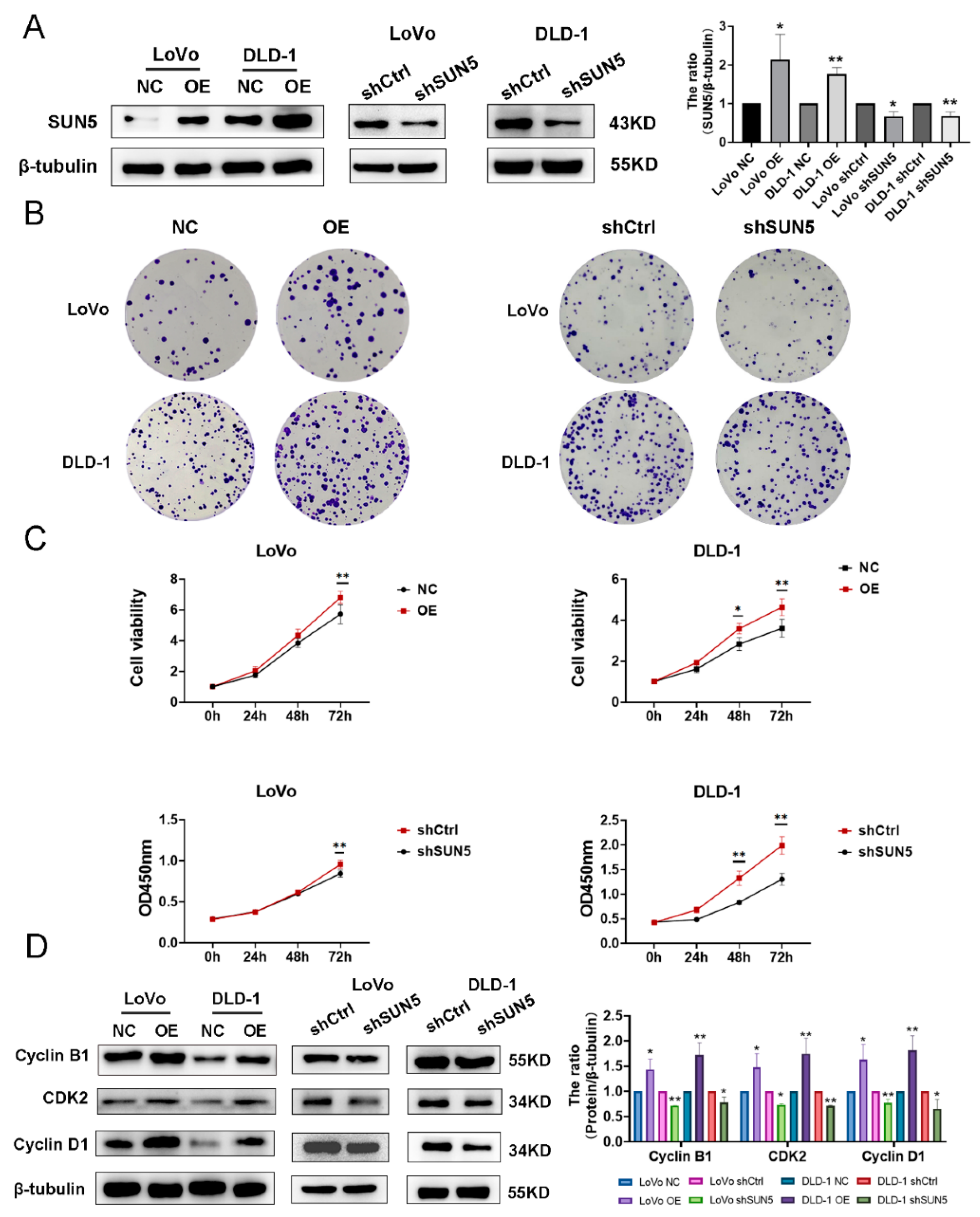
3.2. SUN5 Promotes the Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer Cells
3.3. SUN5 Promotes the Migration of Colorectal Cancer Cells
3.4. SUN5 Regulates the ERK Pathway in Colorectal Cancer
3.5. Overexpression of SUN5 Attenuates the Effect of PD0325901 on Colorectal Cancer Cells
3.6. SUN5 Accelerates Tumor Growth In Vivo
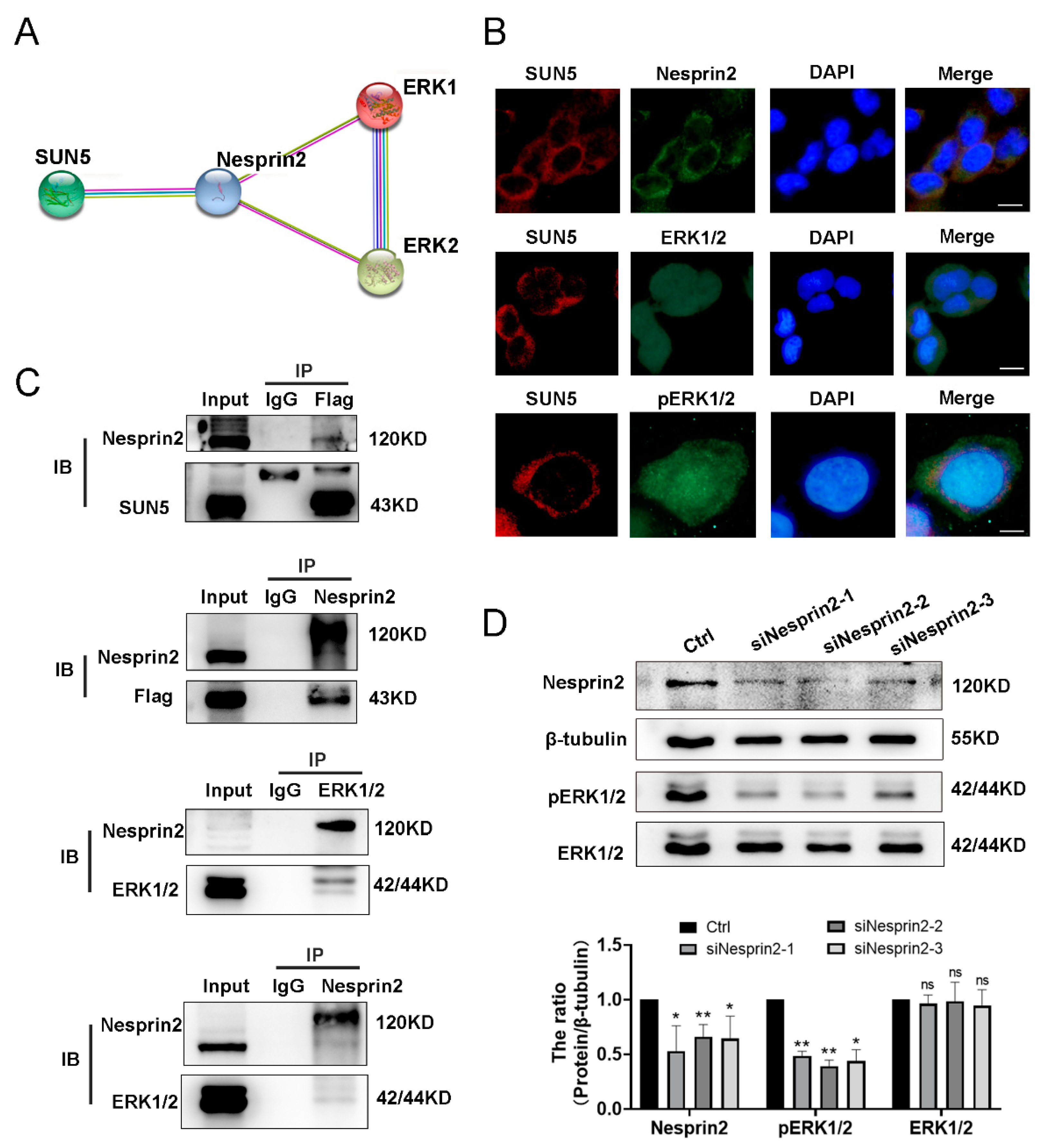
3.7. SUN5 Promotes the ERK Pathway via Nesprin2 Mediation
3.8. SUN5 Promotes Phosphorylated ERK Nuclear Translocation by Interacting with Nup93
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, K.; Chen, R.; Li, L.; Wei, W.; He, J. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2016. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2022, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Chen, H.D.; Yu, Y.W.; Li, N.; Chen, W.Q. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: A secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, K.H.; Factor, R.E.; Ullman, K.S. The nuclear envelope environment and its cancer connections. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.B.; Liu, L.; Cheng, C.; Yu, B.; Xiong, L.; Hu, K.; Tang, J.; Zeng, L.; Sang, Y. SUN2 exerts tumor suppressor functions by suppressing the Warburg effect in lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, Y.; Imaizumi, H.; Imada, J.; Katahira, J.; Matsuura, N.; Hieda, M. SUN1 splice variants, SUN1_888, SUN1_785, and predominant SUN1_916, variably function in directional cell migration. Nucleus 2016, 7, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Du, X.; Cai, Z.; Greene, M.I. Characterization of the structures involved in localization of the SUN proteins to the nuclear envelope and the centrosome. DNA Cell Biol. 2006, 25, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Guttinger, S.; Muhlhausser, P.; Anderegg, F.; Burgler, S.; Kutay, U. Nuclear envelope localization of human UNC84A does not require nuclear lamins. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.Z.; Yang, M.G.; Huang, L.H.; Li, C.Q.; Xing, X.W. SPAG4L, a novel nuclear envelope protein involved in the meiotic stage of spermatogenesis. DNA Cell Biol. 2011, 30, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodzic, D.M.; Yeater, D.B.; Bengtsson, L.; Otto, H.; Stahl, P.D. Sun2 is a novel mammalian inner nuclear membrane protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25805–25812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Hieda, M.; Yokoyama, Y.; Nishioka, Y.; Yoshidome, K.; Tsujimoto, M.; Matsuura, N. Global loss of a nuclear lamina component, lamin A/C, and LINC complex components SUN1, SUN2, and nesprin-2 in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, S.W.; Yuan, W.; Tang, J.; Sang, Y. Downregulation of SUN2 promotes metastasis of colon cancer by activating BDNF/TrkB signalling by interacting with SIRT1. J. Pathol. 2021, 254, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaup, K.X.; Monti, J.; Hackenbeck, T.; Jobst-Schwan, T.; Klanke, B.; Schietke, R.E.; Wacker, I.; Behrens, J.; Amann, K.; Eckardt, K.U.; et al. Hypoxia regulates the sperm associated antigen 4 (SPAG4) via HIF, which is expressed in renal clear cell carcinoma and promotes migration and invasion in vitro. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Jiang, J.; Huang, L.; Feng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, L.; Xing, X. Spermassociated antigen 4 (SPAG4) as a new cancer marker interacts with Nesprin3 to regulate cell migration in lung carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Yu, J.; Ge, C.; Zhao, F.; Chen, J.; Miao, C.; Jin, W.; Zhou, Q.; Geng, Q.; Lin, H.; et al. Sperm associated antigen 4 promotes SREBP1-mediated de novo lipogenesis via interaction with lamin A/C and contributes to tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2022, 536, 215642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, X.W.; Li, L.Y.; Liu, G.; Fu, J.J.; Tan, X.J.; Lu, G.X. Identification of a novel gene SRG4 expressed at specific stages of mouse spermatogenesis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2004, 36, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, L.; Liu, G.; Nie, X.; Zhang, X.; Xing, X. SUN5 Interacting With Nesprin3 Plays an Essential Role in Sperm Head-to-Tail Linkage: Research on Sun5 Gene Knockout Mice. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 684826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.L.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Deng, B.; Zhu, B.S.; Cao, T.; Li, Y.K.; Xiao, J.; Han, Q.; Wu, Q. Colorectal cancer (CRC) as a multifactorial disease and its causal correlations with multiple signaling pathways. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20200265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koveitypour, Z.; Panahi, F.; Vakilian, M.; Peymani, M.; Seyed Forootan, F.; Nasr Esfahani, M.H.; Ghaedi, K. Signaling pathways involved in colorectal cancer progression. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.Y.; Richardson, B.C. The MAPK signalling pathways and colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, H.; Gagnon, J.; Therrien, M. ERK signalling: A master regulator of cell behaviour, life and fate. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 607–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, D.T.; Tajsic, T.; Mellad, J.A.; Searles, R.; Zhang, Q.; Shanahan, C.M. Novel nuclear nesprin-2 variants tether active extracellular signal-regulated MAPK1 and MAPK2 at promyelocytic leukemia protein nuclear bodies and act to regulate smooth muscle cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsenovic, P.T.; Ramachandran, I.; Bathula, K.; Zhu, R.; Narang, J.D.; Noll, N.A.; Lemmon, C.A.; Gundersen, G.G.; Conway, D.E. Nesprin-2G, a Component of the Nuclear LINC Complex, Is Subject to Myosin-Dependent Tension. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustino, R.S.; Maddaford, T.G.; Pierce, G.N. Mitogen activated protein kinase at the nuclear pore complex. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lin, D.H.; Hoelz, A. The Structure of the Nuclear Pore Complex (An Update). Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 725–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataraj, N.B.; Noronha, A.; Lee, J.S.; Ghosh, S.; Mohan Raju, H.R.; Sekar, A.; Zuckerman, B.; Lindzen, M.; Tarcitano, E.; Srivastava, S.; et al. Nucleoporin-93 reveals a common feature of aggressive breast cancers: Robust nucleocytoplasmic transport of transcription factors. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Li, C.R.; He, Q.F.; Li, X.H.; Yang, L.F.; Zou, Y.; Yang, Z.X.; Zhang, D.; Xing, X.W. Downregulation of the ubiquitin ligase KBTBD8 prevented epithelial ovarian cancer progression. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolillo, M.; Schinelli, S. Extracellular Matrix Alterations in Metastatic Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, L.; She, X.; Zhou, G.; Yu, F.; Xiang, J.; Li, G. Inhibiting CD164 expression in colon cancer cell line HCT116 leads to reduced cancer cell proliferation, mobility, and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Investig. 2012, 30, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, J. Silencing of cytoskeleton-associated protein 2 represses cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atienza, J.M.; Roth, R.B.; Rosette, C.; Smylie, K.J.; Kammerer, S.; Rehbock, J.; Ekblom, J.; Denissenko, M.F. Suppression of RAD21 gene expression decreases cell growth and enhances cytotoxicity of etoposide and bleomycin in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubaki, M.; Takeda, T.; Noguchi, M.; Jinushi, M.; Seki, S.; Morii, Y.; Shimomura, K.; Imano, M.; Satou, T.; Nishida, S. Overactivation of Akt Contributes to MEK Inhibitor Primary and Acquired Resistance in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieda, M. Signal Transduction across the Nuclear Envelope: Role of the LINC Complex in Bidirectional Signaling. Cells 2019, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweifel, M.E.; Courtemanche, N. A LINC between the nucleus and the cytoskeleton takes form(in). Structure 2021, 29, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.H.; Chien, C.L.; Lee, Y.H.; Lin, C.I.; Hsieh, J.Y.; Chao, M.E.; Liu, D.J.; Chu, S.S.; Chen, W.; Lin, S.C.; et al. Downregulation of SUN2, a novel tumor suppressor, mediates miR-221/222-induced malignancy in central nervous system embryonal tumors. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2164–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.A.; Tang, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, Q. Human sperm-associated antigen 4 as a potential biomarker of glioblastoma progression and prognosis. Neuroreport 2019, 30, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, C.; Sebire, K.; de Kretser, D.M.; O’Bryan, M.K. Human sperm associated antigen 4 (SPAG4) is a potential cancer marker. Cell Tissue Res. 2004, 315, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkura, H. Meiosis: An overview of key differences from mitosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a015859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuderland, D.; Konson, A.; Seger, R. Identification and characterization of a general nuclear translocation signal in signaling proteins. Mol. Cell 2008, 31, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maik-Rachline, G.; Hacohen-Lev-Ran, A.; Seger, R. Nuclear ERK: Mechanism of Translocation, Substrates, and Role in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.S.; Liang, Y.; Su, S.G.; Zheng, Y.L.; Yang, X.; Jiang, N.; Fu, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, R.; et al. Nucleoporin 93 mediates beta-catenin nuclear import to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2022, 526, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, X.; Li, R.; Liu, G.; Huang, L.; Li, P.; Feng, W.; Gao, Q.; Xing, X. Nuclear Membrane Protein SUN5 Is Highly Expressed and Promotes Proliferation and Migration in Colorectal Cancer by Regulating the ERK Pathway. Cancers 2022, 14, 5368. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215368
Song X, Li R, Liu G, Huang L, Li P, Feng W, Gao Q, Xing X. Nuclear Membrane Protein SUN5 Is Highly Expressed and Promotes Proliferation and Migration in Colorectal Cancer by Regulating the ERK Pathway. Cancers. 2022; 14(21):5368. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215368
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Xiaoyue, Ruhong Li, Gang Liu, Lihua Huang, Peng Li, Wanjiang Feng, Qiujie Gao, and Xiaowei Xing. 2022. "Nuclear Membrane Protein SUN5 Is Highly Expressed and Promotes Proliferation and Migration in Colorectal Cancer by Regulating the ERK Pathway" Cancers 14, no. 21: 5368. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215368
APA StyleSong, X., Li, R., Liu, G., Huang, L., Li, P., Feng, W., Gao, Q., & Xing, X. (2022). Nuclear Membrane Protein SUN5 Is Highly Expressed and Promotes Proliferation and Migration in Colorectal Cancer by Regulating the ERK Pathway. Cancers, 14(21), 5368. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215368






