Molecularly Targeted Photothermal Ablation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Expressing Cancer Cells with a Polypyrrole–Iron Oxide–Afatinib Nanocomposite
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Material Synthesis
2.2.2. In Vitro Methods
2.2.3. Characterization of NCs
2.2.4. Photothermal Properties of NCs
2.2.5. In Vitro Cellular Uptake
2.2.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
2.2.7. In Vitro ROS Generation by NC
2.2.8. Assessment of Apoptosis
2.2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
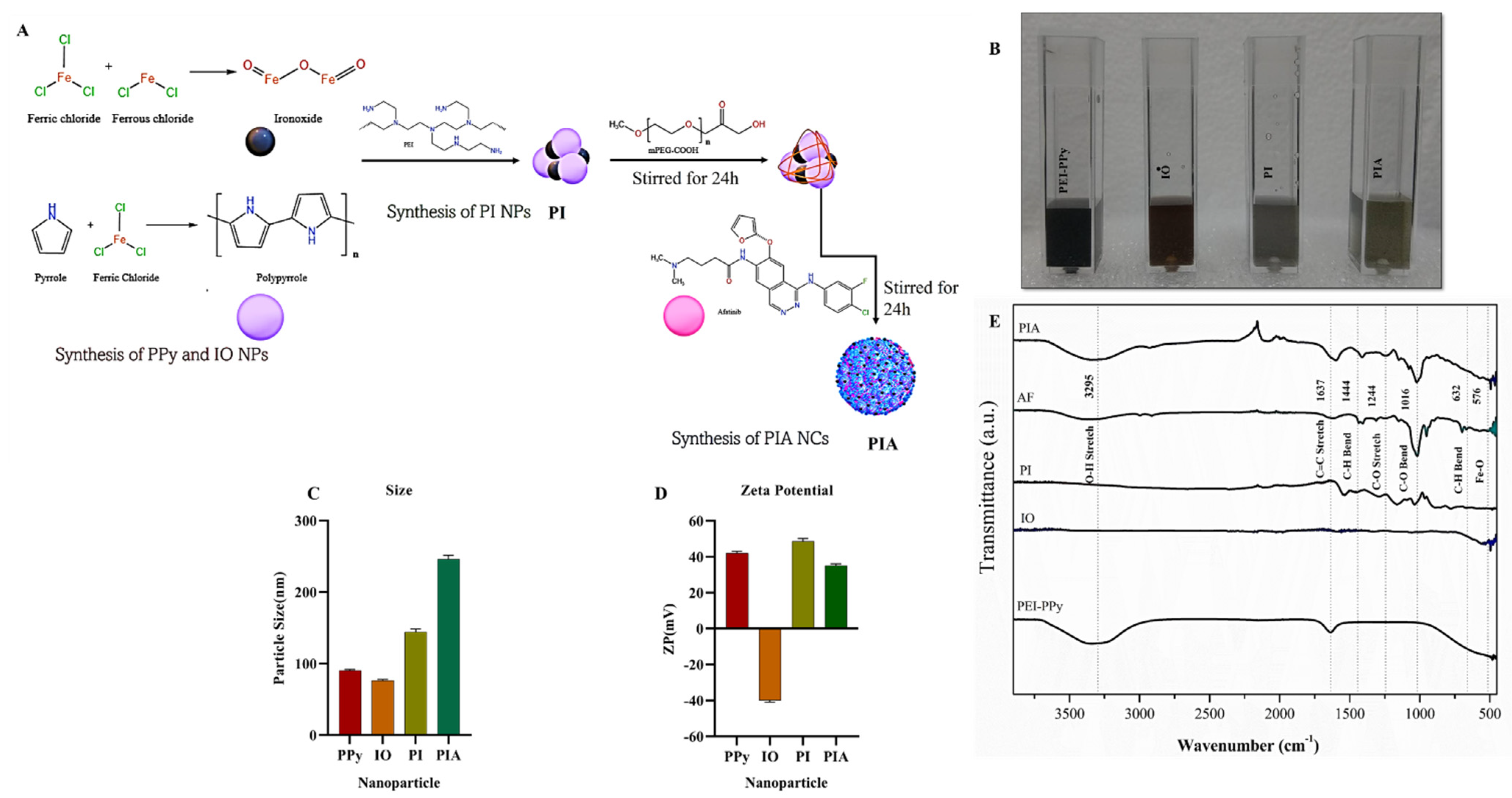
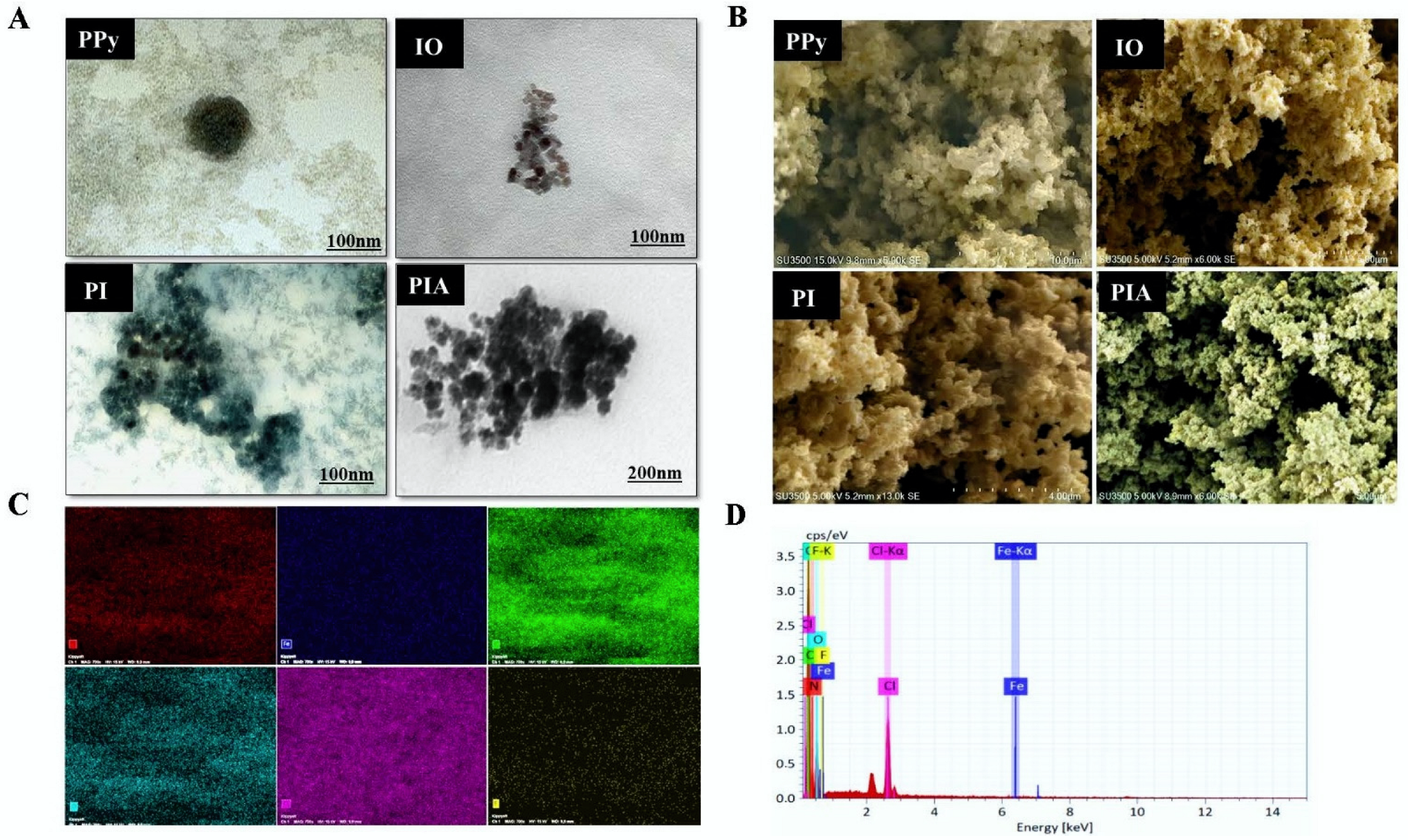
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of PIA NC
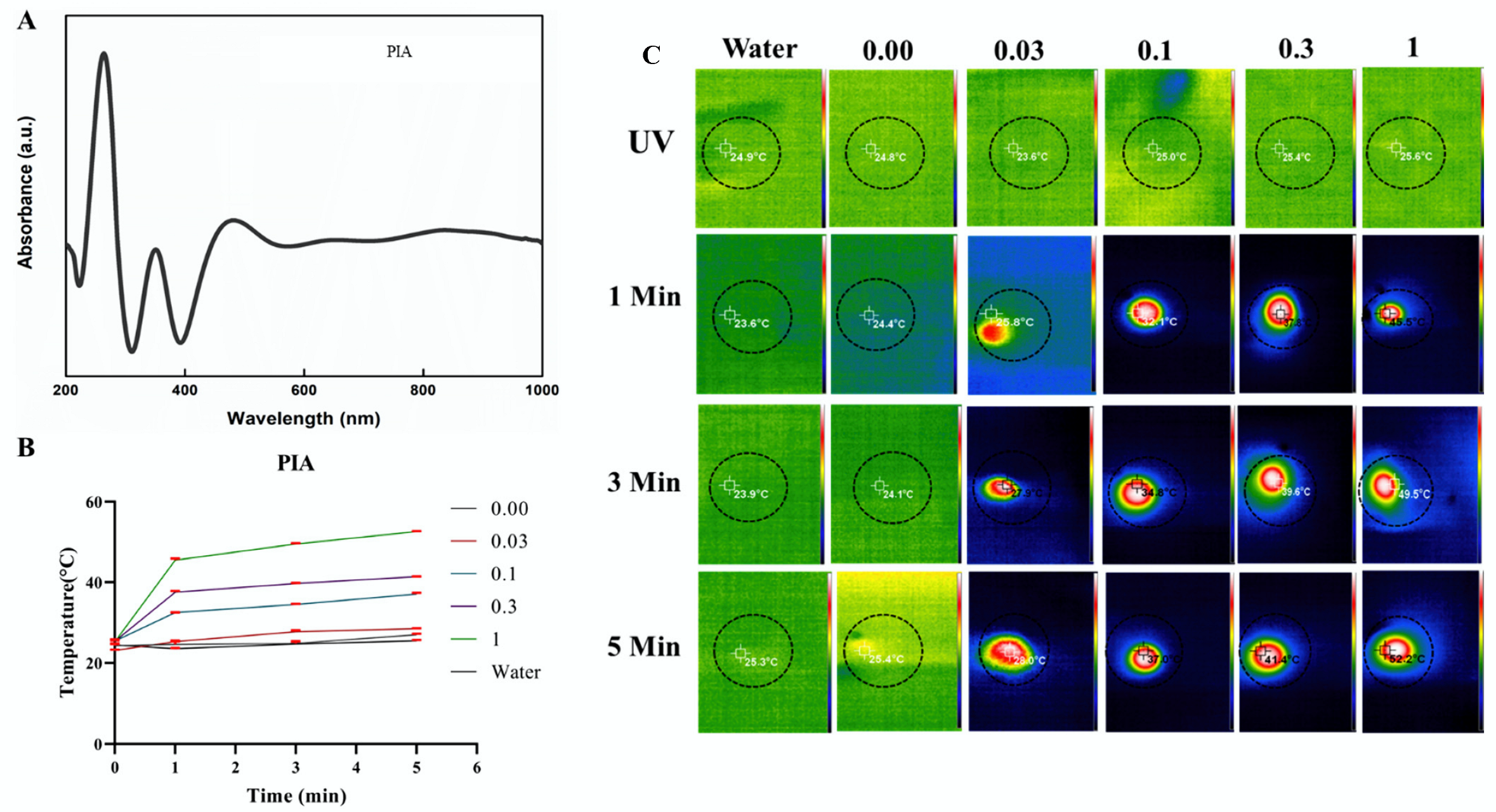
3.2. Photothermal Studies
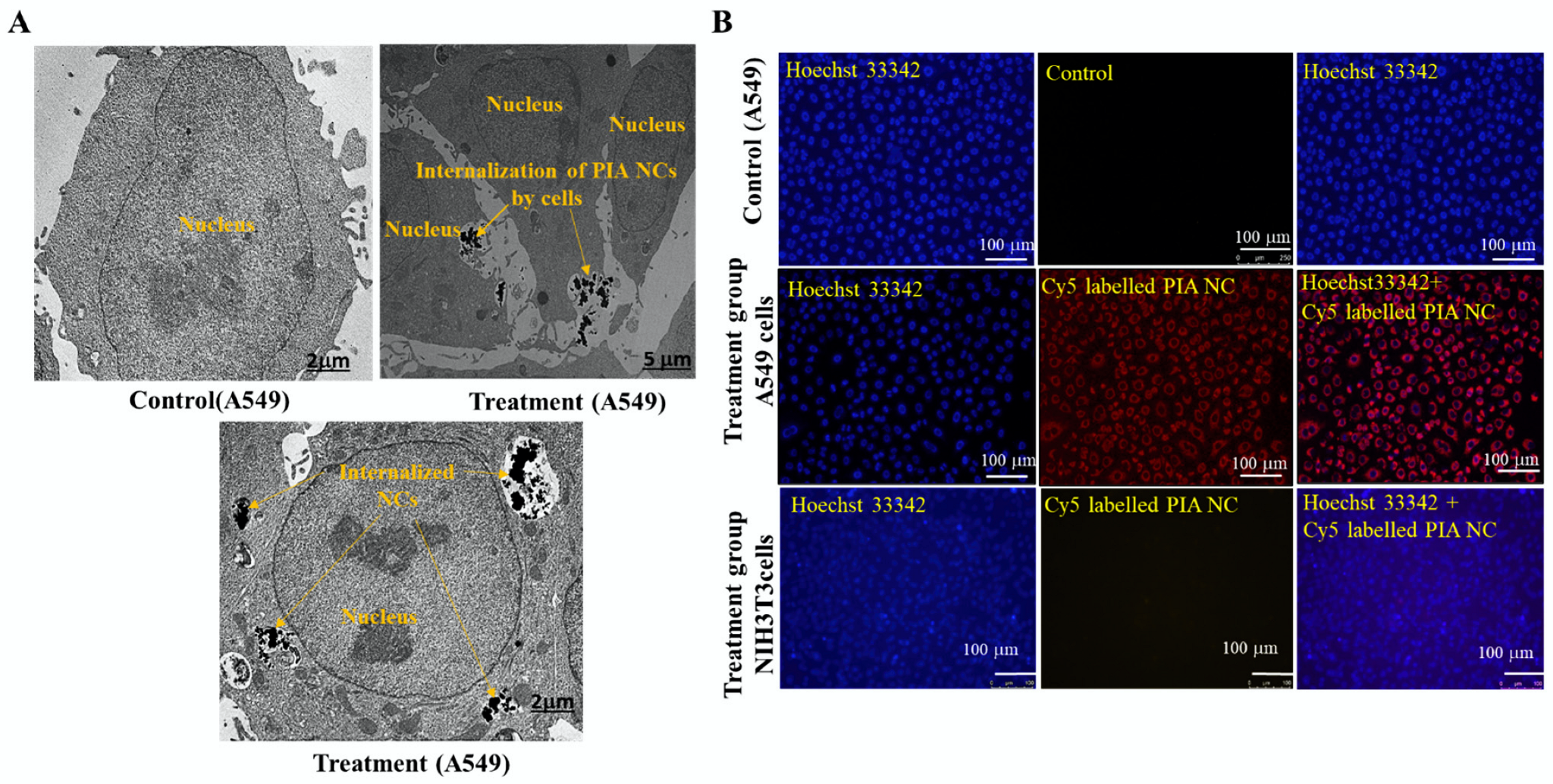
3.3. In Vitro Cellular Uptake
3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
3.5. ROS Generation by PIA NCs
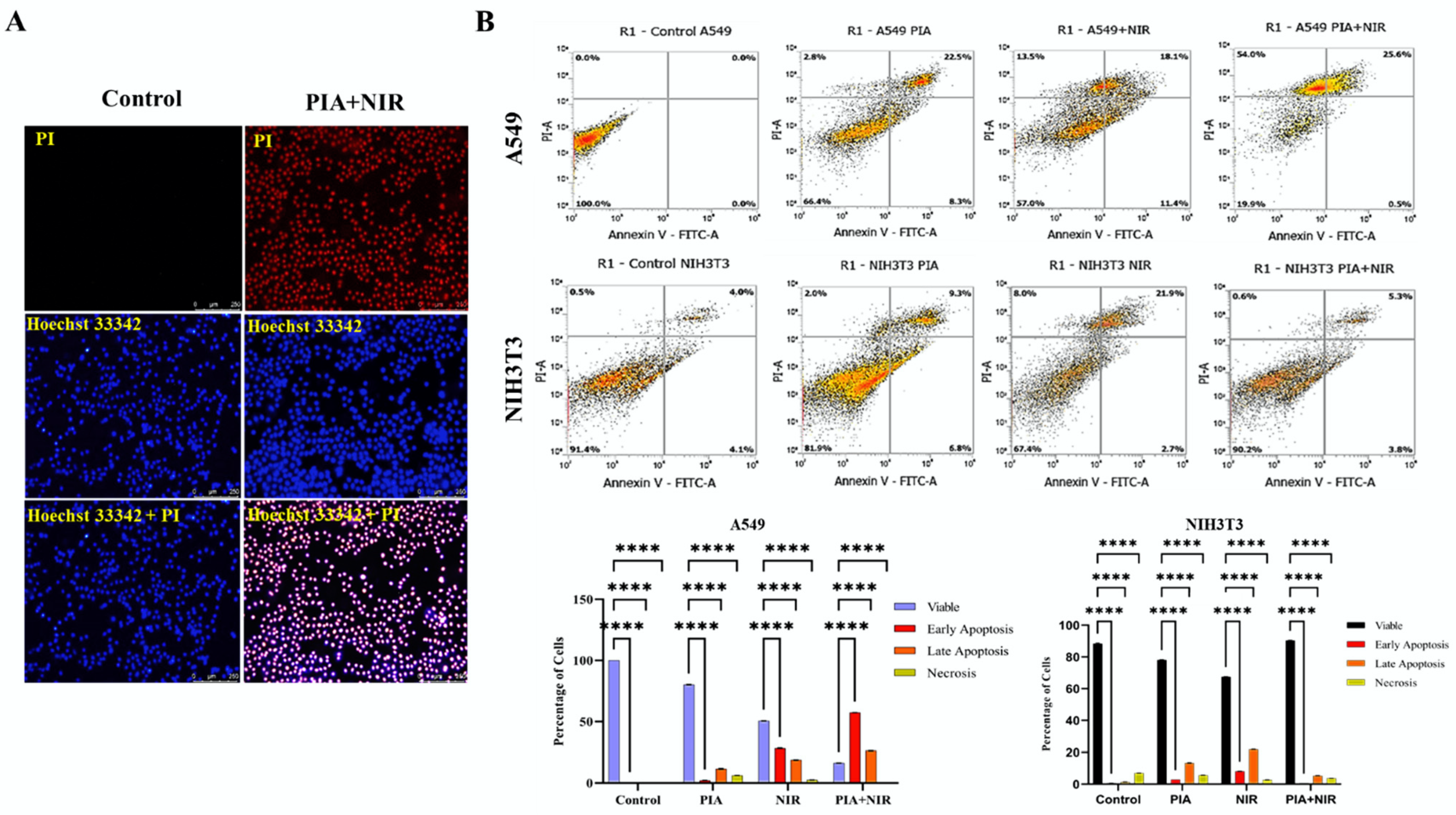
3.6. Apoptosis Induced by NCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cancer.Net. Lung Cancer—Non-Small Cell—Statistics. Available online: https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/lung-cancer-non-small-cell/statistics#:~:text=Worldwide%2C%20lung%20cancer%20is%20the,be%20diagnosed%20with%20lung%20cancer (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Tomasini, P.; Brosseau, S.; Mazières, J.; Merlio, J.-P.; Beau-Faller, M.; Mosser, J.; Wislez, M.; Ouafik, L.H.; Besse, B.; Rouquette, I. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors versus chemotherapy in EGFR wild-type pre-treated advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer in daily practice. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zöchbauer-Müller, S.; Kaserer, B.; Prosch, H.; Cseh, A.; Solca, F.; Bauer, M.J.; Müllauer, L. Case report: Afatinib treatment in a patient with NSCLC harboring a rare EGFR exon 20 mutation. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 593852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solca, F.; Dahl, G.; Zoephel, A.; Bader, G.; Sanderson, M.; Klein, C.; Kraemer, O.; Himmelsbach, F.; Haaksma, E.; Adolf, G.R. Target binding properties and cellular activity of afatinib (BIBW 2992), an irreversible ErbB family blocker. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 343, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, N. Optimizing outcomes in EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC: Which tyrosine kinase inhibitor and when? Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, R.D.; Adams, V.R.; Beardslee, T.; Medina, P. Afatinib for the treatment of EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC: A review of clinical findings. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 26, 1461–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Zhang, X.-c.; Yan, H.-h.; Yang, J.-j.; Wu, Y.-l. Efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors versus chemotherapy as second-line treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with wild-type EGFR: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Lung Cancer 2014, 85, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Mulshine, J.L.; Kwon, R.; Curran Jr, W.J.; Wu, Y.-L.; Paz-Ares, L. Lung cancer: Current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 2017, 389, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Jiang, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, Q.; Chen, B.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Song, W. TAZ sensitizes EGFR wild-type non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib by promoting amphiregulin transcription. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Naylor, M.F.; Le, H.; Nordquist, R.E.; Teague, T.K.; Howard, C.A.; Murray, C.; Chen, W.R. Clinical effects of in situ photoimmunotherapy on late-stage melanoma patients: A preliminary study. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, L.; Liang, C.; Wang, C.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Photothermal therapy with immune-adjuvant nanoparticles together with checkpoint blockade for effective cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.targetedonc.com/view/immunotherapy-versus-targeted-therapywhich-has-greater-impact-in-nsclc (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Peyret, A.; Ibarboure, E.; Pippa, N.; Lecommandoux, S. Liposomes in polymersomes: Multicompartment system with temperature-triggered release. Langmuir 2017, 33, 7079–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, S.M.; Bachelet, I.; Church, G.M. A logic-gated nanorobot for targeted transport of molecular payloads. Science 2012, 335, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuller, V.J.; Heidegger, S.; Sandholzer, N.; Nickels, P.C.; Suhartha, N.A.; Endres, S.; Bourquin, C.; Liedl, T. Cellular immunostimulation by CpG-sequence-coated DNA origami structures. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 9696–9702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigderman, L.; Khanal, B.P.; Zubarev, E.R. Functional gold nanorods: Synthesis, self-assembly, and sensing applications. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4811–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde, J.; Oliva, N.; Zhang, Y.; Artzi, N. Local triple-combination therapy results in tumour regression and prevents recurrence in a colon cancer model. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cui, W.; Qu, X.; Wu, H.; Qu, L.; Zhang, X.; Mäkilä, E.; Salonen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Z. Photothermal-responsive nanosized hybrid polymersome as versatile therapeutics codelivery nanovehicle for effective tumor suppression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7744–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Yu, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, A.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, H.; et al. A NIR-I light-responsive superoxide radical generator with cancer cell membrane targeting ability for enhanced imaging-guided photodynamic therapy. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 10279–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, S.; Ding, B.; Qu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Sun, Y.; Fang, H.; Long, Y.; Zhang, R. Cancer cell membrane-coated rare earth doped nanoparticles for tumor surgery navigation in NIR-II imaging window. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.; Wang, J.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Cheng, K. Biomimetic metal–organic framework nanoparticles for cooperative combination of antiangiogenesis and photodynamic therapy for enhanced efficacy. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhen, X.; Lyu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, J.; Pu, K. Cell membrane coated semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for enhanced multimodal cancer phototheranostics. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 8520–8530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-H.; You, S.; Taghizadeh, A.; Taghizadeh, M.; Kim, H.S. Cell Membrane-Cloaked Nanotherapeutics for Targeted Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh, A.; Taghizadeh, M.; Sabzehmeidani, M.M.; Sadeghfar, F.; Ghaedi, M. Chapter 1—Electronic structure: From basic principles to photocatalysis. In Interface Science and Technology; Ghaedi, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 32, pp. 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Sheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H. Ultrathin polypyrrole nanosheets via space-confined synthesis for efficient photothermal therapy in the second near-infrared window. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 2217–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, J.; Wu, C.; Ye, C.; Huang, M.; Wang, S. Preparation of injectable temperature-sensitive chitosan-based hydrogel for combined hyperthermia and chemotherapy of colon cancer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.-Y.; Jheng, P.-R.; Lu, L.-S.; Rethi, L.; Mi, F.-L.; Chuang, E.-Y. Enhanced anticancer effect of ROS-boosted photothermal therapy by using fucoidan-coated polypyrrole nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, E.D.; Lu, T.-Y.; Liu, K.-T.; Fan, Y.-J.; Chuang, E.-Y.; Yu, J. Glycol chitosan/iron oxide/polypyrrole nanoclusters for precise chemodynamic/photothermal synergistic therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 203, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liang, C.; Feng, L.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z. Iodine-131-labeled, transferrin-capped polypyrrole nanoparticles for tumor-targeted synergistic photothermal-radioisotope therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: Synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, S.; Xie, P. Preparation of electrospray ALG/PDA–PVP nanocomposites and their application in cancer therapy. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.-P.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, X.-C.; Ji, S.-C.; Tan, X.-Y.; Cheng, L.; Liang, H. Water-soluble hyaluronic acid–hybridized polyaniline nanoparticles for effectively targeted photothermal therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 3767–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, Y. Solutions to the drawbacks of photothermal and photodynamic cancer therapy. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Duan, X.; Guan, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, F.; Huang, P.; Shen, J.; Shuai, X.; Cao, Z. Mesoporous polydopamine carrying manganese carbonyl responds to tumor microenvironment for multimodal imaging-guided cancer therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, S.-Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Gu, D.; Yang, W.; Tang, W.; Liu, F. Integration of cascade delivery and tumor hypoxia modulating capacities in core-releasable satellite nanovehicles to enhance tumor chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2019, 223, 119465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Tang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, H. PEGylated polypyrrole–gold nanocomplex as enhanced photothermal agents against tumor cells. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 5587–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, F.; Jia, Q.; Xue, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Ge, J.; Wang, P. Iron phthalocyanine-derived nanozyme as dual reactive oxygen species generation accelerator for photothermally enhanced tumor catalytic therapy. Biomaterials 2022, 284, 121495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Nanocatalytic medicine. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-based nanomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4881–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-L.; Huang, P.-Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; Shi, Q.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.-H.; Zhang, X.-Z. A self-delivery chimeric peptide for high efficient cell membrane-targeting low-temperature photothermal/photodynamic combinational therapy and metastasis suppression of tumor. Biomaterials 2022, 286, 121593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, E.A.; Pinto, D.V.B.S.; Oliveira, J.I.S.d.; Mattos, E.d.C.; Dutra, R.d.C.L. Synthesis, characterization and applications of iron oxide nanoparticles-a short review. J. Aerosp. Technol. Manag. 2015, 7, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Fang, X.; Tang, S.; Zheng, N. Polypyrrole nanoparticles for high-performance in vivo near-infrared photothermal cancer therapy. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8934–8936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Liang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, G.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Iron oxide@ polypyrrole nanoparticles as a multifunctional drug carrier for remotely controlled cancer therapy with synergistic antitumor effect. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6782–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Gong, H.; Yin, S.; Cheng, L.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Liu, Z. Ultra-small iron oxide doped polypyrrole nanoparticles for in vivo multimodal imaging guided photothermal therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xu, H.; Cheng, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. In vitro and in vivo near-infrared photothermal therapy of cancer using polypyrrole organic nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5586–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.-W.; Chuang, E.-Y. Biofunctional core-shell polypyrrole–polyethylenimine nanocomplex for a locally sustained photothermal with reactive oxygen species enhanced therapeutic effect against lung cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, K.; Huang, J.; Xiao, K. Uptake, distribution, clearance, and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles with different sizes and coatings. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Absolute Mag™ PEI Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles, n.-C.B.; Absolute Mag™ PEI Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles, n.-C.B.R.M. Available online: https://www.cd-bioparticles.com/p/Absolute-Mag%E2%84%A2-PEI-Coated-Iron-Oxide-Nanoparticles-20-nm_20_197_197_4992.html (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Attia, M.F.; Anton, N.; Khan, I.U.; Serra, C.A.; Messaddeq, N.; Jakhmola, A.; Vecchione, R.; Vandamme, T. One-step synthesis of iron oxide polypyrrole nanoparticles encapsulating ketoprofen as model of hydrophobic drug. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 508, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodipo, B.K.; Azlan, A.A. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles incorporated into silica nanoparticles by inelastic collision via ultrasonic field: Role of colloidal stability. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbatanony, R.S.; Parvathaneni, V.; Kulkarni, N.S.; Shukla, S.K.; Chauhan, G.; Kunda, N.K.; Gupta, V. Afatinib-loaded inhalable PLGA nanoparticles for localized therapy of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)—Development and in-vitro efficacy. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.; Ahmad, T.; Rhee, I.; Chang, Y.; Jin, S.-U.; Hong, S. Carbon-coated iron oxide nanoparticles as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, A.; Khasim, S.; Darwish, A.; Hamdalla, T.A.; Al-Ghamdi, S. High Performance Organic Coatings of Polypyrrole Embedded with Manganese Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Corrosion Protection of Conductive Copper Surface. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 32, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lett, J.A.; Sagadevan, S.; Alshahateet, S.F.; Murugan, B.; Jasni, A.H.; Fatimah, I.; Hossain, M.M.; Mohammad, F.; Oh, W.C. Synthesis and characterization of polypyrrole-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 025007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Z.; Yue, X.; Ren, Q.; Dai, Z. Uniform polypyrrole nanoparticles with high photothermal conversion efficiency for photothermal ablation of cancer cells. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Perez, L.; Rizzello, L.; Wang, J.; Li, N.; Battaglia, G.; Pei, Y. Polypyrrole and polyaniline nanocomposites with high photothermal conversion efficiency. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 4569–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.T.V.; Bui, N.Q.; Moorthy, M.S.; Lee, K.D.; Oh, J. Synthesis and in vitro performance of polypyrrole-coated iron–platinum nanoparticles for photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjigian, Y.; Groen, H.; Horn, L.; Smit, E.; Fu, Y.; Wang, F.; Shahidi, M.; Denis, L.; Pao, W.; Miller, V. Activity and tolerability of afatinib (BIBW 2992) and cetuximab in NSCLC patients with acquired resistance to erlotinib or gefitinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 7525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Chen, H.-Y.; Harris, I.S.; Stover, D.G.; Selfors, L.M.; Bronson, R.T.; Deraedt, T.; Cichowski, K.; Welm, A.L.; Mori, Y. Cancer cells co-opt the neuronal redox-sensing channel TRPA1 to promote oxidative-stress tolerance. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 985–1003.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, J.C.; Catalá, C.; Navalon, S.; Ferrer, B.; Álvaro, M.; Garcia, H. Iron oxide nanoparticles supported on diamond nanoparticles as efficient and stable catalyst for the visible light assisted Fenton reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 226, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaye, R.; Zhao, J.; Bowman, L.; Ding, M. Genotoxicity and carcinogenicity of cobalt-, nickel-and copper-based nanoparticles. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 4, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.-D.; Yang, W.-X. Engineered nanoparticles induce cell apoptosis: Potential for cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Kronenberger, P.; Teugels, E.; Umelo, I.A.; De Grève, J. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer cells: The effect of combining RNA interference with tyrosine kinase inhibitors or cetuximab. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, Y.; Shen, X.; Jin, C.; Sun, Q.; Li, H. A wood–polypyrrole composite as a photothermal conversion device for solar evaporation enhancement. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 20706–20712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikhari, B.; Mani, S.P.; Rajendran, N. Electrochemical behavior of polypyrrole/chitosan composite coating on Ti metal for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, R.; Sundarrajan, S.; Venugopal, J.R.; Mukherjee, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Applications of conducting polymers and their issues in biomedical engineering. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, S559–S579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulińska-Litewka, J.; Łazarczyk, A.; Hałubiec, P.; Szafrański, O.; Karnas, K.; Karewicz, A. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles—Current and prospective medical applications. Materials 2019, 12, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.-I.; Lu, T.-Y.; Chang, S.-H.; Shen, M.-Y.; Chiu, H.-C. Dual stimuli-guided lipid-based delivery system of cancer combination therapy. J. Control. Release 2020, 318, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Wan-Teck Lim, D.; Okamoto, I.; Yang, J.C.-H. First-line afatinib for the treatment of EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the ‘real-world’clinical setting. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919836374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Kobayashi, Y. Afatinib in lung cancer harboring EGFR mutation in the LUX-Lung trials: Six plus three is greater than seven? Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroozandeh, P.; Aziz, A.A. Insight into cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking of nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, B.; Parvathaneni, V.; Kulkarni, N.S.; Shukla, S.K.; Damon, J.K.; Sarode, A.; Kanabar, D.; Garcia, J.V.; Mitragotri, S.; Muth, A. Cyclodextrin modified erlotinib loaded PLGA nanoparticles for improved therapeutic efficacy against non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, S.; Serpooshan, V.; Tao, W.; Hamaly, M.A.; Alkawareek, M.Y.; Dreaden, E.C.; Brown, D.; Alkilany, A.M.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Mahmoudi, M. Cellular uptake of nanoparticles: Journey inside the cell. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4218–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toy, R.; Roy, K. Engineering nanoparticles to overcome barriers to immunotherapy. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2016, 1, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panariti, A.; Miserocchi, G.; Rivolta, I. The effect of nanoparticle uptake on cellular behavior: Disrupting or enabling functions? Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2012, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coelho, S.C.; Almeida, G.M.; Pereira, M.C.; Santos-Silva, F.; Coelho, M.A. Functionalized gold nanoparticles improve afatinib delivery into cancer cells. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lin, Y.H.; Yang, L.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.C.; Chen, G.W.; Yan, J.; Sawettanun, S.; Lin, C.H. Improved anticancer photothermal therapy using the bystander effect enhanced by antiarrhythmic peptide conjugated dopamine-modified reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1600804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Xie, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Tang, W.; Yang, W.; Yu, X.; Liu, H. PEGylated polyethylenimine-stabilized polypyrrole nanoparticles loaded with DOX for chemo-photothermal therapy of cancer cells. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2018, 20, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redza-Dutordoir, M.; Averill-Bates, D.A. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 2977–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rethi, L.; Mutalik, C.; Rethi, L.; Chiang, W.-H.; Lee, H.-L.; Pan, W.-Y.; Yang, T.-S.; Chiou, J.-F.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chuang, E.-Y.; et al. Molecularly Targeted Photothermal Ablation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Expressing Cancer Cells with a Polypyrrole–Iron Oxide–Afatinib Nanocomposite. Cancers 2022, 14, 5043. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205043
Rethi L, Mutalik C, Rethi L, Chiang W-H, Lee H-L, Pan W-Y, Yang T-S, Chiou J-F, Chen Y-J, Chuang E-Y, et al. Molecularly Targeted Photothermal Ablation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Expressing Cancer Cells with a Polypyrrole–Iron Oxide–Afatinib Nanocomposite. Cancers. 2022; 14(20):5043. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205043
Chicago/Turabian StyleRethi, Lekshmi, Chinmaya Mutalik, Lekha Rethi, Wei-Hung Chiang, Hsin-Lun Lee, Wen-Yu Pan, Tze-Sen Yang, Jeng-Fong Chiou, Yin-Ju Chen, Er-Yuan Chuang, and et al. 2022. "Molecularly Targeted Photothermal Ablation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Expressing Cancer Cells with a Polypyrrole–Iron Oxide–Afatinib Nanocomposite" Cancers 14, no. 20: 5043. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205043
APA StyleRethi, L., Mutalik, C., Rethi, L., Chiang, W.-H., Lee, H.-L., Pan, W.-Y., Yang, T.-S., Chiou, J.-F., Chen, Y.-J., Chuang, E.-Y., & Lu, L.-S. (2022). Molecularly Targeted Photothermal Ablation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Expressing Cancer Cells with a Polypyrrole–Iron Oxide–Afatinib Nanocomposite. Cancers, 14(20), 5043. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205043









