Simple Summary
Androgen receptor splice variant 7 (AR-V7) has always been considered a key driver for triggering enzalutamide resistance of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). In recent years, both the homeostasis of AR-V7 protein and AR-V7’s relationship with LncRNAs have gained great attention with in-depth studies. Starting from protein stability and LncRNA, the paper discusses and summarizes the mechanisms and drugs that affect the CRPC patients’ sensitivity to enzalutamide by regulating the protein or transcriptional stability of AR-V7, hoping to provide therapeutic ideas for subsequent research to break through the CRPC therapeutic bottleneck.
Abstract
Prostate cancer (PCa) has the second highest incidence of malignancies occurring in men worldwide. The first-line therapy of PCa is androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). Nonetheless, most patients progress to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) after being treated by ADT. As a second-generation androgen receptor (AR) antagonist, enzalutamide (ENZ) is the current mainstay of new endocrine therapies for CRPC in clinical use. However, almost all patients develop resistance during AR antagonist therapy due to various mechanisms. At present, ENZ resistance (ENZR) has become challenging in the clinical treatment of CRPC. AR splice variant 7 (AR-V7) refers to a ligand-independent and constitutively active variant of the AR and is considered a key driver of ENZR in CRPC. In this review, we summarize the mechanisms and biological behaviors of AR-V7 in ENZR of CRPC to contribute novel insights for CRPC therapy.
1. Introduction
As the most common urological malignant tumor, prostate cancer (PCa) occurs in the prostate epithelium, and is the fifth leading cause of death from cancer in men. New cancer cases among men worldwide exceeded 10 million in 2020, 1.4 million of which were newly diagnosed with PCa and accounted for 14.1% of all incident cases in men. And the number of deaths from PCa was 375,304, making up 6.8% of all cancer deaths in men [1]. The incidence of PCa, ranking the highest in 112 countries and regions, is lower in East Asia than that in European and American countries, whereas men in East Asia had higher PCa mortality rates than those in European and American countries [2]. The occurrence and development of PCa are closely related to androgens that can stimulate the growth of PCa cells and promote the progression of PCa. Consequently, PCa is an androgen-dependent tumor [3]. For this reason, androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) has become the standard treatment for PCa. It slows the progression of PCa by reducing androgen levels in the body or inhibiting the androgen receptor (AR) through surgery or medical castration such as the application of AR signaling inhibitors (ARSI). However, most patients develop drug resistance within 2 to 3 years after ADT and progress to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) [4,5].
The introduction of second-generation ARSI has greatly impacted the treatment of CRPC [6]. Enzalutamide (ENZ) is the second-generation ARSI by the FDA approval and the most important new drug of endocrine therapies for CRPC [7]. ENZ is one of the important options for both metastasis CRPC (mCRPC) and non-metastatic CRPC (nmCRPC) patients [3]. A phase III clinical trial investigating the efficacy and safety of ENZ in patients with nmCRPC showed that nmCRPC patients treated with ENZ had significantly improved metastasis-free survival, suggesting that ENZ significantly improves overall survival in nmCRPC [8]. Additionally, a recent meta-analysis also supported this view [9]. More than this, the overall survival and progression free survival of mCRPC patients treated with ENZ were prolonged, and the five-year survival rate was significantly improved [10,11].
ENZ mainly acts through the blockade of the AR signaling pathway, including blocking the binding of androgens to AR, impeding the AR nuclear translocation, and inhibiting the AR transcriptional activity for the treatment of CRPC [4,12,13]. Scher et al. demonstrated through a double-blind placebo-controlled trial the median survival of 18.4 months of the ENZ-treated patients, compared with 13.6 months in the placebo group [14]. ENZ thereby can significantly improve the survival of patients with CRPC after chemotherapy. However, Azuma et al. showed the insensitivity of some patients with CRPC ENZ during the clinical application of ENZ [15]. Also, drug resistance still occurred even after 11.2 years since the effective primary treatment [16]. These findings indicate that drug resistance develops through multiple mechanisms in nearly all patients with PCa treated by ARSI.
AR-related signaling pathways have always been seen as one of the considerable mechanisms responsible for ENZ resistance (ENZR) in CRPC, such as the aberrant amplification and/or overexpression of AR [17,18], AR mutation [19,20], generation of androgen splice variants (AR-Vs) [20]. Further, ENZR in CRPC has been strongly affected by neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) as a result of AR-mediated lineage plasticity [21], and by the activation of related signaling pathways like Wnt, PI3K, and NF-kB [22,23]. The insensitivity of CRPC to ENZ has been attributed in a large part to the generation of AR-V7 [24,25]. A plethora of research in this field centered on the relationship between cofactors and AR-V7. The transcriptional coactivator four-and-a-half LIM domain protein 2 (FHL-2) can act as an AR-V7 agonist [26]. Vav guanine nucleotide exchange factor 3 (VAV3) can promote the activity of AR-V7 to enhance the progression of CRPC [27,28]. Moreover, cofactors can affect ENZR through the interaction with AR-V7, such as mediator complex subunit 1(MED1) [29], fork head box01 (FOX01) [30], GATA binding protein 2 (GATA2) [31], and src-associated in mitosis of 68KD (SAM68) [32]. Nowadays, related research has paid attention to proteostasis and the role of Long noncoding RNA (LncRNA) in cancer. The changes of AR-V’s protein homeostasis are closely related to prostate cancer, and its relationship with LncRNA has also attracted the attention of researchers and has been studied in depth. This article reviews and summarizes the related research, to provide clues to solve ENZR and to improve the treatment of CRPC.
2. The Relationship between AR-V7 and AR-FL
2.1. AR-V7 Is Derived from the Splicing of AR-FL
The full-length AR (AR-FL) is mapped to chromosome Xq11-Xq12 [33]. For the first time, Chang et al. cloned the AR cDNA of human beings and rats in 1988 [34]. AR-FL is approximately 919 amino acids [35,36], mainly consisting of four structures which are the N-terminal domain (NTD), the DNA-binding domain (DBD), the hinge domain (HD), and the ligand-binding domain (LBD) [37]. AR-Vs result from alternative splicing of AR-FL during the treatment of CRPC using the second-generation ARSI. Currently, the mechanism that underlies the production of AR-Vs has been mostly understood by AR gene rearrangements [38,39], which is the primary mechanism leading to the generation of AR-V7 and AR-V567es [40], point mutations in the AR gene [41], post-translational modifications [42], and involvement of related splicing factors such as heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNPA1) [43], U2 small nuclear RNA auxiliary factor 2 (U2AF2) [44], Sam68 [45].
2.2. AR-V7 and AR-FL Have Similar Structures
AR-Vs were first discovered over 20 years ago and reported by Tepper et al. [46]. At present, more than 20 types of AR-Vs have been found and identified [47], the majority of which contain complete DBD and NTD (AR8 with the lack of the functional DBD and AR-V3 with no zinc fingers of DBD, with the exception of AR45 that does not contain NTD). Most of them have primarily LBD and HD loss [47]. AR-V7 retains the complete NTD and DBD while lacking the LBD and HD which is displaced by a short peptide sequence encoded by cryptic exon 3 (CE3) instead [48]. Therefore, AR-V7 that contains a complete activation functions (AF)-1 transactivation domain is constitutively active at the transcriptional level and maintains gene transcription without the need for ligand (independent of androgen) binding [49]. Given that ENZ targets LBD [50], the truncated LBD in AR-V7 is the primary cause why ENZ cannot bind to the AR-V7 and further play its role, subsequently leading to ENZR (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
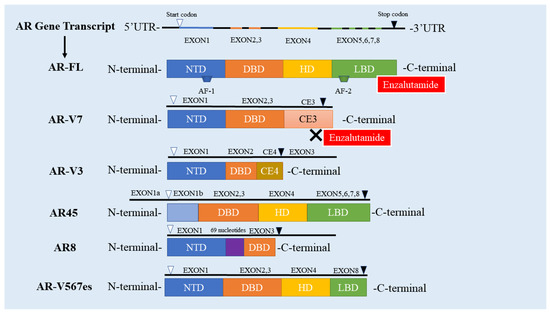
Figure 1.
The Structure of AR-FL and AR-Vs. The human AR gene contains eight exons; AR has four domains, including NTD, DBD, HD and LBD. Exon 1 encodes NTD, DBD is encoded by exons 2 and 3, exon 4 encodes HD, and LBD is encoded by exons 5,6,78; AR-V7 has no LBD, so enzalutamide cannot bind to AR-V7; The DBD domain of AR-V3 is only encoded by exon 2, and lacks zinc finger; AR45 starts coding from exon 1b and lacks the NTD domain; The DBD domain formed by AR8 is only encoded by exon 3 and is not functional. AR8 inserts 69 nucleotides upstream of exon 3; AR-V567es does not contain exon 5.6.7; UTR: Untranslated Region; AR-FL: full-length androgen receptor; AR-V: androgen receptor splicing variant; NTD: N-end domain; DBD: DNA binding; HD: hinge domain; LBD: ligand binding domain; CE3: recessive exon 3; AF: Activate the function.
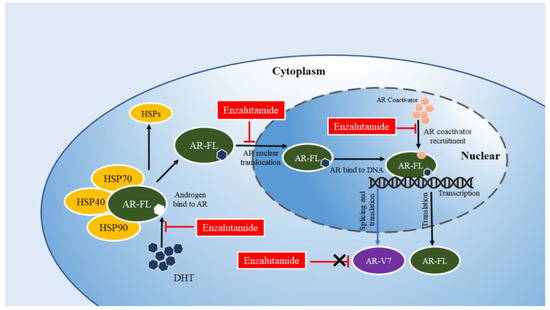
Figure 2.
Enzalutamide acts on the AR signaling pathway. Enzalutamide binds to the LBD and blockades the AR signaling pathway by blocking the binding of androgens to AR, impeding the AR nuclear translocation, and inhibiting the AR transcriptional activity. AR-FL: full-length androgen receptor; AR-V7: androgen receptor splice variant 7; DHT: dihydrotestosterone. HSP: heat shock proteins.
2.3. There Are Differences between AR-V7 and AR-FL
AR-V7 is a mimic of AR, or AR-V7 has unique activity or whether AR-V7 contains a unique binding site is the focus of researchers. A recent study has found that AR-V7 induces a slightly higher proportion of total regulatory genes in the cell model than AR-FL, and its differential binding with chromatin is stronger than AR-FL [51]. Some studies also have shown that AR-V7 has specific targeted genes, which cannot be targeted by AR-FL [52]. These results together indicate that AR-V7 has unique activity and is not just a mimic of AR-FL.
2.4. AR-V7 Plays a Role Independently of AR-FL
AR-V7 is derived from AR-FL and is almost always co-expressed with AR-FL in the clinical environment. Therefore, the topic of whether the role of AR-V7 in PCa depends on AR-FL has been widely debated. Some researchers have concluded that AR-V7 works with AR-FL or requires AR-FL to perform activities, because AR-V transcriptional activity requires AR-V homologous dimerization [53]. AR-V7 can also form heterodimers with AR-FL [54]. In addition, in the model of the expression of AR-FL, AR-V7 activity depends on AR-FL to a large extent [55,56]. However, other researchers believe that exogenous overexpressed AR-V7 can act as a heterodimer of AR-FL, but whether the endogenous AR-V7 functions depend on heterodimerization with AR-FL remains to be further studied, because in AR-FL null cell models and/or AR-FL depleted models, many AR-Vs have been proven to have the ability to regulate gene transcription without AR-FL [48,57,58]. Similarly, the experimental study of Liang et al. also emphasized that AR-FL deletion would not damage the chromatin binding of ARv7 splicing variants, and that AR-FL and AR-V7 independently participated in AR transcriptional activity [59], which seems to be a shred of strong evidence that AR-V7 plays a role independently of AR-FL.
3. The Close Relationship between AR-V7 and the Treatment of CRPC with ENZ
Sharp et al. assessed the expression of AR-V7 protein in 358 primary prostate specimens and 293 metastatic biopsy specimens [60]. The results showed a very low level (<1%) of the expression of AR-V7 protein in cases with primary PCa and a detectable level of in 75% in cases treated by ADT. A marked increase in the expression of AR-V7 protein in cases with ENZ demonstrated that the use of ENZ can enhance the generation of AR-V7. However, the use of ENZ is not an absolute factor in the production of AR-V7, because AR-V7 expression is also detected in patients with primary PCa. This is also consistent with the research of Sciarra et al. [61]. They classified 56 cases of PCa according to clinical risk, examined the expression of AR-V7 and found that 24 of 32 high-risk patients were AR-V7 positive, 4 of 13 in the medium risk group and 2 of 11 in the low risk group. Therefore, AR-V7 could be detected by immunohistochemistry in more than 50% of nmPCa patients without treatment. It also showed that there was a significant correlation between AR-V7 positive and PCa risk classification (p < 0.001)
The generation of AR-V7 is one of the causes of the poor prognosis and low overall survival rate of CRPC patients after treatment. Compared with AR-V7 negative patients, the prognosis of PCa patients treated with ENZ became worse if they were also AR-V7 positive [62]. The research team selected 31 men using ENZ and Abiraterone (ABI) respectively. Among the patients treated with ENZ, it was found that the PSA response rate of AR-V7 positive ones was lower than that of negative ones (0% vs. 53%, p = 0.004). Moreover, it was also found that the AR-V7 positive patients had a shorter PSA progression-free survival (median 1.4 months vs. 6.0 months; p < 0.001), shorter clinical or radiographic progression-free survival (median 2.1 months vs. 6.1 months; p < 0.001) and shorter overall survival (median 5.5 months vs. not reached; p = 0.002), indicating insufficient therapeutic efficacy and prognosis as a consequence of the decreased sensitivity of AR-V7 positive patients to ENZ. Similarly, research detected in various ways the AR-V7 in the CTCs of blood samples belonging to high-risk CRPC patients being treated by ENZ and came to the same conclusion: the AR-V7 expression is independently related to shorter clinical progression-free survival (PFS) and poorer overall survival (OS) [63]. Meanwhile, it further showed that the continuous subsequent treatment with ENZ would not result in a good endpoint for patients with CRPC who were AR-V7 positive. Therefore, ENZ leads to the generation of AR-V7 and drug resistance, which impedes the therapeutic efficacy and survival rate of patients. Up to now, the treatment of AR-V7 positive CRPC patients has become a challenging issue in the clinic.
A large number of preclinical research results show that AR-V7 can be used as a biological marker of ENZR in CRPC [64,65]. Besides, AR-V7 is considered helpful in guiding the treatment selection after ABI or ENZ progress in mCRPC. It has available commercial test methods and has been prospectively validated in multiple centers [66]. Therefore, improving the detection efficiency and accuracy of AR-V7 can help not only patient diagnosis but also the precise guidance of medical use for CRPC patients in the clinic. As previously mentioned, Zhu et al. developed an analytical method of in situ hybridization with AR-V7 RNA. The technology can overcome the limitation that AR-V7 cannot be accurately detected by observing single splicing connections in cells and tissues [67]. Maillet et al. applied enrichment analysis (the AdnaTest) to detect the mRNA-based AR-V7 in circulating tumor cells (CTCs), and performed the pre-amplification PCR step before real-time qPCR analysis to establish a highly sensitive method for detecting in CTCs AR-V7, and significantly improves the detection efficiency of AR-V7 [68]. Despite that the clinical utility of these detection methods remains controversial, they do offer new hope to patients with CRPC who are ENZR to get early treatment.
4. AR-V7 as the Cause of ENZR in CRPC
AR-V7 has long been a crucial research focus in exploring the mechanism of ENZR. In cell-level experiments, it has been found that the ENZ therapy of CRPC enhances the level of AR-V7 and aids the expression of its target genes in PCa cells, and that the knockdown of AR-V7 can restore the sensitivity of cancer cells to ENZ, suggesting that AR-V7 is one of the salient factors leading to drug resistance [69]. Similarly, Zhu et al. found that patient-derived xenografts (PDX) with high expression of AR-FL could resist the first-generation ARSI but not the second-generation ARSI ENZ, proving that ENZR was closely related to AR-V7 expression [70]. The authors further demonstrated through subsequent cell experiments that ENZR required the high-level AR-FL and critical-level AR-V7 expression. Although the precise mechanism by which AR-V7 plays its role remains unknown, all the above indicates that AR-V7 is crucial in mediating ENZR of CRPC. Moreover, basic research has centered on the change of AR-V7 proteostasis and how its interaction with LncRNAs works on ENZR in CRPC in recent years, which also provides new therapeutic insights for the treatment of drug resistance in CRPC.
4.1. Heat Shock Protein Participates in Regulating the Protein Stability of AR-V7
Heat shock proteins (HSP) refer to a group of proteins generated by cells under the induction of stressors, especially environmental high temperature [71]. They are highly conservative molecular chaperones, including HSP70, HSP40, HSP90, etc. [72,73,74,75,76]. As molecular chaperones, HSPs regulate the stability and function of client proteins in a variety of ways, including preventing the aggregation of misfolded proteins, promoting intracellular protein transport, maintaining protein conformation to achieve ligand binding, and promoting the degradation of severely damaged proteins by mediating the ubiquitin proteasome [77,78].
AR/AR-V7 is one of the client proteins of HSP [79]. In the cytoplasm, free AR/AR-V7 combines with chaperone HSP70-HSP40 to form a protein complex, and then HSP90 and chaperone bind to AR/AR-V7, which dissociates AR/AR-V7 from HSP70-HSP40. HSP90 can ensure that AR/AR-V7 retains the conformational structure with a high affinity for its ligand dihydrotestosterone, and promote the binding of AR/AR-V7 with ligand [80]. After AR binds dihydrotestosterone, phosphorylation and dimerization occur. The combination of HSP27 and AR homodimer further promotes the nuclear translocation of the androgen response element (ARE) in AR and specific gene promoter regions, thus promoting the regulation of transcriptional activity [81]. A promising strategy for the treatment of cancer is to increase the degradation of oncogenic proteins by targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome system [52,53]. Therefore, it is one of the potential strategies to affect the protein stability of AR/AR-V7 or treat the resistance of CRPC to ENZ by regulating heat shock proteins (Figure 3).
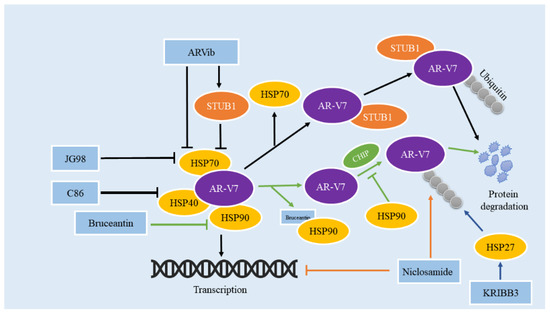
Figure 3.
Natural/compound drugs affect the transcriptional activity and protein stability of AR-V7 through the HSP family. ARVib, JG98, and C86 promote AR-V7 degradation by inhibiting HSP40/HSP70 axis; bruceantin promotes AR-V7 degradation by directly binding to HSP90 and disrupting the interaction between HSP90 and AR-V7; KRIBB3 promotes the degradation of AR by interacting with HSP27; niclosamide not only inhibits the transcriptional activity of AR-V7 but also promotes the degradation of AR-V7.
HSP70 has been identified as a biomarker for the survival and prognosis of PCa owing to the relationships between its overexpression and carcinogenesis as well as drug resistance in PCa [82]. HSP70 inhibitor JG98 can impede protein levels and transcriptional activities of AR-FL and AR-Vs, and degrade other oncogenic proteins at the same time [77,83]. Moses et al. also revealed that PCa patients who had developed drug resistance to the standard antiandrogen therapy would benefit from targeting the Hsp40/Hsp70 chaperone axis [83]. One of the reasons that niclosamide, an anti-worm drug, has been proven to be an effective inhibitor to reverse ENZR in CRPC, is that it can promote the protein degradation of AR-V7 by activating the ubiquitin protease hydrolysis pathway [84]. STIP1 homology and U-box containing protein 1(STUB1) is a co-chaperone protein and a functional E3 ubiquitin ligase [85]. AR/AR-V7 proteostasis requires the interaction of STUB1, the E3 ubiquitin ligase, and the HSP70 complex. STUB1 separates AR/AR-V7 from HSP70, provoking the ubiquitination and degradation of AR/AR-V7 [86]. Liu et al. found an analog that targeted and degraded AR/AR-V7 through a niclosamide analog library. It was identified and termed ARVib [87]. ARVib-7 which had a higher bioavailability than niclosamide, can inhibit the proliferation of AR-V7 transcriptional activity in PCa cells. Follow-up experiments discovered that ARVib-7 can inhibit the AR-V7 transcriptional activity in cells of ENZR in PCa, and also that it was able to promote the nuclear translocation of STUB1 by inhibiting the expression of HSP70. To treat drug resistance in CRPC, the increased nuclear penetration of STUB1 further binds to AR-V7 to facilitate its ubiquitination and degradation and to impair the expression of AR-V7 downstream genes in PCa cells. All eukaryotic cells contain the expression of the stress protein Hsp90, which is essential for the correct folding, hormone binding, and transcriptional activity of AR.
Moon et al. screened and identified the drug bruceantin (BCT) from a small antimalarial drug library, by directly binding to HSP90 which can not only disrupt the interaction between HSP90 and AR-FL/AR-V7 but also inhibit the chaperone function of HSP90, causing the degradation of AR-FL/AR-V7 through the ubiquitin-proteasome system [88]. These results indicate that BCT is a promising option for anti-CRPC medication. Geldanamycin (GA), the Hsp90 inhibitor, has also been reported to impair the AR proteostasis with no impact on the protein level of AR-V7. In the same way, it can impede AR transcriptional activity but has little impact on AR-V7 activity. All uncovered that AR-V7 is resistant to Hsp90 inhibitors [89]. Similar results have been reported in an article, and it is important to note that the second-generation HSP90 inhibitor Onalespib mainly affects the splicing of AR-V7 rather than directly affecting the protein levels of AR-V7 [90]. This experiment showed that Onalespib was able to induce AR-FL proteasomal degradation but had little effect on AR-V7 stability, and it was able to cause a decrease in AR-V7 mRNA levels, but did not affect total AR transcript levels [91]. Clearly, a close connection exists between HSPs and AR/AR-V7. Further research is required to confirm the impact of the HSP90 inhibitor on the proteostasis of AR-V7 and to investigate the role of other HSPs.
4.2. Natural Products and Compounds Can Regulate the Stability of AR-V7
In recent years, the application of natural products and their analogues in tumors has received much attention. AR-V7 is a substrate for the proteasome, as Liu et al. demonstrated [92]. They extracted nobiletin from citrus peel, a type of polymethoxylated flavonoid, which induced cancer cells to block in the G0/G1 phase and prevented the interaction of AR-V7 with ubiquitin specific peptidase 14 (USP14) and USP22, so as to selectively stimulate the proteasome destruction of AR-V7. AR-V7 positive PCa cells were thereby more sensitive to ENZ. In addition, this study highlighted that nobiletin was able to downregulate AR-V7 in a manner dependent on dose and time, but had no significant effect on the protein level of AR-FL. Previous research has also reported that nobiletin inhibits the growth of PCa cells by impeding the signaling pathway of TLR4/TRIF/IRF3, TLR9/IRF7, and AKT [93,94]. Huaier extract, derived from medicinal fungi, has been found to be anti-proliferative in CRPC cells. By inhibiting the transcriptional activity and nuclear translocation of AR-FL/AR-V7, it enhances the proteasome-mediated degradation of AR-FL/AR-V7 proteins through the down-regulation of USP14 and can consequently be applied as an effective inhibitor of AR-FL and AR-V7 in PCa [95]. Coincidentally, Liao et al. screened and identified rutin (Rut), the main component of Evodia rutaecarpa, from the natural product library, and revealed that it can be used as an inhibitor of AR-V7 [96]. They demonstrated that this alkaloid inhibited AR-V7 signaling by selectively accelerating the degradation of the K48-binding ubiquitinated proteasome.
A novel protac small molecule named MTX-23 was designed and developed by Lee et al. [97], which was made to bind both the VHL ligand of E3 ubiquitin ligase and the DNA binding domain (DBD) of AR simultaneously. It was found in the research that MTX-23 had no crucial effect on the mRNA level of AR-FL and AR-V7, and that, however, MTX-23 can specifically stimulate the ubiquitination and degradation of AR-V7 and AR-FL through the VHL E3 ligase/proteasome axis at the protein level to inhibit drug resistance. Interestingly, the authors discovered that MTX-23 was more effective than AR-FL in the degradation of AR-V7 (DC 50 of 0.37 and 2μmol/L respectively), given the fact that MTX-23 played its role through targeting DBD substantially. Theoretically speaking, MTX-23 should be able to degrade both AR-V7 and AR-FL with similar efficacy. The LBD remaining in AR-FL or the protein bound to LBD, according to the authors, may physically interfere with the interaction of MTX-23 with DBD, as a consequence of the possibility that the biological outcomes of MTX-23-mediated ubiquitination may vary in AR-V7 and AR-FL.
One approach to treating cancer is to screen and create small molecule compounds from databases. Nevertheless, continuous discovery of natural products and their derivatives has demonstrated an extraordinary anti-cancer effect as well as their abilities to reverse tumor resistance, suggesting the crucial clinical value of natural products and their derivatives (Table 1). Moreover, there are still many possibilities for the development in the utilization of natural products and their derivatives to treat ENZR in CRPC. Deep research will develop stronger and safer medications against drug resistance in the treatment of tumors.

Table 1.
Drugs and correlated mechanisms in CRPC.
4.3. LncRNA Has Multiple Effects on AR-V7
LncRNA has been widely researched in the past decade, which is defined as an RNA transcript longer than 200 nucleotides without protein coding [110]. Earlier research has shown that LncRNAs play an important role in cell cycle regulation [111], cell differentiation regulation [112], cell metabolism regulation [113], and other cellular processes. Meanwhile, LncRNAs can regulate its transcriptional level and epigenetic modification through interaction with DNA, proteostasis, and so on [114,115].
Recent research has displayed close relationships between LncRNAs and the occurrence and development of malignancies [116,117]. LncRNA-PCA3 has evolved into the most PCa-specific LncRNA which is an important diagnostic marker of PCa [118,119,120]. LncRNA-HOTAIR and LncRNA-GAS5 also play an indispensable role through various mechanisms in the progression of CRPC [121,122]. Shang et al. found that LncRNA-PCAT1 regulated PHLPP/FKBP51/IKK α complex to activate AKT and NF-κB signaling [123]; Wen et al. identified and termed a special LncRNA that transcribed at the CHPT1 enhancer as CHPT1-eRNA, and discovered that the level of the LncRNA in ENZR tumors was higher than that in the control group. Further cell experiments showed that this LncRNA was engaged in the generation of SE and regulated the transcriptional activity of SE by directly binding to BRD4, thus significantly provoking ENZR in CRPC [124]. Together, all research mentioned above revealed the status of LncRNAs in CRPC.
Wang et al. revealed the relevance between LncRNAs and the expression of AR-V7 in CRPC. Specifically, LncRNA-Malat1 is essential for the generation of AR-V7 [125]. They focused on the role of 32 LncRNAs associated with drug resistance in CRPC and verified how they worked in ENZR in CRPC through the construction of multiple ENZR-PCa cells and human clinical data. The authors mainly discussed the role of LncRNA-PCGEM1 and LncRNA-Malat1 in the mechanism of drug resistance, with LncRNA-PCGEM1 being identified as an AR/AR-V7 signal-regulated LncRNA [126], and LncRNA-MALAT1 proved to be upregulated in CRPC and to be likely to participate in RNA splicing [127,128]. They also discovered the correlation between the rise in SF2 activity and the overexpression of LncRNA-MALAT1 in ENZR C4-2 cells. Their previous research pointed out that introns between exon 3 and exon 4 of AR transcripts can be recognized and bound by SF2, which aided the generation of AR-V7 and consequently led to ENZR [129]. Meanwhile, knockdown of LncRNA-Malat1 with siRNA to inhibit the expression of LncRNA-MALAT1 leads to a significant reduction in AR-V7 expression, indicating that LncRNA-Malat1 is indispensable for ENZ induced AR-V7 expression.
The LncRNA was related to the generation of AR-V7. Additionally, the most recent research uncovered that LncRNA might also change the expression level and/or function of AR-V7 through a series of mechanisms, affecting the drug sensitivity of ENZ in CRPC. Zhang et al. found that LncRNA-PCBP1-AS1 can accelerate the progression of ENZR in CRPC by binding to NTD to improve the stability of the USP14-AR-V7 complex. AR-V7 and USP22 were found in this experiment to be greatly reduced by PCBP1-AS1 depletion [130]. Therefore, targeting PCBP1-AS1 could impede the expression of AR-V7 and strengthen the sensitivity of CRPC to ENZ. In 2022, Ghildiyal et al. discovered a type of LncRNA named NXTAR with the ability to inhibit drug resistance in PCa, and reported that NXTAR directly bound to AR upstream of the AR promoter to enhance EZH2 recruitment, leading to the down-regulation of the AR and AR-V7 expression and positive feedback to increase NXTAR expression [131]. This discovery provides a therapeutic strategy for treating recurrent CRPC. As previously mentioned, the role of LncRNAs in ENZR in CRPC has been further expanded, which may serve as new potential for clinical diagnosis and targeted therapy.
NTD is one of the necessary structures for AR transcription. Hirayama et al. [54] found that antagonizing NTD can decrease the transcriptional efficacy of AR-FL and AR-V7, effectively improving the efficacy of ENZ [69]. Targeting AR-NTD is thus one of the effective ways to inhibit AR-V7 and another option to treat ENZR in CRPC. Zhang et al. reported that LncRNA-KDM4A-AS1 enhanced the stability of the USP14-AR/AR-Vs complex and promoted the ubiquitination of AR/AR-Vs through the binding with NTD to protect itself from the MDM2-mediated degradation of ubiquitin-proteasome, thereby intensifying ENZR in CRPC. At present, many medicines designed to target AR-V7 NTD are under development [132]. This also suggests that targeting other structures in AR-V7 may have the same effect, such as DBD.
Generally speaking, LncRNAs and AR-V7 are closely related to each other, playing an important role through various mechanisms in ENZR in CRPC (Table 2). In addition, LncRNA-P21 [133], LncRNA-H19 [134], and so forth have also been reported to promote the occurrence of NEPC and consequently lead to ENZR. Therefore, targeting LncRNA and AR-V7-related signaling pathways may contribute new insights for the clinical treatment of drug resistance in CRPC.

Table 2.
The expression of LncRNAs in patients with CRPC affects its benefit from ENZ.
4.4. Interaction between Other Molecules and AR-V7
Recent studies have reported that many molecules regulate the expression of AR-V7 in different ways (Table 3). AKR1C3, a member of the NAD(P)H-linked oxidoreductase superfamily, is highly expressed in PCa and its precancerous tissues in the human body [139]. Previous research has demonstrated that AKR1C3 can provoke ENZR by triggering the androgen biosynthesis pathway and AR signaling [140]. Through the ubiquitin-mediated proteasome pathway, AKR1C3 can induce the generation of AR-V7 and enhance its proteostasis. Indomethacin, an AKR1C3 inhibitor, can be utilized through the ubiquitin-mediated proteasome pathway targeting AKR1C3, to significantly reduce the expression of AR/AR-V7 protein in vitro and in vivo, and thus the sensitivity of patients to ENZ increases [101]. This is consistent with the findings of Wang et al. who found that AKR1C3 bound to AR-V7 protein in CRPC cells and mutually improved the proteostasis of AR-V7 and AKR1C3 by inhibiting ubiquitin activity in a positive feedback mechanism [102].

Table 3.
Some molecules in patients with CRPC affect the therapeutic effect of ENZ.
The kinesin family encompasses kinesin family member 15 (KIF15) which is essential for the development of bipolar spindles [141]. KIF15 is directly bound to the N-terminal of AR/AR-V7 to increase the binding between USP14 and AR/AR-V7 protein, thereby inhibiting the degradation of AR/AR-V7 protein and promoting ENZR [142]. Deleted in breast cancer 1 (DBC1) is a human nuclear protein that modulates the activities of various proteins [143]. Su et al. discovered that DBC1 interacted with AR-V7 to enhance the DNA binding activity of AR-V7 and competed with CHIP for AR-V7 binding to inhibit the ubiquitination and degradation of AR-V7 mediated by the CHIP E3 ligase, and thus stabilizing and activating AR-V7 [144]. As a result, the possibility exists in this situation that DBC1 could be targeted to decrease the stability of AR-V7 or reverse ENZR in CRPC. Aberrant expression of casein kinase 2 (CK2) is associated with tumorigenesis and progression of PCa [145], the novel CK2-selective inhibitor CX4945, which selectively downregulates AR-V7 at the mRNA and protein levels, offers a potential option for the treatment of PCa, especially CRPC [103].
How AR-V7 mediates genome function in CRPC remains largely unknown. homeobox B13 (HOXB13), a member of the homeobox proteins family, is a key regulator of the epithelial differentiation in the prostate gland [146]. Zhong et al. reported that HoxB13 firstly combined with AR-V7 through direct physical interaction, and cooperated with AR-V7 to up regulate target oncogenes, which is a key upstream regulator of the AR-V7 driven transcriptome, indicating that HoxB13 can be used as a therapeutic target for AR-V7 driven prostate tumors [147]. The discovery of HoxB13 is helpful for us to further understand how AR-V7 mediates genome function in CRPC.
Therefore, if key regulatory molecules such as AKR1C3, KIF15, DBC1 and HOXB13 can be targeted, thereby reducing the stability of AR-V7, promoting the protein ubiquitin-proteasome of AR-V7 may be able to reverse ENZR of CRPC.
5. Conclusions and Prospects
ENZ, a second-generation ARSI, has given hope to CRPC patients and increased the overall survival rate. Nevertheless, ENZR has become challenging in the clinical treatment of CRPC. Scientific research has also focused on the mechanism of ENZR in CRPC. Numerous studies have thus far reported that the occurrence of ENZR is mediated by different mechanisms, which are AR-related mechanisms, glucocorticoid receptor-related processes, neuroendocrine transformation, related pathway activation, etc. There is no doubt about the role of AR in mediating ENZR in CRPC. As the most important AR-Vs, AR-V7 have been shown to play an important role in the development of drug resistance in CRPC and in predicting treatment response.
In addition to expanding our understanding of the AR signal axis in the past, the research into AR-V7 in the mechanism of ENZR in CRPC also offers the most recent therapeutic approaches to treating CRPC. One of the recent research hotspots and foci are the relationships between LncRNA with proteostasis and AR-V7. In order to treat ENZR in CRPC, continuous investigation is explored on strategies targeting the stability of the AR-V7 protein or the AR-V7 transcription levels. For example, the conventional drug niclosamide has been applied in a new way. Some newly developed small-molecule compounds such as ARVib-7 and MTX-23, as well as natural products such as nobiletin and Hsp90, have also shown efficient therapeutic effects.
Although the data of preclinical studies are encouraging, the specific mechanism of AR-V7 activation is not clear at present, and most drugs are limited to the results of preclinical studies now. No further clinical trials have been carried out. In addition, there are still problems of limited efficacy or unacceptable toxicity in clinical trials in clinical development. Therefore, there is still a long way to go to develop drugs that inhibit the expression of AR-V7 or promote the degradation of AR-V7 and finally put them into clinical treatment for patients with CRPC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Z., J.L. and Y.L.; investigation, Z.Z. and Z.X.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Z., J.L., Y.L., Z.X., Z.S., Y.B., M.F., H.S. and C.S.; writing—review and editing, Z.Z., Z.S., K.Y., C.X., H.S. and C.S; visualization, Z.Z. and Q.X.; supervision, H.S. and C.S.; funding acquisition, H.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81972373) and the Scientific Research Foundation for Advanced Talents of Xiang’an Hospital of Xiamen University (No. PM201809170001) and a Research Fund of Fujian Key Laboratory of Precision Diagnosis and Treatment in Breast Cancer and Xiamen Key Laboratory of Endocrine-Related Cancer Precision Medicine.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study are available from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornford, P.; Bellmunt, J.; Bolla, M.; Briers, E.; De Santis, M.; Gross, T.; Henry, A.M.; Joniau, S.; Lam, T.B.; Mason, M.D.; et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part II: Treatment of Relapsing, Metastatic, and Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, L.J. Enzalutamide: A review in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Drugs 2018, 78, 1913–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, A.; Conteduca, V.; Zoubeidi, A.; Beltran, H. Biological evolution of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.T.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Chau, C.H.; Figg, W.D. Resistance to second-generation androgen receptor antagonists in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2021, 18, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bono, J.S.; Logothetis, C.J.; Molina, A.; Fizazi, K.; North, S.; Chu, L.; Chi, K.N.; Jones, R.J.; Goodman, O.B., Jr.; Saad, F.; et al. Abiraterone and increased survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokeshwar, S.D.; Klaassen, Z.; Saad, F. Treatment and trials in non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2021, 18, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, M.; Salciccia, S.; Del Giudice, F.; Busetto, G.M.; Falagario, U.G.; Carrieri, G.; Ferro, M.; Porreca, A.; Di Pierro, G.B.; Fasulo, V.; et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials with novel hormonal therapies for non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: An update from mature overall survival data. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 700258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.N.; Gordon, M.J.; Beer, T.M. Safety and effectiveness of enzalutamide in men with metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer. Expert Opin. Pharm. 2015, 16, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.J.; Lin, P.; Tombal, B.; Saad, F.; Higano, C.S.; Joshua, A.M.; Parli, T.; Rosbrook, B.; van Os, S.; Beer, T.M. Five-year survival prediction and safety outcomes with enzalutamide in men with chemotherapy-naive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer from the PREVAIL trial. Eur. Urol. 2020, 78, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, C.; Ouk, S.; Clegg, N.J.; Chen, Y.; Watson, P.A.; Arora, V.; Wongvipat, J.; Smith-Jones, P.M.; Yoo, D.; Kwon, A.; et al. Development of a second-generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Science 2009, 324, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baciarello, G.; Sternberg, C.N. Treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) with enzalutamide. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 106, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, H.I.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Taplin, M.E.; Sternberg, C.N.; Miller, K.; de Wit, R.; Mulders, P.; Chi, K.N.; Shore, N.D.; et al. Increased survival with enzalutamide in prostate cancer after chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, T. Comparing sequencing of abiraterone and enzalutamide in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A retrospective study. Prostate 2018, 78, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, T.M.; Armstrong, A.J.; Rathkopf, D.E.; Loriot, Y.; Sternberg, C.N.; Higano, C.S.; Iversen, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Carles, J.; Chowdhury, S.; et al. Enzalutamide in metastatic prostate cancer before chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Loriot, Y.; Beraldi, E.; Zhang, F.; Wyatt, A.W.; Al Nakouzi, N.; Mo, F.; Zhou, T.; Kim, Y.; Monia, B.P.; et al. Generation 2.5 antisense oligonucleotides targeting the androgen receptor and its splice variants suppress enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer cell growth. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, A.A.; Yen, A.E.; Weigel, N.L. Androgen receptors in hormone-dependent and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 140, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, K.; Yang, Z.; Pascal, L.E.; Nelson, J.B.; Takubo, K.; Wipf, P.; Wang, Z. A novel androgen receptor antagonist JJ-450 inhibits enzalutamide-resistant mutant AR(F876L) nuclear import and function. Prostate 2020, 80, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, C.S.; Wu, Y.M.; Robinson, D.R.; Cao, X.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Khan, A.P.; Quist, M.J.; Jing, X.; Lonigro, R.J.; Brenner, J.C.; et al. The mutational landscape of lethal castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, C.; Ceder, J.; Iglesias-Gato, D.; Chuan, Y.C.; Pang, S.T.; Bjartell, A.; Martinez, R.M.; Bott, L.; Helczynski, L.; Ulmert, D.; et al. REST mediates androgen receptor actions on gene repression and predicts early recurrence of prostate cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 999–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Farah, E.; Atallah, N.M.; Pascuzzi, P.E.; Gupta, S.; Liu, X. Inhibition of the wnt/beta-catenin pathway overcomes resistance to enzalutamide in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3147–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, N.; Sikka, S.C. Interplay between SOX9, wnt/beta-catenin and androgen receptor signaling in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Lu, C.; Luber, B.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Silberstein, J.L.; Taylor, M.N.; Maughan, B.L.; Denmeade, S.R.; et al. Clinical significance of androgen receptor splice variant-7 mRNA detection in circulating tumor cells of men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with first- and second-line abiraterone and enzalutamide. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Laere, B.; van Dam, P.J.; Whitington, T.; Mayrhofer, M.; Diaz, E.H.; Van den Eynden, G.; Vandebroek, J.; Del-Favero, J.; Van Laere, S.; Dirix, L.; et al. Comprehensive profiling of the androgen receptor in liquid biopsies from castration-resistant prostate cancer reveals novel intra-AR structural variation and splice variant expression patterns. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, M.J.; Binge, L.C.; Sriratana, A.; Wang, H.; Robinson, P.A.; Pook, D.; Fedele, C.G.; Brown, S.; Dyson, J.M.; Cottle, D.L.; et al. Regulation of the transcriptional coactivator FHL2 licenses activation of the androgen receptor in castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5066–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magani, F.; Peacock, S.O.; Rice, M.A.; Martinez, M.J.; Greene, A.M.; Magani, P.S.; Lyles, R.; Weitz, J.R.; Burnstein, K.L. Targeting AR variant-coactivator interactions to exploit prostate cancer vulnerabilities. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Peacock, S.O.; Lo, C.H.; Heidman, L.M.; Rice, M.A.; Fahrenholtz, C.D.; Greene, A.M.; Magani, F.; Copello, V.A.; Martinez, M.J.; et al. Arginine vasopressin receptor 1a is a therapeutic target for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, aaw4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboukameel, A.; Muqbil, I.; Baloglu, E.; Senapedis, W.; Landesman, Y.; Argueta, C.; Kauffman, M.; Chang, H.; Kashyap, T.; Shacham, S.; et al. Down-regulation of AR splice variants through XPO1 suppression contributes to the inhibition of prostate cancer progression. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 35327–35342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mediwala, S.N.; Sun, H.; Szafran, A.T.; Hartig, S.M.; Sonpavde, G.; Hayes, T.G.; Thiagarajan, P.; Mancini, M.A.; Marcelli, M. The activity of the androgen receptor variant AR-V7 is regulated by FOXO1 in a PTEN-PI3K-AKT-dependent way. Prostate 2013, 73, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Lanz, R.B.; Fiskus, W.; Geng, C.; Yi, P.; Hartig, S.M.; Rajapakshe, K.; Shou, J.; Wei, L.; Shah, S.S.; et al. GATA2 facilitates steroid receptor coactivator recruitment to the androgen receptor complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18261–18266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockley, J.; Markert, E.; Zhou, Y.; Robson, C.N.; Elliott, D.J.; Lindberg, J.; Leung, H.Y.; Rajan, P. The RNA-binding protein Sam68 regulates expression and transcription function of the androgen receptor splice variant AR-V7. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubahn, D.B.; Joseph, D.R.; Sullivan, P.M.; Willard, H.F.; French, F.S.; Wilson, E.M. Cloning of human androgen receptor complementary DNA and localization to the X chromosome. Science 1988, 240, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.S.; Kokontis, J.; Liao, S.T. Molecular cloning of human and rat complementary DNA encoding androgen receptors. Science 1988, 240, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, B.; Beitel, L.K.; Nadarajah, A.; Paliouras, M.; Trifiro, M. The androgen receptor gene mutations database: 2012 update. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelmann, E.P. Molecular biology of the androgen receptor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 3001–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Thummel, C.; Beato, M.; Herrlich, P.; Schütz, G.; Umesono, K.; Blumberg, B.; Kastner, P.; Mark, M.; Chambon, P.; et al. The nuclear receptor superfamily: The second decade. Cell 1995, 83, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehm, S.M.; Schmidt, L.J.; Heemers, H.V.; Vessella, R.L.; Tindall, D.J. Splicing of a novel androgen receptor exon generates a constitutively active androgen receptor that mediates prostate cancer therapy resistance. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5469–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyquist, M.D.; Li, Y.; Hwang, T.H.; Manlove, L.S.; Vessella, R.L.; Silverstein, K.A.; Voytas, D.F.; Dehm, S.M. TALEN-engineered AR gene rearrangements reveal endocrine uncoupling of androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17492–17497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, D.; Nakao, S.; Nakayama, K.; Araki, S.; Nakayama, Y.; Aparicio, S.; Hara, T.; Nakanishi, A. The RNA helicase DDX39B and its paralog DDX39A regulate androgen receptor splice variant AR-V7 generation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceraline, J.; Cruchant, M.D.; Erdmann, E.; Erbs, P.; Kurtz, J.E.; Duclos, B.; Jacqmin, D.; Chopin, D.; Bergerat, J.P. Constitutive activation of the androgen receptor by a point mutation in the hinge region: A new mechanism for androgen-independent growth in prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libertini, S.J.; Tepper, C.G.; Rodriguez, V.; Asmuth, D.M.; Kung, H.J.; Mudryj, M. Evidence for calpain-mediated androgen receptor cleavage as a mechanism for androgen independence. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9001–9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadiminty, N.; Tummala, R.; Liu, C.; Lou, W.; Evans, C.P.; Gao, A.C. NF-kappaB2/p52:c-Myc:hnRNPA1 Pathway Regulates Expression of Androgen Receptor Splice Variants and Enzalutamide Sensitivity in Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1884–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.L.; Xie, N.; Sun, S.; Plymate, S.; Mostaghel, E.; Dong, X. Mechanisms of the androgen receptor splicing in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3140–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Sun, X.; Zheng, W.; Wier, E.M.; Hodgson, A.; Tran, D.Q.; Richard, S.; Wan, F. Sam68 modulates the promoter specificity of NF-kappaB and mediates expression of CD25 in activated T cells. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, C.G.; Boucher, D.L.; Ryan, P.E.; Ma, A.H.; Xia, L.; Lee, L.F.; Pretlow, T.G.; Kung, H.J. Characterization of a novel androgen receptor mutation in a relapsed CWR22 prostate cancer xenograft and cell line. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6606–6614. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Zhan, Y.; Dong, Y. Emerging data on androgen receptor splice variants in prostate cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, T199–T210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Lu, C.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Gurel, M.; Tannahill, C.; Edwards, J.; Isaacs, W.B.; Nelson, P.S.; Bluemn, E.; et al. Distinct transcriptional programs mediated by the ligand-dependent full-length androgen receptor and its splice variants in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3457–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehm, S.M.; Tindall, D.J. Alternatively spliced androgen receptor variants. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2011, 18, R183–R196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Kagechika, H. Androgen receptor modulators: A review of recent patents and reports (2012–2018). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basil, P.; Robertson, M.J.; Bingman, W.E., III; Dash, A.K.; Krause, W.C.; Shafi, A.A.; Piyarathna, B.; Coarfa, C.; Weigel, N.L. Cistrome and transcriptome analysis identifies unique androgen receptor (AR) and AR-V7 splice variant chromatin binding and transcriptional activities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, M.; Sato, H.; Okabe, A.; Fukuyo, M.; Mano, Y.; Shinohara, K.I.; Rahmutulla, B.; Higuchi, K.; Maimaiti, M.; Kanesaka, M.; et al. Identification of AR-V7 downstream genes commonly targeted by AR/AR-V7 and specifically targeted by AR-V7 in castration resistant prostate cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.C.; Selth, L.A.; Li, Y.; Nyquist, M.D.; Miao, L.; Bradner, J.E.; Raj, G.V.; Tilley, W.D.; Dehm, S.M. Targeting chromatin binding regulation of constitutively active AR variants to overcome prostate cancer resistance to endocrine-based therapies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 5880–5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Zhan, Y.; Qi, Y.; Cao, B.; Bai, S.; Xu, W.; Gambhir, S.S.; Lee, P.; Sartor, O.; Flemington, E.K.; et al. Androgen receptor splice variants dimerize to transactivate target genes. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3663–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cato, L.; de Tribolet-Hardy, J.; Lee, I.; Rottenberg, J.T.; Coleman, I.; Melchers, D.; Houtman, R.; Xiao, T.; Li, W.; Uo, T.; et al. ARv7 represses tumor-suppressor genes in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 401–413 e406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.A.; Chen, Y.F.; Balbas, M.D.; Wongvipat, J.; Socci, N.D.; Viale, A.; Kim, K.; Sawyers, C.L. Constitutively active androgen receptor splice variants expressed in castration-resistant prostate cancer require full-length androgen receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16759–16765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lonergan, P.E.; Nacusi, L.P.; Wang, L.; Schmidt, L.J.; Sun, Z.; Van der Steen, T.; Boorjian, S.A.; Kosari, F.; Vasmatzis, G.; et al. The cistrome and gene signature of androgen receptor splice variants in castration resistant prostate cancer cells. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uo, T.; Dvinge, H.; Sprenger, C.C.; Bradley, R.K.; Nelson, P.S.; Plymate, S.R. Systematic and functional characterization of novel androgen receptor variants arising from alternative splicing in the ligand-binding domain. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1440–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, L.; Poluben, L.; Nouri, M.; Arai, S.; Xie, L.; Voznesensky, O.S.; Cato, L.; Yuan, X.; Russo, J.W.; et al. Androgen receptor splice variant 7 functions independently of the full length receptor in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2021, 519, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, A.; Coleman, I.; Yuan, W.; Sprenger, C.; Dolling, D.; Rodrigues, D.N.; Russo, J.W.; Figueiredo, I.; Bertan, C.; Seed, G.; et al. Androgen receptor splice variant-7 expression emerges with castration resistance in prostate cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarra, A.; Maggi, M.; Salciccia, S.; Nicolai, A.; Tortorella, E.; Giantulli, S.; Magliocca, F.M.; Silvestri, I.; Taglieri, L.; Cattarino, S.; et al. Tissue expression of androgen receptor splice variant 7 at radical prostatectomy predicts risk of progression in untreated nonmetastatic prostate cancer. Oncology 2021, 99, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Lu, C.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Nakazawa, M.; Roeser, J.C.; Chen, Y.; Mohammad, T.A.; Chen, Y.; Fedor, H.L.; et al. AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.J.; Halabi, S.; Luo, J.; Nanus, D.M.; Giannakakou, P.; Szmulewitz, R.Z.; Danila, D.C.; Healy, P.; Anand, M.; Rothwell, C.J.; et al. Prospective multicenter validation of androgen receptor splice variant 7 and hormone therapy resistance in high-risk castration-resistant prostate cancer: The PROPHECY study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Dong, Q.; Liu, L.R.; Wei, Q. ARV-7: A biomarker for the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue 2019, 25, 172–176. [Google Scholar]
- Iacovelli, R.; Ciccarese, C.; Schinzari, G.; Rossi, E.; Maiorano, B.A.; Astore, S.; D’Angelo, T.; Cannella, A.; Pirozzoli, C.; Teberino, M.A.; et al. Biomarkers of response to advanced prostate cancer therapy. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csizmarik, A.; Hadaschik, B.; Kramer, G.; Nyirady, P.; Szarvas, T. Mechanisms and markers of resistance to androgen signaling inhibitors in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 728.e713–728.e724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sharp, A.; Anderson, C.M.; Silberstein, J.L.; Taylor, M.; Lu, C.; Zhao, P.; De Marzo, A.M.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Wang, M.; et al. Novel junction-specific and quantifiable in situ detection of AR-V7 and its clinical correlates in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, D.; Allioli, N.; Peron, J.; Plesa, A.; Decaussin-Petrucci, M.; Tartas, S.; Ruffion, A.; Crouzet, S.; Rimokh, R.; Gillet, P.G.; et al. Improved androgen receptor splice variant 7 detection using a highly sensitive assay to predict resistance to abiraterone or enzalutamide in metastatic prostate cancer patients. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, Y.; Tam, T.; Jian, K.; Andersen, R.J.; Sadar, M.D. Combination therapy with androgen receptor N-terminal domain antagonist EPI-7170 and enzalutamide yields synergistic activity in AR-V7-positive prostate cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 2455–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Dalrymple, S.L.; Coleman, I.; Zheng, S.L.; Xu, J.; Hooper, J.E.; Antonarakis, E.S.; De Marzo, A.M.; Meeker, A.K.; Nelson, P.S.; et al. Role of androgen receptor splice variant-7 (AR-V7) in prostate cancer resistance to 2nd-generation androgen receptor signaling inhibitors. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6935–6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Li, Y.; Tan, X.; Fu, L. Small heat shock proteins in cancers: Functions and therapeutic potential for cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftekharzadeh, B.; Banduseela, V.C.; Chiesa, G.; Martinez-Cristobal, P.; Rauch, J.N.; Nath, S.R.; Schwarz, D.M.C.; Shao, H.; Marin-Argany, M.; Di Sanza, C.; et al. Hsp70 and Hsp40 inhibit an inter-domain interaction necessary for transcriptional activity in the androgen receptor. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, W.B.; Toft, D.O. Regulation of signaling protein function and trafficking by the hsp90/hsp70-based chaperone machinery. Exp. Biol. Med. 2003, 228, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, W.B.; Gestwicki, J.E.; Osawa, Y.; Lieberman, A.P. Targeting Hsp90/Hsp70-based protein quality control for treatment of adult onset neurodegenerative diseases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 55, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiliccioglu, I.; Konac, E.; Dikmen, A.U.; Sozen, S.; Bilen, C.Y. Hsp-27 and NF-kappaB pathway is associated with AR/AR-V7 expression in prostate cancer cells. Gene 2019, 697, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stope, M.B.; Schubert, T.; Staar, D.; Ronnau, C.; Streitborger, A.; Kroeger, N.; Kubisch, C.; Zimmermann, U.; Walther, R.; Burchardt, M. Effect of the heat shock protein HSP27 on androgen receptor expression and function in prostate cancer cells. World J. Urol. 2012, 30, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.A.; Zoubeidi, A.; Gleave, M.E.; Chi, K.N. Targeting heat shock proteins in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2015, 12, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, D. Regulation of Hsf1 and the heat shock response. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1243, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, L.Q.; Lavery, D.N.; Bevan, C.L. Mini-review: Foldosome regulation of androgen receptor action in prostate cancer. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2013, 369, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Fliss, A.E.; Robins, D.M.; Caplan, A.J. Hsp90 regulates androgen receptor hormone binding affinity in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 28697–28702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoubeidi, A.; Zardan, A.; Beraldi, E.; Fazli, L.; Sowery, R.; Rennie, P.; Nelson, C.; Gleave, M. Cooperative interactions between androgen receptor (AR) and heat-shock protein 27 facilitate AR transcriptional activity. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10455–10465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Manola, J.B.; Oh, W.K.; Parslow, D.L.; George, D.J.; Austin, C.L.; Kantoff, P.W. Plasma levels of heat shock protein 70 in patients with prostate cancer: A potential biomarker for prostate cancer. Clin. Prostate Cancer 2004, 3, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, M.A.; Kim, Y.S.; Rivera-Marquez, G.M.; Oshima, N.; Watson, M.J.; Beebe, K.E.; Wells, C.; Lee, S.; Zuehlke, A.D.; Shao, H.; et al. Targeting the Hsp40/Hsp70 chaperone axis as a novel strategy to treat castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4022–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Lou, W.; Zhu, Y.; Nadiminty, N.; Schwartz, C.T.; Evans, C.P.; Gao, A.C. Niclosamide inhibits androgen receptor variants expression and overcomes enzalutamide resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3198–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, K.; Chen, S.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Long, Y.; Hu, Z.; Xu, G. The E3 ubiquitin ligase STUB1 attenuates cell senescence by promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of the core circadian regulator BMAL1. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4696–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lou, W.; Yang, J.C.; Liu, L.; Armstrong, C.M.; Lombard, A.P.; Zhao, R.; Noel, O.D.V.; Tepper, C.G.; Chen, H.W.; et al. Proteostasis by STUB1/HSP70 complex controls sensitivity to androgen receptor targeted therapy in advanced prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Armstrong, C.M.; Ning, S.; Yang, J.C.; Lou, W.; Lombard, A.P.; Zhao, J.; Wu, C.Y.; Yu, A.; Evans, C.P.; et al. ARVib suppresses growth of advanced prostate cancer via inhibition of androgen receptor signaling. Oncogene 2021, 40, 5379–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.J.; Jeong, B.C.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, J.E.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, G.Y.; Jackman, J.A.; Kim, J.H. Bruceantin targets HSP90 to overcome resistance to hormone therapy in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Theranostics 2021, 11, 958–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, A.A.; Cox, M.B.; Weigel, N.L. Androgen receptor splice variants are resistant to inhibitors of Hsp90 and FKBP52, which alter androgen receptor activity and expression. Steroids 2013, 78, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, J.L.; Selth, L.A.; Centenera, M.M.; Townley, S.L.; Sun, S.; Plymate, S.R.; Tilley, W.D.; Butler, L.M. Constitutively-active androgen receptor variants function independently of the HSP90 chaperone but do not confer resistance to HSP90 inhibitors. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraldeschi, R.; Welti, J.; Powers, M.V.; Yuan, W.; Smyth, T.; Seed, G.; Riisnaes, R.; Hedayat, S.; Wang, H.; Crespo, M.; et al. Second-generation HSP90 inhibitor onalespib blocks mRNA splicing of androgen receptor variant 7 in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2731–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, C.; Shao, Z.; Xia, X.; Hu, T.; Kong, W.; He, X.; Sun, W.; Deng, Y.; Liao, Y.; et al. Selective degradation of AR-V7 to overcome castration resistance of prostate cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deveci Ozkan, A.; Kaleli, S.; Onen, H.I.; Sarihan, M.; Guney Eskiler, G.; Kalayci Yigin, A.; Akdogan, M. Anti-inflammatory effects of nobiletin on TLR4/TRIF/IRF3 and TLR9/IRF7 signaling pathways in prostate cancer cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 42, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Creed, A.; Chen, A.Y.; Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Rankin, G.O.; Ye, X.; Xu, G.; Chen, Y.C. Nobiletin suppresses cell viability through AKT pathways in PC-3 and DU-145 prostate cancer cells. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Yan, K.; Liu, J.; Fang, Z.; Fan, Y. Huaier extract inhibits prostate cancer growth via targeting AR/AR-V7 pathway. Front Oncol. 2021, 11, 615568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, X.; Shao, Z.; Huang, C.; He, J.; Jiang, L.; Tang, D.; Liu, J.; Huang, H. Targeting GRP78-dependent AR-V7 protein degradation overcomes castration-resistance in prostate cancer therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3366–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.T.; Nagaya, N.; Desantis, J.; Madura, K.; Sabaawy, H.E.; Kim, W.J.; Vaz, R.J.; Cruciani, G.; Kim, I.Y. Effects of MTX-23, a novel PROTAC of androgen receptor splice variant-7 and androgen receptor, on CRPC resistant to second-line antiandrogen therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, K.; Shiota, M.; Tanaka, M.; Otsuka, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Kato, M.; Tamada, S.; Iwao, H.; Miura, K.; Nakatani, T.; et al. Heat shock protein 70 inhibitors suppress androgen receptor expression in LNCaP95 prostate cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Armstrong, C.M.; Lou, W.; Lombard, A.P.; Cucchiara, V.; Gu, X.; Yang, J.C.; Nadiminty, N.; Pan, C.X.; Evans, C.P.; et al. Niclosamide and bicalutamide combination treatment overcomes enzalutamide- and bicalutamide-resistant prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, N.; Generali, D.; D’Angelo, A.; Aieta, M.; Roviello, G. Current status of androgen receptor-splice variant 7 inhibitor niclosamide in castrate-resistant prostate-cancer. Invest New Drugs 2018, 36, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, J.C.; Armstrong, C.M.; Lou, W.; Liu, L.; Qiu, X.; Zou, B.; Lombard, A.P.; D’Abronzo, L.S.; Evans, C.P.; et al. AKR1C3 promotes AR-V7 protein stabilization and confers resistance to AR-targeted therapies in advanced prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1875–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, S.; Fang, Y.; Sun, G.; He, D.; Hsieh, J.T.; Wang, X.; Zeng, H.; Wu, K. The AKR1C3/AR-V7 complex maintains CRPC tumour growth by repressing B4GALT1 expression. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 12032–12043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Chen, J.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, F.; et al. CX4945 suppresses the growth of castration-resistant prostate cancer cells by reducing AR-V7 expression. World J. Urol. 2017, 35, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.B.; Ji, X.; Singh, S.V. Therapeutic potential of leelamine, a novel inhibitor of androgen receptor and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 2079–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Yamashita, H.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Franco, O.E.; Wang, Y.; Hayward, S.W.; Matusik, R.J. Inhibition of NF-kappa B signaling restores responsiveness of castrate-resistant prostate cancer cells to anti-androgen treatment by decreasing androgen receptor-variant expression. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3700–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Park, S.E.; Moon, J.W.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, H.G.; Jeong, I.G.; Yoo, S.; Ahn, J.B.; You, D.; Pak, J.H.; et al. Downregulation of androgen receptors by NaAsO2 via inhibition of AKT-NF-kappaB and HSP90 in castration resistant prostate cancer. Prostate 2017, 77, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, S.; Lai, K.P.; Chuang, K.L.; Xu, D.; Miyamoto, H.; Tochigi, T.; Pang, S.T.; Li, L.; Arai, Y.; Kung, H.J.; et al. ASC-J9 suppresses castration-resistant prostate cancer growth through degradation of full-length and splice variant androgen receptors. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiki-Ito, A.; Naiki, T.; Kato, H.; Iida, K.; Etani, T.; Nagayasu, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Inaguma, S.; Onishi, M.; et al. Recruitment of miR-8080 by luteolin inhibits androgen receptor splice variant 7 expression in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, J.E.; Steri, V.; Nguyen, H.G.; Hann, B.; Feng, F.Y.; Shokat, K.M. The splicing modulator sulfonamide indisulam reduces AR-V7 in prostate cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, M.C.; Daulagala, A.C.; Kourtidis, A. LNCcation: LncRNA localization and function. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, M.; Kitagawa, K.; Kotake, Y.; Niida, H.; Ohhata, T. Cell cycle regulation by long non-coding RNAs. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4785–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delas, M.J.; Sabin, L.R.; Dolzhenko, E.; Knott, S.R.; Munera Maravilla, E.; Jackson, B.T.; Wild, S.A.; Kovacevic, T.; Stork, E.M.; Zhou, M.; et al. lncRNA requirements for mouse acute myeloid leukemia and normal differentiation. Elife 2017, 6, 25607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirey, T.M.; Roberts, K.; Haerty, W.; Bedoya-Reina, O.; Rogatti-Granados, S.; Tan, J.Y.; Li, N.; Heather, L.C.; Carter, R.N.; Cooper, S.; et al. The long non-coding RNA Cerox1 is a post transcriptional regulator of mitochondrial complex I catalytic activity. Elife 2019, 8, 45051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, J.L.; Kim, S.Y.; Hwang, J.A.; Kunkeaw, N.; Jung, S.Y.; Kim, T.J.; et al. nc886 is induced by TGF-beta and suppresses the microRNA pathway in ovarian cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postepska-Igielska, A.; Giwojna, A.; Gasri-Plotnitsky, L.; Schmitt, N.; Dold, A.; Ginsberg, D.; Grummt, I. LncRNA Khps1 regulates expression of the proto-oncogene SPHK1 via triplex-mediated changes in chromatin structure. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.T.; Lin, J.F.; Li, T.; Li, J.J.; Xu, R.H.; Ju, H.Q. LncRNA-mediated posttranslational modifications and reprogramming of energy metabolism in cancer. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cho, K.B.; Li, Y.; Tao, G.; Xie, Z.; Guo, B. Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-mediated competing endogenous RNA networks provide novel potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.J.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, C.Q.; Lim, M.C.; An, O.; Mayakonda, A.; Ding, L.W.; Long, L.; Sun, C.; et al. Super-enhancer-driven long non-coding RNA LINC01503, regulated by TP63, is over-expressed and oncogenic in squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 2137–2151.e2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessels, D.; Klein Gunnewiek, J.M.; van Oort, I.; Karthaus, H.F.; van Leenders, G.J.; van Balken, B.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Witjes, J.A.; Schalken, J.A. DD3(PCA3)-based molecular urine analysis for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2003, 44, 8–15, Discussion 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.L.; Dobi, A.; Srivastava, S. Prostate cancer: Diagnostic performance of the PCA3 urine test. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2011, 8, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Long, W.; Liu, Q. Targeting super-enhancers as a therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabari, B.R.; Dall’Agnese, A.; Boija, A.; Klein, I.A.; Coffey, E.L.; Shrinivas, K.; Abraham, B.J.; Hannett, N.M.; Zamudio, A.V.; Manteiga, J.C.; et al. Coactivator condensation at super-enhancers links phase separation and gene control. Science 2018, 361, aar3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Z.; Yu, J.; Sun, L.; Tian, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, B.; Dong, Q.; Jiang, N.; Flores-Morales, A.; Chang, C.; et al. LncRNA PCAT1 activates AKT and NF-kappaB signaling in castration-resistant prostate cancer by regulating the PHLPP/FKBP51/IKKalpha complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 4211–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Quan, C.; Niu, Y.; Huang, H. Aberrant activation of super enhancer and choline metabolism drive antiandrogen therapy resistance in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6556–6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Niu, Y.; Lin, W.; Lin, C.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Luo, J.; Yeh, S.; Chang, C. Preclinical study using malat1 small interfering RNA or androgen receptor splicing variant 7 degradation enhancer ASC-J9((R)) to suppress enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer progression. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lin, C.; Jin, C.; Yang, J.C.; Tanasa, B.; Li, W.; Merkurjev, D.; Ohgi, K.A.; Meng, D.; Zhang, J.; et al. lncRNA-dependent mechanisms of androgen-receptor-regulated gene activation programs. Nature 2013, 500, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Sun, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, F.; Wei, M.; Shen, J.; Hou, J.; Gao, X.; et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 is a new potential therapeutic target for castration resistant prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 2278–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, V.; Ellis, J.D.; Shen, Z.; Song, D.Y.; Pan, Q.; Watt, A.T.; Freier, S.M.; Bennett, C.F.; Sharma, A.; Bubulya, P.A.; et al. The nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutschner, T.; Hammerle, M.; Eissmann, M.; Hsu, J.; Kim, Y.; Hung, G.; Revenko, A.; Arun, G.; Stentrup, M.; Gross, M.; et al. The noncoding RNA MALAT1 is a critical regulator of the metastasis phenotype of lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 2013, 73, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, M.; Shen, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, F.; Hou, J.; Yao, W. LncRNA PCBP1-AS1-mediated AR/AR-V7 deubiquitination enhances prostate cancer enzalutamide resistance. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildiyal, R.; Sawant, M.; Renganathan, A.; Mahajan, K.; Kim, E.H.; Luo, J.; Dang, H.X.; Maher, C.A.; Feng, F.Y.; Mahajan, N.P. Loss of long noncoding RNA NXTAR in prostate cancer augments androgen receptor expression and enzalutamide resistance. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhu, S.; Niu, Y.; Shang, Z. Targeting KDM4A-AS1 represses AR/AR-Vs deubiquitination and enhances enzalutamide response in CRPC. Oncogene 2022, 41, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Wang, K.; Yeh, S.; Sun, Y.; Liang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, W.; Niu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Maity, S.N.; et al. LncRNA-p21 alters the antiandrogen enzalutamide-induced prostate cancer neuroendocrine differentiation via modulating the EZH2/STAT3 signaling. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Ramnarine, V.R.; Song, J.H.; Pandey, R.; Padi, S.K.R.; Nouri, M.; Olive, V.; Kobelev, M.; Okumura, K.; McCarthy, D.; et al. The long noncoding RNA H19 regulates tumor plasticity in neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhao, J.C.; Kim, J.; Fong, K.W.; Yang, Y.A.; Chakravarti, D.; Mo, Y.Y.; Yu, J. LncRNA HOTAIR enhances the androgen-receptor-mediated transcriptional program and drives castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, F.J.; Lin, C.; Tian, H.; Lin, W.; You, B.; Lu, J.; Sahasrabudhe, D.; Huang, C.P.; Yang, V.; Yeh, S.; et al. Preclinical studies using cisplatin/carboplatin to restore the Enzalutamide sensitivity via degrading the androgen receptor splicing variant 7 (ARv7) to further suppress Enzalutamide resistant prostate cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Pitchiaya, S.; Cieslik, M.; Niknafs, Y.S.; Tien, J.C.; Hosono, Y.; Iyer, M.K.; Yazdani, S.; Subramaniam, S.; Shukla, S.K.; et al. Analysis of the androgen receptor-regulated lncRNA landscape identifies a role for ARLNC1 in prostate cancer progression. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Pu, X.; Luo, M.; Wen, H.; Xu, Z.; Wei, Q.; Dang, Q. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 interacts and suppresses androgen receptor activity in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2021, 81, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guise, C.P.; Abbattista, M.R.; Singleton, R.S.; Holford, S.D.; Connolly, J.; Dachs, G.U.; Fox, S.B.; Pollock, R.; Harvey, J.; Guilford, P.; et al. The bioreductive prodrug PR-104A is activated under aerobic conditions by human aldo-keto reductase 1C3. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lou, W.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.C.; Nadiminty, N.; Gaikwad, N.W.; Evans, C.P.; Gao, A.C. Intracrine androgens and AKR1C3 activation confer resistance to enzalutamide in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsler, H.; McAinsh, A.D. Kinesin-12 motors cooperate to suppress microtubule catastrophes and drive the formation of parallel microtubule bundles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1635–E1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, F.; Liu, H.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Su, P.; et al. KIF15-mediated stabilization of AR and AR-V7 contributes to enzalutamide resistance in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.; Bellanti, J.A.; Zheng, S.G. Advances on the role of the deleted in breast cancer (DBC1) in cancer and autoimmune diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 109, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.J.; Jeong, B.C.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, J.E.; Kwon, G.Y.; Kim, J.H. DBC1 promotes castration-resistant prostate cancer by positively regulating DNA binding and stability of AR-V7. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1326–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trembley, J.H.; Kren, B.T.; Abedin, M.J.; Shaughnessy, D.P.; Li, Y.; Dehm, S.M.; Ahmed, K. CK2 pro-survival role in prostate cancer is mediated via maintenance and promotion of androgen receptor and NFkappaB p65 expression. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouhtit, A.; Al-Kindi, M.N.; Kumar, P.R.; Gupta, I.; Shanmuganathan, S.; Tamimi, Y. Hoxb13, a potential prognostic biomarker for prostate cancer. Front. Biosci. 2016, 8, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, D.; Thomas-Ahner, J.M.; Lu, C.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Q.; Geraghty, C.; Yan, P.S.; Hankey, W.; Sunkel, B.; et al. Diverse AR-V7 cistromes in castration-resistant prostate cancer are governed by HoxB13. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6810–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Jerome, J.M.; Dang, T.D.; Souto, E.P.; Mallam, J.N.; Rowley, D.R. Androgen receptor variant-7 regulation by tenascin-c induced src activation. Cell Commun. Signal 2022, 20, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Fan, L.; Jeon, H.Y.; Zhang, F.; Cui, X.; Mickle, M.B.; Peng, G.; Hussain, A.; Fazli, L.; Gleave, M.E.; et al. p300-mediated acetylation of histone demethylase JMJD1A prevents its degradation by ubiquitin ligase STUB1 and enhances its activity in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 3074–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).