Prognostic Factors for Overall Survival in Patients with HCV-Related HCC Undergoing Molecular Targeted Therapies: Beyond a Sustained Virological Response
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Treatment Regimens
2.3. Clinical Outcome Assessment and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
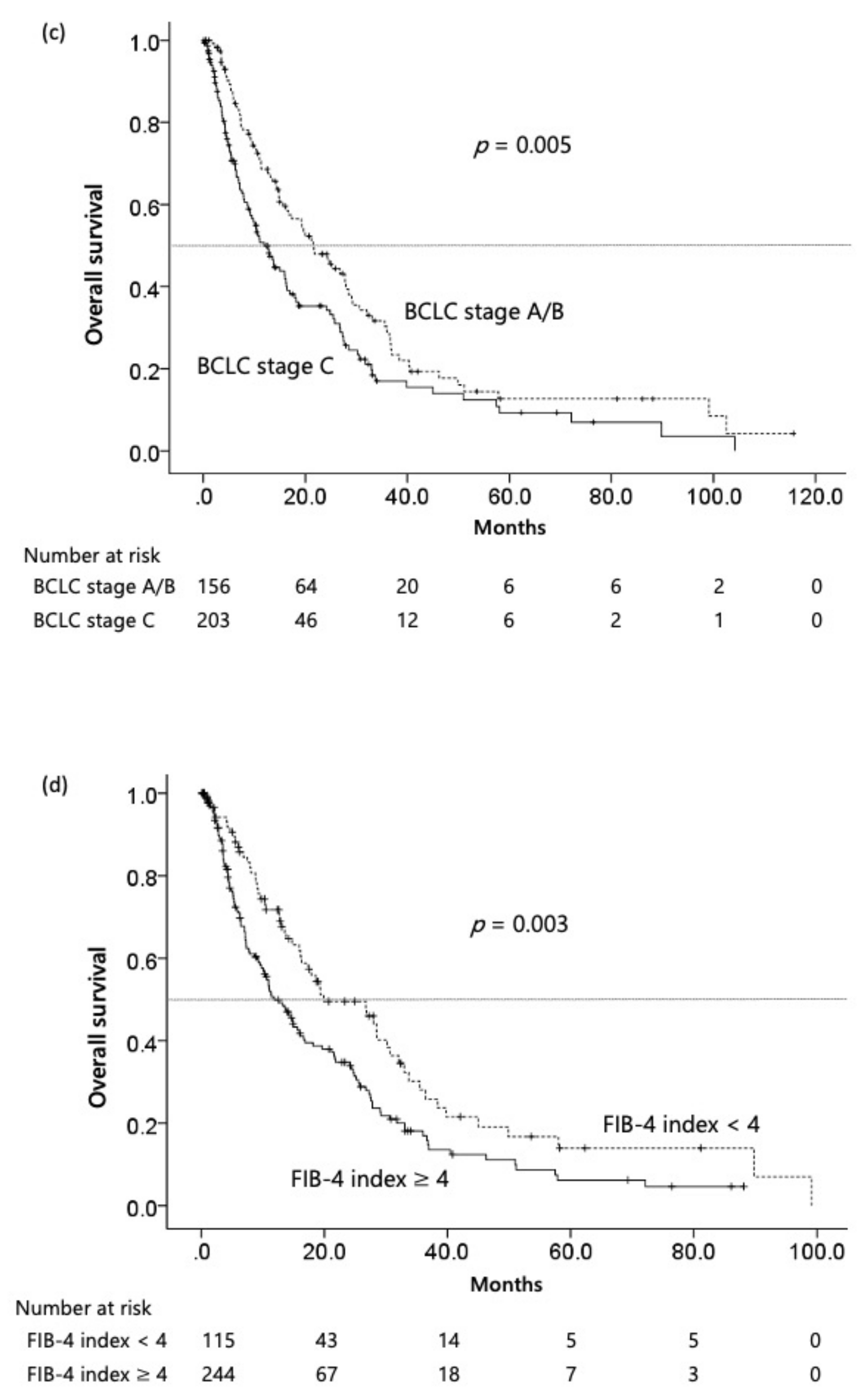
3.2. Survival Analysis
3.3. Independent Factors for OS of HCV-Related HCC Patients after Molecular Targeted Chemotherapy
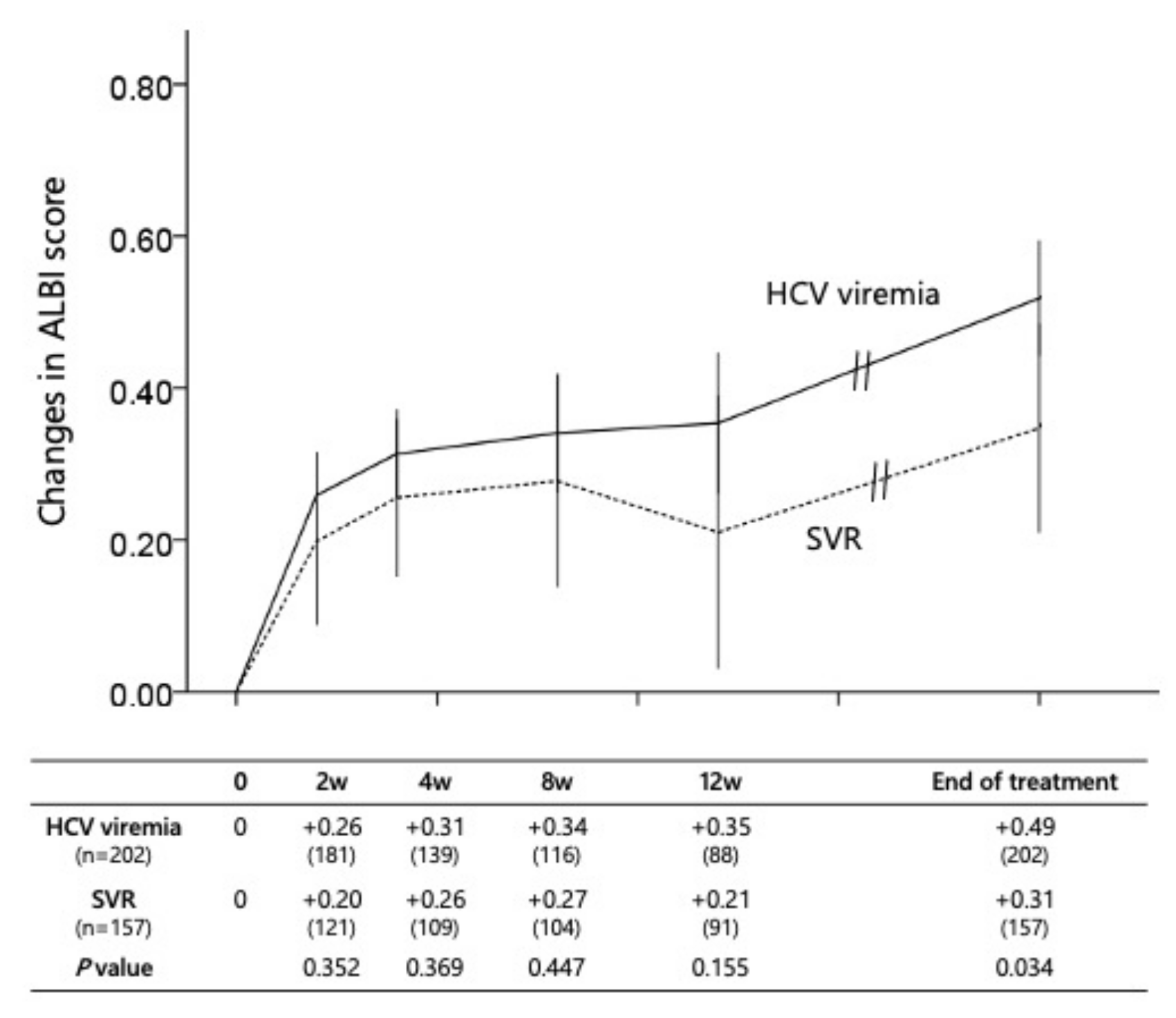
3.4. Dynamic Changes in the Liver Abnormality during First Chemotherapy
3.5. Second and Subsequent Chemotherapies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | angiotensin converting enzyme |
| AFP | alpha-fetoprotein |
| ALBI | albumin-bilirubin |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| ARB | angiotensin receptor blocker |
| ATZ/BV | combination of atezolizumab and bevacizumab |
| BCLC | Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer |
| DCP | des-γ-carboxy prothrombin |
| FIB-4 | fibrosis-4 |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | hepatitis C virus |
| ICI | immune checkpoint inhibitor |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| SVR | sustained virological response |
| TKI | tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vescovo, T.; Refolo, G.; Vitagliano, G.; Fimia, G.M.; Piacentini, M. Molecular mechanisms of hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Montal, R.; Sia, D.; Finn, R.S. Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M. Recent advances in systemic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in an aging society: 2020 update. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 640–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan: Current trends. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M. A paradigm change in the treatment strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Tsao, G.; Abraldes, J.G.; Berzigotti, A.; Bosch, J. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 2017, 65, 310–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Tsao, G.; Lim, J.K.; Members of Veterans Affairs Hepatitis C Resource Center Program. Management and treatment of patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension: Recommendations from the Department of Veterans Affairs Hepatitis C Resource Center Program and the National Hepatitis C Program. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 1802–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourlière, M.; Gordon, S.C.; Flamm, S.L.; Cooper, C.L.; Ramji, A.; Tong, M.; Ravendhran, N.; Vierling, J.M.; Tran, T.T.; Pianko, S.; et al. Sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and voxilaprevir for previously treated HCV infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2134–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiji, H.; Nagoshi, S.; Akahane, T.; Asaoka, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kurosaki, M.; Sakaida, I.; Shimizu, M.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for Liver Cirrhosis 2020. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, H.; Yeo, Y.H.; Yasuda, S.; Huang, C.F.; Iio, E.; Landis, C.; Jun, D.W.; Enomoto, M.; Ogawa, E.; Tsai, P.C.; et al. Cure with interferon-free direct-acting antiviral is associated with increased survival in patients with hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma from both East and West. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1910–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.C.; Lin, Y.S.; Chang, C.W.; Chang, C.W.; Wang, T.E.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, M.J. Impact of direct-acting antiviral therapy for hepatitis C–related hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, M.L.; Liang, P.C.; Tsai, P.C.; Wang, S.C.; Leong, J.; Ogawa, E.; Jun, D.W.; Tseng, C.H.; Landis, C.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Characteristics and survival outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma developed after HCV SVR. Cancers 2021, 13, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Sherman, M. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Bashir, M.R.; Corwin, M.T.; Cruite, I.; Dietrich, C.F.; Do, R.K.G.; Ehman, E.C.; Fowler, K.J.; Hussain, H.K.; Jha, R.C. Evidence Supporting LI-RADS Major Features for CT- and MR Imaging-based Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Radiology 2018, 286, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.L.; Baack, B.; Smith, B.D.; Yartel, A.; Pitasi, M.; Falck-Ytter, Y. Eradication of hepatitis C virus infection and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabibbo, G.; Celsa, C.; Cammà, C.; Craxì, A. Should we cure hepatitis C virus in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma while treating cancer? Liver Int. 2018, 38, 2108–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Shen, D.; Che, Y.Q. Eradication of hepatitis C virus (HCV) improves survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with active HCV infection—A real-world cohort study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 5323–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seko, Y.; Moriguchi, M.; Takahashi, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Umemura, A.; Okuda, K.; Kataoka, S.; Unozawa, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Ogasawara, S.; et al. Hepatitis C virus eradication prolongs overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving molecular-targeted agents. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 57, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Shao, P.P.; Chen, W.T.; Lin, C.C.; Lin, W.R.; Yeh, C.T. Direct-acting antiviral therapy improves the outcome of chronic hepatitis C/intermediate-stage B hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-S.; Chao, Y.-C.; Lin, H.H.; Chen, D.-S.; Kao, J.-H. Systematic review: Impact of interferon-based therapy on HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, B.K.; Teo, J.Y.; Chan, C.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Jeyaraj, P.; Cheow, P.C.; Chow, P.K.; Ooi, L.L.; Chung, A.Y. Importance of tumor size as a prognostic factor after partial liver resection for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma: Implications on the current AJCC staging system. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 113, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, R.; Jin, K.; Zhangyuan, G.; Yu, W.; Yin, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Sun, B. Prognostic value of marital status on stage at diagnosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wen, Z. Survival improvement and prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis of the SEER database. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1157. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Hanna, D.L.; Usher, J.; LoCoco, J.; Chaudhari, P.; Lenz, H.J.; Setiawan, V.W.; El-Khoueiry, A. Impact of sex on the survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A Surveillance, epidemiology, and end results analysis. Cancer 2014, 120, 3707–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Prognostic indicators in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of 72 studies. Liver Int. 2009, 29, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Kiriyama, S.; Sone, Y.; Tanikawa, M.; Hisanaga, Y.; Kitabatake, S.; Kuzuya, T.; Nonogaki, K.; et al. Relationship between Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive α-fetoprotein and pathologic features of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2005, 25, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, Y.; Shiratori, Y.; Sato, S.; Obi, S.; Teratani, T.; Imamura, M.; Yoshida, H.; Shiina, S.; Omata, M. Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin as a useful predisposing factor for the development of portal venous invasion in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective analysis of 227 patients. Cancer 2001, 91, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, H.; Kumada, T.; Osaki, Y.; Oka, H.; Kudo, M. Role of tumor markers in assessment of tumor progression and prediction of outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 37 (Suppl. 2), S166–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Imamura, H.; Matsuyama, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Beck, Y.; Sugawara, Y.; Makuuchi, M.; Kokudo, N. Significance of alpha-fetoprotein and des-γ-carboxy prothrombin in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing hepatectomy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 2795–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, J.; Yamanaka, N.; Nakasho, K.; Tanaka, T.; Ando, T.; Yasui, C.; Kuroda, N.; Takata, M.; Maeda, S.; Matsushita, K.; et al. Clinicopathologic analysis of stage II-III hepatocellular carcinoma showing early massive recurrence after liver resection. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 15, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macías, J.; Girón-González, J.A.; González-Serrano, M.; Merino, D.; Cano, P.; Mira, J.A.; Arizcorreta-Yarza, A.; Ruíz-Morales, J.; Lomas-Cabeza, J.M.; García-García, J.A.; et al. Prediction of liver fibrosis in human immunodeficiency virus/hepatitis C virus coinfected patients by simple non-invasive indexes. Gut 2006, 55, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, R.J.; Lok, A.S.F. Noninvasive monitoring of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2002, 36, S57–S64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calès, P.; Oberti, F.; Michalak, S.; Hubert-Fouchard, I.; Rousselet, M.C.; Konaté, A.; Gallois, Y.; Ternisien, C.; Chevailler, A.; Lunel, F. A novel panel of blood markers to assess the degree of liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, T. L, Liu, P.H. Too many versus too few platelets in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Good or bad? Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 108–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Hui, J.M.; Marchesini, G.; Bugianesi, E.; George, J.; Farrell, G.C.; Enders, F.; Saksena, S.; Burt, A.D.; Bida, J.P.; et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: A noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology 2007, 45, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, B.; Park, S.; Shin, D.W.; Yun, J.M.; Yang, H.K.; Yu, S.J.; Shin, C.I.; Kim, J.S.; Ahn, E.; Lee, H.; et al. High liver fibrosis index FIB-4 is highly predictive of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B carriers. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.R.; Mapakshi, S.; Natarajan, Y.; Chayanupatkul, M.; Richardson, P.A.; Li, L.; Desiderio, R.; Thrift, A.P.; Asch, S.M.; et al. Risk of hepatocellular cancer in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1828–1837.e1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M. Newly developed modified ALBI grade shows better prognostic and predictive value for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2022, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadori, G.; Cameron, S. Effects of systemic chemotherapy on the liver. Ann. Hepatol. 2010, 9, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Houshyar, R.; Bhosale, P.; Choi, J.I.; Gulati, R.; Lall, C. Chemotherapy induced liver abnormalities: An imaging perspective. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2014, 20, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczmarek-Borowska, B.; Sałek-Zań, A. Hepatotoxicity of molecular targeted therapy. Contemp. Oncol. 2015, 19, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meadows, K.L.; Hurwitz, H.I. Anti-VEGF therapies in the clinic. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, A.; Scholar, E.M. Role of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudd, T.W.; Guddati, A.K. Management of hepatotoxicity of chemotherapy and targeted agents. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 3461–3474. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, N.; Du, H.; Zhou, B.; Ye, Y. Statins in hepatitis B or C patients is associated with reduced hepatocellular carcinoma risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 33, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, C. Simvastatin ameliorates liver fibrosis via mediating nitric oxide synthase in rats with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related liver fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Shi, J.; Dang, S. Aspirin use and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 56, e293–e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureddin, M.; Abdelmalek, M.F. ACE inhibitors: The secret to prevent cirrhosis complications and HCC in NAFLD? Hepatology 2022, 76, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.B.; Pagadala, M.R.; Dasarathy, J.; Unalp-Arida, A.; Sargent, R.; Hawkins, C.; Sourianarayanane, A.; Khiyami, A.; Yerian, L.; Pai, R.; et al. Renin-angiotensin system and fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiji, H.; Noguchi, R.; Ikenaka, Y.; Kaji, K.; Shirai, Y.; Aihara, Y.; Yamao, J.; Toyohara, M.; Mitoro, A.; Sawai, M.; et al. Soluble VEGF receptor-2 may be a predictive marker of anti-angiogenic therapy with clinically available safe agents. Oncol. Lett. 2011, 2, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sex | |
|---|---|
| Male/Female | 277/82 |
| Age (year) | |
| Median (range) | 74 (42–94) |
| Body mass index | |
| Median (range) | 22.2 (13.1–32.0) |
| BCLC stage C, % | 56.3 |
| Vascular invasion, % | 29.8 |
| Extrahepatic spread, % | 33.4 |
| FIB-4 index | |
| Median (range) | 5.50 (0.81–28.9) |
| Serum albumin (g/dl) | |
| Median (range) | 3.5 (1.9–5.1) |
| Serum total bilirubin (g/dl) | |
| Median (range) | 0.80 (0.2–2.5) |
| Serum ALT (IU/mL) | |
| Median (range) | 35 (8–232) |
| ALBI score | |
| Median (IQR) | −2.23 (−3.55 to −1.10) |
| Child–Pugh class A, % | 75.2 |
| Serum AFP (ng/mL) | |
| Median (range) | 148.5 (1.0–1,523,200) |
| Serum DCP | |
| Median (range) | 687.0 (7.0–1,805,900) |
| First-line chemotherapy regimen | |
| Sorafenib/Lenvatinib/ATZ/BV | 275/48/36 |
| Factor | Category | Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <70 | 1 | ||
| ≥70 | 1.150 | 0.83–1.592 | NS | |
| Sex | Female | 1 | ||
| Male | 1.009 | 0.715–1.424 | NS | |
| BCLC stage | stage A/B | 1 | ||
| sage C | 1.816 | 1.331–2.477 | <0.001 | |
| Extrahepatic spread | No | 1 | ||
| Yes | 1.976 | 1.405–2.780 | <0.001 | |
| Vascular invasion | No | 1 | ||
| Yes | 1.130 | 0.771–1.657 | 0.530 | |
| AFP | <90 | 1 | ||
| 90≥ | 1.433 | 1.021–2.012 | 0.038 | |
| DCP | <500 | 1 | ||
| ≥500 | 1.605 | 1.135–2.270 | <0.001 | |
| ALT | <27 IU/l | 1 | ||
| ≥27 IU/l | 1.201 | 0.859–1.680 | NS | |
| ALBI grade | grade I | 1 | ||
| grade II/III | 1.484 | 1.060–2.079 | 0.022 | |
| FIB-4 index | <4.00 | 1 | ||
| ≥4.00 | 1.522 | 1.079–2.146 | 0.017 | |
| Achievement of SVR | No | 1 | ||
| Yes | 0.464 | 0.294–0.732 | 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minami, Y.; Aoki, T.; Chishina, H.; Takita, M.; Hagiwara, S.; Ida, H.; Ueshima, K.; Nishida, N.; Kudo, M. Prognostic Factors for Overall Survival in Patients with HCV-Related HCC Undergoing Molecular Targeted Therapies: Beyond a Sustained Virological Response. Cancers 2022, 14, 4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194850
Minami Y, Aoki T, Chishina H, Takita M, Hagiwara S, Ida H, Ueshima K, Nishida N, Kudo M. Prognostic Factors for Overall Survival in Patients with HCV-Related HCC Undergoing Molecular Targeted Therapies: Beyond a Sustained Virological Response. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194850
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinami, Yasunori, Tomoko Aoki, Hirokazu Chishina, Masahiro Takita, Satoru Hagiwara, Hiroshi Ida, Kazuomi Ueshima, Naoshi Nishida, and Masatoshi Kudo. 2022. "Prognostic Factors for Overall Survival in Patients with HCV-Related HCC Undergoing Molecular Targeted Therapies: Beyond a Sustained Virological Response" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194850
APA StyleMinami, Y., Aoki, T., Chishina, H., Takita, M., Hagiwara, S., Ida, H., Ueshima, K., Nishida, N., & Kudo, M. (2022). Prognostic Factors for Overall Survival in Patients with HCV-Related HCC Undergoing Molecular Targeted Therapies: Beyond a Sustained Virological Response. Cancers, 14(19), 4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194850










