Dickkopf-Related Protein 1 as Response Marker for Transarterial Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinomas
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. HCC Diagnosis and Treatment Evaluation
2.3. Quantification of DKK-1 and AFP
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
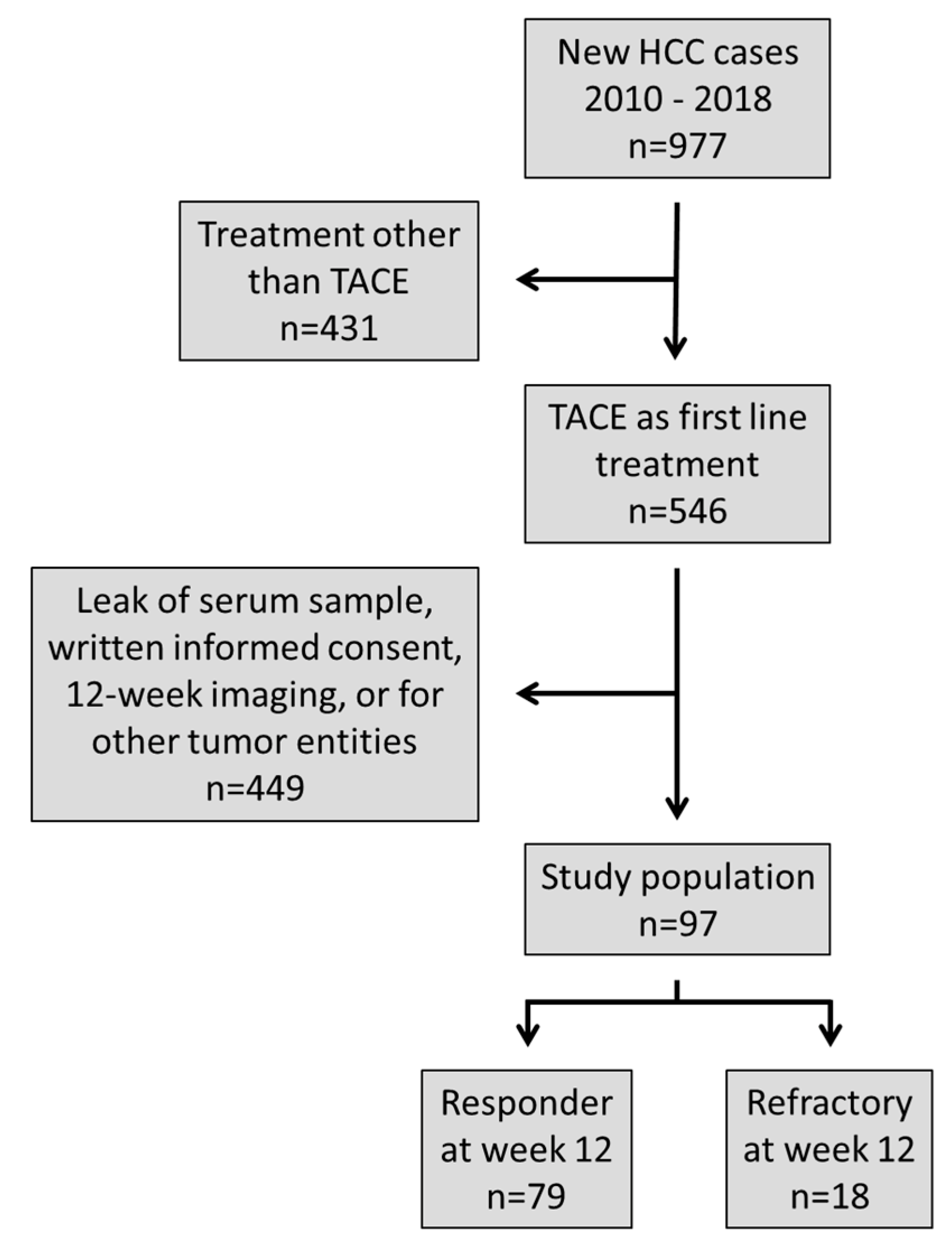
3.1. Patient Selection and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Treatment Response and Overall Survival
3.3. DKK-1 and AFP Levels before Treatment
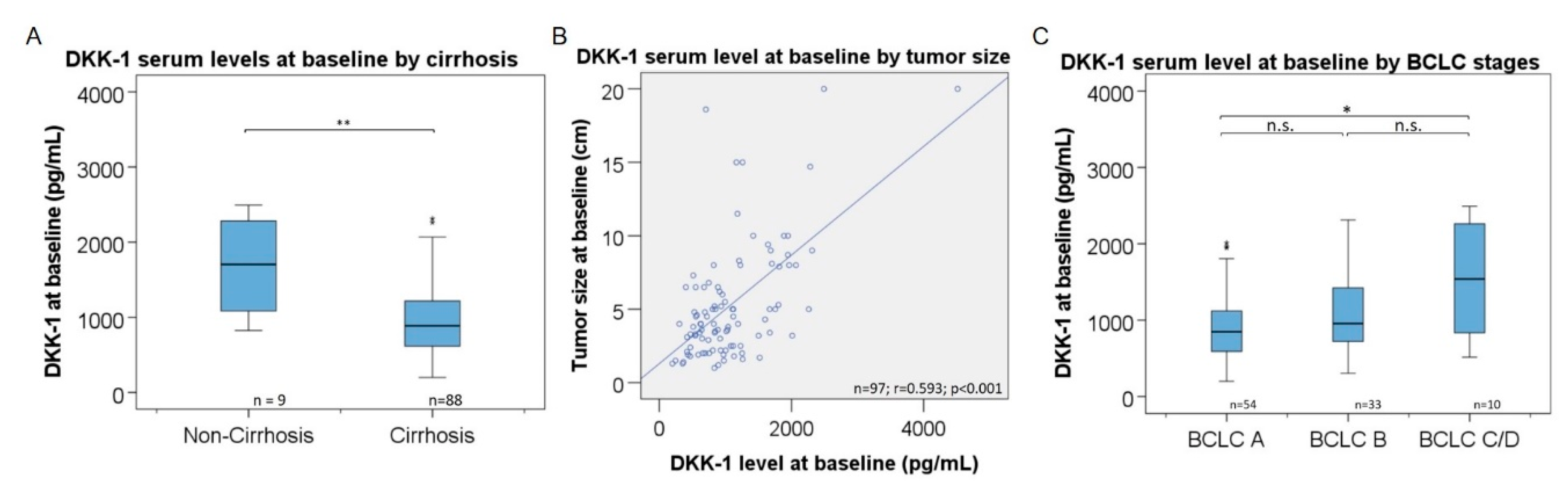
3.4. Association of DKK-1 Levels with Patient Characteristics
3.5. Association of DKK-1 Levels with Tumor Distribution
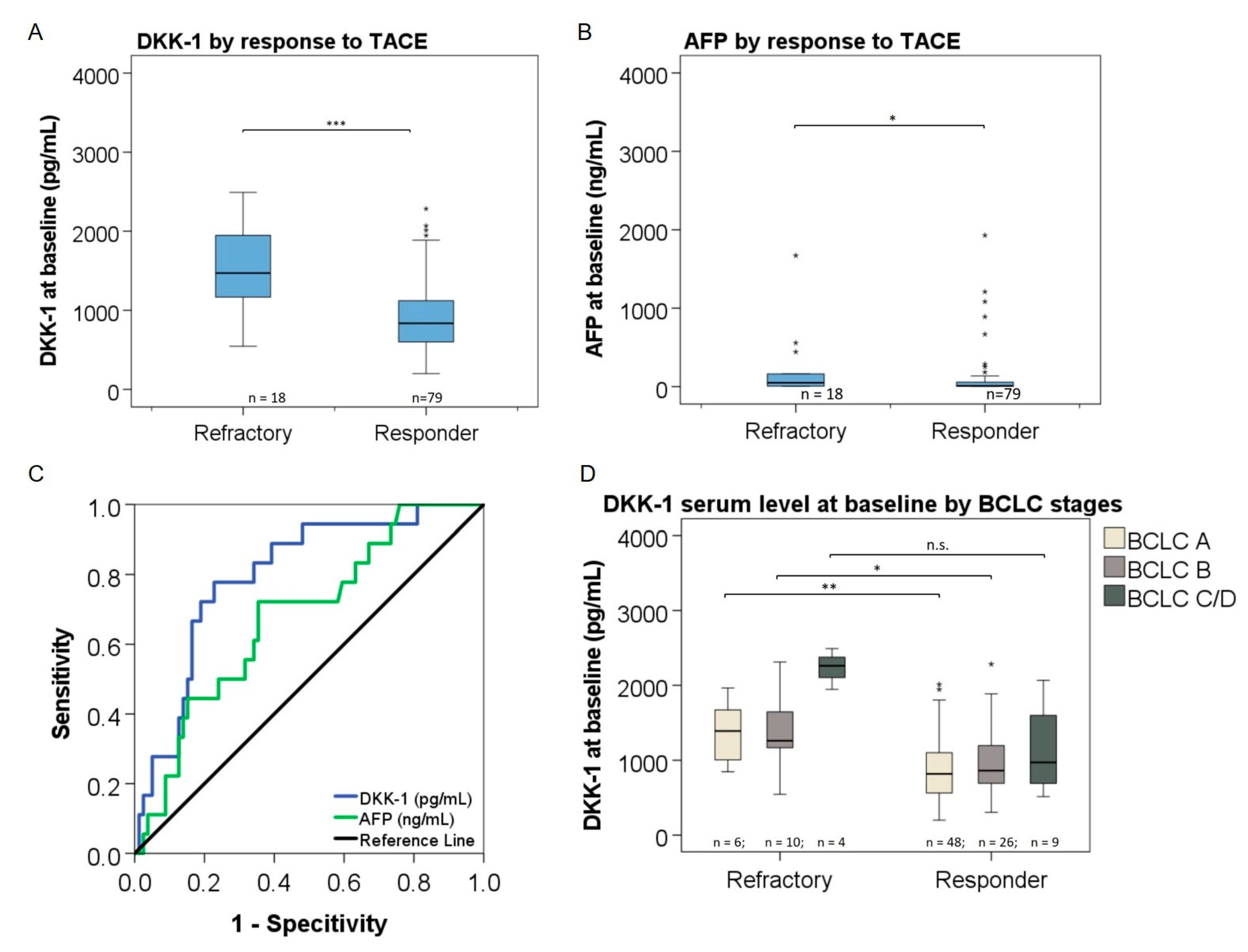
3.6. Association of DKK-1 and AFP Levels with Response to TACE
3.7. DKK-1 and Treatment Response in Patients with Low AFP Levels
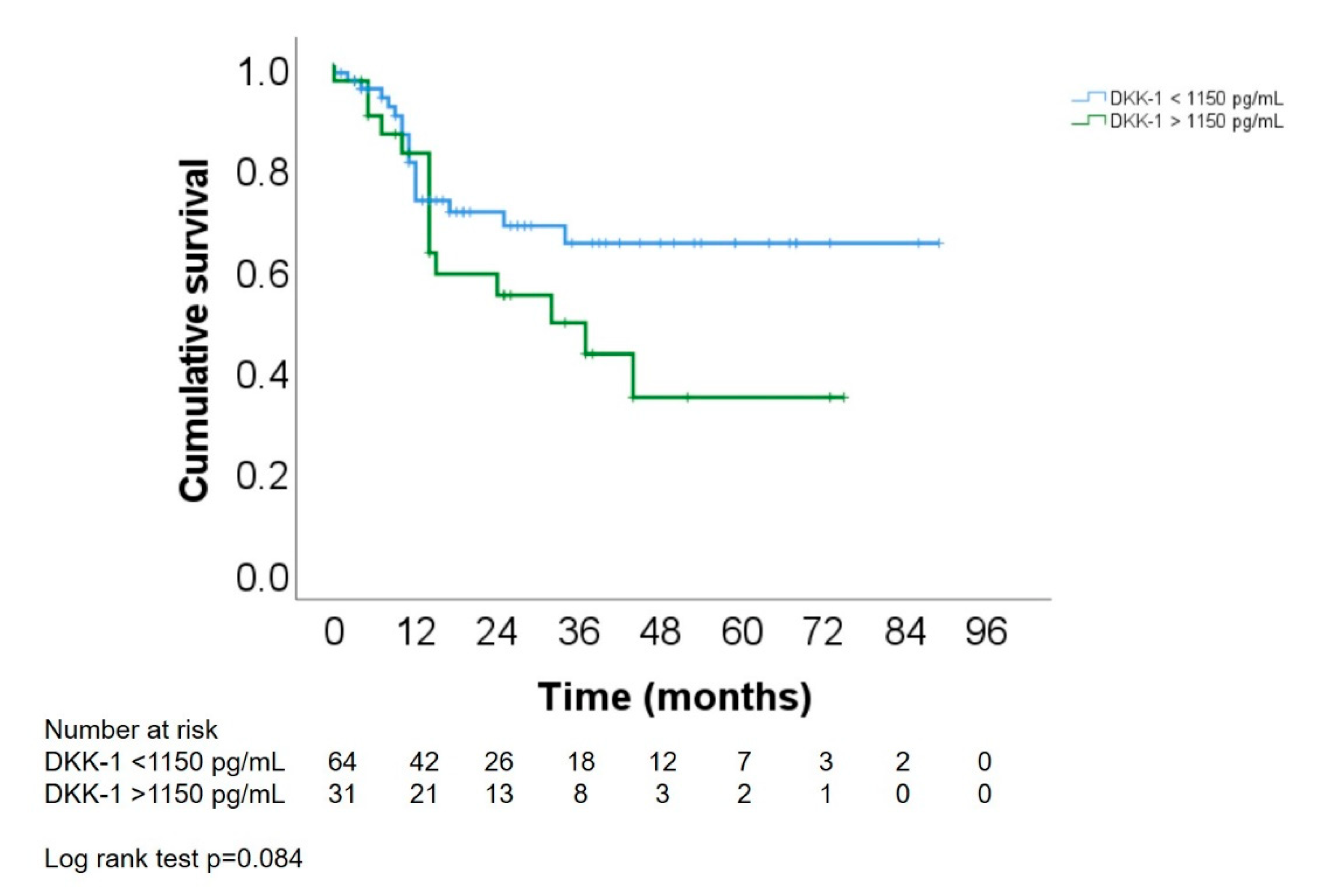
3.8. Association of DKK-1 Levels with Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tirnitz-Parker, J.E. (Ed.) Hepatocellular Carcinoma; Codon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, A.; Cervantes, A.; Chau, I.; Daniele, B.; Llovet, J.M.; Meyer, T.; Nault, J.-C.; Neumann, U.; Ricke, J.; Sangro, B.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 238–255, Correction in Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 871–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Kang, S.; Ning, Z.; Deng, H.; Shen, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, X.; Gong, W.; et al. Residual convolutional neural network for predicting response of transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma from CT imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 30, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Brú, C.; Bruix, J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin. Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoul, J.-L.; Forner, A.; Bolondi, L.; Cheung, T.T.; Kloeckner, R.; de Baere, T. Updated use of TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: How and when to use it based on clinical evidence. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 72, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.J. A concise review of updated guidelines regarding the management of hepatocellular carcinoma around the world: 2010–2016. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2016, 22, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Young Jang, J.; Jae Kim, Y. Recent Updates of Transarterial Chemoembolilzation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colli, A.; Nadarevic, T.; Miletic, D.; Giljaca, V.; Fraquelli, M.; Štimac, D.; Casazza, G. Abdominal ultrasound and alpha-foetoprotein for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in adults with chronic liver disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 4, cd013346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toader, E.; Bancu, A.; Mitrică, D.E.; Constantinescu, G.; Ştefănescu, G.; Bălan, G.G. Interrelations between elevated alpha-fetoprotein levels and tumor morphology of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2019, 60, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, A.E.; Ebrahim, M.A.; Eissa, L.A.; El-Shishtawy, M.M. Dickkopf-1 and Amphiregulin as Novel Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2019, 13, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Mou, L.; Gao, H.; Zeng, Y.; Tang, X.; Deng, X.; Pu, Z.; Ni, Y.; Zhan, Y. Diagnostic accuracy of serum dickkopf-1 protein in diagnosis hepatocellular carcinoma: An updated meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e16725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Lin, H.-M.; Broering, R.; Shi, X.; Yu, X.-H.; Xu, L.-B.; Wu, W.-R.; Liu, C. Dickkopf-1 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Fan, J.; Yang, X.-R.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, N.; Niu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. Serum DKK1 as a protein biomarker for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A large-scale, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yao, G.; Shu, H.; Lin, B.; Hood, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Gu, J.; et al. Elevated expression of DKK1 is associated with cytoplasmic/nuclear beta-catenin accumulation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinomas. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Song, J.; Chen, W.; Yuan, D.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Su, H.; Zhu, J. Expression and Role of Dickkopf-1 (Dkk1) in Tumors: From the Cells to the Patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Yang, C.; Yu, H.; Cao, F.; Shan, Y.; Zhao, W. The predictive values of serum dickkopf-1 and circulating tumor cells in evaluating the efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization treatment on hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine 2019, 98, e16579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Matsui, O.; Izumi, N.; Kadoya, M.; Okusaka, T.; Miyayama, S.; Yamakado, K.; Tsuchiya, K.; Ueshima, K.; Hiraoka, A.; et al. Transarterial chemoembolization failure/refractoriness: JSH-LCSGJ criteria 2014 update. Oncology 2014, 87, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, B.I.; Pancoska, P.; Branch, R.A. Low alpha-fetoprotein hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Wu, S.; Yu, Y.; Ming, X.; Li, S.; Zuo, X.; Tu, J. Current Status and Perspective Biomarkers in AFP Negative HCC: Towards Screening for and Diagnosing Hepatocellular Carcinoma at an Earlier Stage. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2019, 26, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liang, H.; Hu, S.; Li, P.; Liu, L.; Duan, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, P. Dishevelled 1, a pivotal positive regulator of the Wnt signalling pathway, mediates 5-fluorouracil resistance in HepG2 cells. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, W.-J.; Bothwell, A.L.M. Dickkopf1: An immunomodulatory ligand and Wnt antagonist in pathological inflammation. Differentiation 2019, 108, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.U.; Park, J.H.; Kim, H.-S.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.H.; Baek, S.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.Y.; et al. Serum Dickkopf-1 as a Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Yonsei Med. J. 2015, 56, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldeeb, M.; Magour, G.; Bedair, R.; Shamseya, M.; Hammouda, M. Study of Dickkopf-1 (DKK-1) in patients with chronic viral hepatitis C-related liver cirrhosis with and without hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2020, 6, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shayeb, A.F.; El-Habachi, N.M.; Mansour, A.R.; Zaghloul, M.S. Serum midkine is a more sensitive predictor for hepatocellular carcinoma than Dickkopf-1 and alpha-L-fucosidase in cirrhotic HCV patients. Medicine 2021, 100, e25112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.; Shen, Q.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Z.; Chu, W.; Lv, X.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, W.; Fan, J.; et al. Diagnostic values of alpha-fetoprotein, dickkopf-1 and osteopontin for hepatocellular carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Facciorusso, A.; Sacco, R.; Bartalena, L.; Mosconi, C.; Cea, U.V.; Cappelli, A.; Antonino, M.; Modestino, F.; Brandi, N.; et al. TRANS-TACE: Prognostic Role of the Transient Hypertransaminasemia after Conventional Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J. Serum T Cell Immunoglobulin Mucin 3 Predicts Worse Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization. Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e935326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Study Population (n = 97) |
|---|---|
| n (%) | |
| Sex (male) | 86 (89) |
| Age (years) * | 63 ± 8.8 [range, 31–83] |
| Liver cirrhosis | 88 (91) |
| Underlying liver disease | |
| Viral hepatitis | 15 (17) |
| Alcohol-related cirrhosis | 53 (60) |
| NASH | 9 (10) |
| others | 11 (13) |
| Child-Pugh-Turgott classification | |
| A | 68 (77) |
| B | 17 (19) |
| C | 3 (3) |
| BCLC stages | |
| A | 54 (56) |
| B | 33 (34) |
| C | 8 (8) |
| D | 2 (2) |
| ECOG performance status | |
| 0 | 57 (59) |
| 1 | 20 (21) |
| 2 | 8 (8) |
| n.a. | 12 (12) |
| Primary tumor site | |
| Left lobe | 21 (22) |
| Right lobe | 52 (54) |
| Bilobar | 24 (25) |
| Number of tumor lesions | |
| 1 | 50 (52) |
| 2 | 26 (27) |
| 3 | 12 (12) |
| >3 | 9 (9) |
| Total tumor diameter (mRECIST) | |
| <3 cm | 29 (30) |
| 3–5 cm | 39 (40) |
| 6–10 cm | 22 (23) |
| >10 cm | 7 (7) |
| Extrahepatic HCC at baseline | 31 (32) |
| DKK-1 (pg/mL) * | 1073 ± 636 [range, 199–4514] |
| AFP (ng/mL) * | 388 ± 1628 [range, 1.4–13019] |
| Albumin (g/L) * | 38 ± 6 [range, 18.6–49] |
| ALT (µkat/L) * | 0.8 ± 0.7 [range, 0.16–5.7] |
| Bilirubin (µmol/L) * | 25 ± 27 [range, 4–189] |
| CRP (mg/L) * | 8.9 ± 12.5 [range, 0.3–78] |
| Leukocytes (exp9/L) * | 6.2 ± 2.5 [range, 1.4–15.6] |
| Neutrophils (exp9/L) * | 4.0 ± 2.1 [range, 0.62–12.9] |
| Platelets (exp9/L) * | 149 ± 97 [range, 40–531] |
| AFP Subgroups | DKK-1 * | p-Value | AUC [95% CI] | DKK-1 Cutoff | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refractory | Responder | ||||||
| AFP < 130 ng/mL (n = 80/97) | 1391 [546, 2313] pg/mL (n = 12) | 868 [199, 2284] pg/mL (n = 68) | 0.005 | 0.756 [0.613, 0.900] | 1150 pg/mL | 75% | 75% |
| AFP < 20 ng/mL (n = 58/97) | 1646 [936, 2313] pg/mL (n = 7) | 840 [199, 2284] pg/mL (n = 51) | 0.003 | 0.843 [0.721, 0.965] | 1150 pg/mL | 86% | 77% |
| AFP < 8 ng/mL (n = 42/97) | 1646 [936, 2313] pg/mL (n = 5) | 840 [305, 2284] pg/mL (n = 37) | 0.023 | 0.816 [0.666, 0.967] | 933 pg/mL | 100% | 60% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olbrich, A.; Gros, O.; Ebel, S.; Denecke, T.; Gößmann, H.; Linder, N.; Lordick, F.; Forstmeyer, D.; Seehofer, D.; Sucher, R.; et al. Dickkopf-Related Protein 1 as Response Marker for Transarterial Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinomas. Cancers 2022, 14, 4807. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194807
Olbrich A, Gros O, Ebel S, Denecke T, Gößmann H, Linder N, Lordick F, Forstmeyer D, Seehofer D, Sucher R, et al. Dickkopf-Related Protein 1 as Response Marker for Transarterial Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinomas. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4807. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194807
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlbrich, Anne, Olga Gros, Sebastian Ebel, Timm Denecke, Holger Gößmann, Nicolas Linder, Florian Lordick, Dirk Forstmeyer, Daniel Seehofer, Robert Sucher, and et al. 2022. "Dickkopf-Related Protein 1 as Response Marker for Transarterial Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinomas" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4807. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194807
APA StyleOlbrich, A., Gros, O., Ebel, S., Denecke, T., Gößmann, H., Linder, N., Lordick, F., Forstmeyer, D., Seehofer, D., Sucher, R., Rademacher, S., Niemeyer, J., Matz-Soja, M., Berg, T., & Bömmel, F. v. (2022). Dickkopf-Related Protein 1 as Response Marker for Transarterial Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinomas. Cancers, 14(19), 4807. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194807








