High Blood Concentration of Leukocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Is Predictive of Favorable Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer: Results from a Multicenter Prospective Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Blood Collection
2.3. Flow Cytometry Detection of Extracellular Vesicles
2.4. Flow Cytometry Subtyping of Extracellular Vesicles
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of PC Patients Enrolled
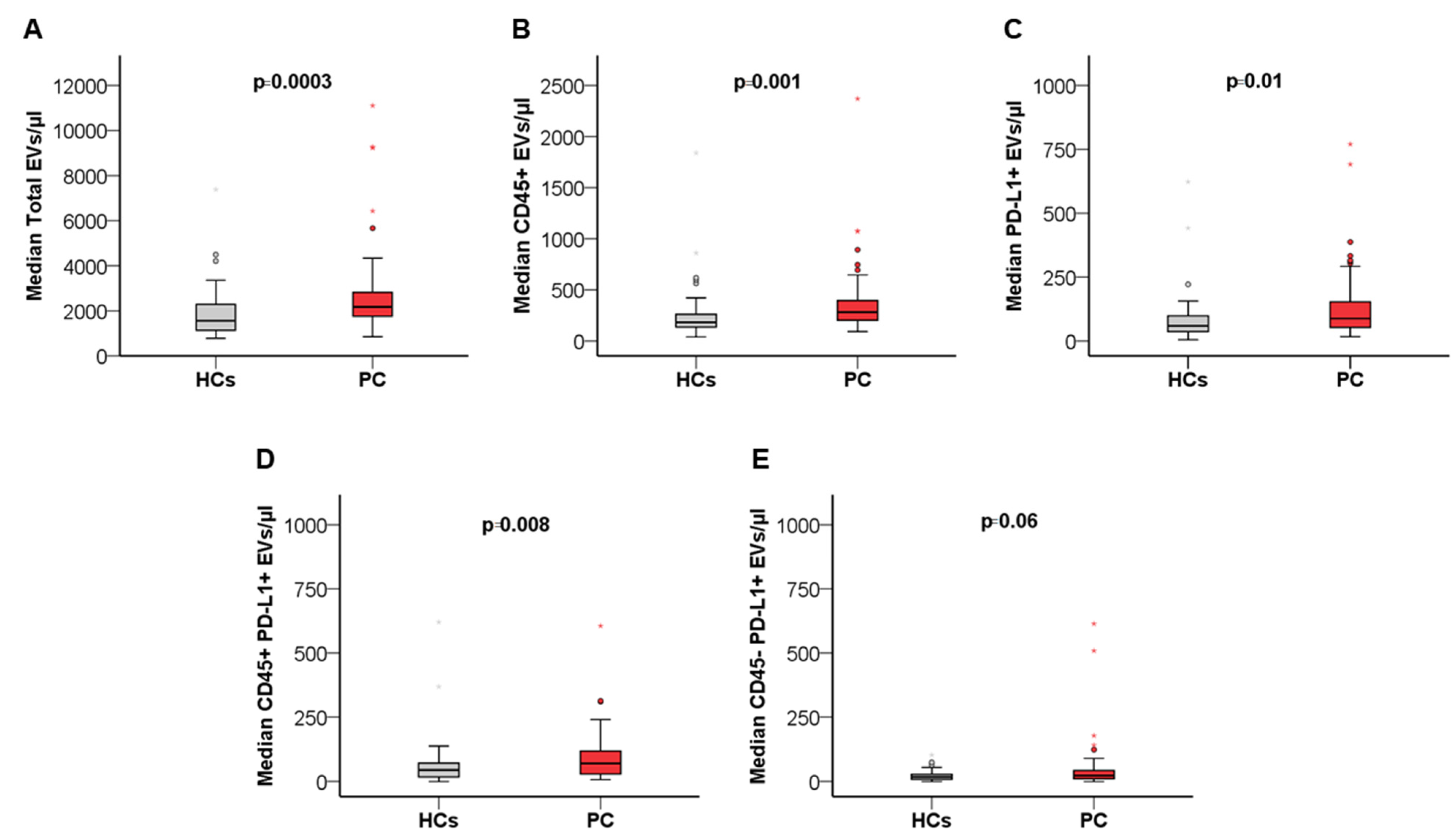
3.2. Patients with PC Present Increased Blood Levels of Leukocyte-Derived and PD-L1+ EVs
3.3. Blood-Circulating PD-L1+ and PD-L1+CD45+ EVs Are Associated with Site of Metastasis in Patients with PC
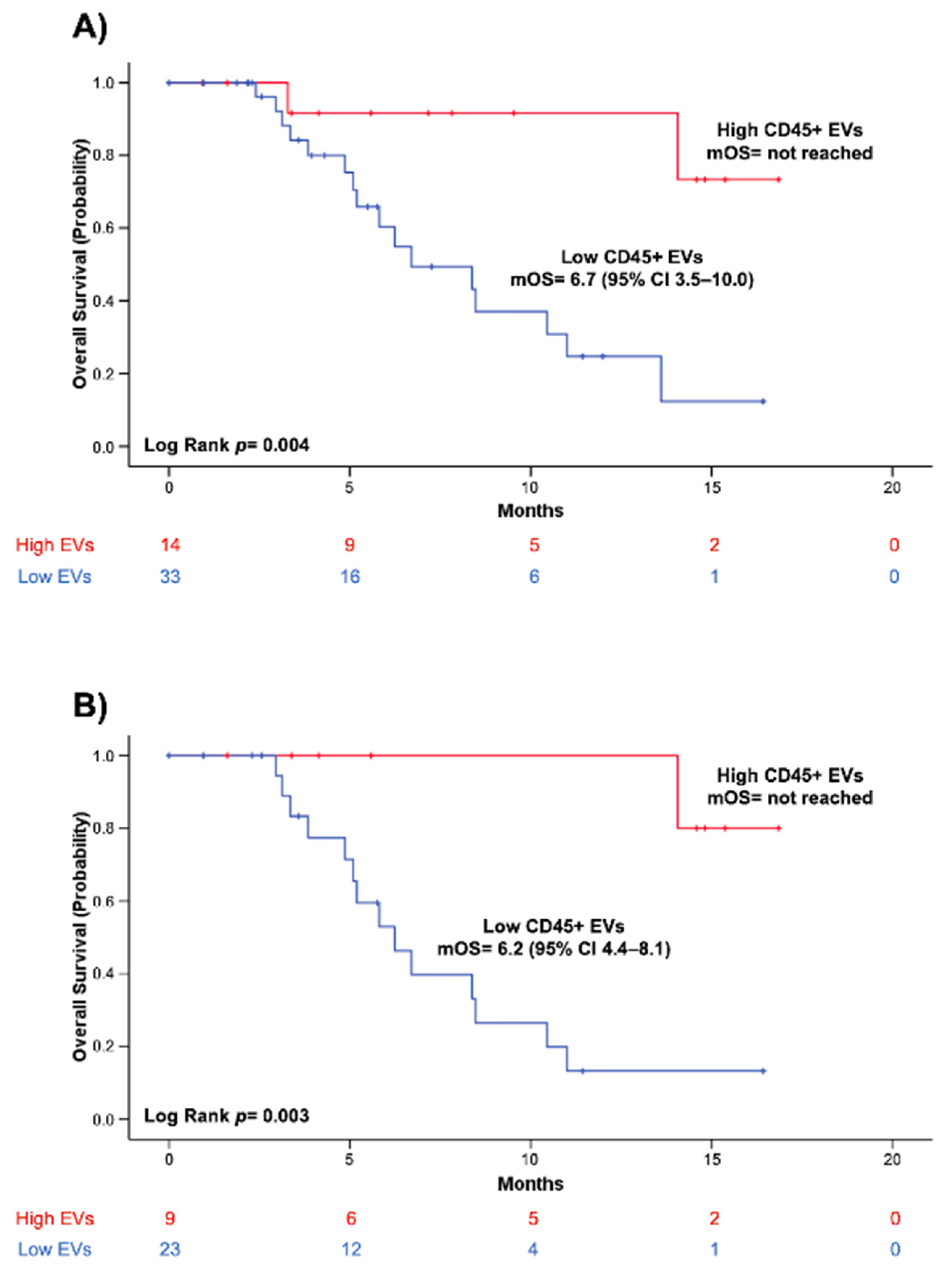
3.4. High Blood Levels of CD45+ EVs Independently Predict Improved Survival in Patients with Borderline Resectable and Primary Unresectable PC
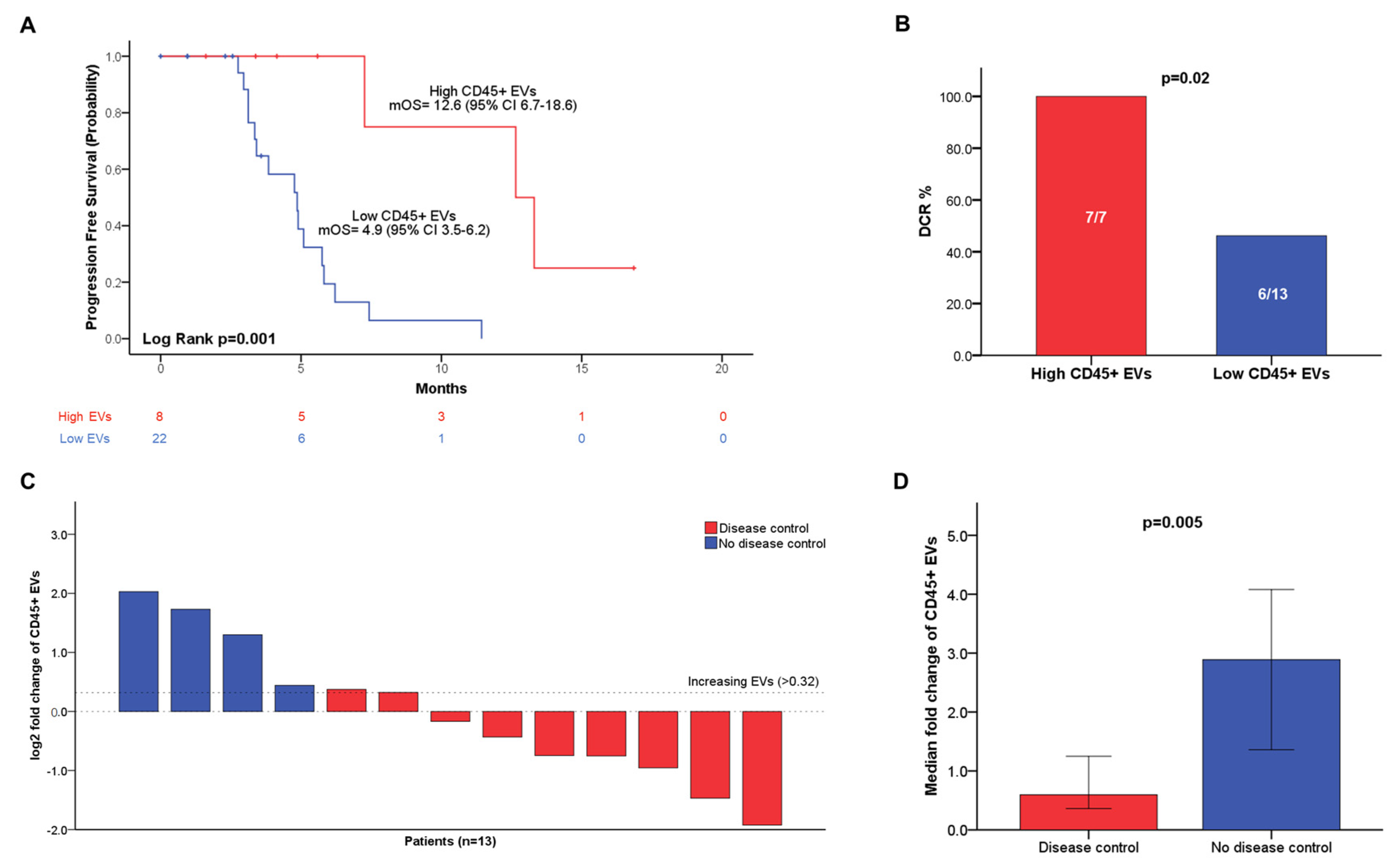
3.5. Increased Blood Levels of Circulating CD45+ EVs Are Associated with Higher Disease Control Rate and Longer Progression-Free Survival in Patients with Advanced PC
3.6. Blood-Circulating CD45+ EV Dynamics Predicts Disease Control in Patients with Advanced PC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.; Lok, V.; Ngai, C.H.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, J.; Lao, X.Q.; Ng, K.; Chong, C.; Zheng, Z.-J.; Wong, M.C.S. Worldwide Burden of, Risk Factors for, and Trends in Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of Pancreatic Cancer: Global Trends, Etiology and Risk Factors. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeff, J.; Korc, M.; Apte, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Johnson, C.D.; Biankin, A.V.; Neale, R.E.; Tempero, M.; Tuveson, D.A.; Hruban, R.H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Wang, Z.-F.; Wu, X.-L.; Zhou, C.-H.; Yan, J.-Y.; Hu, B.-Y.; et al. The molecular biology of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Translational challenges and clinical perspectives. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, N.; Ettrich, T.J.; Perkhofer, L. The Impact of Biomarkers in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma on Diagnosis, Surveillance and Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyabi, N.; Bernard, V.; Maitra, A. Liquid biopsies in pancreatic cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2019, 19, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goonetilleke, K.S.; Siriwardena, A.K. Systematic review of carbohydrate antigen (CA 19–9) as a biochemical marker in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 33, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsen, A.; Barbara, M.; Rosenkranz, L. Dilemma of elevated CA 19–9 in biliary pathology. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lellis, L.; Florio, R.; Di Bella, M.C.; Brocco, D.; Guidotti, F.; Tinari, N.; Grassadonia, A.; Lattanzio, R.; Cama, A.; Veschi, S. Exosomes as Pleiotropic Players in Pancreatic Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Lam, E.W.-F.; Sun, Y. Extracellular vesicles in the tumor microenvironment: Old stories, but new tales. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Gupta, P.; Chaluvally-Raghavan, P.; Pradeep, S. Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Immune Regulation and Cancer Progression. Cancers 2020, 12, 3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-H.; Pauklin, S. Extracellular vesicles in pancreatic cancer progression and therapies. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binenbaum, Y.; Fridman, E.; Yaari, Z.; Milman, N.; Schroeder, A.; Ben David, G.; Shlomi, T.; Gil, Z. Transfer of miRNA in Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Induces Drug Resistance in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5287–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Ma, T.; Huang, B.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, J.; Zou, Y.; Chen, S. Macrophage-derived exosomal microRNA-501–3p promotes progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through the TGFBR3-mediated TGF-β signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Yi, J.; Dong, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Miao, L.; Zhou, W. miR-365 secreted from M2 Macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression through the BTG2/FAK/AKT axis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 4671–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, A.; Venturelli, E.; Brizzi, M.F. Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Liquid Biopsy-Based Diagnosis for the Central Nervous System, Head and Neck, Lung, and Gastrointestinal Cancers: Current and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2021, 13, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasuleva, K.; Elamurugan, S.; Bauer, A.; Khan, M.; Wen, Q.; Li, Z.; Steen, P.; Guo, A.; Xia, W.; Mathew, S.; et al. β-Sheet Richness of the Circulating Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Noninvasive Pancreatic Cancer Screening. ACS Sensors 2021, 6, 4489–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Ota, Y.; Kogure, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Yamakita, K.; Kitano, Y.; Fujii, S.; Haneda, M.; Patel, T.; et al. Circulating extracellular vesicle-encapsulated HULC is a potential biomarker for human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, S.A.; Luecke, L.B.; Kahlert, C.; Fernandez, A.F.; Gammon, S.T.; Kaye, J.; LeBleu, V.S.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Weitz, J.; Rahbari, N.; et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 523, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggio, M.; Hu, T.; Pai, C.-C.; Chu, B.; Belair, C.D.; Chang, A.; Montabana, E.; Lang, U.E.; Fu, Q.; Fong, L.; et al. Suppression of Exosomal PD-L1 Induces Systemic Anti-tumor Immunity and Memory. Cell 2019, 177, 414–427.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huang, A.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Xu, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, H.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 2018, 560, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Miguel-Perez, D.; Russo, A.; Arrieta, O.; Ak, M.; Barron, F.; Gunasekaran, M.; Mamindla, P.; Lara-Mejia, L.; Peterson, C.B.; Er, M.E.; et al. Extracellular vesicle PD-L1 dynamics predict durable response to immune-checkpoint inhibitors and survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lux, A.; Kahlert, C.; Grützmann, R.; Pilarsky, C. c-Met and PD-L1 on Circulating Exosomes as Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers for Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocco, D.; Lanuti, P.; Pieragostino, D.; Cufaro, M.C.; Simeone, P.; Bologna, G.; Di Marino, P.; De Tursi, M.; Grassadonia, A.; Irtelli, L.; et al. Phenotypic and Proteomic Analysis Identifies Hallmarks of Blood Circulating Extracellular Vesicles in NSCLC Responders to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancers 2021, 13, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocco, D.; Lanuti, P.; Simeone, P.; Bologna, G.; Pieragostino, D.; Cufaro, M.C.; Graziano, V.; Peri, M.; Di Marino, P.; De Tursi, M.; et al. Circulating Cancer Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Biomarker for Clinical Outcome Evaluation. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 5879616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocco, D.; Simeone, P.; Buca, D.; Di Marino, P.; De Tursi, M.; Grassadonia, A.; De Lellis, L.; Martino, M.T.; Veschi, S.; Iezzi, M.; et al. Blood Circulating CD133+ Extracellular Vesicles Predict Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchisio, M.; Simeone, P.; Bologna, G.; Ercolino, E.; Pierdomenico, L.; Pieragostino, D.; Ventrella, A.; Antonini, F.; Del Zotto, G.; Vergara, D.; et al. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Circulating Extracellular Vesicle Subtypes from Fresh Peripheral Blood Samples. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellano, G.; Raineri, D.; Rolla, R.; Giordano, M.; Puricelli, C.; Vilardo, B.; Manfredi, M.; Cantaluppi, V.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Castello, L.; et al. Circulating Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Are a Hallmark of Sars-Cov-2 Infection. Cells 2021, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, P.; Celia, C.; Bologna, G.; Ercolino, E.; Pierdomenico, L.; Cilurzo, F.; Grande, R.; Diomede, F.; Vespa, S.; Canonico, B.; et al. Diameters and Fluorescence Calibration for Extracellular Vesicle Analyses by Flow Cytometry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossarizza, A.; Chang, H.-D.; Radbruch, A.; Akdis, M.; Andrä, I.; Annunziato, F.; Bacher, P.; Barnaba, V.; Battistini, L.; Bauer, W.M.; et al. Guidelines for the use of flow cytometry and cell sorting in immunological studies. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 1584–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budczies, J.; Klauschen, F.; Sinn, B.V.; Győrffy, B.; Schmitt, W.D.; Darb-Esfahani, S.; Denkert, C. Cutoff Finder: A Comprehensive and Straightforward Web Application Enabling Rapid Biomarker Cutoff Optimization. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatiadis, M.; Sledge, G.W.; Jeffrey, S.S. Liquid biopsy enters the clinic—Implementation issues and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Hurley, J.; Roberts, D.; Chakrabortty, S.K.; Enderle, D.; Noerholm, M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J.K. Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: Opportunities and challenges. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2021, 32, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, R.; Dovizio, M.; Marcone, S.; Szklanna, P.B.; Bruno, A.; Ebhardt, H.A.; Cassidy, H.; Ní Áinle, F.; Caprodossi, A.; Lanuti, P.; et al. Platelet-Derived Microparticles From Obese Individuals: Characterization of Number, Size, Proteomics, and Crosstalk with Cancer and Endothelial Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Wu, F.; Kang, B.; Sun, X.; Heskia, F.; Pachot, A.; Liang, J.; Li, D. Plasma extracellular vesicles detected by Single Molecule array technology as a liquid biopsy for colorectal cancer. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1809765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liao, Y.; Hosseinifard, H.; Imani, S.; Wen, Q. Diagnostic Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.H.; Quan, Y.H.; Rho, J.; Hong, S.; Park, Y.; Choi, Y.; Park, J.-H.; Yong, H.S.; Han, K.N.; Choi, Y.H.; et al. Levels of Extracellular Vesicles in Pulmonary and Peripheral Blood Correlate with Stages of Lung Cancer Patients. World J. Surg. 2020, 44, 3522–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Thakur, B.K.; Weiss, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Peinado, H.; Lyden, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-Cell Mediators of Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanou, A.; Zeune, L.L.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Leukocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Blood with and without EpCAM Enrichment. Cells 2019, 8, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, X.; Li, Q.; Lai, H.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, S. EV-origin: Enumerating the tissue-cellular origin of circulating extracellular vesicles using exLR profile. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2851–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auber, M.; Svenningsen, P. An estimate of extracellular vesicle secretion rates of human blood cells. J. Extracell. Biol. 2022, 1, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliha, N.; Heider, U.; Ozimkowski, T.; Wiemann, M.; Bosio, A.; Wild, S. Melanoma Affects the Composition of Blood Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltraminelli, T.; Perez, C.R.; De Palma, M. Disentangling the complexity of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 108960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Jiang, S. Immune Cell-Derived Exosomes in the Cancer-Immunity Cycle. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-L.; Luo, X.; Sheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.-L.; Li, J.-N.; Wang, F.-H.; Xu, R.-H. PD-L1 expression in liver metastasis: Its clinical significance and discordance with primary tumor in colorectal cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawazoe, A.; Shitara, K.; Kuboki, Y.; Bando, H.; Kojima, T.; Yoshino, T.; Ohtsu, A.; Ochiai, A.; Togashi, Y.; Nishikawa, H.; et al. Clinicopathological features of 22C3 PD-L1 expression with mismatch repair, Epstein–Barr virus status, and cancer genome alterations in metastatic gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2019, 22, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Soon, Y.Y.; Lum, J.H.Y.; Tan, C.L.; Tey, J.C.S. Frequency of discordance in programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression between primary tumors and paired distant metastases in advanced cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Oncol. 2020, 59, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzas, E.I. The roles of extracellular vesicles in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Donninger, H.; Eaton, J.; Yaddanapudi, K. Regulatory Role of Immune Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: The Message Is in the Envelope. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, C.; Lee, M.; Hoen, D.; Weiss, K.; Kelly, D.W.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Paik, P.K.; Plitas, G.; Ladanyi, M.; Postow, M.A.; et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and mutational burden as biomarkers of tumor response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugholm, L.H.; Bæk, R.; Søndergaard, E.K.L.; Revenfeld, A.L.S.; Jørgensen, M.M.; Varming, K. Phenotyping of Leukocytes and Leukocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 6391264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versteijne, E.; van Dam, J.L.; Suker, M.; Janssen, Q.P.; Groothuis, K.; Akkermans-Vogelaar, J.M.; Besselink, M.G.; Bonsing, B.A.; Buijsen, J.; Busch, O.R.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Versus Upfront Surgery for Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer: Long-Term Results of the Dutch Randomized PREOPANC Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Overall Study Cohort (n = 56) | |
|---|---|
| Variable | Frequency (%) |
| Primary Tumor Location | |
| Head | 36 (33.0) |
| Body/Tail | 17 (15.6) |
| Isthmus | 3 (2.8) |
| Clinical Stage | |
| Stage I–III | 25 (44.6) |
| Stage IV | 31 (55.4) |
| Tumor grading | |
| 1 | 2 (3.6) |
| 2 | 21 (37.5) |
| 3 | 9 (16.1) |
| Missing | 24 (42.9) |
| Primary Treatment | |
| Surgery | 9 (16.1) |
| Systemic Therapy (Borderline Resectable) | 15 (26.7) |
| Systemic Therapy (Locally Advanced/Metastatic) | 32 (57.1) |
| Systemic Therapy | |
| Gemcitabine + Nab-paclitaxel | 29 (51.8) |
| FOLFIRINOX | 12 (21.4) |
| Gemcitabine | 2 (3.6) |
| FOLFIRI | 1 (1.8) |
| PAX-G | 1 (1.8) |
| Not evaluable/Missing | 11 (19.6) |
| Locally Advanced/Metastatic Cohort (n = 32) | |
|---|---|
| Variable | Frequency (%) |
| Line of therapy | |
| 1 | 29 (90.6) |
| 2 | 2 (6.3) |
| ≥3 | 1 (3.1) |
| Number of metastatic sites | |
| 0 | 1 (3.1) |
| 1 | 23 (71.9) |
| 2 | 5 (15.6) |
| ≥3 | 3 (9.4) |
| Liver Metastasis | |
| Yes | 20 (64.5) |
| No | 11 (35.4) |
| Peritoneal Metastasis | |
| Yes | 8 (25.0) |
| No | 23 (71.9) |
| Lung Metastasis | |
| Yes | 5 (16.1) |
| No | 26 (83.9) |
| PC (n = 56) | HC (n = 48) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (%) | |||
| ≥65 | 34 (60.7) | 22 (39.3) | 0.17 |
| <65 | 22 (39.3) | 26 (54.2) | |
| Sex (%) | |||
| Male | 28 (50.0) | 31 (52.5) | 0.17 |
| Female | 28 (50.0) | 17 (37.8) | |
| Total EVs/µL (95% CI) | 2168.6 (1940.9–2576.5) | 1559.4 (1339.5–1985.5) | 0.0003 |
| Leukocyte-derived (CD45+) EVs/µL (95% CI) | 280.0 (229.5–343.9) | 182.1 (167.4–233.3) | 0.001 |
| PD-L1+ EVs/µL (95% CI) | 87.5 (70.0–115.6) | 58.7 (42.8–82.9) | 0.01 |
| PD-L1+CD45+ EVs/µL (95% CI) | 68 (47.0–96.1) | 44.1 (26.0–57.6) | 0.008 |
| PD-L1+CD45- EVs/µL (95% CI) | 22.6 (13.5–30.2) | 18.1 (11.2–23.0) | 0.06 |
| Univariate Analysis | Bootstrap Results (1000 Replicas) | Multivariate Analysis 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | p. | Bias | SE | 95 % CI | p. | HR (95% CI) | p. |
| Total EVs | ||||||||
| <2710 EVs/µL | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| >2710 EVs/µL | 0.20 (0.05–0.90) | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.98 | −4.01 to −0.23 | 0.04 | ||
| CD45+ EVs | ||||||||
| <379.1 EVs/µL | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| >379.1 EVs/µL | 0.14 (0.03–0.65) | 0.01 | −0.42 | 1.02 | −4.47 to −0.77 | 0.01 | 0.17 (0.04–0.79) | 0.02 |
| PD-L1+ EVs | ||||||||
| <124.8 EVs/µL | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| >124.8 EVs/µL | 0.21 (0.06–0.75) | 0.02 | −0.18 | 0.84 | −3.99 to −0.39 | 0.02 | ||
| PD-L1+CD45+ EVs | ||||||||
| <108.5 EVs/µL | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| >108.5 EVs/µL | 0.18 (0.04–0.78) | 0.02 | −0.16 | 0.96 | −4.09 to −0.39 | 0.02 | ||
| PD-L1+CD45- EVs | ||||||||
| <42.7 EVs/µL | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| >42.7 EVs/µL | 0.26 (0.07–0.94) | 0.04 | −0.24 | 0.88 | −3.98 to −0.27 | 0.01 | ||
| ECOG PS | ||||||||
| 0 | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| 1–2 | 1.78 (0.70–4.55) | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.53 | −0.33 to −1.80 | 0.20 | ||
| Age (years) | ||||||||
| ≥65 | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| <65 | 0.85 (0.31–2.29) | 0.75 | −0.01 | 0.57 | −1.36 to 0.86 | 0.74 | ||
| No. of metastatic sites | ||||||||
| >1 | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| 1 | 0.71 (0.19–2.59) | 0.60 | 0.04 | 0.97 | −1.76 to 3.12 | 0.59 | ||
| BMI | ||||||||
| Continuous Variable | 0.89 (0.79–1.00) | 0.07 | −0.01 | 0.07 | −0.29 to −0.01 | 0.06 | ||
| CA 19.9 | ||||||||
| Continuous Variable | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.14 | −0.00 | 0.00 | −0.001 to 0.00 | 0.12 | ||
| Tumor Grading | ||||||||
| 1–2 | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| 3 | 0.85 (0.31–2.29) | 0.75 | −0.01 | 0.57 | −1.37 to 0.87 | 0.75 | ||
| Primary tumor location | ||||||||
| Body/Isthmus/Tail | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| Head | 2.03 (0.66–6.22) | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.80 | −0.54 to 2.59 | 0.28 | ||
| Clinical Stage | ||||||||
| Stage I–II | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| Stage III–IV | 1.26 (0.29–5.59) | 0.75 | 0.28 | 1.40 | −1.51 to 3.41 | 0.80 | ||
| Liver Metastasis | ||||||||
| Yes | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| No | 1.95 (0.74–5.16) | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.48 | −0.29 to 1.66 | 0.12 | ||
| Peritoneal Metastasis | ||||||||
| Yes | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| No | 0.24 (0.07–0.77) | 0.02 | −0.48 | 2.00 | −9.58 to 0.00 | 0.008 2 | ||
| NLR | ||||||||
| NLR > 5 | 1 [reference] | |||||||
| NLR < 5 | 0.24 (0.08–0.74) | 0.01 | −0.29 | 1.77 | −7.73 to 0.00 | 0.008 | 0.16 (0.08–0.76) | 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brocco, D.; De Bellis, D.; Di Marino, P.; Simeone, P.; Grassadonia, A.; De Tursi, M.; Grottola, T.; Di Mola, F.F.; Di Gregorio, P.; Zappacosta, B.; et al. High Blood Concentration of Leukocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Is Predictive of Favorable Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer: Results from a Multicenter Prospective Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 4748. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194748
Brocco D, De Bellis D, Di Marino P, Simeone P, Grassadonia A, De Tursi M, Grottola T, Di Mola FF, Di Gregorio P, Zappacosta B, et al. High Blood Concentration of Leukocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Is Predictive of Favorable Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer: Results from a Multicenter Prospective Study. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4748. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194748
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrocco, Davide, Domenico De Bellis, Pietro Di Marino, Pasquale Simeone, Antonino Grassadonia, Michele De Tursi, Tommaso Grottola, Fabio Francesco Di Mola, Patrizia Di Gregorio, Barbara Zappacosta, and et al. 2022. "High Blood Concentration of Leukocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Is Predictive of Favorable Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer: Results from a Multicenter Prospective Study" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4748. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194748
APA StyleBrocco, D., De Bellis, D., Di Marino, P., Simeone, P., Grassadonia, A., De Tursi, M., Grottola, T., Di Mola, F. F., Di Gregorio, P., Zappacosta, B., Angelone, A., Lellis, L. D., Veschi, S., Florio, R., De Fabritiis, S., Verginelli, F., Marchisio, M., Caporale, M., Luisi, D., ... Lanuti, P. (2022). High Blood Concentration of Leukocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Is Predictive of Favorable Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer: Results from a Multicenter Prospective Study. Cancers, 14(19), 4748. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194748










