Derivatives of Plastics as Potential Carcinogenic Factors: The Current State of Knowledge
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Aim of the Review and Search Strategy
3. Definition and Classification of Micro- and Nanoplastics
3.1. Microplastic Components
3.2. Industrial Classification of Chemical Contaminants
3.3. Chemical Classification of Main Chemical Contaminants
3.3.1. Heavy Metals
3.3.2. Organic Components
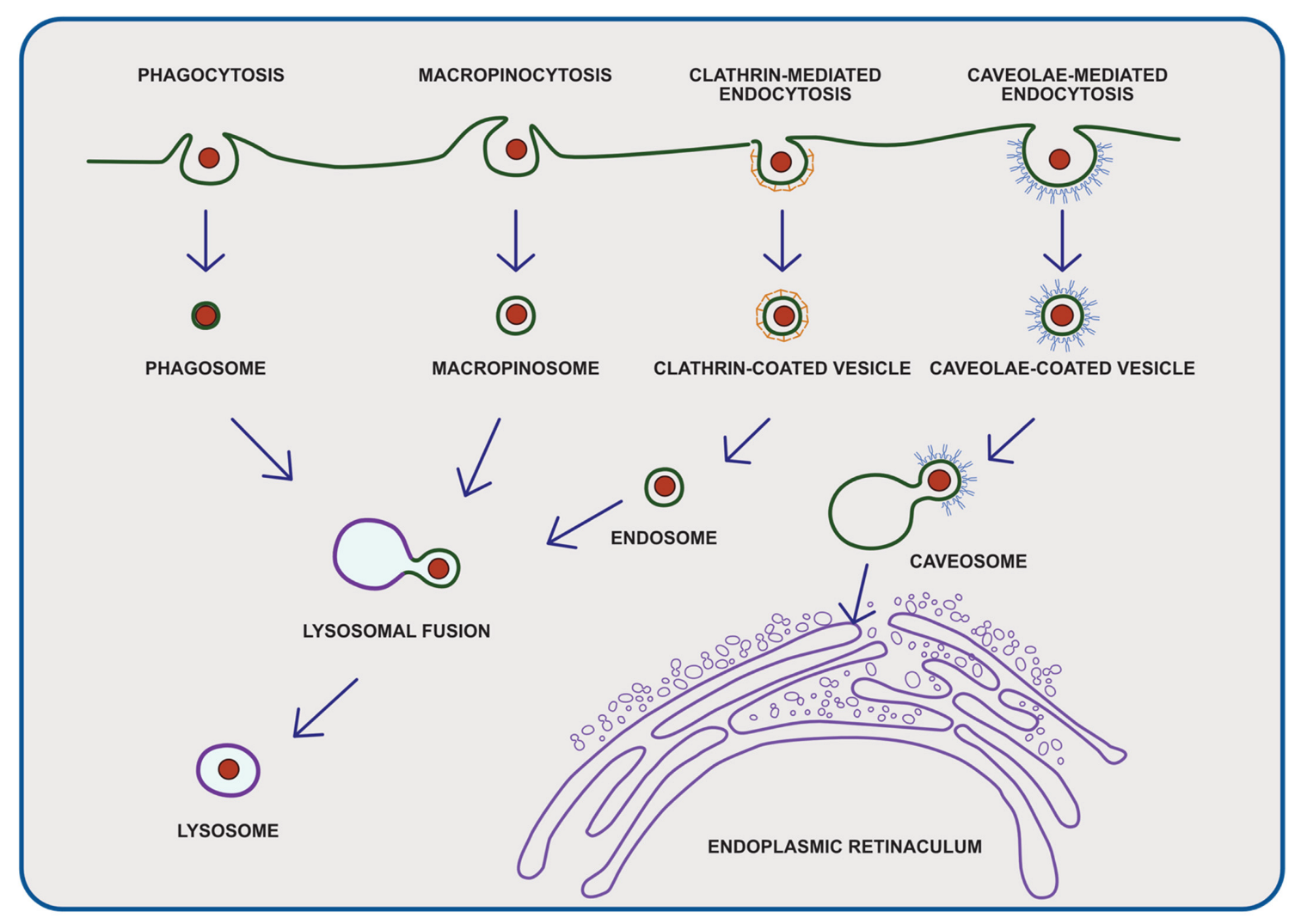
4. Exposure Routes
4.1. Gastrointestinal Tract
4.2. Respiratory System
4.3. Skin
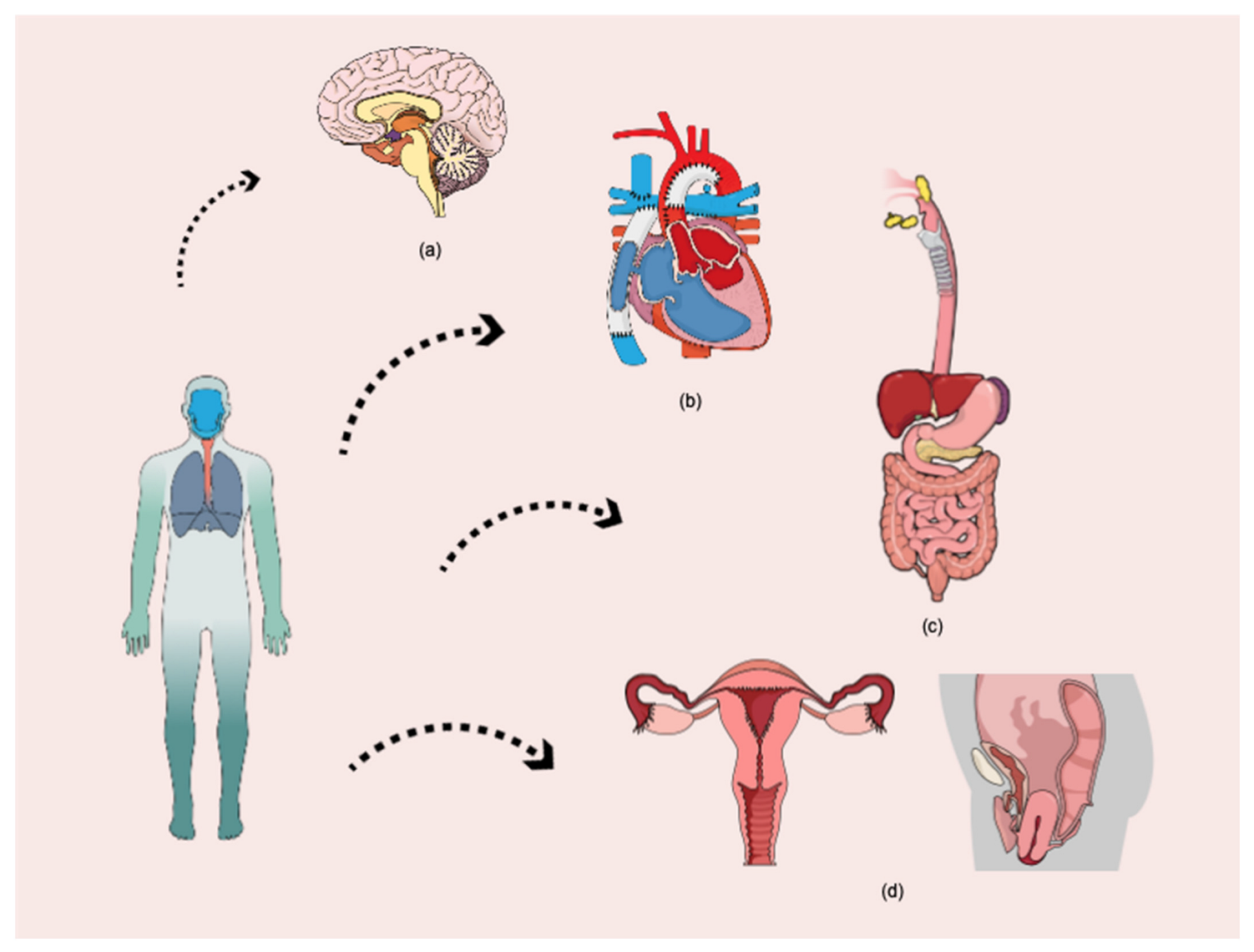
5. Micro and Nanoplastic in Organs of the Systems
5.1. Cardiovascular System
5.2. Gastrointestinal System
5.3. Reproductive System
5.4. Nervous System
6. Cytotoxic Effect of Micro- and Nanoplastic
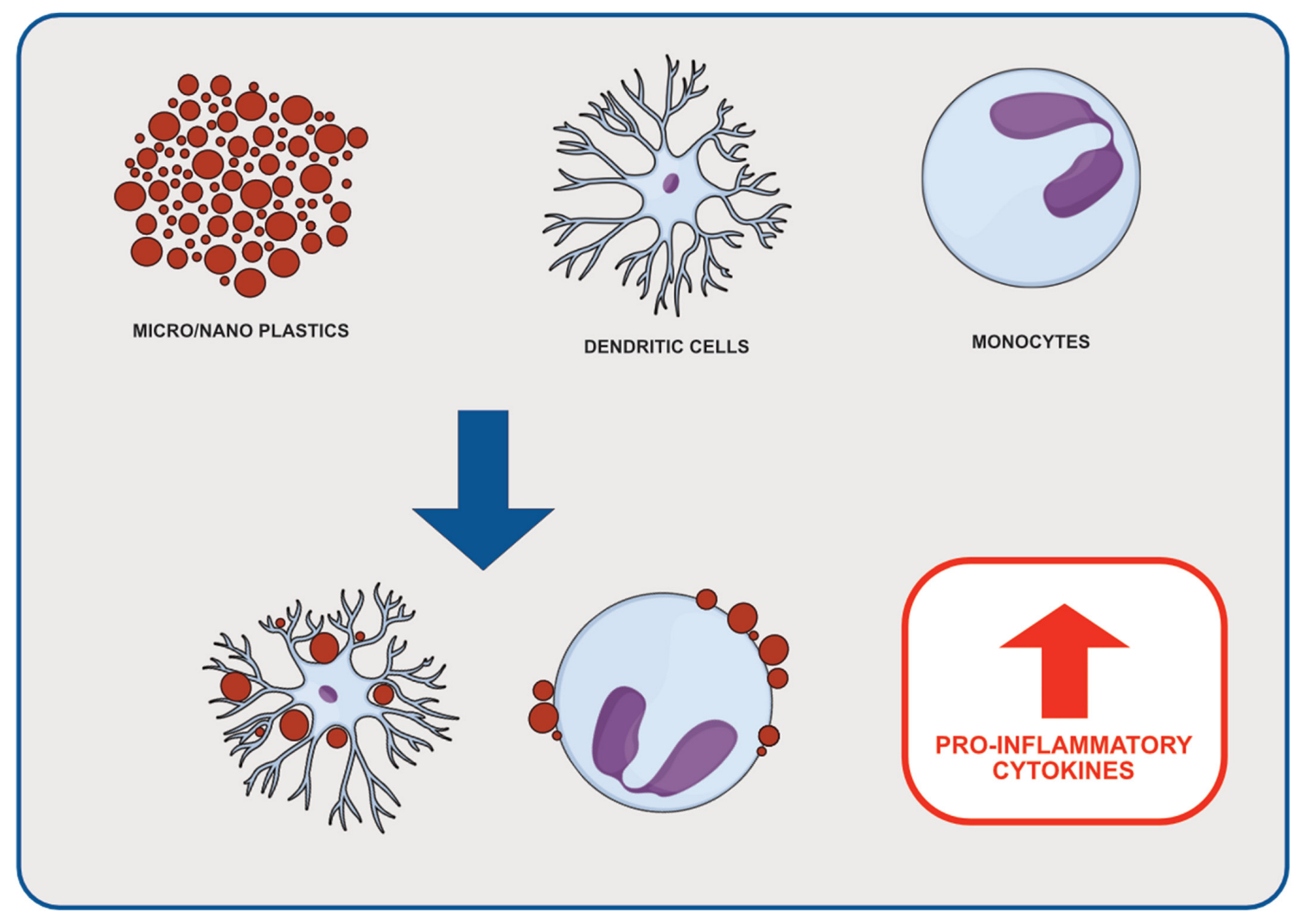
6.1. Inflammation
6.2. Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis
6.3. Toxic Compounds from Plastic
7. Potential Carcinogenic Effects of Micro-/Nanoplastics and Their Derivatives
7.1. Endocrine-Related Cancers
7.2. Biliary Tract Cancer
7.3. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
7.4. Pancreatic Involvement
7.5. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDA)
7.6. Pancreatic Cancer
7.7. Leukemia
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alimba, C.G.; Faggio, C. Microplastics in the marine environment: Current trends in environmental pollution and mechanisms of toxicological profile. Env. Toxicol. Pharm. 2019, 68, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakowski, M.; Grzelak, A. A new occupational and environmental hazard-nanoplastic. Med. Pr. 2020, 71, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Plastic Production 1950–2020. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/282732/global-production-of-plastics-since-1950/ (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- Fast Facts about Plastic Pollution. Available online: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/plastics-facts-infographics-ocean-pollution (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- Rhodes, C.J. Plastic pollution and potential solutions. Sci. Prog. 2018, 101, 207–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunola, O.S.; Onada, O.A.; Falaye, A.E. Mitigation measures to avert the impacts of plastics and microplastics in the marine environment (a review). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9293–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuten, E.L.; Rowland, S.J.; Galloway, T.S.; Thompson, R.C. Potential for plastics to transport hydrophobic contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7759–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, P.R.; Shirgaonkar, S.S.; Patil, R.B. Plastic marine debris: Sources, distribution and impacts on coastal and ocean biodiversity. Publ. Biol. Sci. 2016, 3, 40–54. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, C.; Krauth, T.; Wagner, S. Export of plastic debris by rivers into the sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12246–12253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.; Andrady, A. Future scenarios of global plastic waste generation and disposal. Palgrave Commun. 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelle, S.B.; Ringma, J.; Law, K.L.; Monnahan, C.C.; Lebreton, L.; McGivern, A.; Murphy, E.; Jambeck, J.; Leonard, G.H.; Hilleary, M.A.; et al. Predicted growth in plastic waste exceeds efforts to mitigate plastic pollution. Science 2020, 369, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.W.Y.; Shiran, Y.; Bailey, R.M.; Cook, E.; Stuchtey, M.R.; Koskella, J.; Velis, C.A.; Godfrey, L.; Boucher, J.; Murphy, M.B.; et al. Evaluating scenarios toward zero plastic pollution. Science 2020, 369, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, L.J.J.; van Emmerik, T.; van der Ent, R.; Schmidt, C.; Lebreton, L. More than 1000 rivers account for 80% of global riverine plastic emissions into the ocean. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eaaz5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, N. Mechanistic implications of plastic degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brine, T.; Thompson, R.C. Degradation of plastic carrier bags in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2279–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Jung, S.W.; Shim, W.J. Combined Effects of UV Exposure Duration and Mechanical Abrasion on Microplastic Fragmentation by Polymer Type. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4368–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, N.; Yang, X.; Xia, Y.; Wu, D. Effects induced by polyethylene microplastics oral exposure on colon mucin release, inflammation, gut microflora composition and metabolism in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Dissanayake, A.; Galloway, T.S.; Lowe, D.M.; Thompson, R.C. Ingested Microscopic Plastic Translocates to the Circulatory System of the Mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5026–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J. Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: A rapidly increasing, long-term threat. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.; Nelson, K. Trophic level transfer of microplastic: Mytilus edulis (L.) to Carcinus maenas (L.). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 177, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, O.; Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Lehtiniemi, M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall, S.; Thompson, R. The impact of debris on marine life. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.; Ossendorp, B.C.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; Verschoor, A.; van Wezel, A.P.; Scheffer, M. Risks of Plastic Debris: Unravelling Fact, Opinion, Perception, and Belief. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11513–11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conchubhair, D.Ó.; Fitzhenry, D.; Lusher, A.; King, A.L.; Van Emmerik, T.; Lebreton, L.; Ricaurte-Villota, C.; Espinosa, L.F.; O’Rourke, E. Joint effort among research infrastructures to quantify the impact of plastic debris in the ocean. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 065001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantoro, I.; Löhr, A.J.; Van Belleghem, F.G.; Widianarko, B.; Ragas, A.M.J. Microplastics in coastal areas and seafood: Implications for food safety. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 674–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honingh, D.; Van Emmerik, T.; Uijttewaal, W.; Kardhana, H.; Hoes, O.; Van De Giesen, N. Urban river water level increase through plastic waste accumulation at a rack structure. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Emmerik, T.; Schwarz, A. Plastic debris in rivers. WIREs Water 2020, 7, e1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, R.; Harris, R.; Mitchell, S. Plastic contamination of the food chain: A threat to human health? Maturitas 2018, 115, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Kelly, F.J. Plastic and Human Health: A Micro Issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Cavalcanti, J.S.; Silva, J.D.B.; de França, E.J.; de Araújo, M.C.B.; Gusmão, F. Microplastics ingestion by a common tropical freshwater fishing resource. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, B.; Raffael, B.; Angers-Loustau, A.; Gilliland, D.; Kestens, V.; Petrillo, M.; Rio-Echevarria, I.M.; Van den Eede, G. Review of micro- and nanoplastic contamination in the food chain. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 639–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, M.; Hii, L.-W.; Looi, C.; Lim, W.-M.; Wong, S.-F.; Kok, Y.-Y.; Tan, B.-K.; Wong, C.-Y.; Leong, C.-O. Impact of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Human Health. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebere, E.C.; Wirnkor, V.A.; Ngozi, V.E. Uptake of microplastics by plant: A reason to worry or to be happy? World Sci. News 2019, 131, 256–267. [Google Scholar]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Low numbers of microplastics detected in drinking water from ground water sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperi, J.; Wright, S.L.; Dris, R.; Collard, F.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Kelly, F.J.; Tassin, B. Microplastics in air: Are we breathing it in? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2020, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabl, P.; Köppel, S.; Königshofer, P.; Bucsics, T.; Trauner, M.; Reiberger, T.; Liebmann, B. Detection of Various Microplastics in Human Stool. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Y.S.; Tuan Anuar, S.; Azmi, A.A.; Wan Mohd Khalik, W.M.A.; Lehata, S.; Hamzah, S.R.; Ismail, D.; Ma, Z.F.; Dzulkarnaen, A.; Zakaria, Z.; et al. Detection of microplastics in human colectomy specimens. JGH Open 2020, 5, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenech, J.; Marcos, R. Pathways of human exposure to microplastics, and estimation of the total burden. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 39, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarus, G.M.; Muianga, C.; Hunter, C.M.; Pappas, R.S. A review of data for quantifying human exposures to micro and nanoplastics and potential health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 756, 144010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriend, P.; Hidayat, H.; van Leeuwen, J.; Cordova, M.R.; Purba, N.P.; Löhr, A.J.; Faizal, I.; Ningsih, N.S.; Agustina, K.; Husrin, S.; et al. Plastic pollution research in indonesia: State of science and future research directions to reduce impacts. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 692907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Calls for More Research into Microplastics and a Crackdown on Plastic Pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/22-08-2019-who-calls-for-more-research-into-microplastics-and-a-crackdown-on-plastic-pollution (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- Anderson, A.; Grose, J.; Pahl, S.; Thompson, R.; Wyles, K. Microplastics in personal care products: Exploring perceptions of environmentalists, beauticians and students. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (Contam). Presence of microplastics and nanoplastics in food, with particular focus on seafood. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Savino, I.; Locaputo, V.; Uricchio, V.F. A Detailed Review Study on Potential Effects of Microplastics and Additives of Concern on Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, M.R. Plastic ‘scrubbers’ in hand cleansers: A further (and minor) source for marine pollution identified. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1996, 32, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chatterjee, S. Microplastic pollution, a threat to marine ecosystem and human health: A short review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21530–21547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendall, L.S.; Sewell, M.A. Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: Microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Characterisation, quantity and sorptive properties of microplastics extracted from cosmetics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Cho, H.S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Gu, H.; Lian, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, G.; Huth, C.; Wang, L.; et al. Fluorescent Polystyrene-Fe3O4Composite Nanospheres for In Vivo Imaging and Hyperthermia. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2170–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microplastics in Drinking-Water; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland. 2019. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/326499/9789241516198eng.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 28 November 2019).
- Ryan, P.G.; Moore, C.J.; Van Franeker, J.A.; Moloney, C. Monitoring the abundance of plastic debris in the marine environment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.; Moore, C.; Andrady, A.; Gregory, M.; Takada, H.; Weisberg, S. New Directions in Plastic Debris. Science 2005, 310, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, P.K.; Fok, L. Evidence of microbeads from personal care product contaminating the sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewert, B.; Plassmann, M.M.; MacLeod, M. Pathways for degradation of plastic polymers floating in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pironti, C.; Ricciardi, M.; Motta, O.; Miele, Y.; Proto, A.; Montano, L. Microplastics in the Environment: Intake through the Food Web, Human Exposure and Toxicological Effects. Toxics 2021, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, R.C.; Seeley, M.E.; La Guardia, M.J.; Mai, L.; Zeng, E.Y. A Global Perspective on Microplastics. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, e2018JC014719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, O.; Proto, A.; De Carlo, F.; Santoro, E.; Brunetti, L.; Capunzo, M. Utilization of chemically oxidized polystyrene as co-substrate by filamentous fungi. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2009, 212, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Methods Used for Identification and Quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Hamidian, A.H.; Tubić, A.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, J.K.; Wu, C.; Lam, P.K. Understanding plastic degradation and microplastic formation in the environment: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, R.; Jones, D.L.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yan, C. Behavior of microplastics and plastic film residues in the soil environment: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 703, 134722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Jung, S.Y.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. Potential toxicity of polystyrene microplastic particles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddah, H.A. Polypropylene as a Promising Plastic: A Review. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kik, K.; Bukowska, B.; Sicińska, P. Polystyrene nanoparticles: Sources, occurrence in the environment, distribution in tissues, accumulation and toxicity to various organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneswaran, C.; Ananthasubramanian, M.; Kandhavadivu, P. 4-Bioprocessing of synthetic fibres. In Bioprocessing of Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Delhi, India, 2014; pp. 189–250. ISBN 978-93-80308-42-5. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, F.R. Unsaturated Polyester Resins. In Brydson’s Plastics Materials, 8th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 247–278. ISBN 9780323358248. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.-J.; Seo, M.-K. Chapter 6-Element and Processing. In Interface Science and Technology; Park, S.-J., Seo, M.-K., Eds.; Interface Science and Composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 18, pp. 431–499. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Qin, C.; Friedberger, T.; Guan, Z.; Huang, Z. Efficient and selective degradation of polyethylenes into liquid fuels and waxes under mild conditions. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Velis, C.A.; Weber, R.; Iacovidou, E.; Purnell, P. An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrady, A.L.; Rajapakse, N. Additives and Chemicals in Plastics. In Hazardous Chemicals Associated with Plastics in the Marine Environment; Takada, H., Karapanagioti, H.K., Eds.; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-3-319-95568-1. [Google Scholar]
- Polymer Additives. Available online: https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/psr-2016-0130/html (accessed on 11 October 2021).
- Sastri, V.R. Plastics in Medical Devices: Properties, Requirements, and Applications; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-323-26563-8. [Google Scholar]
- Verla, A.W.; Enyoh, C.E.; Verla, E.N.; Nwarnorh, K.O. Microplastic–toxic chemical interaction: A review study on quantified levels, mechanism and implication. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirnkor, V.A.; Ebere, E.C.; Ngozi, V.E. Microplastics, an Emerging Concern: A Review of Analytical Techniques for Detecting and Quantifying Microplatics. Anal. Methods Environ. Chem. J. 2019, 2, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Phoenix, V.; Le Roux, G.; Jiménez, P.D.; Simonneau, A.; Binet, S.; Galop, D. Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Saad, M.; Mirande, C.; Tassin, B. Synthetic fibers in atmospheric fallout: A source of microplastics in the environment? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran; Das, K.R.; Naik, M.M. Co-selection of multi-antibiotic resistance in bacterial pathogens in metal and microplastic contaminated environments: An emerging health threat. Chemosphere 2018, 215, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, H.; Carpenter, E.J.; Komada, T.; Palmer, P.T.; Rochman, C.M. Biofilm facilitates metal accumulation onto microplastics in estuarine waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, J. Polychlorinated Biphenyls. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Science, 2nd ed.; Worsfold, P., Townshend, A., Poole, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 56–61. ISBN 9780123693976. [Google Scholar]
- Pascall, M.A.; Zabik, M.E.; Zabik, M.J.; Hernandez, R.J. Uptake of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) from an Aqueous Medium by Polyethylene, Polyvinyl Chloride, and Polystyrene Films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 53, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, E.J.; Smith, K.L. Plastics on the Sargasso Sea Surface. Science 1972, 175, 1240–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, L.M.; Moore, C.; Jones, P.R. Persistent organic pollutants carried by synthetic polymers in the ocean environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Togo, A.; Mizukawa, K.; Murakami, M.; Takada, H.; Zakaria, M.P.; Chiem, N.H.; Tuyen, B.C.; Prudente, M.; Boonyatumanond, R.; et al. Sources of sedimentary PAHs in tropical Asian waters: Differentiation between pyrogenic and petrogenic sources by alkyl homolog abundance. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, B.G.; Takada, H.; Hosoda, J.; Kondo, A.; Yamashita, R.; Saha, M.; Maes, T. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Hopanes in Plastic Resin Pellets as Markers of Oil Pollution via International Pellet Watch Monitoring. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.B.; Shaikh, S.; Jain, K.R.; Desai, C.; Madamwar, D. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Sources, Toxicity, and Remediation Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 562813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Manoharadas, S.; Altaf, M.; Alrefaei, A.F. Organochlorine Pesticides Negatively Influenced the Cellular Growth, Morphostructure, Cell Viability, and Biofilm-Formation and Phosphate-Solubilization Activities of Enterobacter cloacae Strain EAM. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 5548–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, R.; Megha, P.; Sreedev, P. Review Article. Organochlorine pesticides, their toxic effects on living organisms and their fate in the environment. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2016, 9, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, R.; Sharpanabharathi, N.; Prusty, B.A.K.; Azeez, P.A.; Kurakalva, R.M. Organochlorine pesticide residues in plants and their possible ecotoxicological and agri food impacts. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winid, B. Environmental Threats of Natural Water Contamination with Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs). Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, T.; Mattern, D.; Brunn, H. Toxicology of perfluorinated compounds. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2011, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.; Raposo, A.; Almeida-González, M.; Carrascosa, C. Bisphenol A: Food Exposure and Impact on Human Health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1503–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowski, R.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Grześkowiak, T.; Sójka, K. The presence of bisphenol A in the thermal paper in the face of changing European regulations—A comparative global research. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, F.L.P.; Routledge, E.; Heidlberger, A.; Rentsch, D.; Guenther, K.; Giger, W.; Sumpter, J.P.; Kohler, H.-P.E. Isomer-Specific Degradation and Endocrine Disrupting Activity of Nonylphenols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6399–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Gan, J. Isomer-Specific Biodegradation of Nonylphenol in River Sediments and Structure-Biodegradability Relationship. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.; Guieysse, B.; Jefferson, B.; Cartmell, E.; Lester, J. Nonylphenol in the environment: A critical review on occurrence, fate, toxicity and treatment in wastewaters. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 1033–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Health Impacts of Microplastics and Nanoplastics; New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (NJDEP) Science Advisory Board: Trenton, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–23.
- Mato, Y.; Isobe, T.; Takada, H.; Kanehiro, H.; Ohtake, C.; Kaminuma, T. Plastic Resin Pellets as a Transport Medium for Toxic Chemicals in the Marine Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 35, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilevar, Z.; Bahrami, A.; Beikzadeh, S.; Hosseini, H.; Jafari, S.M. Migration of styrene monomer from polystyrene packaging materials into foods: Characterization and safety evaluation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Hentschel, B.T.; Kaye, S. Long-Term Field Measurement of Sorption of Organic Contaminants to Five Types of Plastic Pellets: Implications for Plastic Marine Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human Consumption of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7068–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pico, Y.; Alfarhan, A.; Barcelo, D. Nano- and microplastic analysis: Focus on their occurrence in freshwater ecosystems and remediation technologies. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 113, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Shi, H.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Jabeen, K.; Kolandhasamy, P. Microplastic Pollution in Table Salts from China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13622–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebezeit, G.; Liebezeit, E. Synthetic particles as contaminants in German beers. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 1574–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Cermakova, L.; Novotna, K.; Peer, P.; Cajthaml, T.; Janda, V. Occurrence of microplastics in raw and treated drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oßmann, B.E.; Sarau, G.; Holtmannspötter, H.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Christiansen, S.H.; Dicke, W. Small-sized microplastics and pigmented particles in bottled mineral water. Water Res. 2018, 141, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, D.; Goldbeck, C.; Humpf, H.-U.; Fürst, P. Analysis of microplastics in water by micro-Raman spectroscopy: Release of plastic particles from different packaging into mineral water. Water Res. 2017, 129, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Xue, Y.; Li, J.; Zou, L.; Tang, M. Potential health impact of environmental micro- and nanoplastics pollution. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 40, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, A.P.; Kramer, E.; Hendriksen, P.J.M.; Tromp, P.; Helsper, J.P.F.G.; van der Zande, M.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Bouwmeester, H. Translocation of differently sized and charged polystyrene nanoparticles in in vitro intestinal cell models of increasing complexity. Nanotoxicology 2014, 9, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw, P. Marine Plastic Debris and Microplastics–Global Lessons and Research to Inspire Action and Guide Policy Change; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Prata, J.C. Airborne microplastics: Consequences to human health? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Mirande, C.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Tassin, B. A first overview of textile fibers, including microplastics, in indoor and outdoor environments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, A.I.; Macchia, V.; Sanderson, W.G.; Thompson, R.C.; Henry, T.B. Low levels of microplastics (MP) in wild mussels indicate that MP ingestion by humans is minimal compared to exposure via household fibres fallout during a meal. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehr, P.; Bachofen, M.; Weibel, E.R. The normal human lung: Ultrastructure and morphometric estimation of diffusion capacity. Respir. Physiol. 1978, 32, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Blank, F.; Mühlfeld, C.; Gehr, P. In vitro models of the human epithelial airway barrier to study the toxic potential of particulate matter. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 1075–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deville, S.; Penjweini, R.; Smisdom, N.; Notelaers, K.; Nelissen, I.; Hooyberghs, J.; Ameloot, M. Intracellular dynamics and fate of polystyrene nanoparticles in A549 Lung epithelial cells monitored by image (cross-) correlation spectroscopy and single particle tracking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2015, 1853, 2411–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacobi, N.R.; DeMaio, L.; Xie, J.; Hamm-Alvarez, S.F.; Borok, Z.; Kim, K.-J.; Crandall, E.D. Polystyrene nanoparticle trafficking across alveolar epithelium. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2008, 4, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atis, S. The respiratory effects of occupational polypropylene flock exposure. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 25, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Turner, A.; Kelly, F.J.; Dominguez, A.O. Distribution and potential health impacts of microplastics and microrubbers in air and street dusts from Asaluyeh County. Iran. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 244, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boag, A.H.; Colby, T.V.; Fraire, A.E.; Kuhn, C.; Roggli, V.L.; Travis, W.D. The pathology of interstitial lung disease in nylon flock workers. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1999, 23, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, M.; Dahlman-Höglund, A.; Torén, K. Respiratory health effects and exposure to superabsorbent polymer and paper dust-an epidemiological study. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, L.M.; Yousefi, N.; Tufenkji, N. Are There Nanoplastics in Your Personal Care Products? Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Stracke, F.; Hansen, S.; Schaefer, U.F. Nanoparticles and their interactions with the dermal barrier. Derm. Endocrinol. 2009, 1, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Roman, R.; Naik, A.; Kalia, Y.N.; Guy, R.H.; Fessi, H. Skin penetration and distribution of polymeric nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2004, 99, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.S.; Contreras-Rojas, L.R.; Delgado-Charro, M.B.; Guy, R.H. Objective assessment of nanoparticle disposition in mammalian skin after topical exposure. J. Control. Release 2012, 162, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, L.; Oberdörster, G.; Pentland, A.P.; De Louise, L.A. In Vivo skin penetration of quantum dot nanoparticles in the murine model: The effect of UVR. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2779–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatana, S.; Callahan, L.M.; Pentland, A.P.; DeLouise, L.A. Impact of cosmetic lotions on nanoparticle penetration through ex Vivo C57BL/6 hairless mouse and human skin: A comparison study. Cosmetics 2016, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.A.; Kozal, J.S.; Jayasundara, N.; Massarsky, A.; Trevisan, R.; Geitner, N.; Wiesner, M.; Levin, E.D.; Di Giulio, R.T. Uptake, tissue distribution, and toxicity of polystyrene nanoparticles in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 194, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneman, W.J.; Spaink, H.P.; Brun, N.R.; Bosker, T.; Vijver, M.G. Pathway analysis of systemic transcriptome responses to injected polystyrene particles in zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 190, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Ding, R.; Ma, Y.; Sun, Q.; Ren, X.; Sun, Z.; Duan, J. Cardiovascular toxicity assessment of polyethylene nanoplastics on developing zebrafish embryos. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, H.; Ru, S. Polystyrene microplastics cause tissue damages, sex-specific reproductive disruption and transgenerational effects in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Kilgallen, A.B.; Münzel, T.; Wolf, E.; Lecour, S.; Schulz, R.; Daiber, A.; Van Laake, L.W. Influence of mental stress and environmental toxins on circadian clocks: Implications for redox regulation of the heart and cardioprotection. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 177, 5393–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Q.; Wei, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene microplastics cause cardiac fibrosis by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and promoting cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ding, G.; Sun, J.; Du, M.; Liu, Q.; Cong, Y.; Jin, F.; Zhang, W. The uptake and elimination of polystyrene microplastics by the brine shrimp, Artemia parthenogenetica, and its impact on its feeding behavior and intestinal histology. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Qiao, Y.; Klobučar, G.; Li, M. Toxicological effects of polystyrene microplastics on earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 259, 113896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Wang, C.; Pan, Z.; Jin, C.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Maternal polystyrene microplastic exposure during gestation and lactation altered metabolic homeostasis in the dams and their F1 and F2 offspring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10978–10992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-M.; Byeon, E.; Jeong, H.; Kim, M.-S.; Chen, Q.; Lee, J.-S. Different effects of nano- and microplastics on oxidative status and gut microbiota in the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 405, 124207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xiong, H.; Mi, K.; Xue, W.; Wei, W.; Zhang, Y. Toxicity comparison of nano-sized and micron-sized microplastics to Goldfish Carassius auratus Larvae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 122058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, L.; Tu, W.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z. Impacts of polystyrene microplastic on the gut barrier, microbiota and metabolism of mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 649, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Wan, Z.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce gut microbiota dysbiosis and hepatic lipid metabolism disorder in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.-N.; Liu, X.-T.; Liang, Z.-H.; Wang, J.-H. Gut microbiota in obesity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3837–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wen, K.; Ding, D.; Liu, J.; Lei, Z.; Chen, X.; Ye, G.; Zhang, J.; Shen, H.; Yan, C. Size-dependent adverse effects of microplastics on intestinal microbiota and metabolic homeostasis in the marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ. Int. 2021, 151, 106452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-N.; Wen, B.; Zhu, J.-G.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Gao, J.-Z.; Chen, Z.-Z. Exposure to microplastics impairs digestive performance, stimulates immune response and induces microbiota dysbiosis in the gut of juvenile guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 138929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhou, J.; Shen, M.; Wang, X.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Effects of polystyrene microplastics on the composition of the microbiome and metabolism in larval zebrafish. Chemosphere 2018, 217, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qin, Z.; Huang, Z.; Bao, Z.; Luo, T.; Jin, Y. Effects of polyethylene microplastics on the microbiome and metabolism in larval zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 282, 117039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, G.; Ramprasath, T.; Gilles, M.; Swaminathan, K.; Ramasamy, S. Gut mi-crobiota, endocrine-disrupting chemicals, and the diabetes epidemic. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandino, G.; Inturri, R.; Lazzara, F.; Di Rosa, M.; Malaguarnera, L. Impact of gut mi-crobiota on diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. 2016, 42, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitai, T.; Tang, W.W. The Role and Impact of Gut Microbiota in Cardiovascular Disease. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 799–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, S.; Martin, A. Insights into the role of the intestinal microbiota in colon cancer. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Gong, Z.; Wang, L. Barrier function of zebrafish embryonic chorions against microplastics and nanoplastics and its impact on embryo development. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-C.; Chen, M.-Y.; Fang, C.; Zheng, R.-H.; Jiang, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Wang, K.-J.; Bailey, C.; Segner, H.; Bo, J. Microplastics negatively impact embryogenesis and modulate the immune response of the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, E.; Huh, Y.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, B.; Kang, T.; Lee, J.S.; Jeong, J. Bioaccumulation of polystyrene nanoplastics and their effect on the toxicity of Au ions in zebrafish embryos. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3173–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, J.A.; Trevisan, R.; Massarsky, A.; Kozal, J.S.; Levin, E.D.; Di Giulio, R.T. Maternal transfer of nanoplastics to offspring in zebrafish (Danio rerio): A case study with nanopolystyrene. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringer, A.; Cachot, J.; Prunier, G.; Dubillot, E.; Clérandeau, C.; Thomas, H. Experimental ingestion of fluorescent microplastics by pacific oysters, Crassostrea gigas, and their effects on the behaviour and development at early stages. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amereh, F.; Babaei, M.; Eslami, A.; Fazelipour, S.; Rafiee, M. The emerging risk of exposure to nano(micro)plastics on endocrine disturbance and reproductive toxicity: From a hypothetical scenario to a global public health challenge. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Deng, T.; Duan, J.; Xie, J.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M. Exposure to polystyrene microplastics causes reproductive toxicity through oxidative stress and activation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 190, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z. Reproductive toxicity of polystyrene microplastics: In vivo experimental study on testicular toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 405, 124028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmanli, A.; İleri, E.; Yüksel, B. Experimental investigation of engine performance and exhaust emissions of a diesel engine fueled with diesel–n-butanol–vegetable oil blends. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 81, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, N.; Beckers, N.; Onur, O.; Dietlein, M.; Tittgemeyer, M.; Kracht, L.; Neumaier, B.; Fink, G.R.; Kukolja, J. Effect of cholinergic treatment depends on cholinergic integrity in early Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2018, 141, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson, K.; Johnson, E.V.; Malmendal, A.; Linse, S.; Hansson, L.A.; Cedervall, T. Brain damage and behavioural disorders in fish induced by plastic nanoparticles de-livered through the food chain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasamma, S.; Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Malhotra, N.; Lai, Y.-H.; Liang, S.-T.; Chen, J.-R.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Hsiao, C.-D. Nanoplastics Cause Neurobehavioral Impairments, Reproductive and Oxidative Damages, and Biomarker Responses in Zebrafish: Throwing up Alarms of Wide Spread Health Risk of Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolnik, B.S.; González-Fernaández, A.; Sadrieh, N.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A. Nanoparticles and the Immune System. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.M.; Wilson, M.R.; MacNee, W.; Stone, V.; Donaldson, K. Size-Dependent Proinflammatory Effects of Ultrafine Polystyrene Particles: A Role for Surface Area and Oxidative Stress in the Enhanced Activity of Ultrafines. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 175, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, M.; Iachetta, G.; Tussellino, M.; Carotenuto, R.; Prisco, M.; De Falco, M.; Laforgia, V.; Valiante, S. Polystyrene nanoparticles internalization in human gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 31, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prietl, B.; Meindl, C.; Roblegg, E.; Pieber, T.R.; Lanzer, G.; Fröhlich, E. Nano-sized and micro-sized polystyrene particles affect phagocyte function. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2013, 30, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, X.; Sheng, D.; Xu, Z.; Rong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. Polyethylene microplastics affect the distribution of gut microbiota and inflammation development in mice. Chemosphere 2019, 244, 125492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, A.-K.; Syrovets, T.; Haas, K.A.; Loos, C.; Musyanovych, A.; Mailänder, V.; Landfester, K.; Simmet, T. Carboxyl- and amino-functionalized polystyrene nanoparticles differentially affect the polarization profile of M1 and M2 macrophage subsets. Biomaterials 2016, 85, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. An assessment of the toxicity of polypropylene microplastics in human derived cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, V.; Böhmert, L.; Lisicki, E.; Block, R.; Cara-Carmona, J.; Pack, L.K.; Selb, R.; Lichtenstein, D.; Voss, L.; Henderson, C.J.; et al. Uptake and effects of orally ingested polystyrene microplastic particles in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1817–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Size, source and chemical composition as determinants of toxicity attributable to ambient particulate matter. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 504–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlachogianni, T.; Fiotakis, K.; Loridas, S. Pulmonary oxidative stress, inflammation and cancer: Respirable particulate matter, fibrous dusts and ozone as major causes of lung carcinogenesis through reactive oxygen species mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 3886–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, K.; Song, N.; Wang, B.; Lin, H. DEHP-induce damage in grass carp hepatocytes and the remedy of Eucalyptol. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yin, K.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, B.; Qu, Y.; Li, S.; Lin, H. Mixed plasticizers aggravated apoptosis by NOD2-RIP2-NF-κB pathway in grass carp hepatocytes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 402, 123527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włoch, A.; Stygar, D.; Bahri, F.; Bażanów, B.; Kuropka, P.; Chełmecka, E.; Pruchnik, H.; Gładkowski, W. Antiproliferative, Antimicrobial and Antiviral Activity of β-Aryl-δ-iodo-γ-lactones, Their Effect on Cellular Oxidative Stress Markers and Biological Membranes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, X.; Xu, X.; Lu, J. Design of a phosphinate-based bioluminescent probe for superoxide radical anion imaging in living cells. Luminescence 2018, 33, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paget, V.; Dekali, S.; Kortulewski, T.; Grall, R.; Gamez, C.; Blazy, K.; Aguerre-Chariol, O.; Chevillard, S.; Braun, A.; Rat, P.; et al. Specific Uptake and Genotoxicity Induced by Polystyrene Nanobeads with Distinct Surface Chemistry on Human Lung Epithelial Cells and Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruenraroengsak, P.; Tetley, T.D. Differential bioreactivity of neutral, cationic and anionic polystyrene nanoparticles with cells from the human alveolar compartment: Robust response of alveolar type 1 epithelial cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thubagere, A.; Reinhard, B.M. Nanoparticle-Induced Apoptosis Propagates through Hydrogen-Peroxide-Mediated Bystander Killing: Insights from a Human Intestinal Epithelium In Vitro Model. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3611–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, L.R.; Barguilla, I.; Domenech, J.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Biological effects, including oxidative stress and genotoxic damage, of polystyrene nanoparticles in different human hematopoietic cell lines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122900. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, H.-W.; Xia, T.; Lee, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Tsai, J.-C.; Wang, Y.-J. Cationic polystyrene nanospheres induce autophagic cell death through the induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nanoscale 2014, 7, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Liong, M.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Cationic Polystyrene Nanosphere Toxicity Depends on Cell-Specific Endocytic and Mitochondrial Injury Pathways. ACS Nano. 2007, 2, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, N.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Yao, J.; Zhang, L. The impact of polystyrene microplastics on cardiomyocytes pyroptosis through nlrp3/caspase-1 signaling pathway and oxidative stress in wistar rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Endocrine Society. Plastics pose threat to human health, report shows. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020. Available online: https://www.endocrine.org/news-and-advocacy/news-room/2020/plastics-pose-threat-to-human-health (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Gopinath, P.M.; Saranya, V.; Vijayakumar, S.; Meera, M.M.; Ruprekha, S.; Kunal, R.; Pranay, A.; Thomas, J.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Assessment on interactive prospectives of nanoplastics with plasma proteins and the toxicological impacts of virgin, coronated and environmentally released-nanoplastics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt-Rauf, P.W.; Li, Y.; Long, C.; Monaco, R.; Kovvali, G.; Marion, M.-J. Plastics and carcinogenesis: The example of vinyl chloride. J. Carcinog. 2012, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, O.; Planelló, R.; Morcillo, G. The plasticizer benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) alters the ecdysone hormone pathway, the cellular response to stress, the energy metabolism, and several detoxication mechanisms in Chironomus riparius larvae. Chemosphere 2015, 128, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, L.V.; Viana, J.; Dempster, E.L.; Trznadel, M.; Bisphenol, L.A. A causes reproductive toxicity, decreases dnmt1 transcription, and reduces global DNA methylation in breeding zebrafish (Danio rerio). Epigenetics 2016, 11, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshad, R.; Kormoker, T.; Islam, S.; Haque, M.A.; Rahman, M.; Mithu, M.R. Toxic effects of plastic on human health and environment: A consequences of health risk assessment in Bangladesh. Int. J. Health 2017, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipelli, R.; Harries, L.; Okuda, K.; Yoshihara, S.; Melzer, D.; Galloway, T. Bisphenol A modulates the metabolic regulator oestrogen-related receptor-α in T-cells. Reproduction 2014, 147, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, I.A.; Galloway, T.S.; Scarlett, A.; Henley, W.E.; Depledge, M.; Wallace, R.B.; Melzer, D. Association of Urinary Bisphenol A Concentration with Medical Disorders and Laboratory Abnormalities in Adults. JAMA 2008, 300, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Song, Y.; He, F.; Jing, M.; Tang, J.; Liu, R. A review of human and animals exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Health risk and adverse effects, photo-induced toxicity and regulating effect of microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmeier, C.J.; Trickler, W.J.; Miller, N.W. Comparison of Drug Efflux Transport Kinetics in Various Blood-Brain Barrier Models. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heudorf, U.; Mersch-Sundermann, V.; Angerer, J. Phthalates: Toxicology and exposure. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2007, 210, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engler, R.E. The Complex Interaction between Marine Debris and Toxic Chemicals in the Ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12302–12315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebtsov, N.; Dykman, L. Biodistribution and toxicity of engineered gold nanoparticles: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1647–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Cheng, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chai, M. Contamination and risk of heavy metals in soils and sediments from a typical plastic waste recycling area in North China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krimsky, S. An epistemological inquiry into the endocrine disruptor thesis. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2006, 948, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.-P.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endocrine Disruptors. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. Available online: www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/agents/endocrine/ (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Crisp, T.M.; Clegg, E.D.; Cooper, R.L.; Wood, W.P.; Anderson, D.G.; Baetcke, K.P.; Hoffmann, J.L.; Morrow, M.S.; Rodier, D.J.; Schaeffer, J.E.; et al. Environmental Endocrine Disruption: An Effects Assessment and Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 11–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, F.; Susiarjo, M.; Bartolomei, M.S. Multigenerational and transgenerational effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals: A role for altered epigenetic regulation? Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 43, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattan, S.; Zhou, C.; Chiang, C.; Mahalingam, S.; Brehm, E.; Flaws, J.A. Exposure to endocrine disruptors during adulthood: Consequences for female fertility. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 233, R109–R129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucic, A.; Galea, K.S.; Duca, R.C.; El Yamani, M.; Frery, N.; Godderis, L.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Iavicoli, I.; Ndaw, S.; Ribeiro, E.; et al. Potential Health Risk of Endocrine Disruptors in Construction Sector and Plastics Industry: A New Paradigm in Occupational Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, C.; Johansson, A.L.; Bergdahl, I.A.; Dickman, P.W.; Plato, N.; Adami, J.; Boffetta, P.; Lagergren, J. Occupational exposures and risk of esophageal and gastric cardia cancers among male Swedish construction workers. Cancer Causes Control 2005, 16, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Perez, J.; Lopez-Abente, G.; Fernandez-Navarro, P.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, M.; Castello, A. Cancer mortality in towns in the vicinity of installations for the production of cement, lime, plaster and magnesium oxide. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Béranger, R.; Le Cornet, C.; Schüz, J.; Fervers, B. Occupational and Environmental Exposures Associated with Testicular Germ Cell Tumours: Systematic Review of Prenatal and Life-Long Exposures. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, W.; Mambetova, C.; Bourdon-Raverdy, N.; Llopis-González, A.; Guénel, P.; Hardell, L.; Merletti, F.; Morales-Suárez-Varela, M.; Olsen, J.; Olsson, H.; et al. Occupational exposure to endocrine-disrupting compounds and biliary tract cancer among men. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 2007, 33, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Erkekoglu, P.; Oral, D.; Chao, M.-W.; Kocer-Gumusel, B. Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Possible Chemical and Biological Causes: A Review. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2017, 36, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludewig, G.; Robertson, L.W. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) as initiating agents in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2012, 334, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.W.; Hansen, L.G. PCBs: Recent Advances in Environmental Toxicology and Health Effects; University Press of Kentucky: Lexington, KY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mayes, B. Comparative Carcinogenicity in Sprague–Dawley Rats of the Polychlorinated Biphenyl Mixtures Aroclors 1016, 1242, 1254, and 1260. Toxicol. Sci. 1998, 41, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberhorn, E.M.; Glauert, H.P.; Robertson, L.W. Critical Reviews in: Carcinogenicity of Polyhalogenated Biphenyls: PCBs and PBBs. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1990, 20, 440–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onozuka, D.; Yoshimura, T.; Kaneko, S.; Furue, M. Mortality after Exposure to Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans: A 40-Year Follow-up Study of Yusho Patients. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 169, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, F.; Moneda, M.; Portolani, N.; Rossini, A.; Molfino, S.; Ministrini, S.; Contessi, G.B.; Pesenti, S.; De Palma, G.; Gaia, A.; et al. Polychlorinated biphenyls and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in the population living in a highly polluted area in Italy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zani, C.; Gelatti, U.; Donato, F.; Capelli, M.; Portolani, N.; Bergonzi, R.; Apostoli, P. Polychlorinated biphenyls in serum, liver and adipose tissue of subjects with hepatocellular carcinoma living in a highly polluted area. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, L.; Shi, Q.; Lehmler, H.-J.; Fu, J.; Su, C.; Xia, X.; Song, E.; Song, Y. Polychlorinated Biphenyl Quinone Metabolite Promotes p53-Dependent DNA Damage Checkpoint Activation, S-Phase Cycle Arrest and Extrinsic Apoptosis in Human Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 2160–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, R.E.; Kaufmann, W.K.; Paules, R.S. Oxidative stress and cell cycle checkpoint function. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1387–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettner, M.A.; Flor, S.; Ludewig, G.; Wagner, J.; Robertson, L.W.; Lehmann, L. Quinoid Metabolites of 4-Monochlorobiphenyl Induce Gene Mutations in Cultured Chinese Hamster V79 Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 100, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dong, H.; Su, C.; Xia, X.; Li, L.; Song, E.; Song, Y. Polychlorinated biphenyl quinone-induced genotoxicity, oxidative DNA damage and γ-H2AX formation in HepG2 cells. Chem. Interactions 2014, 212, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wagner, B.A.; Lehmler, H.-J.; Buettner, G.R. Semiquinone Radicals from Oxygenated Polychlorinated Biphenyls: Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Studies. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kalen, A.L.; Li, L.; Lehmler, H.-J.; Robertson, L.W.; Goswami, P.C.; Spitz, D.R.; Aykin-Burns, N. Polychlorinated-biphenyl-induced oxidative stress and cytotoxicity can be mitigated by antioxidants after exposure. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 1762–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norback, D.H.; Weltman, R.H. Polychlorinated biphenyl induction of hepatocellular carcinoma in the Sprague-Dawley rat. Environ. Health Perspect. 1985, 60, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whysner, J.; Wang, C.-X. Hepatocellular Iron Accumulation and Increased Cell Proliferation in Polychlorinated Biphenyl-Exposed Sprague-Dawley Rats and the Development of Hepatocarcinogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 62, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Menéndez-Pedriza, A.; Jaumot, J.; Bedia, C. Lipidomic analysis of single and combined effects of polyethylene microplastics and polychlorinated biphenyls on human hepatoma cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 421, 126777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Wu, T.; Sun, L.; Lin, J.J.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, C. Aroclor 1254 causes atrophy of exocrine pancreas in mice and the mechanism involved. Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 31, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyska, A.; Jokinen, M.P.; Brix, A.E.; Sells, D.M.; Wyde, M.E.; Orzech, D.; Haseman, J.K.; Flake, G.; Walker, N. Exocrine pancreatic pathology in female Harlan Sprague-Dawley rats after chronic treatment with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and dioxin-like compounds. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, M.; López, T.; Pumarega, J.; Jariod, M.; Crous-Bou, M.; Marco, E.; Rifà, J.; Grimalt, J.O.; Malats, N.; Real, F.X.; et al. In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma blood concentrations of some organochlorine compounds and coffee intake are independently associated with KRAS mutations. Mutagenesis 2009, 24, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, M.; Malats, N.; Jariod, M.; Grimalt, J.O.; Rifà, J.; Carrato, A.; Guarner, L.; Salas, A.; Santiago-Silva, M.; Corominas, J.M.; et al. Serum concentrations of organochlorine compounds and K-ras mutations in exocrine pancreatic cancer. Lancet 1999, 354, 2125–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, M.; Malats, N.; Guarner, L.; Carrato, A.; Rifa, J.; Salas, A.; Corominas, J.M.; Andreu, M.; Real, F.X. Association between coffee drinking and K-ras mutations in exocrine pancreatic cancer. PANKRAS II Study Group. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1999, 53, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Basea, M.B.; Porta, M.; Alguacil, J.; Puigdomènech, E.; Gasull, M.; Garrido, J.A.; López-Jiménez, T.; For the PANKRAS II Study Group. Relationships between occupational history and serum concentrations of organochlorine compounds in exocrine pancreatic cancer. Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 68, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppin, J.A.; Tolbert, P.E.; Holly, E.A.; Brock, J.W.; Korrick, S.A.; Altshul, L.M.; Zhang, R.H.; Bracci, P.M.; Burse, V.W.; Needham, L.L. Pancreatic cancer and serum organochlorine levels. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2000, 9, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Poulia, K.A.; Sarantis, P.; Antoniadou, D.; Koustas, E.; Papadimitropoulou, A.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Pancreatic Cancer and Cachexia—Metabolic Mechanisms and Novel Insights. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasull, M.; Porta, M.; Pumarega, J.; Vioque, J.; de Basea, M.B.; Puigdomènech, E.; Morales, E.; Grimalt, J.; Malats, N. The relative influence of diet and serum concentrations of organochlorine compounds on K-ras mutations in exocrine pancreatic cancer. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, E.; Porta, M.; Vioque, J.; López-Jiménez, T.; Mendez, M.A.; Pumarega, J.; Malats, N.; Crous-Bou, M.; Ngo, J.; Rifà, J.; et al. Food and nutrient intakes and K-ras mutations in exocrine pancreatic cancer. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2007, 61, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, M.; Ayude, D.; Alguacil, J.; Jariod, M. Exploring environmental causes of alteredras effects: Fragmentation plus integration? Mol. Carcinog. 2003, 36, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.A.; Vioque, J.; Porta, M.; Morales, E.; López, T.; Malats, N.; Crous, M.; Gómez, L.I.; López-Jiménez, T.; For the PANKRAS II Study Group. Estimating dietary intakes from a brief questionnaire: A simulation study of reliability in a molecular epidemiologic study of pancreatic and biliary diseases. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 21, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Xu, K.; Yu, L.; Pu, Y.; Xiong, F.; He, Y.; Huang, Q.; Tang, M.; Chen, M.; Yin, L.; et al. Preliminary study on impacts of polystyrene microplastics on the hematological system and gene expression in bone marrow cells of mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 218, 112296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Cancer | Effect on Pathogenesis |
|---|---|
| Endocrine-related cancers | Endocrine disruptors are chemicals found in many everyday products, including plastic bottles and containers Endocrine disruptors interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body Endocrine disruptors may act through estrogen/testosterone coupling receptors |
| Biliary tract cancer | Endocrine-disrupting agents, with recognized estrogenic activity (alkylphenols, PCB, bisphenol A), increase the risk of extrahepatic biliary tract cancer Cancers were mainly located in the extrahepatic bile duct and ampulla of Vater |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | PCB contributes to potential development of HCC Serum lipid-adjusted PCB concentration is a viable indicator of PCB body storage The PCB29-pQ—PCB metabolite causes ROS formation and affects cell cycle by suppressing cyclins A/D1/E and cyclin-dependent kinases, while upregulating Fas/FasL and activating caspase 8/3 PCB exposures generates substantial lipidomic alterations, causing a major modification of cell membrane integrity and susceptibility |
| Pancreatic cancer | Organochlorine compounds may modulate KRAS activation or maintenance p,p′-DDT and PCBs may all play a role in the etiology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and exocrine pancreatic cancer by altering KRAS activation |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baj, J.; Dring, J.C.; Czeczelewski, M.; Kozyra, P.; Forma, A.; Flieger, J.; Kowalska, B.; Buszewicz, G.; Teresiński, G. Derivatives of Plastics as Potential Carcinogenic Factors: The Current State of Knowledge. Cancers 2022, 14, 4637. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194637
Baj J, Dring JC, Czeczelewski M, Kozyra P, Forma A, Flieger J, Kowalska B, Buszewicz G, Teresiński G. Derivatives of Plastics as Potential Carcinogenic Factors: The Current State of Knowledge. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4637. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194637
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaj, Jacek, James Curtis Dring, Marcin Czeczelewski, Paweł Kozyra, Alicja Forma, Jolanta Flieger, Beata Kowalska, Grzegorz Buszewicz, and Grzegorz Teresiński. 2022. "Derivatives of Plastics as Potential Carcinogenic Factors: The Current State of Knowledge" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4637. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194637
APA StyleBaj, J., Dring, J. C., Czeczelewski, M., Kozyra, P., Forma, A., Flieger, J., Kowalska, B., Buszewicz, G., & Teresiński, G. (2022). Derivatives of Plastics as Potential Carcinogenic Factors: The Current State of Knowledge. Cancers, 14(19), 4637. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194637








